Current Issue
2026, Volume 47, Issue 2
2026,
47(2):
1-13.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260201
Abstract:
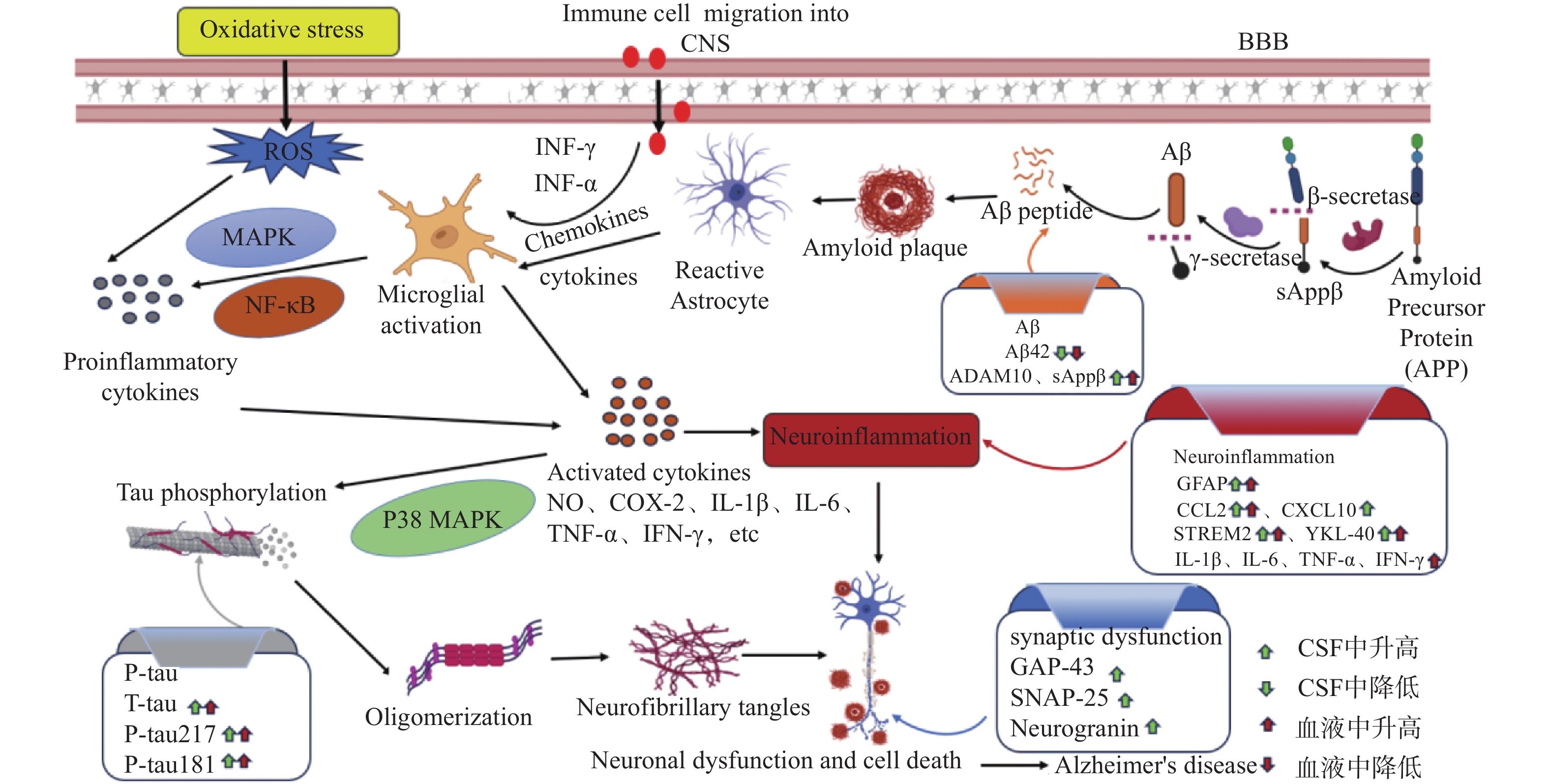
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common chronic neurodegenerative disorders, characterized by a series of pathological processes. Neuroinflammation, marked by activation of the glial cell system, constitutes a key component of AD pathogenesis. Timely prevention of neuroinflammation or monitoring of inflammatory responses may serve as a prospective therapeutic approach for AD. This article reviews the potential application value of neuroinflammation biomarkers in early diagnosis of AD and their clinical significance in disease progression, and summarizes the current therapeutic research progress on AD-related neuroinflammation drugs, with the aim of providing reference for subsequent research and clinical practice in this field.
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common chronic neurodegenerative disorders, characterized by a series of pathological processes. Neuroinflammation, marked by activation of the glial cell system, constitutes a key component of AD pathogenesis. Timely prevention of neuroinflammation or monitoring of inflammatory responses may serve as a prospective therapeutic approach for AD. This article reviews the potential application value of neuroinflammation biomarkers in early diagnosis of AD and their clinical significance in disease progression, and summarizes the current therapeutic research progress on AD-related neuroinflammation drugs, with the aim of providing reference for subsequent research and clinical practice in this field.
2026,
47(2):
14-20.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260202
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the mechanism of collagen-related integrins α1, α2 and β1 on the Caveolin-1 (Cav-1)/aquaporin 1 (AQP1) signaling pathway during scleral remodeling in the recovery phase of form-deprivation myopia (FDM). Methods 50 guinea pigs were randomly divided into a study group (n = 40) and a control group (n = 10). The study group underwent FDM induction with monocular occlusion for 4 consecutive weeks. After removing the eye cover, FDM guinea pig models at different recovery time points were established: 4-week deprivation, 3-day recovery, 7-day recovery, and 14-day recovery (n = 10 each). The contralateral eye of study group animals served as internal control, and both eyes of the 10 control group animals served as normal control. Refraction and axial length of control eyes, 4-week deprivation eyes, 3-day recovery eyes, 7-day recovery eyes, and 14-day recovery eyes were measured. RT-PCR was used to detect the mRNA expression of collagen-related integrin α1, α2, and β1 in the scleral tissue; electron microscopy was used to observe the ultrastructure of the sclera; HE staining was used to observe the morphology of the sclera; and immunoblotting was used to detect the expression of Caveolin-1 and AQP1 proteins in the scleral tissue. Results Compared with the control eyes, 4-week deprivation eyes, 3-day recovery eyes, and 7-day recovery eyes showed decreased refraction and AQP1 protein, with increased axial length and Caveolin-1 (P < 0.05). At 14-day recovery, no significant changes were observed (P > 0.0083). Compared with 4-week deprivation and 3-day recovery eyes, 7-day recovery eyes showed elevated refraction and AQP1 protein expression, with decreased axial length and Caveolin-1 (P < 0.05). No significant differences were found between 4-week deprivation and 3-day recovery eyes (P > 0.0083). Compared with control eyes, Integrinα1, α2, and β1 mRNA levels were decreased in 4-week deprivation, 3-day recovery, and 7-day recovery eyes (P < 0.05), with no significant changes at 14-day recovery (P > 0.0083). Compared with 4-week deprivation eyes, Integrinα1, α2 and β1 mRNA levels increased in 3-day and 7-day recovery eyes, with the highest levels at 7-day recovery (P < 0.05). Electron microscopy showed improved collagen fibril distribution in 7-day and 14-day recovery eyes, with 14-day recovery eyes showing near-normal distribution. HE staining revealed that 14-day recovery eyes had near-normal scleral morphology. Conclusion During scleral remodeling in the recovery period of form-deprivation myopia, collagen-related integrins α1, α2 and β1 may directly or indirectly regulate the Caveolin-1/AQP1 pathway, affecting water transport and signal transduction in scleral cells, thereby participating in scleral remodeling.
2026,
47(2):
21-34.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260203
Abstract:
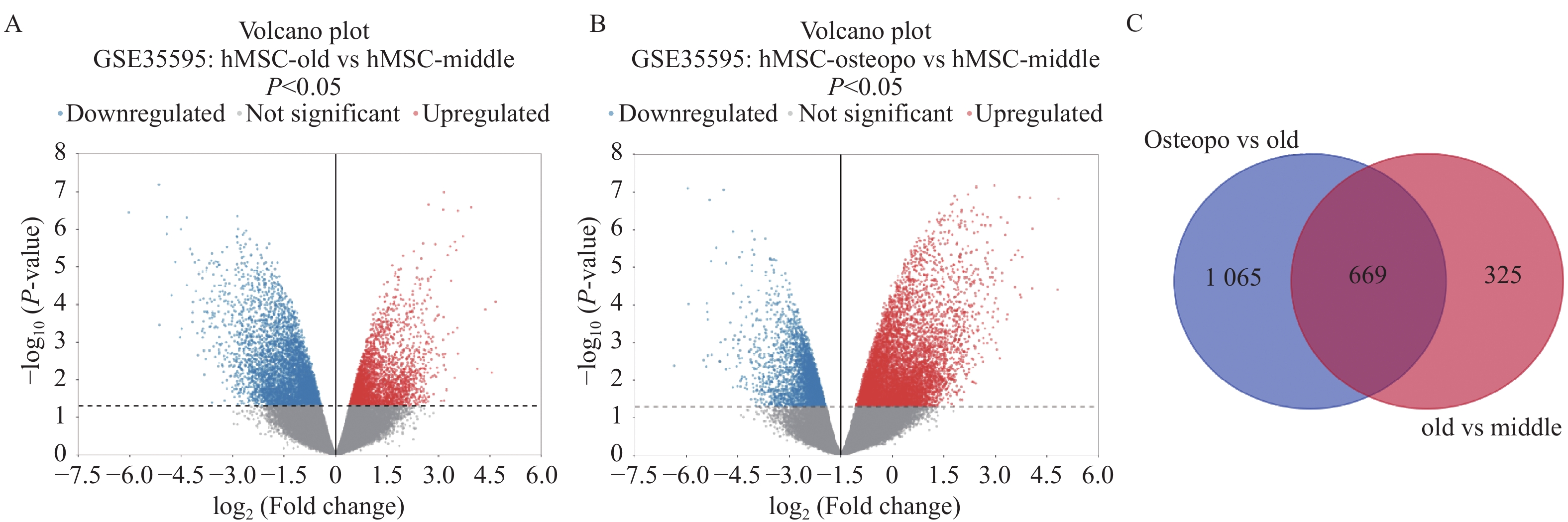
Objective To explore potential active components of Chinese herbal medicines (CHMs) for treating bone aging and their mechanisms of action using reverse network pharmacology and molecular docking techniques, with preliminary experimental validation. Methods Transcriptomic data were obtained from the GEO database. GEO2R was used to analyze differentially expressed genes, identifying a characteristic bone aging gene set. A Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) network was constructed to identify key targets, followed by Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses. Core disease targets were identified by intersecting results from three algorithms (Degree, MCC, and Stress). These core targets were used to reversely identify CHMs with potential anti-bone aging effects, followed by drug activity analysis. Molecular docking was performed between active components and core disease targets to further screen representative compounds. Senescent bone cell models and animal models were established for preliminary efficacy verification. Cell experiments were divided into 4 groups: control group (Control), bone aging group (D-Gal), quercetin + bone aging group (Que+D-Gal), and quercetin group (Que). An aging bone cell model was constructed using D-galactose (10 g/L), and quercetin (10 µM) was used to treat D-Gal-induced senescent cells. Cellular senescence was observed by SA-β-Gal staining, and p53 protein expression was detected by immunofluorescence and Western blot. Twenty-four C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into 4 groups (6 mice per group) with the same grouping as cells. A bone aging mouse model was established via subcutaneous injection of D-galactose (500 mg/kg) on the dorsal neck, and quercetin (50 mg/kg) was administered by gavage. HE staining of femoral sections was used to observe bone protective effects. Results A total of 669 characteristic bone aging genes were identified, primarily enriched in as PI3K-AKT, MAPK, osteoclast differentiation, and longevity regulation pathways. Core targets were TP53, HSPA4, ESR1, ERBB2, GSK3B, and STAT1. Reverse screening identified CHMs acting on all six core targets: Ardisia japonica , Artemisia argyi , Zingiber officinale, Glycine max , Carthamus tinctorius , Cannabis sativa , and Smilax glabra. The main active components included β-sitosterol, stigmasterol, quercetin, and luteolin. Molecular docking between the six core targets and the active components revealed that stigmasterol, quercetin, and luteolin exhibited strong binding (binding energy ≤ -7 kcal/mol) to all six core targets. Considering both binding energy and oral bioavailability, quercetin was selected as the representative drug for this study. SA-β-Gal staining showed that the positive area of senescent cells in the Que+D-Gal group was significantly reduced compared to the D-Gal group (P < 0.01). Immunofluorescence and Western blot confirmed that that p53 fluorescence signal intensity (P < 0.01) and p53 protein expression (P < 0.001) were significantly decreased in the Que+D-Gal group compared to the D-Gal group. Conclusion Through reverse network pharmacology, this study screened active components from traditional Chinese herbs such as Ardisia japonica and Artemisia argyi from large databases. Components like stigmasterol, quercetin, and luteolin may regulate the key aging target TP53 and synergize with genes in bone metabolism-related pathways (e.g., ESR1, GSK3B), thereby exerting bone protective effects. Preliminary experimental verification has found that one of the predicted representative drugs, quercetin, can indeed improve bone aging and downregulate the expression of the key aging factor p53.
2026,
47(2):
35-42.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260204
Abstract:
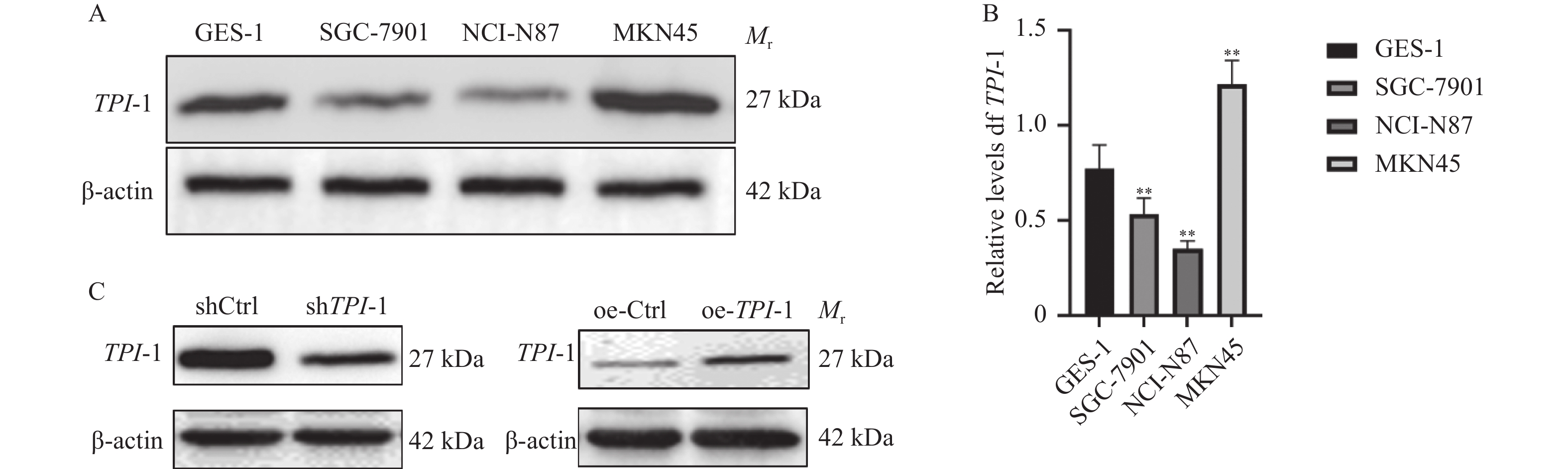
Objective To investigate the potential mechanism of TPI-1 intervention in gastric cancer progression from the perspective of glycolytic reprogramming. Methods TPI-1 knockdown and overexpression gastric cancer cell models were constructed. Experimental cells were divided into four groups: shCtrl, shTPI-1, oe-Ctrl, and oe-TPI-1. Cell viability was detected using the CCK-8 assay; invasive capacity was assessed using the Transwell assay; glycolytic capacity was measured using glycolytic stress test to detect ECAR reflecting the glycolytic capacity of different groups of gastric cancer cells; Western blot was used to analyze the expression levels of apoptosis-related, invasion-related, and glycolysis-related characteristic markers in different groups; immunofluorescence and co-IP experiments were performed to verify the colocalization and binding relationship between TPI-1 and HK2. Results Compared with the shCtrl group, the shTPI-1 group showed reduced cell proliferation and invasion capacity (P < 0.01); compared with the oe-Ctrl group, the oe-TPI-1 group demonstrated enhanced proliferation and invasion capacity (P < 0.01); after TPI-1 knockdown, both basal glycolytic capacity and maximum glycolytic capacity were decreased (P < 0.01); in the shTPI-1 group, protein levels of glycolytic key enzymes HK2 and PKM2 were significantly reduced (P < 0.01), and MMP-2, MMP-9, N-cadherin, Bcl-2, and COX4I1 were significantly downregulated (P < 0.01), while NOX4, E-cadherin, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 were significantly upregulated (P < 0.01); the oe-TPI-1 group showed opposite trends; immunofluorescence analysis revealed colocalization of TPI-1 and HK2 within cells; co-immunoprecipitation preliminarily confirmed that TPI-1 and HK2 may interact. Conclusion TPI-1 promotes gastric cancer progression by interacting with HK2, continuously activating the initiation step of glycolysis, and promoting glycolysis reprogramming.
2026,
47(2):
43-50.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260205
Abstract:
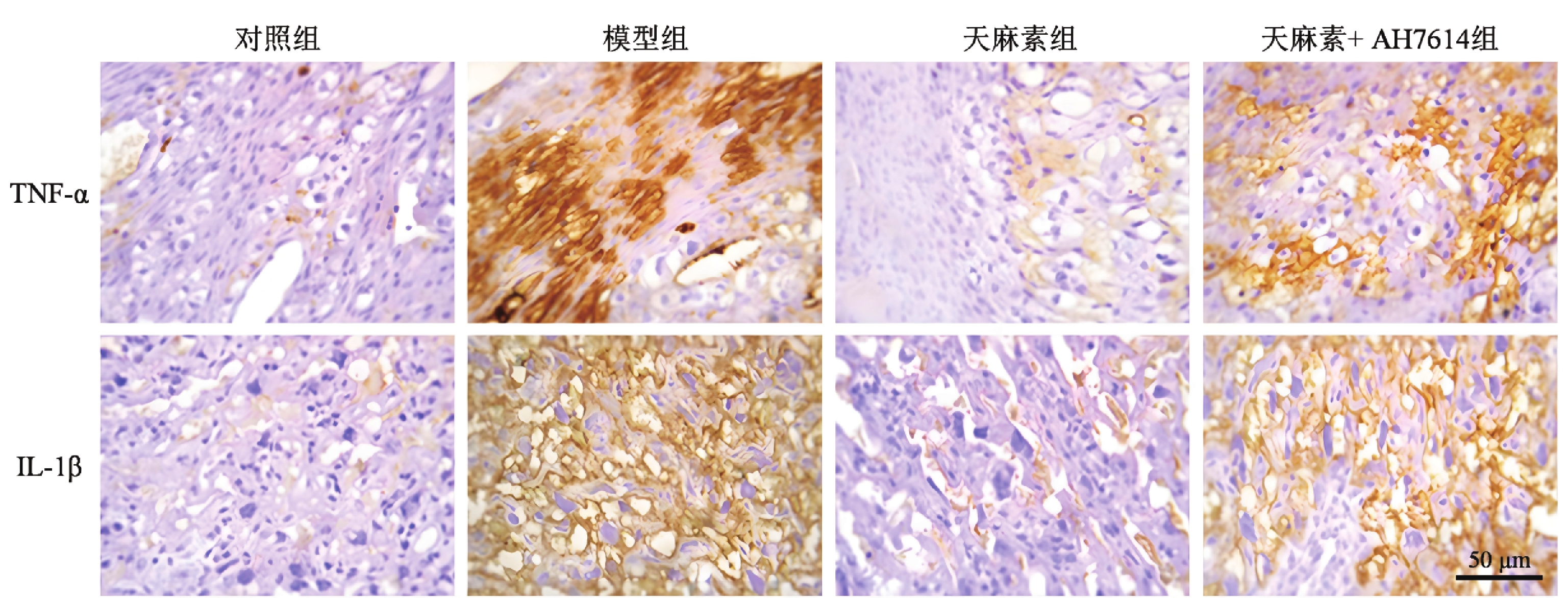
Objective To investigate the effects and mechanisms of gastrodin on lipotoxicity damage at the maternal-fetal interface in rats with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). Methods A GDM rat model was established using intraperitoneal injection of streptozotocin. Thirty pregnant rats were randomly divided into three groups: model group, gastrodin group (100 mg/kg), and gastrodin (100 mg/kg) + G protein-coupled receptor 120 (GPR120) antagonist AH7614 (25 mg/kg) group. An additional 10 pregnant rats were used as a control group. Each group received intraperitoneal injection or gavage of corresponding drugs once daily until the 20th day of pregnancy. Serum fasting blood glucose (FBG), free fatty acids (FFA), total cholesterol (TC), and triglycerides (TG) levels, as well as maternal body weight and fetal survival rate, were measured. ELISA and immunohistochemistry were used to measure serum and maternal-fetal interface tissue TNF-α and IL-1β levels. Flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis in maternal-fetal interface tissue. Immunofluorescence was used to detect GPR120 and adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) protein distribution and expression. Western blot was used to detect GPR120, AMPK, and phosphorylated AMPK (p-AMPK) protein expression in maternal-fetal interface tissue. Results Compared with the control group, the model group showed significantly increased serum FBG, FFA, TC, TG, TNF-α, and IL-1β, maternal body weight, maternal-fetal interface tissue TNF-α, IL-1β, and cell apoptosis levels (P < 0.05), while fetal rat survival rate and maternal-fetal interface tissue GPR120 and p-AMPK/AMPK levels were significantly decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the gastrodin group showed significantly decreased serum FBG, FFA, TC, TG, TNF-α, and IL-1β, maternal body weight, maternal-fetal interface tissue TNF-α, IL-1β, and cell apoptosis levels(P < 0.05), while fetal rat survival rate and maternal-fetal interface tissue GPR120 and p-AMPK/AMPK levels were significantly increased (P < 0.05). AH7614 reversed the intervention effect of gastrodin on GDM rats (P < 0.05). Conclusion Gastrodin can improve glucose and lipid metabolism, obesity, and adverse pregnancy outcomes in GDM rats, inhibit inflammation and apoptosis at the maternal-fetal interface, and its mechanism may be related to the activation of the GPR120/AMPK pathway.
2026,
47(2):
51-59.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260206
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of low-molecular-weight heparin, insulin, combined with fenofibrate on local inflammation in patients with hyperlipidemic acute pancreatitis (HL-SAP). Methods 157 HL-SAP patients admitted to the Gastroenterology Department of Xi'an Third Hospital from January 2022 to February 2024 were enrolled and randomly divided into a conventional group (n = 79) and a combined group (n = 78). The conventional group received standard treatment combined with fenofibrate capsules, while the combined group received standard treatment combined with low-molecular-weight heparin, insulin supplemented with fenofibrate capsules. The symptoms, blood lipid levels, inflammatory factors, liver and kidney functions, pancreatic enzyme indicators, MCTSI scores, pancreatic edema, local complications, adverse reactions and efficacy of the two groups were analyzed. Results Compared with the conventional group, the combined group showed significantly improved effectiveness (P < 0.05). After one week of treatment, the combined group had shorter times for abdominal pain relief, peritoneal sign resolution, gastrointestinal function recovery, and hospital stay (P < 0.05). The combined group showed better improvements in TC, TG, CRP, TNF-α, IL-6, ALT, AST, Scr, BUN, LPS, AMS, APACHE II scores, and MCTSI scores compared to the conventional group (P < 0.05). Pancreatic edema volume was smaller in the combined group, with superior improvement; complications and adverse reactions were lower in the combined group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Low-molecular-weight heparin, insulin combined with fenofibrate capsules can effectively improve clinical outcomes in HL-SAP patients, reduce inflammatory factor levels, stabilize blood lipids, improve liver and kidney function and pancreatic enzyme indicators, reduce local pancreatic complications and adverse reactions, and demonstrate good clinical value and treatment safety, warranting further clinical promotion.
2026,
47(2):
60-67.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260207
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the value of lipoprotein(a) [Lp(a)] and coronary perivascular fat attenuation index (FAI) in risk assessment of coronary heart disease (CHD). Methods A retrospective study was conducted to collect clinical data from 81 CHD patients diagnosed by coronary CT angiography and 125 normal controls from Wenshan Prefecture People’ s Hospital between October 2021 and January 2023. Clinical information, Lp(a) results, plaque characteristics, the number of lesion vessels, calcification scores, Gensini scores, and FAI values related to the anterior segments and lesion segments of the left anterior descending artery (LAD), left circumflex artery (LCx), and right coronary artery (RCA) were gathered from all subjects. Differences in Lp(a), calcification score, Gensini score, and FAI between CHD and control groups as well as among different CHD vessel groups were analyzed. Comparisons were made between plaques of different characteristics and FAI values. Logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors for CHD and the interactive effects of Lp(a) and FAI on CHD risk. Pearson correlation analysis was performed to assess the correlation between Log-Lp(a) and FAI. ROC curves were used to evaluate the diagnostic value of Lp(a) and FAI for CHD, with DeLong test to compare differences in AUC values. Results Lp(a) levels and mean FAI values of the proximal segments of the three coronary arteries showed statistically significant differences between CHD and control groups (P < 0.05 for all). Lp(a) concentration was positively correlated with calcification score (r = 0.385, P < 0.001). With increasing number of affected vessels in the CHD group, calcification score and Gensini score progressively increased (P < 0.05 for all). Lp(a) and FAI of the proximal three coronary arteries showed statistically significant differences only between single-vessel and multi-vessel disease groups (P < 0.05). Lesion segment FAI showed statistically significant differences only between non-calcified and calcified plaques (P < 0.05). Multivariate logistic regression showed Log-Lp(a) and FAI as independent risk factors for CHD, with weak correlation between FAI and Log-Lp(a) (r = 0.352, P < 0.001). ROC curve analysis revealed AUC values of 0.729, 0.856, and 0.879 for Lp(a), FAI, and their combination respectively for CHD diagnosis. DeLong test demonstrated that FAI and their combination had significantly larger AUC values than Lp(a) (P < 0.05 for all). Interaction analysis showed that the interactive OR value for high Lp(a) and high FAI was 78.111 (95%CI: 20.778~293.645, P < 0.001), indicating synergistic effects in increasing CHD risk. Conclusion Lp(a) and FAI are independent risk factors for CHD with synergistic amplification effects, and can serve as effective indicators for CHD prevention and risk stratification.
2026,
47(2):
68-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260208
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of coronary angiography-based microcirculatory resistance index for coronary microcirculatory dysfunction through cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR), and further explore the correlation between coronary microcirculatory dysfunction and silent cerebral infarction. Methods 231 patients from the Cardiovasology Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University between January 2021 and December 2024 were selected. The caIMR value of the left anterior descending coronary artery was analyzed using the FlashAngio system, with patients divided into normal coronary microcirculation group (caIMR<25, n = 126) and coronary microcirculatory dysfunction group (caIMR≥25, n = 105). General clinical data, laboratory indicators (complete blood count, biochemical panel, glycated hemoglobin), cranial CT/MRI results, cardiac microcirculatory perfusion MRI parameters (time to peak [tpeak], relative signal intensity at peak [RSIpeak], maximum upslope [Slopemax]), and routine transthoracic echocardiography parameters of all patients were collected. Results (1) Among 50 patients who completed both CMR and caIMR, the caIMR≥25 group showed varying degrees of tpeak prolongation, with reduced RSIpeak and Slopemax, indicating coronary microcirculatory dysfunction. Cohen's Kappa consistency analysis showed a Kappa value of 0.839 (P < 0.05), suggesting high accuracy of caIMR in identifying CMD; (2) 127 diabetic patients were categorized based on HbA1c levels into good glycemic control group (4%≤HbA1c<6%), moderate glycemic control group (6%≤HbA1c<8%), and poor glycemic control group (HbA1c≥8%). Comparing 40 patients in the good control group, 59 in the moderate control group, and 28 in the poor control group, the median caIMR values in the moderate and poor control groups were higher than the good control group (P < 0.05). The moderate control group's median caIMR of 24.60 was close to the diagnostic threshold of 25, while the poor control group's median caIMR of 32.15 was significantly higher; (3) In the coronary microcirculatory dysfunction group, several patients simultaneously had silent cerebral infarction, which was less common in the normal microcirculation group, with statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). Further Phi coefficient correlation analysis showed a coefficient of 0.562, with statistically significant difference (P < 0.001), suggesting a correlation between coronary microcirculatory dysfunction and silent cerebral infarction. Conclusion caIMR demonstrates high accuracy in identifying coronary microcirculatory dysfunction, with good consistency with CMR assessment. The high prevalence of silent cerebral infarction in patients with coronary microcirculatory dysfunction suggests potential interconnected pathological development in cerebral and cardiac microvascular systems.
2026,
47(2):
83-92.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260209
Abstract:
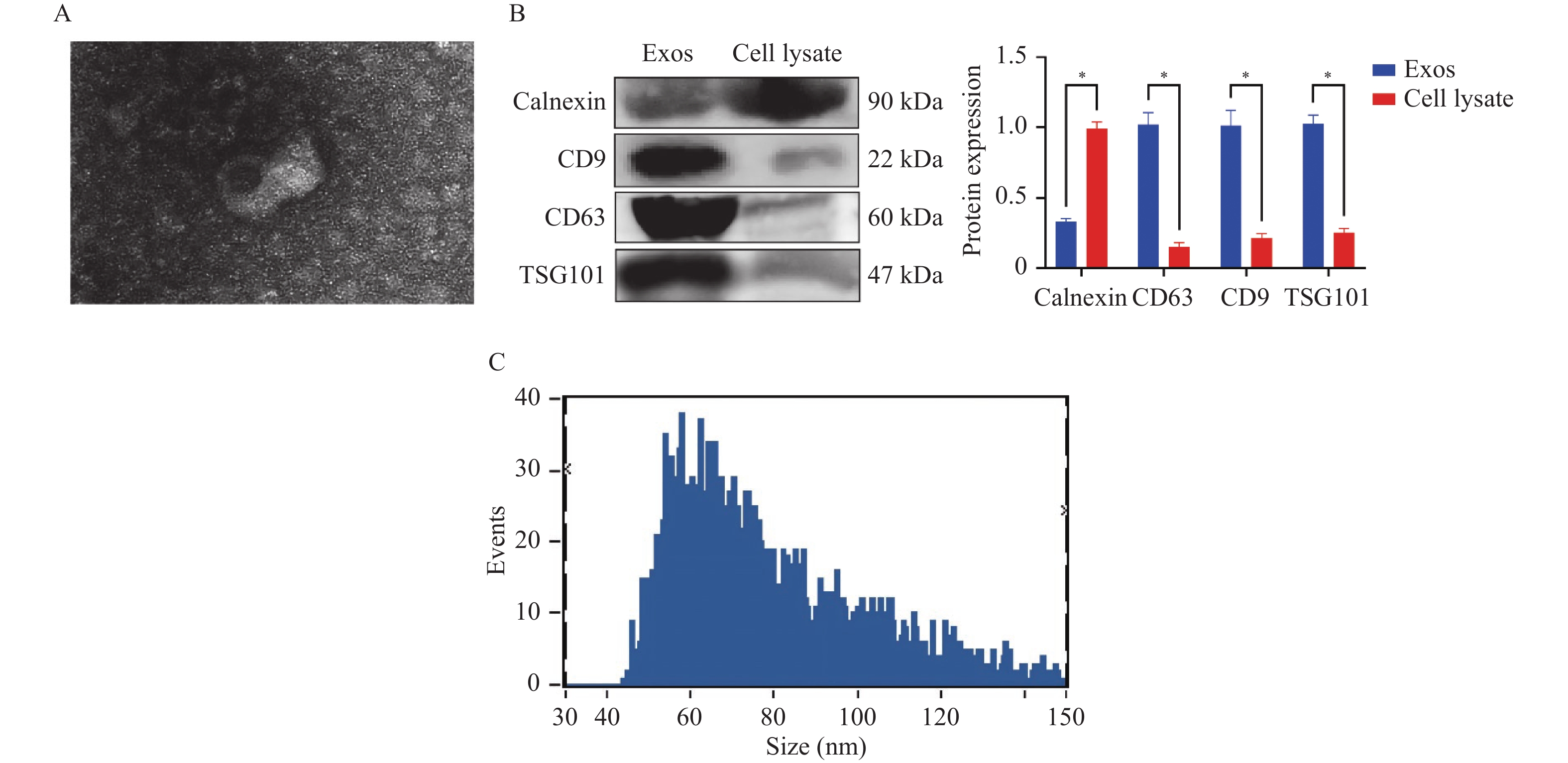
Objective To investigate the intervention mechanism of miR-155 in alveolar macrophage (AM)-derived exosomes (Exos) on ferroptosis of endothelial cells in septic patients. Methods This was a single-center study of 106 septic patients admitted to Handan Central Hospital from January 2022 to June 2023. Patients were further stratified into ARDS group (n = 21) and non-ARDS group (n = 85) based on the presence or absence of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In vitro, exosomes from lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated Raw 264.7 cells were co-cultured with mouse pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVEC) as the LPS-Exos group. Exosomes extracted from normal Raw 264.7 culture supernatant served as the normal control group (NC-Exos), and PMVEC cell culture alone served as the blank control group (Con). Exosomes were isolated from conditional culture medium of macrophages or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from septic patients. miR-155 expression was analyzed by RT-qPCR, and GPX4 and Nrf2 protein expression was analyzed by Western blotting. Changes in Fe2+, SOD and ROS levels in PMVEC cells were detected using assay kits. Results Compared to the non-ARDS group, the ARDS group exhibited higher age, SOFA score, miR-155 expression, and lactate levels (P < 0.05). miR-155 expression was significantly upregulated in LPS-Exos compared to NC-Exos (P < 0.01). Compared with Con group, the activity and SOD level of PMVEC cells in LPS-Exos group decreased (P < 0.01), while the levels of Fe2+ and ROS in cells increased (P < 0.05). Compared with NC-Exos group, the protein expression of classical ferroptosis suppressor genes such as GPX4 and Nrf2 in PMVEC cells was decreased in LPS-Exos group (P < 0.05). Compared with Con group, PMVEC cell viability, SOD levels, and GPX4 and Nrf2 protein expression were decreased in the Inhibitor-NC+LPS-Exos group (P < 0.001), while Fe2+ and ROS levels were increased (P < 0.0001 ). Compared with the Inhibitor-NC+LPS-Exos group, PMVEC cell viability, SOD levels, and GPX4 and Nrf2 protein expression were increased in the miR-155 Inhibitor+LPS-Exos group (P < 0.001), while Fe2+ and ROS levels were decreased (P < 0.01). Dual-luciferase reporter analysis confirmed direct binding between miR-155 and Nrf2. Conclusion The elevated level of miR-155 in AM-derived Exos has a superior predictive ability for ARDS development in septic patients compared to the SOFA score. When combined with the SOFA score, it demonstrates high predictive capability for ARDS development in septic patients. LPS-induced AM-derived Exos may promote ferroptosis of PMVEC cells by transporting miR-155, and this mechanism may be related to suppression of Nrf2 expression.
2026,
47(2):
93-100.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260210
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the awareness of cervical cancer, high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) infection status, and accuracy of self-sampling HPV detection among rural women in Xiangyun County, Yunnan Province. Methods From December 2023 to December 2024, rural women aged 21~65 years with sexual history from three townships in Xiangyun County were recruited for health education. Questionnaire surveys on cervical cancer awareness were conducted before and after the health education intervention. Subsequently, enrolled participants were instructed to self-collect vaginal secretion specimens, while gynecologists collected cervical exfoliated cell specimens. All samples were tested for 15 types of high-risk HPV using polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based HPV detection methods. Women with positive HPV results were recommended to undergo colposcopy or further treatment. Observed indicators included awareness rates regarding cervical cancer and related prevention knowledge, high-risk HPV positivity rate, and detection concordance rate. Results A total of 615 women were enrolled, of whom 85.0% were Han Chinese and 15.0% were ethnic minorities. Among these, 357 women (58.0%) had received primary school education or no formal education, while 258 women (42.0%) had received junior high school education or above. Following health education, the awareness rates among women regarding cervical cancer (100.0% vs 88.0%), HPV (100.0% vs 64.6%), the correlation between HPV and cervical cancer (58.9% vs 10.1%), cervical cancer prevention (98.0% vs 56.1%), HPV vaccination (99.0% vs 31.1%), and the free rural cervical cancer screening program (98.9% vs 31.7%) all showed significant improvements (P < 0.05). The HPV positivity rate for self-sampling was 9.9%, with HPV-16/18 positivity rate of 1.6%, while the HPV positivity rate for physician-sampling was 8.6%, with HPV-16/18 positivity rate of 1.8%. The Kappa value for concordance between self-sampling and physician-sampling results was 0.517, indicating fair consistency; however, only 40% of screened women preferred the self-sampling method. Conclusion The awareness level of cervical cancer and its prevention among rural women in Xiangyun County, Yunnan Province is relatively low. Health education can effectively improve awareness levels, necessitating provision of easily understandable health education to screening participants. Self-sampling and physician-sampling HPV detection results demonstrate good concordance and may serve as a complementary approach for cervical cancer screening in areas with limited rural medical resources.
2026,
47(2):
101-114.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260211
Abstract:
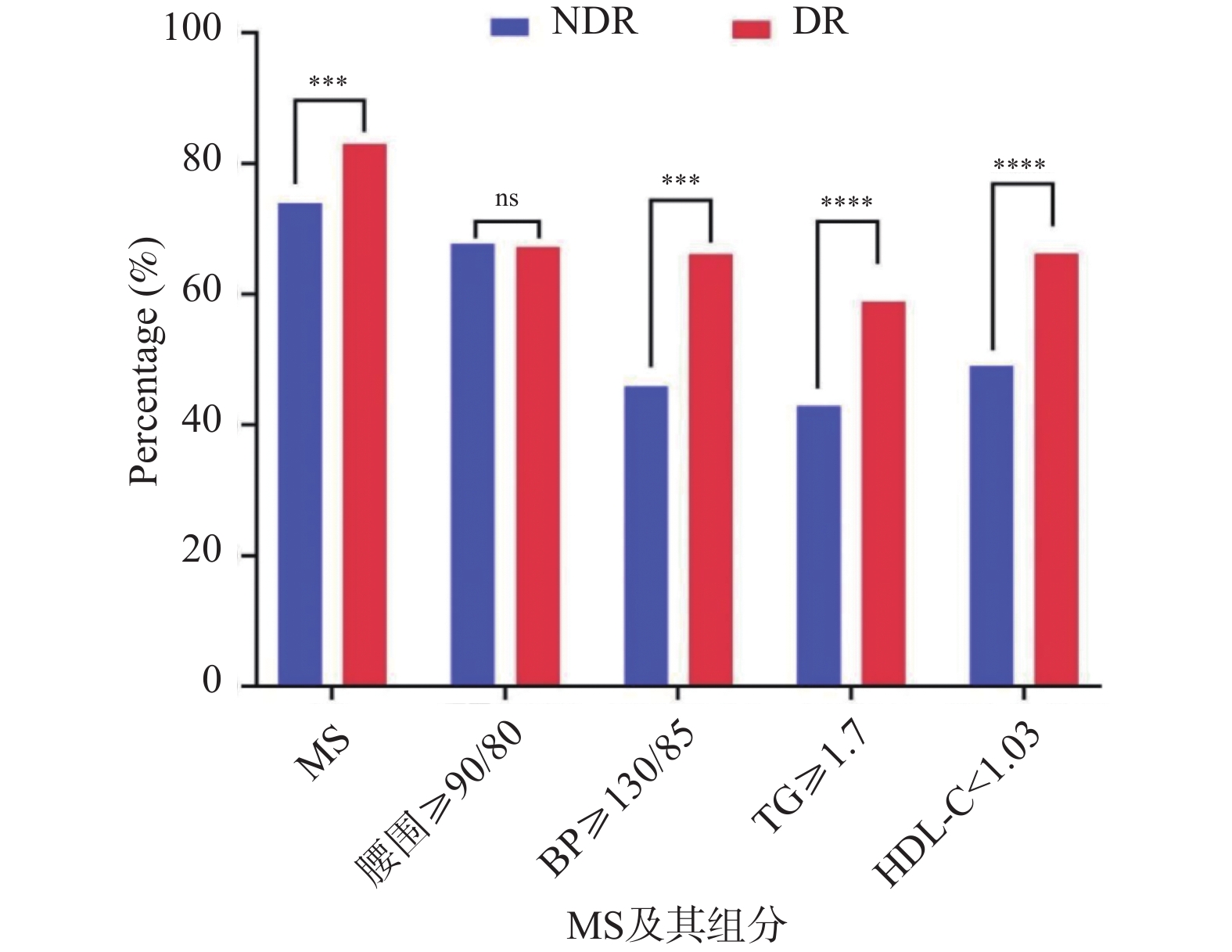
Objective To analyze the correlation between metabolic syndrome (MS) and its components with the risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on clinical data of 2441 T2DM patients hospitalized in the Departments of Ophthalmology and Endocrinology at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2019 to October 2024. Based on fundoscopic findings, enrolled patients were divided into DR group (n = 619) and NDR group (n = 1591). Univariate analysis was used to compare the detection rates of metabolic syndrome (MS) and its components between the two patient groups. Logistic regression analysis was performed to assess the correlation between MS and its components with the risk of diabetic retinopathy (DR). Results According to the NECP-ATP III criteria, among 2210 T2DM patients, 619 had DR, and 514 had concurrent MS, with a detection rate of 83.00%. The detection rates of concurrent MS, elevated blood pressure, elevated triglycerides (TG), and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in the DR group were all significantly higher than those in the NDR group, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). After adjusting for confounding factors in multivariate Logistic regression analysis, concurrent MS, hypertension, elevated TG, and decreased HDL-C were all significantly positively associated with the risk of DR, with OR values and 95%CI of 2.025 (1.462~2.806), 2.879 (2.316~3.578), 2.259 (1.803~2.829), and 2.500 (1.993~3.136), respectively. Conclusion MS is associated with the occurrence of DR in T2DM patients, with elevated blood pressure, elevated TG, and reduced HDL-C being particularly significant. As the number of MS components increases, the risk of DR shows an increasing trend.
2026,
47(2):
115-123.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260212
Abstract:
Objective To explore the correlation between sleep patterns and cognitive development in children aged 6~35 months with sleep problems. Methods A total of 290 children (154 boys, 136 girls) aged 6~35 months with sleep problems, who presented to the Department of Child Health Care at Kunming Children’s Hospital between October 2023 and March 2025, were selected as the study subjects. Their sleep patterns and cognitive development levels were assessed using the Brief Infant Sleep Questionnaire (BISQ) and the Griffiths Development Scales-Chinese Language Edition (GDS-C), respectively. Linear regression analysis were employed to investigate the correlation between sleep and cognitive development. Results Both nighttime sleep duration and the frequency of nighttime awakenings were associated with development in the motor and personal-social domains (all P < 0.05). Linear regression analysis identified that a nighttime sleep duration of > 9 hours was beneficial for motor developmen (all P < 0.05). In contrast, the frequency of nighttime awakenings was negatively associated with both motor and personal-social development, showing adverse effects on these domains (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Sleep deprivation and nighttime awakenings are closely related to cognitive developmental levels in children aged 6~35 months.
2026,
47(2):
124-132.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260213
Abstract:
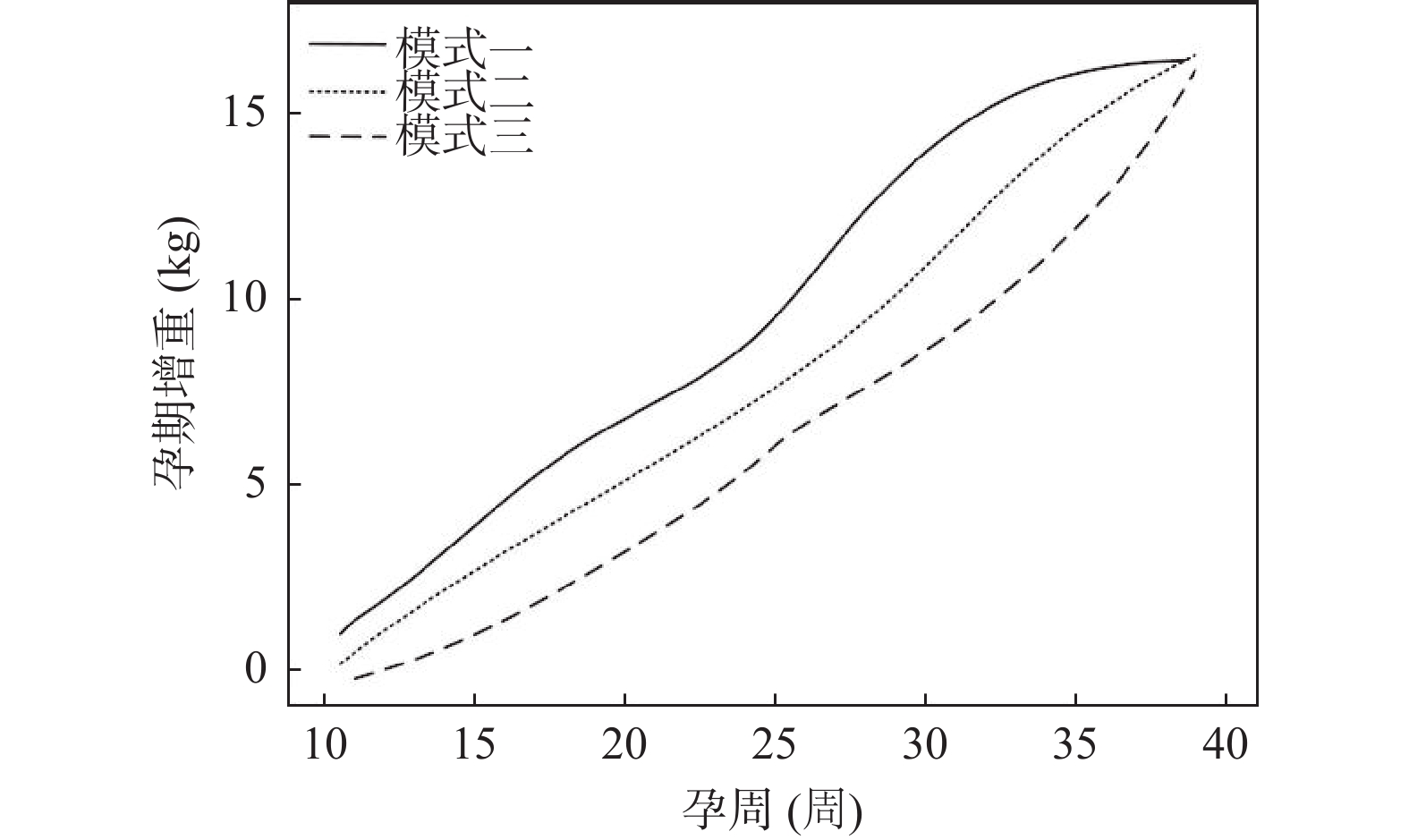
Objective To examine the association between gestational weight gain patterns and childbirth fear in primiparous women, as well as the mediating effect of childbirth fear on the connection between gestational weight gain patterns and cesarean section rates. Methods A total of 242 pregnant women who delivered in Pingliang Maternal and Child Health Hospital from March 2024 to March 2025 were selected as the study subjects. Latent growth mixed model (LGMM) was used to identify the gestational weight gain patterns of the subjects. Multivariate Logistic regression was employed to analyze the influencing factors of various pregnancy weight gain patterns. The cesarean section rates were compared across different weight gain patterns and levels of childbirth fear. Restricted cubic splines (RCS) were used to analyze the relationship between fear of childbirth score and cesarean section selection under different gestational weight gain patterns. A mediating effect model was applied to investigate the mediating effect of fear of childbirth on gestational weight gain patterns and cesarean section rate. The incidence of pregnancy complications and adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with different weight gain patterns was compared. A Log-binomial model was used to estimate the association between gestational weight gain patterns and pregnancy complications. Results The LGMM model identified three patterns of gestational weight gain among the study subjects: Pattern I was characterized by mid-pregnancy accelerated weight gain (n = 60); Pattern II was defined as a steady accelerated weight gain pattern (n = 98); and Pattern III was identified as a late-pregnancy accelerated weight gain pattern (n = 84). Multinomial logistic regression analysis indicated that, compared to Patterns I and II, higher pre-pregnancy BMI, younger age, higher childbirth fear scores, and lower pre-pregnancy exercise levels were more likely to lead to Pattern III weight gain (P < 0.05). Among women with Pattern III weight gain, those with childbirth fear scores ≥40 exhibited the highest proportion of cesarean sections (36.90%). RCS curve analysis revealed a significant positive correlation between childbirth fear scores and cesarean section rates across the three gestational weight gain patterns. The mediation effect model demonstrated that childbirth fear played a partial mediating role between gestational weight gain patterns and cesarean section rates, with the mediation effect accounting for 48.72% of the total effect. Women with Pattern I weight gain experienced significantly fewer cases of gestational hypertension and gestational diabetes compared to those with Patterns II and III (P < 0.05). The Log-binomial model indicated that gestational weight gain patterns consistently had a significant impact on pregnancy complications (P < 0.05). Conclusion Under different growth patterns during pregnancy, the fear of childbirth scores were all positively correlated with the choice of cesarean section. For primiparous pregnant women with an accelerated weight gain pattern in the late pregnancy stage, their fear of childbirth scores were higher, suggesting that pregnant women in the late stage of pregnancy should pay attention to weight management.
2026,
47(2):
133-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260214
Abstract:
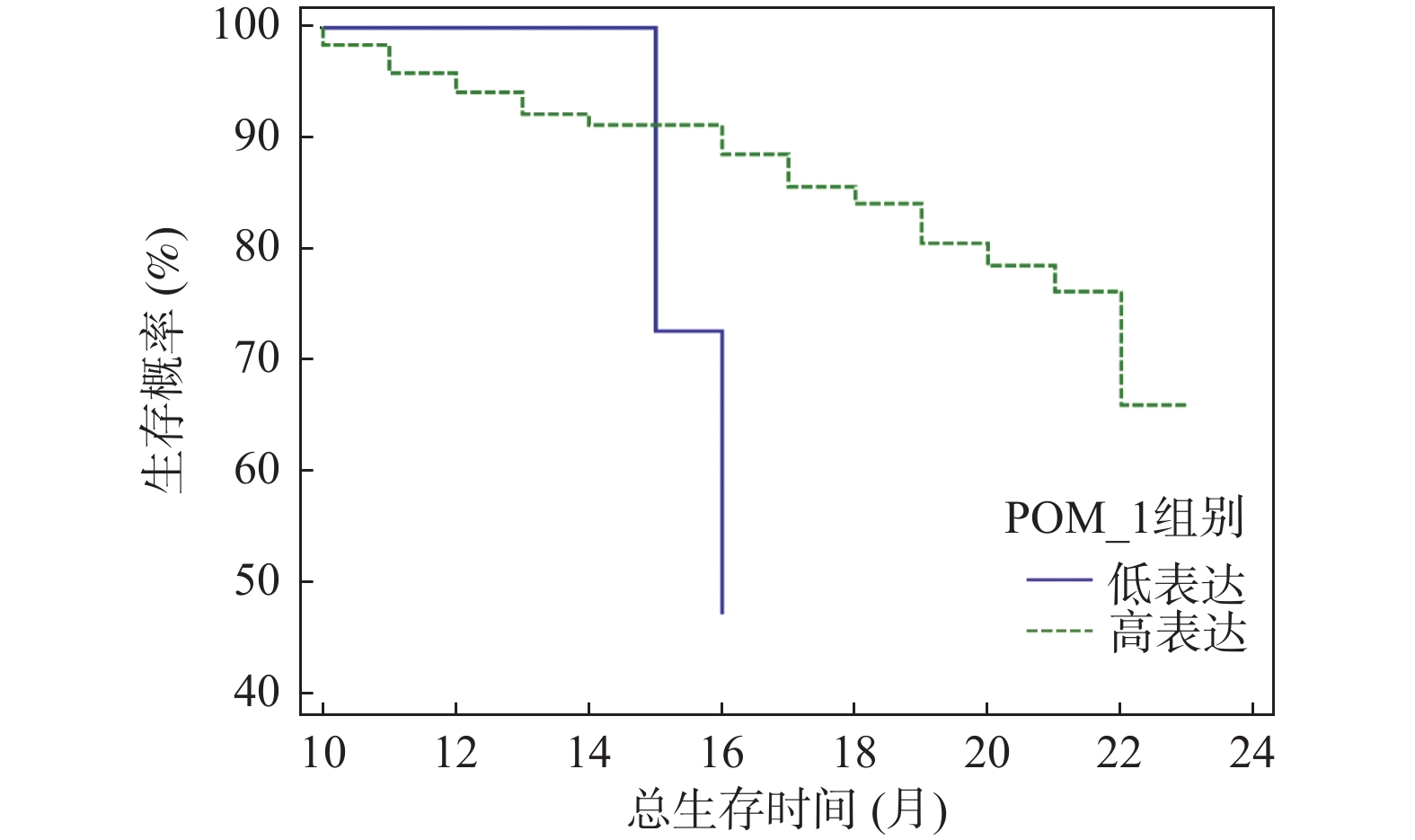
Objective To explore the intrinsic relationship between serum Paraoxonase-1 (PON-1), N-Myc downstream-regulated gene 4 (NDRG4), secreted frizzled-related protein 4 (SFRP4) expression levels, peripheral blood immune cell distribution, and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Methods Clinical data from 187 gastric cancer patients diagnosed and treated at Rizhao Lanshan District People's Hospital between April 2020 and August 2023 were selected as the case group, with 180 suspected patients from the same period serving as the control group. Fasting venous blood was collected from all study subjects, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was utilized to measure serum PON-1, NDRG4, and SFRP4 expression levels. Flow cytometry was employed to detect the proportions of various immune cells in the peripheral blood of the case group, providing a comprehensive evaluation of peripheral blood immune cell distribution. Survival information was gathered through follow-up, and overall survival (OS) was recorded. The case group was divided into high and low expression groups based on the median serum biomarker expression, allowing for a comparison of immune status and prognostic differences between groups. The Kaplan-Meier method and Cox proportional hazards regression model were used to analyze the correlation between markers and prognosis, while Spearman analysis was employed to assess the association between indicators and survival prognosis. Results Compared to the control group, the case group showed no statistically significant differences in age, gender, and BMI (P > 0.05), but exhibited increased expression of PON-1, SFRP4, and CD8+ T cells, alongside decreased expression of NDRG4, CD3+ T, CD4+ T, B lymphocytes, and NK cells (P < 0.05). After grouping by median values, the PON-1 high expression group demonstrated a lower proportion of CD8+ T cells compared to the low expression group (P < 0.05), while the NDRG4 high expression group had a higher proportion of CD4+ T cells than the low expression group (P < 0.05). Additionally, the SFRP4 high expression group exhibited a lower proportion of CD4+ T and NK cells compared to the low expression group (P < 0.05). Univariate Cox regression analysis revealed that age, PON-1, NDRG4, SFRP4 expression, and lymph node metastasis were associated with the prognosis of gastric cancer patients (P < 0.05). Cox regression analysis indicated that NDRG4≥0.85ng/mL, lymph node metastasis, PON-1<120.56 pg/mL, SFRP4≥210.32 pg/mL, and age≥60 years were risk factors for mortality in gastric cancer patients (P < 0.05). By the end of follow-up, 61 out of 187 gastric cancer patients had died, with a median survival of 14.5 months (3~24 months). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the PON-1 high expression group had a median survival of 16.00 (12.75, 21.00) months, significantly longer than the low expression group’ s 15.00 (15.00, 16.00) months (P < 0.01); the NDRG4 high expression group had a median survival of 12.00 (10.00, 14.00) months, significantly shorter than the low expression group's 17.50 (13.00, 20.00) months (P < 0.01); the SFRP4 high expression group had a median survival of 9.00 (8.00, 12.00) months, significantly shorter than the low expression group's 19.00 (15.00, 22.00) months (P < 0.01). Spearman analysis revealed that age, lymph node metastasis, NDRG4, and SFRP4 were positively correlated with survival prognosis (P < 0.05), while PON-1 was negatively correlated (P < 0.05). Conclusion Serum PON-1, NDRG4, and SFRP4 expression levels in gastric cancer patients are closely related to peripheral blood immune cell distribution, exhibit clear interrelationships, and critically impact patient prognosis, providing potential reference indicators for gastric cancer prognosis assessment.
2026,
47(2):
143-155.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260215
Abstract:
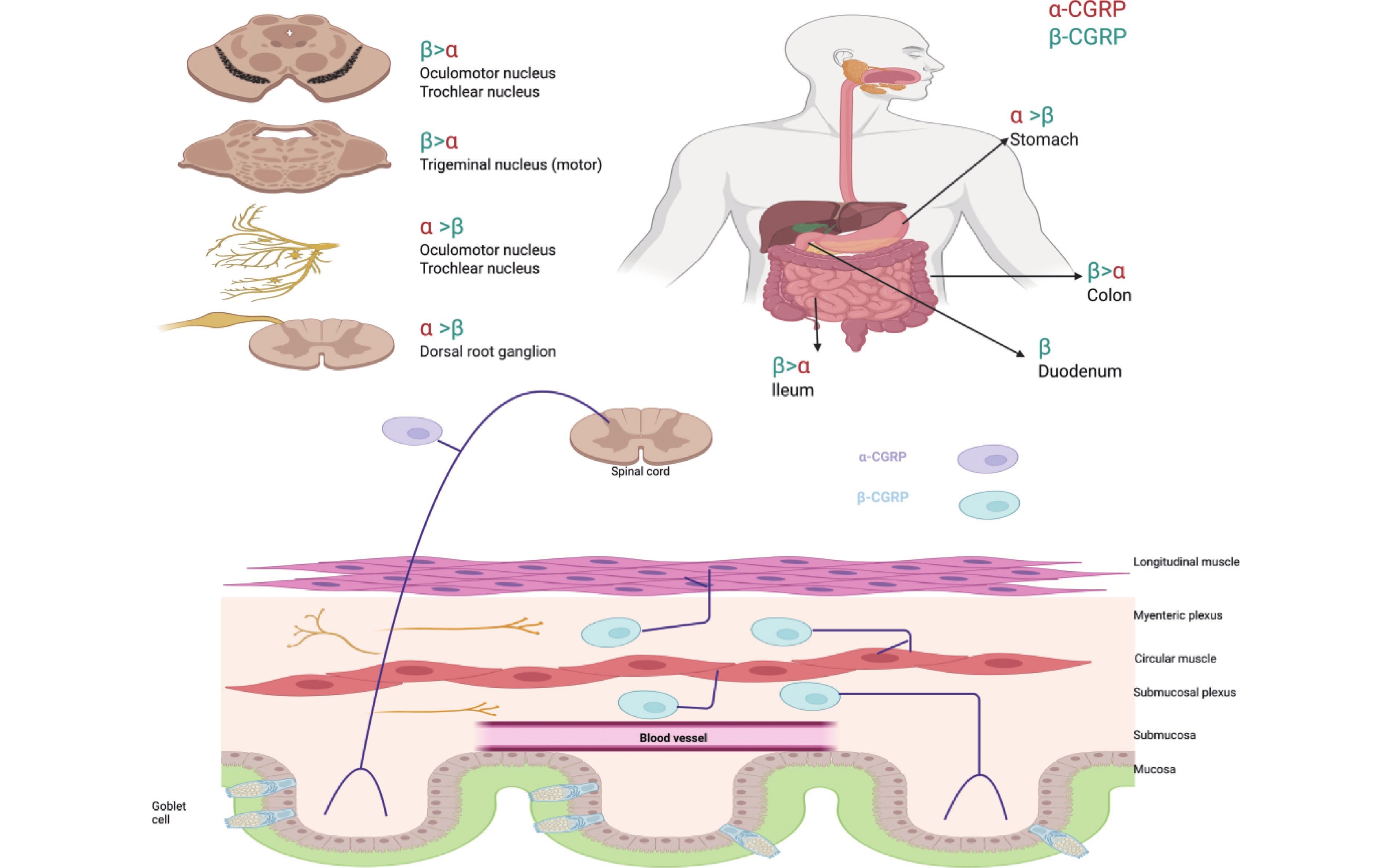
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) exerts a central-peripheral synergistic amplification effect in the development and maintenance of cancer pain. This effect is mediated through the activation of signaling pathways, including NGF and BMP2, leading to increased sensory nerve excitability, the promotion of peripheral and central sensitization, and the formation of a "pain-tumor progression" positive feedback loop with the tumor microenvironment. Preclinical evidence has demonstrated the significant analgesic and anti-tumor potential of CGRP antagonists in models including breast cancer, oral cancer, and pancreatic cancer, among others. Furthermore, CGRP levels are closely correlated with cancer pain intensity, suggesting its potential value as a biomarker and intervention target for targeted cancer pain therapy. This review summarizes the mechanistic roles of CGRP in cancer pain and tumor progression, as well as recent advances in related therapeutic research, and explores future strategies for cancer pain management through targeting the CGRP pathway in combination with existing treatment modalities.
Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) exerts a central-peripheral synergistic amplification effect in the development and maintenance of cancer pain. This effect is mediated through the activation of signaling pathways, including NGF and BMP2, leading to increased sensory nerve excitability, the promotion of peripheral and central sensitization, and the formation of a "pain-tumor progression" positive feedback loop with the tumor microenvironment. Preclinical evidence has demonstrated the significant analgesic and anti-tumor potential of CGRP antagonists in models including breast cancer, oral cancer, and pancreatic cancer, among others. Furthermore, CGRP levels are closely correlated with cancer pain intensity, suggesting its potential value as a biomarker and intervention target for targeted cancer pain therapy. This review summarizes the mechanistic roles of CGRP in cancer pain and tumor progression, as well as recent advances in related therapeutic research, and explores future strategies for cancer pain management through targeting the CGRP pathway in combination with existing treatment modalities.
2026,
47(2):
156-163.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260216
Abstract:
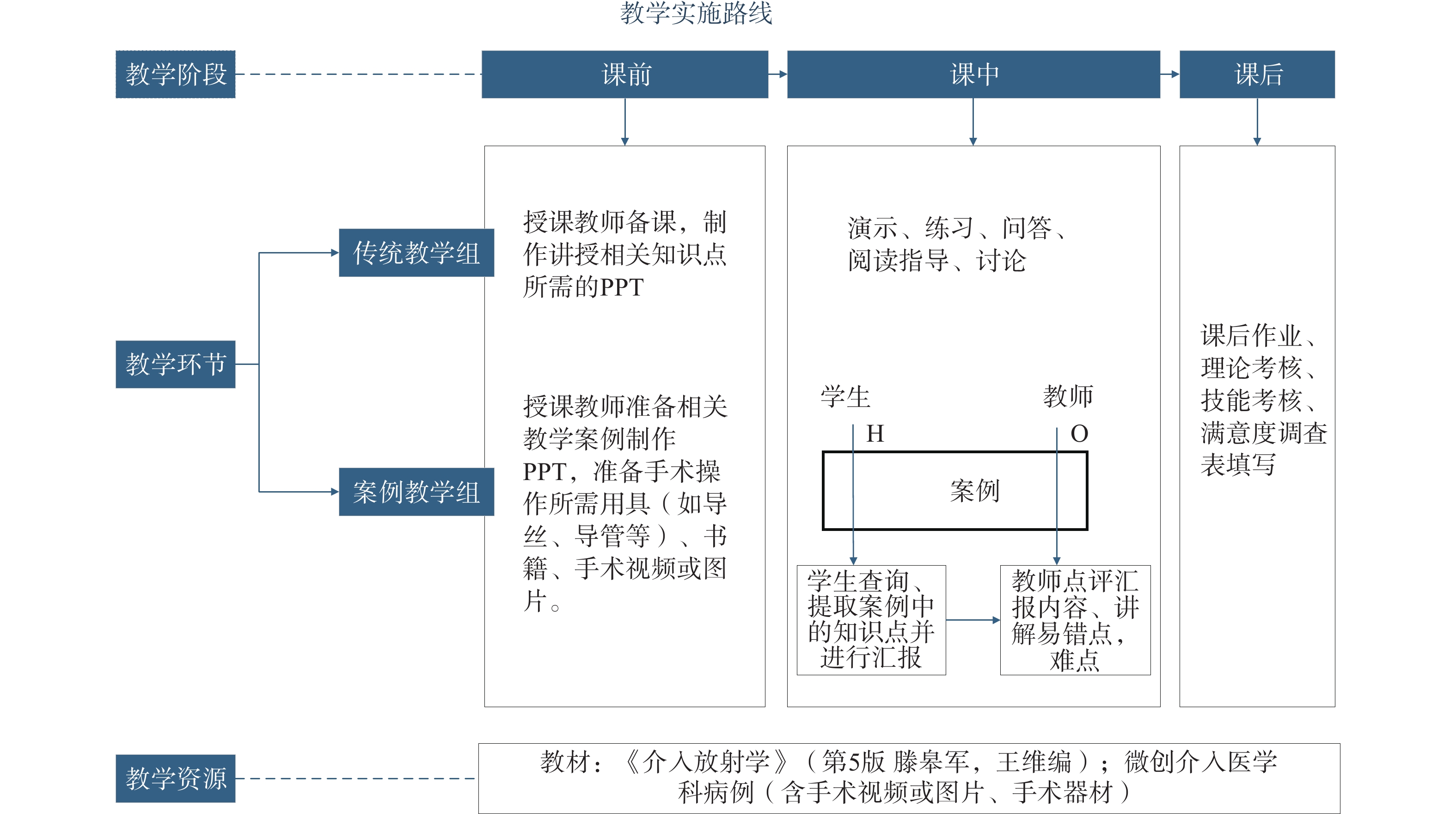
Objective To explore the application value of case-based heuristic teaching method in cultivating critical thinking ability among undergraduate medical students in tumor interventional radiology. A total of 120 undergraduate students enrolled in the course "Interventional Radiology" taught by the Department of Minimally Invasive Interventional Medicine from June 2023 to December 2024 were selected as research subjects. They were divided into two groups using alternating grouping method: traditional teaching group (n = 60, receiving conventional teaching method) and case-based teaching group (n = 60, receiving case-based heuristic teaching method). Critical thinking disposition inventory (CTDI-CV) scores were compared between the two groups, satisfaction with clinical teaching was assessed, and comprehensive examination results and course pass rates were compared. Results The average comprehensive assessment score for the case-based teaching group was 84.43 points, compared to 81.93 points for the traditional teaching group. The course pass rates for students in the case-based teaching group and traditional teaching group were 98.33% (59/60) and 93.33% (56/60), respectively. No statistically significant differences were found between the two groups in comprehensive scores and course pass rates (P > 0.05). After instruction, students in the case-based teaching group demonstrated significantly higher scores in truth-seeking, open-mindedness, analytical ability, systematicity, evaluative confidence, inquisitiveness, cognitive maturity, and overall critical thinking scores compared to the traditional teaching group (P < 0.05). The average course satisfaction score for the case-based teaching group (14.22 points) was significantly higher than that of the traditional teaching group (13.52 points) (P < 0.05). Conclusion The application of case-based heuristic teaching method in the instruction of undergraduate medical students in tumor interventional radiology can effectively enhance students' critical thinking ability. While maintaining the effectiveness of foundational teaching, this method can effectively improve students' critical thinking ability and course satisfaction, demonstrating high value for promotion and application.
2026,
47(2):
164-170.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260217
Abstract:
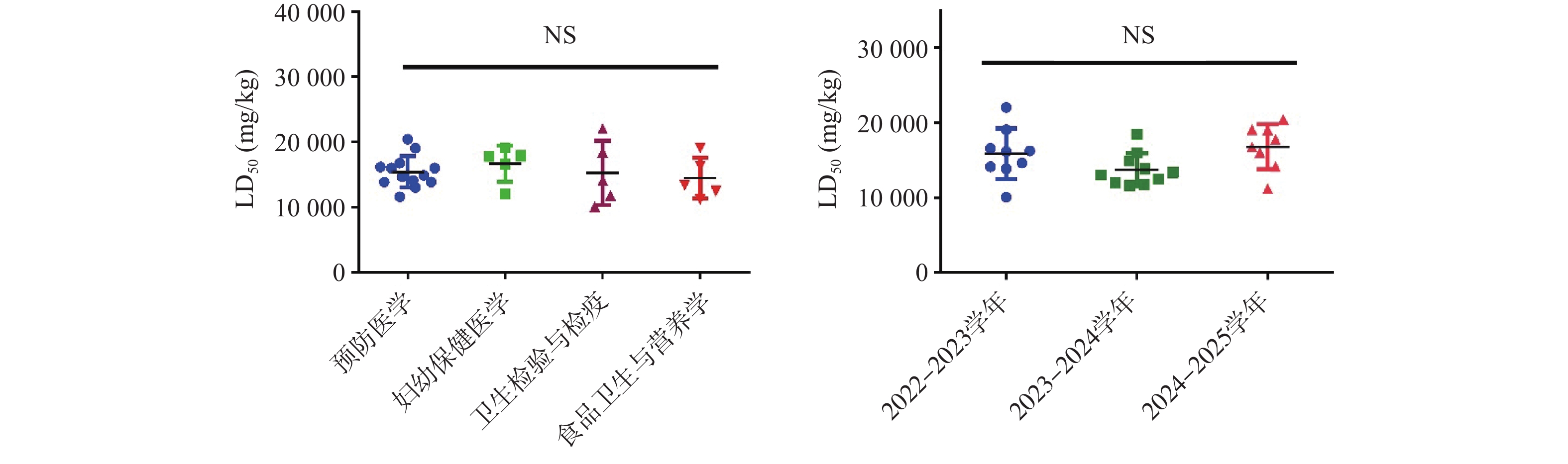
Objective To explore the feasibility, safety, and teaching equivalence of substituting ethanol (alcohol) for highly toxic test substances in experimental teaching. Methods Undergraduate students majoring in preventive medicine and related disciplines from the classes of 2019—2022 were enrolled. An oral gavage LD50 experiment with ethanol was conducted using Kunming mice in the course Fundamentals of Toxicology Experiment. Five dose groups (5683 ~23670 mg/kg) were designed, and toxic symptoms and mortality rates within 1 hour were observed. The LD50 and 95% confidence interval were calculated using the modified Kärber method, and teaching safety and sex differences were assessed. Results The mean LD50 of ethanol was 15439 mg/kg (range: 10046 ~22039 mg/kg), which was significantly higher than the literature value (3450 mg/kg), primarily due to the shortened 1-hour observation period. Experimental data were classified and analyzed according to different majors, academic years, and sex of test animals. No statistically significant differences were found in ethanol LD50 values between different majors and academic years (P > 0.05), nor between female and male mice (P > 0.05). Experimental data Ethanol demonstrated a clear dose-response relationship, readily observable toxic symptoms, and high safety. Additionally, teaching costs were reduced, operational efficiency improved, and students' experimental experience was enhanced. Conclusion Ethanol serves as a safe, economical, and easy-to-operate test substance for LD50 experiments that fully meets core teaching objectives and complies with the "3Rs" principle (particularly the replacement principle), demonstrating significant value for promotion.
2026,
47(2):
171-180.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20260218
Abstract:
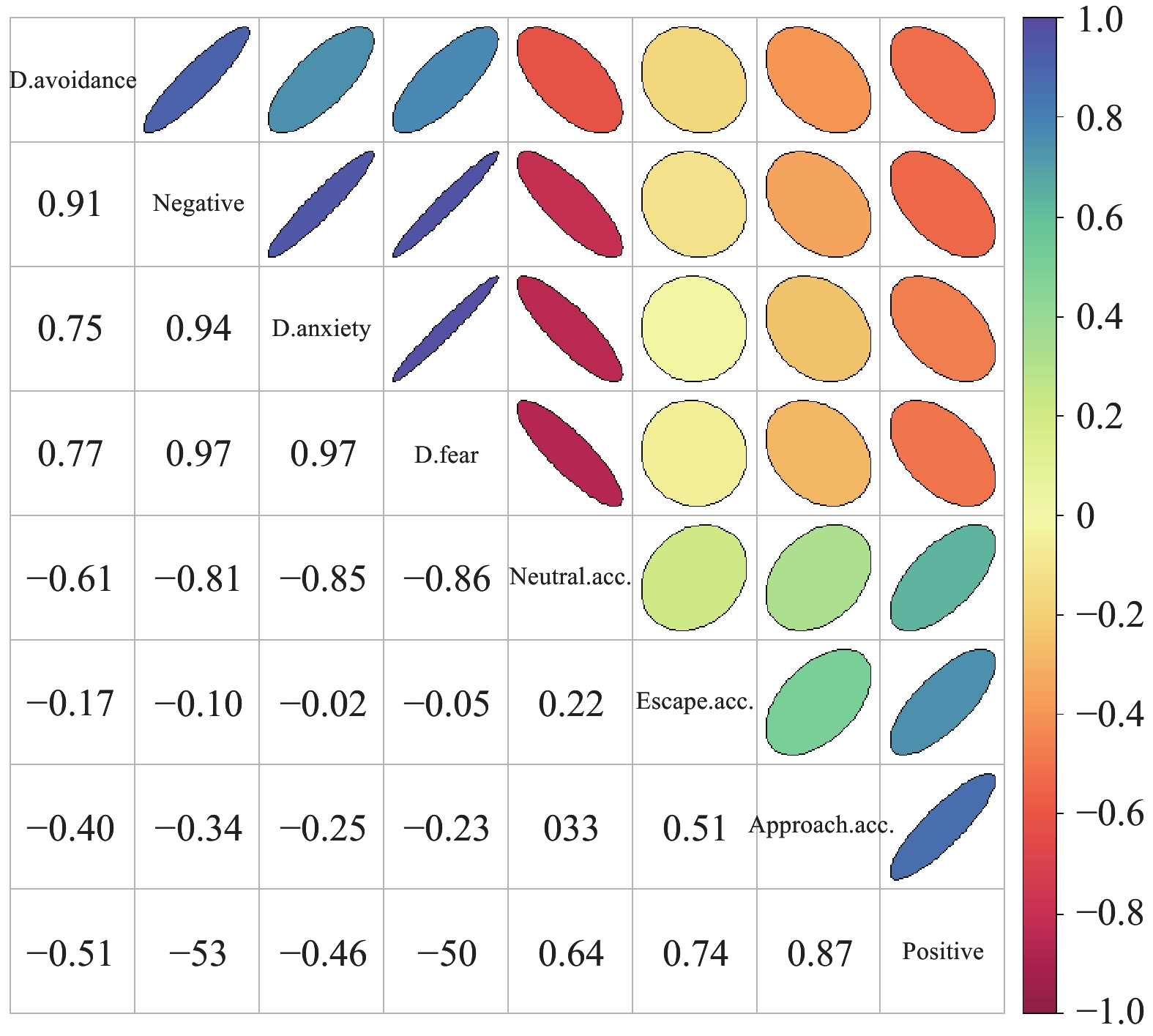
Objective To understand the current status of death anxiety and death attitudes among patients with advanced lung cancer, explore their influencing factors, and examine the correlation between these two variables. Methods A cross-sectional survey design was employed. From March 2025 to July 2025, 164 patients with advanced lung cancer were conveniently sampled from a tertiary Grade-A hospital in Kunming, Yunnan Province. Data were collected using a general information questionnaire, the Chinese version of the Death Anxiety Scale (CT-DAS), and the Chinese version of the Death Attitude Profile-Revised (DAP-R). Results The death anxiety score among patients with advanced lung cancer was 36.41±17.86, indicating a relatively high level. The mean score for positive death attitude items was 2.83±0.64, and for negative death attitude items was 2.75±1.12, suggesting a relatively positive death attitude overall. The predominant tendency was natural acceptance with a score of 4.27±0.96, accounting for 67.1%. Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that discussing death with family and friends was a positive influencing factor for death anxiety, death fear, death avoidance, and negative death attitudes (P < 0.05), and a negative influencing factor for natural acceptance and positive death attitudes (P < 0.05). The frequency of cancer treatment was a positive influencing factor for natural acceptance (P < 0.05). Cancer stage was a negative influencing factor for approach acceptance (P < 0.05). Duration since diagnosis was a positive influencing factor for escape acceptance (P < 0.05). Death anxiety was positively correlated with negative death attitudes, death fear, and death avoidance (P < 0.05), and negatively correlated with positive death attitudes, natural acceptance, and approach acceptance (P < 0.05). Conclusion Educational guidance should focus on addressing death anxiety among patients with advanced lung cancer, with particular emphasis on vulnerable groups such as those with severe disease, multiple courses of anticancer treatment, prolonged diagnosis duration, and weak psychological coping abilities. This support aims to help them establish a positive psychological support system, thereby fostering a constructive attitude toward death and enabling them to face mortality with calmness and composure.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS