2025 Vol. 46, No. 3
2025, 46(3): 7-10.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250302
Abstract:
Objective To study the chemical composition of and identify its active components. Methods The chemical constituents of Dendrobium Primulinum were extracted using solvents, followed by separation through silica gel and gel column chromatography, with structural identification performed via spectral analysis. The in vitro activity screening of some compounds was conducted using the MTT assay. Results Seven compounds were isolated and identified from Dendrobium primulinum, namely 7-dihydroxy-2, 4-methoxyphenanthrene(1), densiflorol B (2), 3, 4, 7-trihydroxy-2-methoxy-9, 10-dihydrophenanthrene (3), thunalbene (4), phillygenin (5), 3β-hydroxy-5α, 8α-epidioxyergosta-6, 22-diene (6)、4-hydroxy-3, 5-dimethoxy--cinnamaldehyde (7) . Antitumor activity tests were performed on compounds 1 to 5, revealing that compound 1 exhibited strong inhibitory activity against the MCF-7/S cell line, with an IC50 of 5.13 μM. Conclusion Compounds 1 to 6 are reported for the first time from Dendrobium primulinum, while compound 7 is reported for the first time from this genus.
2025, 46(3): 11-18.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250303
Abstract:
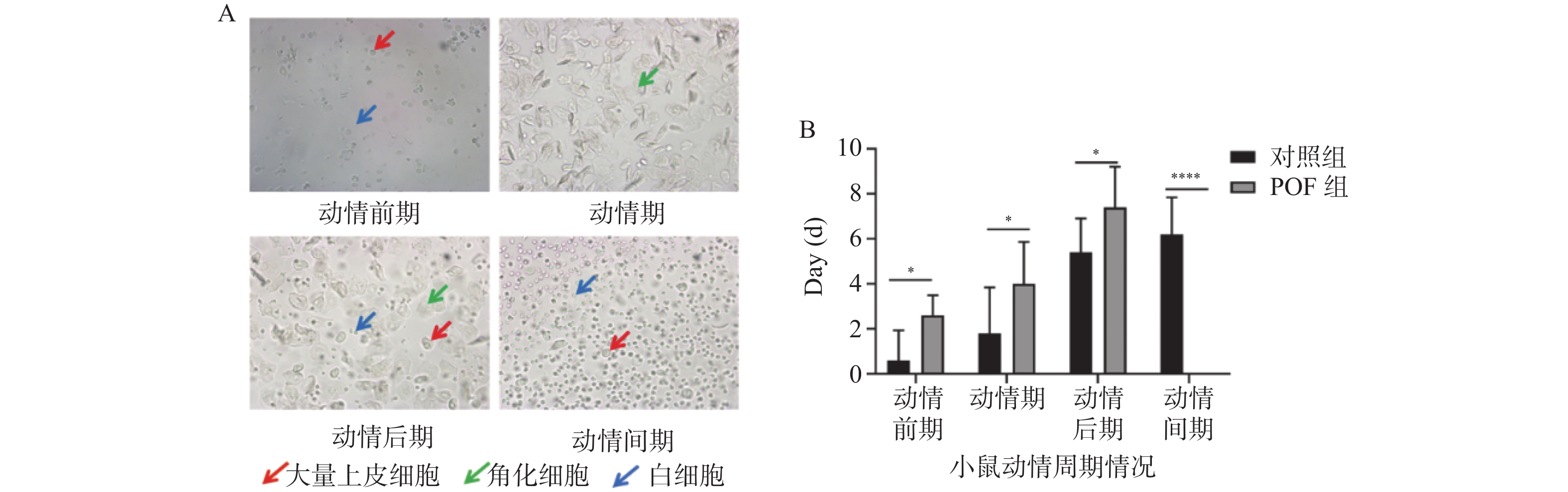
Objective To explore the mechanism of methyltransferase METTL3 in premature ovarian failure (POF) using a POF mouse model, providing a theoretical basis for the pathological research and clinical treatment of POF. Methods C57BL/6 female mice aged 6 to 8 weeks were selected for the study. The experimental group consisted of mice with a premature ovarian failure (POF) model established using the D-galactose metabolic method, while the control group comprised normal mice subjected to the same intervention with an equal volume of physiological saline. The levels of sex hormones were measured using ELISA, and histopathological changes in ovarian tissue were observed through HE staining to verify the successful establishment of the POF mouse model and to explore the correlation between METTL3 and POF at the tissue level. Additionally, stable transgenic mouse granulosa cell lines with METTL3 overexpression and knockdown were constructed at the cellular level. Cell proliferation and apoptosis were assessed using CCK-8 and FITC/PI dual staining methods to clarify the regulatory role of METTL3 in granulosa cell apoptosis and its impact on the occurrence of POF. Results The POF mouse model was successfully established. TUNEL staining revealed a significant increase in apoptotic granulosa cells in the ovarian tissue of the POF group (P < 0.05), which also exhibited high expression of METTL3. In cellular experiments, stable transcriptional cell lines of mouse granulosa cells with METTL3 overexpression and knockdown were successfully constructed. Upregulation of METTL3 expression promoted granulosa cell apoptosis and inhibited their proliferation (P < 0.05). Conclusion METTL3 participates in the development of POF by promoting granulosa cell apoptosis.
2025, 46(3): 19-26.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250304
Abstract:
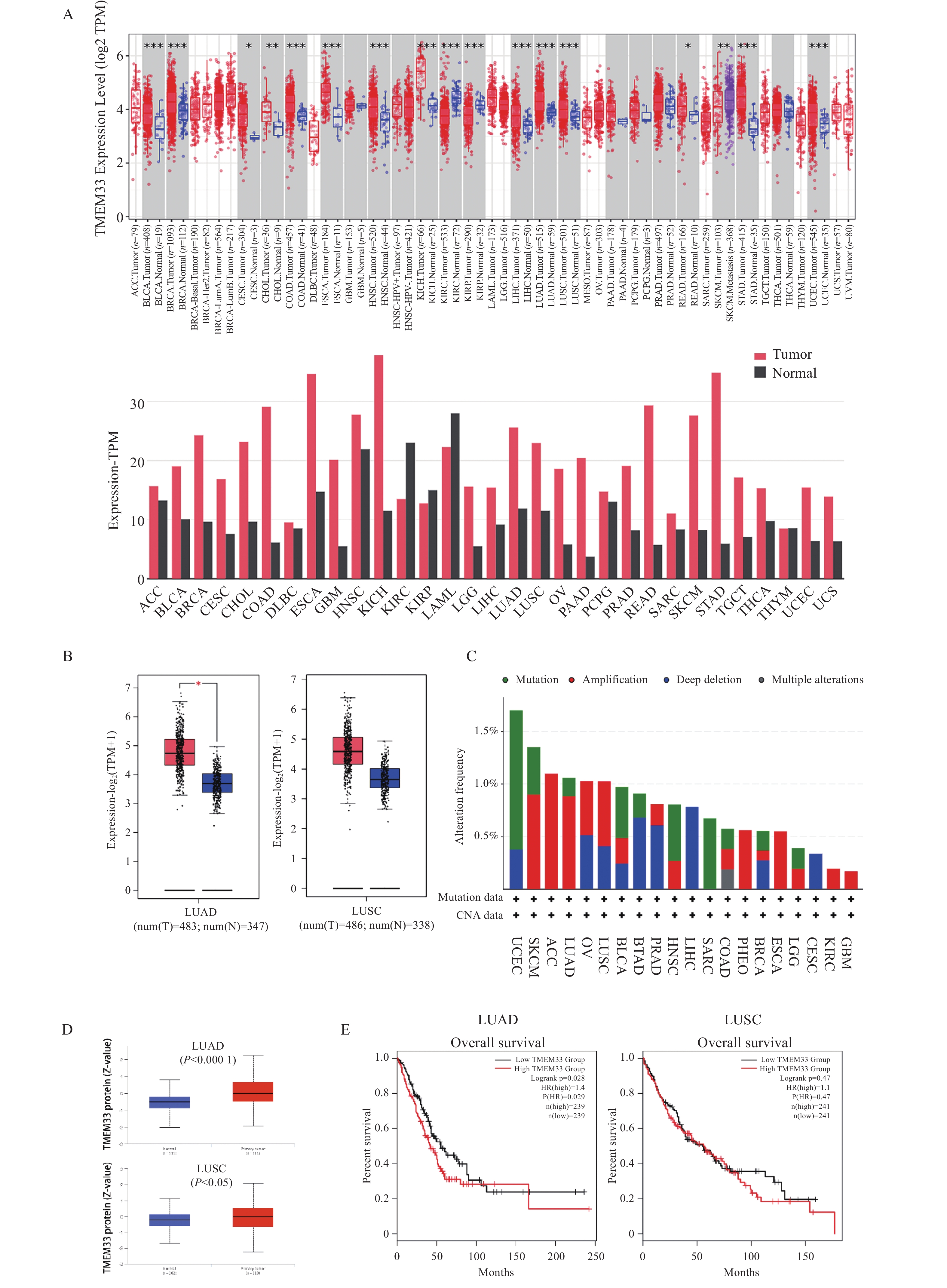
Objective This study aimed to explore the expression pattern of transmembrane protein 33 (TMEM33) in lung adenocarcinoma and its correlation with clinical pathological features. Methods Bioinformatics tools and public databases (e.g., TCGA and GEO) were used to analyze TMEM33 expression data in lung cancer. Then, immunoblotting and real-time quantitative PCR were performed to detect TMEM33 protein and mRNA levels in four cell lines. Immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry were also used to assess TMEM33 expression and localization in lung adenocarcinoma and normal lung tissue samples. Results Bioinformatics analysis revealed higher TMEM33 expression in lung adenocarcinoma than in normal lung tissue (P < 0.05) and a significant correlation between TMEM33 and SLC30A9 expression (P < 0.0001). Logistic regression analysis indicated an association between TMEM33 expression and tumor T stage (OR = 0.48, P = 0.044). Experimental results showed higher TMEM33 protein (P < 0.01) and mRNA (P < 0.001) levels in lung adenocarcinoma cell lines than in normal lung epithelial cells. Similarly, TMEM33 protein (P < 0.05) and mRNA (P < 0.01) levels were higher in lung adenocarcinoma tissues than in adjacent tissues. Immunohistochemistry confirmed high TMEM33 expression in lung adenocarcinoma tissues. Conclusion TMEM33 is highly expressed in lung adenocarcinoma, associated with malignancy and T stage, and may be a potential prognostic and therapeutic target.
2025, 46(3): 27-33.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250305
Abstract:
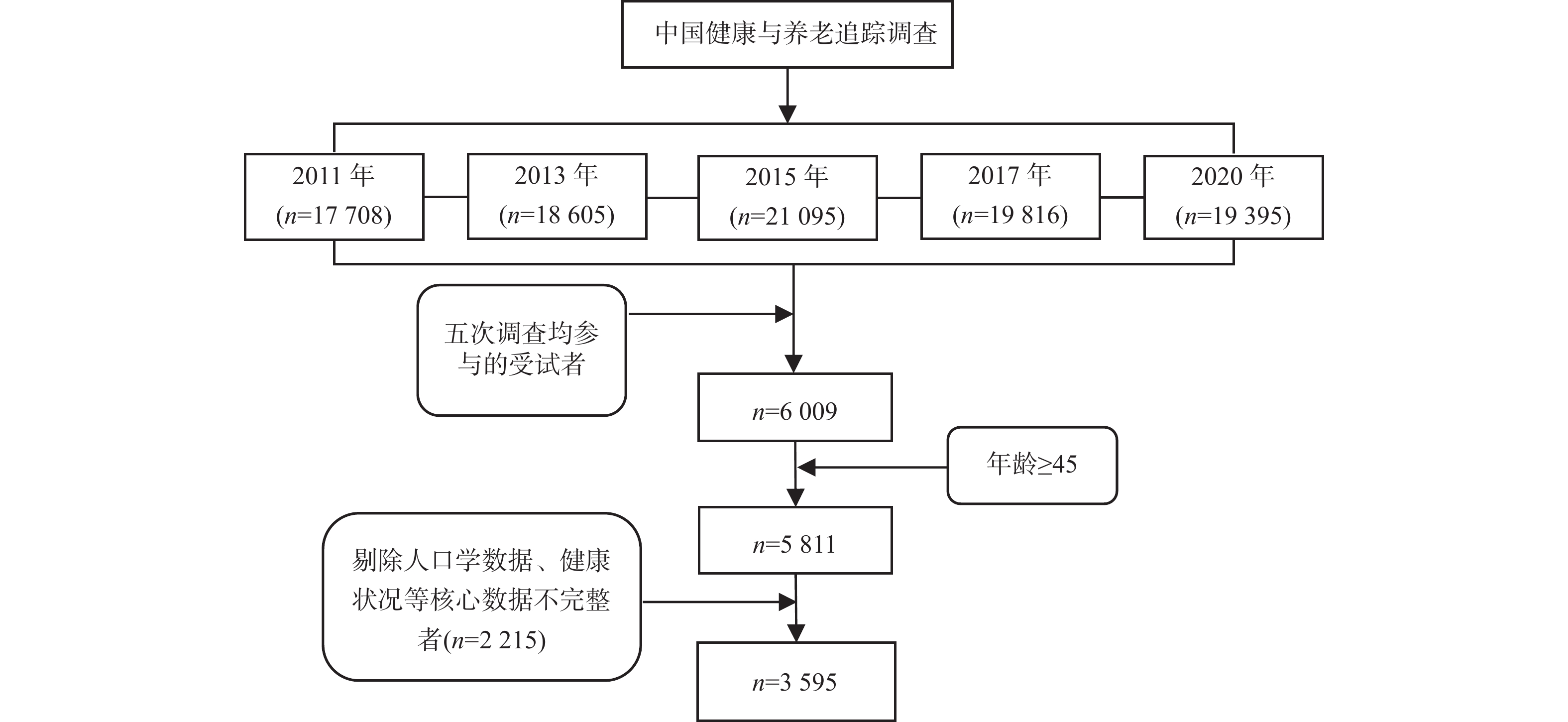
Objective To understand the changes in self-rated health among middle-aged and elderly individuals in China and the influencing factors, providing a reference for improving health and promoting healthy aging. Methods Using data from the China Health and Aged Care Tracking Survey (CHARLS) from 2011 to 2020, this study analyzed 3595 middle-aged and elderly individuals (≥45 years old) who participated in all five rounds of the survey from 2011 to 2020. Univariate analysis and multinomial logistic regression were employed to analyze the influencing factors of self-rated health changes. Results Among the 3 595 middle-aged and elderly individuals, 26.54 % reported an increase in self-rated health, 28.40 % reported a decrease, and 45.06 % reported no change. The multinomial logistic regression results indicated that compared to those with unchanged self-rated health, individuals whose self-rated health declined were more likely to have an increased number of Activities of Daily Living (ADLs), a higher number of chronic diseases, not engaging in at least 10 minutes of light physical activity per week, and a decline in life satisfaction levels. The odds ratios for these factors were 1.415 (OR = 1.415, 95%CI: 1.181~1.694), 1.479 (OR = 1.479, 95%CI: 1.225~1.785), 1.454 (OR = 1.486, 95%CI: 1.172~1.804), and 1.263 (OR = 1.237, 95%CI: 1.043~1.530), respectively. In contrast, individuals whose self-rated health improved, compared to those with unchanged health, were more likely to report an increase in life satisfaction levels, while an increase in ADLs and chronic diseases negatively impacted self-rated health improvement. The odds ratios for these factors were 1.698 (OR = 1.698, 95%CI: 1.425~2.023), 0.769 (OR = 0.769, 95%CI: 0.646~0.915), and 0.689 (OR = 0.689, 95%CI: 0.549~0.865), respectively. Conclusion From 2011 to 2020, the self-rated health of middle-aged and elderly individuals in China has slightly declined, with a focus on improving physical health status, increasing physical activity, and addressing mental health as key areas for enhancing self-rated health among the elderly in China.
2025, 46(3): 34-38.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250306
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the in vitro antiviral effects of Blumea balsamifera(L.)DC. extract against Coxsackievirus B5 (CVB5). Methods A series of dilutions of Coxsackievirus were prepared and co-cultured with RD cells to determine the TCID50 value. Subsequently, different concentrations of the extract were added to a 96-well plate containing RD cells to evaluate their impact on cell viability. The ability of Blumea balsamifera extract to inhibit Coxsackievirus was further observed in the 96-well plate containing RD cells and the extract. Results The TCID50 value of Coxsackie virus solution was 10−7.67. The inhibition rate of Blumea balsamifera extract against Coxsackievirus increased with concentration, with an IC50 value of 7.26 mg/L. At a concentration of 50 mg/L, the extract caused a decrease in RD cell viability(P < 0.05), but within the concentration range of 6.25 to 50 mg/L, it increased the viability of virus-infected RD cells(P < 0.05), with a selectivity index (SI) exceeding 6.89. Conclusion Blumea balsamifera(L.)DC. extract exhibits in vitro activity against Coxsackievirus.
2025, 46(3): 39-43.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250307
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the prevalence of hyperuricemia among ethnic groups in Gongshan county, Yunnan province through a cross-sectional study. Methods A total of 229 residents aged ≥18 years from Dulong, Nu, Tibetan, Bai and Lisu ethnic groups were randomly selected in Gongshan County of Yunnan Province for questionnaire survey, physical examinations and laboratory tests. SPSS 22.0 was used for t test, Chi-square test, correlation analysis, and multivariate logistic regression analysis. Results A total of 107 cases of hyperuricemia were identified, with a detection rate of 46.7%, among which the prevalence was 43.9% in males, 52.63% in female, 48% in the Dulong, 51% in the Lisu, 47% in the Nu, 37.5% in the Bai, 52% in the Tibetan and 50% in the Han. There were no statistically significant differences in prevalence among all nationalities (P > 0.05). The proportion of individuals with a history of diabetes, as well as levels of urea nitrogen and serum creatinine, were significantly higher in the hyperuricemia group compared to the non-hyperuricemia group (P < 0.05). Correlation analysis showed a positive correlation between hyperuricemia and diabetes, urea nitrogen and serum creatinine. (P < 0.05). Multivariate regression analysis showed that diabetes and elevated serum creatinine were independent risk factors for the onset of hyperuricemia(P < 0.05). Conclusion The detection rate of hyperuricemia is relatively high in Gongshan County, Yunnan Province, and there is no significant differences in prevalence among ethnic groups. Diabetes and elevated serum creatinine are associated with hyperuricemia, which increase the risk of developing hyperuricemia.
2025, 46(3): 44-50.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250308
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the bacterial distribution characteristics, drug resistance characteristics and related risk factors of multidrug-resistant organisms (MDRO) in patients with diabetic foot infection (DFI) in some areas of Yunnan Province to provide empirical reference for clinical treatment. Methods Clinical data of 300 DFI patients admitted to the Department of Endocrinology of the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2019 to December 2023 were collected. Based on the results of drug sensitivity tests and matching of basic data, patients were divided into the MDRO group (n = 60) and the non-MDRO group (n = 240). A retrospective analysis was conducted on the distribution of pathogenic bacteria, drug resistance characteristics of MDRO and risk factors for MDRO infection in DFI patients. Results In 60 patients with MDRO infections, 62 strains of MDRO were cultured, with 58 strains from single MDRO infections and 4 strains from mixed MDRO infections. Of the 60 patients, 2 were cultured for 2 types of MDRO. Among the strains, there were 45 gram-positive bacteria (72.58%) which were all Staphylococcus aureus, 17 strains of gram-negative bacteria (27.42%) mainly including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterobacter cloacae and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Among common MDRO, Staphylococcus aureus showed complete resistance to penicillin G and oxacillin(100%), with high resistance to erythromycin and clindamycin ( > 80%), but no resistance to tigacycline vancomycin was observed. The resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Enterobacter cloacae to cephalosporin antibiotics was obvious, and the resistance rate to imipenem and amikacin was low. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was 100% resistant to ticacillin/clavulanate potassium, imipenem, tigacycline and cotrimoxazole, but showed no resistance to cefepime, ciprofloxacin, gentamicin and amikacin. There were statistically significant differences between the two groups in regional distribution, duration of diabetic foot, lower extremity arterial disease, venous plasma glucose levels and glycosylated hemoglobin (P < 0.05). Binary Logistic regression analysis showed that region and duration of diabetic foot disease were independent risk factors for MDRO infection in DFI patients (P < 0.05). Conclusion In some areas of Yunnan Province, the distribution of MDRO in DFI patients is mainly gram-positive bacteria, with varying antibiotic sensitivities among different pathogens. Multiple factors lead to MDRO infections in DFI patients, which assists clinical practitioners in early identification of high-risk DFI patients with MDRO infections and provide empirical reference for clinical treatment.
2025, 46(3): 51-57.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250309
Abstract:
Objective To explore the immediate, long-term, and delayed effects of spiral stabilizing muscle chain technique compared to static distraction and Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation(PNF) stretching techniques on the flexibility of hip flexors. Methods Ninety subjects were randomly divided intothree groups of 30 each. Group 1 underwent the static stretching of the hip joint. Group 2 received PNF stretching, and Group 3 participated in SPS training. All participants were measured for hip extension angle to assess hip flexor flexibility before training, immediately after the first training session, at the end of 4 weeks of training, and 2 weeks after training cessation. Results Within-group comparisons showed significant increases in hip extension angles after one training session, after 4 weeks of training, and after 2 weeks of cessation compared to pre-training (P < 0.05). Between-group comparisons indicated no statistically significant differences in hip extension angle improvements among the three groups after one training session, after 4 weeks of training, and after 2 weeks of cessation (P > 0.05). Conclusion SPS training, static stretching, and PNF stretching all demonstrate good immediate, long-term, and delayed effects on improving hip extension angles, with consistent stretching outcomes.
2025, 46(3): 58-65.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250310
Abstract:
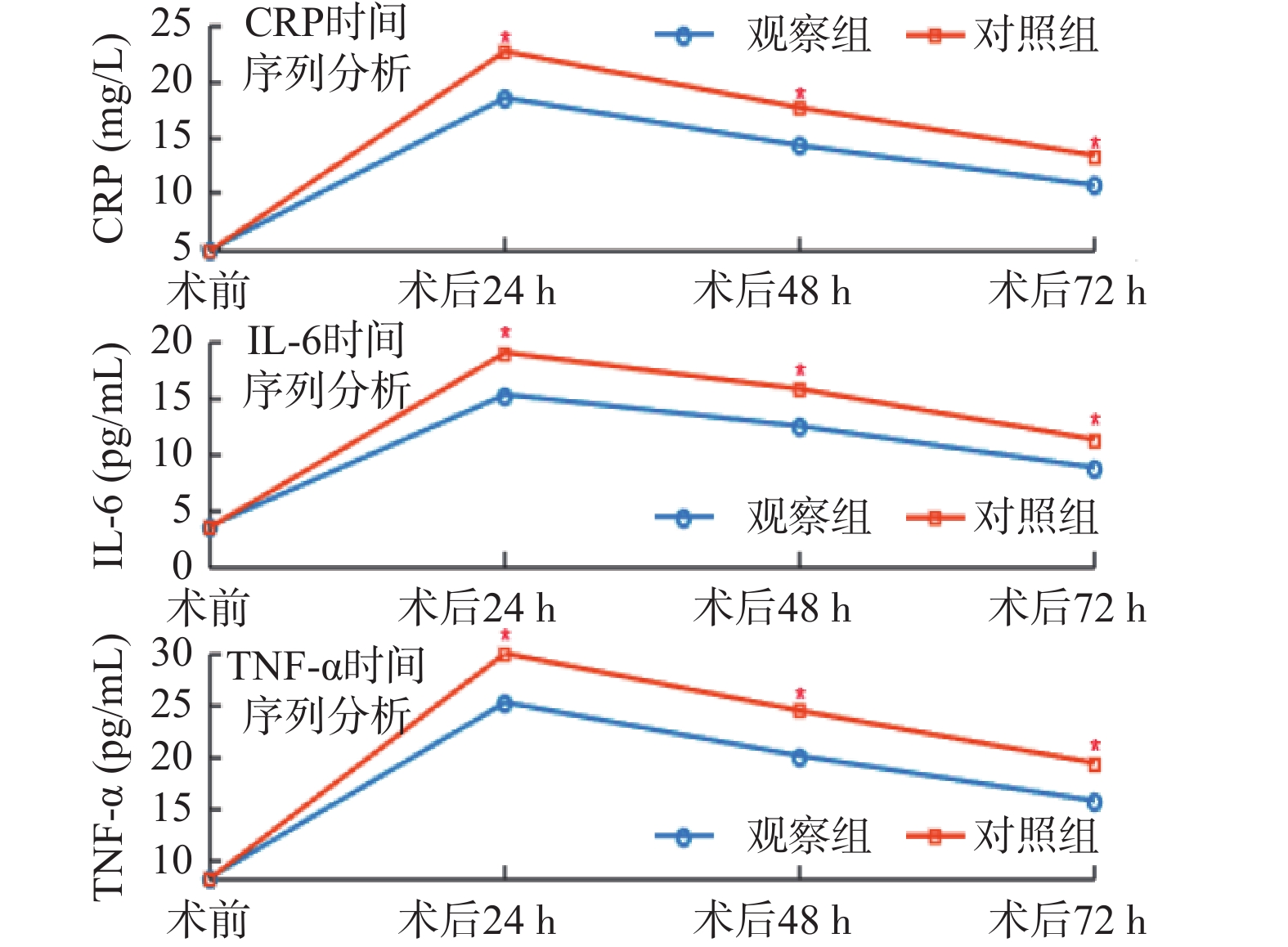
Objective This study aims to explore the effects of Minimally Invasive Extracorporeal Circulation (MECC) on systemic inflammatory response and transfusion requirements following Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG). Methods A total of 126 patients who underwent CABG from January 2023 to January 2024 were selected and randomly divided into an observation group and a control group, with 63 patients in each group. The observation group received MECC, while the control group was treated with Conventional Extracorporeal Circulation (CECC). Inflammatory response indicators, immune system function, coagulation function, renal function, cardiac function, and clinical symptoms were monitored preoperatively and at 24, 48, and 72 hours postoperatively for comparison and analysis. Results At 24 hours postoperatively, CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α levels in the observation group were (18.5±3.7) mg/L, (15.2±3.4) pg/mL and (25.3±5.6) pg/mL, respectively, which were significantly lower than those in the control group(P < 0.05). At 48 hours postoperatively, the CD4+/CD8+ ratio in the observation group was 1.6±0.3, which was higher than that in the control group (P < 0.05). At 72 hours postoperatively, the PT and APTT in the observation group were (12.1±1.2) seconds and (30.4±3.2) seconds, respectively, which were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Additionally, 72 hours after surgery, SCr and BUN in the observation group were (1.1±0.2) mg/dL and 14.6±3.1 mg/dL, respectively, which were significantly lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). In terms of cardiac function indexes, at 24 hours postoperatively, CI, LVEF, cTnI and BNP in the observation group were (2.6±0.5) L/min/m2, (55.6±4.0)%, (0.14±0.03) ng/mL, and (280±30) pg/mL, respectively, which were significantly better than those in the control group(P < 0.05). At all postoperative time points, the VAS score, complication rate, length of hospital stay and ICU stay were significantly better in the observation group than in the control group (P < 0.05), with the VAS score at 24 hours postoperatively being (4.8±1.2) compared to (5.5±1.3) in the control group(P < 0.05). Conclusions MECC demonstrates significant advantages in attenuating systemic inflammatory response after CABG, protecting multi-system function, reducing postoperative blood transfusion requirements, and improving postoperative recovery. Compared with traditional extracorporeal circulation, MECC effectively reduce postoperative inflammatory reactions and complications, enhancing the quality of life for patients post-surgery, and shows broad clinical application prospects.
2025, 46(3): 66-71.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250311
Abstract:
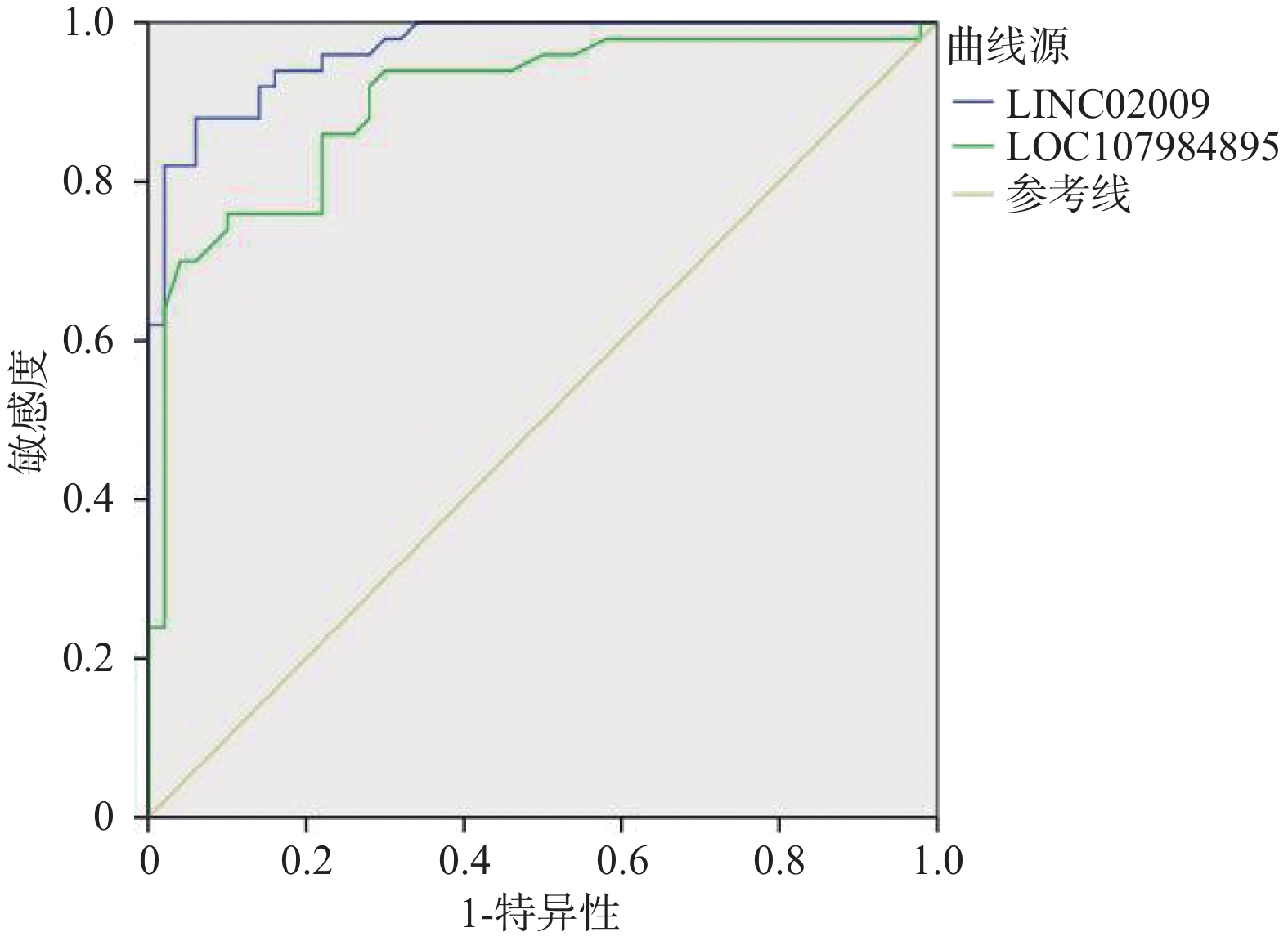
Objective To investigate the expression levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in peripheral lymphocytes of patients with atrial fibrillation and their clinical significance. Methods A total of 75 hospitalized patients with atrial fibrillation (50 with persistent atrial fibrillation and 25 with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation) from Kunming First People’ s Hospital between January 2023 and December 2023 were selected as study subjects, along with 50 normal control patients. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in peripheral blood leukocytes of patients with atrial fibrillation. Logistic regression analysis was employed to assess the relationship between expression levels and risk factors for atrial fibrillation, and ROC curves were used to predict the diagnostic cut-off values for LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in diagnosing atrial fibrillation. Results There were statistically significant differences in baseline diseases such as hypertension and coronary heart disease, biochemical indicators such as Cr and BNP, and myocardial remodeling indicators such as LAd and LVEF between the AF (paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and persistent atrial fibrillation) group and the Normal group (P < 0.05). The expression levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in the plasma of the atrial fibrillation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05) and were negatively correlated with LVEF (P < 0.05). The areas under the curve (AUC) of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in predicting atrial fibrillation were 0.967 (95%CI: 0.938 ~ 0.995) and 0.900 (95%CI: 0.838 ~ 0.963), respectively. The optimal cut-off values were 1.985 and 0.915, with sensitivities of 88% and 76%, respectively, and specificities of 94% and 90%, respectively. Conclusion LINC02009 and LOC107984895 are independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation and have certain predictive value for the occurrence of atrial fibrillation.
2025, 46(3): 72-78.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250312
Abstract:
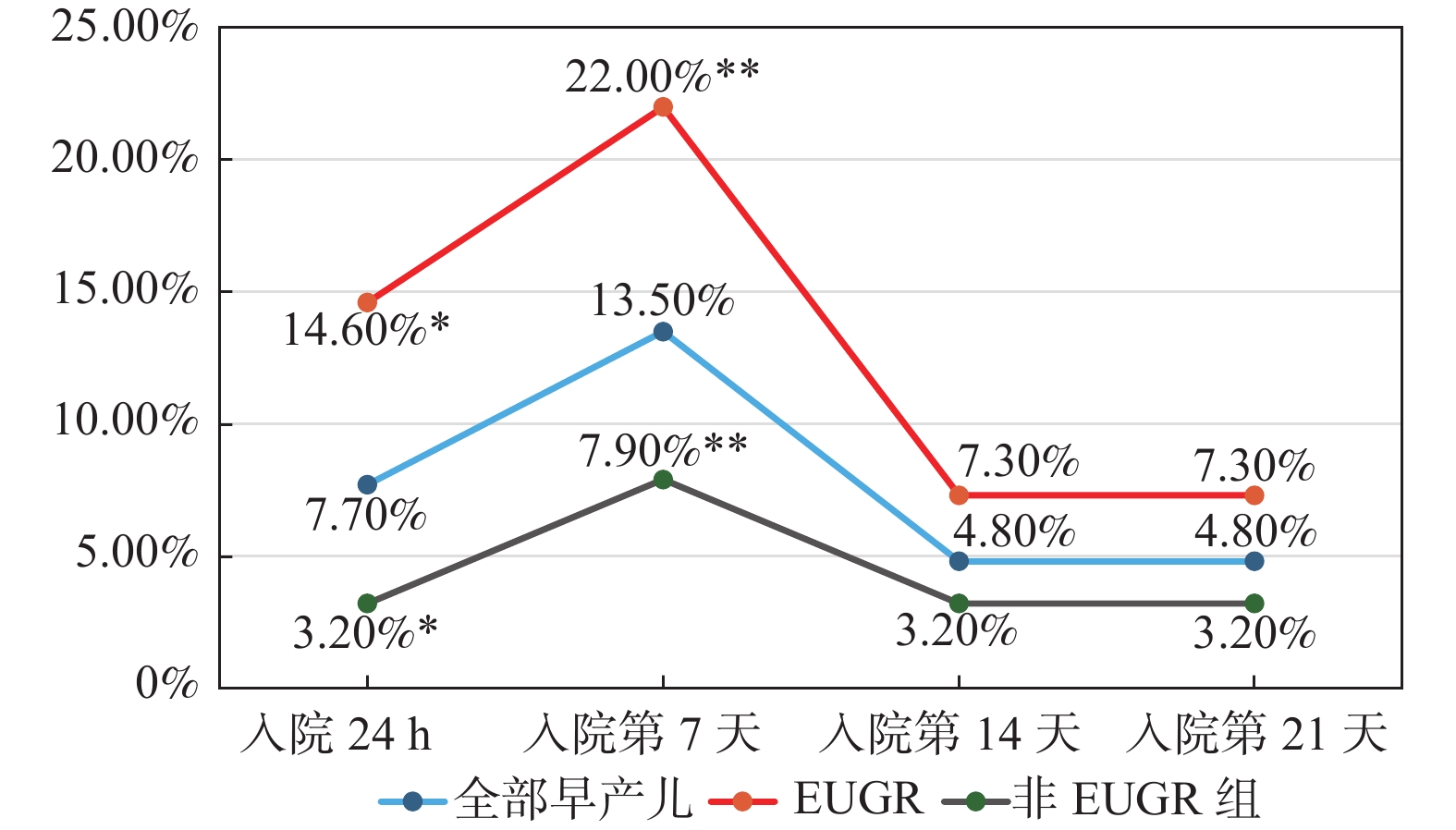
Objective To apply a multidimensional neonatal nutritional risk screening scale for hospitalized premature infants to explore its predictive value for extrauterine growth restriction (EUGR) at the time of discharge. Methods A total of 104 premature infants hospitalized in the Neonatal Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2023 to September 2023 were selected as research subjects. Nutritional risk screening was conducted within 24 hours of admission and weekly thereafter using the multidimensional neonatal nutritional risk screening scale. Scoring was based on four dimensions (birth status, weight changes, nutritional intake methods, and disease diagnosis), with a total score of ≥8 indicating high risk; ≥4 and <8 indicating moderate risk; and <4 indicating low risk. EUGR at the time of discharge was the primary clinical outcome indicator. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed to explore the predictive value of neonatal nutritional risk screening for EUGR in premature infants. Results At discharge, 40 premature infants (38.5%) experienced EUGR. The nutritional risk screening scores of the EUGR group on day 7 of hospitalization were higher than those of the non-EUGR group (P < 0.05). The rate of high nutritional risk on day 7 of hospitalization was highest (7.9% in the non-EUGR group, 22% in the EUGR group, and 13.5% overall). On both day 1 and day 7 of hospitalization, the rate of high nutritional risk in the EUGR group was higher than that in the non-EUGR group (P < 0.05). There were significant differences in the nutritional risk screening scores on day 7, birth weight Z-scores, discharge corrected gestational age weight Z-scores, and serum albumin levels between the EUGR and non-EUGR groups (P < 0.05). ROC curves were plotted, yielding AUCs of 0.625 (95%CI 0.514, 0.736), 0.652 (95%CI 0.544, 0.760), 0.674 (95%CI 0.561, 0.786), and 0.641 (95%CI 0.531, 0.750), indicating certain predictive value. A combined predictive ROC model yielded an AUC of 0.786 (95%CI 0.692, 0.880) for EUGR, which was higher than the AUCs for individual indicators (P < 0.001). Conclusion The occurrence of EUGR is relatively common among hospitalized premature infants. The nutritional risk is highest during the first week of hospitalization. The multidimensional neonatal nutritional risk screening scale can dynamically assess nutritional risk during hospitalization and may serve as one of the early warning indicators for EUGR in premature infants. The predictive efficacy for EUGR is enhanced when combined with birth weight Z-scores, discharge weight Z-scores, and serum albumin, providing a basis for individualized nutritional management of premature infants.
2025, 46(3): 79-88.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250313
Abstract:
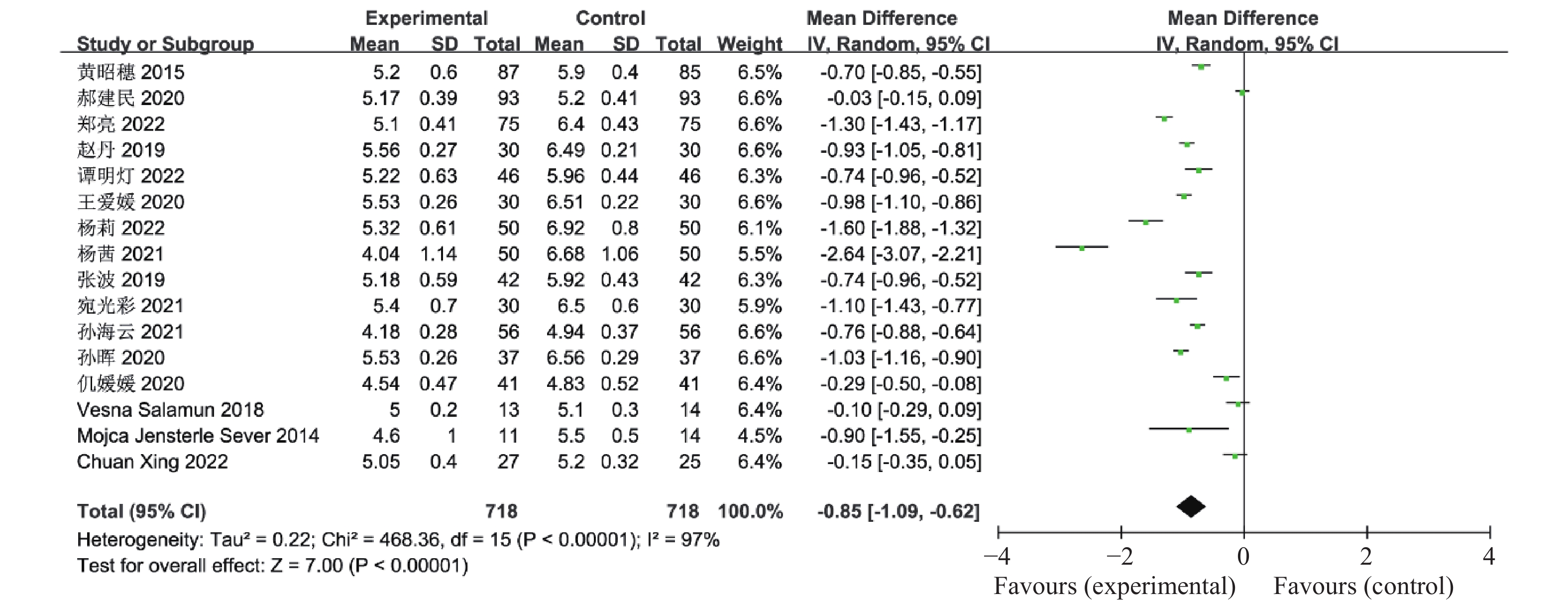
Objective To systematically evaluate the effects of liraglutide combined with metformin on glucose and lipid metabolism, sex hormones, reproductive function, and gastrointestinal reactions in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Methods We searched databases such as PubMed, WanFang Medical Network, WanFang Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI), and VIP Journals to collect randomized controlled trials published from January 2011 to August 2022 on the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with liraglutide combined with metformin, using Revman 5.4 for the meta-analysis. Results A total of 16 case-control studies were included, involving 1436 patients. Compared to metformin alone, the combination of liraglutide and metformin significantly lowered fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood glucoseafter 2 hours, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, FINS, BMI, as well as LH, FSH, and total testosterone in patients with PCOS. It improved lipid levels, helped establish menstrual cycles, and increased the normal ovulation rate and natural conception rate in these patients. However, there was a significantly higher incidence of gastrointestinal reactions in the liraglutide plus metformin group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The combination of liraglutide and metformin can improve glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), reduce levels of LH, FSH, and total testosterone, help establish regular menstrual cycles, and increase ovulation and pregnancy rates, but it significantly increases gastrointestinal side effects.
2025, 46(3): 89-96.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250314
Abstract:
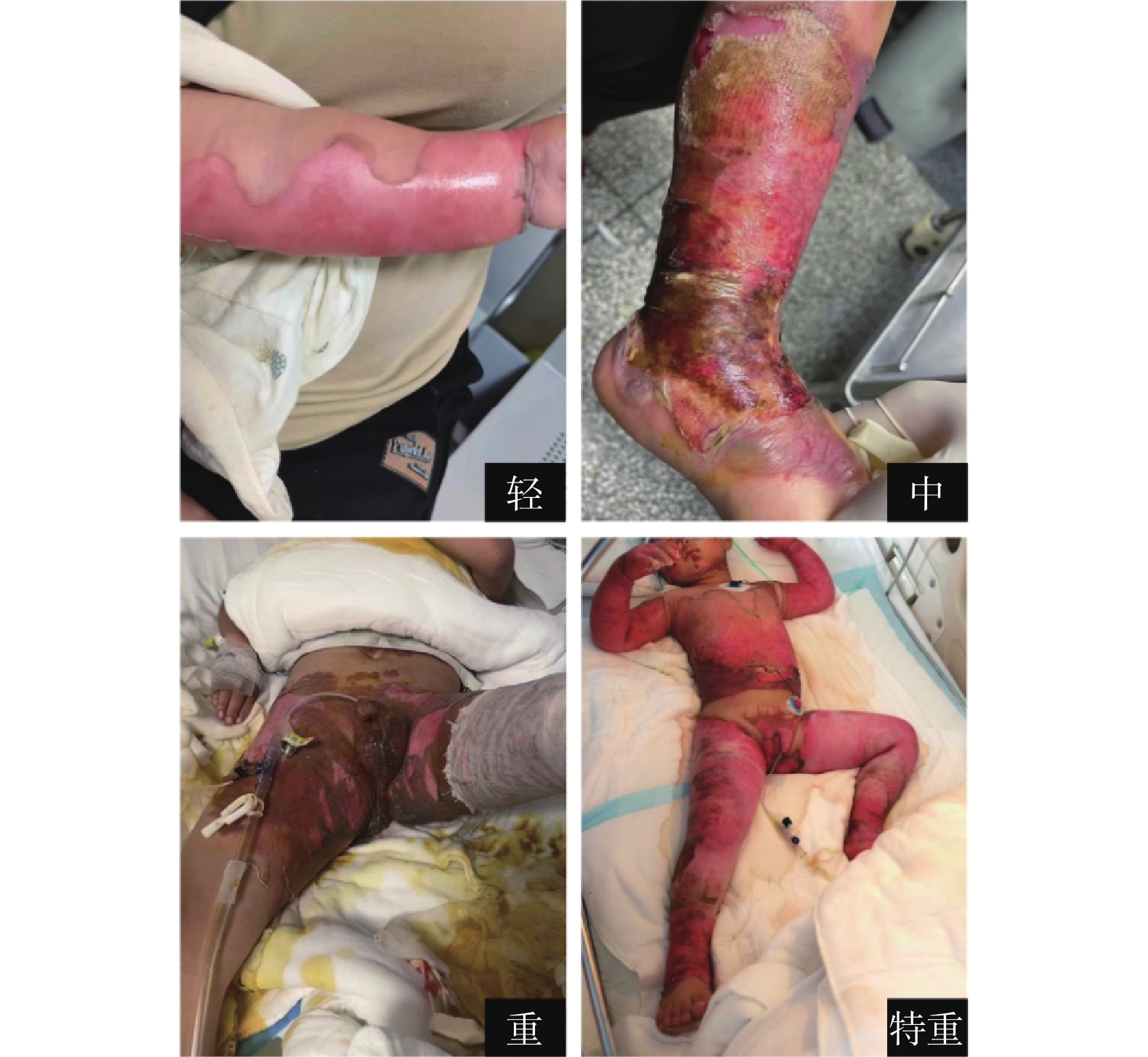
Objective To study the characteristics of pediatric burn epidemiology in this area. Methods Data of 1500 pediatric burn patients admitted to the Burn Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 1, 2018 to December 31, 2022 were collected. The age, sex, time of burn occurrence, type of burn, burn area, burn site, proportion of pediatric burn patients in the same period, length of hospitalization, payment method, hospitalization cost and residence of pediatric burn patients were statistically analyzed. Results The most common time for childhood burns to occur is during early childhood (873 cases, 58.2%), with male children more likely to suffer burns compared to female children (male∶female = 1.9∶1). The most frequent season for these burns is spring (404 cases, 26.9%). Scalding from hot liquids is the primary cause of injury (1211 cases, 81.0%). Most childhood burns are classified as moderate severity (945 cases, 63.0%). The maximum burn area recorded was 98.0% TBSA, the minimum was 0.1% TBSA, the average burn area was 14.5% TBSA, and the median was 10.0% TBSA. The most common site of burns in children is the trunk (982 cases, 23.4%). From 2018 to 2022, the proportion of pediatric burn patients among all burn patients has been decreasing annually (χ2 = 18.852, P < 0.001). The average length of hospitalization for pediatric burn patients was 12.4 days, with an average hospitalization cost of 15667.08 yuan. Most of the families of pediatric burn patients live in county-level areas or below (1027 cases, 68.5%). The severity of the burns, treatment methods, and presence of complications all significantly affect the clinical outcomes of pediatric burns, with statistically significant differences (χ2 = 23.453, P < 0.001). Conclusion Pediatric burn patients exhibit a range of significant characteristics. The majority of these patients are male, with the most common age group being toddlers. Spring has been identified as the season with the highest incidence of burns, while autumn sees relatively fewer cases. Scald injuries from hot liquids are the most common type of burn, with moderate burns being the most prevalent. The average burn area is approximately 14.5% of the total body surface area (TBSA). The limbs and trunk are the most commonly affected areas. In recent years, there has been a noticeable decrease in the proportion of pediatric burn patients, which is attributed to the growing awareness of burn prevention among the general population.
2025, 46(3): 97-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250315
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of bicyclol combined with ganciclovir in the treatment of children with Epstein-barr virus related infectious mononucleosis (IM) based on liver function, immunoglobulin A (IgA), immunoglobulin M (IgM) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels. Methods A total of 150 children with EB virus infected and IM admitted to the People's Hospital of Susong County from January 2019 to January 2024 were selected as the study subjects. Random grouping was performed using a digital expression method, dividing them into a control group and an observation group (n = 75). All children received routine symptomatic treatment upon admission. The control group were treated with ganciclovir, while the observation group were treated with bicyclol in addition to ganciclovir. Both groups underwent treatment for 7 days. The therapeutic effects , liver function indexes, immunoglobulin indexes, quality of life, and adverse reaction rates were compared between the two groups. The therapeutic effects, liver function indicators, immunoglobulin indicators, quality of life, and adverse reaction rates were compared between the two groups. Results The total effective rate of treatment in the observation group was 93.33% (70/75), which was significantly higher than that of control group (61.33% (46/75) (P < 0.05). After treatment, the liver function indexes of both groups were significantly decreased, and the observation group showing lower levels (all P < 0.05). After treatment, immunoglobulin indexes were significantly increased in both groups, with the observation group having higher levels (P < 0.05). After treatment, the scores of life quality in both groups significantly increased, and those in observation group were higher (all P < 0.05). Quality of life scores significantly improved in both groups, with the observation group achieving higher scores (P < 0.05). The total adverse reaction rate in the observation group was 6.67% (5/75), compared to 5.33% (4/75) in the control group, but there was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion The application of bicyclol combined with ganciclovir in the treatment of Epstein-barr virus related IM can significantly improve the therapeutic effect, improve liver function and immunoglobulin indexes, and improve the quality of life in children, with relatively low adverse reactions, demonstrating high clinical efficacy and safety.
2025, 46(3): 103-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250316
Abstract:
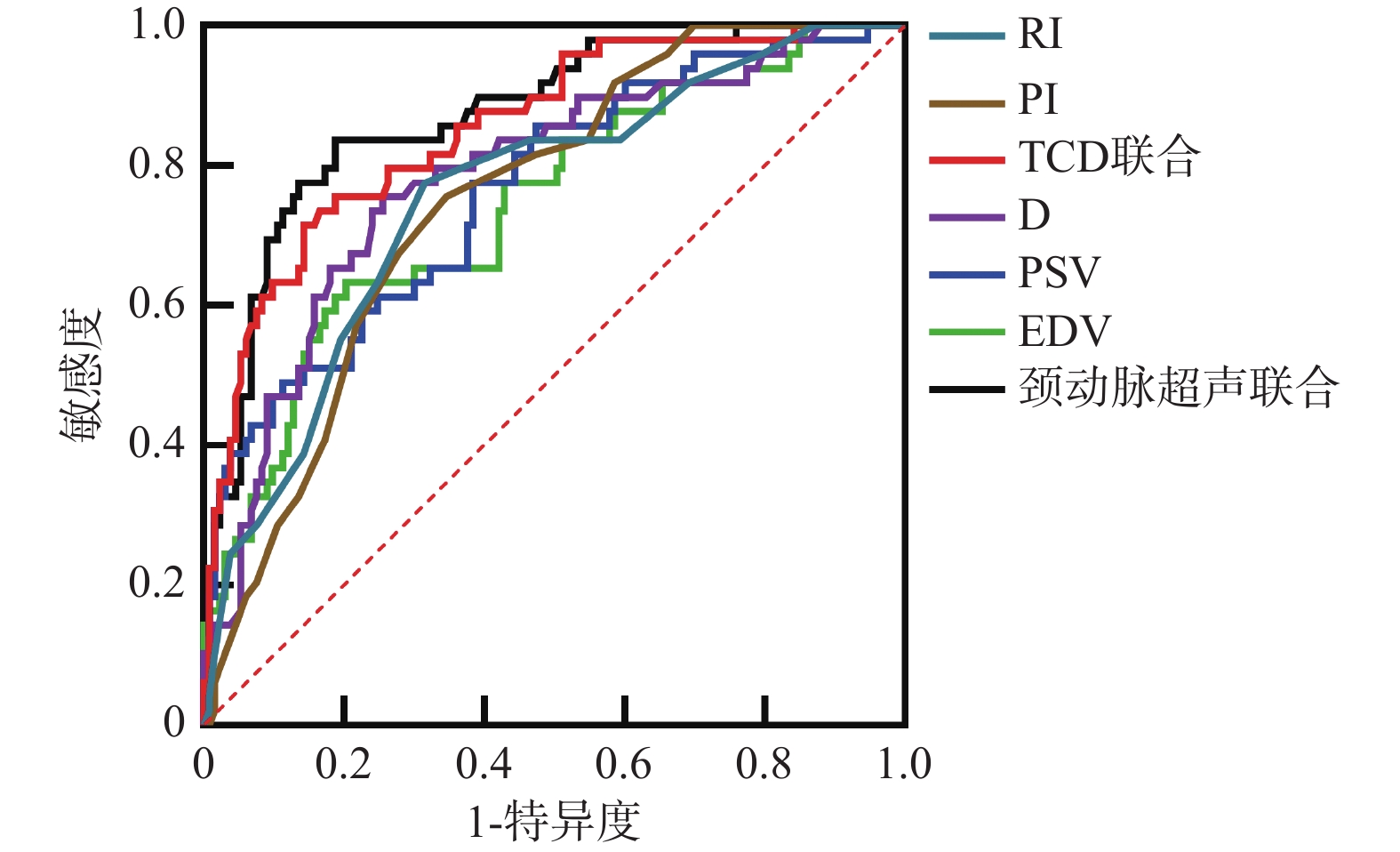
Objective To explore the evaluation value of thyroid function indicators [thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), free thyroxine (FT4), free triiodothyronine (FT3)] combined with transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD) and carotid ultrasound in the assessment of vascular stenosis in atherosclerotic cerebral infarction (ASCI), providing a reference for clinical targeted treatment. Methods A total of 182 patients with ASCI admitted to Handan Frist Hospital from October 2021 to September 2023 were selected and all of them underwent TCD, carotid artery ultrasound and thyroid function examination. Digital subtraction angiography was used as the gold standard to analyze the evaluation effect of TCD and carotid artery ultrasound combined with TSH, FT4 and FT3 in vascular stenosis of ASCI. Results Among the 182 patients with ASCI, DSA confirmed 64 cases(35.16%) with mild internal carotid artery stenosis, 69 cases(37.91%) with moderate stenosis, 29 cases(15.93%) with severe stenosis, and 20 cases(10.99%) with complete occlusion. There was no statistically significant difference in clinical data among groups with different degrees of vascular stenosis (P > 0.05). The peak systolic velocity (PSV) and end-diastolic volume (EDV) of the internal carotid artery in different groups with different degrees of vascular stenosis showed an increasing trend with the severity of vascular stenosis, while the pulse index (PI), resistance index (RI), and diameter (D) showed a decreasing trend (P < 0.05). In different groups with different degrees of vascular stenosis, TSH and FT4 levels increased with the severity of stenosis, while FT3 levels decreased (P < 0.05). TSH and FT4 were positively correlated with the degree of vascular stenosis, while FT3 was negatively correlated(P < 0.05). TSH and FT4 were positively correlated with PSV and EDV, and negatively correlated with RI, PI, and D. FT3 was positively correlated with RI, PI, and D, and negatively correlated with PSV and EDV (P < 0.05). The combined evaluation of RI, PI, D, PSV, EDV, TSH, FT4, and FT3 yielded the highest area under the curve (AUC) value of 0.941 for assessing ASCI vascular stenosis (P < 0.05). Conclusion The combination of TCD, carotid ultrasound, and thyroid function tests have high value in the assessment of ASCI vascular stenosis. The joint evaluation of RI, PI, D, PSV, EDV, TSH, FT4 and FT3 is beneficial for diagnosing different degrees of vascular stenosis, providing a reference for clinical treatment. r clinical treatment.
2025, 46(3): 110-116.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250317
Abstract:
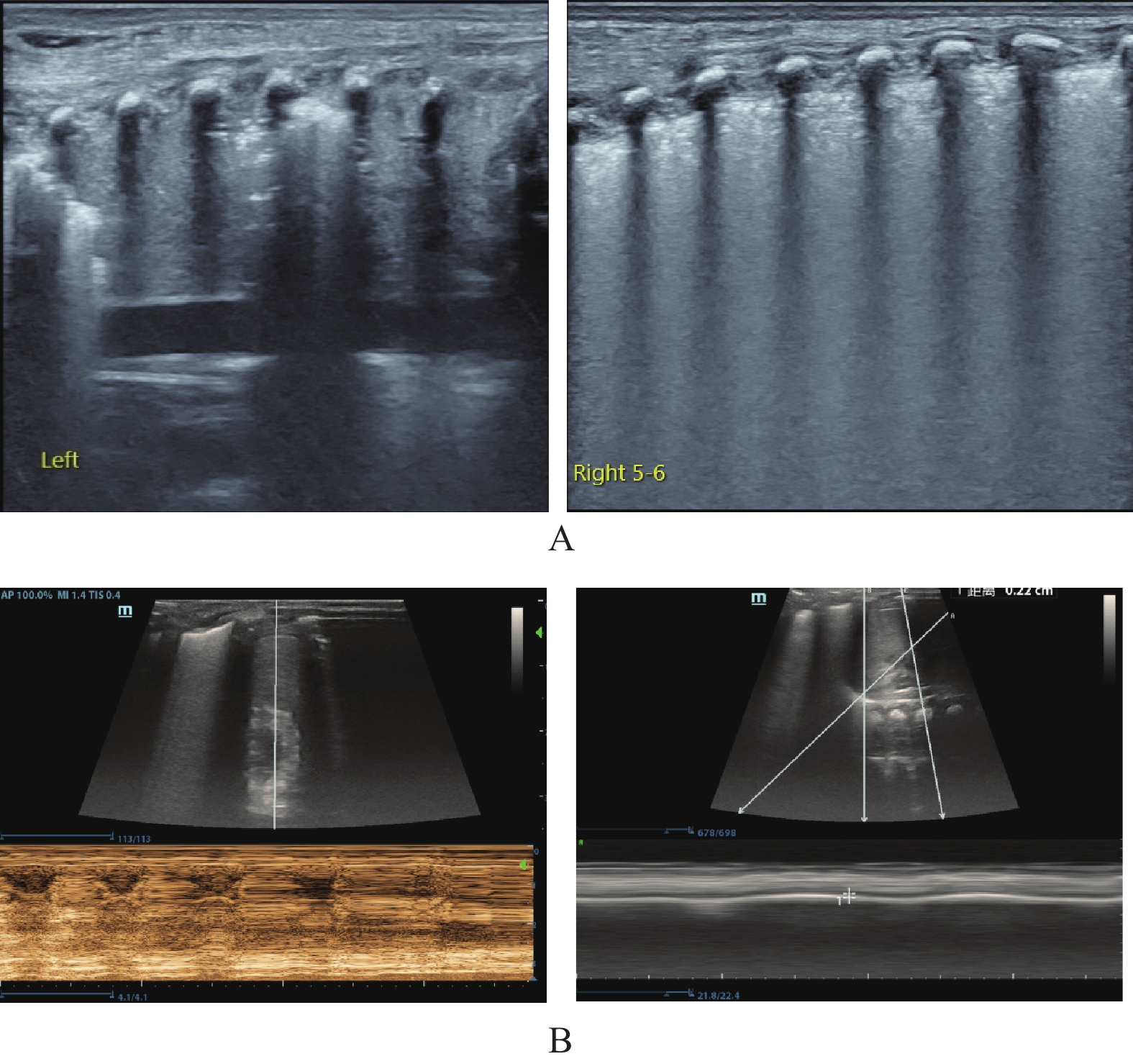
Objective To explore the value of lung ultrasound score (LUS) and diaphragm ultrasound combined with routine indicators in predicting the occurrence of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children with severe pneumonia (SP). Methods A total of 160 patients with SP were selected from Kunming Children’s Hospital from August 2022 to August 2023, all of whom underwent lung ultrasound and diaphragm ultrasound examination to obtain LUS and diaphragm ultrasound parameters [diaphragm mobility (DM), diaphragm thickness change rate (TF)]. The patients with SP were divided into ARDS group and non-ARDS group according to whether they were complicated with ARDS during hospitalization. The general data, serum inflammatory factor levels, LUS and diaphragm ultrasound parameters were compared between the two groups at admission, and the influencing factors of ARDS in children with SP were analyzed, and the value of LUS and diaphragm ultrasound parameters in predicting ARDS in children with SP was analyzed. Results The incidence of ARDS in SP patients was 41.88% (67/160). APS, APACHEⅡ scores, serum C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), high mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) levels, LUS and DM in ARDS group were higher than those in non-ARDS group, TF were lower than those in non-ARDS group (P < 0.05). APS, APACHEⅡ scores, serum CRP, IL-6, HMGB1 levels, LUS, DM, TF were the influencing factors of ARDS in SP children at admission (P < 0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) of LUS, DM and TF predicted ARDS were 0.718, 0.742 and 0.720, respectively. The AUC of the conventional prediction scheme (APS, APACHEⅡ score combined with serum CRP, IL-6 and HMGB1 levels at admission) was 0.852, while that of the new prediction scheme (combined with LUS, DM and TF based on the conventional prediction scheme) was 0.930. The AUC of the new prediction scheme was significantly higher than that of the conventional prediction scheme (P < 0.05). Conclusion LUS, DM, TF, and SP parameters of the diaphragm are significantly correlated with ARDS in children with SP, and the combination of routine indicators can provide reliable evidence for clinical prediction of ARDS in children with SP.
2025, 46(3): 117-123.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250318
Abstract:
Objective To explore the therapeutic effects of temperature-controlled radiofrequency combined with electrical stimulation biofeedback on postpartum dyspareunia in women. Methods In this study, 166 patients suffering from dyspareunia due to pelvic floor muscle hypertonicity who visited the Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Medicine Center of our hospital were selected as subjects. They were randomly divided into three groups: the electrical stimulation biofeedback treatment group (55 cases), the radiofrequency treatment group (55 cases), and the combined electrical stimulation biofeedback and radiofrequency treatment group (56 cases). Patients in the electrical stimulation biofeedback therapy group received only electrical stimulation biofeedback therapy; patients in the radiofrequency group were treated solely with radiofrequency therapy; and patients in the combined treatment group began receiving gynecological radiofrequency treatment from the second week, in addition to the same treatment as the electrical stimulation biofeedback treatment group. To evaluate the effectiveness of the three treatment methods, comparative analyses were conducted on the pelvic floor modified Oxford muscle strength measurement results, pelvic floor surface electromyography values, and sexual function (FSFI) scores of the three groups of patients before and after treatment. Results After treatment, the average resting electromyography (EMG) value of the combined treatment group decreased (P < 0.05), indicating a significant improvement in muscle relaxation function. After treatment, the combined treatment group showed significant improvements in the pelvic floor modified Oxford muscle strength test, the maximum EMG value of fast-twitch (type II fibers) muscles, the average EMG value of slow-twitch (type I fibers) muscles, and the average EMG value of endurance test, and also demonstrated significant improvements in sexual function (FSFI) scores, which were superior to the electrical stimulation biofeedback treatment group and the radiofrequency treatment group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The combined treatment of temperature control radiofrequency and electrical stimulation with biofeedback has shown significant therapeutic effects in the treatment of postpartum dyspareunia, offering a broad prospect for clinical application.
2025, 46(3): 124-131.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250319
Abstract:
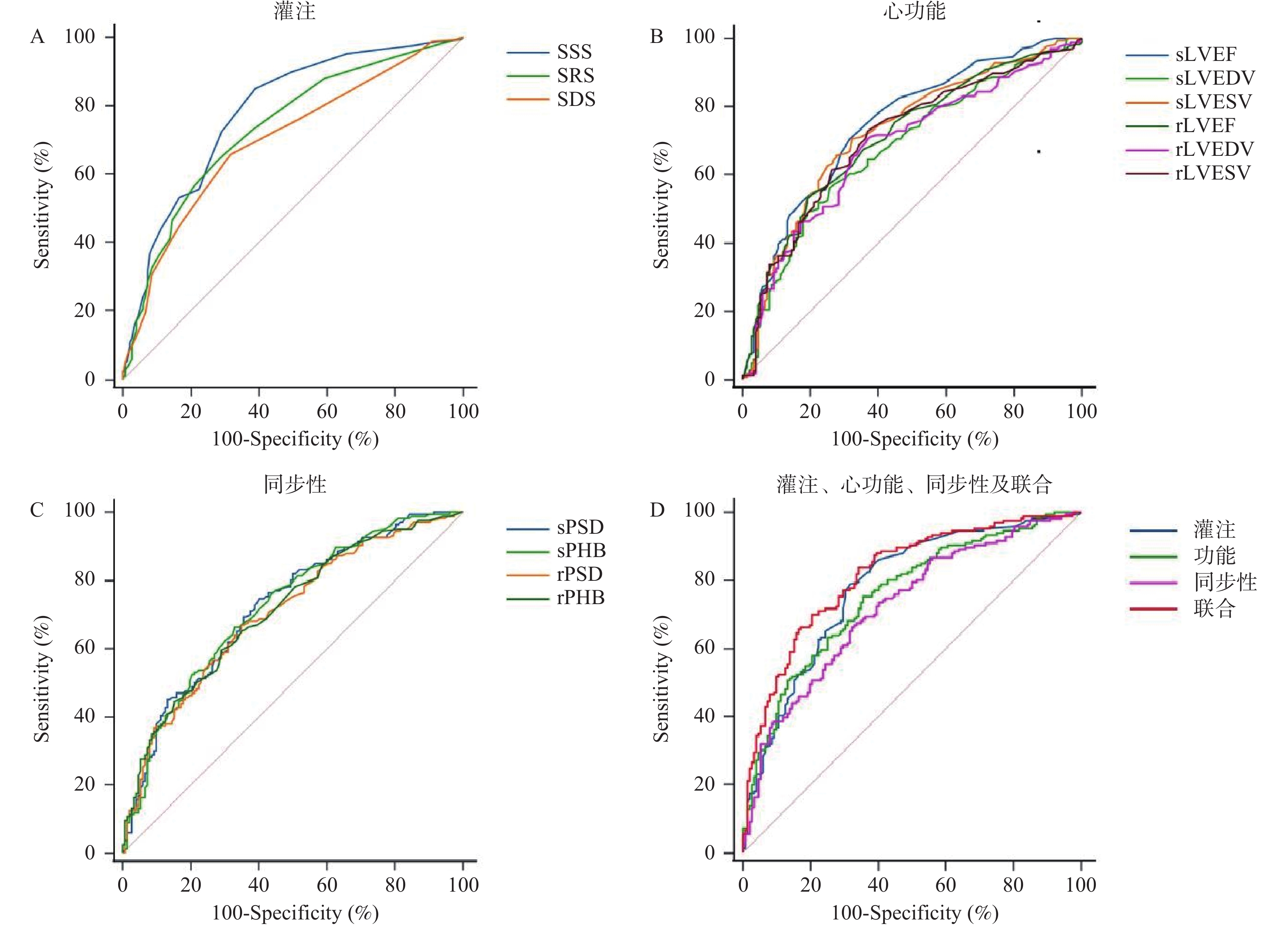
Objective To evaluate the diagnostic value of adenosine load - resting gated myocardial perfusion imaging for three-vessel disease in coronary artery disease (CAD) patients using coronary angiography as the gold standard. Methods A retrospective study was conducted, including 318 patients diagnosed with CAD who underwent coronary angiography at Yanan Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from January 2021 to December 2022. Based on the results of coronary angiography, the 318 CAD patients were divided into a three-vessel disease group (n = 166) and a non-three-vessel disease group (single and double vessel disease group, n = 152). All the subjects underwent adenosine stress-resting GMPI within two weeks. Adenosine stress-resting GMPI myocardial perfusion parameters (SSS, SRS, SDS), cardiac function parameters (LVEF, LVEDV, LVSV) and left ventricular mechanical contraction synchronization parameters (PSD, PHB) were collected. The diagnostic value of adenosine stress - resting gated myocardial perfusion imaging for three-vessel disease in CAD was explored. Results Among the perfusion parameters, SSS had the highest AUC of 0.781, while sLVEF had the highest AUC of 0.748 among cardiac function parameters, and sPHB had the highest AUC of 0.724 among synchrony parameters. The AUCs of combined parameters were all higher than those of perfusion parameters, cardiac function parameters, and synchrony parameters (P < 0.05). The changes in ΔLVESV and ΔLVEF between the three-vessel disease group and the non-three vessel disease group showed statistical significance (P < 0.05). Conclusion The perfusion, cardiac function and synchronization parameters of adenosine stress-resting gated myocardial perfusion imaging have high diagnostic value for three-vessel coronary heart disease, and the combined detection of the three parameters provides even greater diagnostic value for three-vessel coronary heart disease.
2025, 46(3): 132-138.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250320
Abstract:
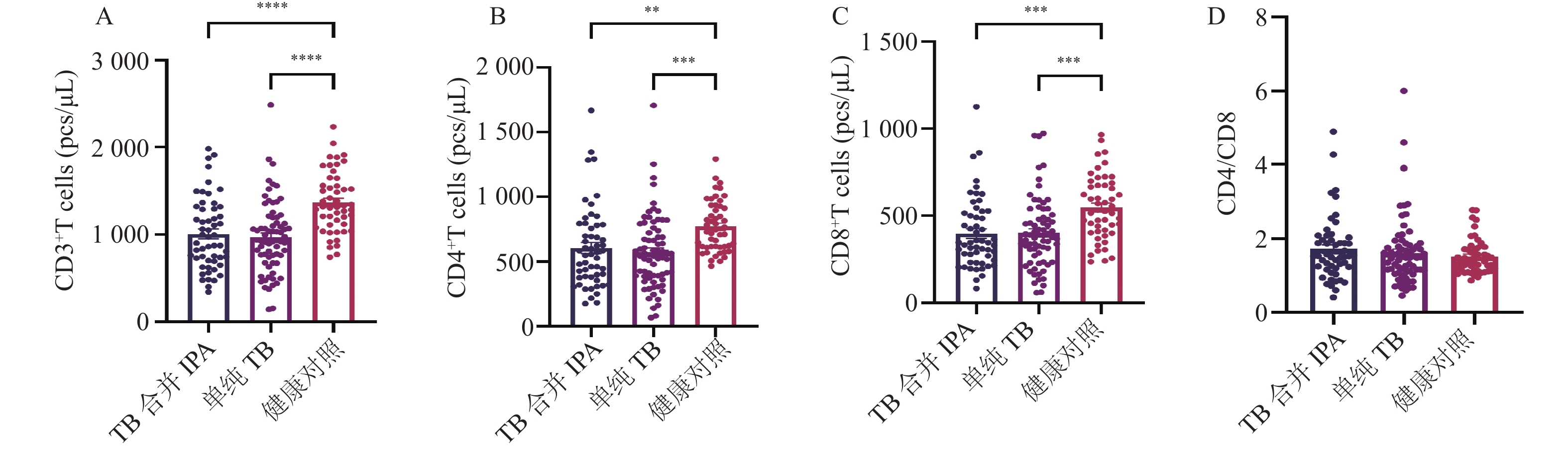
Objective To analyze the diagnostic value of serum biomarkers in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis complicated by invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Methods A retrospective collection of laboratory test results, including blood analysis, liver function, lymphocyte counts, and cytokine levels, from 54 patients diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis and invasive pulmonary aspergillosis admitted to the Third People's Hospital of Kunming between January 2021 and May 2024. Additionally, 70 patients with simple pulmonary tuberculosis and 50 healthy individuals were collected as control groups to compare serum biomarker levels across the three groups and analyze relevant factors and diagnostic value for pulmonary tuberculosis patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Results Among different age groups, the incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis was 29 cases (53.7%) in youth, 15 cases (27.8%) in middle age, and 10 cases (18.5%) in the elderly. In terms of gender distribution, there were 41 males (75.9%) and 13 females (24.1%). The serum levels of CRP (6.85 [2.10, 27.0]) ng/L, PCT (0.05 [0.05, 0.15]) ng/mL, RBC (4.55±0.65)×1012/L, Hb (129.13±19.10) g/L, TP (66.23±6.82) g/L, ALB (37.03±4.77) g/L, and CHOL (4.30 [3.71, 4.91]) mmol/L in the invasive pulmonary aspergillosis group showed no significant difference compared to the simple tuberculosis group and healthy control group (P > 0.05). The levels of CD3+ T, CD4+ T, and CD8+ T in the invasive pulmonary aspergillosis group were significantly lower than those in the simple tuberculosis group and healthy control group (P < 0.05). The levels of IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IFN - α, and TNF - α in the invasive pulmonary aspergillosis group were significantly higher than those in the healthy control group (P < 0.05); IL-8, IL-12p70, and IFN-α were also higher compared to the simple tuberculosis group, with statistical significance (P < 0.05). Conclusion The population with pulmonary tuberculosis complicated by invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is predominantly male and younger.The serum indicators of infection severity and nutritional status in these patients are similar to those with simple tuberculosis and lack specificity; however, their immune function is significantly lower than that of simple tuberculosis patients. Multiple cytokines are elevated, particularly IL-8, IL-12p70, and IFN-α, which can aid in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis infection.
2025, 46(3): 139-147.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250321
Abstract:
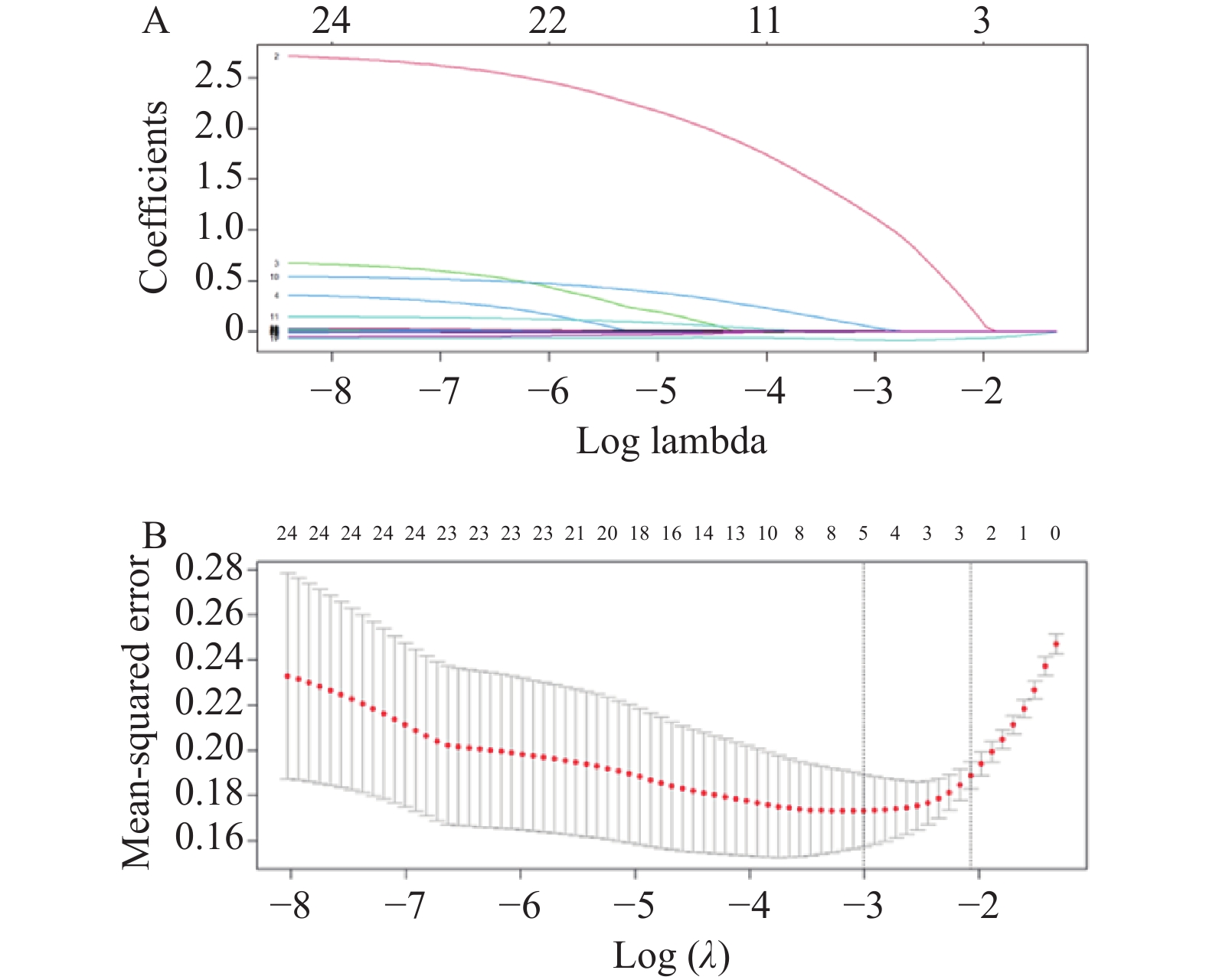
Objective To analyze the influencing factors of chronic liver failure in patients with primary hepatic carcinoma (PHC) before intervention, and to establish and evaluate a nomogram risk prediction model. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted by collecting general data and clinical test data within 24 hours of admission for PHC patients. Univariate analysis and Lasso regression were used for variable selection, followed by multivariate logistic regression analysis to identify independent influencing factors for CLF before PHC intervention, leading to the establishment of a nomogram risk prediction model. The model was evaluated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow test, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration curve, clinical decision curve, and clinical impact curve. Result A total of 353 cases of PHC patients were collected, including 153 cases in the liver failure group and 200 cases in the non-liver failure group, with a prevalence rate of 43.3%. Variables selected by Lasso regression included gastrointestinal bleeding, prothrombin time (PT), albumin (ALB), total bilirubin (TBIL), and gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that gastrointestinal bleeding (OR = 13.549, 95%CI: 2.899~63.322, P = 0.001), PT (OR = 1.599, 95%CI: 1.282~1.995, P < 0.001), TBIL (OR = 1.016, 95%CI: 1.006~1.025, P = 0.002), and GGT (OR = 1.002, 95%CI: 1.000~1.003, P = 0.028) were independent risk factors for chronic liver failure prior to PHC intervention, leading to the establishment of a nomogram risk prediction model. The Hosmer Lemeshow test showed that the model had a good fit (χ2 = 6.152, P > 0.05); the area under ROC was 0.902 (0.869-0.934), with a sensitivity of 80.4% and a specificity of 87.5%. The calibration curve indicated that the model predicts chronic liver failure prior to PHC intervention with good consistency. Clinical decision curve analysis and clinical impact curve analysis showed that the model has good clinical utility within a certain threshold range. Conclusion Gastrointestinal bleeding, PT≥16.05s, TBIL≥37.80 mmol/L, and GGT≥99.00 U/L are independent risk factors for the occurrence of chronic liver failure before PHC intervention. The established nomogram risk prediction model has certain clinical application value in predicting the risk of chronic liver failure before PHC intervention.
2025, 46(3): 148-158.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250322
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the effects of erector spinae plane block (ESPB) on postoperative analgesic consumption, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, and postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) in breast cancer patients, and to evaluate its advantages and disadvantages compared to general anesthesia (GA), thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB), and pectoral nerve block (PECS), providing a systematic review of its clinical application. Methods We searched English databases including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, as well as Chinese databases such as CNKI, Wanfang, and Weipu, including randomized controlled trials. The Cochrane bias risk assessment tool was used for bias risk evaluation, and RevMan 3.5 software was utilized for meta-analysis. Results A total of 31 randomized controlled trials involving 2296 patients were included. The meta-analysis results indicated that the morphine consumption in the ESPB group was lower than that in the GA group at 24 hours postoperative (MD -17.57, 95% CI -23.99 to -11.14, P < 0.05). VAS scores at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours postoperative were also lower in the ESPB group compared to the GA group (P < 0.05), and the incidence of PONV in patients was reduced (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.47 to 0.69, P < 0.05), with all differences being statistically significant. No statistically significant differences were found in morphine consumption at 24 hours postoperative between the ESPB and TPVB groups, nor in VAS scores at 2, 12, and 24 hours postoperative, and the number of PONV cases showed no statistically significant difference. The morphine consumption in the PECS group at 24 hours postoperative was lower than that in the ESPB group (MD 10.94, 95% CI 4.40 to 17.48, P < 0.05), and the VAS score at 12 hours postoperative in the PECS group was lower than that in the ESPB group (MD 0.59, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.99, P < 0.05), indicating statistical significance, while no significant differences were observed at other time points. Conclusions The analgesic effect of the ESPB group is superior to that of the GA group and similar to that of the TPVB group, but inferior to that of the PECS group. Compared to the GA group, ESPB significantly reduces the incidence of postoperative PONV, showing similarity with the TPVB and PECS groups.
2025, 46(3): 159-163.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250323
Abstract:
Endometriosis is a common and refractory gynecological disease characterized by the growth of active endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity, leading to corresponding clinical symptoms. The etiology and pathogenesis of this condition remain unclear. Galectin plays an important role in inflammation, tumor, immunity and reproduction. In recent years, the role of galectin in endometriosis has garnered increasing attention. This review discusses the role of galectin in endometriosis.
Endometriosis is a common and refractory gynecological disease characterized by the growth of active endometrial tissue outside the uterine cavity, leading to corresponding clinical symptoms. The etiology and pathogenesis of this condition remain unclear. Galectin plays an important role in inflammation, tumor, immunity and reproduction. In recent years, the role of galectin in endometriosis has garnered increasing attention. This review discusses the role of galectin in endometriosis.
2025, 46(3): 164-170.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250324
Abstract:
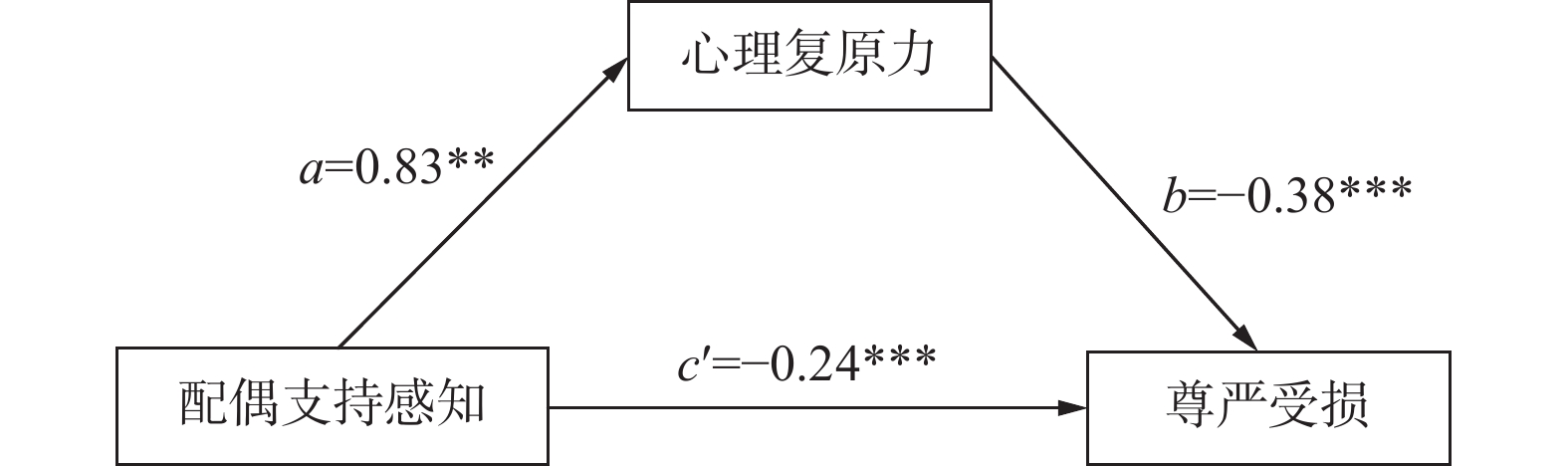
Objective To explore the mediating effect of psychological resilience between perceived spousal support and dignity loss in breast cancer patients. Methods A convenience sampling method was employed, involving 377 breast cancer patients who met the study criteria and received treatment at a tertiary oncology hospital in Yunnan Province from March to September 2023. Data were collected using a general information questionnaire, the Dignity Scale, the Perceived Spousal Support Scale, and the Psychological Resilience Scale. Data analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS 26.0 software. Results The scores for dignity loss, perceived spousal support, and psychological resilience of breast cancer patients were (41.72±6.77), (100.42±6.93), and (75.27±8.50), respectively. Pearson correlation analysis showed that dignity loss was negatively correlated with both perceived spousal support and psychological resilience (r1=-0.568, r2=-0.640, both P < 0.05). Mediation effect analysis indicated that psychological resilience had a mediating effect between perceived spousal support and dignity loss, with a value of -0.320 (95%CI -0.409 to -0.246), accounting for 57.1% of the total effect. Conclusion The dignity of breast cancer patients in this study is in a state of mild loss, and psychological resilience plays a partial mediating role between perceived spousal support and dignity loss. This suggests that clinical medical staff should pay attention to the spousal support situation of breast cancer patients, provide timely guidance and health education to spouses, enhance the level of support from spouses, and strengthen the confidence and capability of couples in jointly coping with the disease, thereby alleviating dignity loss in breast cancer patients and improving their quality of life.
2025, 46(3): 171-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250325
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of active respiratory circulation technique (ACBT) combined with resistance breathing training on pulmonary function and exercise capacity in patients with acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AECOPD). Methods A total of 60 hospitalized AECOPD patients from the Geriatrics Department of a tertiary hospital in Kunming were selected as research subjects from January to May 2024. Patients were randomly divided into two groups, with 30 patients in each group. The control group received conventional pulmonary rehabilitation nursing, and the observation group received ACBT combined with resistance breathing training. Pulmonary function indicators, modified British Medical Council(mMRC) dyspnea scores, 6-minute walk test (6MWT) distances, and the COPD Assessment Test (CAT) scores were collected 4 weeks after discharge to evaluate the intervention's effectiveness. Results After the intervention, the observation group showed significant improvements in lung function, mMRC scores, 6MWT distances, and CAT scores compared to pre-intervention levels, and all were superior to the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion ACBT combined with resistance breathing training can more effectively promote sputum clearance, reduce respiratory muscle fatigue, increase exercise endurance, and improve dyspnea severity and lung function in AECOPD patients.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS