Application of Electroencephalogram, Short Latency Somatosensory Evoked Potential and Transcranial Doppler Ultrasound in the Determination of Brain Death
-
摘要:
目的 探究脑电图、短潜伏期体感诱发电位和经颅多普勒超声在脑死亡判定中的价值和应用。 方法 收集昆明市第一人民医院经临床判定为脑死亡的患者31例,对每位患者均进行2次脑电图、短潜伏期体感诱发电位和经颅多普勒超声检测,根据脑死亡确认实验标准将其分为脑死亡阳性组和脑死亡阴性组,比较3种检查方式的敏感性、特异性和准确性。 结果 脑电图的敏感性、特异性和准确性均高于短潜伏期体感诱发电位和经颅多普勒超声检测,其敏感性为100%、特异性为75%和准确性为93.55%。脑死亡组脑电图和短潜伏期体感诱发电位阳性人数显著高于非脑死亡组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 ROC曲线分析显示脑电图对诊断脑死亡效果佳。 -
关键词:
- 脑死亡 /
- 脑电图 /
- 短潜伏期体感诱发电位 /
- 经颅多普勒超声
Abstract:Objective To explore the value and application of electroencephalogram, short latency somatosensory evoked potential and transcranial Doppler ultrasound in the determination of brain death. Methods 31 patients with brain death in our hospital were enrolled. Each patient was tested twice by electroencephalogram, short latency somatosensory evoked potential and transcranial Doppler ultrasound. According to the experimental standard of brain death confirmation, they were divided into brain death positive group and brain death negative group. The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of the three tests were compared. Results The sensitivity, specificity and accuracy of EEG were higher than those of short latency somatosensory evoked potentials and transcranial Doppler, with sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 75% and accuracy of 93.55%. The number of positive EEG and short latency somatosensory evoked potential in brain death group was significantly higher than that in non-brain death group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion ROC curve analysis showed that electroencephalogram was effective in diagnosing brain death. -
脑死亡是指包括脑干在内的全脑功能的不可逆转的丧失[1]。临床表现为:不可逆性深昏迷,脑干反射消失和无自主呼吸[1]。脑死亡判定包括2部分:临床判定和确认实验[1]。临床判定的标准[2]:原因明确的深昏迷(格拉斯哥评分为2T分,且强力按压双侧眶上切迹或针刺面部未出现任何肌肉活动)并排除了各种可逆性昏迷原因;包括双侧瞳孔对光反射、双侧角膜反射、双侧头眼反射、双侧前庭眼反射和咳嗽反射在内的5项脑干反射全部消失;必须依靠呼吸机维持通气且经自主呼吸激发试验证实无自主呼吸[3]。以上3项临床判定实验必须全部符合[3]。确认实验标准包括:脑电图(electroencephalogram,EEG)呈静息电位;双侧正中神经短潜伏期体感诱发电位(short latency somatosensory evoked potential,SLSEP)显示双侧N9和(或)N13存在,双侧P14、N18、N20消失[1];经颅多普勒超声(transcranial doppler,TCD)显示颅内前后循环血流均呈震荡波、尖小收缩波、或无血流信号[1, 4]。以上3项确认实验至少2项符合。本实验通过研究比较3项确认实验的灵敏性和特异性,探讨其在脑死亡判定中的价值和应用。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
本实验共收集昆明市第一人民医院神经外科和ICU于2020年07月至2021年08月收治的经临床判定为脑死亡患者31例。纳入标准[1]:根据判定先决条件(昏迷原因明确的不可逆性深昏迷、脑干反射全部消失、无自主呼吸依赖呼吸机维持呼吸),因自主呼吸激发试验过程中患者可能出现血压下降、血氧饱和度下降心率下降或心律失常,进而干扰确认实验的进行,故自主呼吸激发试验于确认实验完成后再进行,最终自主呼吸激发试验不能完成或不能证实无自主呼吸的患者排除入组。排除标准:(1)各种可逆性昏迷(例如酒精、一氧化碳、镇静麻醉及抗精神药物等中毒,严重酸碱平衡紊乱、严重内分泌及代谢功能障碍、低体温、休克、肝肾脑病等);(2)自主呼吸激发试验证实有自主呼吸。根据脑死亡确认实验(金标准)分为脑死亡阳性组和脑死亡阴性组,脑死亡阳性组23例,阴性组8例。其中男性24例,女性7例。年龄18~56岁。其中脑外伤性脑死亡组14例,脑出血性脑死亡组13例,其他病因导致的心肺复苏后的脑死亡组4例。
1.2 研究方法
符合条件的患者纳入此项研究,本研究通过昆明市第一人民医院伦理委员会批准,并取得患者家属知情同意。收集患者的性别、年龄、脑损伤病因等资料。
1.2.1 脑电图
用酒精和磨砂膏去脂、去角质,根据国际10·20系统[5],用导电膏将盘状电极固定在记录电极(额极 Fpl、Fp2,额部 F3、F4,前颞部 F7、F8,中央区 C3、C4,顶 部P3、P4,枕部Ol、O2,中颞部 T3、T4,后颞部 T5、T6)、参考电极(双侧耳垂或乳突)和接地电极头皮上。仪器校准、输入10 μV方波,检测各导联灵敏度,灵敏度一致后排除各种干扰状态下至少描记30 min,纪录过程中给予疼痛及声音刺激,全程脑电图波形均 < 2 μV,认为符合脑死亡的EEG表现,见图1。
1.2.2 短潜伏期体感诱发电位
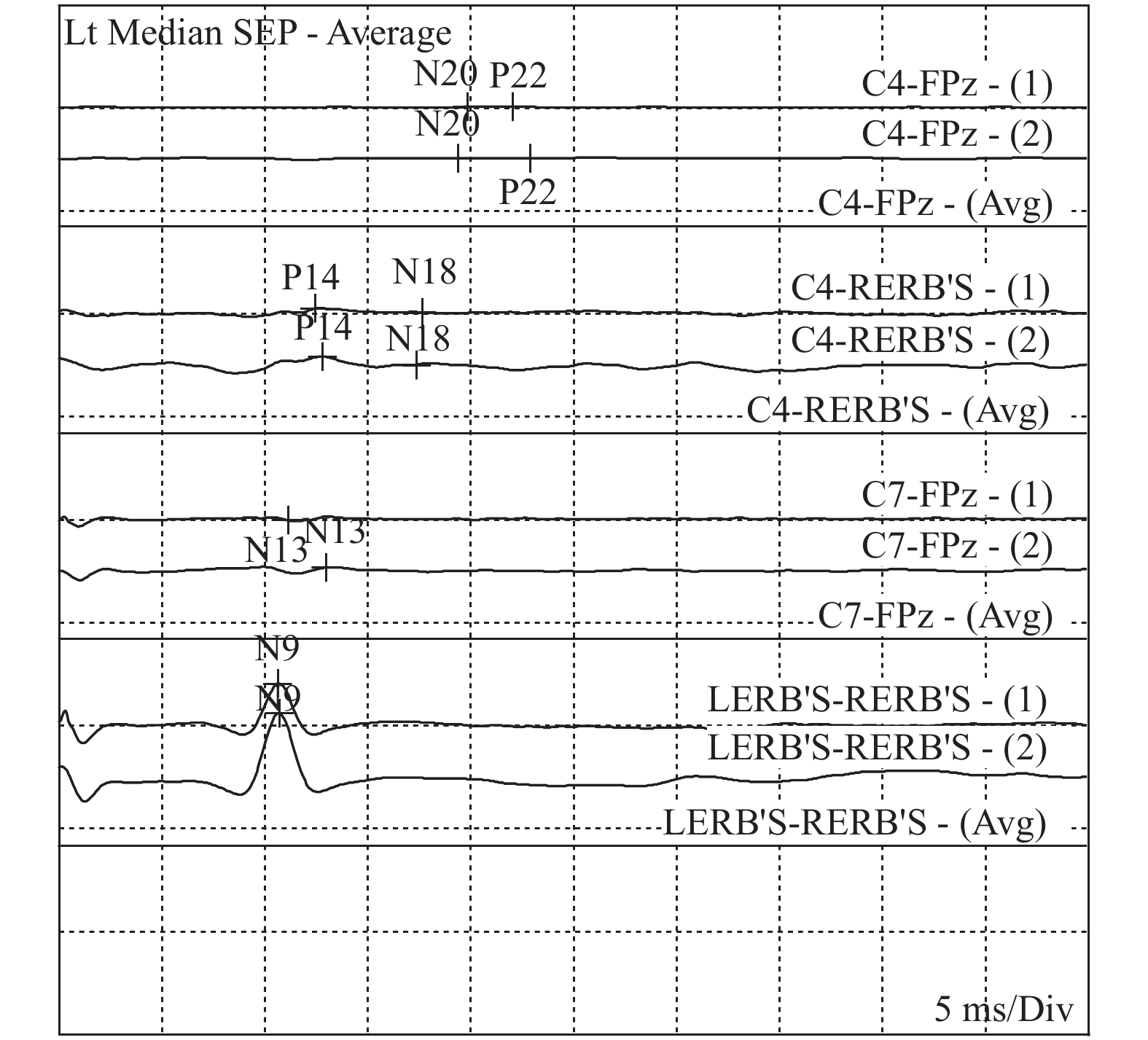
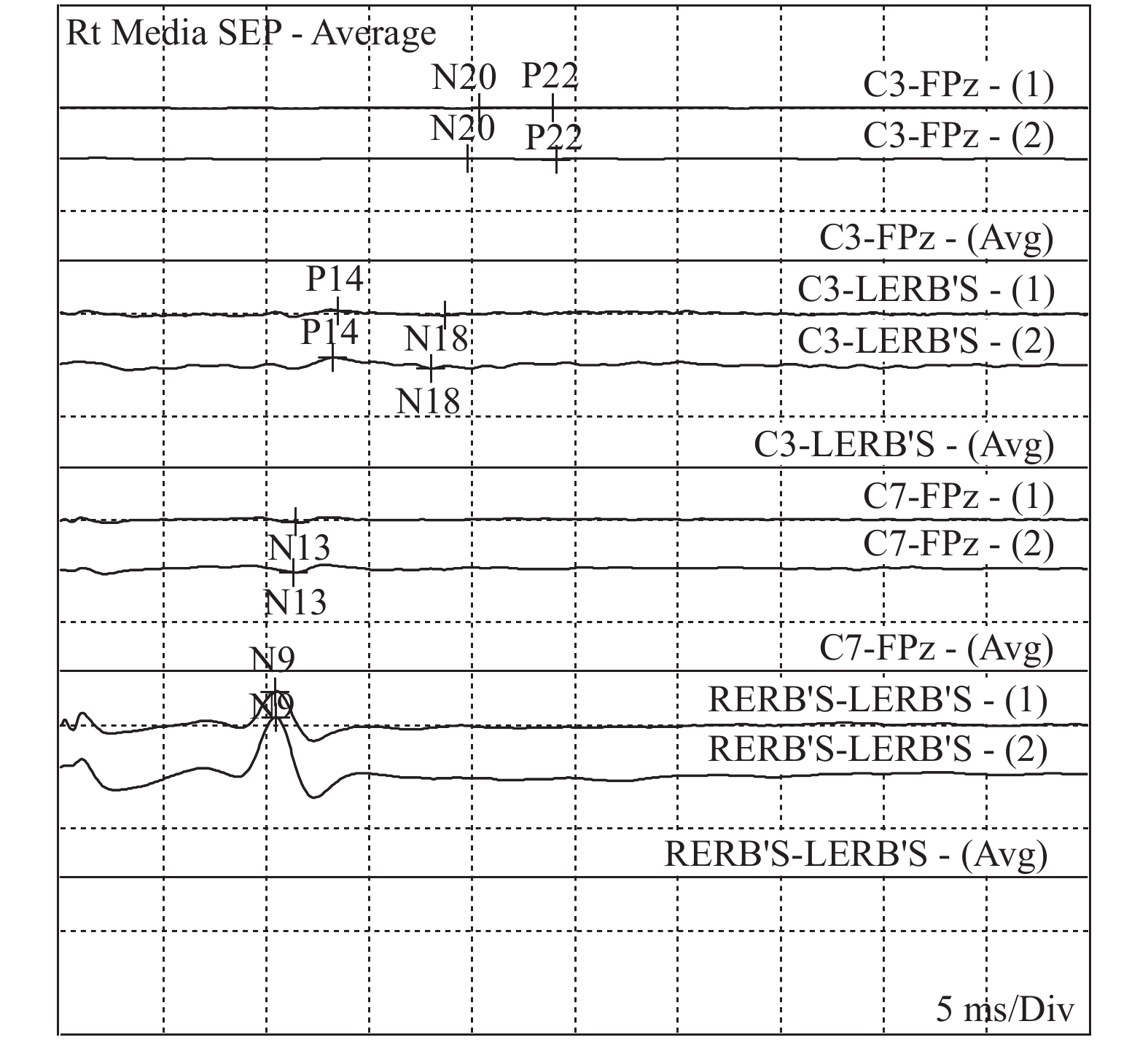
经酒精皮肤消毒后,一次性使用针电极固定在C’3、C’4、Fz、Cv6、CLi、CLc,刺激腕正中神经(腕横纹中点上2 cm),刺激电流2~25 mA,刺激强度以引起拇指屈曲1 cm为宜,平均叠加500~1000次,记录双侧N9、N13、P14、N18、N20。双侧N9和(或)N13存在,且P14、N18、N20消失,判定为符合脑死亡的SLSEP表现,见图2、图3。
1.2.3 经颅多普勒超声
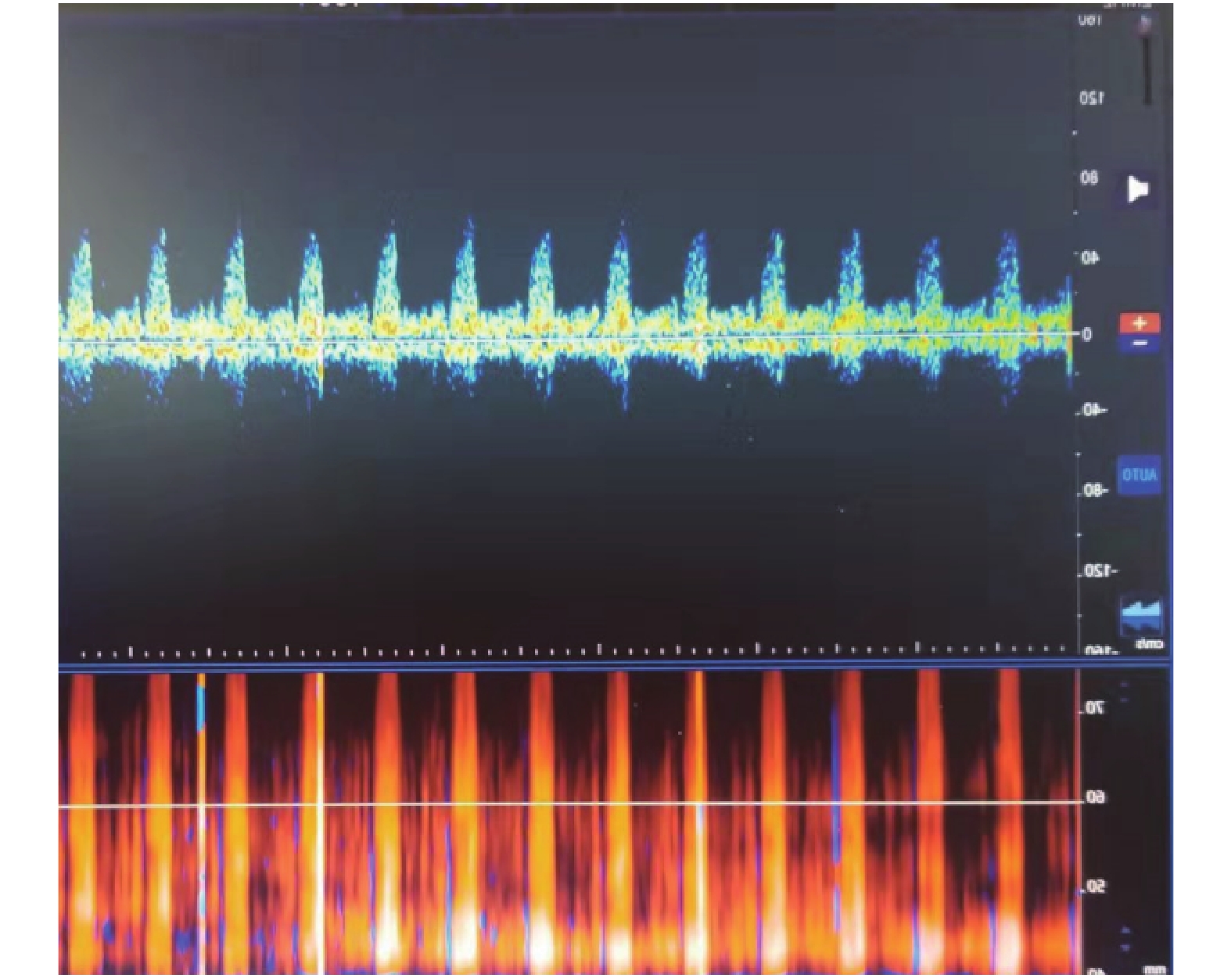
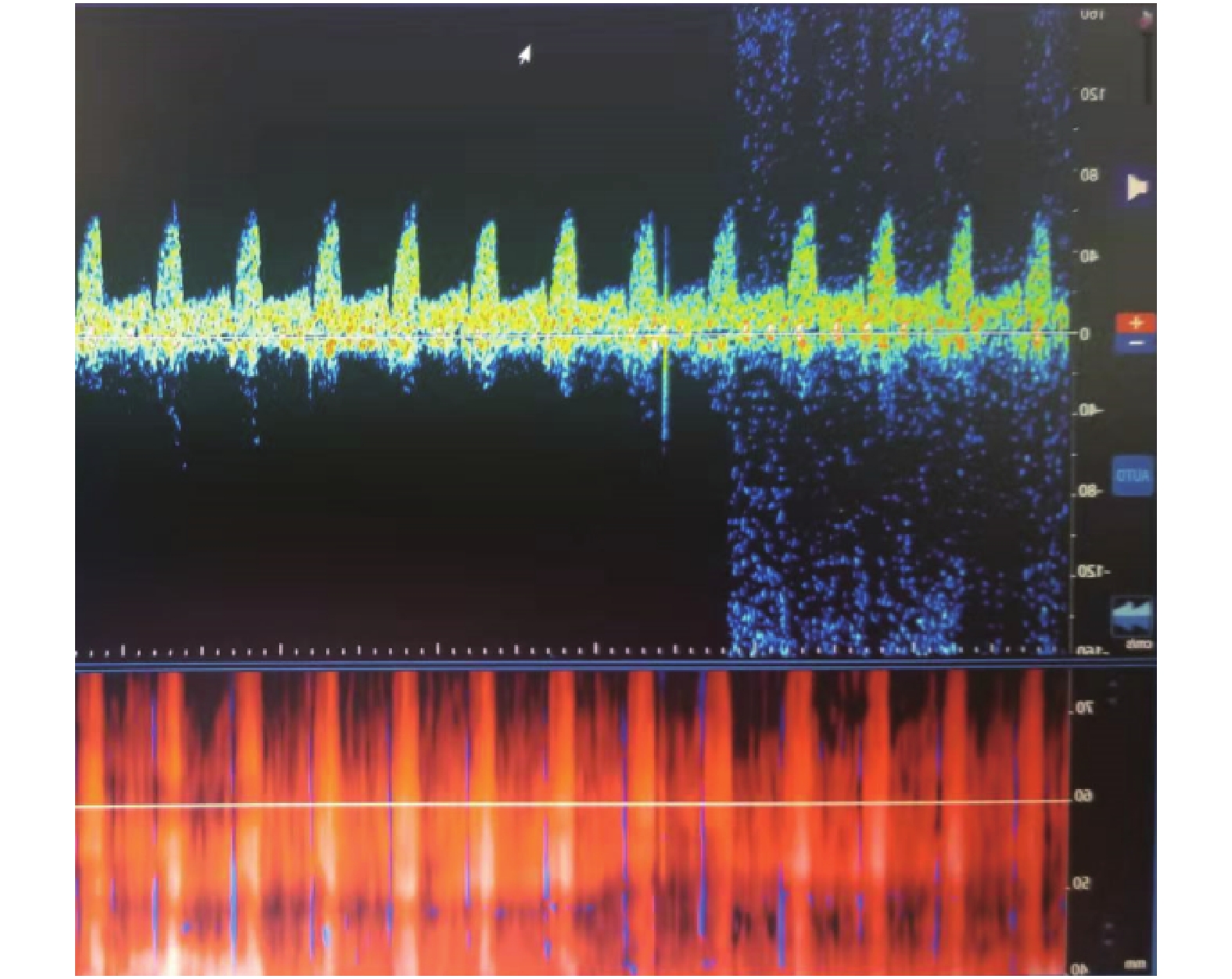
经颅多普勒超声检测仪配备1.6或2.0 MHz脉冲波的多普勒超声探头,取样容积10~15 mm,屏幕扫描,每屏6~8 s,低频滤波≤50 Hz。血流频谱成震荡波、收缩早期尖小收缩波或血流信号消失,间隔30 min,重复检测1次。2次检查颅内前后循环血流均为上述任意一项频谱表现,认为符合TCD的脑死亡判定标准,见图4、图5。首次检测不到血流信号时必须排除假象,首次检测血流信号消失,结果仅做参考。
1.3 统计学处理
应用统计软件SPSS26.0进行统计学分析,计数资料(%)使用χ2检验,以P < 0.05差异有统计学意义。计算3种检测方式的敏感性、特异性、准确性,根据绘制ROC曲线判断各检测方式的诊断价值。
2. 结果
2.1 EEG、SLSEP和TCD检测对脑死亡的诊断价值比较
在31例进行脑死亡确认实验病例中,每位患者均进行2次EEG、SLSEP和TCD检测,其中符合脑死亡诊断标准(即:脑死亡确认实验)23例,阳性符合率74.19%。23例脑死亡患者中16例进行器官捐献。1例患者家属放弃继续抢救治疗。6例患者家属坚持抢救至心跳呼吸停止(我国的死亡标准),占脑死亡诊断标准的26.09%。计算每种检测结果的敏感性、特异性和准确性,EEG的敏感性、特异性和准确性均高于SLSEP和TCD检测,见表1。
2.2 3种检测结果的比较
脑死亡阳性组EEG和SLSPE阳性人数显著高于脑死亡阴性组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表2。
表 1 3种检测方法对脑死亡的诊断价值比较(%)Table 1. Comparison of the diagnostic value of three testing methods for brain death (%)项目 敏感性 特异性 准确性 EEG 100.00 75.00 93.55 SLSEP 95.65 50.00 83.87 TCD 86.96 12.50 67.74 表 2 3种检测结果的比较[n(%)]Table 2. Comparison of the results of the three tests [n(%)]检查方式 脑死亡阳性组(n = 23) 脑死亡阴性组(n = 8) 合计 χ2 P EEG 21.390 < 0.001* 阳性 23(100) 2(25) 25 阴性 0(0) 6(75) 6 SLSPE 9.144 0.002* 阳性 22(95.65) 4(50) 26 阴性 1(4.35) 4(50) 5 TCD 0.002 0.968 阳性 20(86.96) 7(87.5) 27 阴性 3(13.04) 1(12.5) 4 *P < 0.05。 2.3 对3种检查方式进行ROC曲线分析
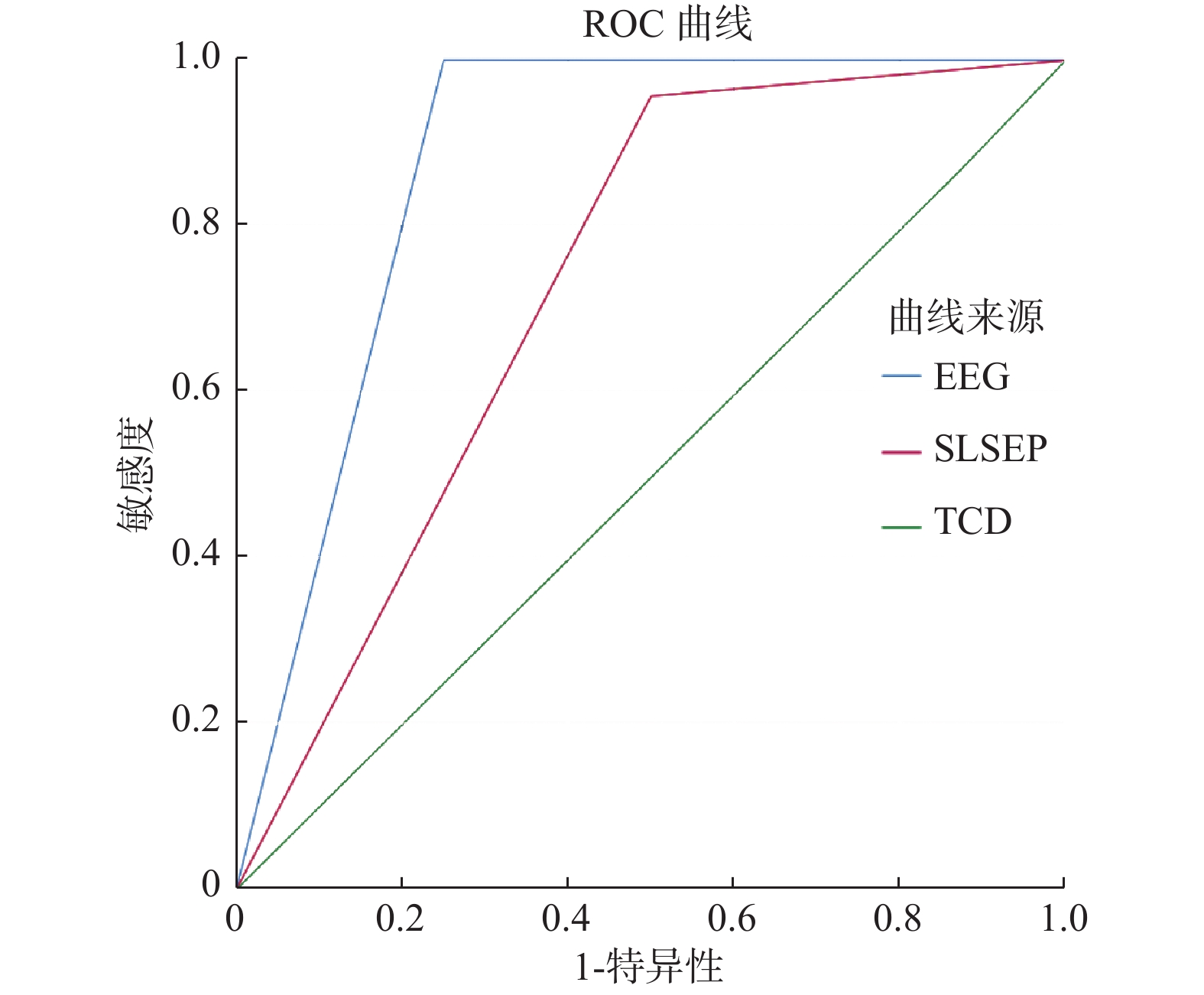
对3种检测方式进行 ROC曲线分析以确定最佳的诊断方式,结果显示EEG对诊断脑死亡效果最佳。曲线下面积越大,说明该检查方法的灵敏度和特异性越高,对脑死亡的判断越准确。EEG、SLSEP和TCD的曲线下面积分别为0.875、0.728和0.497,见图6。
3. 讨论
SLSEP是指躯体感觉神经传导系统的感受器接受适当强度的电刺激,该神经传导系统通路上任意部位在较短时间内均能检测出电反应[6- 7]。其具有:(1)反应形式恒定(同一个体、不同时间、同一部位都能引出特定形式的电反应);(2)分布在一定的空间范围(其电反应只有在躯体感觉神经传导通路上才能记录到);(3)电位与刺激具有明确的锁时关系(SLSEP各波的潜伏期相对固定)。其具有较强的客观性,受患者的意识状态、是否应用镇静药物以及监测医师的主观因素较小[8]。周围神经传导速度受温度影响较明显,因此SLSEP受肢体温度影响显著,在检查过程中需观察肢体温度,注意保暖,必要时进行复温[9]。在检查过程中发现上肢严重水肿亦会导致SLSEP各波的波幅变小,产生假阳性,为了脑死亡判定的严谨性,笔者对合并有上肢水肿、骨折患者全部进行3种确认实验的验证。
1例严重脑干出血患者SLSEP检查,双侧N9、N13存在,且P14、N18、N20消失,但其在进行脑电图检查时脑电波波幅 > 2 μV,呈非静息状态,后进行自主呼吸激发试验亦正式存在微弱的自主呼吸,未判定为脑死亡,经治疗后患者自主呼吸逐渐恢复,4个月后终因并发症死亡。N13-N20反映的是从颈脊髓到大脑皮层的传导通路,在脑干出血的部分患者中发现N13及以上各波全部消失。据其他文献报道亦发现颈髓至延髓病变患者可出现双侧N13消失,根据《中国成人脑死亡判定标准与操作规范(第二版)》要求[10- 11],SLSEP双侧N9和(或)N13存在[12],换而言之,N13必须存在,此时SLSEP作为脑死亡判定标准结果受到质疑。因此判定为不符合SLSEP脑死亡诊断标准,结合患者EEG和TCD检查,仍有部分患者符合脑死亡判定标准,可以解除质疑,最终判定为脑死亡。实验也从侧面证实SLSEP检查在脑死亡判定实验中灵敏度高,特异性不高的特点。
EEG是指通过脑电图器,在头皮上将大脑的自发性生物电活动通过放大、记录而获得的图形,是通过电极记录下来的大脑皮层的自发性、节律性电活动[13]。EEG记录≥30 min、脑电波波幅≤2 μV(呈静息状态),记录时对患者进行疼痛及声光刺激,脑电图波形无变化,此时认为脑电图符合脑死亡表现[14]。具有无创、操作简单、费用低、图形容易辨认等特点。本实验过程中31例患者全部进行了床旁EEG检查,由于EEG容易受环境或者药物影响,尤其是电信号的干扰,因此笔者在做EEG检查前停用不必要的巴比妥类、苯二氮䓬类及其他麻醉药物、升高体温。此类患者通常需要在重症监护病房内通过多种设备进行生命支持,而且昆明市第一人民医院重症监护病房无法提供独立电源,电干扰较大,对EEG的判定造成一定的影响。尽管如此,本结果显示EEG仍然是诊断脑死亡的最佳检查方式。在31例进行脑死亡确认实验病例中,符合脑死亡诊断标准23例,阳性符合率74.19%,出于对脑死亡判定的严谨性要求,笔者均在仔细地排查各种干扰因素地情况下谨慎地得出结论。
且EEG仅能反映大脑皮层的功能状态,不能反映脑干的功能状态,具有一定的局限性。在检查过程中发现1例严重大脑半球出血患者,脑电图检查大脑皮层无电活动,EEG检查呈静息状态,但随后的SLSEP检查提示P14存在,提示残存脑干功能的保留,此时未判定为脑死亡,该患者3 d后再次进行SLSEP检查,此时P14消失,间隔12 h重复检查1次,均证实P14消失,此时才判定为脑死亡。
TCD是指通过脉冲多普勒技术,以2 MHz的发射频率,使超声束穿过颞窗和枕窗(颅骨相对较薄的部位),描述记录脑底动脉血流的多普勒信号,获得血流的动力参数,来反映脑组织的血流状态,俗称脑血流图检查。脑组织完全缺血、缺氧4~6 min,脑组织即开始出现不可逆的死亡。脑灌注压等于平均动脉压减去颅内压[15],正常值为70~100 mmHg,此时脑组织可以获得有效的血液灌注。随着颅内压的逐渐增高,脑组织灌注血流逐渐减少,当颅内压增高到一定程度后脑组织血液供应停止,此时TCD检查颅内前后循环均呈震荡波、尖小收缩波,或不能探测到脑血流,持续大于30 min,可判定为符合脑死亡的TCD表现[16]。其受环境和药物影响小,具有可重复、方便、快捷、可动态实时监测等特点,但其受检查医师的操作熟练程度影响较大,因此,所有患者的每次TCD检查均有专人、固定的骨窗进行。此外,TCD检查对透声窗的要求高,在评价脑死亡时笔者尽可能避免在去骨瓣减压、颅骨骨缝未闭、严重颅骨骨折及脑室外引流等此类颅腔不完整患者中应用或仅为参考,容易造成假阴性。在本研究中TCD诊断脑死亡的敏感性、特异性均和准确性在3种检查方式中最低。
达到脑死亡状态的患者已不存在好转的可能性,生命体征的维持需要多种药物和设备的支持,一定程度上增加患者家属的经济负担,同时造成医疗资源的浪费。由于脑死亡概念及器官捐献意义普及的不充分,部分(6例)患者家属坚持抢救至心死亡状态。前期临床判定脑死亡的患者中有8例未达到确认判定标准。
除2例患者家属放弃继续抢救外,仍有6例患者家属坚持要求抢救,直至心死亡,好转率为0。因此在临床工作中,应继续加强脑死亡概念的普及与交流,对于虽经确认实验检查不符合脑死亡判定标准的患者,笔者亦应该反复向患者家属告知病情及预后,使患者家属充分理解病情,尽量减轻患者家属经济负担、尽可能减少医疗资源的浪费。
-
表 1 3种检测方法对脑死亡的诊断价值比较(%)
Table 1. Comparison of the diagnostic value of three testing methods for brain death (%)
项目 敏感性 特异性 准确性 EEG 100.00 75.00 93.55 SLSEP 95.65 50.00 83.87 TCD 86.96 12.50 67.74 表 2 3种检测结果的比较[n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of the results of the three tests [n(%)]
检查方式 脑死亡阳性组(n = 23) 脑死亡阴性组(n = 8) 合计 χ2 P EEG 21.390 < 0.001* 阳性 23(100) 2(25) 25 阴性 0(0) 6(75) 6 SLSPE 9.144 0.002* 阳性 22(95.65) 4(50) 26 阴性 1(4.35) 4(50) 5 TCD 0.002 0.968 阳性 20(86.96) 7(87.5) 27 阴性 3(13.04) 1(12.5) 4 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 宿英英,张艳,叶红,等. 脑死亡判定标准与技术规范(成人质控版)[J]. 中国现代神经疾病杂志,2015,15(12):935-939. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2015.12.002 [2] Greer D M,Shemie S D,Lewis A,et al. Determination of brain death/death by neurologic criteria:The World Brain Death Project[J]. JAMA,2020,324(11):1078-1097. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.11586 [3] 刘春峰,陆国平,钱素云,等. 脑死亡判定标准与技术规范(儿童质控版)[J]. 中华移植杂志(电子版),2015,9(2):54-57. [4] 国家卫生健康委员会脑损伤质控评价中心. 中国儿童脑死亡判定标准与操作规范[J]. 中华儿科杂志,2019(5):331-335. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.05.003 [5] 中国抗癫痫协会脑电图和神经电生理分会. 临床脑电图基本技术标准[J]. 癫痫杂志,2022,8(1):3-11. doi: 10.7507/2096-0247.20220002 [6] 赵红,宿英英. 体感诱发电位的分级标准[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2004,5(4):283-284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2004.04.029 [7] 杜宏生,李牧,马景鋻. 临床脑死亡病例判定12例报告[J]. 实用器官移植电子杂志,2016,4(5):286-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5332.2016.05.006 [8] Scarpino M,Lolli F,Lanzo G,et al. Neurophysiology and neuroimaging accurately predict poor neurological outcome within 24 hours after cardiac arrest:the ProNeCA prospective multicentre prognostication study[J]. Resuscitation,2019,143(5):115-123. [9] Nevalainen P,Marchi V,Metsäranta M,et al. Evoked potentials recorded during routine EEG predict outcome after perinatal asphyxia[J]. Clinical Neurophysiology,2017,128(7):1337-1343. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2017.04.025 [10] 陈奥,练巧燕,徐鑫,等. 肺移植术后早期急性肾损伤的研究进展[J]. 器官移植,2020,11(6):743-748. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2020.06.015 [11] 国家卫生健康委员会脑损伤质控评价中心,中华医学会神经病学分会神经重症协作组,中国医师协会神经内科医师分会神经重症专业委员会. 中国成人脑死亡判定标准与操作规范(第二版)[J]. 中华医学杂志,2019,1(17):1288-1292. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.17.003 [12] 蒋光伟,骆建军,郭丽叶,等. 脑死亡患者内源性皮质醇水平及补充甲泼尼龙琥珀酸钠对血流动力学的影响[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2021,23(12):900-904. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-4237.2021.12.005 [13] Buchner H,Ferbert A. Irreversibilitätsnachweis der klinischen Ausfallssymptome des Gehirns[J]. Der Nervenarzt,2016,87(2):128-143. doi: 10.1007/s00115-015-0049-x [14] Gobert F,Dailler F,Fischer C,et al. Proving cortical death after vascular coma:Evoked potentials,EEG and neuroimaging[J]. Clinical Neurophysiology,2018,129(6):1105-1116. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2018.02.133 [15] Robba C,Iaquaniello C,Citerio G. Death by neurologic criteria:Pathophysiology,definition,diagnostic criteria and tests[J]. Minerva Anestesiologica,2019,85(7):774-781. [16] Chang J,Tsivgoulis G,Katsanos A,et al. Diagnostic accuracy of transcranial doppler for brain death confirmation:Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. American Journal of Neuroradiology,2016,37(3):408-414. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4548 -







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:

