Role of the Key Gene LRP1 of Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition in the Progression of Silicosis Fibrosis
-
摘要:
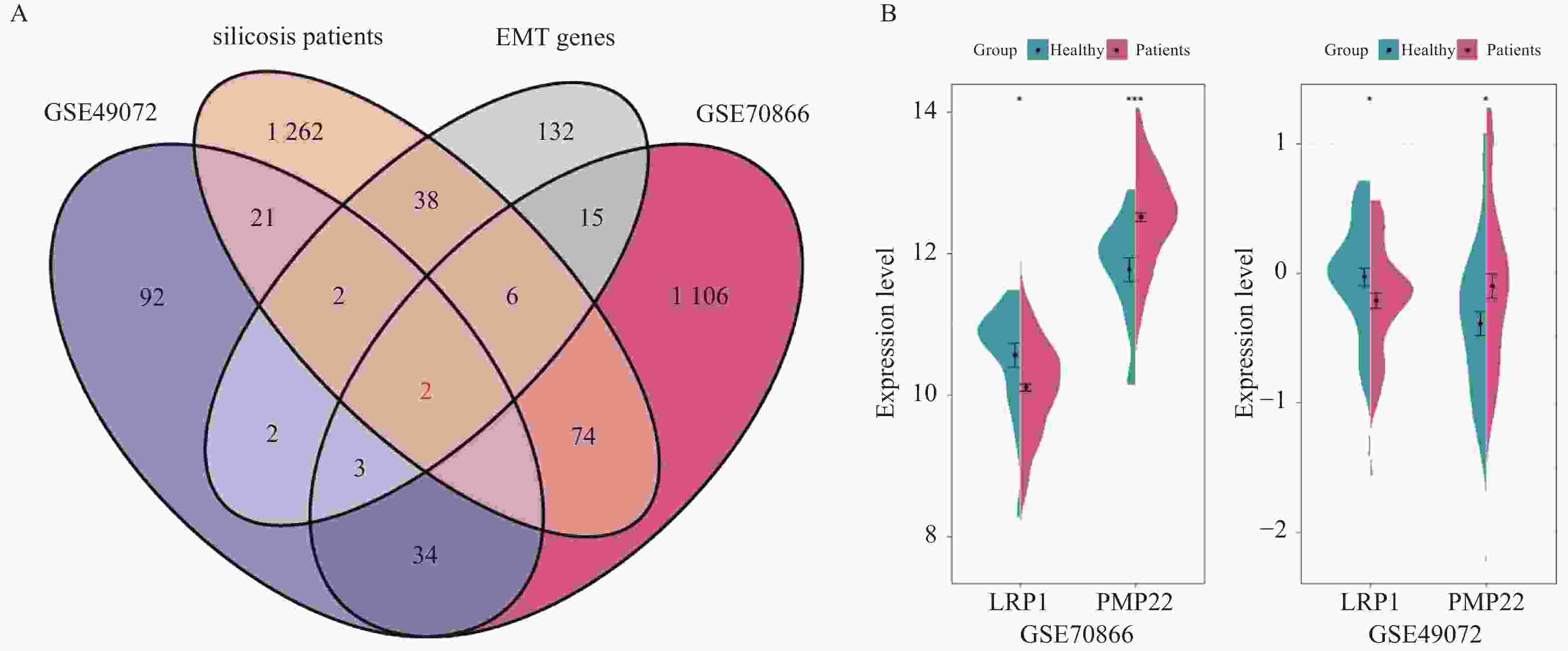
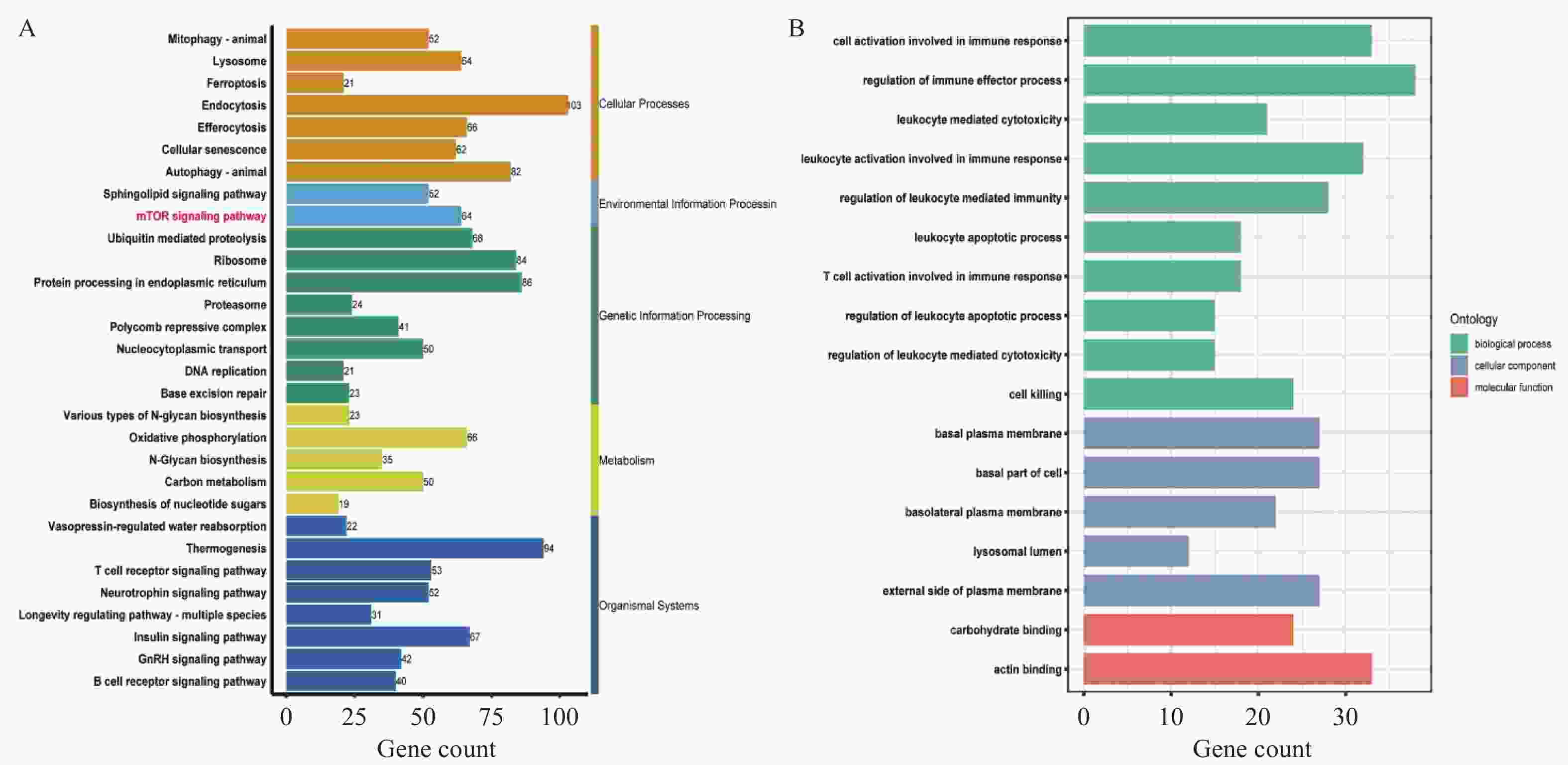
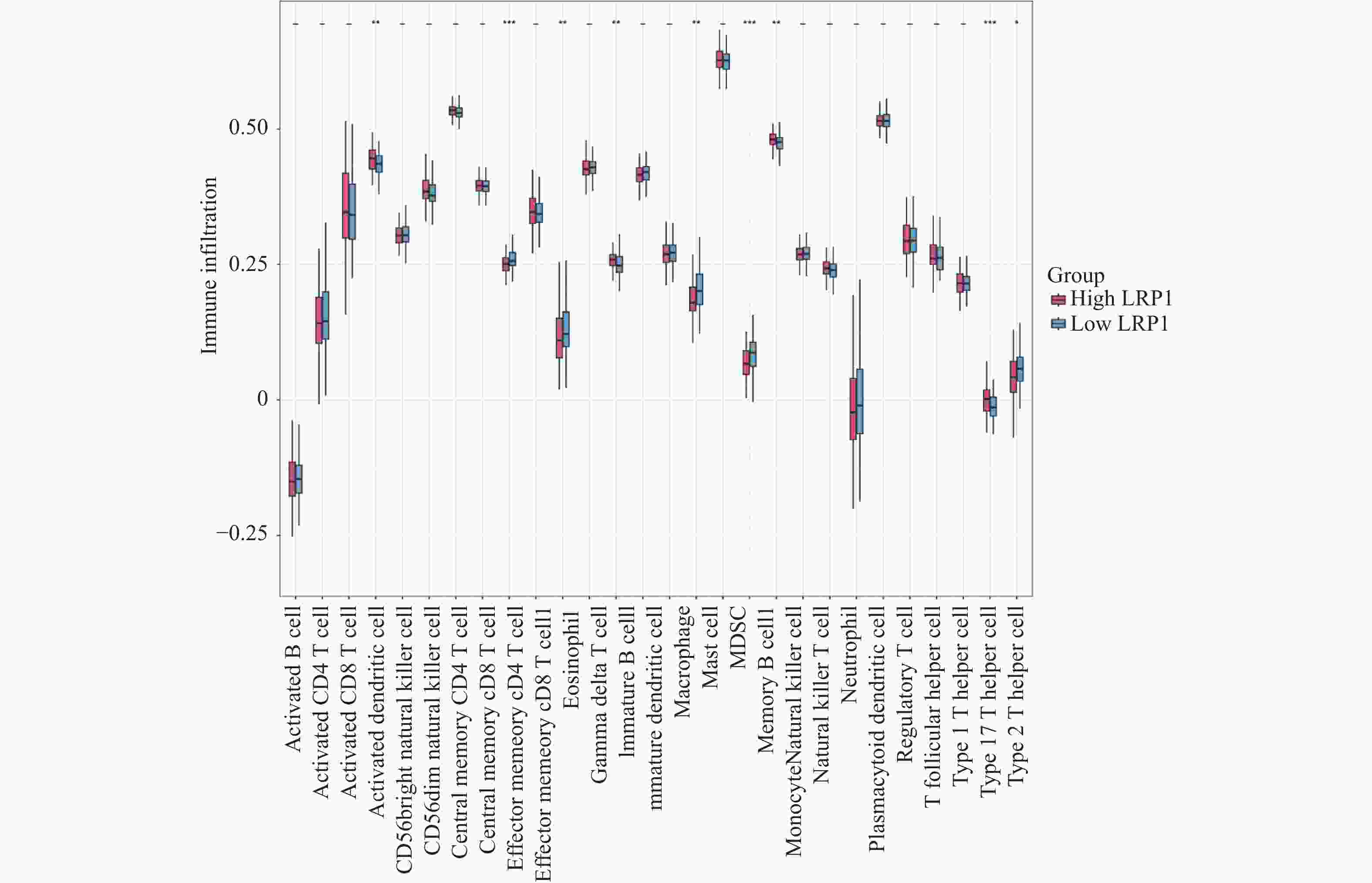
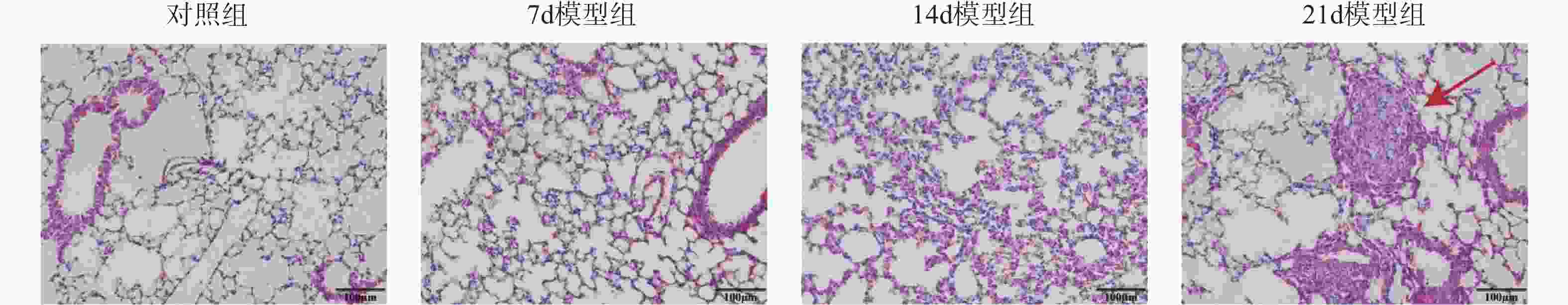
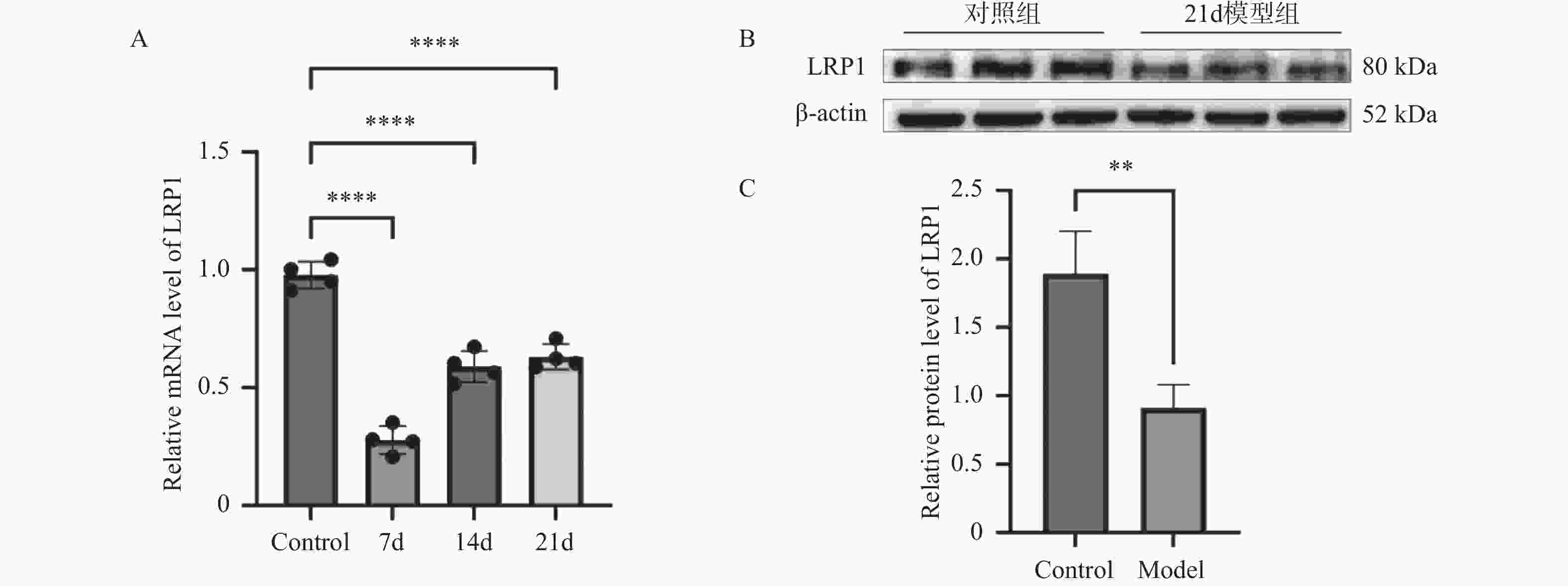
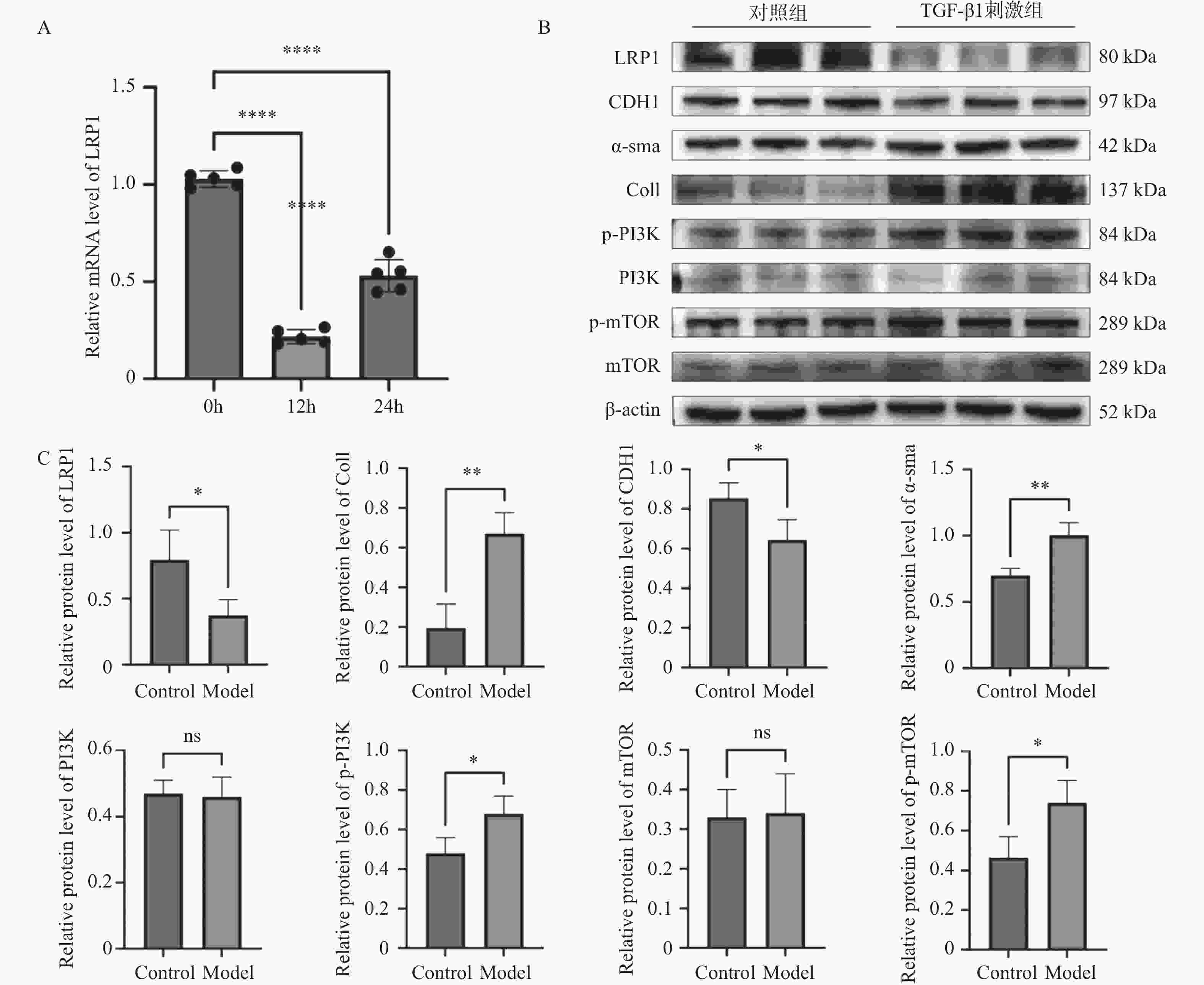
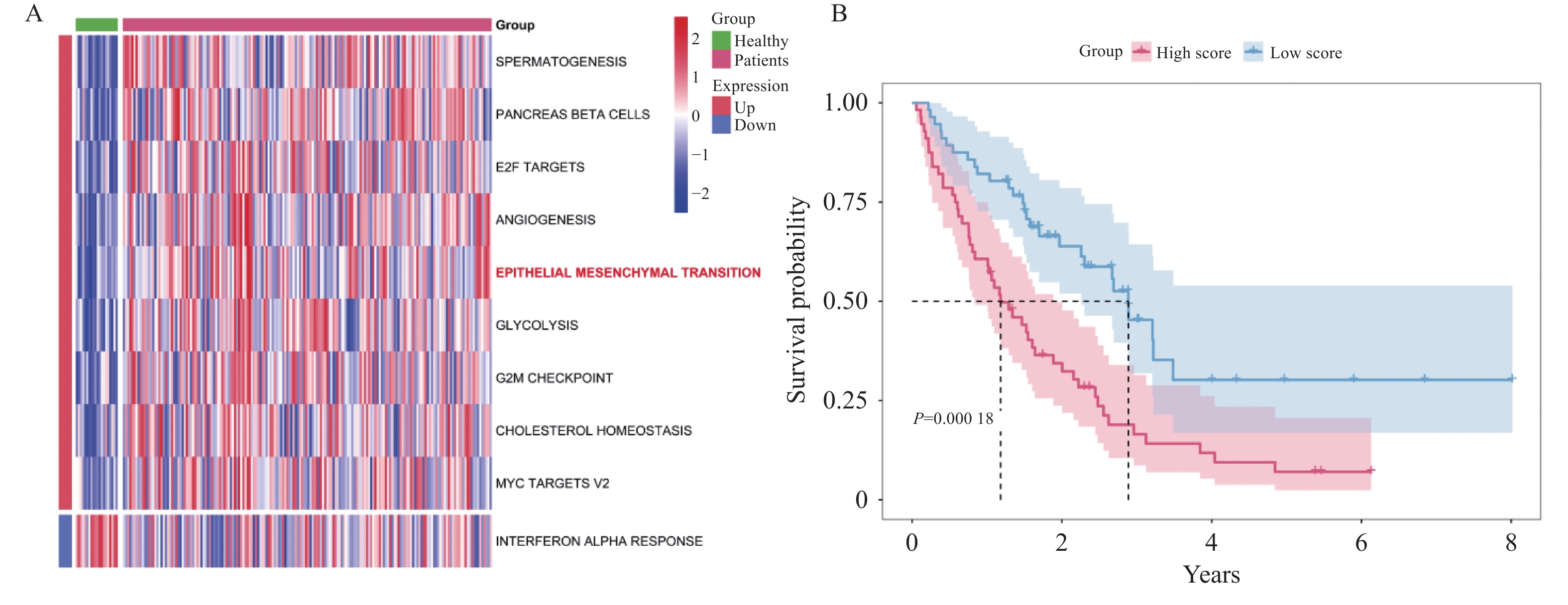
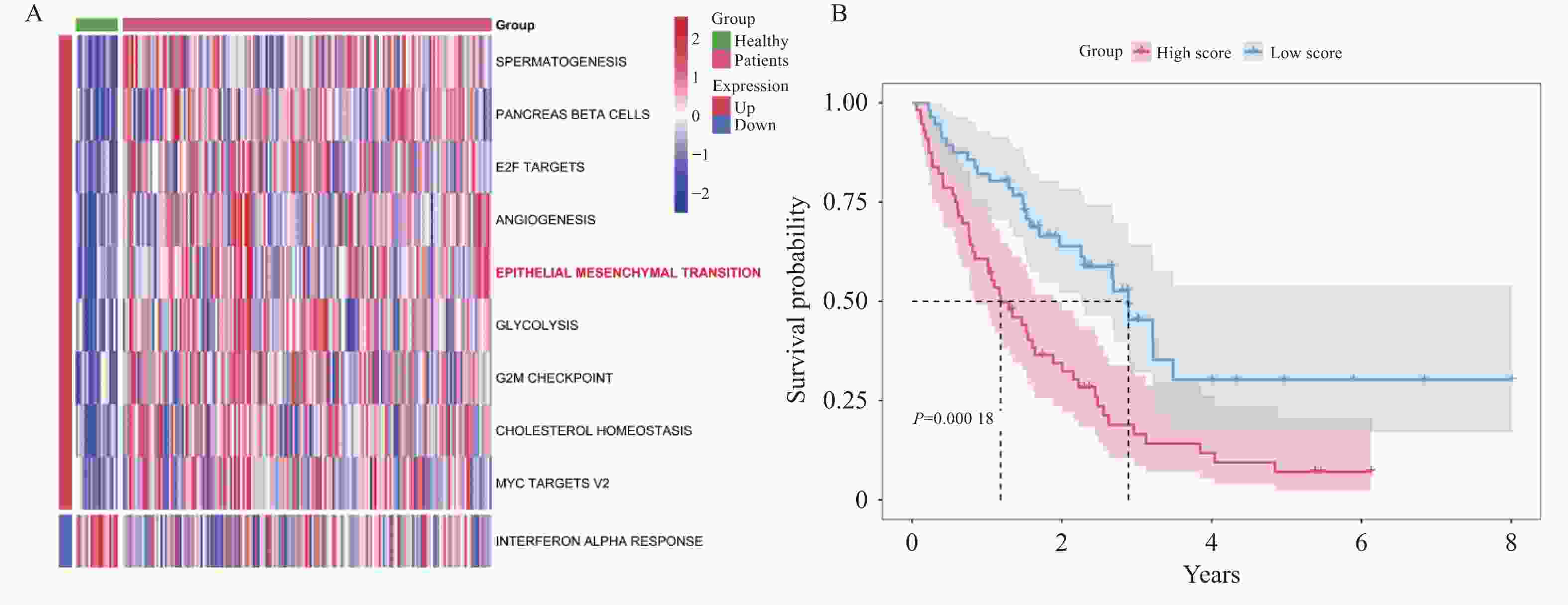
目的 探讨上皮间充质转化关键基因低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白1(lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1,LRP1)在矽肺纤维化发展中的作用及机制。 方法 (1)将来自基因表达综合数据库(gene expression omnibus,GEO)的GSE70866、GSE49072数据采用基因集变异分析(gene set variation analysis,GSVA)评估上皮间充质转化基因集表达变化,通过韦恩图取交集筛选出关键基因LRP1。进一步构建多因素Cox比例风险回归模型(校正年龄、性别),验证LRP1表达的独立预后价值。基于LRP1的表达量将患者分组,通过差异分析、富集分析、相关性分析、免疫浸润分析探索LRP1在肺纤维化中的功能以及免疫作用机制。(2)用10 mg SiO2混悬液一次性注入C57BL/6J小鼠气管内制作矽肺模型;灌注100 μL 0.9%氯化钠溶液作为对照组。苏木素-伊红染色观察小鼠肺组织病理学变化。TGF-β1诱导A549细胞不同时间构建上皮间充质转化体外模型。RT-qPCR检测矽肺模型肺组织及A549细胞中LRP1 mRNA水平。Western blot检测肺组织及A549细胞的LRP1、E-Cadherin、α-SMA、Collagen Ⅰ、p-PI3K、PI3K、p-mTOR、mTOR蛋白的表达。 结果 上皮间充质转化基因集在患者中的评分显著高于健康对照组,并且高评分患者生存时间显著降低(P < 0.01)。生物信息学分析提示LRP1主要通过mTOR信号通路发挥作用。免疫浸润分析显示,LRP1高表达患者中激活的树突细胞、效应记忆CD4 T细胞及Th17/Th2细胞活性显著增强,提示其可能调控适应性免疫应答。矽肺模型小鼠肺组织中有明显的矽结节形成。RT-qPCR和western blot检测结果显示,矽肺模型肺组织及A549细胞中,LRP1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05)。 A549细胞内E-Cadherin蛋白表达下调、α-SMA和Collagen Ⅰ蛋白表达增高(P < 0.05);p-PI3K/PI3K和p-mTOR/mTOR的比率上调(P < 0.05)。 结论 LRP1下调可能通过激活PI3K/mTOR信号通路,促进矽肺模型EMT过程及纤维化。 -
关键词:
- 矽肺 /
- 上皮-间质转化 /
- 低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白1
Abstract:Objective To investigate the role of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), the key gene of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, in silicosis fibrosis progression, and to preliminarily explore its regulatory mechanisms. Methods Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) was employed on GSE70866 and GSE49072 from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to assess the activity of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene set. LRP1 was screened via Venn diagram intersection. A multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model (adjusted for age and sex) was constructed to validate the independent prognostic value of LRP1. Patients were grouped based on LRP1 expression, and its function mechanisms in pulmonary were explored through differential analysis, enrichment analysis, correlation analysis, and immune infiltration analysis. The silicosis model was established by a single intratracheal injection of 10 mg SiO2 suspension in C57BL/6J mice, with 100 μL of 0.9% saline administered as the control group. Pathological changes were assessed by hematoxylin-eosin staining in lung tissues. EMT model was induced in A549 cells by TGF-β1 at varying time points. LRP1 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR in lung tissues and A549 cells of TGF-β1-induced EMT model. Protein expression of LRP1, E-Cadherin, α-SMA, collagen I, p-PI3K, PI3K, p-mTOR and mTOR were detected by Western blot in lung tissues and A549 cells. Results The epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene set score was significantly higher in patients than in healthy control, with high-score patients showing reduced survival time (P < 0.01). Bioinformatics analysis revealed that LRP1 primarily acts through the mTOR signaling pathway. Immune infiltration analysis demonstrated enhanced activities of activated dendritic cells, effector memory CD4+ T cells, and Th17/Th2 cells in LRP1 high-expression patients, suggesting its potential regulatory role in adaptive immune responses. Histopathological observation confirmed obvious silica nodule formation in lung tissues of mouse silicosis model. RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses showed that the expression levels of LRP1 mRNA and protein were significantly downregulated in both silicosis mouse lungs and A549 cells (P < 0.05). E-cadherin protein expression was downregulated, while α-SMA and collagen I expression were upregulated (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the phosphorylation ratios of PI3K (p-PI3K/PI3K) and mTOR (p-mTOR/mTOR) were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Conclusion LRP1 downregulation may activate the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway, promoting the EMT process and fibrosis in silicosis. Targeting LRP1 regulation might become a new therapeutic strategy for silicosis. -
表 1 LRP1的mRNA引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences for LRP1 mRNA
基因
名称引物序列 长度
(bp)LRP1 上游5'-TCCTGCCTGCTCCTCAGTAT-3' 112 下游5'-TTCCAGGGGTATGCTCGGTA-3' GAPDH 上游5'-GCAAGTTCAACGGCACAGTCA-3' 141 下游5'- ATACAGCACCTCAGATGACCGC-3' 表 2 多因素COX回归分析结果
Table 2. Results of multivariable Cox regression analysis
变量 HR(95%CI) P 年龄 (连续变量) 1.003 (0.981~1.026) 0.791 性别 (男性/女性) 1.221 (0.685~2.177) 0.499 LRP1 (连续变量) 0.618 (0.425~0.900) 0.012* *P < 0.05。 表 3 Hallmark基因集评分与LRP1表达量的相关性分析结果
Table 3. Correlation analysis between Hallmark gene set scores and LRP1 expression levels
通路名称 r P HEDGEHOG SIGNALING 0.44685670 <0.01* WNT BETA CATENIN SIGNALING 0.43215262 <0.01* PI3K-AKT-mTOR SIGNALING 0.31477978 <0.01* P53 PATHWAY 0.28339695 <0.01* NOTCH SIGNALING 0.25402705 <0.01* IL6 JAK STAT3 SIGNALING 0.25231215 <0.01* *P < 0.01。 -
[1] Hoy R F,Chambers D C. Silica-related diseases in the modern world[J]. Allergy,2020,75(11):2805-2817. doi: 10.1111/all.14202 [2] 毛翎,彭莉君,王焕强,等. 尘肺病治疗中国专家共识(2024年版)[J]. 环境与职业医学,2024,41(1):1-21. doi: 10.11836/JEOM23379 [3] Wang M,Zhang Z,Liu J,et al. Gefitinib and fostamatinib target EGFR and SYK to attenuate silicosis: A multi-omics study with drug exploration[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther,2022,7(1):157. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00959-3 [4] Dongre A,Weinberg R A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2019,20(2):69-84. [5] Hao X,Jin Y,Zhang Y,et al. Inhibition of oncogenic src ameliorates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis via PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2023,24(1):774. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010774 [6] 李欣颖,郝小惠,张劲松,等. LPA在小鼠矽肺模型的表达及其对小鼠肺上皮细胞EMT影响[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2022,57(5):771-775. [7] Tian Y,Xia J,Yang G,et al. A2aR inhibits fibrosis and the EMT process in silicosis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf,2023,249:114410. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114410 [8] Zhao W,Wang L,Yang J,et al. Endothelial cell-derived MMP19 promotes pulmonary fibrosis by inducing E(nd)MT and monocyte infiltration[J]. Cell Commun Signal,2023,21(1):56. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01040-4 [9] Yamamoto K,Scilabra S D,Bonelli S,et al. Novel insights into the multifaceted and tissue-specific roles of the endocytic receptor LRP1[J]. J Biol Chem,2024,300(8):107521. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107521 [10] Schnieder J,Mamazhakypov A,Birnhuber A,et al. Loss of LRP1 promotes acquisition of contractile-myofibroblast phenotype and release of active TGF-β1 from ECM stores[J]. Matrix Biol,2020,88:69-88. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2019.12.001 [11] Chen C C,Hsu L W,Chen K D,et al. Extracellular calreticulin regulates fibrogenic and immunogenic properties of hepatic stellate cells[J]. Int Immunopharmacol,2025,148:114129. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114129 [12] Zhang J,Hu W,Liu K,et al. Integrated mRNA and microRNA profiling in lung tissue and blood from human silicosis[J]. J Gene Med,2023,25(8):e3518. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3518 [13] Ye Z,Cheng M,Lian W,et al. GPX4 deficiency-induced ferroptosis drives endometrial epithelial fibrosis in polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Redox Biol,2025,83:103615. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103615 [14] Spottiswoode N,Tsitsiklis A,Chu V T,et al. Microbial dynamics and pulmonary immune responses in COVID-19 secondary bacterial pneumonia[J]. Nat Commun,2024,15(1):9339. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53566-x [15] Wu T,Hu E,Xu S,et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data[J]. Innovation (Camb),2021,2(3):100141. [16] Wang J,Tu W,Qiu J,et al. Predicting prognosis and immunotherapeutic response of clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Pharmacol,2022,13:984080. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.984080 [17] Phan T H G,Paliogiannis P,Nasrallah G K,et al. Emerging cellular and molecular determinants of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci,2021,78(5):2031-2057. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03693-7 [18] Prasse A,Binder H,Schupp J C,et al. BAL Cell Gene Expression Is Indicative of Outcome and Airway Basal Cell Involvement in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2019,199(5):622-630. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201712-2551OC [19] Lee J,Lee H,Lee H,et al. ANKS1A regulates LDL receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1)-mediated cerebrovascular clearance in brain endothelial cells[J]. Nat Commun,2023,14(1):8463. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44319-3 [20] Chen K,Martens Y A,Meneses A,et al. LRP1 is a neuronal receptor for α-synuclein uptake and spread[J]. Mol Neurodegener,2022,17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00560-w [21] Sizova O,John L S,Ma Q,et al. Multi-faceted role of LRP1 in the immune system[J]. Front Immunol,2023,14:1166189. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1166189 [22] Mishra A,Yao X,Saxena A,et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 attenuates house dust mite-induced eosinophilic airway inflammation by suppressing dendritic cell-mediated adaptive immune responses [J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol,2018,142(4): 1066-1079. e6. [23] Actis Dato V,Chiabrando G A. The Role of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 in Lipid Metabolism,Glucose Homeostasis and Inflammation[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2018,19(6):1780. [24] Guo X,Pan Y,Xiong M,et al. Midkine activation of CD8(+) T cells establishes a neuron-immune-cancer axis responsible for low-grade glioma growth[J]. Nat Commun,2020,11(1):2177. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15770-3 -





 下载:
下载: