2024 Vol. 45, No. 12
2024, 45(12): 1-9.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241201
Abstract:
Caloric restriction (CR) and intermittent fasting (IF) are two dietary intervention strategies that have garnered increasing attention for their potential role in regulating inflammation and metabolic disorders. With the widespread adoption of high-calorie diets and sedentary lifestyles, the incidence of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases has risen significantly, posing major public health challenges. This review explores how CR and IF impact inflammation reduction and metabolic health improvement through mechanisms such as metabolic reprogramming, autophagy activation, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Notably, both strategies have shown promising intervention effects in inflammatory diseases like multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Additionally, CR and IF demonstrate positive effects in the metabolic regulation of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Despite their clinical potential, long-term adherence and safety remain key challenges for widespread implementation. Future research should focus on personalized interventions and the integration of multiple therapeutic approaches to further validate the clinical value of CR and IF. In summary, CR and IF offer novel, non-pharmacological strategies for managing chronic diseases, presenting significant potential for future clinical application.
Caloric restriction (CR) and intermittent fasting (IF) are two dietary intervention strategies that have garnered increasing attention for their potential role in regulating inflammation and metabolic disorders. With the widespread adoption of high-calorie diets and sedentary lifestyles, the incidence of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases has risen significantly, posing major public health challenges. This review explores how CR and IF impact inflammation reduction and metabolic health improvement through mechanisms such as metabolic reprogramming, autophagy activation, and inhibition of inflammatory pathways. Notably, both strategies have shown promising intervention effects in inflammatory diseases like multiple sclerosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Additionally, CR and IF demonstrate positive effects in the metabolic regulation of obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Despite their clinical potential, long-term adherence and safety remain key challenges for widespread implementation. Future research should focus on personalized interventions and the integration of multiple therapeutic approaches to further validate the clinical value of CR and IF. In summary, CR and IF offer novel, non-pharmacological strategies for managing chronic diseases, presenting significant potential for future clinical application.
2024, 45(12): 10-18.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241202
Abstract:
Objective To study the therapeutic effect and mechanism of geraniin on experimental osteoporotic fracture (OPF) in rabbits. Methods Rabbits were randomly divided into sham operation group, model group, different doses of geraniin groups ( 20, 10, 5 mg/kg ) and simvastatin group ( 5 mg/kg ). OPF model of rabbits was constructed by ovariectomy and bone defect in the middle radius. The changes of bone mineral density in rabbits were detected by bone densitometer. X-ray imaging and Micro CT were used to detect the healing of osteoporotic fractures in rabbits. Bone biomechanical changes were detected by bone strength instrument. The pathological changes of bone tissue were detected by HE staining. Automatic biochemical analyzer and Elisa were used to detect the changes of serum bone turnover biochemical markers and calcium salt and phosphorus salt content in ash composition. Results Geraniin significantly increased the bone mineral density of femur, spine and the whole body of OPF rabbits ( P < 0.01 ), improved the patency of bone marrow cavity and the continuity of bone cortex, increased the bone volume / total volume of OPF rabbits, reduced the bone surface area / bone volume, improved the integrity of trabecular structure, increased the number of trabecular bone and the thickness of trabecular bone, and reduced the spacing of trabecular bone. In addition, geraniin improved biomechanical indexes such as maximum load, structural stiffness and maximum displacement of OPF rabbits, and improved bone microstructure. In addition, geraniin significantly increased the levels of calcium ( Ca2+ ) and phosphorus ( P ) in serum of OPF rabbits, decreased the levels of alkaline phosphatase ( ALP ), tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase ( TRACP ), type I collagen cross-linked carboxyl terminal peptide ( CTX-1 ) and urinary deoxypyridinoline ( DPD ) ( P < 0.01 ), and increased the contents of calcium and phosphorus in bone ash ( P < 0.01 ). Conclusion Geraniin can effectively promote the healing of osteoporotic fractures and improve bone microstructure and biomechanical properties. The mechanism may be related to the increase of bone mineral content and the regulation of bone metabolism.
2024, 45(12): 19-27.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241203
Abstract:
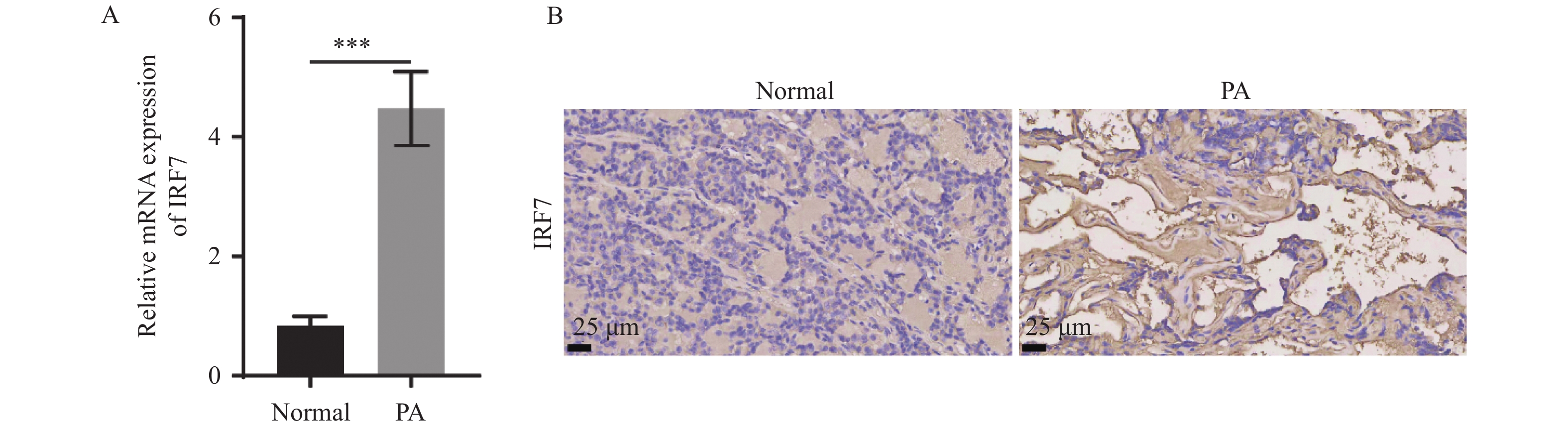
Objective To explore the role and mechanism of crocin in pituitary adenoma (PA) through clinical samples and related molecular biology experiments of HP75 cells. Methods From June 2022 to May 2023, 16 PA samples were collected from the Second Department of Neurology and Otolaryngology skull base surgery of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. Three normal control samples were from the human anatomy of the Forensic College of Kunming Medical University. The expression of IRF7 mRNA in clinical samples was detected, and the proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of HP75 cells were detected by knocking down the expression of IRF7; the expression of NF-κB was regulated by IRF7 in HP75 cells, and crocin regulated the growth of PA cells and its regulatory effect on IRF7/NF-κB signaling pathway. Results RT-qPCR and immunohisto-chemistry showed that compared with the normal control group, the expression of IRF7 mRNA in PA was significantly increased (P < 0.001); the expression of IRF7 protein in si-IRF7 group was significantly decreased (P < 0.001); CCK-8, Transwell and flow cytometry results showed that compared with the control group, knockdown of IRF7 significantly decreased the cell viability of HP75 cells (P < 0.001), inhibited the migration and invasion (P < 0.001), and promoted the apoptosis of HP75 cells (P < 0.001). In addition, knockdown of IRF7 could inhibit the expression of p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65 (P < 0.001) and p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65 (P < 0.001). Overexpression of IRF7 partially reversed the effect of crocin (P < 0.001) and restored the expression of p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65 (P < 0.01). Finally, the biological behavior of HP75 cells showed that compared with crocin group, overexpression of IRF7 could improve the cell viability of HP75 cells, promote their migration and invasion, and inhibit cell apoptosis (P < 0.001). Conclusion Crocin treatment can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of PA cells, promote cell apoptosis, and alleviate the development of PA. In the mechanism, IRF7 is significantly overexpressed in PA, and knockdown of IRF7 can inhibit the malignant growth of PA. Crocin can inhibit the proliferation, migration and invasion of PA cells, and promote apoptosis by inhibiting IRF7/NF-κB signaling pathway.
2024, 45(12): 28-34.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241204
Abstract:
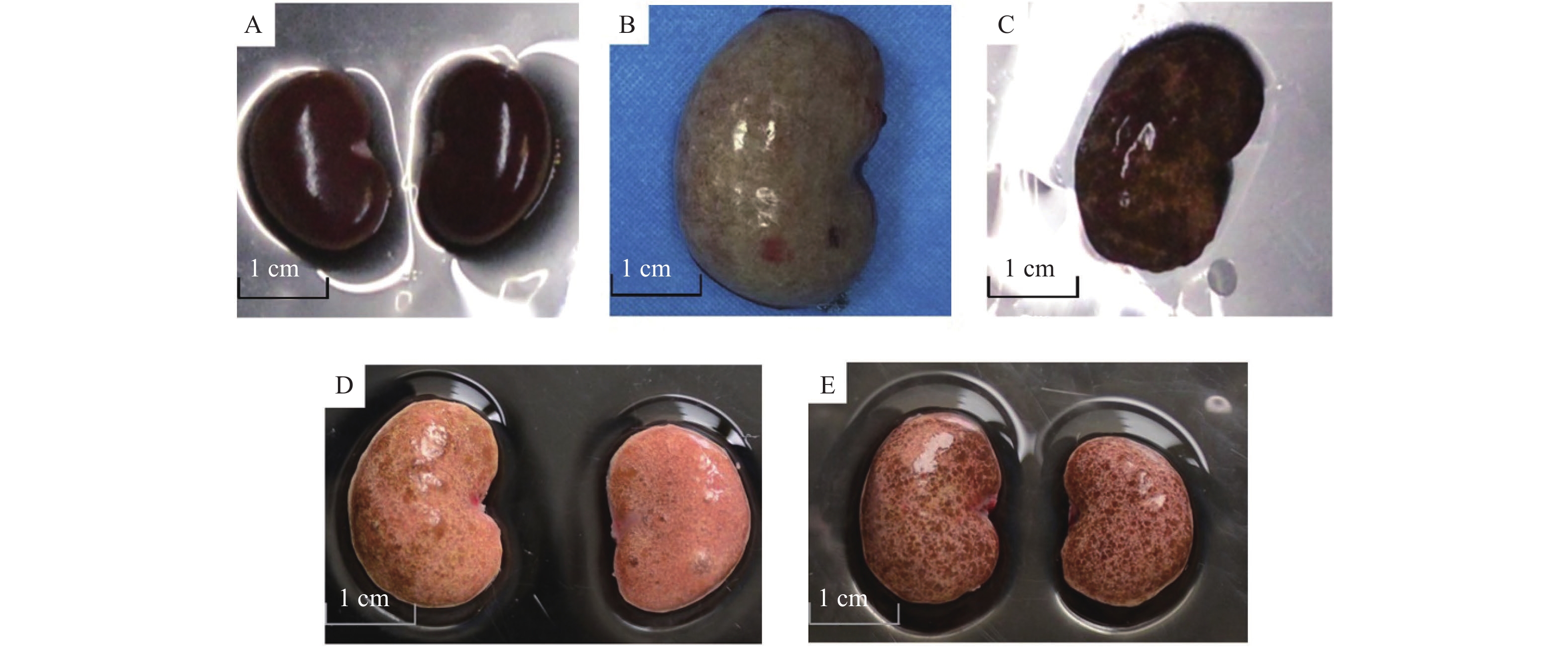
Objective To investigate the stability of the two kinds of rat models of chronic renal failure, aiming to provide a basis for establishing a feasible and stable animal model of chronic renal failure. Methods The rat model of chronic renal failure was established by unilateral nephrectomy + adenine gavage + high-phosphorus diet and high-phosphorus + adenine diet, respectively. Erythrocyte and hemoglobin levels, serum urea and creatinine levels were detected at the end of modeling and 6 weeks after modeling, and histopathological examinations of kidney and bone were performed. The tubulointerstitial fibrosis index (TBI) and the percentage of collagen fiber area in renal tissue were calculated. Results At the end of modeling, compared with the normal group, the erythrocyte and hemoglobin in the model group 1(unilateral nephrectomy + adenine gavage + high-phosphorus) were significantly decreased(P < 0.05), the serum urea and creatinine were significantly increased(P < 0.05), TBI and the percentage of collagen fiber area in kidney tissue were slightly increased(P < 0.05), and the femur lesions were significantly increased. 6 weeks after modeling, compared with the normal group, the erythrocyte and hemoglobin in model group 1 showed a slight decrease (P < 0.05), while there was no significant difference in serum urea and creatinine levels. The TBI and collagen fiber area percentage in renal tissue showed a slight increase (P < 0.05), and there was no obvious change in femoral lesions. At the end of the modeling, the erythrocyte and hemoglobin in the model group 2 (high-phosphorus + adenine diet) were significantly decreased compared with the normal group(P < 0.05), serum urea, creatinine, TBI and the percentage of collagen fiber area in kidney tissue were significantly increased(P < 0.05), and the lesions of femur were obvious. 6 weeks after the end of modeling, compared with the normal group, the erythrocyte and hemoglobin in the model group 2 were significantly decreased(P < 0.05), serum urea, creatinine, TBI and the percentage of collagen fiber area in kidney tissue were significantly increased(P < 0.05), and the lesions of femur were obvious. 6 weeks after the end of modeling, compared with the model group 1, the erythrocyte and hemoglobin in the model group 2 were significantly decreased(P < 0.05), while the serum urea, creatinine, TBI, the collagen fiber area percentage of kidney tissue and femur lesions were significantly increased(P < 0.05). Conclusions A stable rat model of chronic renal failure can be established by high phosphorus + adenine diet.
2024, 45(12): 35-41.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241205
Abstract:
Objective By assessing the uncertainty of the determination results for the concentration of ambroxol hydrochloride injection, the reliability of the concentration measurement results is improved, ensuring the safety and efficacy of high-risk dosage form medications. Methods The uncertainty assessment of the content determination results by HPLC external standard method was conducted using both the TOP-DOWN method and the GUM method in the past. The TOP-DOWN method evaluated after synthesizing two components: the combined bias uncertainty component and the intermediate precision uncertainty component. The GUM method analyzed six sources of uncertainty based on the experimental process and evaluated after synthesizing the uncertainty. Results When the confidence level was 95%, the expanded uncertainty assessed by the TOP-DOWN method and the GUM method was 1.84% and 2.36% respectively (K = 2). Conclusion The results from both assessments indicated that the determination of ambroxol hydrochloride injection content was reliable, ensuring the safety and efficacy of the drug.
2024, 45(12): 42-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241206
Abstract:
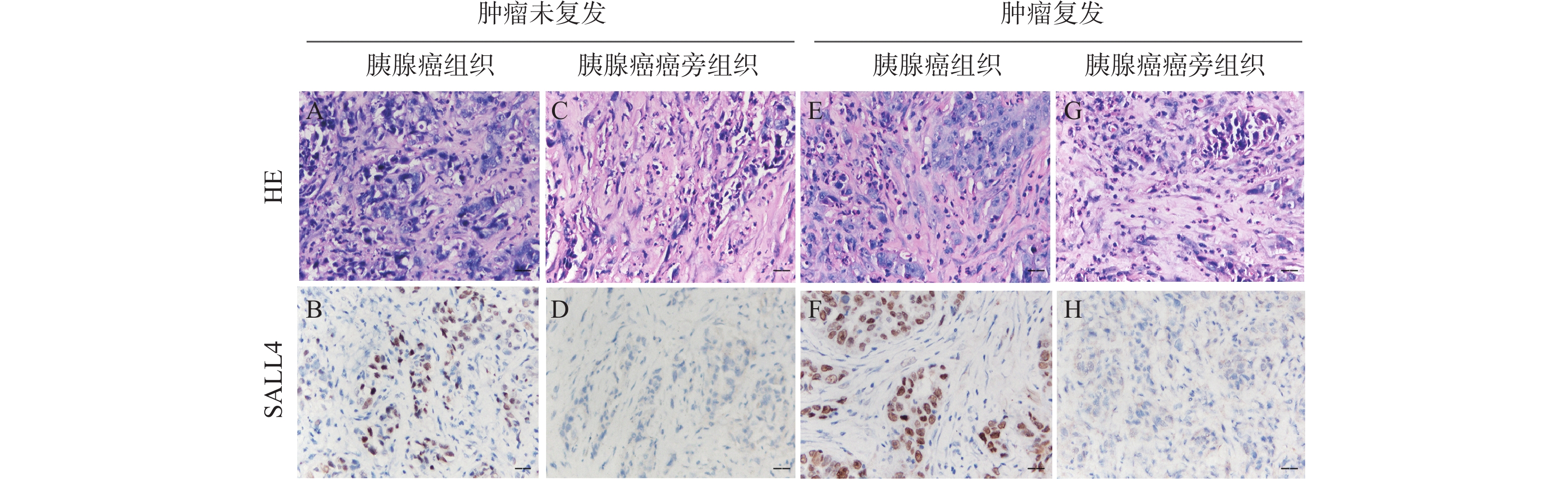
Objective To investigate the expression of spalt like transcription factor 4 (Sall4) in pancreatic cancer tissues and its clinical significance, as well as the impact of inhibiting its gene expression on the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Methods This study involved 64 patients with pancreatic cancer treated at the 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2014 to January 2018. Immunohistochemical staining was used to detect the expression of Sall4 protein in adjacent non-tumor tissues and pancreatic cancer tissues, respectively. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to measure the mRNA expression levels of Sall4 in the cancerous and adjacent non-tumor tissues, respectively. The relationship between the clinicopathological data of these patients and the expression of Sall4 protein was also analyzed. The cells of high Sall4 expression were screened from the human pancreatic cancer cell lines PANC-1, Capan-1, SW 1990, HPAC, and HPAF-II. The pancreatic cancer cells of high Sall4 expression were divided into three groups: control group, shRNA-1 group, and shRNA-2 group. The shRNA-1 and shRNA-2 groups were transfected with the corresponding Sall4 lentiviral inhibitory gene sequences, while the control group was transfected with the reagent without an interference sequence. Western blotting was used to measure the expression of Sall4, and cells with significantly reduced expression were selected for subsequent experiments. The transfected cells were then assessed for their invasive and migratory abilities. Results Among the 64 samples of pancreatic cancer tissues, 28 cases (43.8%) were positive for Sall4 expression, a rate significantly higher than 5 cases (7.8%) in adjacent non-tumor tissues. Furthermore, 16 cases exhibited strong positivity, while 12 cases showed moderate or weak positivity. Recurrence occurred in 11 pancreatic cancer patients. The difference was statistically significant. The expression of Sall4 was correlated with tumor differentiation, staging, and lymph node metastasis, suggesting that Sall4 positivity might be an independent risk factor affecting the prognosis of pancreatic cancer. Among the five cell lines, PANC-1 had the highest relative expression of Sall4 and was selected for further experiments. The shRNA-1 and shRNA-2 groups successfully suppressed the expression of Sall4, with the shRNA-1 group showing a more pronounced effect. Compared to the control group, the invasive and migratory abilities of SW480 cells were significantly reduced in the shRNA-1 group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Sall4 is highly expressed in pancreatic cancer tissues, and higher expression is associated with a greater likelihood of postoperative recurrence. Inhibiting the expression of Sall4 can significantly suppress the invasion and migration abilities of human pancreatic cancer cells.
2024, 45(12): 49-57.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241207
Abstract:
Objective To study the pathogenesis of psoriasisand and to provide new research ideas and directions for the prevention and treatment of psoriasis. Methods Psoriasis-related genes were obtained from genecards and NCBI databases, and intersection genes were obtained. After PPI network constructed, core differential genes were determined. Based on GO and KEGG enrichment analysis, a target gene-signaling pathway network diagram was constructed. The TCMSP and symmap platforms were used to reversely collect potential therapeutic Chinese medicines and related active ingredients, construct a predicted drug-active ingredient network diagram, and screen core targets and core ingredients for molecular docking verification. Results 262 psoriasis genes were obtained, and multiple biological entries and pathways were analyzed by GO and KEGG. Combined with the PPI network, 7 key genes were identified. 20 kinds of traditional Chinese medicine and 264 kinds of ingredients were collected through reverse engineering to construct a network diagram. Molecular docking verified 7 genes and the first 5 components. Conclusion This study discovered potential drugs for the treatment of psoriasis, and verified, through molecular docking, that traditional Chinese medicines and ingredients such as Hedyotis diffusa and Polygonum cuspidatum can regulate IL1B, CXCL8 and other targets, providing a reference for traditional Chinese medicine components in the treatment of psoriasis.
2024, 45(12): 58-64.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241208
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the factors associated with atrial fibrillation(AF) in patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM). Methods Through a case-control study, We selected 688 patients with T2DM who were hospitalized at the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2015 to November 2021. Based on the AF diagnostic criteria, all the patients were divided into a case group (AF group) of 368 cases and a control group (non-AF group) of 320 cases. All patients' clinical data were collected and used Stata 15.1 statistical software were used for analyze the relevant influencing factors of AF in patients with T2DM. Results Age, duration of DM, glycated hemoglobin level, body mass index, left atrial diameter, creatinine, C2HEST score, and heart failure might be risk factors for AF in T2DM patients(P < 0.05); among them, age, glycated hemoglobin level, left atrial diameter, C2HEST score might be independent risk factors for AF in T2DM patients; the use of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (Sodium/Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitor, SGLT2i) andβ-blockers (P < 0.05) might be its protective factors. Conclusion Old age, high HbA1c level, increased left atrial diameter, and high C2HEST score maight be independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in T2DM patients. The use of SGLT2i and β-blockers in T2DM patients may have a protective effect on the occurrence of atrial fibrillation.
2024, 45(12): 65-74.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241209
Abstract:
Objective Immune infiltration, as well as their implications across various cancers, and to establish a clinical prognostic model based on the findings. Methods The expression profile and clinical information of endometrial cancer tissue and adjacent tissues in TCGA endometrial cancer database were used, the differential expression genes were screened out for analysis, and the mRNA co-expressed by LncRNA was analyzed by GO enrichment and KEGG signaling pathway.The differential genes between endometrial cancer and adjacent tissues were intersected with the basement membrane protein genes. The selected differentially expressed genes were combined with survival status and survival time to screen out Hub genes by Lasso-cox regression analysis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to establish a prognostic model, and pan-cancer analysis and immunoinfiltration correlation analysis were further performed. Results Six basal membrane protein Hub genes, ADAMTS5, EVA1C, THBS4, CTSD, ITGAV and LAMA1, were identified as associated with the prognosis of patients with endometrial cancer, and found that the survival rate of patients decreased significantly with the increase of risk score. Pan-cancer analysis found that these 6 genes were significantly different in most cancer types, and high expression in GBMLGG (glioma), LGG (low-grade glioma of the brain), LAML (acute myeloid leukemia), UVM (Uveal melanoma), ACC (adrenal cortical cancer) and other cancers had poor prognosis. The potential role of these genes in tumor immunotherapy was also explored, and significant negative correlation was found with Th17 cells, Th2 cells, NK CD56 bright cells and other immune cells (P < 0.01), and significant positive correlation was found with Tcm, iDC, Eosinophils, aDC and other immune cells (P < 0.01). Conclusion Basal membrane protein gene has high clinical value in the diagnosis and prognosis of endometrial cancer, and can be used as a prognostic marker and potential therapeutic target for patients with endometrial cancer.
2024, 45(12): 75-80.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241210
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical features of the spectrum of upper gastrointestinal diseases in children and to provide assistance in the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of upper gastrointestinal diseases in children. Methods Clinical data of 424 children aged 2 months to 14 years who were hospitalised for gastroscopy in the paediatrics department of the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2018 to June 2023 were collected, and retrospective analyses were performed for the children's clinical presentation, gastroscopy results, and HP infections. Results The symptoms of vomiting and diarrhea in infants were significantly different from those in preschool and school age groups (P < 0.05). The positive rate of lesions under gastroscopy was 96.46%. The main diseases found were non-atrophic gastritis (222 cases), bile reflux gastritis (42 cases), non-atrophic gastritis with erosion (30 cases), duodenitis (25 cases), reflux esophagitis (15 cases) and others (75 cases). Helicobacter pylori (HP) was detected in 300 of the 424 cases, and 105 cases were HP positive, with a detection rate of 35.00%. Conclusion Abdominal pain was the main symptom of upper gastrointestinal diseases in school-age and pre-school children. Vomiting and diarrhea were the main symptoms of upper gastrointestinal diseases in infants. There was no gender difference in HP infection, but there was a difference in age.
2024, 45(12): 81-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241211
Abstract:
Objective To explore the efficacy of the geriatric interdisciplinary team (GIT) service for elderly patients with multimorbidity and malnutrition. Methods We selected 109 elderly patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)or chronic heart failure (CHF) and multimorbidity to the Department of Geriatrics of The 2nd People’ s Hospital of Kunming City from January 2022 to January 2023. The patients were randomly divided into the control group of 53 cases and the observation group of 56 cases. The control group received routine management of multimorbidity and malnutrition, while the observation group used the GIT service model to manage multimorbidity and malnutrition.The disease, nutritional status, and quality of life outcomes of the two groups of elderly patients were evaluated before and 3 months after the intervention.(1) HbA1c was detected in patients with DM in both groups, and the aggravation of patients with COPD or CHF was observed and recorded. (2)Nutrition-related indicators (Tp, ALB and Hb) and Barthel index were evaluated in both groups. Results (1) The HbA1c of patients with DM in the two groups decreased after intervention (P < 0.001), and the decrease in the observation group was more significant than that in the control group (P < 0.001). (2) The number of AECOPEs in patients with COPD in the two groups decreased, and the observation group was less than the control group (P < 0.05). (3) The number of CHF acute exacerbations in patients with CHF in the two groups decreased and the observation group was fewer than the control group (P < 0.05). (4) The TP, ALB, Hb and Barthel index scores of the two groups increased compared with those before intervention, and the observation group increased more significantly than the control group (P < 0.05 ) . Conclusion The geriatric interdisciplinary team service for the elderly has a good effect in the intervention of elderly patients with multimorbidity and malnutrition.
2024, 45(12): 88-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241212
Abstract:
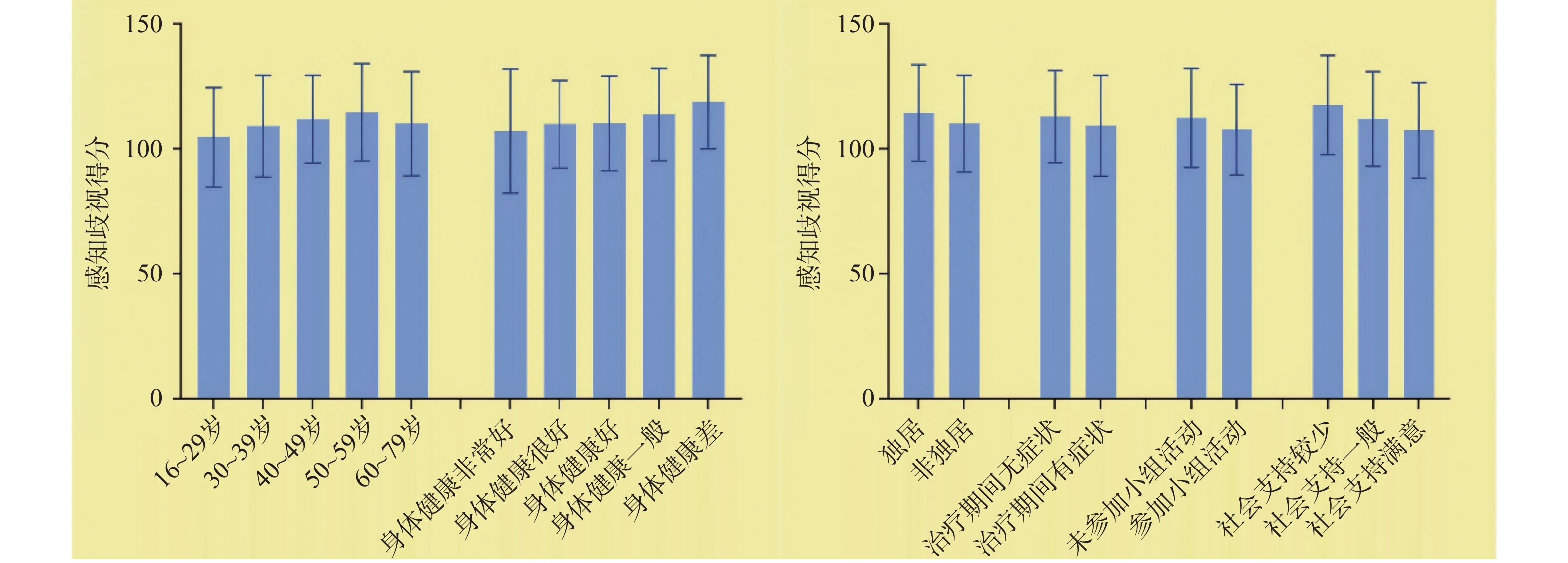
Objective To investigate the status of perceived discrimination among HIV-infected people receiving antiviral treatment and analyze its influencing factors, so as to provide reference for reducing discrimination and improving the life quality of HIV-infected people. Methods The multi-stage stratified cluster sampling method was used to select HIV-infected individuals from designated hospitals in three cities and counties in Yunnan Province, as well as from designated township health centers, for face-to-face survey interviews. The questionnaire included socio-demographic characteristics, AIDS infection disease characteristics, Berger AIDS perceived discrimination Scale and Xiao Shui Yuan Social Support Rating Scale. The influencing factors of perceived discrimination were analyzed by multiple linear regression. Results There were 633 valid questionnaires. The perceived discrimination score of HIV-infected people was (111.11±19.43), which was at a medium high level, and the dimension with the highest average score was fear of publicity. Multiple regression showed that middle-aged people, those who do not participate in group activities and those who have less social support had higher perceived discrimination (P < 0.05). Conclusion The perception discrimination of AIDS patients in Yunnan Province is high. In the prevention and control of AIDS, it is necessary to actively organize and participate in group activities, improve social support and pay attention to middle-aged AIDS patients.
2024, 45(12): 94-98.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241213
Abstract:
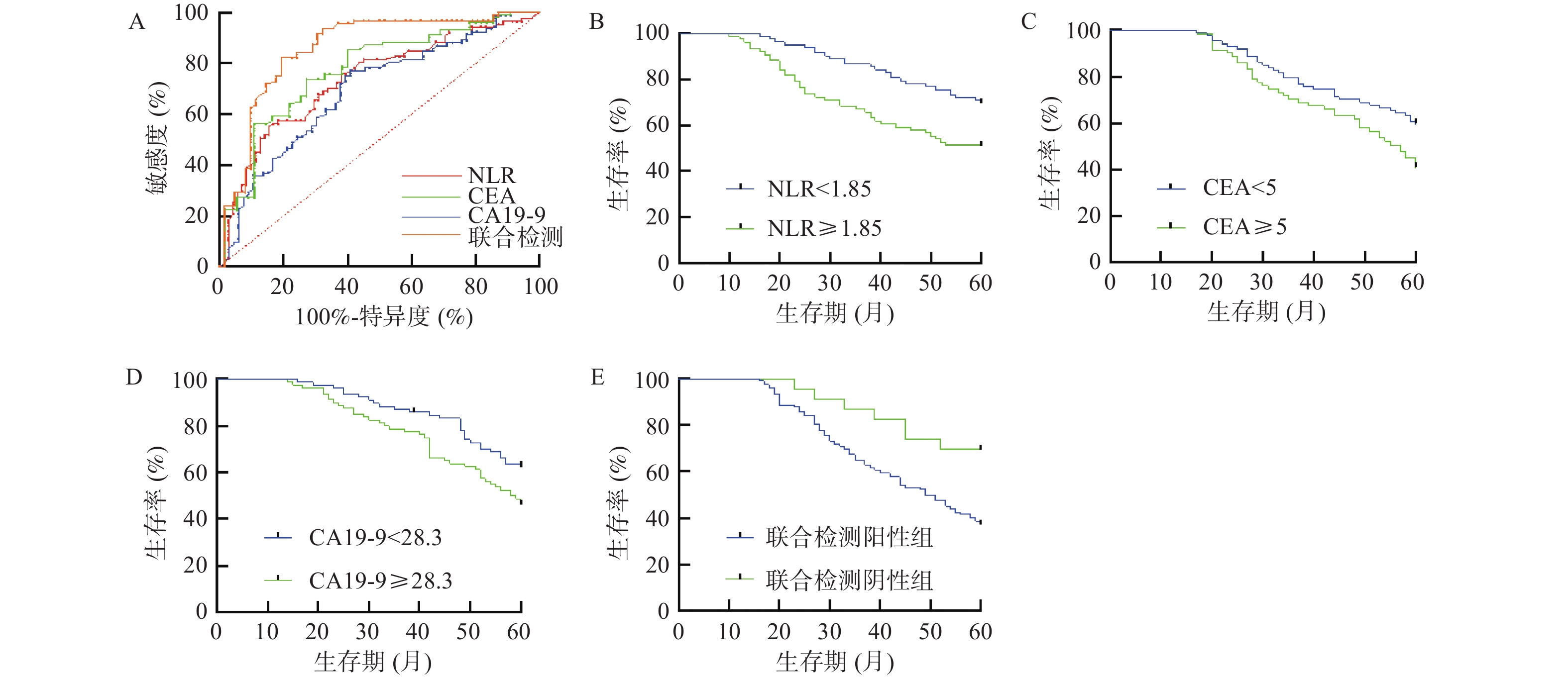
Objective To analyze the prognostic value of preoperative peripheral blood inflammatory markers neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) combined with tumor markers carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and glycoprotein antigen CA19-9 in patients with colon cancer. Methods A retrospective study was conducted on 158 cases of colon cancer patients who visited the 1st Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from May 2018 to October 2020. The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to determine the critical values of various indicators and group them. The Kaplan Meier method was used to analyze the relationship between NLR, CEA, CA19-9, and combined detection of different groups and patient survival prognosis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis was used to analyze the factors affecting patient prognosis. Results The preoperative NLR level (P = 0.035), combined testing group (P = 0.008), and postoperative pathological N stage (P < 0.001) were independent risk factors for OS, and the joint testing group had the highest risk ratio among preoperative indicators (P = 0.008, HR = 2.664, 95%CI 1.503~4.315). Conclusion The combined detection of NLR, CEA, and CA19-9 in peripheral blood before surgery has independent prognostic value for patients with colon cancer.
2024, 45(12): 99-104.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241214
Abstract:
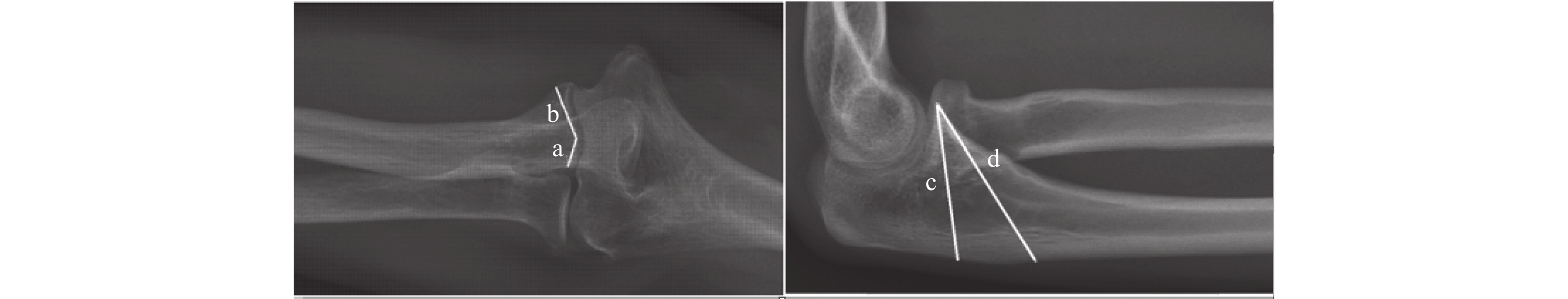
Objective To explore the influence of different factors on the safe screw placement of the ulnar coronoid process based on the DR imaging measurement of the ulnar coronoid process. Methods During the period from July 2020 to November 2021, 102 normal adult elbow joint DR films were randomly included from Yunnan Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Standard elbow joint DR films were selected as the measurement objects, with the apex of the coronoid process as the vertex and two straight lines parallel to the elbow joint space along both sides of the coronoid process. The length of the line segment from the apex of the coronoid process to the intersection of the radius and ulnar cortex of the ulna was the safe distance to place the nail on the coronal surface of the ulna coronoid process; The standard lateral DR film of the elbow joint was selected as the measurement image, and the apex of the coronoid process was used as a point to draw out two safety lines intersecting with the ulnar cortex at the proximal and distal ends. The length of the safety lines at the proximal and distal ends of the coronoid process was the safe nail placement distance on the sagittal plane of the ulnar coronoid process. The differences in safe nail placement distance between different genders, left and right sides, were compared and the correlation between safe nail placement distances on different cross-sections was analyzed. Results There was a statistically significant difference in the safe placement distance of the ulnar coronoid process between males and females (P < 0.05); On the coronal plane, there was a correlation between the safe nail placement distance on the radial and ulnar sides in males; On the sagittal plane (P < 0.05), there was a correlation between the safe placement distance of the ulnar coronoid process in women’ s proximal and distal ends (P < 0.05). Conclusion Studying the safe screw placement distance of the ulnar coronoid process is beneficial to guide the clinical placement of screws for coronoid process fractures, the design of new steel plates, and the correction of deformity.
2024, 45(12): 105-114.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241215
Abstract:
Objective To identify potential biomarkers associated with LN, with the goal of improving early diagnosis, disease monitoring, and the development of more precise treatment strategies. Methods Gene expression data were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database for datasets GSE22221, GSE112943, GSE99967, and GSE32591. Intersecting genes were obtained through the application of weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) and linear models for microarray data (LIMMA). Subsequently, biological function and pathway analyses were conducted on these intersecting genes using Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Next, protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis was performed, and hub genes highly associated with LN were identified using the CytoHubba algorithm, support vector machine (SVM), and random forest (RF) methods. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was performed, and three potential biomarkers were validated using the GSE72798 dataset. Results The green-yellow module (P = 7.4e−40) and the cyan module (P = 1.5e−14) were identified through WGCNA analysis. A total of 193 differentially expressed genes were identified using LIMMA, with 113 intersecting genes related to LN being identified. GO and KEGG analyses indicated that these genes were mainly enriched in viral or bacterial defense, type I interferon signaling pathway, neutrophil-mediated immunity, and Toll-like receptor signaling. MX1, IFI44, and STAT1 were identified as hub genes using CytoHubba, SVM, and RF methods, with AUC values of 0.874, 0.879, and 0.833, respectively. Validation using the GSE72798 dataset demonstrated that the expression of MX1, IFI44, and STAT1 was significantly higher in LN patients compared to healthy individuals (P < 0.001 for all). Conclusion MX1, IFI44, and STAT1 play crucial roles in the pathogenesis of LN and may serve as important biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for LN.
2024, 45(12): 115-121.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241216
Abstract:
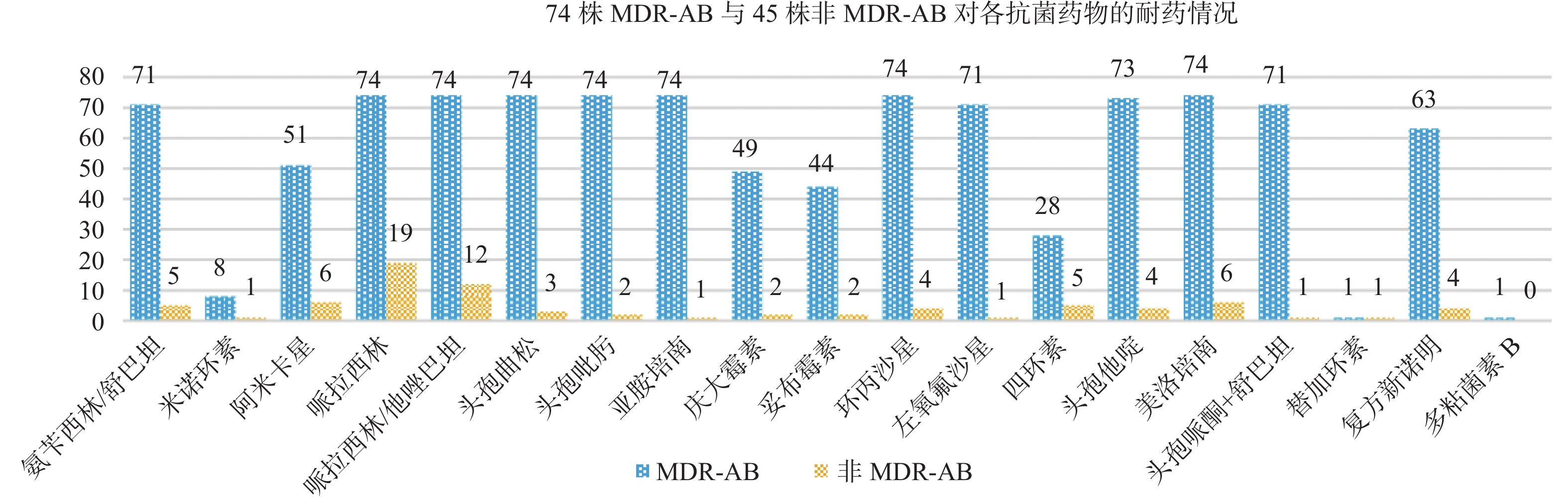
Objective To investigate the correlation between biofilm gene, efflux pump gene, biofilm forming ability and drug resistance of Acinetobacter baumarmii (AB) isolated from the patients of clinical infectious diseases. Methods A total of 119 non-repeating Acinetobacter baumannii isolates (74 MDR-AB strains and 45 non-multi-drug resistant strains) were collected. The effector pump genes (adeB, adeJ, adeG, adeS and adeR) and biofilm-related genes (bap, ompA, csuA, csuB, csuC, csuD, csuE, abaI, bfmR, bfmS) were detected by PCR. Bacterial biofilm was constructed in vitro with 24-well cell culture plates, and the formation of biofilm was qualitatively observed by crystal violet staining. Results Acinetobacter baumannii was resistant to most of the commonly used antibiotics and sensitive to tigacycline, polymyxin B and minocycline. The overall detection rate of biofilm-related genes was about 80%, and the detection rates of bap, csuB, csuC and csuD genes in multi-drug resistant bacteria were significantly higher than those in non-multi-drug resistant bacteria (P < 0.05). The detection rate of active effector pump genes was less than 70%, and the detection rate of adeB, adeJ, adeS and adeR genes in multidrug-resistant bacteria was significantly higher than that in non-multidrug-resistant bacteria (P < 0.05). The adeG carrying rate was opposite. Three multidrug-resistant strains and five non-multidrug-resistant strains did not carry the above efflux pump related genes, and no abeM gene was detected in all strains. The formation of biofilm was observed in 95.80% of strains. Conclusion Acinetobacter baumannii in hospital is mostly multidrug-resistant strains, most of which have strong biofilm forming ability. Multidrug-resistant bacteria have higher biofilm gene and effluent-pump gene carrying rate, which may be involved in the regulation and formation of multidrug resistance.
2024, 45(12): 122-128.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241217
Abstract:
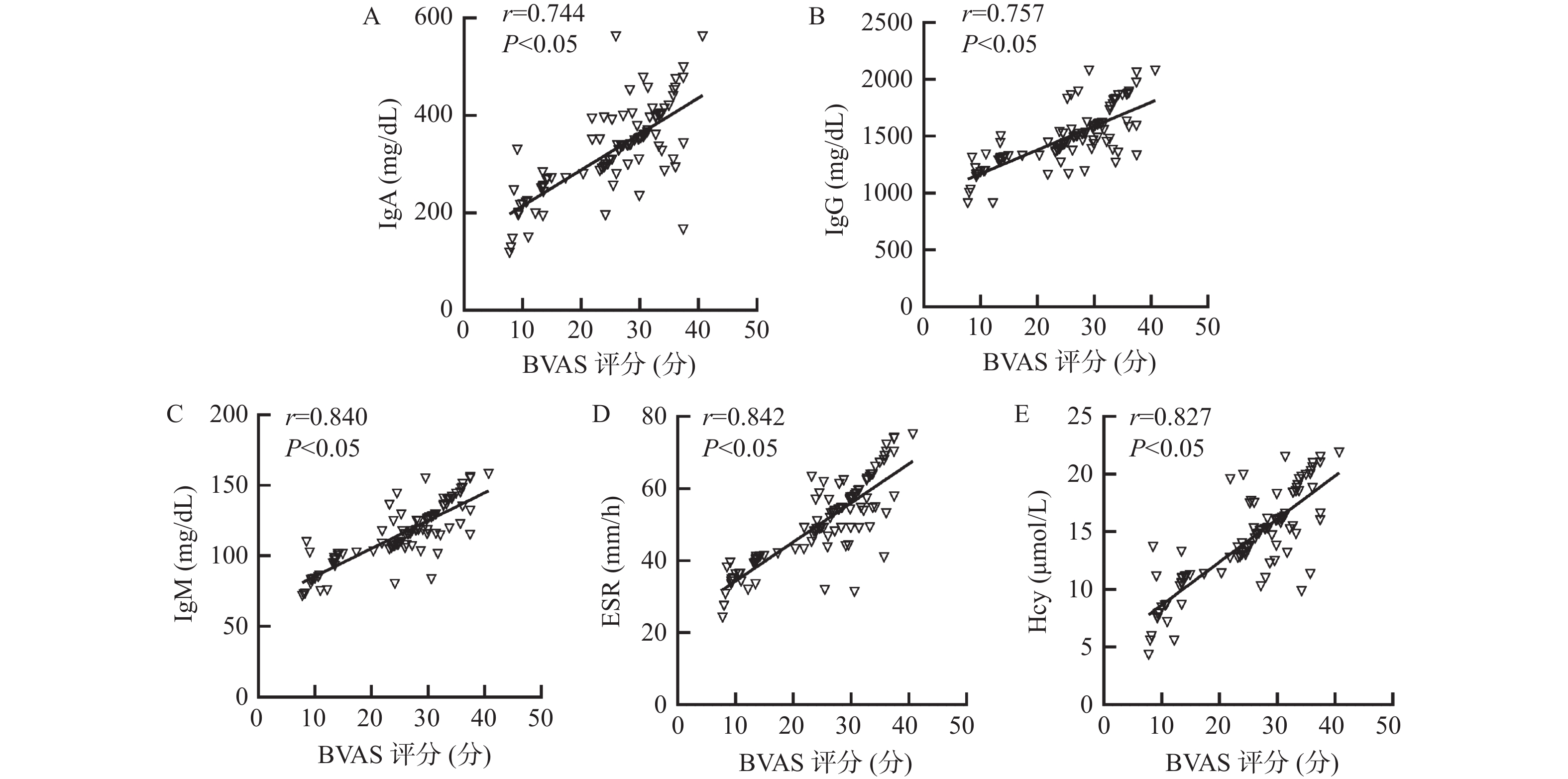
Objective To investigate the relationship between peripheral blood immunoglobulin, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), homocysteine (Hcy) and the severity of central nervous system vasculitis (CNSV) in children, as well as its impact on prognosis. Methods A total of 103 children with CNSV from February 2018 to February 2023 were selected as the study group, and 103 healthy children as the control group. The peripheral blood levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA), immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoglobulin M (IgM), ESR and Hcy were compared between the 2 groups to evaluate the relationship between each index and the degree of CNSV disease [Birmingham vasculitis disease activity score (BVAS)] and its predictive value for prognosis. Results The levels of peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy in the study group were higher than those in the control group of healthy children (P < 0.05); the BVAS scores and the levels of peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy in children with active disease were higher than those in children with inactive disease (P < 0.05); the levels of peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy were positively correlated with the BVAS scores in children with CNSV (P < 0.05); two cases were lost to follow-up after 6 months. Among the children with CNSV, 76 had good prognosis and 25 poor prognosis. The levels of peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy in children with poor prognosis were higher than those in children with good prognosis (P < 0.05); before and after correcting for other factors, peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy were all independent factors affecting the prognosis of children with CNSV (P < 0.05); the area under curve (AUC) of peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy for predicting the prognosis of children with CNSV was 0.747, 0.808, 0.841, 0.839, and 0.746, respectively, with optimal cutoff values of 350.58 mg/dL, 1513.06 mg/dL, 124.84 mg/dL, 51.22 mm/h, and 13.66 μmol/L, respectively; the AUC of peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy for jointly predicting the prognosis of children with CNSV was 0.943 (95%CI 0.878-0.979), with a sensitivity of 92.00% and a specificity of 93.42%, which was superior to individual prediction of each indicator. Conclusion Peripheral blood IgA, IgG, IgM, ESR and Hcy are positively correlated with the severity of CNSV. Abnormally high expression increases the risk of poor prognosis, and the combined predictive value is reliable.
2024, 45(12): 129-134.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241218
Abstract:
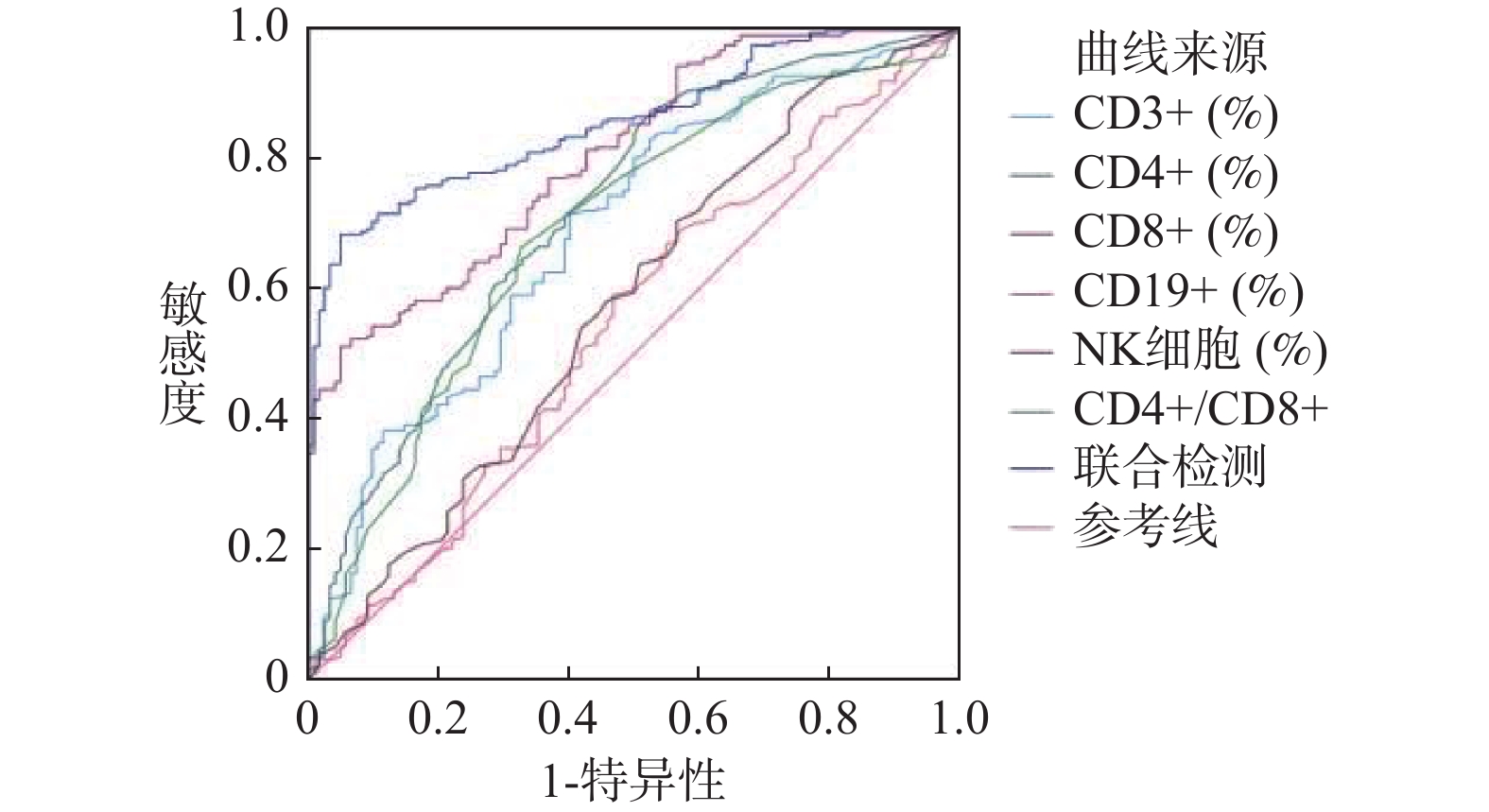
Objective To explore the early predictive value of lymphocyte subsets for cognitive impairment in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Methods A study was conducted on 68 patients with cerebral ischemia admitted to Honghe Hospital affiliated to Kunming Medical University from January 2023 to December 2023, divided into observation group (n = 30) and control group (n = 38).The general situation, lymphocyte subsets detection results and Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale (MoCA) score were compared. Their correlation, sensitivity, specificity were analyzed. Results The proportion of patients with diabetes and levels of CD3+, CD8+ and MoCA score in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05), the levels of CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, NK and CD19+ in the observation group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05); CD3+ and CD8+ were positively correlated with MoCA score (P < 0.05); CD4+, CD4+/CD8+, NK and CD19+ were negatively correlated with MoCA score (P < 0.05). The sensitivity and specificity of lymphocyte subsets combined detection for the diagnosis of cognitive dysfunction in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury were 93.45% and 100.00%, respectively. Conclusion The lymphocyte subsets have good predictive value for the occurrence of cognitive dysfunction in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. It can be used as a specific marker.
2024, 45(12): 135-140.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241219
Abstract:
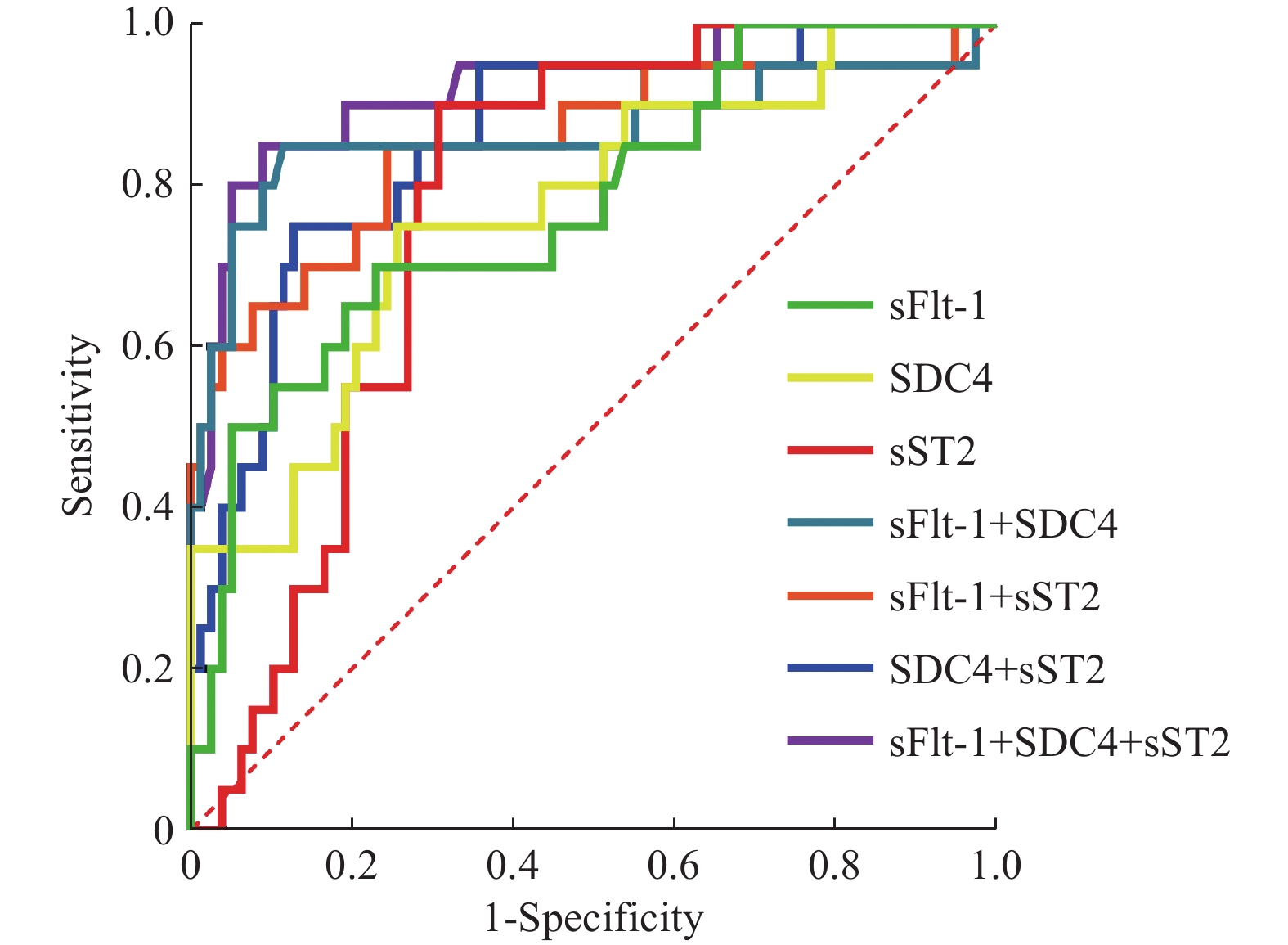
Objective To investigate the correlation between the levels of soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 (sFlt-1), polyligand proteoglycan-4 (SDC4), soluble human stromal lysin 2 (sST2) in serum and renal histopathological grading in children with Henoch-Schnlein purpura nephritis (HSPN), and analyze their predictive value for therapeutic efficacy. Methods A retrospective study was conducted, in which 98 children with HSPN admitted to Xinyang 154th Hospital from April 2021 to April 2023 were selected as the research subjects. According to the clinical efficacy after 2 months of treatment, they were divided into an effective group of 78 cases and an ineffective group of 20 cases. Their clinical data and the levels of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 before and after treatment were compared. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to analyze the factors affecting the efficacy. The predictive value of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 levels after 1 month of treatment on the efficacy after 2 months of treatment was analyzed. Results As the pathological grade increased, the levels of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 showed an upward trend (P < 0.05); the levels of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 in the ineffective group after 1 month of treatment were higher than those in the effective group (P < 0.05); the symptom score of purpura, immunoglobulin A (IgA) level, and the levels of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 after 1 month of treatment were independent risk factors for efficacy (P < 0.05); the AUC of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 levels combined to predict efficacy after 1 month of treatment was greater than that of any two combined predictions or single indicator predictions (P < 0.05). Conclusion The levels of serum sFlt-1, SDC4, and sST2 in children with HSPN are closely related to the pathological grading of the kidney tissue. The combined detection of their levels has certain predictive value for the therapeutic effect.
2024, 45(12): 141-146.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241220
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical application of salpingectomy with preserving salpingum mesothelium under single-port laparoscopy and its influence on ovarian reserve function and assisted pregnancy outcome. Methods From January 2019 to January 2022, 80 cases of salpingectomy in Shuangyashan Double Mine Hospital were selected and randomly divided into control group (n = 40) and observation group (n = 40) . The control group was treated with multi-hole laparoscopic salpingectomy with salpingum mesothelium preserved, while the observation group treated with single-hole laparoscopic salpingectomy with salpingum mesothelium preserved. The operation conditions (operation time, intraoperative blood loss, exhaust time, etc.), anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) before and one month after operation, ovarian function (basal sinus follicle count), postoperative complications, assisted pregnancy outcome and cosmetic effect were analyzed. Results The exhaust time and postoperative hospitalization time in the observation group were shorter than those in the control group, and the operation time was longer than that in the control group (P < 0.05). One month after operation, AMH in both groups decreased, and the number of sinus follicles in observation group A was lower than that in control group. The complication rate was lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05). After a one-year follow-up, there was no significant difference in ovulation rate and pregnancy rate between the two groups (P > 0.05). Follow-up for 3 months showed that the cosmetic effect of the observation group was better than that of the control group(95.00% vs 72.50%) (P < 0.05). Conclusion Single-port laparoscopic salpingectomy with salpingum mesothelium preservation is safe, cosmetic and minimally invasive, and has little adverse effect on ovarian reserve function, which is helpful for successful pregnancy assistance and worthy of clinical application and promotion.
2024, 45(12): 147-152.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241221
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between serum hepatitis B core anbody (anti-HBC), cholinesterase (CHE) and apolipoprotein AI (ApoAI) and the development of viral hepatitis. Methods 388 patients with viral hepatitis admitted to Nanjing Pukou District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from January 2021 to January 2024 were selected as the observation group, another 68 cases of health check-ups in medical check-up centre of Nanjing Pukou District Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine during the same period were selected as the control group. The serum levels of anti-HBC, CHE, and apolipoprotein AI between the observation group and the control group were compared. To compare the serum anti-HBC, CHE, ApoAI levels in patients with different disease severity of chronic hepatitis in the observation group. To compare the number of positive cases of serum anti-HBC, CHE, ApoAI in patients with different disease types in the observation group. To compare the serum anti-HBC, CHE, ApoAI levels in patients with different grades of cirrhosis in the observation group. Results Serum anti-HBC levels (4.52±0.63) log10PEIU/mL were higher in the observation group than in the control group (1.12±0.26) log10PEIU/mL, and the differences were statistically significant (t = -43.822, P < 0.001) , while CHE (4.09±0.91) kU/L, ApoAI (102.54±5.95) mg/dL were lower than the control group(10.65±1.73) kU/L, (120.17±6.06) mg/dL, and the differences were statistically significant (t = 46.580, 22.477, P < 0.001); differences in serum anti-HBC, CHE, and ApoAI levels among patients with different severity of chronic hepatitis in the observation group were statistically significant(P < 0.05), and the serum levels of anti-HBC levels showed mild chronic hepatitis < moderate chronic hepatitis < severe chronic hepatitis, while the levels of CHE and ApoAI showed mild chronic hepatitis > moderate chronic hepatitis > severe chronic hepatitis the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); the number of positive cases of serum anti-HBC, CHE, ApoAI in acute jaundiced hepatitis, severe chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma were significantly higher than those of chronic hepatitis in mild and moderate forms and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The differences in serum anti-HBC, CHE, and ApoAI levels in patients with different grades of cirrhosis in the observation group were statistically significant (P < 0.05) and serum levels of anti-HBC levels increased continuously with the progression of the disease, whereas CHE and ApoAI decreased continuously with the difference being statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The levels of serum anti-HBC in patients with viral hepatitis are significantly increased, while the levels of CHE and apolipoprotein AI are significantly decreased, and the levels of serum anti-HBC, CHE and apolipoprotein AI are related to the development of the disease, which contributes to the development of the disease.
2024, 45(12): 153-159.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241222
Abstract:
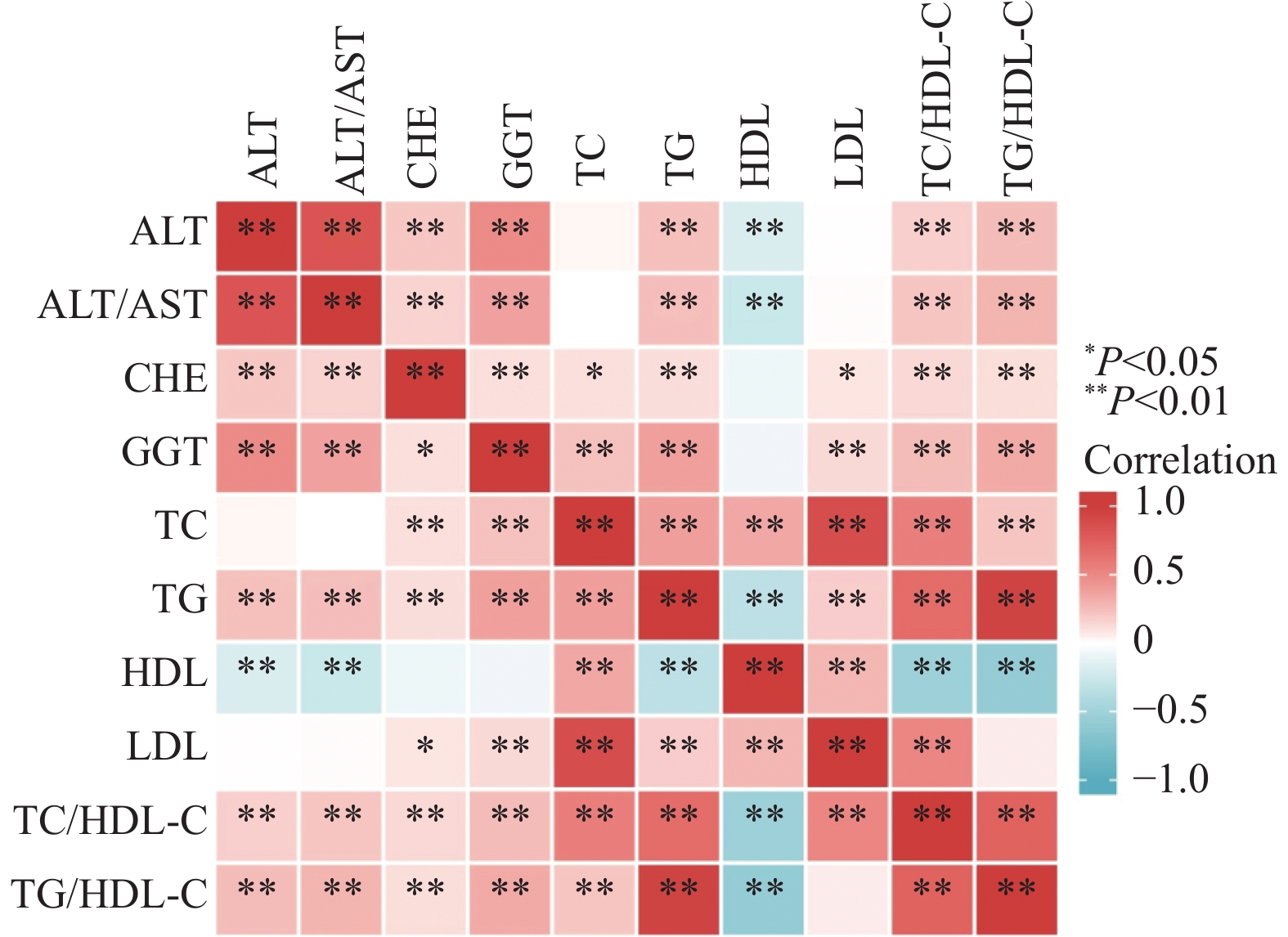
Objective To study the relationship between lipid metabolism and liver function indexes in prediabetic population, and explore the predictive value of these indexes for prediabetes. Methods 546 patients with prediabetes who underwent physical examination in the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University from April 2020 to August 2021 were selected as case group (PreDM group) and 546 patients with normal glucose tolerance as control group (NGT group). There was no significant difference in baseline data between the two groups after tendency matching score. The levels of lipid metabolism and liver function indicators were compared between the two groups; the correlation between lipid metabolism and liver function indicators in the PreDM group was analyzed; the influencing factors of prediabetes were screened by using binary logistic regression analysis; the predictive effect of lipid metabolism and liver function indicators on prediabetes was judged by using the ROC curve. Results Glutamic pyruvic transaminase (ALT), glutamic pyruvic transaminase/glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase ratio (ALT/AST), cholinesterase (CHE), gamma glutamyltransferase (GGT), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol/high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (TC/HDL-C) and triglyceride/high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio (TG/HDL-C) in PreDM group were higher than those in NGT group (all P < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis showed that TG/HDL-C in PreDM group had the positive correlation with ALT, ALT/AST, CHE and GGT (r = 0.256, 0.256, 0.293, 0.122, all P < 0.05). Multivariate stepwise logistic regression analysis showed that ALT/AST, GGT, TC/HDL-C and TG/HDL-C had the greatest effect on prediabetes (OR = 2.124, 1.027, 1.196, 1.260), and the combination of the four had the highest differential diagnostic value (AUC > 0.70). Conclusion There are more abnormal indexes of blood lipid and liver zymogram in prediabetic population, and the combination of ALT/AST, GGT, TC/HDL-C and TG/ HDL-C is more effective in predicting prediabetes.
2024, 45(12): 160-166.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241223
Abstract:
Intestinal flora and their metabolites play an important role in the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis (AS), and have become an important target for the prevention and treatment of AS. In this paper, we focus on the intestinal microecological environment and focus on the relationship between intestinal flora metabolites such as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), phenylacetylglutamine (PAG), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and bile acids (BA), and AS. At the same time, we also discuss the therapeutic strategies of AS that start from adjusting the intestinal flora and its metabolites, with the hope of opening up a new avenue of AS prevention and treatment. We hope to open up new avenues for the prevention and treatment of AS.
Intestinal flora and their metabolites play an important role in the occurrence and development of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis (AS), and have become an important target for the prevention and treatment of AS. In this paper, we focus on the intestinal microecological environment and focus on the relationship between intestinal flora metabolites such as trimethylamine oxide (TMAO), short-chain fatty acids (SCFA), phenylacetylglutamine (PAG), lipopolysaccharides (LPS), and bile acids (BA), and AS. At the same time, we also discuss the therapeutic strategies of AS that start from adjusting the intestinal flora and its metabolites, with the hope of opening up a new avenue of AS prevention and treatment. We hope to open up new avenues for the prevention and treatment of AS.
2024, 45(12): 167-171.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241224
Abstract:
Keloids are benign skin lesions that form during the wound healing process due to abnormal proliferation of fibroblasts and excessive extracellular matrix deposition. It is reported that 86% of keloid patients experience pruritus; however, the symptom of pruritus associated with keloids is often overlooked in clinical treatment. Review the pathogenesis and treatment of pruritusin keloids, with the goal of providing effective strategies for its management.
Keloids are benign skin lesions that form during the wound healing process due to abnormal proliferation of fibroblasts and excessive extracellular matrix deposition. It is reported that 86% of keloid patients experience pruritus; however, the symptom of pruritus associated with keloids is often overlooked in clinical treatment. Review the pathogenesis and treatment of pruritusin keloids, with the goal of providing effective strategies for its management.
2024, 45(12): 172-177.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241225
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application of the "learning by doing" learning theory and methods in the teaching of Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing for undergraduate nursing students. Method By setting up an experimental group of 151 students and a control group of 152 students in the teaching of Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing for undergraduate nursing students, practicing "learning by doing" and evaluating the teaching effect. Result The experimental group students held a positive attitude towards the implementation of "learning by doing" in the teaching of Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing for undergraduate nursing students, with higher scores in both theoretical and skill exams than the control group (P < 0.05), and achieved good practical results. Conclusion By comparing the theoretical and skill exam scores of the experimental group and the control group, the experimental group had a higher average score than the control group (P < 0.05). The application of "learning by doing" in the teaching of Obstetrics and Gynecology Nursing for undergraduate nursing has improved students' self-learning ability and empowered their innovative and collaborative growth.
2024, 45(12): 178-184.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241226
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the current demand for extended nursing services for newborns after discharge. Methods A survey was conducted on the demand for extended nursing services after discharge of newborns using the "Survey Form for Demand for Extended Nursing Services after Discharge of Newborns", and the results were analyzed. Results 62.30% of the data for this survey was provided by the father, possibly due to a Chinese tradition where mothers were confined at home during confinement after their child's discharge, making it inconvenient for them to go out. The educational level of parents was mainly undergraduate or above, with an age of 30.55±5.07 years old, mainly middle-aged and young; The top 5 scores for continuity of care content requirements were: reminder for follow-up visits (4.39±0.08) points, discharge medication guidance (4.35±0.92) points, health assessment (4.29±0.94) points, disease-related knowledge education (4.28±0.95) points, specialized nursing (4.17±1.05) points and basic nursing guidance (4.17±1.04) points;The top four scores of parents' demands for extended nursing channels were: telephone follow-up 2673 (85.45%), discharge education 2529 (80.85%), community two-way referral 2390 (76.41%), and health education network platform 2271 (72.60%) (such as WeChat official account, forum, Tiktok live broadcast); Family members hope that 2340 doctors (74.81%) and 1764 hospital nurses (56.39%) were still the main executors of extended services provided by the hospital; After discharge, if necessary due to the condition, medical staff would come to your doorstep to provide corresponding medical care services. Patients agreed to pay 2759 cases (88.20%) according to the price standard, with the majority agreeing to pay 2189 cases (69.98%) for consultation fees, 2057 cases (65.76%) for material fees and 1997 cases (63.84%) for diagnosis, treatment, and nursing fees. Conclusion Providing continuous extended care services during and after the discharge of newborns can reduce their readmission rate, promote physical development, and reduce complications. With the development of medical technology and information technology, parents of newborns have an increasing demand for extended care services, and it is imperative to carry out extended care services.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS