Effects of Early Statin Therapy on Collateral Circulation,Responsible Vessels,and TXB2/PGF1α in Large Artery Occlusive Stroke
-
摘要:
目的 探究早期他汀类药物治疗对大动脉闭塞性脑卒中(AIS-LVO)对侧支循环、责任血管改善及血栓素B2(TXB2)/前列腺素F1α(PGF1α)的影响。 方法 选取2021年5月至2023年5月太原钢铁(集团)有限公司总医院神经内科收治的105例早期(入院后3 d内)使用他汀类药物治疗的AIS-LVO患者为他汀组,另选取同期105例早期未使用他汀类药物的AIS-LVO患者为非他汀组,比较两组症状评分[美国国立卫生院神经功能缺损评分(NIHSS)、Rankin修订量表(mRS)评分、吞咽功能标准吞咽功能评定量表(SSA)、功能性经口摄食评价量表(FOIS)评分]、责任血管改善情况、TXB2/PGF1α水平、内皮功能指标[碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(bFGF)、外周血循环内皮细胞(CECs)]水平。 结果 他汀组治疗1、2周后NIHSS、mRS、SSA评分水平均低于非他汀组,FOIS评分高于非他汀组(P < 0.02);他汀组责任血管Vm增快、侧支循环代偿改善比例均高于非他汀组(P < 0.05),他汀组CTA侧支循环分级优于非他汀组(P < 0.05);他汀组治疗1、2周后TXB2、TXB2/PGF1α水平均低于非他汀组,PGF1α水平高于非他汀组(P < 0.02);他汀组治疗1、2周后bFGF水平均低于非他汀组,CECs水平高于非他汀组(P < 0.02);他汀组治疗3个月mRS评分0~2分比例高于非他汀组(P < 0.05)。 结论 AIS-LVO患者经早期他汀类药物治疗可改善责任血管血流与内皮功能,调节TXB2/PGF1α水平,促进侧支循环代偿、吞咽功能及神经功能恢复。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of early statin therapy on collateral circulation, responsible vessel improvement, and thromboxane B2 (TXB2)/prostaglandin F1 (PGF1α) in acute ischemic stroke with large vessel occlusion (AIS-LVO). Methods From May 2021 to May 2023, 105 AIS-LVO patients treated with statins within 3 days of admission were selected as the statin group from the Neurology Department of Taiyuan Iron and Steel (Group) General Hospital. Concurrently, 105 early AIS-LVO patients not treated with statins were selected as the non-statin group. The study compared symptom scores [National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS), modified Rankin Scale (mRS), Swallowing Standard Assessment (SSA), and Functional Oral Intake Scale (FOIS) scores], responsible vessel improvement, TXB2/PGF1α levels, and endothelial function indicators [basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and circulating endothelial cells (CECs)]. Results After 1 and 2 weeks , the statin group showed lower NIHSS, mRS, and SSA scores, and higher FOIS scores compared to the non-statin group (P < 0.02). The statin group demonstrated higher rates of responsible vessel velocity increase, collateral circulation compensation, and superior CTA collateral circulation grading (P < 0.05). At 1 and 2 weeks, the statin group had lower TXB2 and TXB2/PGF1α levels, and higher PGF1α levels compared to the non-statin group (P < 0.02). The statin group showed lower bFGF levels and higher CECs levels (P < 0.02). After 3 months, the statin group had a higher proportion of mRS scores of 0~2 (P < 0.05). Conclusion Early statin therapy in AIS-LVO patients can improve responsible vessel blood flow and endothelial function, regulate TXB2/PGF1α levels, promote collateral circulation compensation, and enhance swallowing and neurological function recovery. -
表 1 两组一般资料比较[n(%)/($ \bar x \pm s $)]
Table 1. Comparison of general information between the two groups [n (%)/($ \bar x \pm s $)]
资料 他汀组(n=105) 非他汀组(n=105) χ2/t P 性别(男/女) 57(54.29)/48(45.71) 53(50.48)/52(49.52) 0.305 0.580 年龄(岁) 61.04±4.39 59.86±5.24 1.769 0.078 发病至就诊时间(h) 4.38±0.57 4.25±0.61 1.596 0.112 体质量指数(kg/m2) 24.67±0.96 24.82±1.03 1.092 0.276 基础疾病 高血压 46(43.81) 43(40.95) 0.176 0.675 糖尿病 31(29.52) 27(25.71) 0.381 0.537 高脂血症 33(31.43) 30(28.57) 0.204 0.651 冠心病 37(35.24) 34(32.38) 0.192 0.662 治疗方案 5.446 0.066 静脉溶栓 42(40.00) 50(47.62) 动脉溶栓 36(34.29) 34(32.38) 机械取栓 27(25.71) 21(20.00) 吸烟 30(28.57) 29(27.62) 0.024 0.878 饮酒 35(33.33) 31(29.52) 0.354 0.552 表 2 两组症状评分比较($ \bar x \pm s $,分)
Table 2. Comparison of symptom scores between the two groups ($ \bar x \pm s $,score)
指标 时间 他汀组(n=105) 非他汀组(n=105) t P NIHSS评分 治疗前 22.19±2.57 21.78±2.43 1.188 0.236 治疗1周 11.83±3.51 15.07±3.26 −6.931 <0.001* 治疗2周 5.34±0.85 7.46±1.02 −16.361 <0.001* mRS评分 治疗前 4.63±0.59 4.55±0.54 1.025 0.307 治疗1周 3.41±0.72 3.98±0.67 −5.939 <0.001* 治疗2周 2.66±0.31 3.39±0.42 −14.330 <0.001* SSA评分 治疗前 34.27±6.22 33.91±6.18 0.421 0.674 治疗1周 25.69±4.87 29.43±5.19 −5.385 <0.001* 治疗2周 20.12±3.21 26.57±4.50 −11.957 <0.001* FOIS评分 治疗前 1.37±0.42 1.35±0.41 0.349 0.727 治疗1周 3.10±0.55 2.54±0.58 7.179 <0.001* 治疗2周 3.73±0.68 2.87±0.63 9.507 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 两组责任血管改善与侧支循环建立情况比较[n(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of improvement of responsible vessels and establishment of collateral circulation in the two groups [n (%)]
组别 n 责任血管Vm增快 侧支循环代偿改善 CTA侧支循环分级 好 中 差 他汀组 105 45(42.86) 48(45.71) 67(63.81) 29(27.62) 9(8.57) 非他汀组 105 30(28.57) 33(31.43) 54(51.43) 34(32.38) 17(16.19) χ2/U 4.667 4.522 1.767 P 0.031* 0.033* 0.039* *P < 0.05。 表 4 两组TXB2/PGF1α水平比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
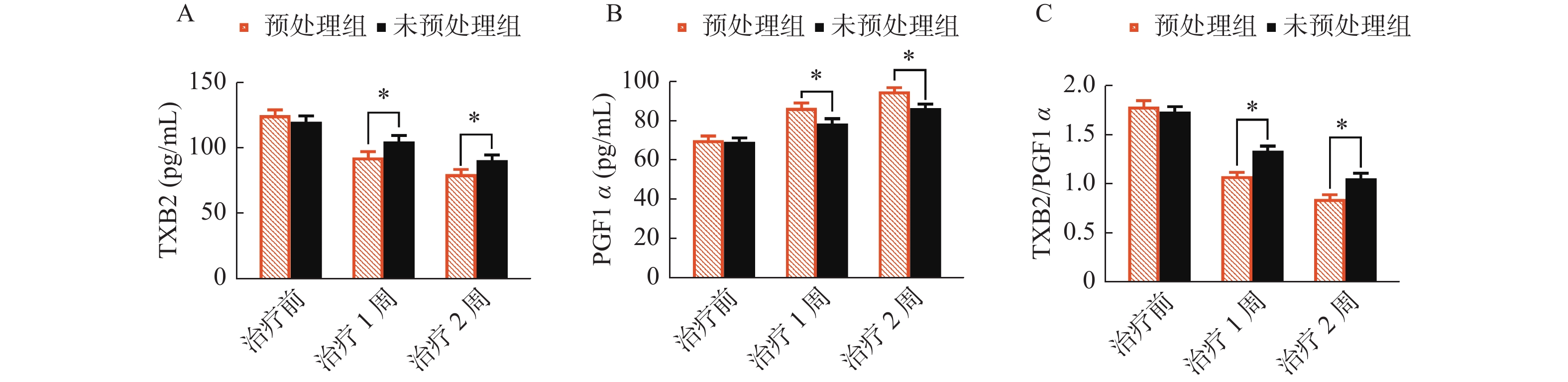
Table 4. Comparison of TXB2/PGF1α levels in the two groups ($ \bar x \pm s $)
指标 时间 他汀组(n=105) 非他汀组(n=105) t P TXB2(pg/mL) 治疗前 124.62±21.83 119.67±23.34 1.587 0.114 治疗1周 92.38±22.75 104.62±24.16 −3.779 <0.001* 治疗2周 79.64±18.71 90.42±20.15 −4.017 <0.001* PGF1α(pg/mL) 治疗前 69.92±11.38 69.14±10.72 0.511 0.610 治疗1周 86.47±12.80 78.55±12.34 4.565 <0.001* 治疗2周 94.82±10.37 86.41±10.75 5.770 <0.001* TXB2/PGF1α 治疗前 1.78±0.18 1.73±0.25 1.663 0.098 治疗1周 1.07±0.21 1.33±0.25 −8.160 <0.001* 治疗2周 0.84±0.22 1.05±0.27 −6.179 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 5 两组内皮功能指标比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 5. Comparison of endothelial function indicators between the two groups ($ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 n bFGF(pg/L) CECs(个/mL) 治疗前 治疗1周 治疗2周 治疗前 治疗1周 治疗2周 他汀组 105 15.08±4.16 18.25±4.23 20.27±5.62 2895.23 ±826.851964.53 ±610.281516.82 ±497.02非他汀组 105 15.43±3.88 17.09±4.12 18.36±5.15 3034.87 ±982.112497.58 ±759.612075.38 ±670.37t −0.630 2.013 2.568 −1.115 −5.606 −6.858 P 0.529 0.045* 0.011* 0.266 <0.001* <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 6 两组治疗后3个月功能预后比较[n(%)]
Table 6. Comparison of functional prognosis at three months after treatment between the two groups [n (%)]
组别 n 0~2分 >2分 他汀组 105 96(91.43) 9(8.57) 非他汀组 105 85(80.95) 20(19.05) χ2 4.841 P 0.028* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Langezaal L C M, van der Hoeven E J R J, Mont'Alverne F J A, et al. Endovascular therapy for stroke due to basilar-artery occlusion[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(20): 1910-1920. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2030297 [2] 毛晶, 赵丰丽. 直接血管内治疗和静脉溶栓机械取栓对前循环大动脉急性闭塞性卒中的疗效[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2022, 50(7): 836-839. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8552.2022.07.024 [3] Uniken Venema S M, Dankbaar J W, van der Lugt A, et al. Cerebral collateral circulation in the era of reperfusion therapies for acute ischemic stroke[J]. Stroke, 2022, 53(10): 3222-3234. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.037869 [4] Almeida S O, Budoff M. Effect of statins on atherosclerotic plaque[J]. Trends Cardiovasc Med, 2019, 29(8): 451-455. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2019.01.001 [5] 赵晨宇, 段亚冰, 丁力, 等. 不同他汀类药物对老年冠状动脉搭桥术患者的有效性与安全性[J]. 国际老年医学杂志, 2022, 43(4): 406-409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7593.2022.04.006 [6] 任国勇, 薛盼, 米英姿, 等. 他汀类药物对心源性大动脉闭塞性脑卒中侧支循环的影响[J]. 中华神经医学杂志, 2019, 18(11): 1142-1145. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-8925.2019.11.011 [7] Zhang X, Pei J M, Xue L P, et al. An-Gong-Niu-Huang-Wan(AGNHW)regulates cerebral blood flow by improving hypoperfusion, cerebrovascular reactivity and microcirculation disturbances after stroke[J]. Chin Med, 2024, 19(1): 73. doi: 10.1186/s13020-024-00945-7 [8] 张林, 刘都, 王恒, 等. 外周血TXB2、NETs、6-K-PGF1α水平对创伤骨折患者深静脉血栓形成的评估价值[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2023, 22(3): 296-300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2023.03.019 [9] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 666-682. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2018.09.004 [10] 单爱军, 吴耀晨, 王佳, 等. 脑损害昏迷患者意识/昏迷深度的无创监测及量化研究[J]. 中华神经外科杂志, 2006, 22(2): 79-82. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1001-2346.2006.02.005 [11] 张世洪, 吴波, 谈颂. 卒中登记研究中Barthel指数和改良的 Rankin量表的适用性与相关性研究[J]. 中国循证医学杂志, 2004, 4(12): 871-874. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2531.2004.12.010 [12] 伍少玲, 马超, 黄粉燕, 等. 标准吞咽功能评定量表的临床应用研究[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2008, 30(6): 396-399. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0254-1424.2008.06.010 [13] 朱亚芳, 张晓梅, 张钦缔, 等. 中文版经口摄食功能评估量表在摄食-吞咽障碍脑卒中患者中的信效度检验[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2017, 33(22): 3826-3829. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2017.22.038 [14] Singer O C, Berkefeld J, Nolte C H, et al. Collateral vessels in proximal middle cerebral artery occlusion: The ENDOSTROKE study[J]. Radiology, 2015, 274(3): 851-858. doi: 10.1148/radiol.14140951 [15] 金正龙, 余涛, 梁敏莹, 等. 桂枝茯苓丸加减对急性缺血性脑卒中患者侧支循环建立及近期预后的影响[J]. 中国中医急症, 2021, 30(2): 317-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2021.02.037 [16] Tao C, Nogueira R G, Zhu Y, et al. Trial of endovascular treatment of acute basilar-artery occlusion[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 387(15): 1361-1372. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206317 [17] Saini H, Cerejo R, Williamson R, et al. Internal carotid artery occlusion: Management[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2022, 22(7): 383-388. doi: 10.1007/s11910-022-01201-x [18] He W, Chen P, Chen Q, et al. Cytokine storm: Behind the scenes of the collateral circulation after acute myocardial infarction[J]. Inflamm Res, 2022, 71(10-11): 1143-1158. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01611-0 [19] Liebeskind D S, Saber H, Xiang B, et al. Collateral circulation in thrombectomy for stroke after 6 to 24 hours in the DAWN trial[J]. Stroke, 2022, 53(3): 742-748. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034471 [20] Fularski P, Krzemińska J, Lewandowska N, et al. Statins in chronic kidney disease-effects on atherosclerosis and cellular senescence[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(13): 1679. doi: 10.3390/cells12131679 [21] 梁先发, 王光曙, 周著文. 早期他汀类药物治疗对的效果分析及对预后的影响[J]. 湖南师范大学学报(医学版), 2022, 19(2): 205-207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-016X.2022.02.057 [22] 吴蕾, 张少兰, 李浩诣, 等. 他汀类药物对创伤性颅脑损伤患者病死率及神经功能预后影响的荟萃分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2022, 102(11): 813-820. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210626-01449 [23] Øverberg L T, Lugg E F, Gaarder M, et al. Plasma levels of BDNF and EGF are reduced in acute stroke patients[J]. Heliyon, 2022, 8(6): 9661. [24] 李易蒸, 张庆欣, 杨晓莉, 等. 急性缺血性脑卒中侧支循环与血管内皮细胞生长因子和碱性成纤维细胞生长因子的相关性[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 24(1): 67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0126.2022.01.018 [25] Zong P Y, Feng J L, Li C X, et al. Activation of endothelial TRPM2 exacerbates blood-brain barrier degradation in ischemic stroke[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2024, 120(2): 188-202. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad126 [26] Mollazadeh H, Tavana E, Fanni G, et al. Effects of statins on mitochondrial pathways[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2021, 12(2): 237-251. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12654 [27] 姜艳艳, 肖红芳. 丹参酮ⅡA磺酸钠联合他汀类药物治疗冠心病对患者炎症因子及凝血功能的影响[J]. 医学临床研究, 2024, 41(1): 129-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2024.01.036 [28] Yu L Y, Liu H G, Ma X X, et al. Anti-atherosclerotic effects of myrtenal in high-fat diet-induced atherosclerosis in rats[J]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2022, 194(12): 5717-5733. doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-04044-x [29] Xu X T, Huang H, Tu Y, et al. Celecoxib alleviates radiation-induced brain injury in rats by maintaining the integrity of blood-brain barrier[J]. Dose Response, 2021, 19(2): 27796-27815. [30] 刘静, 宁慧芳, 吴琴. 高压氧辅助丁苯酞治疗急性缺血性脑卒中患者的疗效及对血清ET-1、TXB2及VEGF水平的影响[J]. 中华航海医学与高气压医学杂志, 2022, 29(1): 32-36. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311847-20210423-00126 [31] Ruan D T, Lu R, Ruan K H. Redirecting thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin biosyntheses from thrombotic to antithrombotic property by an Enzymelink[J]. Future Med Chem, 2021, 13(9): 765-768. doi: 10.4155/fmc-2020-0340 [32] 徐敏, 吴玉层, 魏建辉, 等. TXB2、6-Keto-PGF1α水平与高血压脑出血术后预后的关系[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2022, 21(22): 2376-2379. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4695.2022.22.007 [33] 王维姣, 陈会生. 他汀类药物对急性缺血性卒中患者尿激酶静脉溶栓临床疗效的影响[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2024, 49(2): 152-158. doi: 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2544.2023.0825 [34] Abdul-Rahman T, Bukhari S M A, Herrera E C, et al. Lipid lowering therapy: An era beyond statins[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2022, 47(12): 101342. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2022.101342 [35] 姚宜琪, 袁梦莹, 何霞, 等. 他汀类药物在缺血性卒中二级预防中的作用机制及应用现状[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2023, 39(17): 2556-2560. -






 下载:
下载: