Application of Electroacupuncture for Pain Management in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Patients
-
摘要:
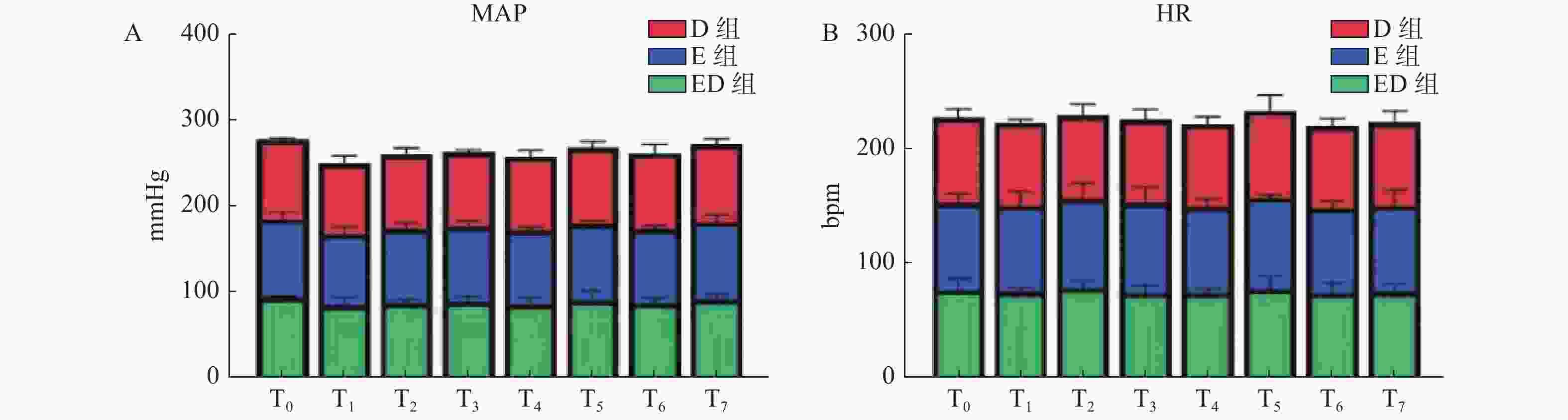
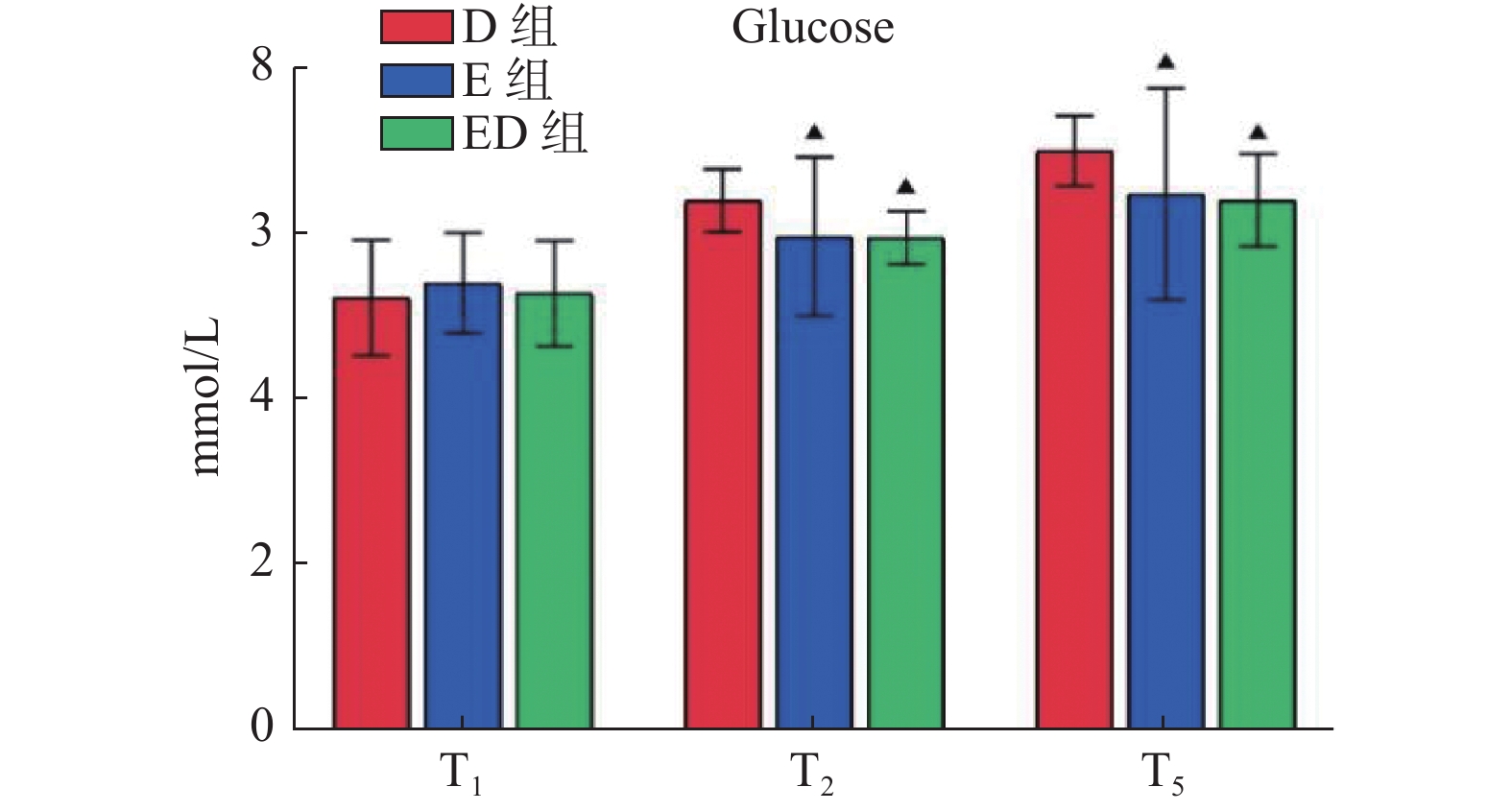
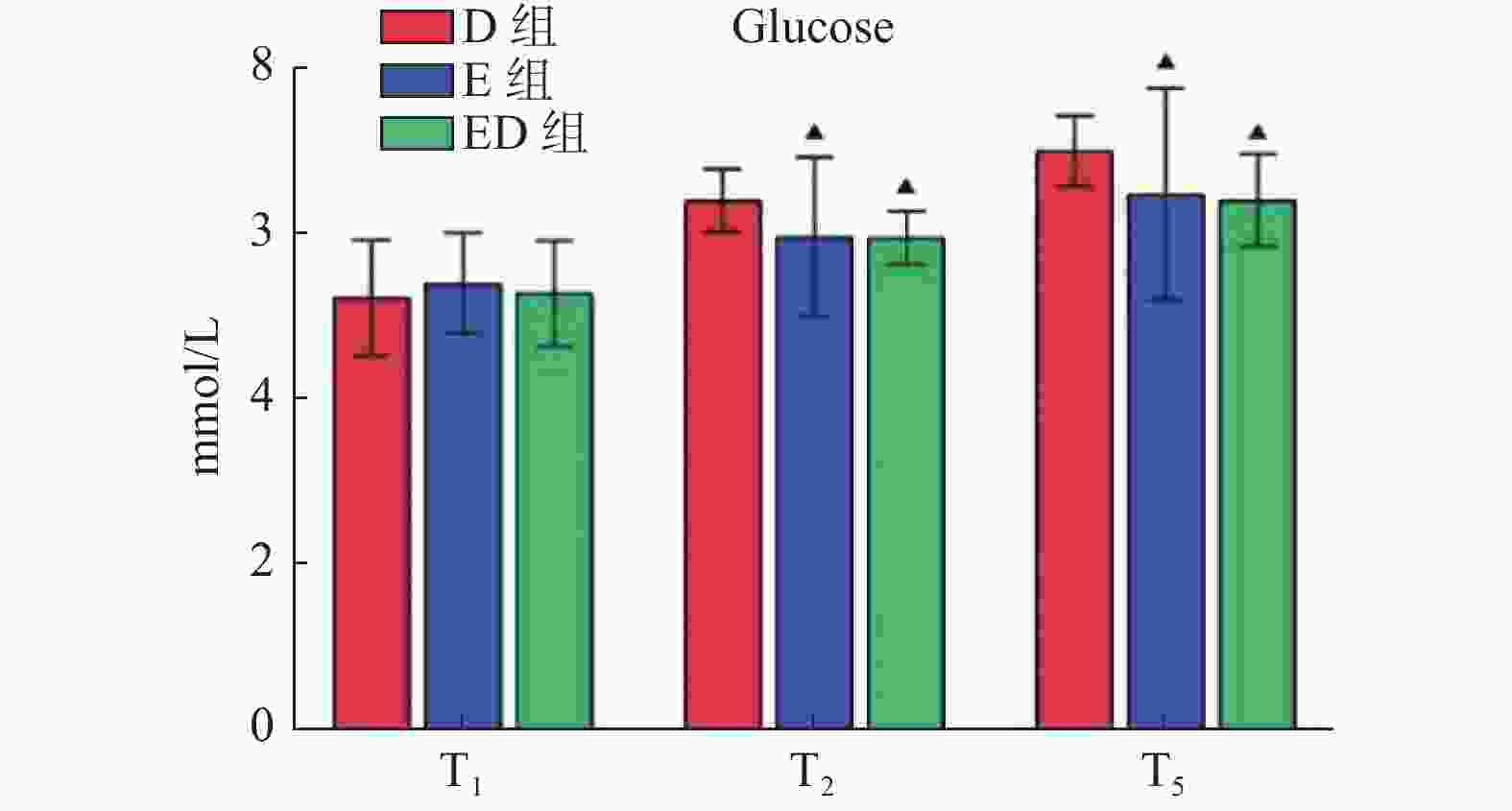
目的 比较中国传统医学中的电针与阿片类辅助药物地佐辛的疗效。 方法 选择2023年10月12日至2024年4月5日在昆明医科大学第二附属医院择期行腹腔镜胆囊切除术的患者122例患者,随机分配为地佐辛组(D组,n = 40)、电针组(E组,n = 42)和电针联合地佐辛组(ED组,n = 40),分别在胆囊切除后给予地佐辛10 mg、电针、电针+地佐辛10 mg,观察手术中不同时间点的镇痛指数(pain threshold index,PTi)、疼痛指数(pain index,Pi)、视觉模拟评分法(visual analogue scale,VAS)评分。并记录各个时间点的生命体征和术后24 h的不良反应发生情况。 结果 电针前时(T1)各组PTi比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),电针结束(T2)和胆囊切除后(T3),E组和ED组均低于D组(P < 0.05),手术结束时(T4)和拔管时(T5)三组PTi值均达到患者可忍受水平,E组和D组高于ED组(P < 0.05)。术后各时点疼痛评分Pi和VAS比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。 结论 电针的镇痛效果不劣于阿片类药物。可推荐作为腹腔镜胆囊切除术患者的术后镇痛技术。 Abstract:Objective To compare the efficacy of electroacupuncture in traditional Chinese medicine with the opioid adjuvant drug dezocine. Methods 122 patients undergoing elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University between October 12, 2023, and April 05, 2024, were randomly allocated into three groups: dezocine group (D group, n = 40), electroacupuncture group (E group, n = 42), and electroacupuncture combined with dezocine group (ED group, n = 40). Patients received 10 mg dezocine, electroacupuncture, or electroacupuncture + 10 mg dezocine after cholecystectomy. Pain threshold index (PTi), pain index (Pi), and visual analogue scale (VAS) scores were observed at different time points during surgery. Vital signs were recorded, and adverse reactions within 24 hours postoperatively were noted. Results There were no statistically significant differences in PTi among groups before electroacupuncture (T1) (P > 0.05). At the end of electroacupuncture (T2) and after cholecystectomy (T3), the PTi values in the E and ED groups were lower than the D group (P < 0.05). At the end of surgery (T4) and upon extubation (T5), the PTi values of all three groups reached a tolerable level for patients, with the E and D groups showing higher PTi values compared to the ED group (P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in postoperative pain scores (Pi) and VAS at various time points (P > 0.05). Conclusion Electroacupuncture demonstrates analgesic efficacy non-inferior to opioid drugs and can be recommended as a postoperative pain management technique for laparoscopic cholecystectomy patients. -
表 1 三组研究对象基本情况($ \bar x \pm s$)
Table 1. Comparison of basic information among three groups ($ \bar x \pm s$)
分组 D组(n=40) E组(n=42) ED组(n=40) χ2/F P 性别(男/女) 17/23 18/24 19/21 0.254 0.881 年龄(岁) 45.78 ± 11.43 45.36 ± 12.82 45.48 ± 12.52 0.013 0.988 体重(kg) 66.75 ± 14.61 62.14 ± 10.69 65.23 ± 10.53 1.557 0.215 身高(cm) 165.08 ± 8.50 164.19 ± 7.35 163.88 ± 7.16 0.262 0.770 BMI(kg/m2) 24.30 ± 3.94 22.91 ± 3.06 24.21 ± 3.11 1.944 0.148 ASA分级(Ⅱ/Ⅲ) 39/1 41/1 38/2 0.557 0.757 手术时间(min) 53.20 ± 15.16 54.14 ± 15.23 54.13 ± 14.45 0.052 0.949 表 2 三组研究对象PTi的比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of PTi among three groups ($ \bar x \pm s $)
时间点 PTi 重复测量F检验 D组(n=40) E组(n=42) ED组(n=40) F P 偏η2 T1 61.58 ± 2.01 70.41 ± 6.96ab 63.05 ± 4.98 T2 60.58 ± 4.47 54.43 ± 4.25a 56.23 ± 3.96a T3 55.50 ± 3.75 53.76 ± 5.18 52.52 ± 6.65a T4 62.05 ± 2.92 67.93 ± 2.31ab 54.70 ± 5.14a T5 86.98 ± 4.81b 86.67 ± 7.71b 81.68 ± 5.65a 组别主效应 29.303 <0.001* 0.330 时间主效应 947.528 <0.001* 0.888 组别×时间 28.650 <0.001* 0.325 *P < 0.05;与D组比较,aP < 0.05;与ED组比较,bP < 0.05。 表 3 三组研究对象Pi的比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of Pi among three groups ($ \bar x \pm s $)
时间点 Pi 重复测量F检验 D组(n=40) E组(n=42) ED组(n=40) F P 偏η2 T5 6.68 ± 1.73 6.57 ± 1.88 6.05 ± 1.28 T6 7.77 ± 2.82 7.57 ± 2.58 7.28 ± 3.48 T7 8.60 ± 3.05 8.48 ± 3.98 7.62 ± 2.95 组别主效应 2.243 0.111 0.036 时间主效应 14.177 <0.001* 0.194 组别×时间 0.102 0.982 0.002 *P < 0.05。 表 4 三组研究对象VAS的比较($ \bar x \pm s $,分)
Table 4. Comparison of VAS among three groups($ \bar x \pm s $,score)
时间点 VAS 重复测量F检验 D组(n=40) E组(n=42) ED组(n=40) F P 偏η2 T6 4.50 ± 2.43 4.81 ± 2.85 4.20 ± 2.28 T7 4.27 ± 2.42 4.76 ± 1.48 4.00 ± 2.11 T8 3.68 ± 1.58 4.17 ± 1.94 3.53 ± 1.89 T9 2.65 ± 1.44 3.19 ± 1.80 2.83 ± 1.88 T10 2.50 ± 1.54 2.38 ± 1.08 2.05 ± 1.20 组别主效应 2.398 0.095 0.039 时间主效应 37.129 <0.001* 0.238 组别×时间 0.379 0.915 0.006 *P < 0.05。 表 5 三组研究对象术后并发症的比较[n(%)]
Table 5. Comparison of complications among three groups [n(%)]
并发症 分组 χ2 P D组(n=40) E组(n=42) ED组(n=40) 恶心 0.165 0.921 0 35 (83.33) 32 (80.00) 33 (82.50) 1 7 (16.67) 8 (20.00) 7 (17.50) 呕吐 0.156 0.925 0 31 (73.81) 31 (77.50) 30 (75.00) 1 11 (26.19) 9 (22.50) 10 (25.00) 头晕 2.745 0.253 0 32 (76.19) 33 (82.50) 36 (90.00) 1 10 (23.81) 7 (17.50) 4 (10.00) 头痛 1.918 0.383 0 32 (76.19) 29 (72.50) 34 (85.00) 1 10 (23.81) 11 (27.50) 6 (15.00) 注:0:未发生;1:发生。 -
[1] 张利东, 徐建国, 王国林, 等. 地佐辛临床镇痛专家共识[J]. 中华麻醉学杂志, 2020, 40(6): 641-645. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn131073.20200320.00601 [2] Zhou P, Zhang C, Zhou M, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture pretreatment on the quality of recovery in the patients undergoing laparoscopic gastrointestinal surgery[J]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2024, 44(12): 1377-1382. [3] Huang X, Wang H, Shi L, et al. Effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation based on wrist-ankle acupuncture theory for pain relief during colonoscopy without anesthesia: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Endoscopy, 2025, 57(2): 158-165. doi: 10.1055/a-2373-0513 [4] Zhang H, Wang L, Zheng Z, et al. The use of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation to reduce opioid consumption in patients undergoing off-pump CABG: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Perioper Med (Lond), 2024, 13(1): 68. doi: 10.1186/s13741-024-00427-2 [5] Zhang M, Cairen Z, Liu X, et al. Transcutaneous electric acupoint stimulation reduced consumption of profopol in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery: A randomized clinical trial[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2024, 103(4): e35730. [6] Pan L P, Yang Y, Shao J, et al. [Effects of perioperative transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing shoulder arthroscopic surgery][J]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2019, 39(1): 19-23. [7] Chen J, Zhang Y, Li X, et al. Efficacy of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation combined with general anesthesia for sedation and postoperative analgesia in minimally invasive lung cancer surgery: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2020, 11(4): 928-934. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13343 [8] 曹德钧, 祖存. 不同全麻方式在老年高血压患者行单孔腹腔镜胆囊切除术的比较[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2015, 36(9): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2015.09.027 [9] 张沛, 邢群智, 李毓, 等. 电针镇痛治疗带状疱疹后神经痛的临床疗效[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2018, 39(9): 95-100. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-4706.2018.09.023 [10] 赵海倩. 电针在腹腔镜胆囊切除术患者镇痛中的应用及对脑状态指数的影响[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2024. [11] Simpson J C, Bao X, Agarwala A. Pain management in enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) protocols[J]. Clin Colon Rectal Surg, 2019, 32(2): 121-128. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1676477 [12] Garimella V, Cellini C. Postoperative pain control[J]. Clin Colon Rectal Surg, 2013, 26(3): 191-196. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1351138 [13] Fiore J J, El-Kefraoui C, Chay M A, et al. Opioid versus opioid-free analgesia after surgical discharge: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials[J]. Lancet, 2022, 399(10343): 2280-2293. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00582-7 [14] Meng X L, Qu Q. Effect of subcutaneous injection of lidocaine in zusanli (ST 36) and jiaji (EX-B 2) regions on immune function in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy[J]. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu, 2016, 41(1): 74-79. [15] Wang S J, Zhang Y P, Candiotti K A. Effects of electroacupuncture on pain sensation in a rat model of hyperalgesia with nicotine dependence[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2022, 17(4): 905-910. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.322477 [16] An G, Wang G, Zhao B, et al. Opioid-free anesthesia compared to opioid anesthesia for laparoscopic radical colectomy with pain threshold index monitoring: A randomized controlled study[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2022, 22(1): 241. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01747-w [17] Liang Z, Xie Y, Chen S, et al. Predicting postoperative pain in children: An observational study using the pain threshold Index[J]. Front Pediatr, 2024, 12: 1398182. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1398182 [18] Du J, Fang J, Xiang X, et al. Effects of low- and high-frequency electroacupuncture on protein expression and distribution of TRPV1 and P2X3 in rats with peripheral nerve injury[J]. Acupunct Med, 2021, 39(5): 478-490. doi: 10.1177/0964528420968845 [19] Chao L, Goncalves A S, Campos A, et al. Comparative effect of dense-and-disperse versus non-repetitive and non-sequential frequencies in electroacupuncture-induced analgesia in a rodent model of peripheral neuropathic pain[J]. Acupunct Med, 2022, 40(2): 169-177. doi: 10.1177/09645284211055751 -





 下载:
下载: