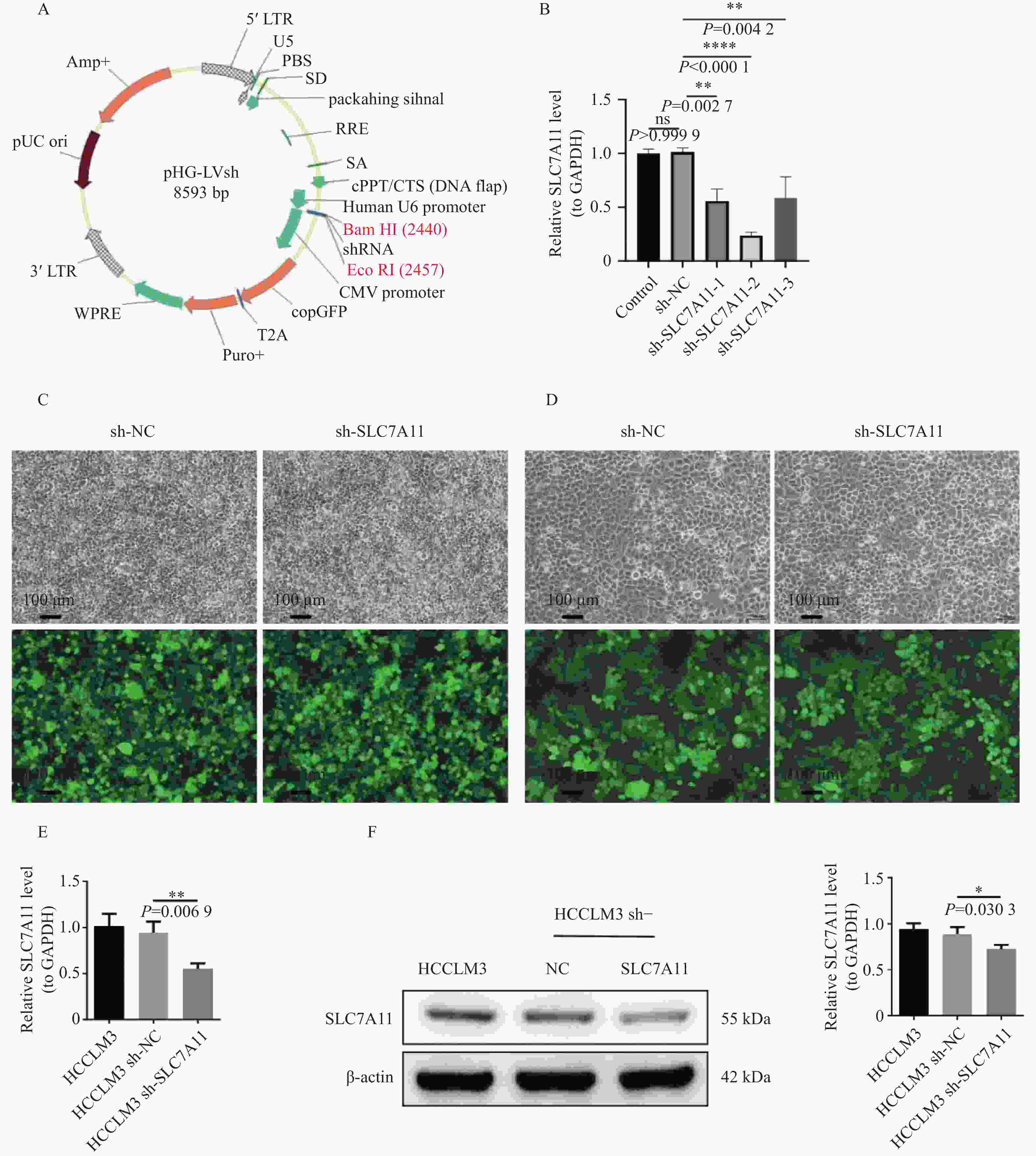
Effect of SLC7A11 Gene on Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regualating Iron Death Pathway
-
摘要:
目的 探讨SLC7A11基因通过铁死亡通路调控肝细胞癌发生发展的机制,并评估其作为潜在治疗靶点的应用价值。 方法 基于TCGA和ICGC数据库筛选肝癌中差异表达的铁死亡相关基因。采用qRT-PCR检测32例临床肝癌样本中癌组织与癌旁组织中TERT、MIOX、MYCN、NOX4和SLC7A11的mRNA表达。进一步通过qRT-PCR、Western blot和IHC分析SLC7A11及其下游分子SLC3A2、GSS和GPX4的表达水平及组织分布。构建SLC7A11干扰型稳定转染的HCCLM3细胞株,并用于建立裸鼠皮下移植瘤模型,以评估其对肿瘤生长的影响。小鼠共分为两组(每组6只):HCCLM3 + sh-NC组和HCCLM3 + sh-SLC7A11组。采用ELISA检测小鼠血清中IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α的含量,通过HE染色观察肿瘤组织的病理变化,并结合多种方法验证上述关键基因的表达。 结果 生物信息学分析显示SLC7A11在肝癌组织中高表达(P < 0.05),与患者不良预后显著相关。临床样本验证中,SLC7A11、SLC3A2、GSS和GPX4在癌组织中表达明显高于对照组(P均< 0.05)。敲减SLC7A11显著抑制肿瘤体积和湿重(P < 0.05),HE染色显示sh-SLC7A11组血管密度降低。ELISA结果显示sh-SLC7A11组血清中IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α水平升高(P均< 0.05)。qRT-PCR、Western blot及IHC均显示SLC7A11、SLC3A2、GSS和GPX4在肿瘤组织中表达水平显著下调(P均< 0.05)。 结论 SLC7A11通过调控GSH-GPX4轴抑制铁死亡,促进肝癌细胞生长。靶向抑制SLC7A11可诱导肿瘤细胞铁死亡,抑制肿瘤进展,提示其有望成为肝癌治疗的重要靶点。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the mechanism by which the SLC7A11 gene regulates the development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCCLM3) through the ferroptosis pathway, and to evaluate its potential as a therapeutic target. Methods Differentially expressed ferroptosis-related genes in liver cancer were screened based on data from the TCGA and ICGC databases. Detection of mRNA expression levels of TERT, MIOX, MYCN, NOX4, and SLC7A11 in tumor and adjacent non-tumorous tissues from 32 clinical liver cancer samples using qRT-PCR. Further analysis of SLC7A11 and its downstream molecules SLC3A2, GSS, and GPX4 was performed through qRT-PCR, Western blot, and IHC to assess expression levels and tissue distribution. A stable SLC7A11-knockdown HCCLM3 cell line was constructed and used to establish a subcutaneous xenograft tumor model in nude mice to evaluate its effect on tumor growth. Mice were divided into two groups (n = 6 per group): HCCLM3 + sh-NC and HCCLM3 + sh-SLC7A11. Serum levels of IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α were measured using ELISA. Histopathological changes in tumor tissues were examined by H&E staining, and the expression of key genes was validated through multiple approaches. Results Bioinformatics analysis showed high expression of SLC7A11 in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues (P < 0.05), significantly associated with poor patient prognosis. Clinical sample validation revealed significantly higher expression of SLC7A11, SLC3A2, GSS, and GPX4 in cancer tissues compared to control groups (All P < 0.05). SLC7A11 knockdown significantly inhibited tumor volume and wet weight (P < 0.05), and H&E staining showed reduced vascular density in the sh-SLC7A11 group. ELISA results showed elevated serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in the sh-SLC7A11 group. qRT-PCR, Western blot, and IHC all showed significantly downregulated expression of SLC7A11, SLC3A2, GSS, and GPX4 in tumor tissues (All P < 0.05). Conclusion SLC7A11 inhibits ferroptosis by regulating the GSH-GPX4 axis, promoting hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth. Targeted inhibition of SLC7A11 can induce tumor cell ferroptosis and suppress tumor progression, suggesting it may be an important therapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. -
Key words:
- SLC7A11 /
- Gene /
- Ferroptosis /
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
-
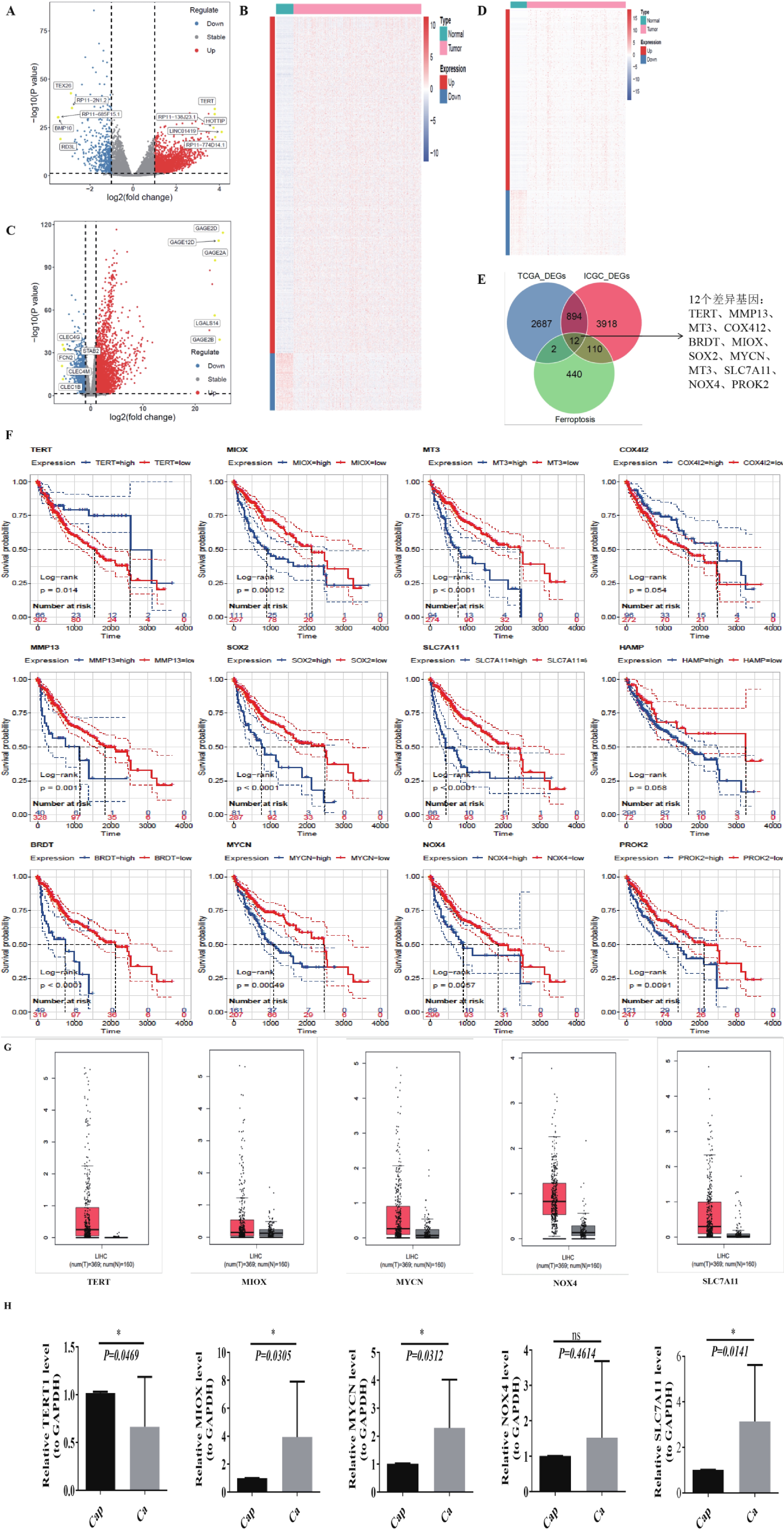
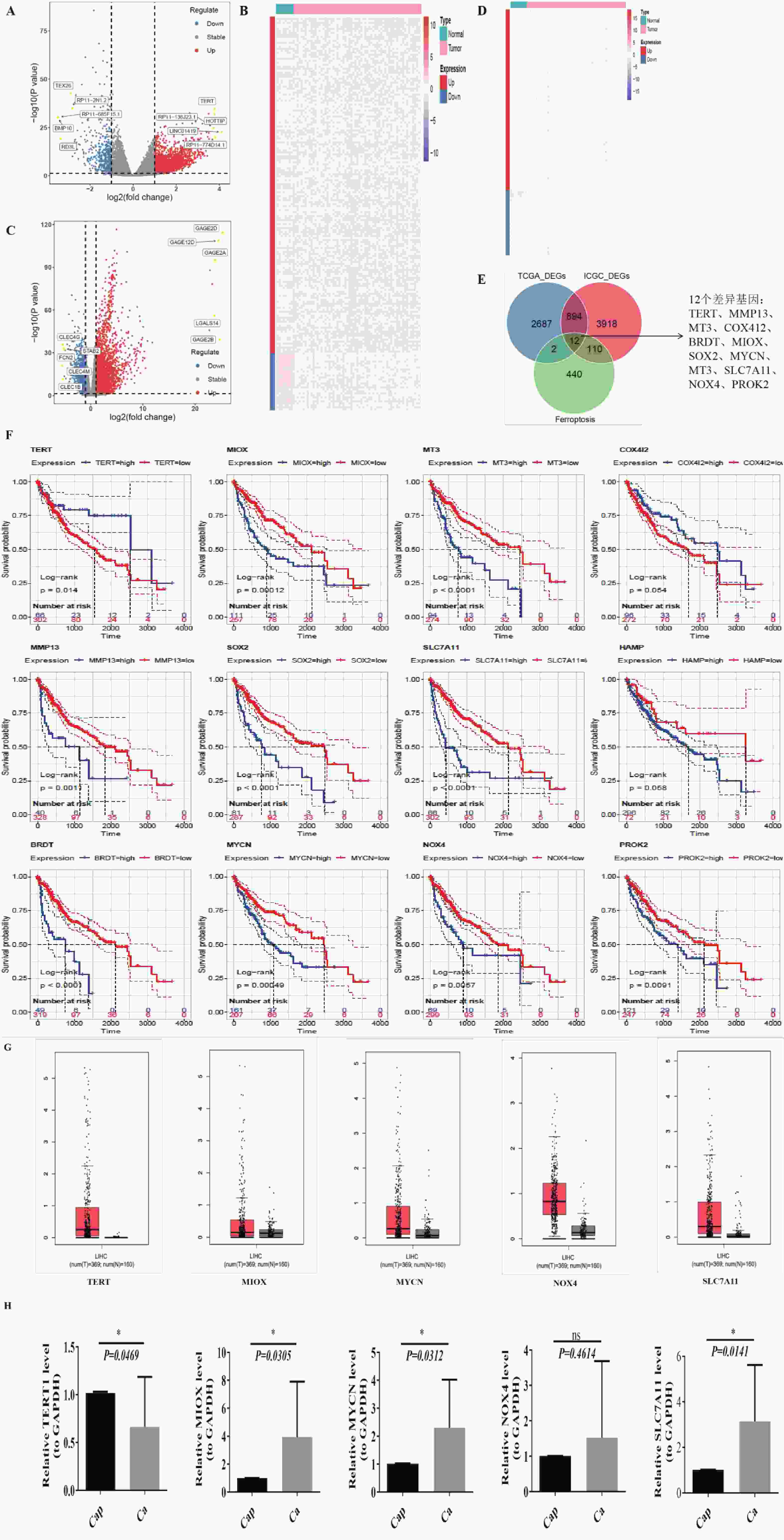
图 1 生信分析发现SLC7A11在肝癌组织中显著高表达
A~B:TCGA-LIHC(A)与 LIHC-US(B)差异表达基因火山图;红色表示上调基因,蓝色为下调,灰色为无显著差异,黄色为上下调中 logFC 绝对值排名前 5 的基因;C~D:TCGA-LIHC(C)与 LIHC-US(D)差异基因热图;红色为高表达,蓝色为低表达;顶部为样本分组(青色:Normal,粉红色:Tumor);左侧为基因分组(红色:上调,蓝色:下调);E:TCGA-LIHC 与 LIHC-US 差异基因与铁死亡相关基因交集韦恩图;F:12个关键基因的 Kaplan-Meier 生存分析曲线;G:GEPIA2 分析肝癌与正常组织中差异表达基因;H:QPCR 检测 TERT、MIOX、MYCN、NOX4、SLC7A11 在临床样本中的表达(GAPDH 为内参);ns:P > 0.05;*P < 0.05。
Figure 1. Bioinformatics analysis reveals significant overexpression of SLC7A11 in hepatocellular carcinoma tissue
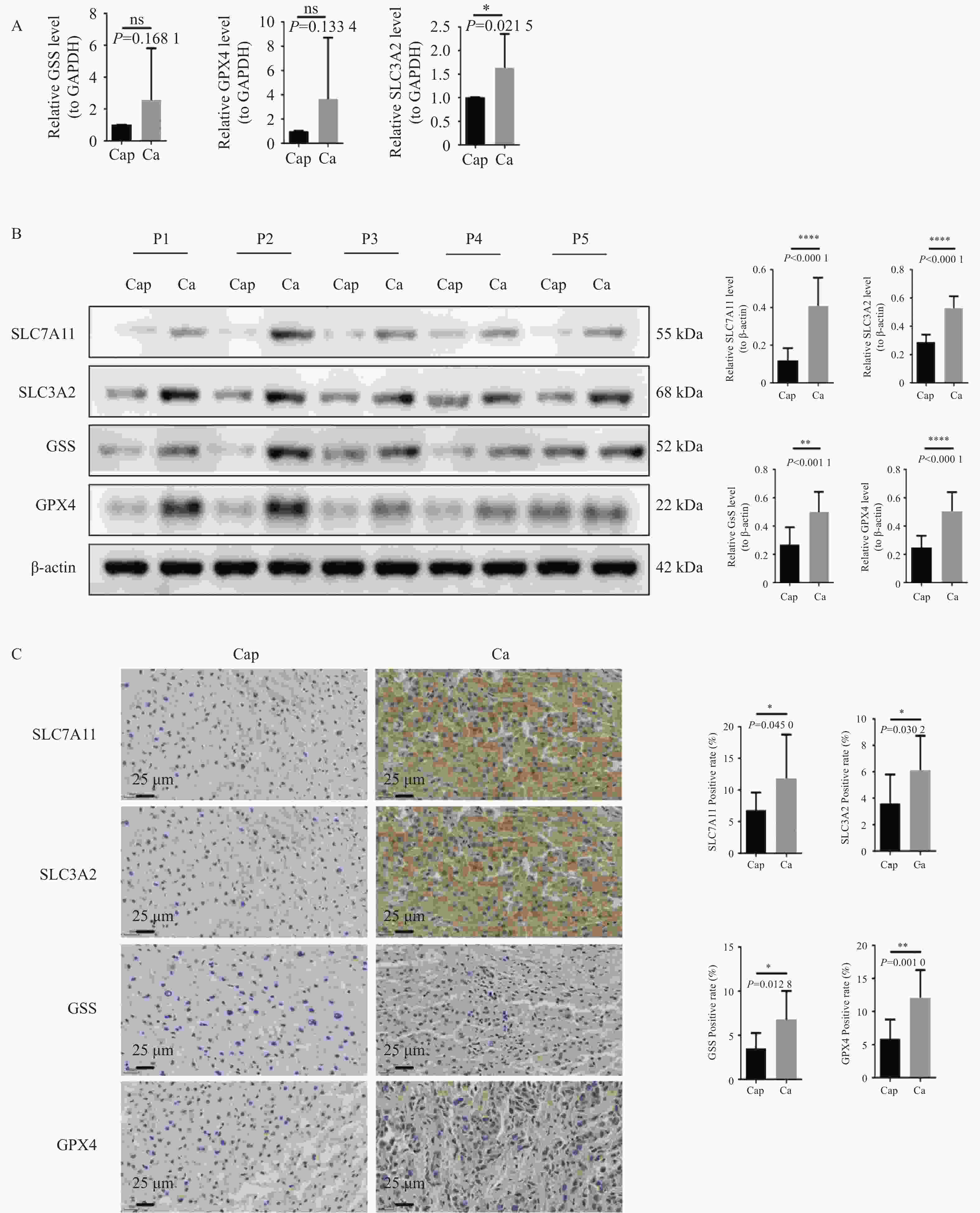
图 2 临床样本中验证SLC7A11及其通路因子的表达情况
A:QPCR检测临床样本中SLC3A2、GSS、GPX4的表达水平,以GAPDH作为内参;B:WB检测SLC7A11、SLC3A2、GSS、GPX4蛋白的表达水平,以β-Actin作为内参,患者姓名采用P开头的编号代替;C:IHC检测SLC7A11、SLC3A2、GSS、GPX4蛋白的表达水平(400×);染色结果呈现:细胞核染色为蓝色,检测目的蛋白的阳性染色为棕黄色;统计图样本n = 32;ns:P > 0.05;*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01;****P < 0.0001。
Figure 2. Verification of SLC7A11 and its pathway factors expression in clinical samples
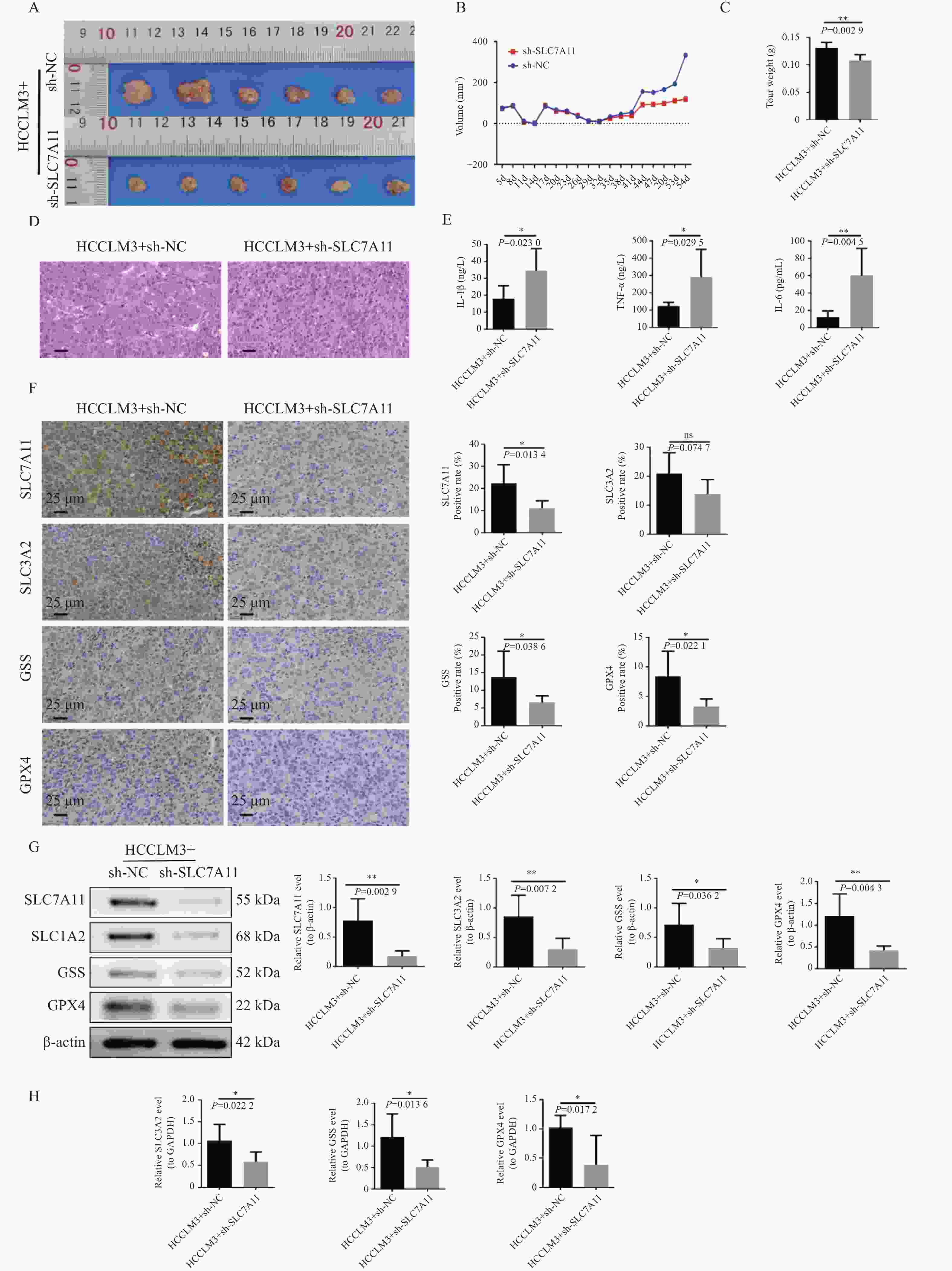
图 4 动物水平验证SLC7A11及其通路因子对肝癌发生发展的影响
A:肿瘤大体图;B:体积数据;C:肿瘤重量数据;D:HE染色;E:ELISA检测血清IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α;F:IHC检测SLC7A11、SLC3A2、GSS、GPX4蛋白的表达水平(400×),染色结果呈现:细胞核染色为蓝色,目的蛋白的阳性染色为棕黄色;G:WB检测SLC7A11、SLC3A2、GSS、GPX4蛋白的表达水平,以β-Actin作为内参;H:RT-qPCR检测动物样本中SLC3A2、GSS、GPX4的表达水平,以GAPDH作为内参;n = 6;ns:P > 0.05;*P < 0.05;**P < 0.01。
Figure 4. Animal level validation of the effects of SLC7A11 and its pathway factors on the occurrence and development of liver cancer
表 1 临床统计 ($\bar x \pm s $)
Table 1. Clinical statistics ($\bar x \pm s $)
临床特征 n SLC7A11 在肿瘤组织中的表达 t P 性别 男 19 8.510±2.250 4.175 0.001* 女 13 15.830±7.190 年龄(岁) ≥50 18 12.910±6.730 1.569 0.130 ﹤50 14 9.650±4.560 TNM分期 0-II 13 7.800±1.600 3.285 0.003* III-IV 19 14.010±6.650 肝内转移 是 18 13.190±7.210 1.864 0.069 否 14 9.290±3.050 术前AFP(ng/mL) ≥25 18 12.180±6.090 1.806 0.081 ﹤25 4 6.570±1.990 肿瘤大小(cm) ≥5 8 14.090±6.700 1.825 0.201 ﹤5 24 10.750±5.750 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Siegel R L , Miller K D , Wagle N S , et al. Cancer statistics, 2023[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2023, 73(1): 17-48. [2] Filho A M , Laversanne M , Ferlay J , et al. The GLOBOCAN 2022 cancer estimates: Data sources, methods, and a snapshot of the cancer burden worldwide[J]. International Journal of Cancer, 2025, 156(7): 1336-1346. [3] 徐若翔, 曾智明, 朱广志, 等. 肝细胞癌AASLD(2023年版)、NCCN(2024年版)、ASCO(2024年版)指南和中国《原发性肝癌诊疗指南(2024年版)》更新解读[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2025, 32(2): 184-191. [4] Lin W, Wang C, Liu G, et al. SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Biological functions and therapeutic implications[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(10): 3106-3126. [5] 刘晓轩, 张驰, 黄思琪, 等. SLC7A11的调控机制及肿瘤治疗应用研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2023, 32(11): 878-885. doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2023.11.A010 [6] Koppula P, Zhang Y, Zhuang L, et al. Amino acid transporter SLC7A11/xCT at the crossroads of regulating redox homeostasis and nutrient dependency of cancer[J]. Cancer Commun(Lond), 2018, 38(1): 12. [7] Liu M R, Zhu W T, Pei D S. System Xc-: A key regulatory target of ferroptosis in cancer[J]. Invest New Drugs, 2021, 39(4): 1123-1131. doi: 10.1007/s10637-021-01070-0 [8] Gong D, Chen M, Wang Y, et al. Role of ferroptosis on tumor progression and immunotherapy[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 427. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01218-8 [9] Mukhopadhyay S, Biancur D E, Parker S J, et al. Autophagy is required for proper cysteine homeostasis in pancreatic cancer through regulation of SLC7A11[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(6): e2021475118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021475118 [10] Liu X, Nie L, Zhang Y, et al. Actin cytoskeleton vulnerability to disulfide stress mediates disulfidptosis[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2023, 25(3): 404-414. [11] 吴伟刚, 田圆, 刘琢冰, 等. SLC7A11基因表达沉默的肝癌细胞株的构建及筛选[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2015, 23(2): 149-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2015.02.02 [12] Liu Y, Ouyang L, Mao C, et al. PCDHB14 promotes ferroptosis and is a novel tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Oncogene, 2022, 41(27): 3570-3583. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02370-2 [13] Yang J , Hu B , Zhang G , et al. Protocadherin 17 weakens the lenvatinib resistance of liver cancer through inducing ferroptosis[J]. Experimental Cell Research, 2025, 447(1): 114495. [14] Zhang B , Bao W , Zhang S , et al. LncRNA HEPFAL accelerates ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating SLC7A11 ubiquitination[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(8): 734. [15] Xie Y , Kang R , Klionsky D J , et al. GPX4 in cell death, autophagy, and disease[J]. Autophagy, 2023, 19(10): 2621-2638. [16] Reem A , Jos V D V , Nicholas H , et al. Glutaredoxin attenuates glutathione levels via deglutathionylation of Otub1 and subsequent destabilization of system xC [J]. Science Advances, 2023, 9(37): eadi5192. [17] Bi F , Qiu Y , Wu Z , et al. METTL9-SLC7A11 axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through ferroptosis inhibition[J]. Cell Death Discovery, 2023, 9(1): 428. [18] Zhang Y , Yao R , Li M , et al. CircTTC13 promotes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through the inhibition of ferroptosis by targeting the miR-513a-5p/SLC7A11 axis[J]. Molecular Cancer, 2025, 24(1): 32. [19] Gnanapradeepan K , Basu S , Barnoud T , et al. The p53 tumor suppressor in the control of metabolism and ferroptosis[J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2018, 9: 124. [20] Parkin D M , Bray M F , Ferlay M J , et al. Global cancer statistics, 2002[J]. Ca A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2005, 55(2): 74-108. [21] Tang W, Chen Z, Zhang W, et al. The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2020, 5(1): 87. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-0187-x [22] Lei G, Zhuang L, Gan B. Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2022, 22(7): 381-396. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00459-0 [23] Li J, Cao F, Yin H L, et al. Ferroptosis: Past, present and future[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 88. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2 [24] Xu S, He Y, Lin L, et al. The emerging role of ferroptosis in intestinal disease[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 289. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03559-1 [25] Jiang X, Stockwell B R, Conrad M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 22(4): 266-282. doi: 10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8 [26] Lindblad K E , Donne R , Liebling I , et al. NOTCH1 drives sexually dimorphic immune responses in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Discov, 2025, 15(3): 495-510. [27] 曾丹宁. 表达下调的FPN1通过调节SLC7A11和GPX4介导的铁死亡来抑制肝细胞癌的生长[D]. 广州: 广州医科大学, 2021. [28] Du A, Li S, Zhou Y, et al. M6A-mediated upregulation of circMDK promotes tumorigenesis and acts as a nanotherapeutic target in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 109. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01575-z [29] Zhao L, Zhou X, Xie F, et al. Ferroptosis in cancer and cancer immunotherapy[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2022, 42(2): 88-116. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12250 [30] Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, et al. Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(5): 280-296. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-00462-0 [31] Zhang C, Liu X, Jin S, et al. Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug resistance[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 47. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01530-y [32] Sun X D, Qin Y, Liu L L, et al. Sodium butyrate inhibits liver cancer cell proliferation by inducing ferroptosis[J]. Journal of Nutrition, 2023, 45(2): 157-162. [33] Ao L, Wang D, Shu S H. The study on the inhibitory effect of propofol on the proliferation and migration of liver cancer cells and its mechanism of iron death pathway[J]. Journal of Molecular Diagnosis and Treatment, 2022, 14(12): 2036-2039+2043. [34] Zheng Y, Huang C, Lu L, et al. STOML2 potentiates metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting PINK1-mediated mitophagy and regulates sensitivity to lenvatinib[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2021, 14(1): 16. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-01029-3 [35] Zhang W, Jiang B P, Liu Y X, et al. Bufotalin induces ferroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by facilitating the ubiquitination and degradation of GPX4[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 180: 75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.01.009 [36] Li D B, Wang Y H, Dong C, et al. CST1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating GPX4 protein stability via OTUB1[J]. Oncogene, 2023, 42(2): 83-98. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02537-x [37] Wang X B, Chen Y Q, Wang X D, et al. Stem cell factor SOX2 confers ferroptosis resistance in lung cancer via upregulation of SLC7A11[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(20): 5217-5229. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0567 -





 下载:
下载: