2025 Vol. 46, No. 2
2025, 46(2): 1-8.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250201
Abstract:
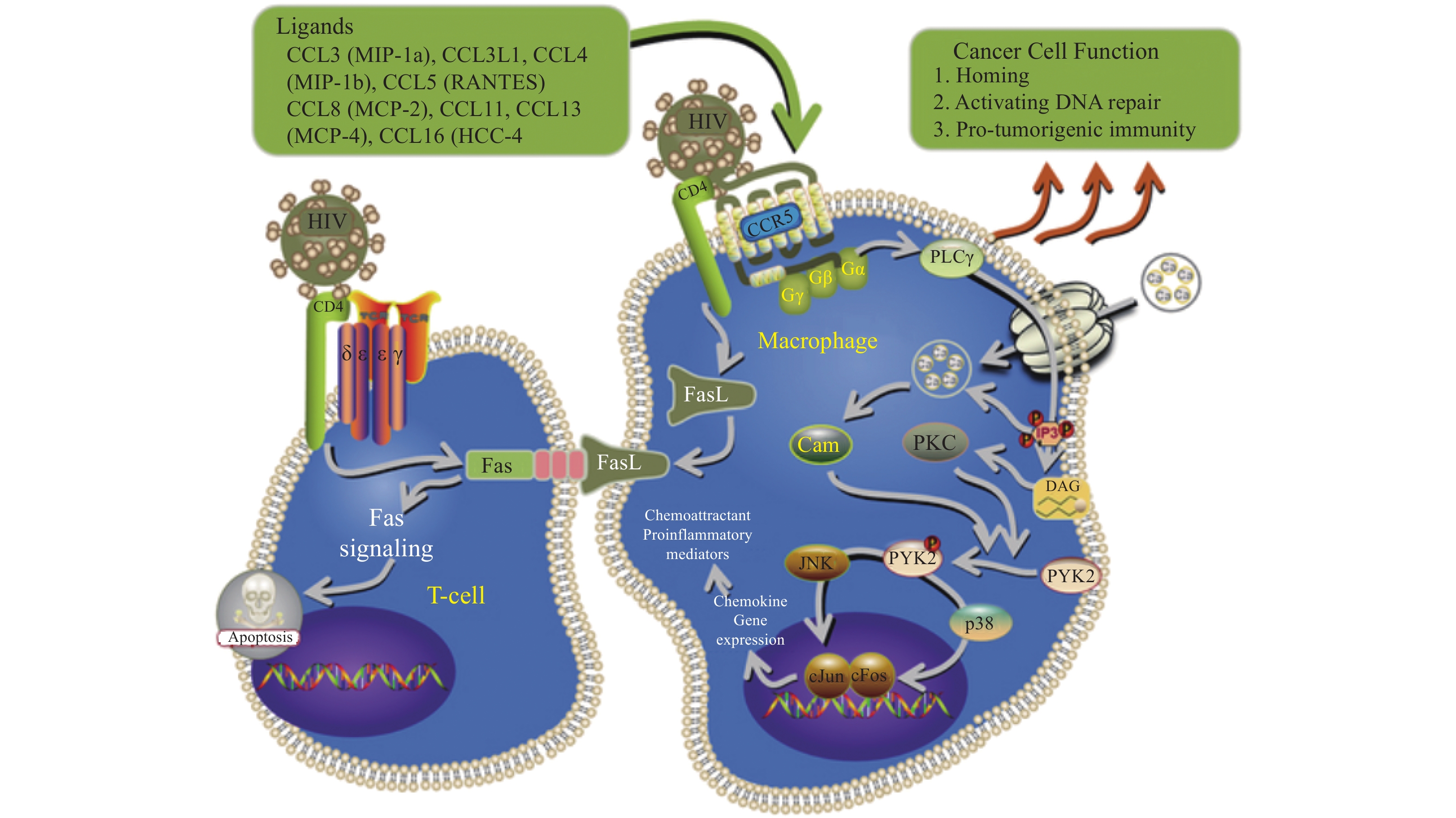
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a systemic disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL3), as a vital member of the chemokine family, plays an indispensable role in the pathogenesis of AIDS. In the context of AIDS, CCL3 exerts significant antiviral and immunomodulatory effects by preventing HIV entry into target cells, activating immune cells to enhance antiviral capabilities, and modulating inflammatory responses, thereby influencing disease progression. Numerous studies have demonstrated that CCL3 gene copy number, specific T-cell responses, CCL3 polymorphisms, and the signaling pathways it participates in all influence the development of HIV and viral load. This article comprehensively reviews the multifaceted roles of CCL3 in AIDS, including its ability to block HIV-1 entry into immune cells, inducing the expression of antiviral proteins to inhibit viral replication, as well as the influence of its polymorphisms and alleles on HIV infection and disease progression, aiming to provide novel theoretical support for AIDS prevention and treatment strategies.
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) is a systemic disease caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (CCL3), as a vital member of the chemokine family, plays an indispensable role in the pathogenesis of AIDS. In the context of AIDS, CCL3 exerts significant antiviral and immunomodulatory effects by preventing HIV entry into target cells, activating immune cells to enhance antiviral capabilities, and modulating inflammatory responses, thereby influencing disease progression. Numerous studies have demonstrated that CCL3 gene copy number, specific T-cell responses, CCL3 polymorphisms, and the signaling pathways it participates in all influence the development of HIV and viral load. This article comprehensively reviews the multifaceted roles of CCL3 in AIDS, including its ability to block HIV-1 entry into immune cells, inducing the expression of antiviral proteins to inhibit viral replication, as well as the influence of its polymorphisms and alleles on HIV infection and disease progression, aiming to provide novel theoretical support for AIDS prevention and treatment strategies.
2025, 46(2): 9-16.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250202
Abstract:
Objective To explore the the detection of MMP-2, -7, -9, and -12 enzymatic activity using the CEACAM1-derived fluorescent peptide substrate Site 84, investigating the application of substrate Site 84 to distinguishing between MMP-2 and MMP-9 in the gelatinase spectrum of MMPs. Methods The fluorescent enzymatic method was employed to observe the detection of MMP-2, -7, -9, and -12 enzymatic activity using substrate Site 84; further observations were made on the sensitivity and specificity of substrate Site 84 to enzymatic activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 within the gelatinase spectrum; the kinetic parameters (Km and Kcat) of the enzymatic reaction between substrate Site 84 and MMP-2 were obtained. Results Using Site 84 as a substrate, enzymic kinetics curves for MMP-12, -7, -2 were obtained, but no enzymatic activity curve for MMP-9 was observed. Furthermore, Site 84 specifically detected the enzymatic activity of MMP-2 within the gelatinase spectrum, capable of detecting low concentration (0.6 μM) of MMP-2 enzymatic activity, but no obvious enzymatic reaction was observed for high concentration (6 μM) of MMP-9; the kinetics parameters for the enzymatic reaction between Site 84 and MMP-2 were Km = 315 μM, Kcat/Km = 2565 /MS. Conclusion The CEACAM1-derived substrate Site 84 serves as a novel fluorescent peptide substrate, enabling the acquisition of enzymatic activity curves for MMP-12, -7 and -2, and specifically detecting the enzymatic activity of MMP-2 within the MMP gelatinase spectrum.
2025, 46(2): 17-22.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250203
Abstract:
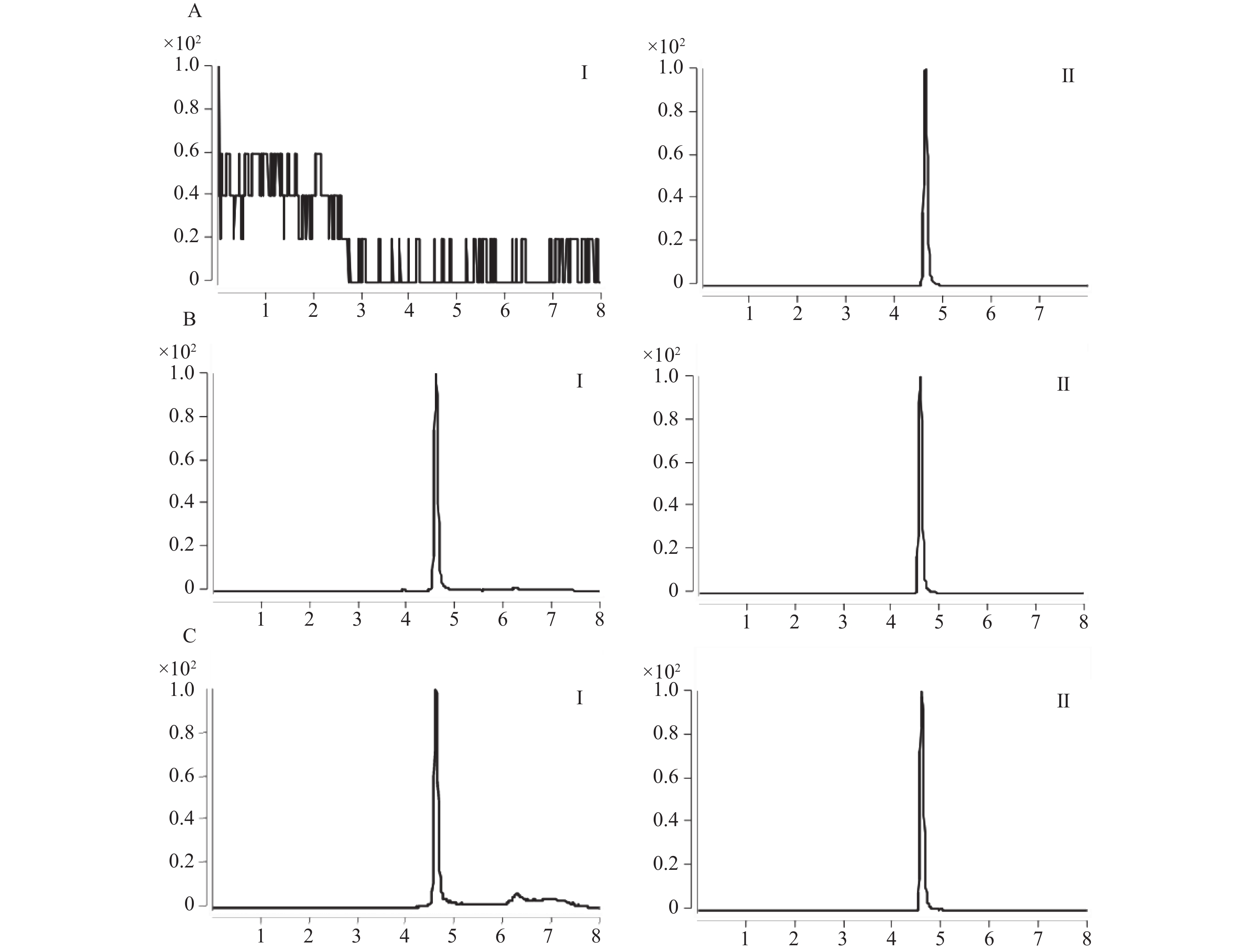
Objective To explore the enzymatic reaction kinetics of metoprolol tartrate in an in vitro human liver microsome incubation experiment and to explore the effect of famotidine on the metabolism of metoprolol tartrate. Methods An LC-MS/MS method was developed to accurately measure the concentration of metoprolol tartrate in a human liver microsomal incubation system. A human liver microsome incubation system was established to determine the optimal incubation time and protein concentration; using the substrate depletion method, the enzymatic reaction kinetics parameters of metoprolol tartrate (such as Vmax and Km). Series concentrations of famotidine were co-incubated with metoprolol tartrate, and the concentration of metoprolol tartrate was measured to evaluate the effect of famotidine on its metabolism. Results The optimal incubation time for metoprolol tartrate in human liver microsomes was found to be 60 minutes, with an optimal protein concentration of 1.0 mg/mL. The enzymatic reaction kinetics parameters were Vmax = 0.07 µmol/min/mg protein and Km = 7.84 µmol/L. Conclusion The results indicated that famotidine did not produce a significant inhibitory effect on the metabolism of metoprolol tartrate in human liver microsome incubation system, suggesting that the combination of these two drugs may be relatively safe.
2025, 46(2): 23-29.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250204
Abstract:
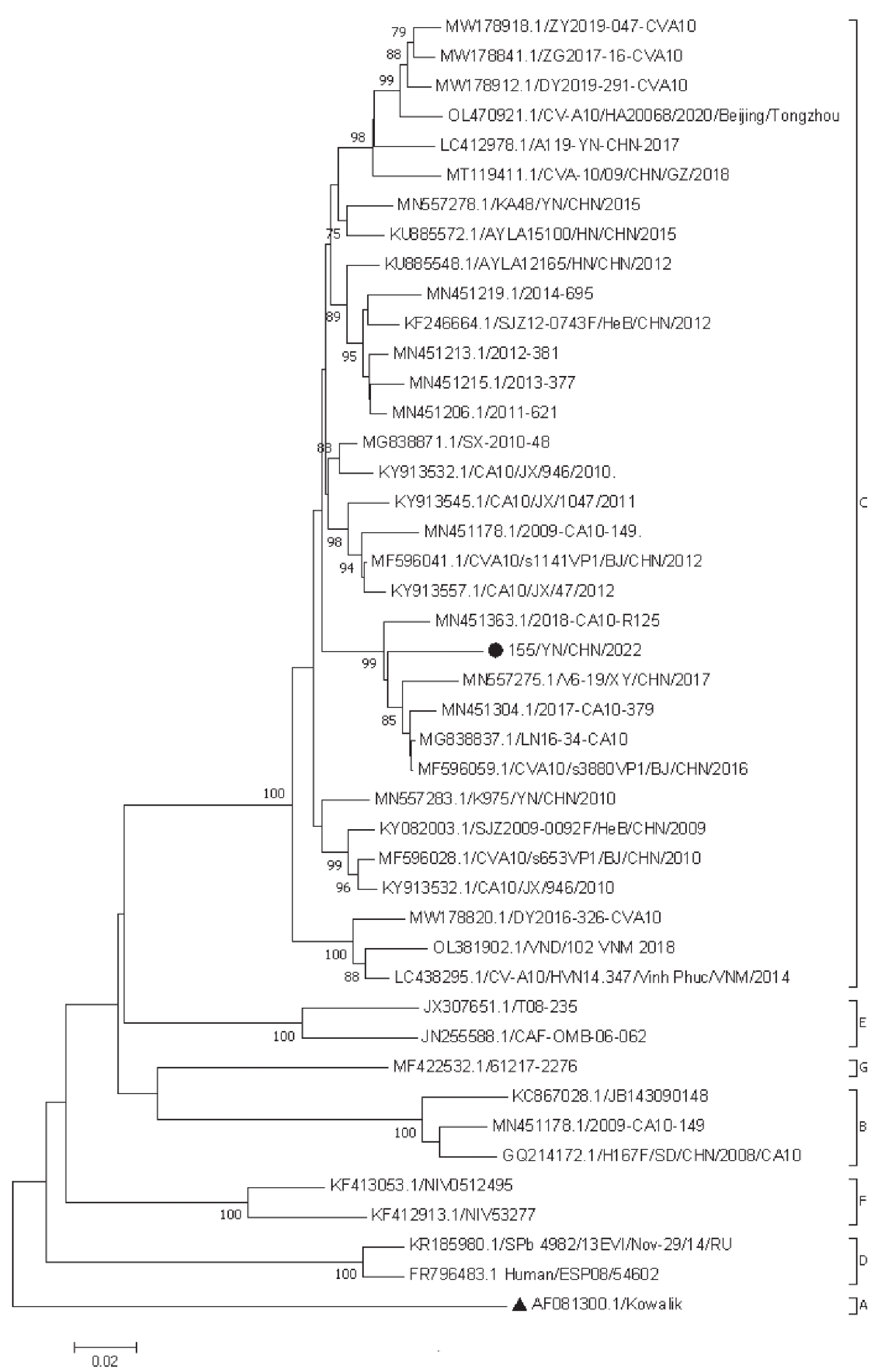
Objective To analyze the whole-genome characteristics of a coxsackievirus A10 (CVA10) isolate obtained from fecal samples of children with hand, foot, and mouth disease in 2022. Methods The isolate was obtained from human rhabdomyosarcoma (RD) cells and named 155/YN/CHN/2022. Viral RNA was extracted, and the VP1 sequence was amplified by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to identify the serotype. The whole genome sequence of 155/YN/CHN/2022 was amplified and assembled. Sequence analyses were performed using software such as MEGA7.0, DNAStar7.1, and Simplot3.5.1. Results The complete genomic sequence of CVA10 isolate 155/YN/CHN/2022 was 7403 nt long, with a 746 nt 5'UTR region, a 76 nt 3'UTR region, and a 6551 nt coding region. The nucleotide and amino acid sequence identities of this isolate compared to the prototype strain of CVA10 were 78.43% and 95.30%, respectively, while the identities compared to other domestic and foreign CVA10 isolates ranged from 91.18% to 95.06% for nucleotide sequences and 97.63% to 98.54% for amino acid sequences. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that 155/YN/CHN/2022 belonged to the C genotype. Phylogenetic analyses of P1, P2, and P3 regions suggested this isolate may have undergone recombination with other serotype strains in the P2 and P3 non-coding regions. Simplot recombination analysis also indicated possible recombination events in the non-coding regions of P2 and P3 for CVA10 isolate 155/YN/CHN/2022. Conclusion CVA10 isolate 155/YN/CHN/2022 belongs to the genotype C, which is consistent with recent epidemic strains in China's mainland.
2025, 46(2): 30-36.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250205
Abstract:
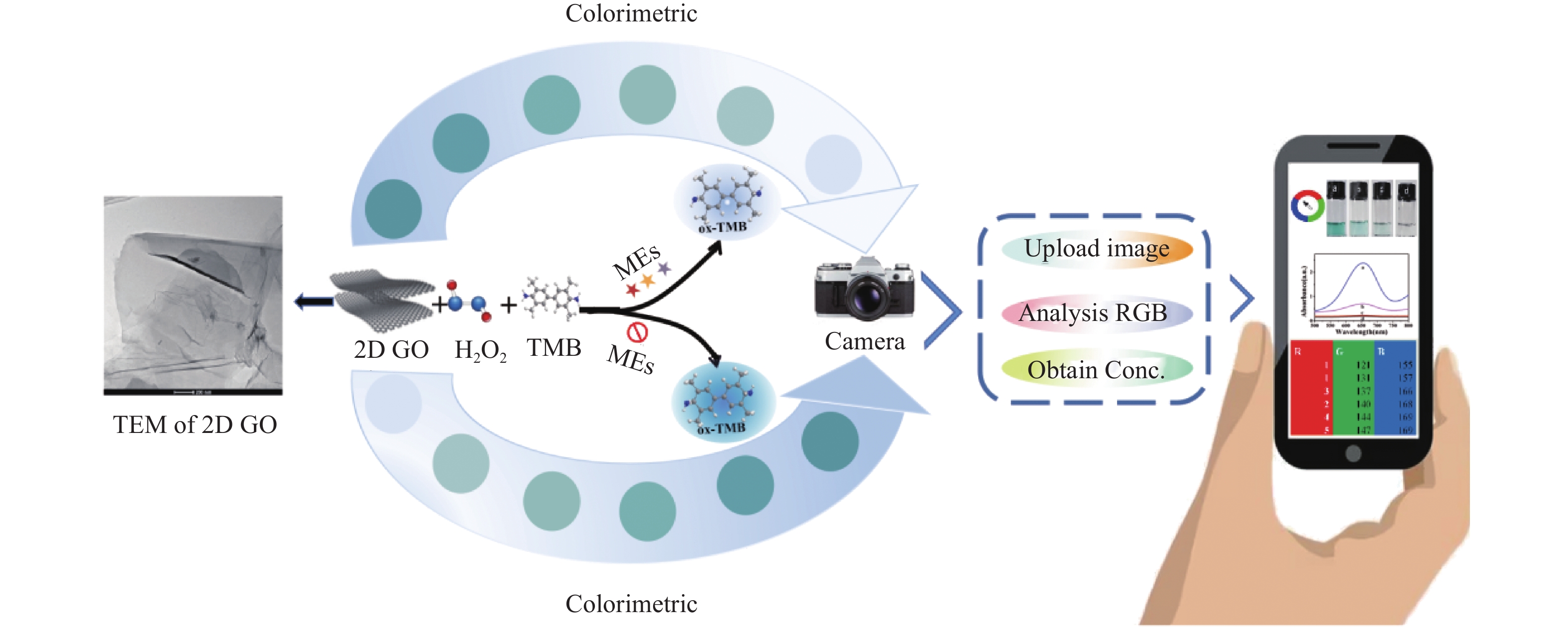
Objective To develop a method capable of real-time, rapid, and visual detection of MEs , providing a powerful tool for early diagnosis and assessment of diseases. Methods In this study, flake graphene oxide (2D GO) with excellent peroxidase-like activity (POD-like) was prepared by a modified Hummers' method, and a sensing strategy for the rapid visual detection of MEs was constructed by integrating colorimetry with a smartphone. Results 2D GO can catalyse the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to produce highly oxidative hydroxyl radicals (·OH), which oxidize the colourless 3, 3', 5, 5'-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) into blue ox-TMB. The strong reducing effect of MEs on the "2D GO + TMB + H2O2" colorimetric sensing system enables rapid visual detection of MEs. Conclusion The colorimetric platform constructed based on 2D GO has a wide linear detection range (10-1000 μmol/L) and a good detection limit (LOD < 7 μM), and was successfully used for the determination of MEs in foetal bovine serum samples, with satisfactory recovery rates.
The Effect of 1800 MHz Electromagnetic Radiation on Learning and Cognitive Functions in 3xTg-AD Mice
2025, 46(2): 37-43.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250206
Abstract:
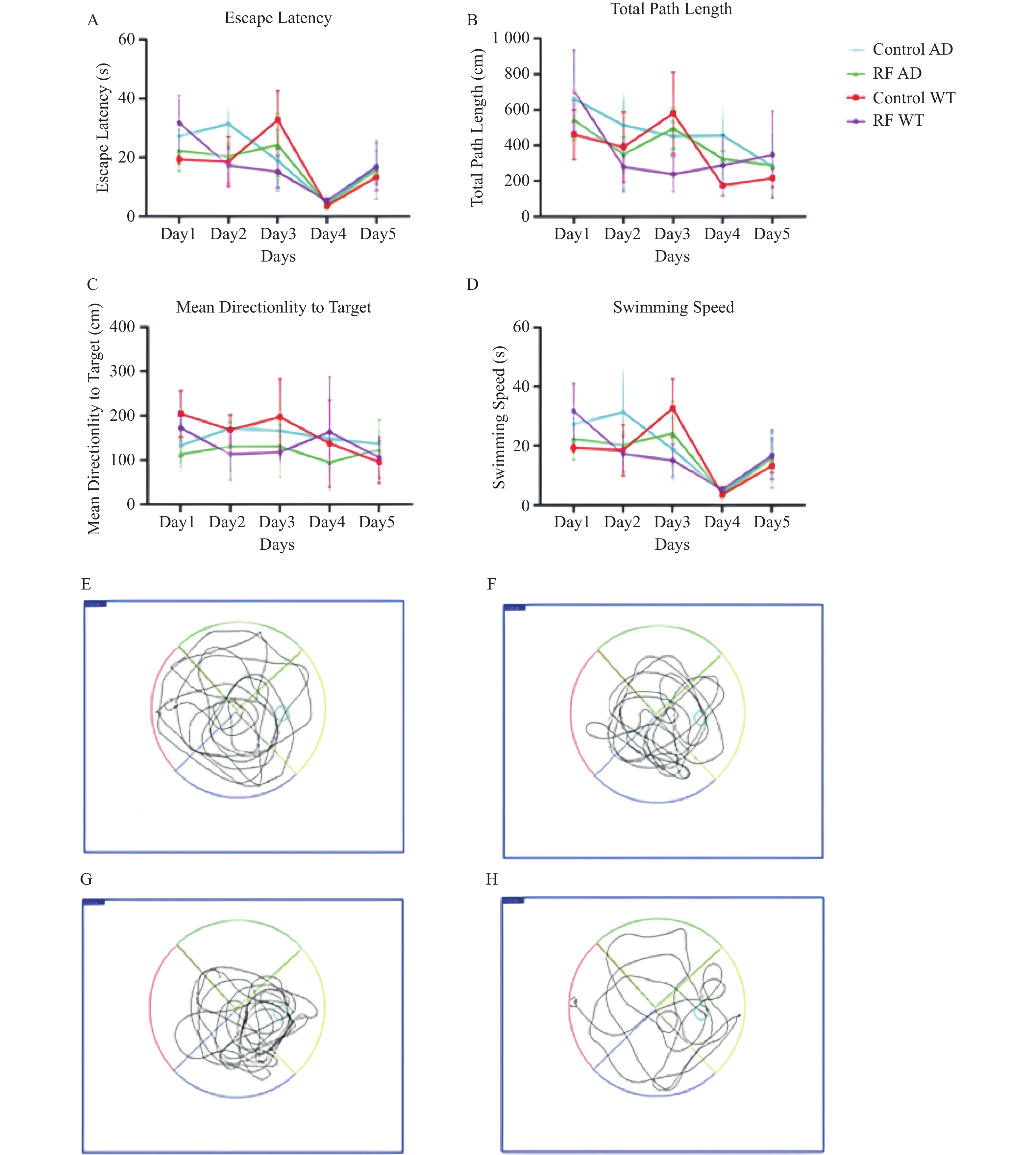
Objective To explore the effects of 1800 MHz electromagnetic radiation (EMR) on cognitive function of 3xTg-AD and 57C mice, providing a theoretical basis for the potential impacts of electromagnetic radiation on the human body. Methods A total of 12 3xTg-AD transgenic mice and 12 wild-type C57 mice were selected as research subjects. The one-month-old mice were divided into four groups: RF WT, Control WT, RF AD, and Control AD, with 6 mice in each group.The 1800 MHz EMR exposure experiments were conducted from 20:00 to 8:00 the next day for a duration of 5 months. After the exposure, a water maze test was conducted to evaluate the effects of EMR on spatial learning and memory abilities of 3xTg AD mice, along with measurements of body weight, brain weight, and calculation of the brain-to-body ratio. Finally, Western Blot technique was used to measure the levels of APP, NR1, and NR2A in hippocampal tissue to analyze effects of 1800 MHz EMR on the cognitive function of 3xTg AD mice. Results Under 1800 MHz EMR exposure, there were no statistically significant differences in Morris water maze spatial learning ability among the four groups (P > 0.05). However, longer escape time, greater swimming distances, and more crossings of target quadrant were exhibited in the RF AD group compared to the other groups (P < 0.05). Western Blot results showed that the APP protein levels in 3xTg AD mice was higher than those in C57 mice (P < 0.05). The expression levels of NR1 protein in the WT group was higher than those in the AD group (P < 0.05); in the AD group, the RF AD group had higher levels than the Control WT group (P < 0.05), and the NR2A protein levels in the Control WT group were higher than in the other groups (P < 0.05). Conclusion Prolonged exposure to 1800 MHz EMR can affect the learning and cognitive function of both 3xTg AD and C57 mice.
2025, 46(2): 44-50.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250207
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) rs57095329 and rs6864584 of miR-146a gene and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) . Methods A total of 96 patients diagnosed with CIN were randomly collected as the CIN group, and 225 healthy individuals examined during the same period were selected as the control group using SPSS software. Genotyping of the above SNP loci was performed using the TaqMan probe method, and their correlation with CIN was analyzed. Results The allele and genotype distribution of rs57095329 showed a statistically significant differences compared to the control group, with the frequency of the allele A in the CIN group significantly lower than that in the control group (P < 0.001; OR = 0.48, 95%CI: 0.32~0.70). In the dominant model, individuals carrying the G allele (A/G-G/G) had a significantly increased risk of CIN (P < 0.001; OR = 2.67, 95%CI: 1.64~4.37). In contrast, no correlation was found between the rs6864584 and the risk of CIN. Conclusion The A allele of the miR-146a gene at the rs57095329 locus may be a protective factor for CIN.
2025, 46(2): 51-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250208
Abstract:
Objective To explore the correlation between serum vitamin D (VD3) level differences and immune inflammatory markers in elderly sepsis patients. Methods A total of 103 elderly patients with sepsis(aged 65-99 years) in the ICU of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2020 to December 2022 were collected and divided into two groups according to the diagnostic criteria for VD3 deficiency: VD3 deficiency group (n = 32) and VD3 severe deficiency group (n = 71). Correlation analysis was conducted by comparing the differences in serum 25- (OH) - D3 (VD3) levels , immune function-related indicators upon admission (blood routine, infection-related proteins, combined detection of 12 cytokines, absolute count analysis of lymphocytes and subgroups, quantitative determination of infection-related immune cells, immunoglobulin, and complement), illness severity, and prognostic indicators (APACHE-II score, SOFA score, duration of ICU stay, and 28-day mortality rate). Result (1) Serum VD3 levels were lower in elderly patients with sepsis. No patient was in the VD3 normal or insufficient group. Patients with severe VD3 deficiency had higher APACHE-II scores, SOFA scores, and 28- day mortality rates than those with VD3 deficiency, and these scores were negatively correlated with serum VD3 levels (P < 0.001), while the difference in ICU stay duration between the two groups was not statistically significant (P > 0.05); (2) WBC, PCT, CRP, and CD4/CD8 in the VD3 deficiency group were all lower than those in the VD3 severe deficiency group (P < 0.05), while IL-6, IL-10, CD45+, CD3+/CD45+, and CD19+Abs were all higher than those in the VD3 severe deficiency group (P < 0.05); In the VD3 deficiency group, VD3 levels were positively correlated with CD45+(P < 0.05 for all), while negatively correlated with IL-6, IL-10, PCT, and CRP (P < 0.05 for all); In the VD3 severe deficiency group, there were fewer correlation indicators and the correlation strength was not as strong as that in the VD3 deficiency group. Conclusion (1) Elderly patients with sepsis generally have lower levels of VD3, with lower levels associated with more severe illness and poorer prognosis; (2) In elderly sepsis patients, compared to patients with severe VD3 deficiency, patients with VD3 deficiency have lower levels of inflammation, stronger cellular immune response, and stronger correlation, suggesting that the effects of different VD3 levels on immune inflammatory responses may vary in elderly sepsis patients.
2025, 46(2): 59-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250209
Abstract:
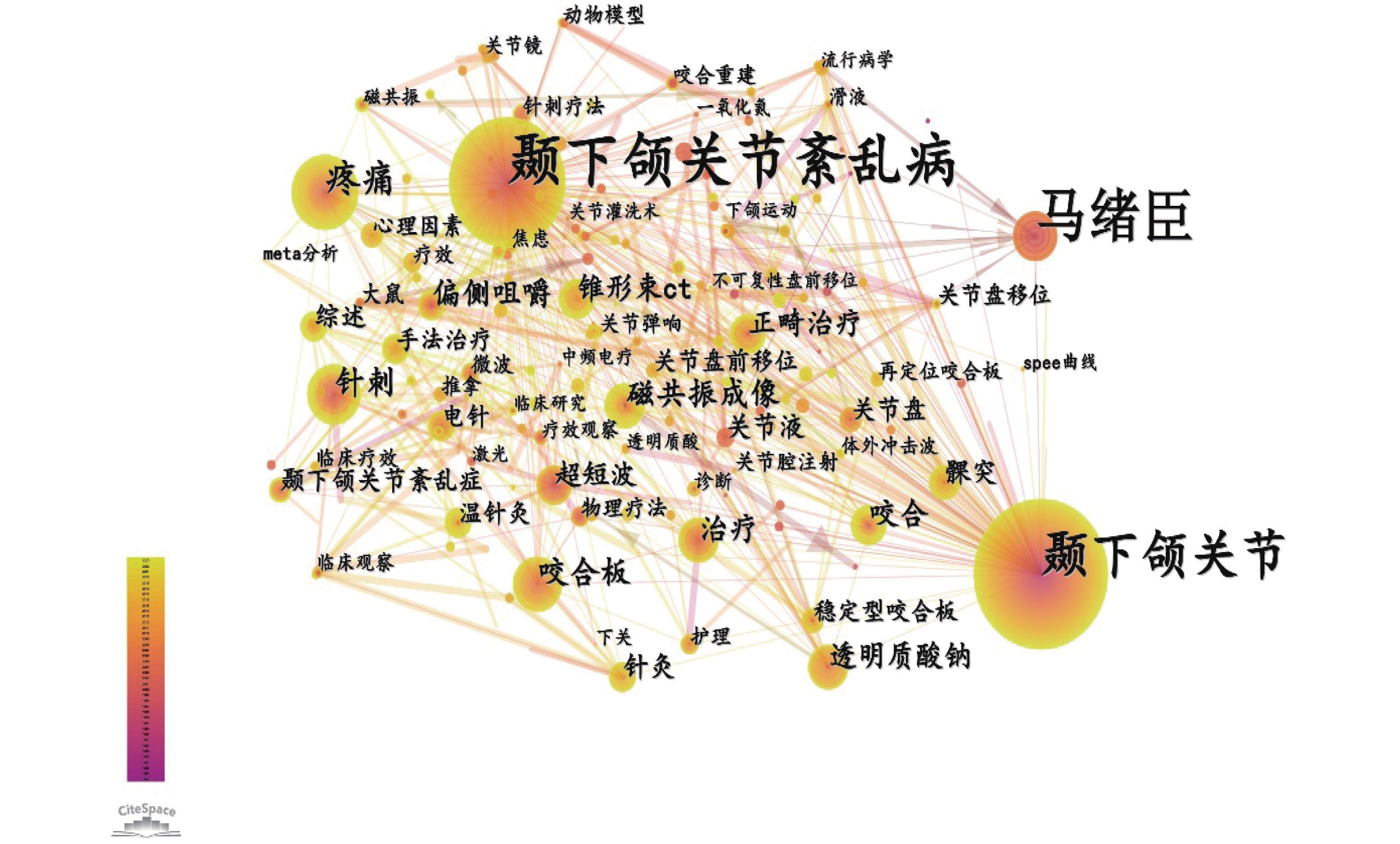
Obejective Based on the Citespace software, this study aims to comb the research hotspots and core contents of the development process of the TMD field in China, and carefully understand the research evolution process of the Temporo-mandibular Disorders (TMD) related fields in China, clarify its development timeline. Methods Using CNKI as the database source, through CiteSpace 6.1R6, we completed keyword co-occurrence, keyword clustering and emergence, and timeline knowledge mapping, and conducted a retrospective analysis of TMD-related literature published in China. Results A total of 2,034 domestic articles related to TMD were counted, and the development characteristics were obtained through data analysis: the treatment methods of TMD had evolved from combining traditional Chinese and Western medicine to Western medicine taking the dominant position, the research population had evolved from special populations to the general population, the focus had shifted from TMD itself to TMD-related and concurrent diseases, and the scope of research had continued to expand. Conclusions The development of literature on TMD disease has gone through three different periods, and there has been a significant shift in the research hotspots of TMD in China. The popularization rate of disease knowledge in TMD is not high, and further education needs to be provided to the general public.
2025, 46(2): 67-73.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250210
Abstract:
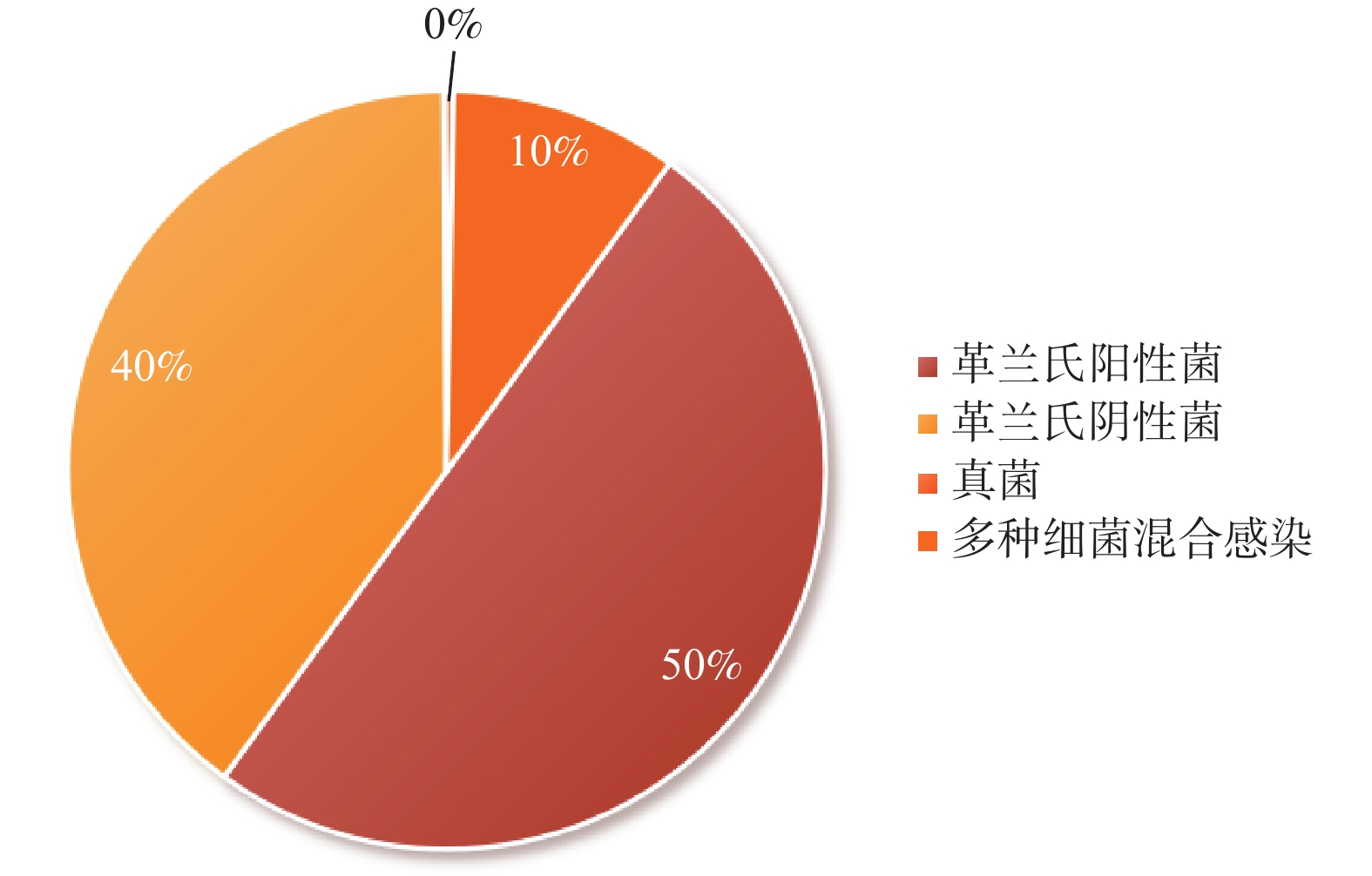
Objective To study the pathogenic bacteria infection in hospitalized diabetic foot patients in the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province and its correlation with different Wagner grades, to understand the the characteristics of pathogenic bacteria and related risk factors in hospitalized diabetic foot patients in the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province, and to further provide theoretical guidance for anti-infection treatment of these patients. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the demographic data, severity of foot ulcers, and related laboratory test results of 536 patients with diabetic foot who were detected to have bacterial infection in the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2019 to January 2023. Results Among the 536 diabetic foot patients, pathogenic bacteria were cultured from 268 cases (50.0%) of Gram-positive bacterial infections, 214 cases(39.9%) of gram-negative bacterial infections, 2 cases(0.4%) of fungal infections, and 52 cases (9.7%) of mixed bacterial infections. The main pathogens among gram-positive bacteria were Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis and Enterococcus faecalis. for Gram-negative bacteria, the main pathogens were Escherichia coli, Enterobacter cloacae and Klebsiella pneumoniae.There were 31 cases of multi-drug resistant bacteria, and the multi-drug resistance rate was (5.78%). Among Gram-positive bacteria, all multidrug-resistant strains were Staphylococcus aureus, while among Gram-negative bacteria, the multi-drug resistant strains included Acinetobacter baumannii (1 case), Klebsiella pneumoniae (2 cases), Proteus common (2 cases), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (5 cases), Proteus mirabilis (1 case) and Enterobacter cloacae (1 case). The 536 patients were divided into Wagner grade 1 and 2 groups (78 cases), Wagner grade 3 group (274 cases), and Wagner grade 4 and 5 groups (184 cases). There were 73 cases of single bacterial infections and 5 cases of mixed bacterial infections in Wagner grade 1 and 2 group, including 51 cases (65.4%) of gram-positive bacteria, 21 cases (26.9%) of gram-negative bacteria and 1 case (1.3%) of fungi. There were 248 cases of single bacterial infections and 26 cases of mixed bacterial infections in Wagner3 group, with 144 cases (52.6%) of gram-positive bacteria, 103 cases (37.6%) of gram-negative bacteria, and 1 case (0.4%) with fungi. In the Wagner grade 4 and 5 groups, there were 163 cases of single bacterial infections and 21 cases of mixed bacterial infection, with 73 strains( 39.7%) of gram-positive bacteria, 90 strains (48.9%) of gram-negative bacteria and 0 strain (0%) of fungi.The predominant infectious pathogens in Wagner grades 1, 2 and 3 were gram-positive bacteria, while those in Wagner grades 4 and 5 patients were mainly gram-negative bacteria. There were statistically significant differences in white blood cell counts, neutrophil percentage, bacterial classification, length of hospital stay, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and albumin levels among diabetic foot patients with different Wagner grades (P < 0.01). With the increase of Wagner grade, patients had higher white blood cell counts and hypersensitive C-reactive protein levels, longer hospital stays, and lower albumin levels; however, there were no statistically significant differences in age, sex, duration of diabetes, smoking history, alcohol consumption history and history of hypertension (P > 0.05). Conclusion The bacterial infection situation in patients with diabetic foot ulcers is related to different Wagner grades. The higher the Wagner grades, the greater the likelihood of infection with gram-negative bacteria. Antibiotics can be reasonably selected according to the Wagner grades of patients upon admission, actively controlling infection, while also enhancing, shortening hospital stays, and reducing amputation rates, thereby improving the prognosis of diabetic foot patients.
2025, 46(2): 74-79.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250211
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the predictive value of the preoperative fasting Triglyceride-Glucose index (TyG) for contralateral new silence ischemic brain lesions (CNSIBL) following carotid artery stenting (CAS). Methods A retrospective study was conducted to analyze the clinical data of 183 patients who underwent carotid CAS. The patients were divided into a CNSIBL group (50 cases) and a non-CNSIBL group (133 cases) based on the occurrence of CNSIBL. Baseline data, laboratory tests, and imaging indicators were collected, and TyG was calculated. Using the occurrence of CNSIBL as the dependent variable, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed with TyG as the independent variable after controlling for confounding factors, and the predictive value of TyG for CNSIBL post-CAS was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Results (1)The number of patients with a history of diabetes mellitus, as well as systolic and diastolic blood pressure on admission in CNSIBL group were statistically significantly higher than that in non-CNSIBL group(P < 0.05).(2) Triglyceride (TC) levels were higher in the CNSIBL group compared to the non-CNSIBL group(P < 0.05); TyG was also higher in the CNSIBL group than in the non-CNSIBL group (P < 0.05); (3) Multivariate Logistic regression analysis results showed that TyG [a OR = 1.125, 95%CI (1.042−1.214), P < 0.001]was an independent risk factor for contralateral new silent ischemic brain lesions after carotid artery stenting;(4) The ROC curve suggested that the AUC for TyG predicting contralateral new silent ischemic brain lesions post-CAS was 0.77 [95%CI (0.71−0.84), P < 0.001], with a cut-off value of 1.93, sensitivity of 86.0%, and specificity of 63.9%. Conclusion TyG is an independent influencing factor for contralateral new silent ischemic brain lesions following carotid artery stenting.
2025, 46(2): 80-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250212
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between physical activity duration, sleep quality, weight control, and PRO(patient- reported outcomes) in individuals with hypertension, providing effective information for enhancing patient-reported outcomes in this population. Methods A total of 625 hypertensive patients were randomly selected from four counties in Yunnan Province from April to June 2020 to participate in a field survey. The questionnaire included patients' basic information, lifestyle, health status and the PRO Scale for Hypertension-PROISCD-HY (V1.0). Statistical analyses including t-tests, one-way ANOVA, and multivariate linear regression were conducted to investigate the relationships between physical activity duration, sleep quality, weight control, and PRO, with the Bootstrap method used to examine potential mediating effects. Results After adjusting for potential covariates, the multiple linear regression model indicated a significant association between a physical activity duration of ≥2 hours with PRO[B = 6.551, 95%CI(2.611, 10.491)]. Stratified analysis showed that this association was only present among males, females, and younger adults, but not in older adults. Additionally, a positive correlation was found between good sleep quality and PRO[B = 1.870, 95%CI(0.449, 3.291)], with this association being consistent across all populations after stratification. Patients who managed their condition through exercise and diet had higher PRO scores[B = 1.904, 95%CI(0.383, 3.424)], while those controlling weight through diet and other methods exhibited a decrease in PRO scores[B = -4.873, 95%CI(-7.860, -1.887); B = -7.105, 95%CI(-12.211, -1.999)], with variations among different groups. The bootstrap method revealed that physical activity duration had both direct and indirect effects on PRO, with sleep quality acting as a partial mediator between physical activity duration and PRO. Conclusion A Physical activity duration of at least 2 hours, good sleep quality, and weight control have been shown to improve PRO in individuals with hypertension.
2025, 46(2): 88-94.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250213
Abstract:
Objective To explore the correlation between blood biochemical indexes and blood pressure levels among college students in Kunming City. Methods In November 2021, a cluster sampling method was used to survey 4,781 college students at a university in Yunnan Province. Data collected included height, weight and blood pressure, and blood samples were collected for blood biochemical testing. The Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis H test were used to compare the distribution differences of hypertension among college students with different demographic characteristics, while a generalized linear model was used to analyze the correlation between blood biochemical indicators and blood pressure levels. Results The prevalence rate of hypertension among college students was 8.45% (404/4781 ). After adjusting confounding variables, blood glucose (GLU, β = 1.48, 95%CI : 0.75~2.20) and serum Total Protein (TP, β = 0.25 , 95%CI : 0.19~0.32) were found to be correlated with systolic blood pressure (SBP) levels (all P < 0.05); blood glucose (GLU, β = 1.25, 95%CI : 0.64~1.86) and serum total protein (TP, β = 0.28, 95%CI : 0.23~0.34) were correlated with diastolic blood pressure (DBP) level (P < 0.05). Stratified group analysis by sex showed that, after controlling for confounding factors, TP (β = 0.32, 95%CI : 0.18~0.45) was correlated with SBP levels in male students; TP (β = 0.32, 95%CI : 0.21~0.43) was correlated with DBP levels in male students (P < 0.05). GLU (β = 2.18, 95%CI : 1.29~3.07) and TP (β = 0.23, 95%CI : 0.15~0.31) were correlated with SBP levels in female students; GLU (β = 1.48, 95%CI : 0.73~2.24) and TP (β = 0.26, 95%CI : 0.20~0.33) were correlated with DBP levels in female students (all P < 0.05). Conclusion Our findings suggest that blood glucose and serum total protein level are correlated with blood pressure levels in female college students, while serum total protein level are correlated with blood pressure levels in male college students.
2025, 46(2): 95-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250214
Abstract:
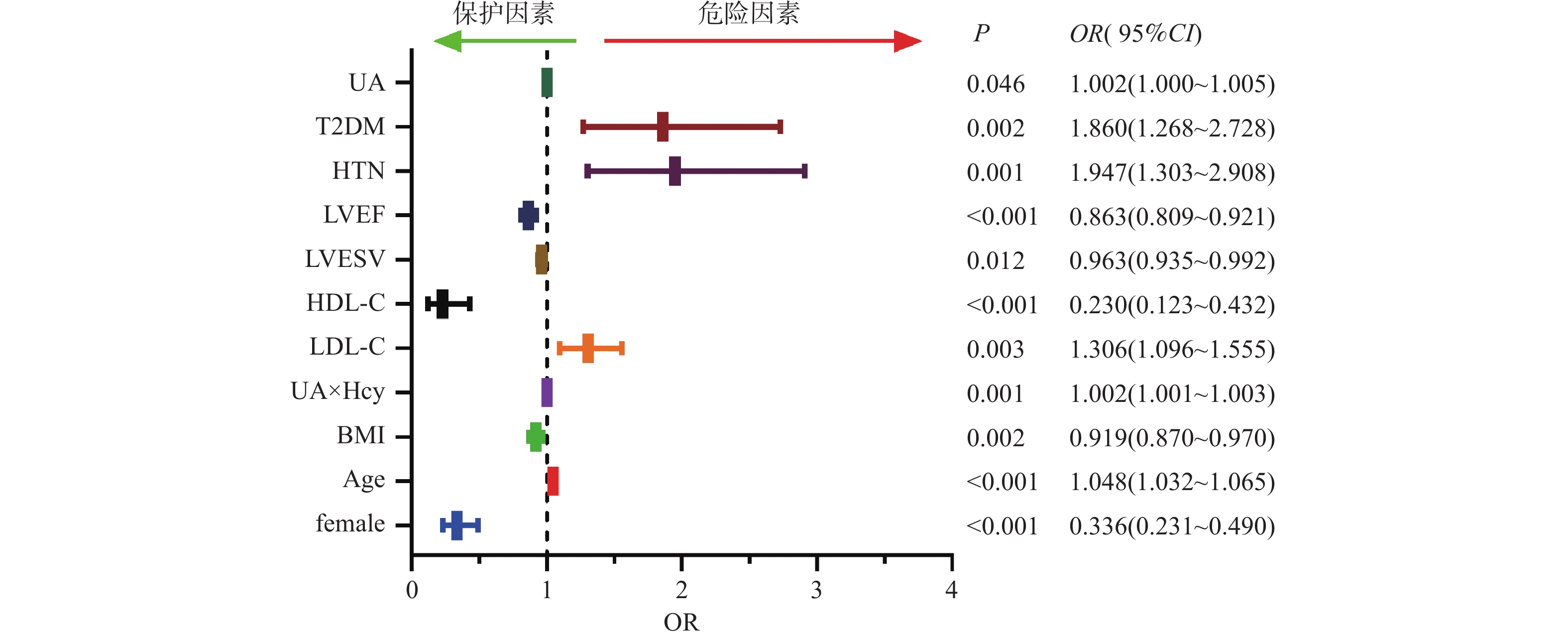
Objective To investigate the predictive value of serum uric acid (UA), homocysteine (Hcy) and the product index of UA and Hcy in patients with stable coronary artery disease (SCAD). Methods A total of 783 patients with suspected coronary heart disease were collected, all of whom underwent coronary angiography. Patients were divided into coronary heart disease (CHD) group and non-coronary heart disease (NCHD) group. The CHD group was further divided into low score group (≤ 35 points) and high score group ( > 35 points) according to Gensini scores. Baseline data, blood lipids, Hcy, UA, left ventricular function ultrasound indicators, and comorbidities were collected. Logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the risk factors associated with the onset of SCAD and severe coronary artery disease, while the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve was conducted to assess the predictive efficacy of the product index of UA and Hcy, and related risk factors, for SCAD onset and severe coronary artery disease. Results 1.In CHD group, UA, Hcy and the product index of UA and Hcy were all higher than in the NCHD group (P < 0.001); the high-score group had higher UA, Hcy and the product index of UA and Hcy than the low Gensini score group (P < 0.001). 2.Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that female age, sex, body mass index (BMI), product index of UA and Hcy, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and hypertension (HTN) were independent risk factors for SCAD (P < 0.05). BMI, the product index of UA and Hcy , HDL-C, LDL-C and LVEF were independent risk factors for severe coronary artery disease (P < 0.05). 3.There was a positive correlation between UA and Hcy product index and Gensini scores (r = 0.433, P < 0.05). 4.Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that the product index of UA and Hcy and combined detection of coronary heart disease risk factors had predictive value for the occurrence of SCAD (P < 0.05), and the predictive value of combined detection was higher (area under the curve 0.808) ; both the product index of UA and Hcy and the combined detection of coronary heart disease risk factors had predictive value for severe coronary artery lesions (P < 0.05), with a higher predictive value for combined detection (area under the curve 0.771). Conclusion As an independent predictor of the risk of SCAD and severe coronary stenosis, the product index of UA and Hcy has a high predictive efficacy regarding disease risk and the severity of coronary artery in patients with SCAD.
2025, 46(2): 103-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250215
Abstract:
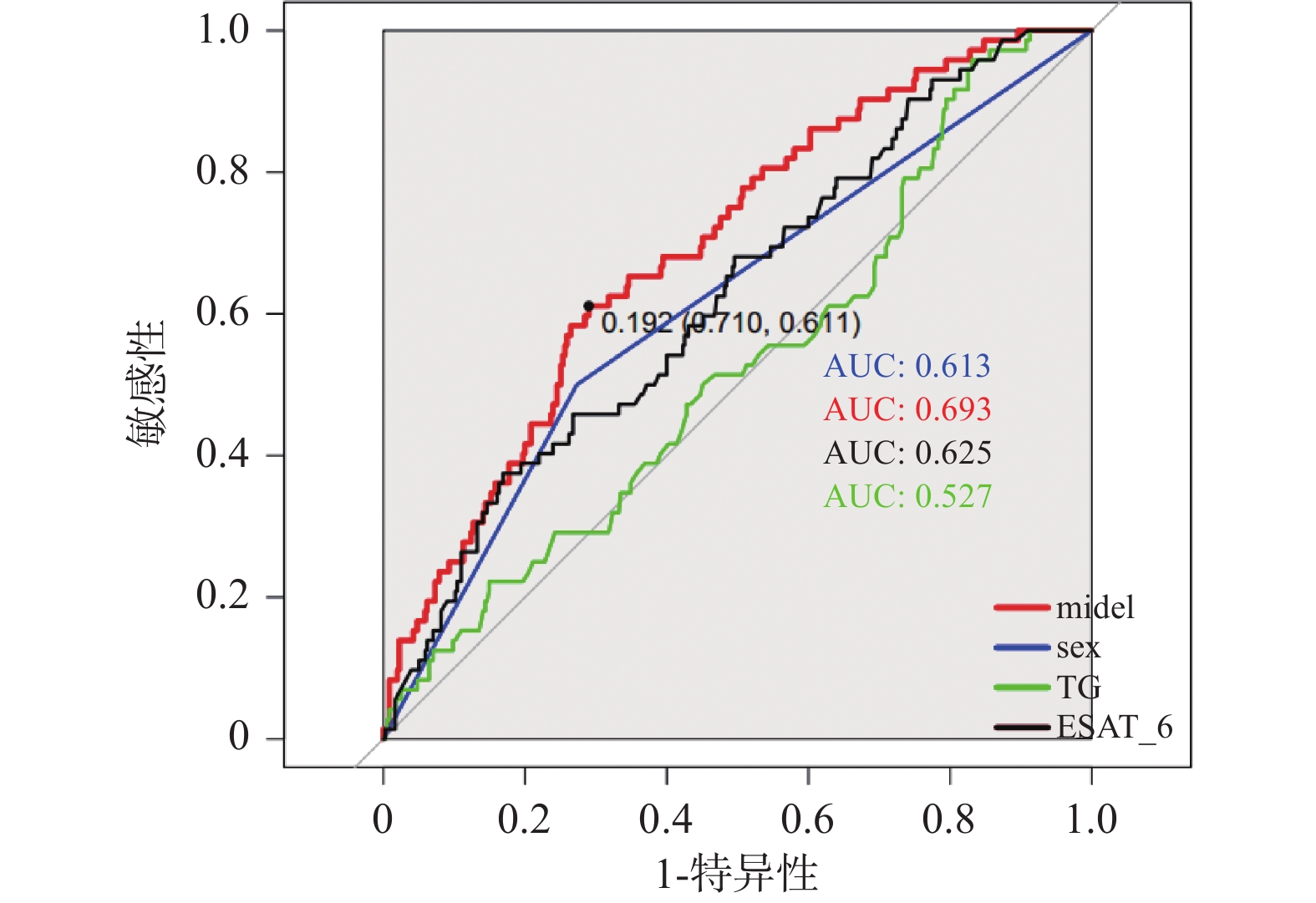
Objective To investigate the factors influencing the development of extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) in patients with viral hepatitis complicated by pulmonary tuberculosis(PTB). Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 427 patients with Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infections complicated by PTB admitted to the tuberculosis department of Kunming Third People’ s Hospital from January 2015 to December 2020. Patients were divided into the EPTB complication group (n = 72) and the non-EPTB complication group (n = 355) based on the presence of EPTB.Clinical treatment data of patients were collected. Univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analyse were used to screen independent risk factors for EPTB as predictive factors. A nomogram prediction model was established for Extrapulmonary Tuberculosis (EPTB) complications in patients with viral hepatitis and Pulmonary Tuberculosis (PTB) , evaluated using the Hosmer-Lemeshow test and ROC curve analysis. Results Among the 427 patients, 292 (68.3%) were male and 135 (31.7%) were female, with 72 cases of EPTB, resulting in an incidence rate of 16.86%. In the EPTB group, there were 34 males (47.2%) and 38 females (52.8%). The types of EPTB included tuberculous pleuritis (21 cases, 29%), tuberculous peritonitis(16 cases, 22%), lymph node tuberculosis (13 cases, 18%), tuberculous encephalitis(5 cases, 6%), intestinal tuberculosis( 6 cases, 8%), bone tuberculosis(5 cases, 6%), pelvic tuberculosis(3 cases, 4%), and genitourinary tuberculosis(3 cases, 4%). Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that gender (OR = 0.425, 95%CI: 0.250-0.722, P = 0.02), low triglyceride (TG) levels (OR = 0.837, 95%CI: 0.717-0.978, P = 0.025), the tuberculosis-specific antigen A (ESAT-6) (OR = 1.007, 95%CI: 1.003 ~ 1.011 were independent influencing factors for EPTB in patients with PTB complicated by HBV and HCV infections. The optimal cutoff value for the nomogram model is 0.192, with a sensitivity of 0.611, specificity of 0.710, Youden index of 0.741, positive likelihood ratio of 2.103, and negative likelihood ratio of 0.548. The Hosmer-Lemeshow test yielded χ2 = 2.631, P = 0.955. ROC curve analysis showed an AUC of 0.693, 95%CI: 0.6291 ~ 0.7574. Conclusion The prediction model based on gender, low TG levels and ESAT-6 can well predict the occurrence of EPTB to some extent, providing a reference for clinical treatment.
2025, 46(2): 110-117.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250216
Abstract:
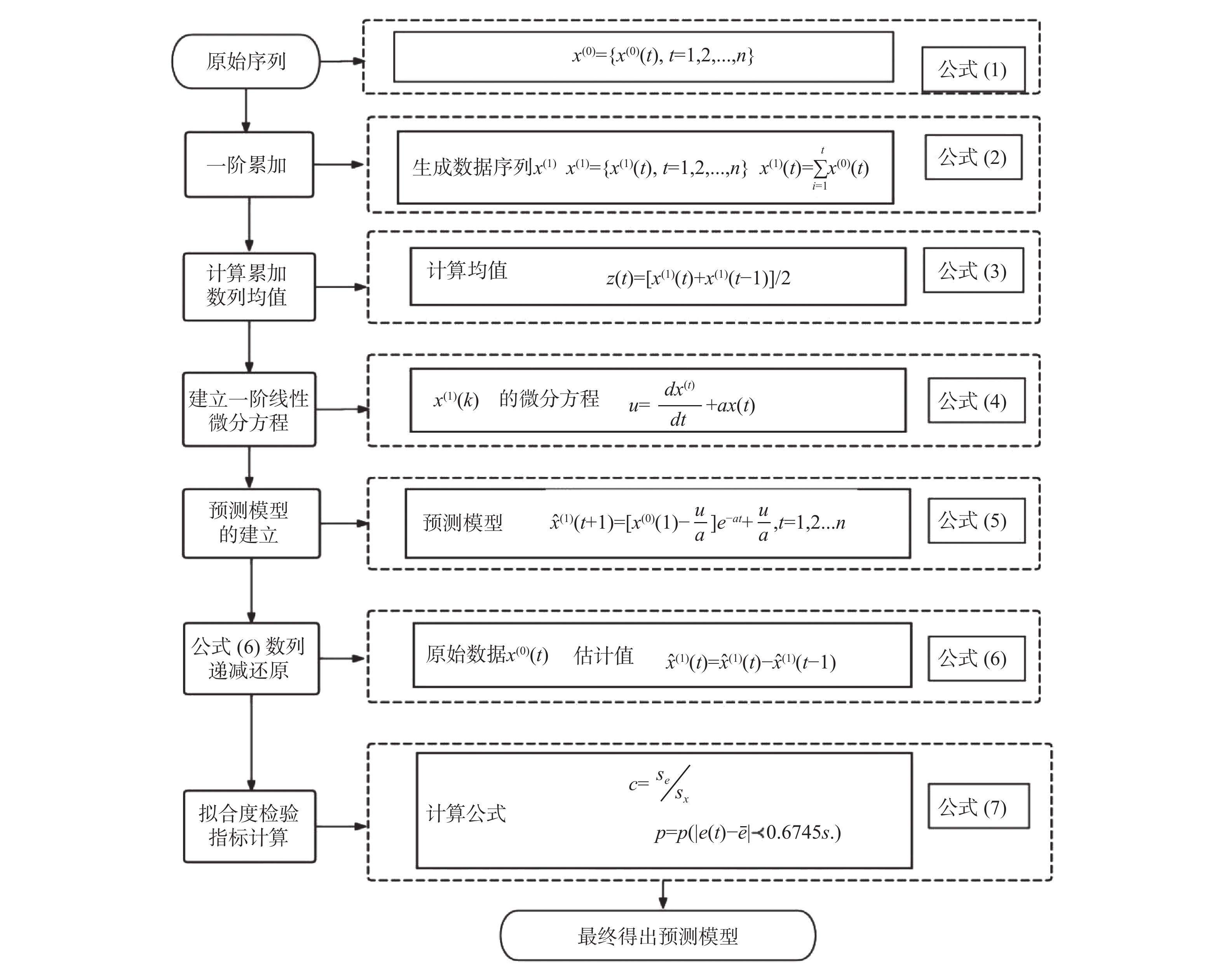
Objective To construct and evaluate the prediction model of maternal mortality in Yunnan Province, and predict the maternal mortality rate in Yunnan Province from 2024 to 2030. Methods Based on the maternal mortality rates in Yunnan Province from 1994 to 2023, a grey prediction model and a autoregressive integrated moving average model were constructed, The models were compared using mean absolute error, mean square error and root mean square error to assess their fitting performance, and the optimal model was used to predict the maternal mortality rate in Yunnan Province from 2024 to 2030. Resuls The maternal mortality rate in Yunnan Province showed a continuous decline from 1994 to 2023(χ2 =50170.0 , P < 0.05). The mean absolute error, mean-square error and root mean-square error for the grey prediction model were 2.424, 12.389, 3.519 , respectively, while for the differential autoregressive moving average model, they were 3.966, 27.651, 5.258, respectively. The prediction effect of the grey prediction model is superior to that of the autoregressive integrated moving average model, with a posterior difference ratio C = 0.079 and a low probability error P = 1, indicating a prediction accuracy of level 1. Using the grey prediction model, the maternal mortality rates for Yunnan Province from 2024 to 2030 are 10.05/100 000, 9.16/100 000, 8.34/100 000, 7.59/100 000, 691/100 000, 6.30/100 000 and 5.73/100 000, respectively. Conclusion The grey prediction model has a good prediction effect on maternal mortality in Yunnan Province. It is predicted that the maternal mortality rate in Yunnan Province in 2030 can meet the control targets outlined in the “Healthy China 2030 Plan”, the “Outline of Chinese Women's Development (2021—2030)” and the “Yunnan Women's Development Plan (2021—2030)”.
2025, 46(2): 118-125.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250217
Abstract:
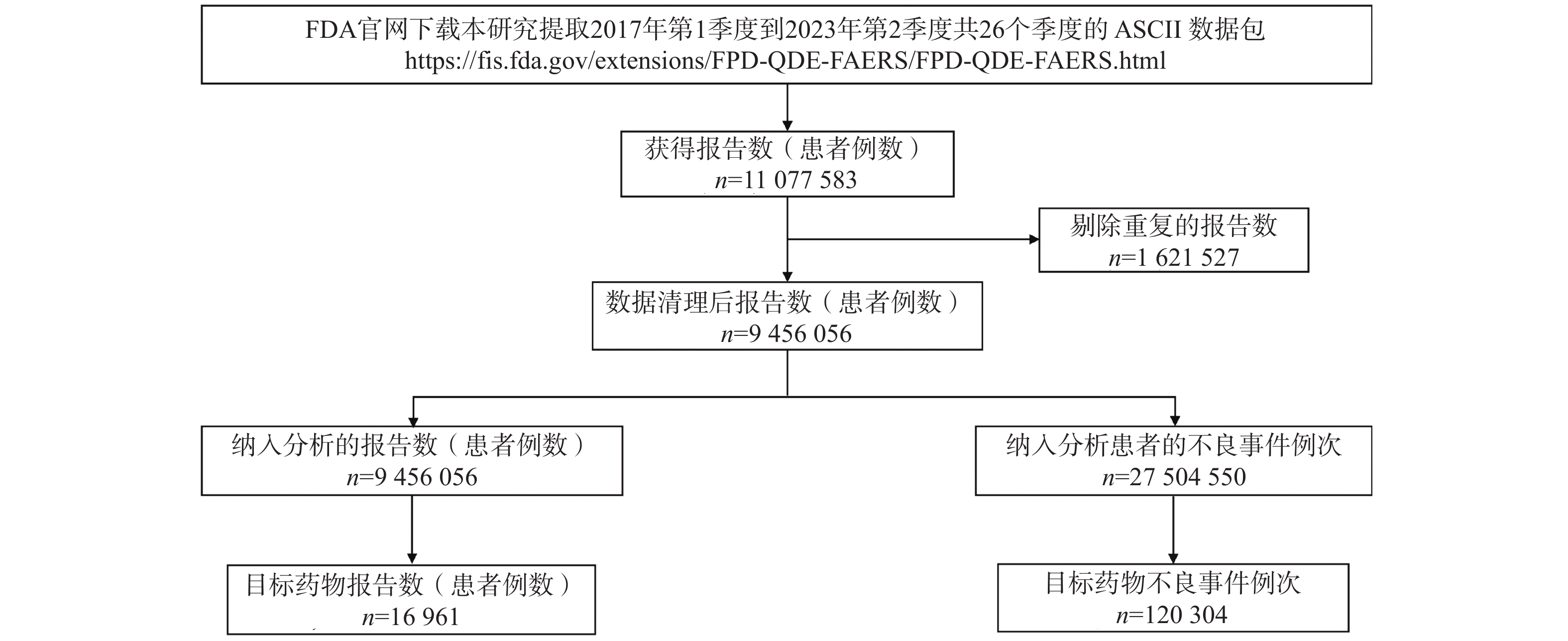
Objective To explore the risk signals of niraparib and provide references for rational and safe clinical medication. Methods Niraparib-related adverse drug events (ADEs) reports from Q1 2017 to Q2 2023 were extracted from the US FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) database. Risk signals were identified using the reporting odds ratio (ROR), proportional reporting ratio (PRR), Bayesian confidence propagation neural network (BCPNN), and multi-item gamma Poisson shrinker (MGPS) methods. The Risk signals were described and classified by preferred system organ classes (SOCs) and preferred terms (PTs) from the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) version 26.1, and the occurrence of niraparib-related ADEs was also analyzed. Results A total of 16,961 ADE reports with niraparib as the primary suspected drug were extracted. Through screening and analysis, 32 PTs were identified involving 11 SOCs, which were largely consistent with the information in the drug label. However, suspicious signals not mentioned in the label, including neuropathy peripheral, decreased red blood cell count, reduced hematocrit, dehydration, and hot flashes, require further attention.The median occurrence time was 22 days (IQR 2-98 days), and the Weibull distribution test indicated an early failure-type curve. Conclusion When using niraparib, particularly in early stages of treatment, it is essential to monitor not only the ADEs mentioned in the drug instructions, such as decreased platelet count, nausea and fatigue, but also to pay close attention to the ADEs not included in the instructions, such as peripheral neuropathy and decreased red blood cell count, which exhibit strong signal values, to ensure patient medication safety.
2025, 46(2): 126-133.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250218
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the current status of frailty in lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy and analyze its influencing factors. Methods The convenience sampling method was used to select 241 lung cancer patients admitted to the radiation therapy department of a tertiary Grade A tumor specialty hospital in Yunnan Province from January to December 2023. A questionnaire survey was conducted using the General Information Survey Questionnaire, Fried Weakness Scale, Anderson Symptom Assessment Scale (MDASI), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (SDS), Nutrition Risk Screening 2002, and Barthel Index Scale. Results The frailty in lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy was 55.19%, with a total frailty score of 3.00(1.00, 4.00) points. The results of logistic regression analysis showed that age, number of radiotherapy sessions, hemoglobin count, Barthel index, Anderson symptom assessment score, and anxiety score were the influencing factors of frailty in lung cancer patients undergoing radiotherapy (P < 0.05). Conclusion The incidence of frailties in patients with lung cancer radiotherapy is high. Age, radiotherapy frequency, hemoglobin count, Barthel index, Anderson symptom rating and anxiety score are the factors affecting frailties in patients with lung cancer radiotherapy. Clinical medical staff should promptly evaluate the frailty of lung cancer radiotherapy patients and identify their risk factors, and actively take intervention measures to prevent or control the occurrence and development of frailty.
2025, 46(2): 134-140.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250219
Abstract:
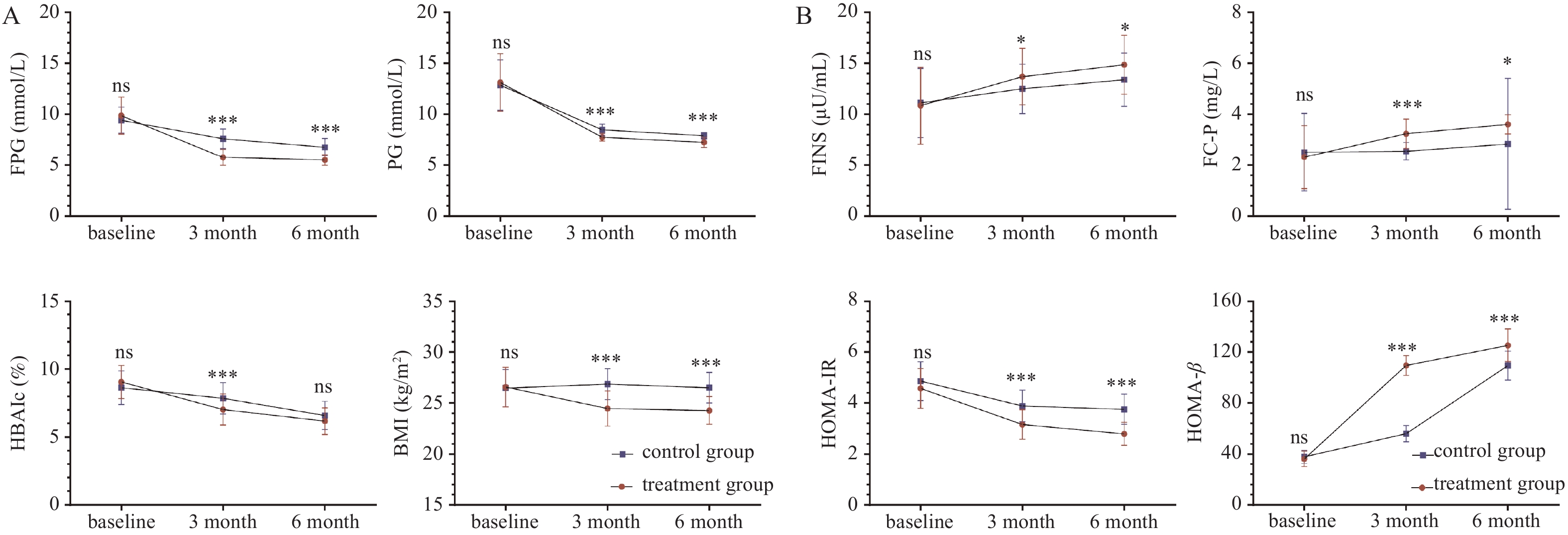
Objective To observe the effect of the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide on β-cell function in patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes patients. Methods Type 2 diabetes patients diagnosed between March 2020 and March 2021 in the Endocrinology Department of Yunnan Provincial Third People's Hospital were recruited and randomly divided into an experimental group and a control group. The experimental group was treated with liraglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, for 6 months, while the control group received treatment with non-GLP-1 receptor agonists for 6 months (monotherapy or dual therapy). Changes in Weight, BMI, FPG, PG, HbA1c, FINS, FC-P, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-β levels were observed and measured before treatment and at 3 and 6 months after treatment. Results A total of 92 patients were included in the clinical observation (45 in the experimental group and 47 in the control group). Compared to baseline, both groups showed significant reductions in FPG, 2hPG, and HbA1c at 3 and 6 months after treatment (P < 0.01). FINS, HOMA-IR, and HOMA-β improved compared to pre-treatment levels (P < 0.05). BMI decreased in the experimental group (P < 0.05), while it slightly increased in the control group, but the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). Compared to the control group, the experimental group showed a greater reduction in FPG and 2hPG from baseline after 6 months of treatment, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). HbA1c showed a certain decrease, but the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). FC-P in the experimental group was superior to pre-treatment levels at both 3 and 6 months (P < 0.05), while in the control group, FC-P was only improved at the end of 6 months of treatment (P < 0.05). Conclusion Early use of GLP-1 analogs in the treatment of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, as opposed to non-GLP-1 analog regimens, can lead to better restoration of β-cell function, weight reduction, and effective improvment of insulin resistance.
2025, 46(2): 141-150.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250220
Abstract:
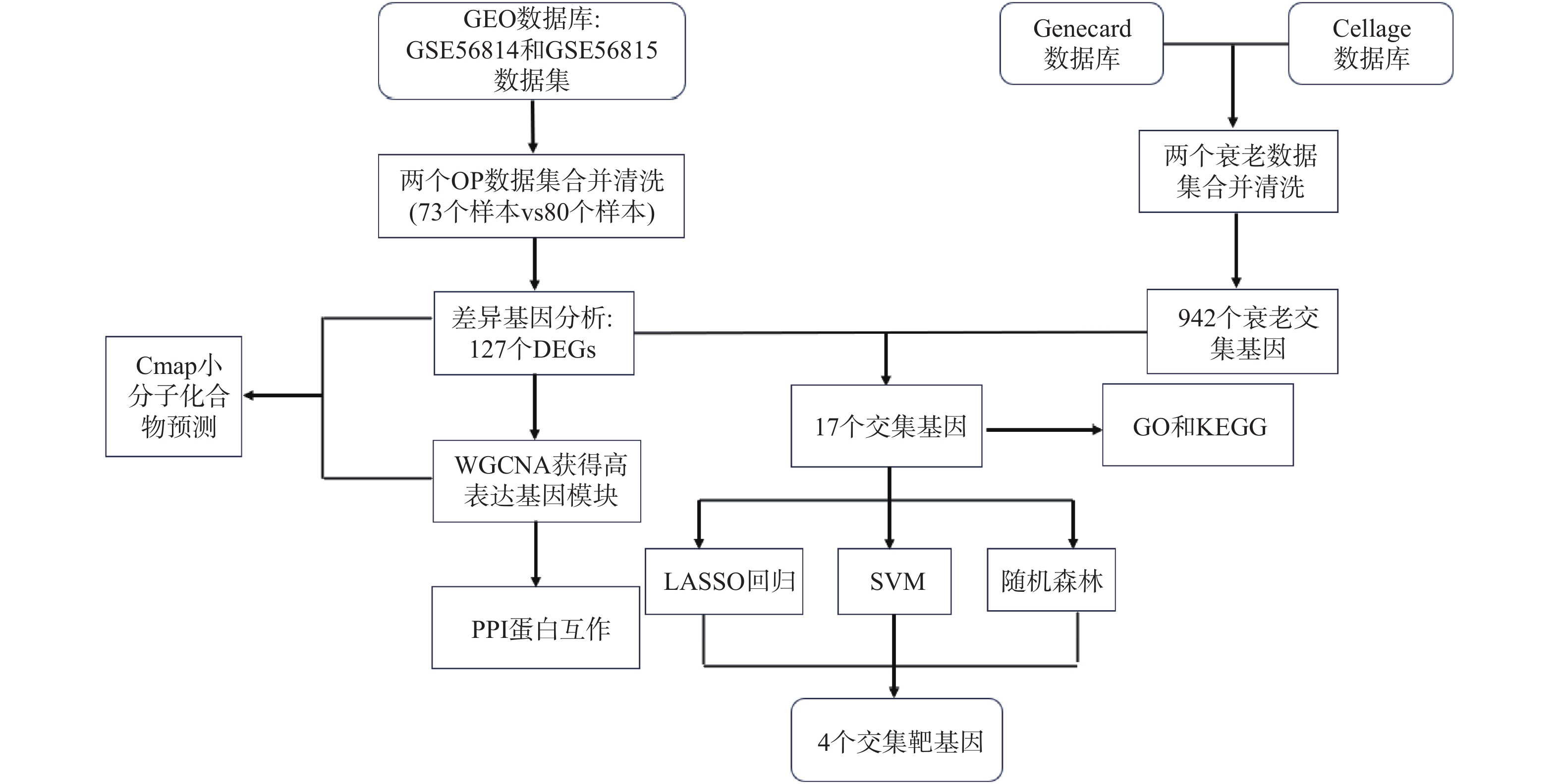
Objective To explore common target genes related to aging and osteoporosis using data from public databases and to screen for small molecule compounds with potential therapeutic effects. Methods Osteoporosis datasets GSE56814 and GSE56815 were downloaded and merged from the public gene expression database (Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO)) . Senescent genes were selected and merged from the genecard database and the cell age database. Data cleaning and differential gene selection were performed using R software, and a volcano plot was created. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis was performed to screen out key modules and genes, and the machine learning methods were employed to screen target genes. A Venn diagram was drawn using the the Microbioinformatics platform, and cytoscape software was used to visualise protein interactions results. Interaction analysis of differentially encoded proteins was carried out using the STRING database, and prediction of small molecule compounds was carried out using Cmap database. Finally, Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted to find out the most meaningful target genes, followed by the establishment of a logistic regression model and the creation of a nomogram. Results A total of 127 differential genes were screened using the limma package. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis was performed on the differential genes and 103 highly expressed genes were screened. Three machine learning methods, lasso regression, support vector machine and random forest model, were used to finally obtain four target genes: FOXO3, HIRA, CBX5 and RAD1. The nomogram and calibration curves showed good predictive results. Five small molecule compounds with potential therapeutic effects were identified using the Cmap database: sakuraflavin (O-methylated isoflavone), XMD-885, kangaroo hyoscyamine, everolimus and XMD-1150. Conclusion FOXO3 and HIRA genes have now been confirmed to be the common target genes for aging and osteoporosis, and sakuraflavin has potential therapeutic effects on both conditions.
2025, 46(2): 151-157.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250221
Abstract:
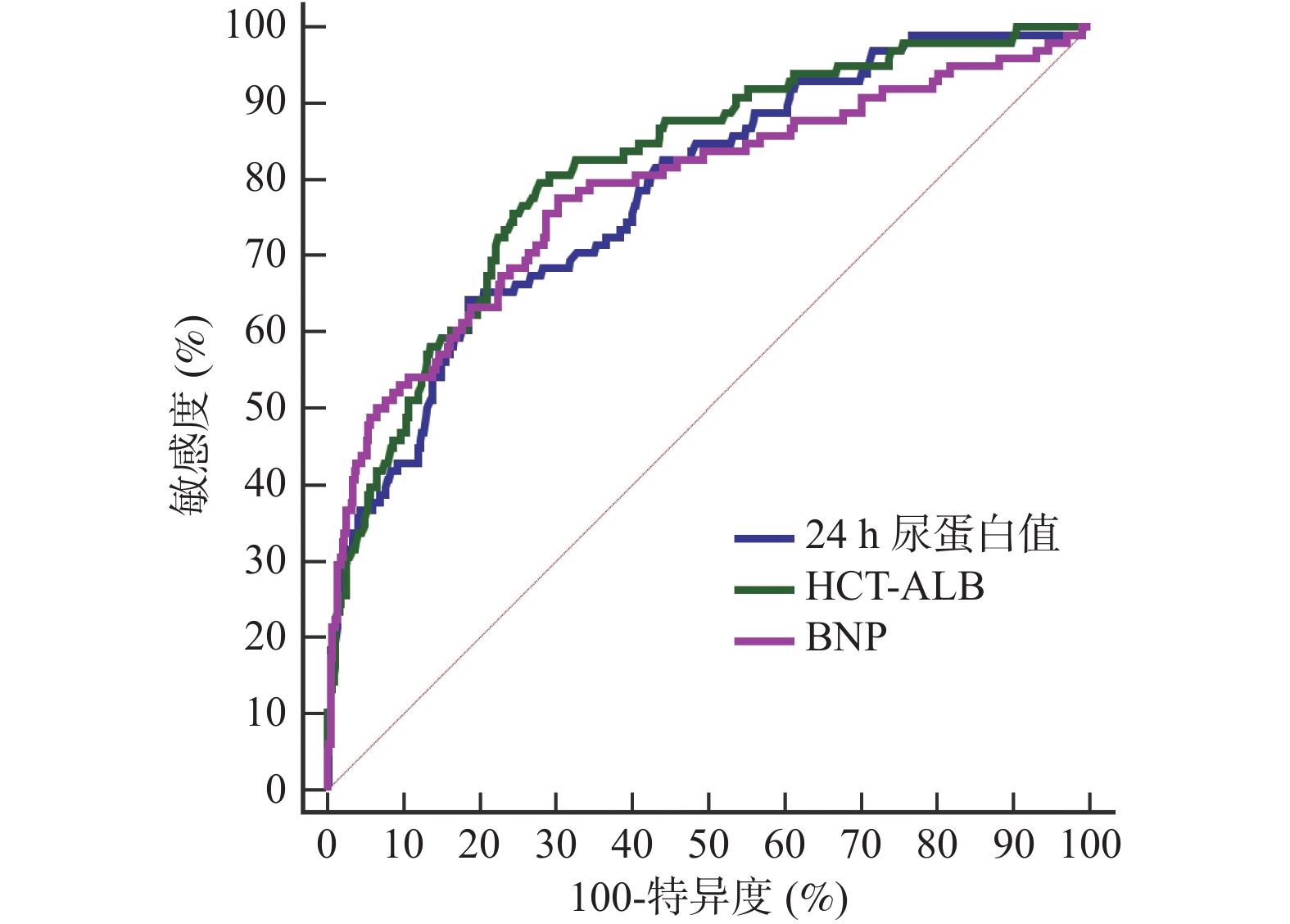
Objective To investigate the efficacy of combined prediction of postpartum hypertension using 24-h urinary protein quantification (24-hUP), hematocrit and plasma albumin difference (HCT-ALB), and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in patients with severe preeclampsia at the end of pregnancy. Methods A retrospective study was conducted using cluster sampling to select 540 patients with severe preeclampsia from the University City Hospital affiliated to Chongqing Medical University between January 2018 and December 2022 . Patients were divided into a hypertension group (n = 98) and a non-hypertension group (n = 442) based on the occurrence of postpartum hypertension. Clinical data [age, body mass index (BMI), maternal type, abortion history, family history of hypertension, smoking history, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), fasting blood glucose (FBG), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP)] and levels of 24-hour urinary protein excretion (UP), hematocrit-albumin (HCT-ALB), and BNP in the third trimester of pregnancy were compared between the two groups to analyze the predictive value of these indicators for postpartum hypertension. Results The levels of BMI, family history of hypertension, TC, TG, FBG, SBP and DBP in hypertensive group were higher than those in non-hypertensive group [(25.63±1.37) kg/m2 vs (23.05±1.23) kg/m2, 70.41% vs 30.54%]. (5.32±1.14) mmol/L vs (3.91±0.95) mmol/L, (3.48±0.82) mmol/L vs (1.66±0.43) mmol/L, (7.24±1.60) mmol/L vs (4.83±1.22) mmol/L, (148.27±13.29) mmHg vs (127.65±10.71) mmHg, (92.36±5.17) mmHg vs (84.20±4.35) mmHg], the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The levels of urinary protein, HCT, HCT-ALB and BNP at 24 h at the end of pregnancy in hypertension group were also higher than those in non-hypertension group [(7.82±2.18) g/24 h vs (6.15±1.26) g/24 h, (34.22±3.15) % vs (32.80±1.77) %]. (6.19±2.01) vs (3.46±0.90), (646.43±170.59) pg/mL vs (523.81±134.62) pg/mL], while ALB level was lower than that of the non-hypertension group [(28.03±1.13) g/L vs (29.34±1.44) g/L], with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). There was a positive correlation between 24-hUP, HCT, HCT-ALB, BNP and SBP, DBP, while ALB was negatively correlated with SBP and DBP, the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). 24-hUP, HCT-ALB and BNP at the end of pregnancy were independent risk factors for postpartum hypertension, with a combined prediction AUC of 0.930 (95%CI: 0.905~0.950), a Jordon index of 0.719, sensitivity of 85.71%, the specificity of 86.20%. The AUC of the combined prediction was significantly greater than that of each individual predictor, with statistically significant differences(P < 0.05). Conclusion 24-hUP, HCT-ALB, and BNP at the end of pregnancy are independent risk factors for postpartum hypertension. Their combined predictive efficacy is significantly superior to that of individual indicators and can be used as an optimal clinical method for predicting whether patients with severe preeclampsia will develop postpartum hypertension.
2025, 46(2): 158-163.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250222
Abstract:
Malignant melanoma is an extremely aggressive tumor that can be surgically treated in its early stage. In advanced stages, the invasive and proliferative capabilities of melanoma cells continue to increase, and traditional treatment methods such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy have limited efficacy, resulting in poor patient prognosis. Due to the presence of mutations in multiple molecular pathways in malignant melanoma, targeted therapy is now regarded as a more viable treatment option for patients with advanced malignant melanoma, with most patients benefiting from it. However, the development of drug resistance to targeted therapy has always been a serious challenge, as the emergence of resistance limits the efficacy. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the mechanism and drug resistance of targeted therapy of malignant melanoma.
Malignant melanoma is an extremely aggressive tumor that can be surgically treated in its early stage. In advanced stages, the invasive and proliferative capabilities of melanoma cells continue to increase, and traditional treatment methods such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy have limited efficacy, resulting in poor patient prognosis. Due to the presence of mutations in multiple molecular pathways in malignant melanoma, targeted therapy is now regarded as a more viable treatment option for patients with advanced malignant melanoma, with most patients benefiting from it. However, the development of drug resistance to targeted therapy has always been a serious challenge, as the emergence of resistance limits the efficacy. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the mechanism and drug resistance of targeted therapy of malignant melanoma.
2025, 46(2): 164-170.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250223
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the impact of scenario class teaching on language expression, communication skills, and final exam performance of non-clinical majors students in the course of Medical Parasitology. Method Undergraduate students of non-clinical medical programs from Kunming Medical University in 2022 were selected as the subjects and randomly divided into a scenario class group and a non- scenario class group. Questionnaires were administered to compare the two groups regarding their interest in the laboratory classes, enjoyment levels, and knowledge retention. Additionally, the final exam scores of the two groups were compared. Results Students in the scenario class group showed significantly higher interest (82.6%) and enjoyment levels (88.3%) for laboratory classes compared to the non-scenario class group (73.0% and 60.1%, respectively, P < 0.05). Students in the scenario class group believed that situational teaching enhanced their self-learning ability (82.06%), interest in learning (83.2%), willingness to express themselves (83.2%), confidence in expression (81.8%), and communication skills (87.9%). Additionally, It effectively facilitated their understanding of the occurrence and development of parasitic diseases (85.9%) and familiarity with the diagnosis and treatment process (86.8%), thereby cultivating clinical thinking. In terms of final exam scores, the scenario class group had a higher average score (22.80 ± 0.18) than the non-situational classroom group (21.47 ± 0.17, P < 0.05). Conclusion Scenario class teaching in Medical Parasitology can effectively improve students' self-learning ability, language expression, and communication skills, cultivate clinical thinking, and enhance academic performance, demonstrating significant teaching advantages.
2025, 46(2): 171-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250224
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effects of tactile/motor stimulation massage on feeding outcomes and neuromotor development levels of preterm infants. Methods A total of 136 preterm hospitalized infants in the neonatal intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital in Yunnan Province from January 2024 to July 2024 were enrolled and randomly assigned to a control group and an experimental group, with 68 cases in each group. The control group received the routine care for preterm infants, while the experimental group received tactile/motor stimulation massage as an intervention in addition to the routine care. The time taken from gavage to oral feeding (d), the rate of complete oral feeding (%), the incidence of feeding intolerance (%), the weight(g), the length(cm), the head circumference(cm), neonatal behavioral neurometric score (NBNA) and Psychomotor development index (PDI) were compared between the two groups. Results The time from gavage to oral feeding in the experimental group (12.73±1.86) days was significantly shorter than that in the control group (13.66±1.68) days, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); the rate of complete oral feeding in the experimental group (89.7%) was significantly higher than that in the control group (70.6%), P < 0.05, and the incidence of feeding intolerance in the experimental group (8.8%) was significantly lower than that in the control group (16.2%), P < 0.05; The experimental group showed superior results in weight, length, and head circumference compared to the control group (P < 0.05); The neonatal behavioral neurometry score of the experimental group (36.16±1.53) was significantly higher than that of the control group (35.10±2.66) , P < 0.05, and the motor development index in the experimental group (76.88±6.12) was significantly higher than that in the control group (74.34±5.07), P < 0.05. Conclusion Tactile/motor stimulation massage can effectively improve the feeding status and promote the neuromotor development of preterm infants.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS