2025 Vol. 46, No. 4
2025, 46(4): 1-7.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250401
Abstract:
Due to their unique peroxide bridge structure, artemisinin and its derivatives have demonstrated the remarkable efficacy in treating severe malaria and exhibited the potent anticancer properties. These compounds interfere with the cancer cell growth through the multiple mechanisms, including the inhibition of cell proliferation, induction of various forms of cell death, cell cycle arrest, suppression of angiogenesis and modulation of the tumor microenvironment. Clinical trials have confirmed the significant anticancer activity of artemisinin-based compounds. This paper summarizes the recent advances and findings regarding the mechanisms of action of artemisinin and its derivatives as the potential anticancer agents, providing the valuable insights for future researches on the anticancer mechanisms of these compounds.
Due to their unique peroxide bridge structure, artemisinin and its derivatives have demonstrated the remarkable efficacy in treating severe malaria and exhibited the potent anticancer properties. These compounds interfere with the cancer cell growth through the multiple mechanisms, including the inhibition of cell proliferation, induction of various forms of cell death, cell cycle arrest, suppression of angiogenesis and modulation of the tumor microenvironment. Clinical trials have confirmed the significant anticancer activity of artemisinin-based compounds. This paper summarizes the recent advances and findings regarding the mechanisms of action of artemisinin and its derivatives as the potential anticancer agents, providing the valuable insights for future researches on the anticancer mechanisms of these compounds.
2025, 46(4): 8-13.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250402
Abstract:
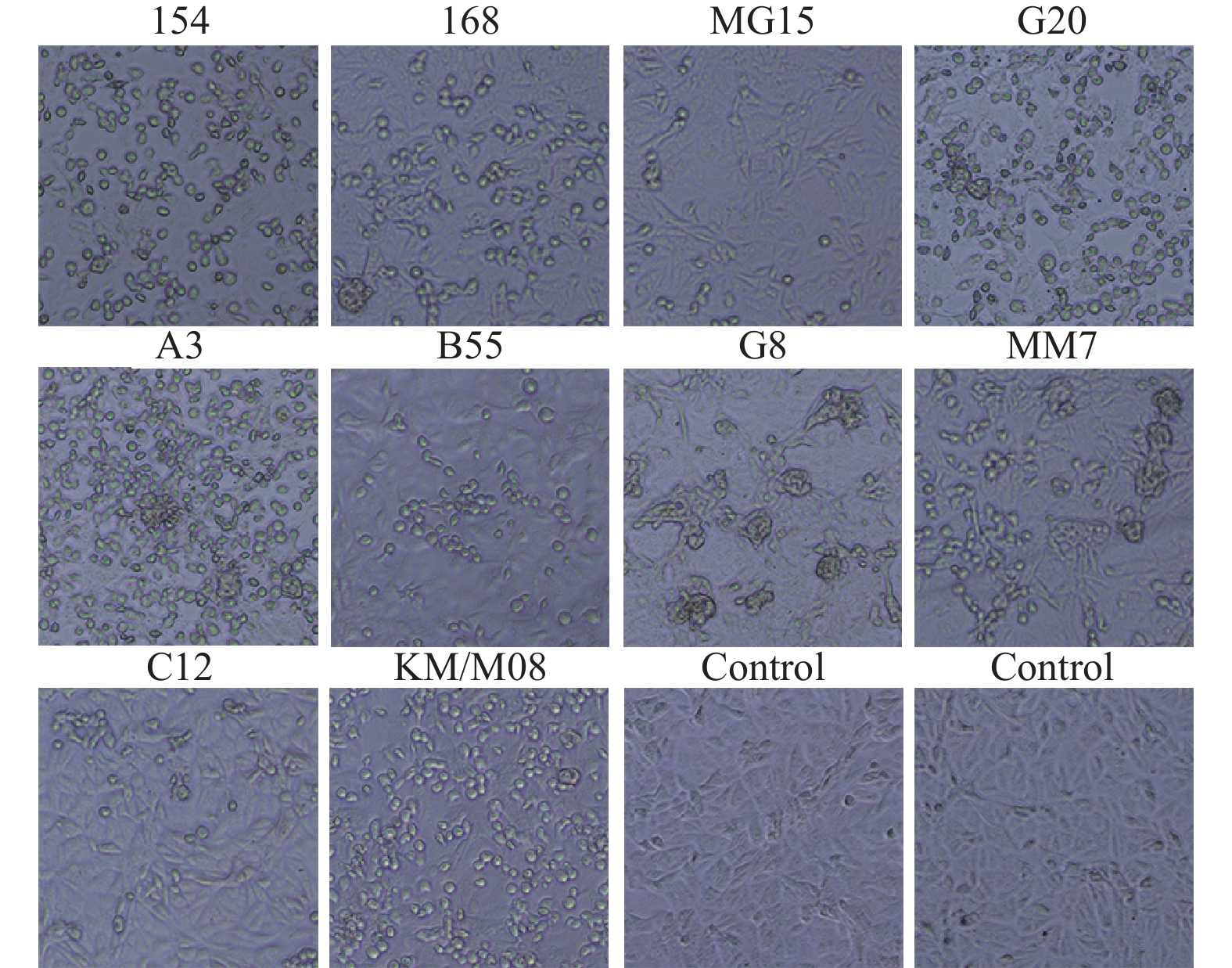
Objective To screen Coxsackievirus A16 (CA16) vaccine candidate strains and provide preliminary basis for the development of vaccine against hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD). Methods Cell inoculation and continuous passage were performed on the 35 clinical specimens of patients with hand, foot, and mouth disease from different areas of Kunming. The harvested solution with cytopathic effects was identified using CA16 standard serum. Positive samples were screened for vaccine strains through the virus titer determination, plaque purification, VP1 sequence homology and evolutionary analysis. Results Among the 35 collected clinical oropharyngeal swab samples, 23 showed cellular lesions, and 10 were identified as CA16 virus by serology, with a positive rate of 43.5%. After the adaptive cultivation, the virus titers of 10 strains gradually increased, but stabilized at 7.0 lgCCID50 from 48 hours onwards. The plaque of the strain showed that all strains can form plaques of 0.2~0.8 cm, showing the regular differences, and the size of KM/M08 plaques was relatively uniform. All strains were B1b type, with nucleotide homology ranging from 93.3~100%. Among them, KM/M08 had the highest homology with other strains, ranging from 95.2~100%. Conclusion Through the analysis of virus proliferation kinetics curve, gene homology, and evolution, KM/M08 meets the expected screening criteria in all aspects of evaluation and is proposed as a vaccine candidate strain for further researches.
2025, 46(4): 14-19.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250403
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of miR-34a on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal stem cells. Methods Twenty healthy teeth that needed to be extracted for orthodontic treatment were collected. Human periodontal stem cells (hPDLSCs) were isolated and cultured in vitro, and miR-34a mimetics were constructed and transfected into hPDLSCs. The experimental groups were subsequently categorized into the mimics group (miR-34a overexpression group) and the mimics-NC group (control group without load). The transfection efficiency was assessed using real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR), while CCK-8 assays were used to evaluate the proliferation capacity of hPDLSCs post-transfection. Osteogenic differentiation of miR-34a-transfected hPDLSCs was induced, with samples being collected at day 0 and day 14 after the osteogenic induction. The expression level of Runx2-associated transcription factor 2 (Runx2) was quantified via qRT-PCR, protein levels of Runx2-associated proteins were analyzed through Western blot, and mineralized nodule formation was examined using alizarin red staining. Results The expression level of miR-34a in the mimics group was significantly higher than that in the mimics-NC group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the value-added rate between the mimics group and the mimics-NC group on days 1~5 (P > 0.05), and the value-added rate between the mimics group and the mimics-NC group was significantly lower than that between the mimics-NC group and the mimics-NC group on days 5~11, and the difference was statistically significant. After the osteogenic induction, the mRNA expression level of Runx2 in the mimics group was higher than that in the mimics-NC group (P < 0.05), and the expression level of Runx2 protein in the mimics group was also higher than that in the mimics-NC group (P < 0.05), and there were more mineralized nodules in the mimics group than in the mimics-NC group after 14 days of osteogenic induction. Conclusion Under in vitro conditions, miR-34a inhibits the proliferative activity of hPDLSCs and promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells.
2025, 46(4): 20-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250404
Abstract:
Objective To conduct a unique and pioneering molecular epidemiological investigation of a case of Eurasian avian-like H1N1 swine influenza identified in Yunnan Province in 2022 (the fourth such case in the province) and to understand its genetic characteristics so as to reveal its potential impact on human health. Methods Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection technology was used for the nucleic acid testing of the case's pharyngeal swab samples, close contacts, and environmental samples from the living area. Positive samples were subjected to virus isolation using MDCK cells. Cell cultures were authenticated using erythrocyte agglutination assay with guinea pig blood and real-time fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR. Whole genome sequencing was performed using the Illumina MiseqNext-generation sequencing platform, and a phylogenetic tree was constructed using MEGA 7.0 software to analyze the genetic molecular characteristics. Results The first G5 genotype Eurasian avian-like H1N1 swine influenza virus in Yunnan Province was successfully isolated, and the whole genome sequence of the virus was obtained. This virus possessed the molecular characteristics associated with increased adaptability, virulence, or transmissibility in mammals and had a nucleotide consistency of 99.2%~99.7% with a porcine strain isolated in Jiangsu province. These findings underscored the potential threat this virus poses to human health. Conclusion The study underscores the importance of further monitoring swine influenza in preventing new influenza virus subtypes that can infect humans.
2025, 46(4): 29-35.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250405
Abstract:
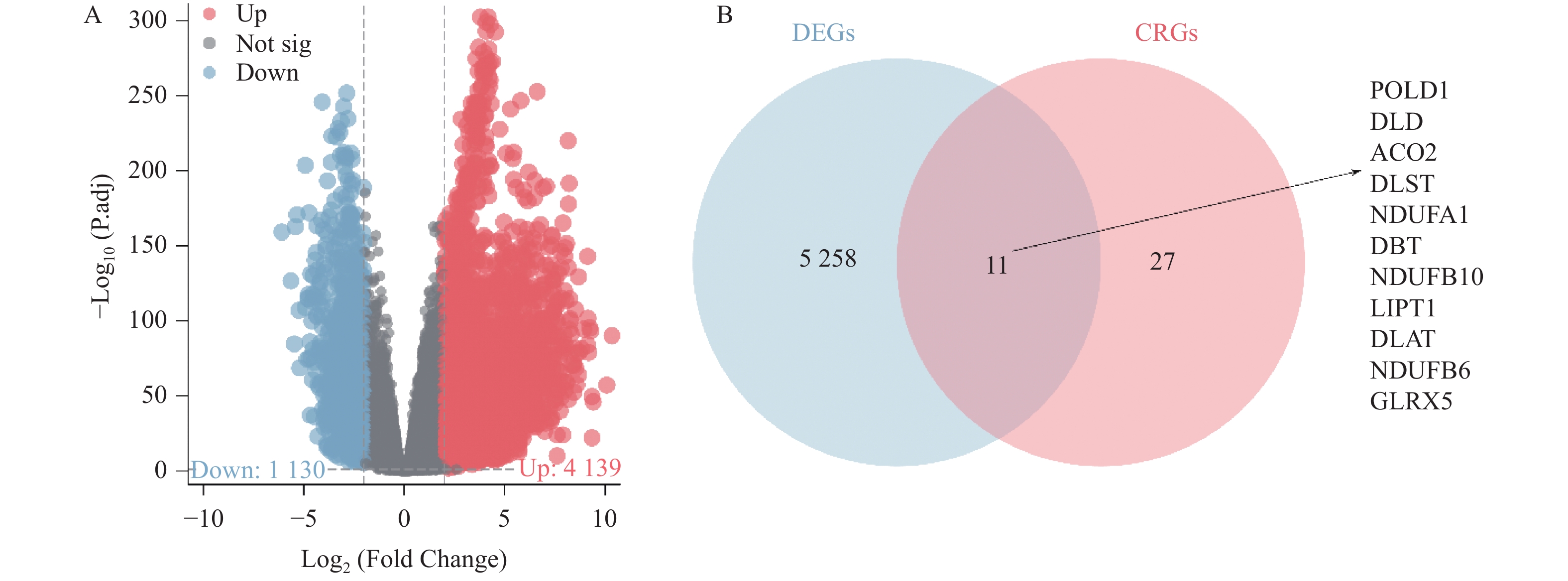
Objective To identify the cuproptosis genes associated with prognosis and immune microenvironment in lung cancer with the use of bioinformatics. Methods The lung cancer dataset used in this study was obtained from the TCGA database. The cuproptosis-related genes (CRGs) were obtained from the previously reported literature. The R software Deseq2 package was used to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in lung cancer. The intersection of DEGs and CRGs was taken to obtain the differentially expressed CRGs (DE-CRGs). COX analysis and R software rms package were used to identify DE-CRGs associated with the prognosis of lung cancer. Estimate and Cibersort algorithms were applied to identify the correlation of DE-CRGs with the immune microenvironment. Results Compared to the normal tissues, a total of 5, 269 DEGs were present in lung cancer tissues in the TCGA database, and there were 11 shared genes between DEGs and CRGs. The 11 DE-CRGs mainly regulated the energy metabolism, carbon metabolism and amino acid metabolism. In the DE-CRGs, LIPT1 was an independent risk factor for lung cancer, and the column chart constructed with the clinical features (age, TNM staging, and residual tumor) predicted the survival of lung cancer patients in a manner similar to their actual outcomes. LIPT1 showed a positive correlation with the infiltration of M1 and M2 type macrophages, activated natural killer cells cells and CD8+ T cells, and showed a significant negative correlation with M0 type macrophages, activated mast cells, neutrophils and Treg cells (P < 0.05). Conclusion LIPT1 may serve as a prognostic and immune microenvironment-associated cuproptosis gene, which is a novel biomarker for lung cancer therapy.
2025, 46(4): 36-45.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250406
Abstract:
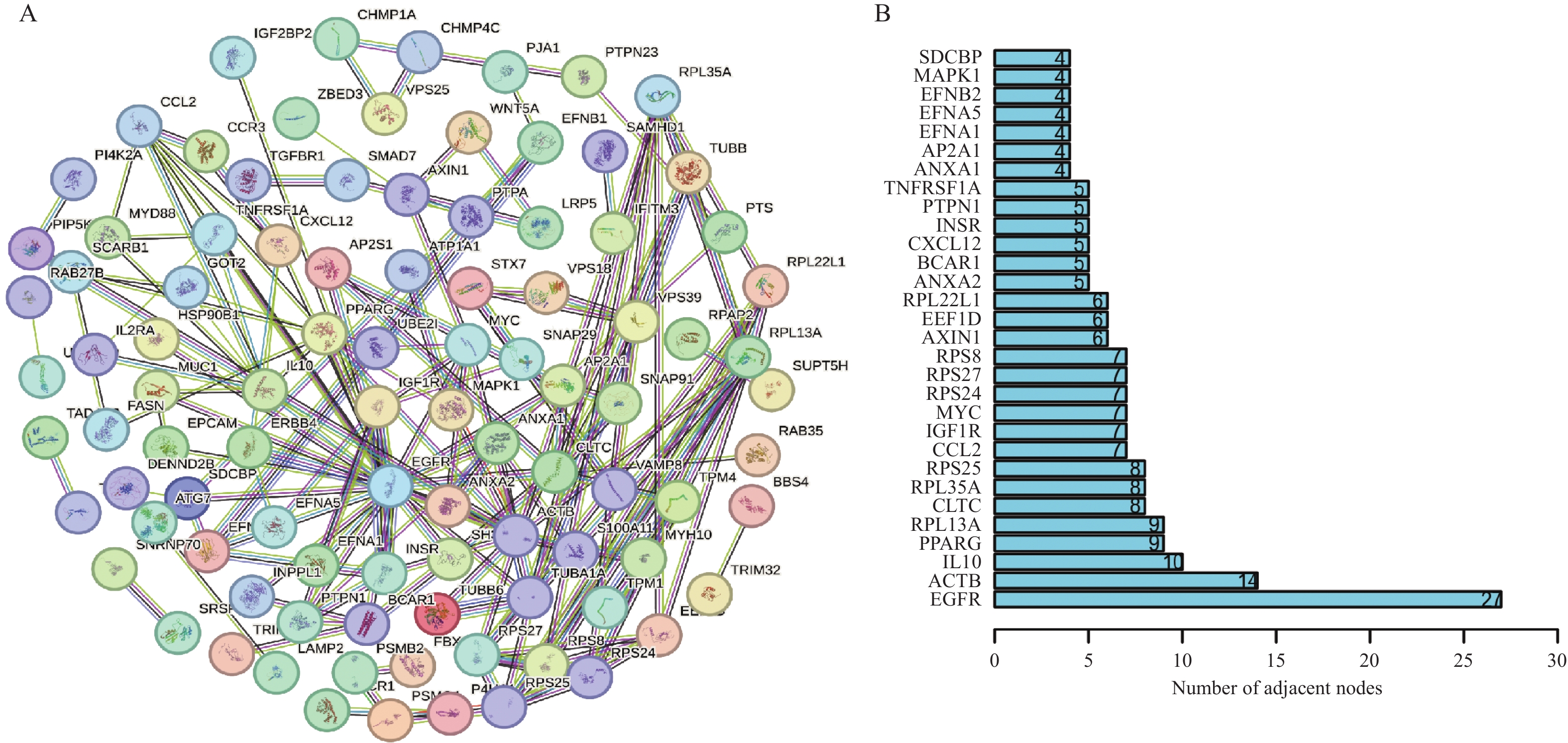
Objective To evaluate the prognostic value of endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT)-related genes in osteosarcoma (OS) based on bioinformatics. Methods Preprocessing was performed on 88 OS sequencing samples (with 29 death outcomes) downloaded from the TARGET database and 257 patient clinical information. The Cox proportional hazards model was constructed using the survival package to screen ESCRT genes related to the survival. The STRING database was used to construct a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network, and core genes were selected based on PPI. KEGG enrichment analysis was performed on the selected core genes with more than 5 nodes. Lasso regression analysis was applied to identify ESCRT-related genes more closely related to the prognosis of OS patients. Results A total of 1486 ESCRT-related genes were identified, of which 164 were associated with the survival. CLTC, MYC, INSR, PTPN1, and TNFRSF1A were identified as core genes related to the prognosis of OS patients. OS patients were randomly divided into a training set (n = 44) and a validation set (n = 44). In the training set, OS patients in the high-risk group had the significantly shorter overall survival than those in the low-risk group (P < 0.05), and the similar results were obtained in the validation set (P < 0.01). The ROC (receiver operating characteristic) curve showed an AUC of 0.846 in the training set and 0.877 in the validation set. Prognostic survival analysis and differential analysis of core genes revealed no difference in MYC between high- and low-risk groups in the validation set, and no difference in INSR in the training set. In the overall dataset, all prognostic core genes showed significant differences (P < 0.05). Survival analysis of core genes using the R package Survival showed significant differences in survival rates for four genes (CLTC, INSR, PTPN1, TNFRSF1A) except MYC (P > 0.05). Univariate independent prognostic analysis identified three genes (TNFRSF1A, PTPN1, MYC) associated with OS survival. Multivariate independent prognostic analysis ultimately identified two key genes (TNFRSF1A, PTPN1) as independent factors influencing OS survival prognosis and closely related to OS patient survival. Conclusion A risk scoring model for OS survival prognosis based on the expression of two key genes, TNFRSF1A and PTPN1, was been successfully constructed using bioinformatics and it can provide more options for clinical treatment and survival prognosis assessment of OS.
2025, 46(4): 46-56.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250407
Abstract:
Objective To establish a prognostic model that predicts the survival and prognosis of gastric adenocarcinoma patients by studying the LncRNAs related to iron death in gastric cancer cells, thereby providing a theoretical basis for the development of their biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Methods The transcript sequencing data of gastric adenocarcinoma patients in the TCGA database were analyzed and intersected with iron death-related genes, which were screened for iron death-related LncRNAs by co-expression and differential analysis methods. One-way and multifactorial Cox regression analyses were used to screen out the prognostic-related LncRNAs in gastric adenocarcinoma patients, so as to establish the prognostic scoring models. On this basis, risk values were calculated for each sample, and the reliability of the model was fully verified. According to the model results, differences in the immune infiltration and immune response between the high- and low-risk groups were analyzed. Results Tumor tissues were screened for 503 LncRNAs (431 up-regulated and 72 down-regulated) associated with iron death compared to the normal tissues; univariate Cox regression analysis yielded 33 LncRNAs that could be used as the independent risk factors, whereas multivariate Cox regression analysis constructed a predictive model consisting of 17 LncRNAs. Survival curves indicated that patients with the high risk had the significantly lower survival rates than those with the low risk (P < 0.001). Unifactorial and multifactorial independent prognostic analyses showed that age, stage, and risk value were independent risk factors for patients; Time-dependent ROC curves suggested that the predicted AUC values of the model's 1-, 2-, and 3-year survival rates were 0.751, 0.799, and 0.779 respectively, proving that the model was reliable and stable. There were significant differences in multiple immune activation responses, the degree of immune cell infiltration, and the expression levels of immune check points between the high- and low-risk groups. Conclusion The established prognostic prediction model based on iron death-related lncRNAs for gastric adenocarcinoma patients can better assess the prognosis of patients, and the lncRNAs included in the model have the feasibility of being developed into biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
2025, 46(4): 57-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250408
Abstract:
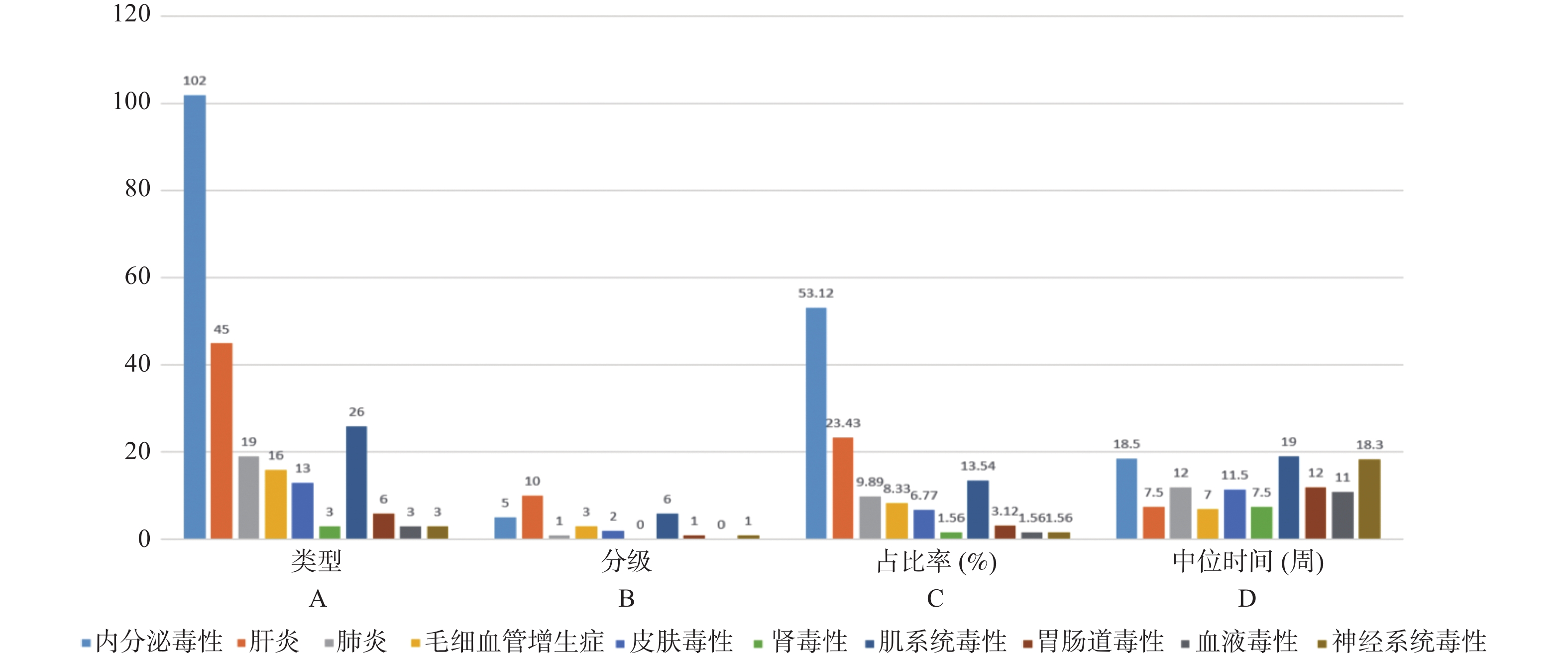
Objective To explore the predictive model and its value of irAEs based on peripheral blood markers. Methods The baseline clinical data, laboratory tests, and irAEs follow-up results of 825 malignant tumor patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 antibodies in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were retrospectively collected from December 2020 to December 2023. The patients were divided into irAEs group and non-irAEs group according to the presence or absence of irAEs. The differences between and within groups were analyzed by t-test, rank-sum test, chi-square test and Fisher exact probability method. LASSO, Ridge and Elastic-net logistic regressions were used to screen the predictors and establish the risk prediction models for irAEs. Results 136 patients experienced 178 irAEs, of which endocrine toxicity accounted for 42.64%, hepatitis 35.29%, pneumonia 20.58%, grade ≥ G3 accounted for 19.07%, involving more than two organs accounted for 24.26% of the total number of irAEs. Univariate analysis showed that baseline CD4+ T cell count, IL-6, IL-17, TSH, GLB and ALB were associated with irAEs. GLB, ALB, IL-17 and TSH were selected as the important risk factors by Ridge, LASSO and Elastic-Net logistic regression. The results showed that the AUC of the three algorithms were over 0.800. The AUC of internal validation set by LASSO-Logistic was 0.800 (95%CI 0.739~0.862). The AUC of external validation set was 0.800 (95%CI 0.739~0.861) and the DCA curve results indicated the highest net return for this predictive model. Conclusion GLB, ALB, IL-17 and TSH are independent predictors of irAEs, and the predictive model of irAEs based on them is effective.
2025, 46(4): 67-76.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250409
Abstract:
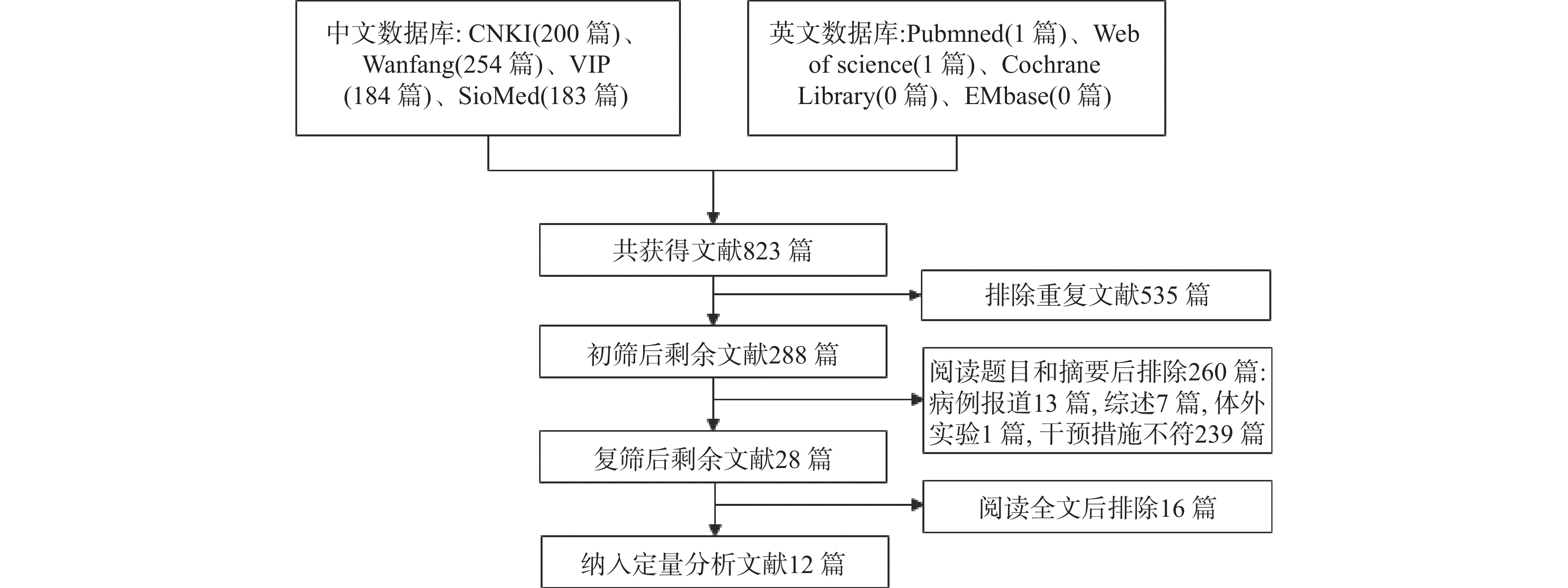
Objective To systematically evaluate the safety and efficacy of Kangfuxin liquid combined with adenosine monophosphate in the treatment of paediatric herpetic stomatitis. Methods Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of Kangfuxin liquid combined with adenosine monophosphate for the treatment of paediatric herpetic stomatitis were searched in various databases, and Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.4 software. Results A total of 12 RCTs with a sample size of 1,094 cases were included. Meta-analysis showed that the combination of Kangfuxin liquid with adenosine monophosphate significantly increased [RR = 1.21, 95%CI (1.16, 1.28), P < 0.00001 ] the overall clinical efficacy rate of paediatric herpetic stomatitis. Compared with the conventional antiviral treatment group with adenosine monophosphate, the incidence of adverse events was lower in the Kangfuxin liquid group [RR = 0.26, 95%CI (0.14, 0.51), P < 0.00001 ]. In addition, the Kangfuxin liquid group could effectively shorten the time for herpes disappearance (skin lesion healing), pain disappearance, fever reduction, salivation disappearance and recovery of diet (P < 0.05), and had advantages in promoting the recovery of lymphocytes (CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+/CD8+), serological levels (CRP, TNF-α, WBC, IL-10, VEGF, EGF, and IL-6) (P < 0.05). Conclusion Kangfuxin liquid combined with adenosine monophosphate has the better efficacy and safety in the treatment of paediatric herpetic stomatitis, and has advantages in shortening the symptomatic recovery time and improving the indicators of lymphocyte and serological levels in paediatric herpetic stomatitis.
2025, 46(4): 77-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250410
Abstract:
Objective To explore the relationship between the coagulation and fibrinolysis function in the early pregnancy and the occurrence of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in women with different pre pregnancy body mass indexes (BMI). Methods 290 pregnant women undergoing the prenatal check ups at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from September 2023 to February 2024 were selected. Pre pregnancy BMI, age, family genetic history, parity, parity, and early pregnancy coagulation and fibrinolysis function test results were collected. Based on whether GDM had occurred, they were divided into GDM group (n = 72) and non GDM group (n = 218), and further divided into low weight GDM group (n = 8), low weight non GDM group (n = 29), normal weight GDM group (n = 39), normal weight non GDM group (n = 145), overweight/obesity GDM group (n = 25), overweight/obesity non GDM group (n = 44) based on pre pregnancy BMI. Basic data comparison was conducted on the total population and BMI groups. Independent sample t-test or Mann Whitney U test was used for quantitative data, and chi square test or Fisher's exact probability method was used for qualitative data. Multivariate logistic regression was used to correct the influencing factors. Results After adjusting the confounding factors such as age, family history, and pre pregnancy BMI, APTT was negatively correlated with the occurrence of GDM in the overall population (P < 0.05, OR = 0.840), while FIB was positively correlated with GDM (P < 0.01, OR = 2.598). In low body weight recombination, APTT was negatively correlated with GDM (P < 0.05, OR = 0.483), FIB was positively correlated with GDM (P < 0.05, OR=82.501), while there was no significant correlation between APTT, FIB and GDM after adjusting the age, family history, and pre pregnancy BMI; In the normal weight group, APTT was negatively correlated with GDM (P < 0.01, OR = 0.786) and FIB was positively correlated with GDM (P < 0.05, OR = 2.413). However, after adjusting the age, family history, and pre pregnancy BMI, APTT remained negatively correlated with GDM (P < 0.05, OR = 0.812) and FIB remained positively correlated with GDM (P < 0.05, OR = 2.391); In the overweight/obese group, TT was negatively correlated with GDM (P < 0.05, OR = 0.510), while there was no significant correlation between TT and GDM after adjusting the age, family history, and pre pregnancy BMI. Conclusion In the normal weight population, APTT is negatively correlated with the occurrence of GDM, while FIB is positively correlated with the occurrence of GDM; In the low weight and overweight/obese populations, coagulation and fibrinolysis related indicators are greatly influenced by BMI and have no significant correlation with the occurrence of GDM.
2025, 46(4): 83-89.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250411
Abstract:
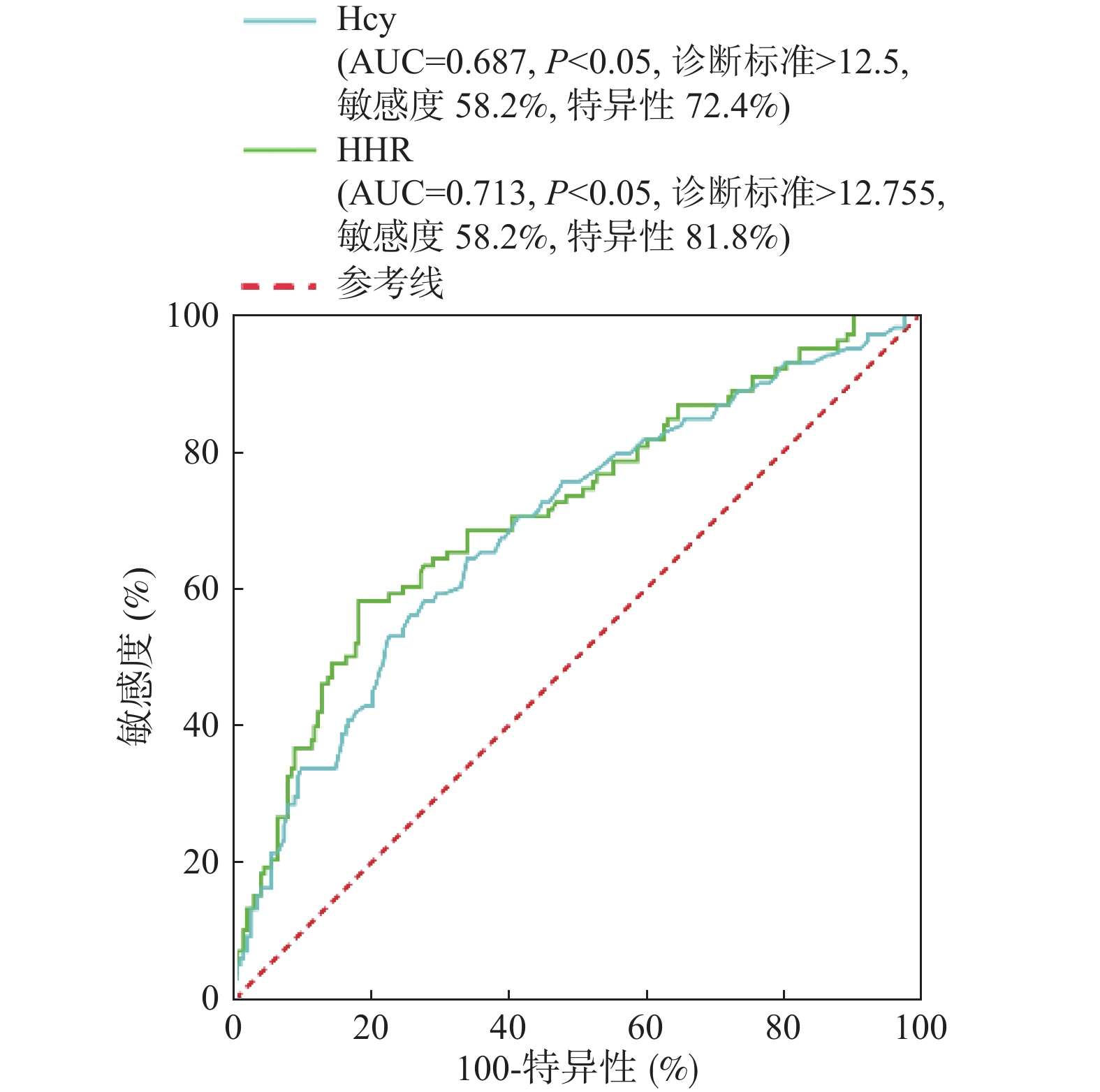
Objective To evaluate the predictive value of changes in serum homocysteine (Hcy), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and the homocysteine-to-HDL-C ratio (HHR) for the incidence and short-term prognosis of patients with premature coronary heart disease (PCHD). Methods Between January 2022 and December 2023, 301 patients with the suspected coronary heart disease (males ≤ 55 years, females ≤ 65 years) were retrospectively selected from the Department of Cardiology at the Third People’ s Hospital of Yunnan Province. All patients who underwent coronary angiography (CAG) were divided into the premature coronary heart disease (PCHD) group (n = 98) and the non-coronary heart disease (NCHD) group (n = 203). Patients with PCHD were followed up six months after the discharge and were further classified into the good prognosis group (n = 55) and the poor prognosis group (n = 43) based on the presence of worsening clinical symptoms such as chest tightness, chest pain, arrhythmias, heart failure, or death. Data collected included general patient information, blood lipid levels, Hcy levels, left ventricular function ultrasound indicators, and the presence of hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Results Hcy and HHR levels were significantly higher in the PCHD group compared to the NCHD group, while HDL-C levels were lower (P < 0.001). In the poor prognosis group, Hcy and HHR levels were elevated, and HDL-C levels were reduced compared to the good prognosis group (P < 0.001). The Hcy and HHR levels in the severe coronary artery stenosis group were markedly higher than those in the normal coronary artery group and the mild to the moderate stenosis group, with HDL-C levels being lower (P < 0.001). Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified that male sex, HHR, Hcy, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were independent factors influencing premature coronary heart disease (P < 0.05). HHR was found to be an independent risk factor for the poor short-term prognosis in PCHD. The analysis of the operating characteristic curve of the subjects showed that serum Hcy and HHR had the predictive value for the occurrence of PCHD (P < 0.05), with HHR showing higher predictive value (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.713). HHR also had the substantial predictive value for the short-term prognosis of PCHD (AUC = 0.715). Conclusion Elevated HHR levels are associated with the severe coronary artery disease in patients with PCHD. HHR serves as a significant predictor for both the occurrence and short-term prognosis of PCHD.
2025, 46(4): 90-98.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250412
Abstract:
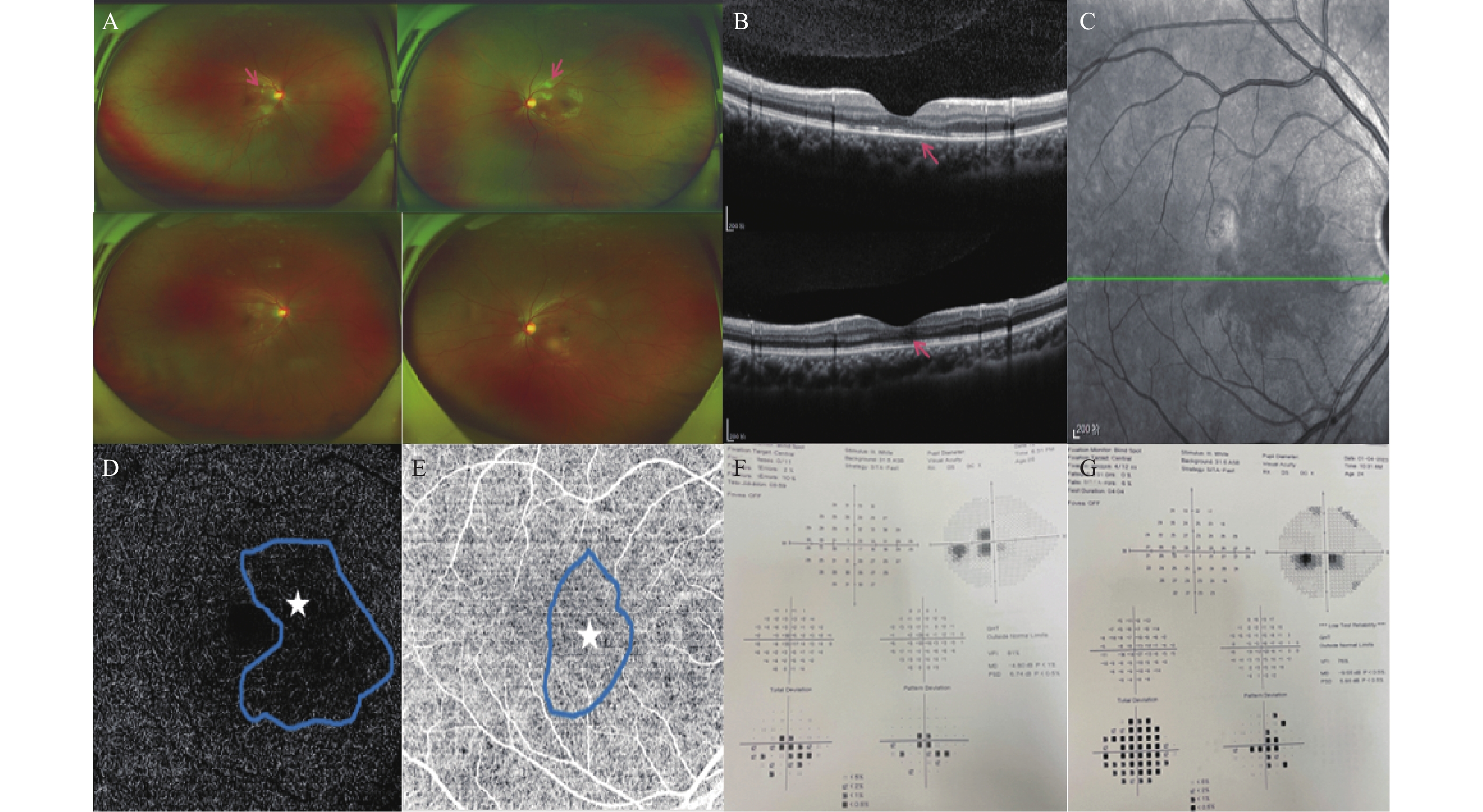
Objective To Observe the clinical characteristics and prognosis of patients with the acute macular neuroretinopathy (AMN) associated with novel coronavirus infection(COVID-19). Methods The data of 13 patients diagnosed with COVID-19-associated AMN attending the Department of Ophthalmology of the Affiliated Hospital of Yunnan University from December 2022 to February 2023, as well as 13 case reports in PubMed and Web of Science databases from 2020 to 2023 and a case series study totaling 41 patients were retrospectively selected and analyzed for their ophthalmic imaging and prognostic outcomes in clinic. Results A total of 13 cases with 25 eyes in the clinical case group were included in the study with a mean age of 30.23±6.02 years, of which 10 were females. The literature case group consisted of 41 cases and 72 eyes with a mean age of 30.12±13.24 years, including 31 female patients. (1) Duration between COVID-19 symptoms/diagnosis and ophthalmic symptoms: 3(2.0, 4.0) days in the clinical case group and 2 (0.75, 5.0) days in the literature case group. (2) Clinical characteristics: 12 (92.31%) of the clinical case group had the binocular onset and the literature case group, 31 (75.61%) had the binocular onset. The symptoms in both groups were mainly dark spots in vision, followed by decreased visual acuity. (3) Ancillary examinations: optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed the ellipsoid zone (EZ) and/or chimeric zone (IZ) breaks with strong reflections in the outer plexiform layer (OPL) and outer nuclear layer (ONL) in 13 patients in the clinical case group, and the near-infrared photography (NIR) showed the low-reflective wedge-shaped foci around the center of the macula, and some patients' optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) showed deep capillary lesions, and some patients' OCTA showed low reflectivity. Reduced blood flow in the deep capillary layer (DCP) and choroidal capillary layer (CC) was observed in all patients, 7 patients with cotton-wool spots also had the reduced blood flow in the superficial capillary layer (SCP), and 33 patients in the case group in the literature had the visible EZ and/or IZ breaks on OCT. (4) Treatment and prognosis: 11 out of 13 patients were treated with oral glucocorticoids, 2 were under the observation. After year, the condition of 23 patients had been improved, 1 case had visual field defects, 1 case had retinal vein occlusion secondary to macular edema, and 1 case had a hyporeflective signal in the outer nuclear layer (ONL) and outer plexiform layer (OPL). Conclusion The age of onset of AMN related to COVID-19 is slightly older, with more cases involving both eyes. The main symptom is visual field scotoma, often accompanied by decreased vision. Near-infrared imaging shows low-reflective wedge-shaped lesions around the fovea, and OCT shows mainly disruption of the EZ and/or IZ. OCTA shows decreased blood flow density in the DCP and CC layers. The visual prognosis of AMN related to COVID-19 is good, but vigilance is needed for the occurrence of complications such as retinal vein occlusion
2025, 46(4): 99-108.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250413
Abstract:
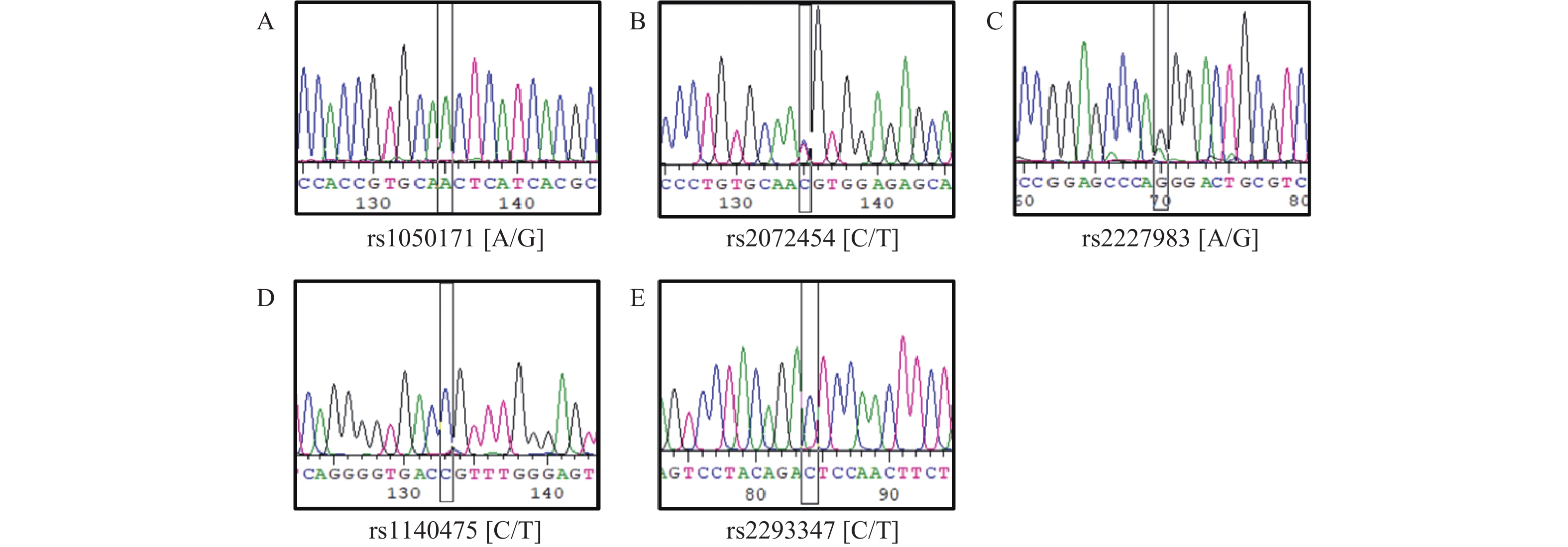
Objective To investigate the correlation between the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) gene polymorphisms and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in Yunnan Han population. Methods A total of 407 NSCLC patients and 526 healthy controls were included. Five SNPs (rs1050171, rs2072454, rs2227983, rs1140475 and rs2293347) in EGFR were genotyped using TaqMan assay. The association between SNPs and NSCLC, as well as pathological types, were analyzed. Results In dominant mode, rs2072454 C/T-T/T may be a risk factor for NSCLC (P = 0.004; OR = 1.50, 95%CI 1.14~1.96). There was a significant difference in genotype frequency between the SCC group and the control group (P = 0.007), but no difference in allele frequency after Bonferroni correction (P > 0.01); In the dominant mode, C/T-T/T at this locus relative to C/C was a risk for AC (P = 0.002; OR = 1.86, 95%CI 1.24~2.80). rs1050171 A/A had a significantly higher risk of SCC in recessive mode (P = 0.006, OR = 2.66, 95%CI 1.33~5.33). In dominant mode, rs2227983 A/G-G/G/G was a risk factor for the development of SCC relative to A/A (P = 0.007; OR = 1.83, 95%CI 1.15~2.89). Conclusion The SNPs rs2072454, rs1050171 and rs2227983 in EGFR gene may be associated with the risk of NSCLC development as well as the type of pathology in Yunnan Han population.
2025, 46(4): 109-114.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250414
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the effects of different gender, gestational age, birth weight and blood collection date on the value of 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) in neonatal screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) and to develop a positive cut-off for CAH screening that is appropriate for the laboratory itself. Methods Time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay was used to detect 17-OHP concentration, and Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis H test were used to compare 17-OHP concentration of newborns with the different gender, birth weight, gestational age and blood collection age. The comparison of rates was conducted using the multi-set rate chi-square test and Fisher's exact probability method. The relationship between the clinical features and 17-OHP concentration was analyzed by multiple linear regression, and the cut-off value of 17-OHP screening was 99.5% percentile. Results The 17-OHP concentration of male neonates was higher than that of female neonates, and the difference was statistically significant (Z= -17.768, P < 0.05). The 17-OHP concentration of neonates in groups with different gestational age, different birth weight, and different blood collection days were compared respectively, and the difference was statistically significant (χ2=5235.187 、3682.665 、493.414 respectively, P = 0.00). Further pair comparison showed that there were statistically significant differences in 17-OHP concentration of neonates at different gestational weeks, gestational age and blood collection days (P < 0.05), except that age of blood collection ≥3 and <4 days and ≥4 and <7 days(Z= -0.950, P = 0.342). Neonatal 17-OHP concentration decreased with the gestational age and birth weight increase. There were statistically significant differences in the initial screening positive rate and screening positive rate of 17-OHP among different gestational ages and different birth weights groups (P < 0.05), and they decreased with the increase of gestational age, birth weight and age at the time of blood collection. The results of multiple linear regression showed that 17-OHP concentration was related to the several factors, including the gestational age, birth weight, age of blood collection and gender in descending order. Conclusion The effects of various factors on the concentration of 17-OHP in neonatal peripheral blood should be comprehensively considered. The cut-off value of 17-OHP for CAH screening in the Screening Center for Neonatal Genetic Metabolic Diseases in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University is modified to ≥14.00 nmol/L for full-term neonates of normal weight and ≥36.00 nmol/L for premature or/and low-weight neonates so as to improve the specificity of neonatal CAH screening and reduce the false positives.
2025, 46(4): 115-122.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250415
Abstract:
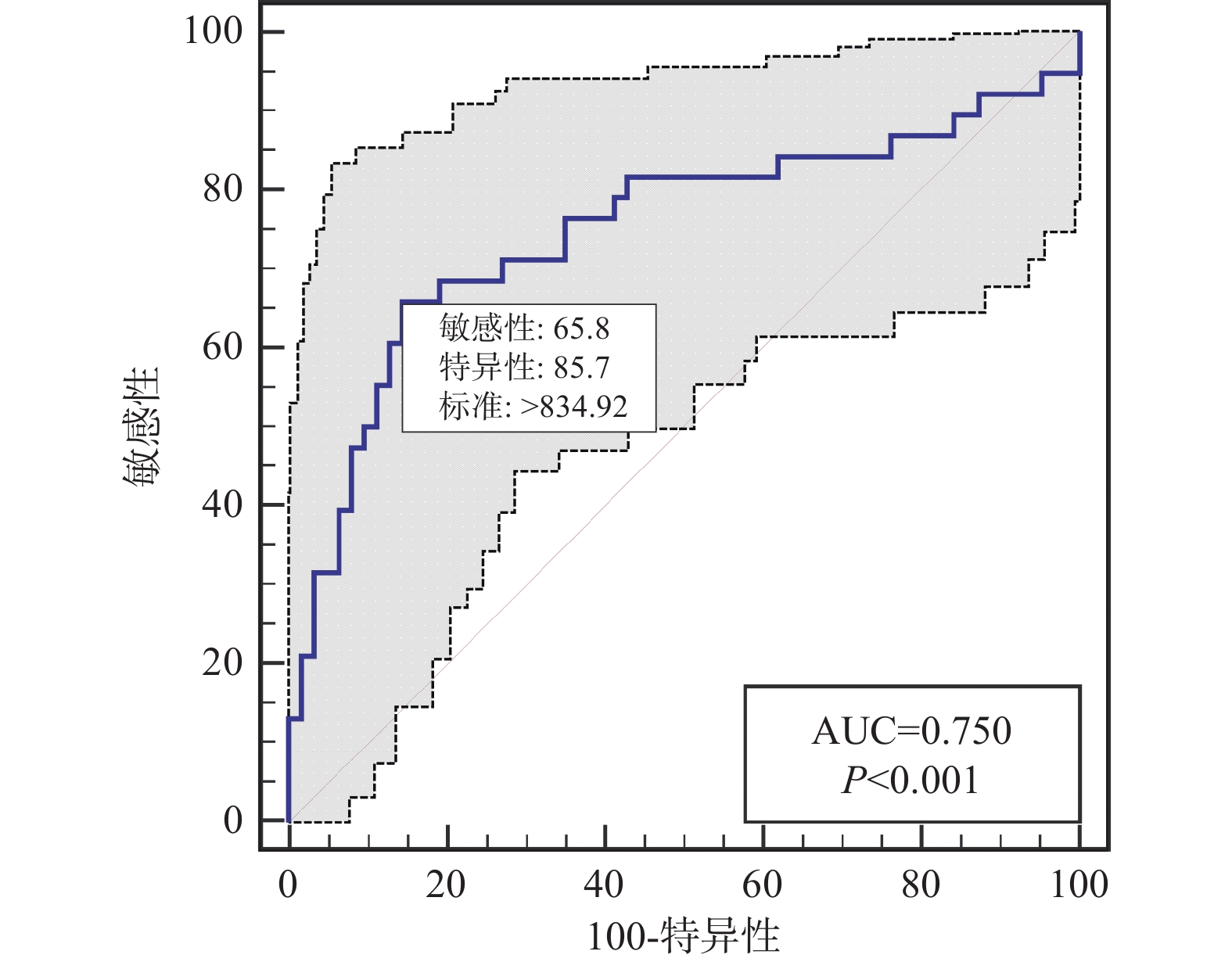
Objective To investigate the predictive value of pan-immune inflammatory values (PIV) in the prognosis of patients with ischemic stroke (AIS) treated with intravascular intervention combined with tirofiban. Methods 102 AIS cases admitted to the Department of Neurology of the First People's Hospital of Zhaotong from January 2019 to December 2023 and treated with intravascular intervention combined with Tirofiban were selected as the study objects. The patients were divided into the mild group (n = 9), moderate group (n = 45) and severe group (n = 48) according to the score of NIHSS after the admission. According to the mRS 90 days after the treatment, the cases were divided into the good prognosis group (n = 63) and poor prognosis group (n = 38). Data were collected and analyzed. The predictive value of PIV level in patients with ischemic stroke treated with intravascular intervention combined with tirofiban was evaluated by ROC. The risk factors of adverse outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke treated with intravascular intervention combined with tirofiban were investigated by multivariate Logistic regression. Results A total of 102 patients with ischemic stroke were included. The PIV level in the good prognosis group 331.1(221.9, 662.7) was lower than that in the poor prognosis group 1025.7 (451.5, 1841.3 ) (P < 0.05). PIV level in the severe group was higher than that in the mild and moderate groups, and PIV level in the moderate group was higher than that in the mild group (P < 0.05). The AUC (95%CI) of PIV for predicting adverse outcomes of intravascular intervention combined with tirofiban in patients with ischemic stroke was 0.750 (95%CI 0.654~0.831), the cut-off point was 834.92, the specificity was 85.71% and the sensitivity was 65.79%. NIHSS score > 18 (OR = 5.944 95%CI 2.011~19.137), PIV > 834.92 (OR = 4.863, 95%CI 1.410~18.685) were the risk factors for the poor outcome of intravascular intervention combined with tirofiban in patients with ischemic stroke (P < 0.05). Conclusion Elevated PIV is closely related to the poor outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke treated with intravascular intervention combined with Tirofiban. High PIV and NIHSS scores are both risk factors for the poor prognosis in patients with ischemic stroke, and can be used as the sensitive indicators for the early identification.
2025, 46(4): 123-128.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250416
Abstract:
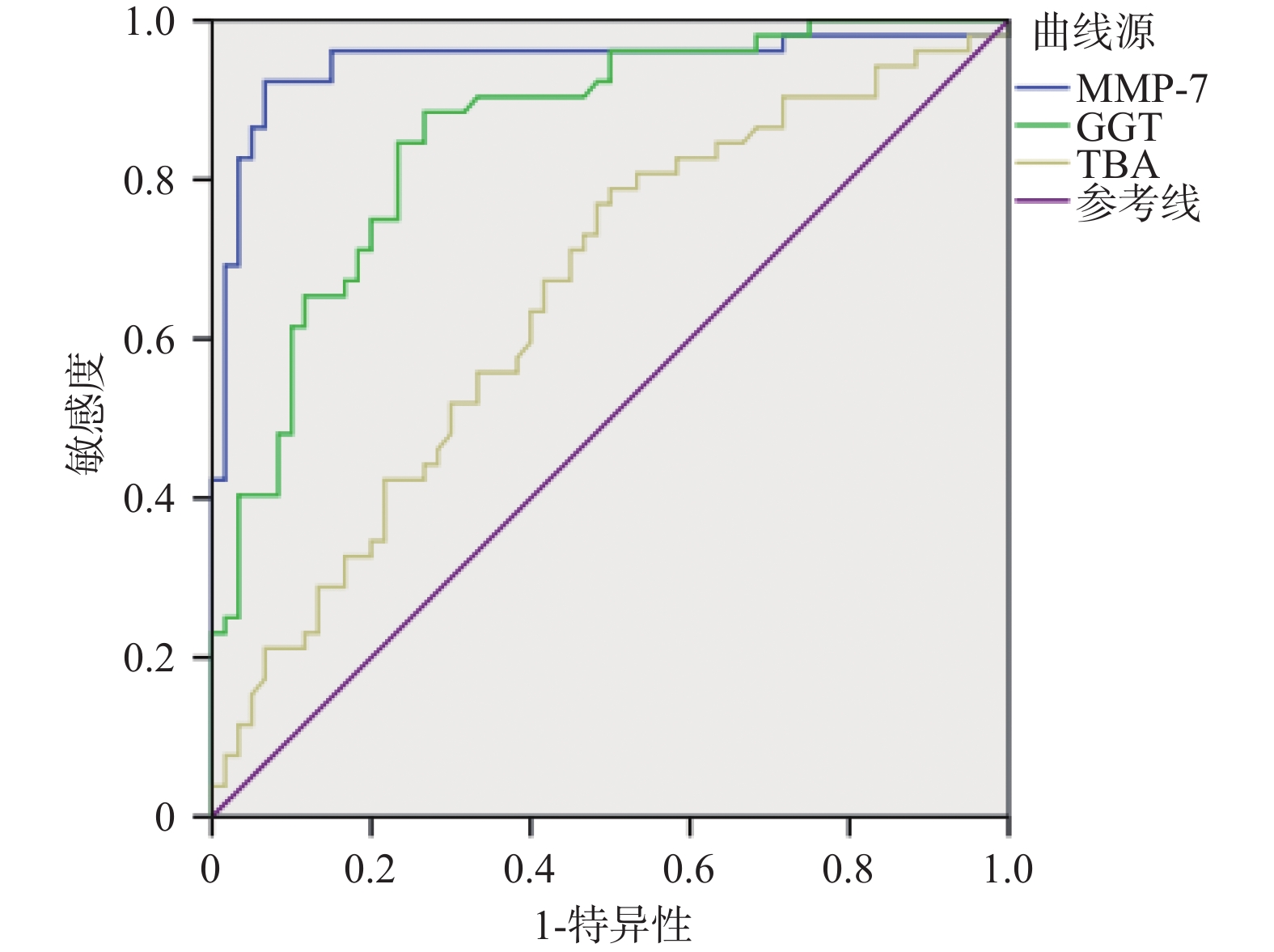
Objective To explore the value of serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 combined with glutamyl transferase and total bile acids in the diagnosis of biliary atresia. Methods 112 children hospitalized in Kunming Children's Hospital with the cholestatic jaundice from July 2023 to September 2024 were selected as the research subjects. According to the surgical exploration, intraoperative cholangiography, liver biopsy and follow-up, the children were divided into the biliary atresia group (BA) (n = 52) and non-biliary atresia group (Non-BA) (n = 60) respecvely. The age, gender, serum matrix metalloproteinase 7 (MMP-7), glutamyl transferase (GGT), alanine aminative aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), total bilirubin (TB), direct bilirubin (DB), total bile acid (TBA) and aspartate aminotransferase/platelet index (APRI) were compared between the two groups. Statistically significant indicators were included in receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis, and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) and optimal diagnostic margin (Youden index) were calculated. Results There was no significant difference in age, ALT, AST, DB, TB and APRI levels between the two groups of patients (P > 0.05); There was a difference in gender composition ratio between the two groups (P = 0.006); MMP-7 , GGT, TBA levels in the BA group were significantly higher than those in the Non-BA group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); the AUC of MMP-7, GGT, and TBA in diagnosing BA were 0.946 (95%CI 0.897~0.996) , 0.857 (95%CI 0.789~0.926), 0.654 (95%CI 0.552~0.755) respectively; When the cut-off value of MMP-7 was 22.37 ng/ml, the sensitivity and specificity for diagnosing BA were 0.923 and 0.933 respectively; When the cut-off value of GGT was 151.5 U/L, the sensitivity and specificity of diagnosing BA were 0.885 and 0.733 respectively; When the cut-off value of TBA was 119.5 μmol/L, the sensitivity and specificity of diagnosing BA were 0.788 and 0.500, respectively. The AUC of MMP-7 + GGT and MMP-7 + TBA combined to diagnose BA were 0.971 (95%CI 0.946~0.997) and 0.943 (95%CI 0.889~0.996) respectively. Conclusion Serum MMP-7 has the good diagnostic value as a single indicator for diagnosing BA; MMP-7 combined with GGT is better than a single indicator for diagnosing BA; MMP-7 combined with TBA cannot improve the diagnostic efficiency.
2025, 46(4): 129-135.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250417
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical characteristics, treatment and prognosis of patients undergoing the maintenance hemodialysis and treatment-naive tuberculosis and to explore the prognostic factors, so as to provide a reference for the clinical treatment of patients undergoing hemodialysis due to tuberculosis. Methods The clinical data of 70 patients undergoing hemodialysis with treatment-naive tuberculosis admitted to the Third People's Hospital of Kunming from October 31, 2020~October 31, 2023 were retrospectively collected, the clinical characteristics of the patients were analyzed, and the occurrence of adverse reactions, treatment outcomes and prognostic factors were observed. Results Among the 70 patients, pulmonary tuberculosis was the primary type (64 cases, accounting for 91.43%), and extrapulmonary tuberculosis was also quite common (56 cases, accounting for 80.00%). The most widely used anti-tuberculosis regimen was isoniazid, rifampicin, ethambutol, and moxifloxacin in a four-drug combination; During the anti-tuberculosis treatment, 55 patients (78.57%) improved. A total of 13 adverse reactions occurred in 11 patients (15.71%), and the most common ones were itching, rash and blurred vision. The hemoglobin, lymphocyte count and CD8+ T lymphocyte count in the treatment improvement group were higher than those in the ineffective group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Dialysis patients have a high risk of tuberculosis infection, mainly pulmonary tuberculosis, and extrapulmonary tuberculosis is more common. 78.57% of the patients hare improved after the tuberculosis treatment, but the overall prognosis is poor, and the low hemoglobin level is associated with ineffective treatment.
2025, 46(4): 136-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250418
Abstract:
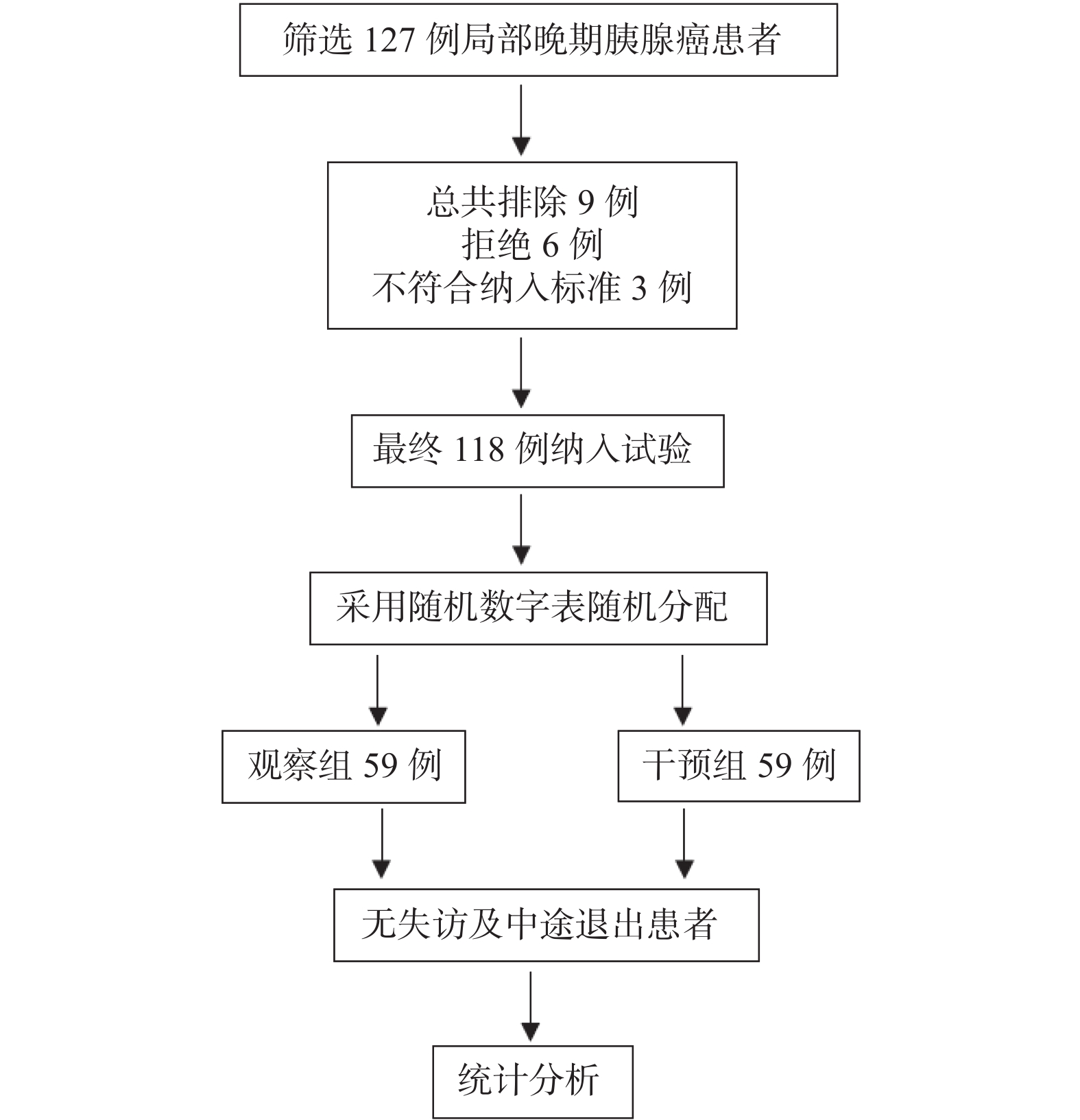
Objective To investigate the impact of nutritional risk-based intervention on the quality of life and survival prognosis of patients with the locally advanced pancreatic cancer and undergoing the chemotherapy. Methods A total of 118 patients with the pancreatic cancer and admitted to the Department of Hepatobiliary and Minimally Invasive Surgery, Lincang People's Hospital from April 2021 to April 2024 were selected and randomly divided into the nutritional intervention group and the control group, with 59 patients in each group. All patients received the palliative chemotherapy, and the control group received the routine dietary guidance, while the intervention group received the nutritional intervention based on the nutritional risk score. The nutritional status, quality of life score, and survival prognosis of the two groups were compared. Results The NRS2002 score of the intervention group and the control group gradually increased from the first to the sixth chemotherapy, and the NRS2002 score of the intervention group was lower than that of the control group at the 4th, 5th, and 6th chemotherapy (P < 0.05). The incidence of malnutrition in the intervention group was lower than that of the control group at the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd chemotherapy (11.9%, 30.9%, and 32.2%, respectively), but there was no significant difference (P > 0.05); The incidence of malnutrition in the intervention group was significantly lower than that of the control group at the 4th, 5th, and 6th chemotherapy (32.2%, 45.8%, and 52.5%, respectively), while the incidence of malnutrition in the control group was 59.3%, 69.5%, and 88.5%, respectively (P < 0.05); The quality of life score of the intervention group in all dimensions was significantly higher than that of the control group after the treatment (P < 0.05). After the nutritional intervention, the median OS time and median PFS time of the patients were significantly improved (P < 0.05). Conclusion Nutritional intervention can reduce the nutritional risk during the chemotherapy for locally advanced pancreatic cancer patients and improve their quality of life.
2025, 46(4): 143-149.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250419
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the sleep problems and temperament characteristics of children aged 12-35 months so as to understand the relationship between the sleep problems and temperament in early childhood. Methods 129 toddlers with sleep problems and 129 normal controls were selected. The brief infant sleep questionnaire (BISQ) was used to investigate children’ s sleep problems and the temperament questionnaire was used to investigate their temperament characteristics. The influence of temperament on sleep problems was analyzed by Logistic regression analysis. Results The temperament types of children aged 12 to 35 months with sleep problems were mainly easy to cultivate and moderately easy to cultivate. There was a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05) in the comparison of easily cultivating temperament types between the children with the sleep problems and the control group; Compared with the control group, there were statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) in the five dimensions of avoidance, adaptability, emotional essence, persistence, and attention dispersion among children with sleep problems. Compared with the temperament type of easy to cultivate, the proportion of sleep problems in children intermediately easy to cultivate and slow to start was higher (both P < 0.05) Conclusion There is a certain relationship between the sleep problems and temperament types in children aged 12 to 35 months. Early understanding of sleep problems and temperament characteristics of toddlers can guide parents to adjust their education methods in time, give parents "individualized" sleep guidance and intervention, reduce the occurrence of long-term development problems and promote the healthy physical and mental development of toddlers.
2025, 46(4): 150-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250420
Abstract:
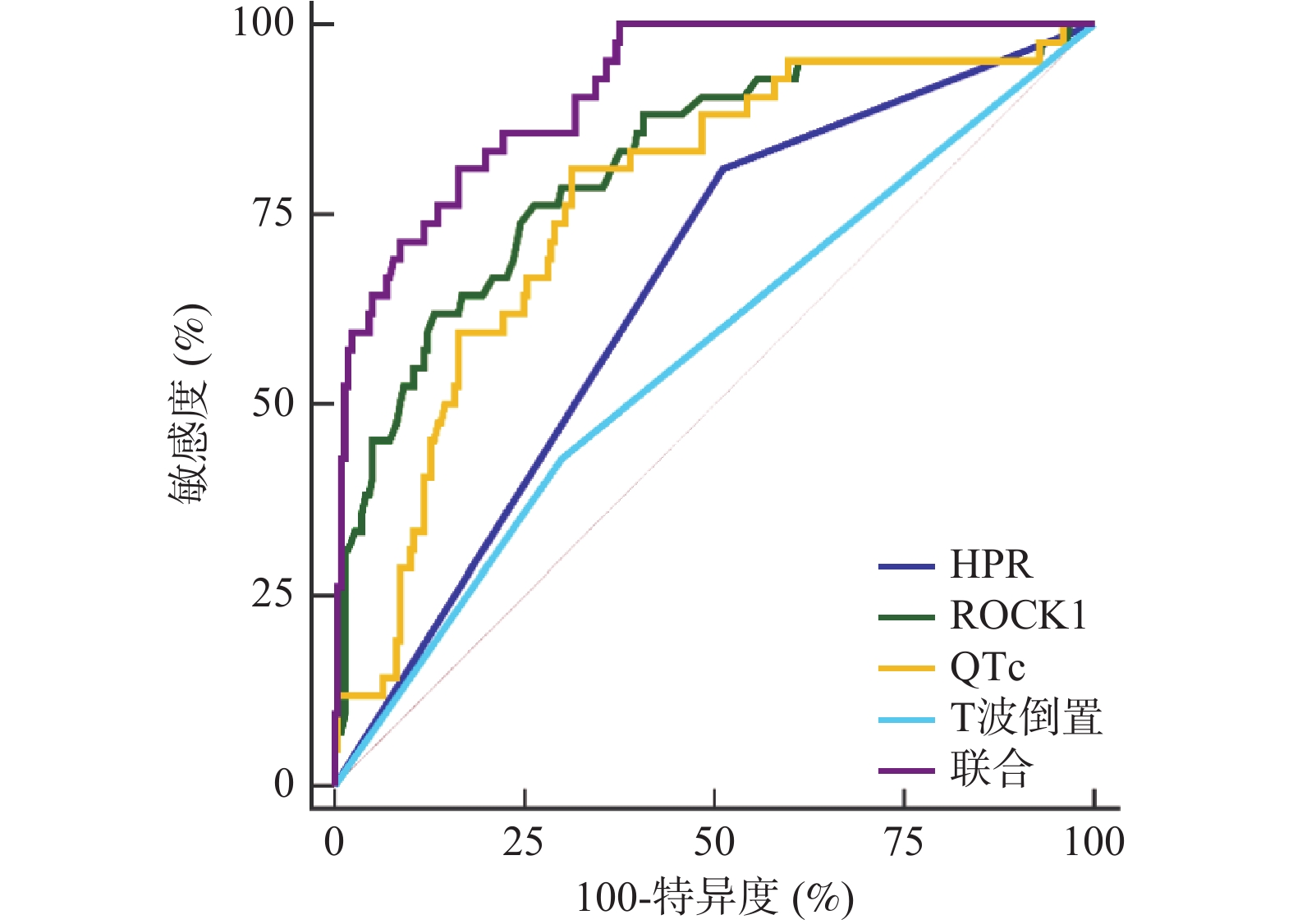
Objective To investigate the predictive value of platelet reactivity, RhoC and Rho kinase 1 (ROCK1) combined with the electrocardiogram performance for slow flow/no reflow (SF/NRF) after the percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in elderly patients. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 263 elderly PCI patients admitted to our hospital from January 2021 to July 2024. According to TIMI flow classification after PCI, they were divided into SF/NRF group (grade 0-II of TIMI flow classification, 42 cases) and the control group (grade III of TIMI flow classification, 221 cases). The baseline data and platelet reactivity, ROCK1, and ECG performance were compared between the two groups and the factors influencing SF/NRF after PCI in the elderly were analyzed. The value of joint predictors, each original covariate to predict SF/NRF after PCI in the elderly was evaluated. Results The proportion of patients with HPR, ROCK1, QTc, and T-wave inversion in SF/NRF group was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05); increased HPR, ROCK1, QTc, and T-wave inversion were independent risk factors for SF/NRF after PCI in the elderly (P < 0.05); the AUC of the combined predictors for predicting SF/NRF after PCI in the elderly was significantly higher than that of the original covariates HPR (X1), ROCK1 (X2, QTc (X3), and T-wave inversion (X4) (Z = 5.112, 3.688, 4.368, 5.697, P < 0.05). Conclusion The increase of HPR, ROCK1, QTc and T wave inversion are independent risk factors for SF/NRF after PCI in the elderly. The combined detection of these indicators has certain predictive value for the occurrence of SF/NRF after PCI in the elderly.
2025, 46(4): 157-162.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250421
Abstract:
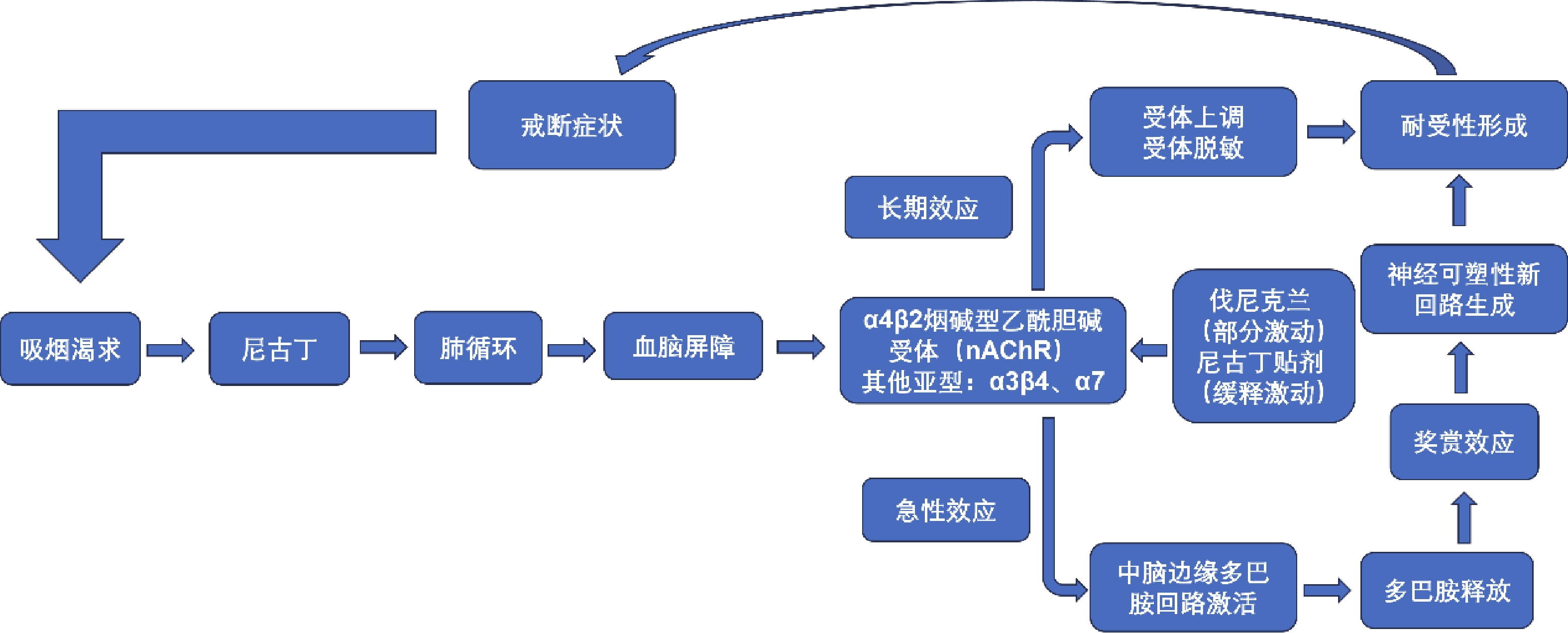
China has the highest number of smokers in the world with more than 1 million tobacco-related deaths each year. Smoking cessation is a feasible intervention to reduce the prevalence of smoking-related diseases and premature deaths. The smoking cessation therapies approved for use in China are ineffective for some tobacco dependent patients. In order to further improve the rate of smoking cessation, a combination of medications can be chosen, including varenicline combined with nicotine replacement therapy. However, there are conflicting evaluation conclusions on the effectiveness and safety of combination therapy. This article aims to review the mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety of varenicline combined with nicotine replacement therapy in the treatment of tobacco dependence, aiming to provide a basis for this combination therapy.
China has the highest number of smokers in the world with more than 1 million tobacco-related deaths each year. Smoking cessation is a feasible intervention to reduce the prevalence of smoking-related diseases and premature deaths. The smoking cessation therapies approved for use in China are ineffective for some tobacco dependent patients. In order to further improve the rate of smoking cessation, a combination of medications can be chosen, including varenicline combined with nicotine replacement therapy. However, there are conflicting evaluation conclusions on the effectiveness and safety of combination therapy. This article aims to review the mechanism of action, efficacy, and safety of varenicline combined with nicotine replacement therapy in the treatment of tobacco dependence, aiming to provide a basis for this combination therapy.
2025, 46(4): 163-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250422
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effects of Emotional Freedom Techniques combined with PERMA model intervention on fear of disease progression and quality of life in postoperative liver cancer patients. Methods A total of 58 liver cancer patients admitted from September 2023 to February 2024 were randomly divided into the experimental group (n = 29) and the control group (n = 29) using a random number table method. The experimental group received Emotional Freedom Techniques combined with PERMA-based positive psychological intervention, while the control group received the holistic nursing and routine psychological guidance. Both groups underwent the continuous intervention for 8 weeks. Outcomes were assessed using the Fear of Progression Questionnaire-Short Form (FoP-Q-SF), Distress Thermometer (DT), Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS), Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS), Cancer Fatigue Scale (CFS), Athens Insomnia Scale (AIS) and Index of Well-Being (IWB). Results After the intervention, the experimental group showed the significantly lower scores than those in the control group in FoP-Q-SF (24.97±2.34 / 34.10±8.46), DT (2.24±0.95 / 2.93±1.33), SAS (49.55±1.35 / 58.55±4.60), SDS (51.86±1.58 / 61.79±4.00), CFS (4.03±0.94 / 5.10±1.18), and AIS (2.45±1.12 / 4.07±0.96) (all P < 0.05), while the IWB score (10.56 ± 1.74/7.39 ± 2.05) was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion The combination of Emotional Freedom Techniques and PERMA model intervention can effectively alleviate the disease-related fears, improve the negative emotions, reduce the physical symptoms and enhance the subjective well-being in postoperative liver cancer patients, and it has a significant clinical application value.
2025, 46(4): 170-174.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250423
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the effect of programmed nursing on dry eye after the phacoemulsification for cataract. Methods A total of 100 cases undergoing the phacoemulsification for cataract in our hospital from January 2022 to January 2024 were divided randomly into the control group and the observation group based on nursing differences with 50 cases in each group. The control group received the routine nursing, while the observation group was given the programmed nursing. The incidence of postoperative dry eye, nursing satisfaction, and dry eye-related complications were compared between the two groups. Results The results showed that the corneal fluorescence staining, tear secretion test, and tear film rupture time in the observation group were (1.46 ± 1.13) points, (17.18 ± 1.45) mm, and (6.86 ± 0.92) s, respectively, which were superior to the control group’ s (2.96 ± 0.09) points, (11.04 ± 2.79) mm, and (5.98 ± 1.26) s (all P < 0.05); The incidence of dry eye complications in the observation group at 45 days and 90 days after the surgery was 8.0% and 6.0%, respectively, lower than that in the control group at 18.0% and 16.0% (both P < 0.05); The satisfaction rate of the observation group with nursing care was 98.0%, which was higher than the control group’ s 84.0% (P < 0.05). The differences between the groups were statistically significant. Conclusion Programmed nursing for patients undergoing the phacoemulsification for cataract can reduce the incidence of dry eye, improve the eye condition of patients and increase the patient satisfaction.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS