2025 Vol. 46, No. 5
2025, 46(5): 1-11.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250501
Abstract:
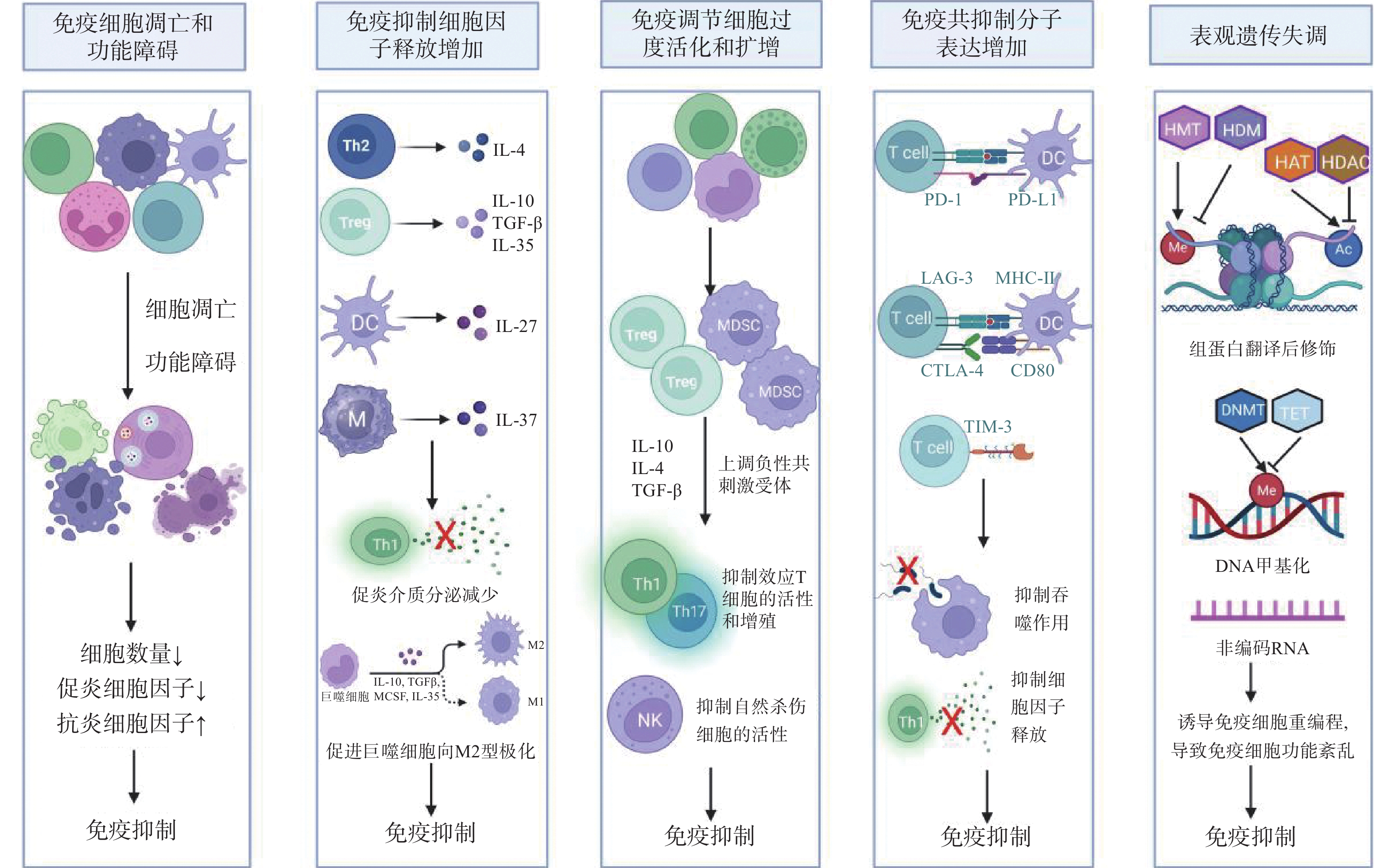
Sepsis is a syndrome caused by a dysregulated host response to infection that leads to life-threatening organ dysfunction. The immune response in sepsis is usually divided into two stages: hyperimmunity and immunosuppression. Immunosuppression is considered as the main cause of secondary infection and increased mortality in patients. This article reviews the main mechanisms of immunosuppression in sepsis, including dysfunction of immune cells, release of immunosuppressive cytokines, excessive activation of immunomodulatory cells, increased expression of immune checkpoints, and epigenetic dysregulation that have attracted much attention in recent years. At the same time, it also summarizes the existing and some new immunotherapy strategies. It includes immunostimulatory cytokines (such as GM-CSF, IL-7, IL-15), immune checkpoint inhibitors (such as PD-1/PD-L1 antibody, CTLA-4 antibody, TIM-3 antibody) and emerging immunotherapy methods (such as mesenchymal stem cells, calprotectin inhibitors, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 inhibitors). This article focuses on epigenetic regulation mechanisms and emerging immunotherapies such as mesenchymal stem cells, aiming to provide theoretical support for individualized precision immunotherapy in patients with sepsis.
Sepsis is a syndrome caused by a dysregulated host response to infection that leads to life-threatening organ dysfunction. The immune response in sepsis is usually divided into two stages: hyperimmunity and immunosuppression. Immunosuppression is considered as the main cause of secondary infection and increased mortality in patients. This article reviews the main mechanisms of immunosuppression in sepsis, including dysfunction of immune cells, release of immunosuppressive cytokines, excessive activation of immunomodulatory cells, increased expression of immune checkpoints, and epigenetic dysregulation that have attracted much attention in recent years. At the same time, it also summarizes the existing and some new immunotherapy strategies. It includes immunostimulatory cytokines (such as GM-CSF, IL-7, IL-15), immune checkpoint inhibitors (such as PD-1/PD-L1 antibody, CTLA-4 antibody, TIM-3 antibody) and emerging immunotherapy methods (such as mesenchymal stem cells, calprotectin inhibitors, triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 inhibitors). This article focuses on epigenetic regulation mechanisms and emerging immunotherapies such as mesenchymal stem cells, aiming to provide theoretical support for individualized precision immunotherapy in patients with sepsis.
2025, 46(5): 12-20.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250502
Abstract:
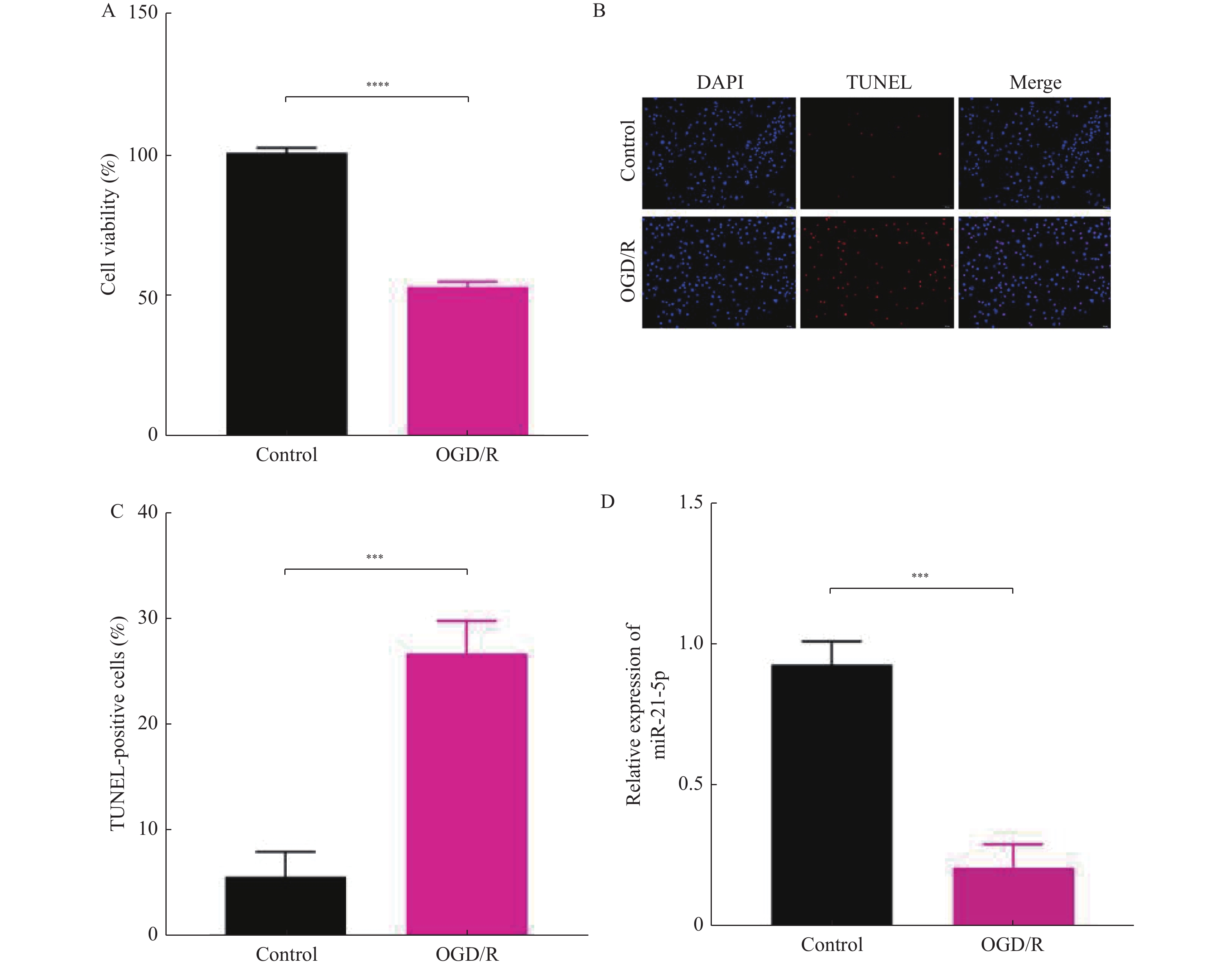
Objective To investigate the potential mechanism of miR-21-5p in alleviating cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting STAT3. Methods The HT22 cells were induced by OGD/R to construct a cell model of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury. The expression of miR-21-5p was detected by RT-qPCR. The CCK-8 assay, TUNEL staining and flow cytometry were respectively used to detect the cell viability and apoptosis. ELISA assay was used to determine the contents of inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α in the cell supernatant. Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of p-STAT3/STAT3, Cleaved-Caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 proteins. The TargetScan database was used to predict the binding sites of miR-21-5p and STAT3. The dual-luciferase reporter gene assay was used to verify the targeting relationship between miR-21-5p and STAT3. Results The relative expression level of miR-21-5p was down-regulated in HT22 cells which induced by OGD/R (P < 0.001). The cell viability (P < 0.0001 ) was decreased and the apoptosis rate (P < 0.001) was increased in OGD/R induced-HT22 cells. The contents of pro-inflammatory factors IL-6 (P < 0.001) and TNF-α (P < 0.001) was increased, while the content of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 (P < 0.001) decreased. After transfection with miR-21-5p mimic, cell viability was enhanced, apoptosis rate was reduced and neuroinflammation was inhibited. MiR-21-5p could target and bind to STAT3. After miR-21-5p inhibitor transfection, cell viability decreased, apoptosis was promoted, and neuroinflammation occurred; STAT3 inhibitor Stattic could reverse the effect of miR-21-5p inhibitor. Conclusion MiR-21-5p could specifically bind to STAT3 and reduce the neuroinflammation and apoptosis of OGD/R induced-HT22 cells.
2025, 46(5): 21-29.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250503
Abstract:
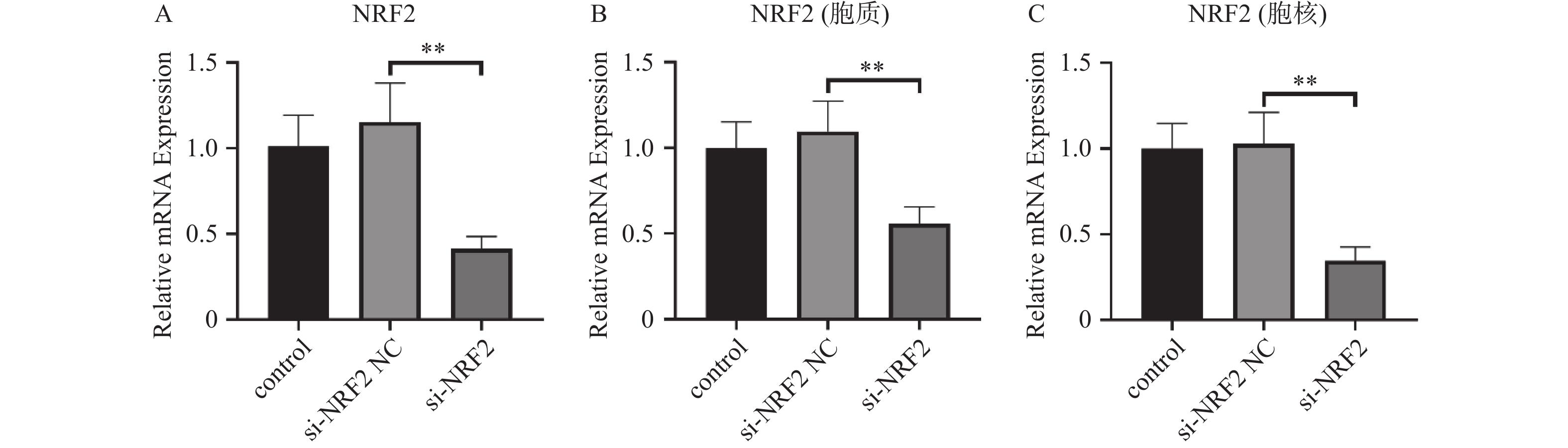
Objective To investigate the correlation mechanism between miR-153-3p and Nrf2 expression in human nucleus pulposus cells and intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). Methods The oxidative damage model of nucleus pulposus cells was duplicated induced by H2O2. MiR-153-3p inhibitor-NC, si-NRF2-NC, miR-153-3p inhibitor, and si-NRF2 were transfected into nucleus pulposus cells according to the grouping require. The transfection efficiency was detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. The cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 assay, when the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and the ratio of mitochondrial membrane potential decline were measured by flow cytometry, RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression levels of Nrf2, MMP-3, Col II, PINK1, Parkin, P62, and p38 MAPK. And dual luciferase reporter assay was used to measure luciferase activity. Results (1) HNPCs treated with H2O2 showed a decrease in HNPCs cell viability, a reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential, an increase in ROS levels, and a decrease in Col II expression (P < 0.05). And the expression of MMP-3, P62, and p38 MAPK increased, while the expression of PINK1 and Parkin decreased. There was no significant change in Nrf2(P > 0.05). (2) Inhibition of miR-153-3p expression in nucleus pulposus cells treated with H2O2 led to increased cell viability, elevated mitochondrial membrane potential, reduced ROS levels, and enhanced Col-II expression, accompanied by decreased expression of MMP-3, P62, and p38 MAPK, while simultaneously increasing the expression of PINK1, Parkin, and Nrf2 (P < 0.05). (3) When miR-153-3p expression was inhibited and Nrf2 expression was silenced in nucleus pulposus cells treated with H2O2, a notable decline in cell viability and mitochondrial membrane potential was observed, along with a marked increase in ROS levels. Additionally, Col-II expression decreased, whereas the expression of MMP-3, P62, and p38 MAPK increased. However, the expression of Nrf2, PINK1, and Parkin decreased (P < 0.05). (4) Dual-luciferase assay analysis revealed binding sites and a binding relationship between miR-153-3p and Nrf2, indicating a negative correlation between miR-153-3p and Nrf2 (P < 0.05). Conclusion Inhibition of miR-153-3p expression can alleviate H2O2 induced degeneration and fibrosis of nucleus pulposus cells, activate autophagy of damaged nucleus pulposus cells, and delay apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. This effect is related to the PINK1/Parkin pathway and p38 MAPK inflammatory response pathway regulated by Nrf2.
2025, 46(5): 30-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250504
Abstract:
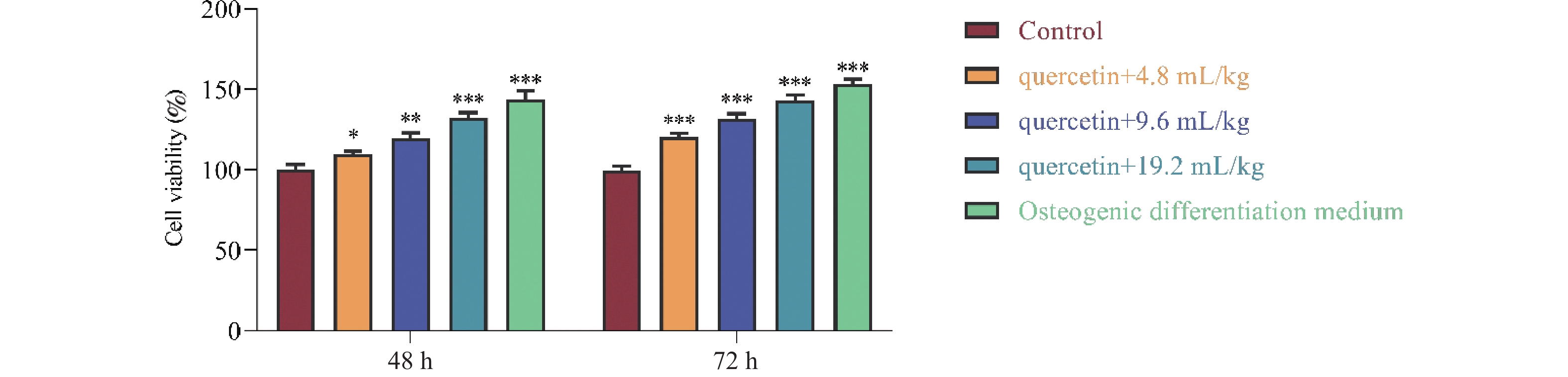
Objective To explore the effect and mechanism of quercetin on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). Methods BMSCs were divided into a blank control group (Control) and quercetin (Quercetin) low-dose group (4.8 mL/kg), medium-dose group (9.6 mL/kg), and high-dose group (19.2 mL/kg) intervened with drug-containing serum, while the positive control group was treated with osteogenic differentiation medium, respectively. The cell cycle was analysed by flow cytometry, cell proliferation was detected by MTT assay, cell activity was determined by Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) assay kit, and calcified nodule formation was observed by alizarin red staining. The expression of β-catenin and the key factors of osteogenic differentiation, runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) and osteocalcin (OCN), were detected by qPCR and Western blot, respectively. Results Compared with the control group, quercetin-containing serum significantly promoted the proliferation of BMSCs (P = 0.000205 , P = 0.000063 ) and enhanced the formation of calcium nodules, and increased osteogenic and ALP activity after osteogenic differentiation. The results of qPCR and Western blot showed that the quercetin group significantly up-regulated the mRNA and protein expression of β-catenin (P < 0.0001 ), RUNX2 (P < 0.0001 ) and OCN (P < 0.0001 ) during osteogenic differentiation. Conclusion Quercetin can effectively promote the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs, and its mechanism is achieved by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and up-regulating the expression of the osteogenesis-related transcription factor RUNX2.
2025, 46(5): 38-47.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250505
Abstract:
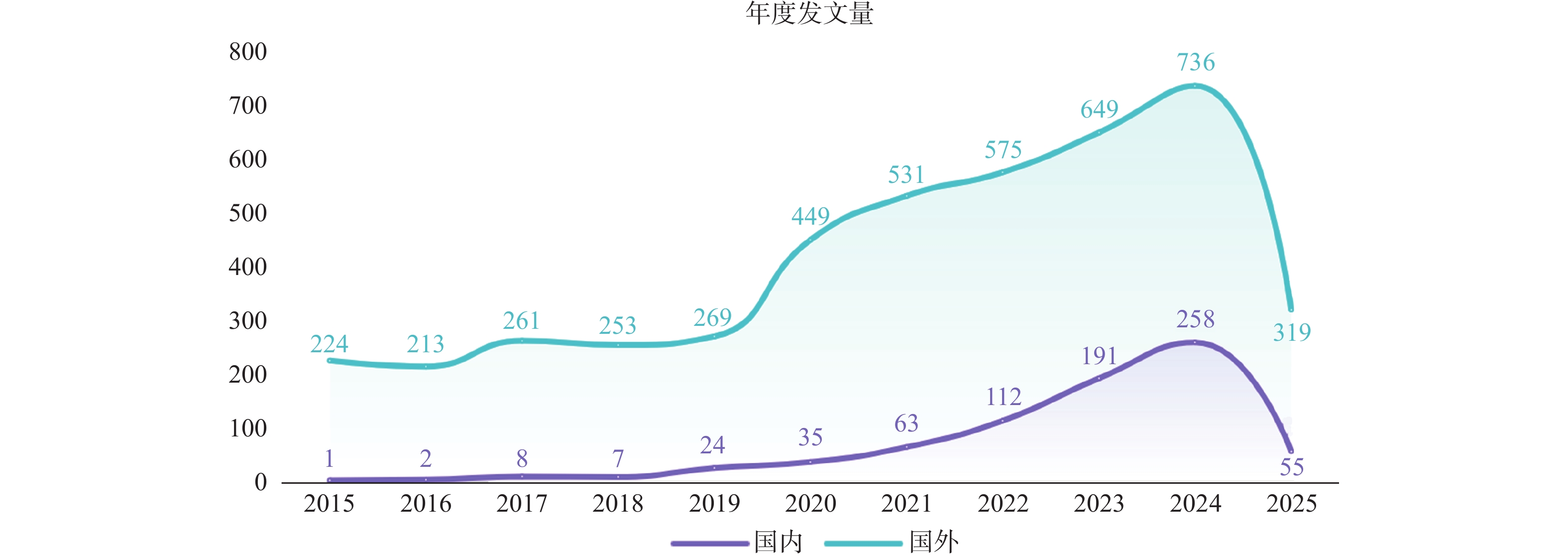
Objective Based on the VOSviewer software, to systematically analyze and compare the trends and hotspots in existing Chinese and English research on kinesiophobia, aiming to provide references for research in the field of clinical intervention and rehabilitation. Methods Chinese literature data sources were selected from CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP databases, while English literature data sources were selected from PubMed and Web of Science databases.Relevant literature on kinesiophobia was selected, and the VOSviewer1.6.18 software was used to analyze the basic information materials of the literature and to draw maps. Results 760 Chinese literature articles and 4491 English literature articles were included. The peak of publication volume was concentrated between 2020 and 2024. Domestically, the overall publication volume, individual author publication volume, and team collaboration among authors were relatively lower compared to international standards. The common high-frequency keywords in both domestic and international research were "kinesiophobia, pain, rehabilitation exercise, disability, anxiety, " and the frequency of these keywords showed correlation and non-randomness. Conclusion Research on kinesiophobia is on an upward trend. Due to different development focuses, there are similarities and differences in research directions between domestic and international studies. Domestic research can achieve in-depth exploration of kinesiophobia through theoretical integration, technological transformation, population expansion, and methodological innovation.
2025, 46(5): 48-54.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250506
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the protective effect of miR-193a-5p on cardiac function and the regulation of IL-33 / ST2 signaling pathway in rats with chronic heart failure (CHF). Methods Forty SPF-grade Wistar rats were randomly divided to four groups: Sham group, CHF group, NC group, and miR-193a-5p group, 10 rats in each group. The model of chronic heart failure was duplicated in the CHF group, NC group, and miR-193a-5p group. Subsequently, the rats in the NC group and miR-193a-5p group were received 5 nmol/L of NC-agomiR or miR-193a-5p-agomiR, respectively, via tail vein injection every 3 days for 4 weeks. In contrast, the rats in the Sham and CHF groups were received an equal amount of saline injection. At the endpoint of the experiment, doppler color ultrasonography was used to detect the left ventricular posterior wall thicknesses (LVPWs), left ventricular posterior wall thickness at end-diastole (LVPWd), systolic interventricular septal thicknesses IVSs, end-diastolic interventricular septal thicknesses (IVSd), and left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEFs) in the above rats, and the changes in the cardiac phenotypic indices of HW/BW vs. LVW/BW in the 4 groups, and cardiac tissues of the rats of the 4 groups were selected. Histomorphological analysis was performed, and the expression levels of miR-193a-5p in the cardiac tissues of the four groups of the rats were detected by qPCR; apoptosis was detected by Tunel staining; the levels of the inflammatory factors interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in the myocardial tissues were measured by Elisa; Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of IL-33 and ST2 protein in myocardial tissues. Results Compared with the Sham group, the hearts in the CHF and NC groups showed increased volume, altered geometry, thinning of the myocardium, and pallor in the infarcted area, whereas the miR-193a-5p group showed partial remission. In addition, the expression levels of miR-193a-5p in cardiac tissues of the CHF and NC groups showed a decreasing trend, whereas showed a significant increase in the miR-193a-5p group (P < 0.01). In CHF group and NC group, LVPWs, LVPWd, IVSS, IVSD HW/BW and LVW/BW increased significantly, and LVEF decreased significantly (P < 0.01). In miR-193a-5p group, LVPWs, LVPWd, IVSs, IVSd, HW/BW and LVW/BW decreased significantly but higher than sham group, and LVEF increased significantly but lower than sham group (P < 0.01). The expression of miR-193a-5p increased significantly in CHF group and NC group, decreased significantly in miR-193a-5p group but still higher than sham group (P < 0.01). The expression of IL-33 and ST2 protein increased significantly in CHF group and NC group, and decreased significantly in miR-193a-5p group (P < 0.01). Conclusion miR-193a-5p has a protective effect on cardiac function in the rats with chronic heart failure. The mechanism might be related to inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors, reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and the inhibition of IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway.
2025, 46(5): 55-64.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250507
Abstract:
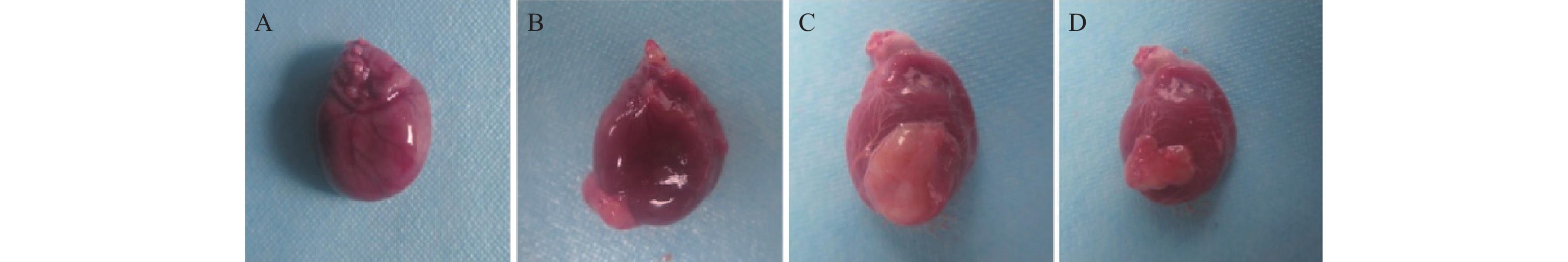
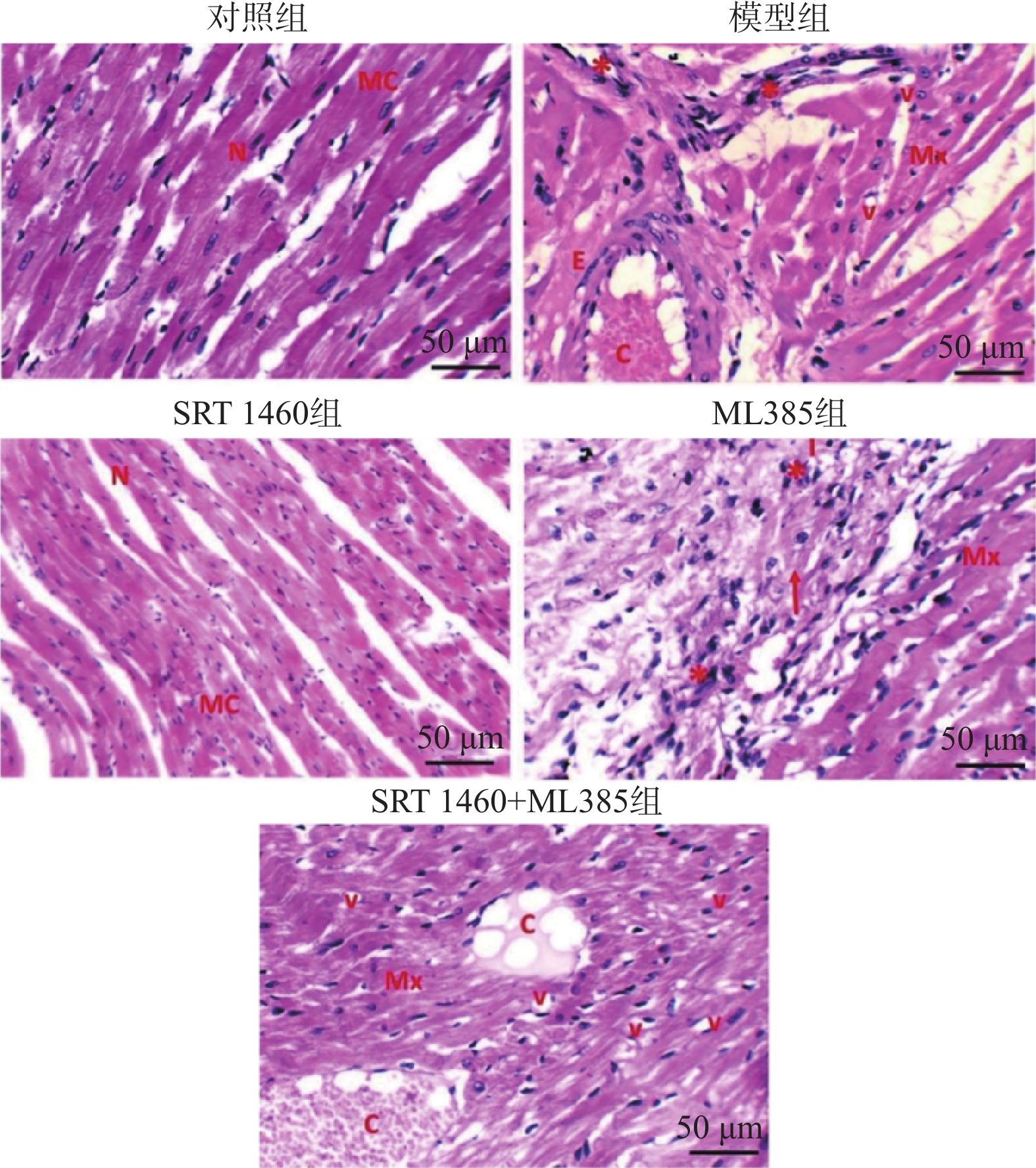
Objective The objective of this research was to examine the cardioprotective properties of a SIRT1 agonist in mice afflicted with coronary artery disease (CAD). Methods Using the random number table method, 60 male C57BL/6J mice were randomly divided into a control group, a model group, an SRT1 agonist group (Group SRT 1460, 30 mg/kg), an Nrf2 inhibitor group (ML385 group, 10 mg/kg), and a combined treatment group of SRT 1460 + ML385, with 12 mice in each group. The control group mice were fed with normal feed, and the other groups of mice were fed with high-fat feed to create atherosclerosis mouse model. The modeling period was 12 weeks. After the successful construction of the model, ultrasonic parameters were used to detect the myocardial function of mice; two-dimensional ultrasound spot tracking technology was used to detect the strain of each layer of left ventricular myocardium. Pathological alterations in myocardial tissue were detected via HE staining, and the levels of cTnI, LDH and CK were measured using ELISA. Cardiomyocyte apoptosis was evaluated using TUNEL analysis, and levels of ROS in myocardial tissue were measured via DHE fluorescence assay. Additionally, SOD activity and MDA, GSH and Fe2+ contents in myocardial tissue were determined using colorimetry. Finally, gene and protein expressions of Nrf2, GPX4, FTH1, and ACSL4 were assessed through qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis. Results A significant decrease in LVEDd and LVPWd levels was observed in the SRT 1460 group (P < 0.05), whereas increases in GLSendo, GLSmid, and GCSendo levels were identified. A decrease in collagen fiber deposition was observed in the SRT 1460 group, in which the myocardium space narrowed. In comparison to the control group, the SRT 1460 group showed reductions in serum cTnI, CK, and LDH levels, cardiomyocyte apoptosis rate, ROS, MDA, and Fe2+ contents, as well as ACSL4 mRNA and protein levels (P < 0.05). An increase in SOD activity and GSH content as well as in Nrf2, GPX4, and FTH1 mRNA and protein levels was observed (P < 0.05). By inhibiting the nuclear translocation of Nrf2, ML385 could significantly block the regulatory effect of SRT 1460 (P < 0.05). Conclusion It has been shown that SRT 1460 enhances GLSendo, GLSmid, and GCSmid, and improves left ventricular remodeling and systolic function in mice with CAD, in part because it regulates the Nrf2-GPX4 ferroptosis pathway.
2025, 46(5): 65-74.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250508
Abstract:
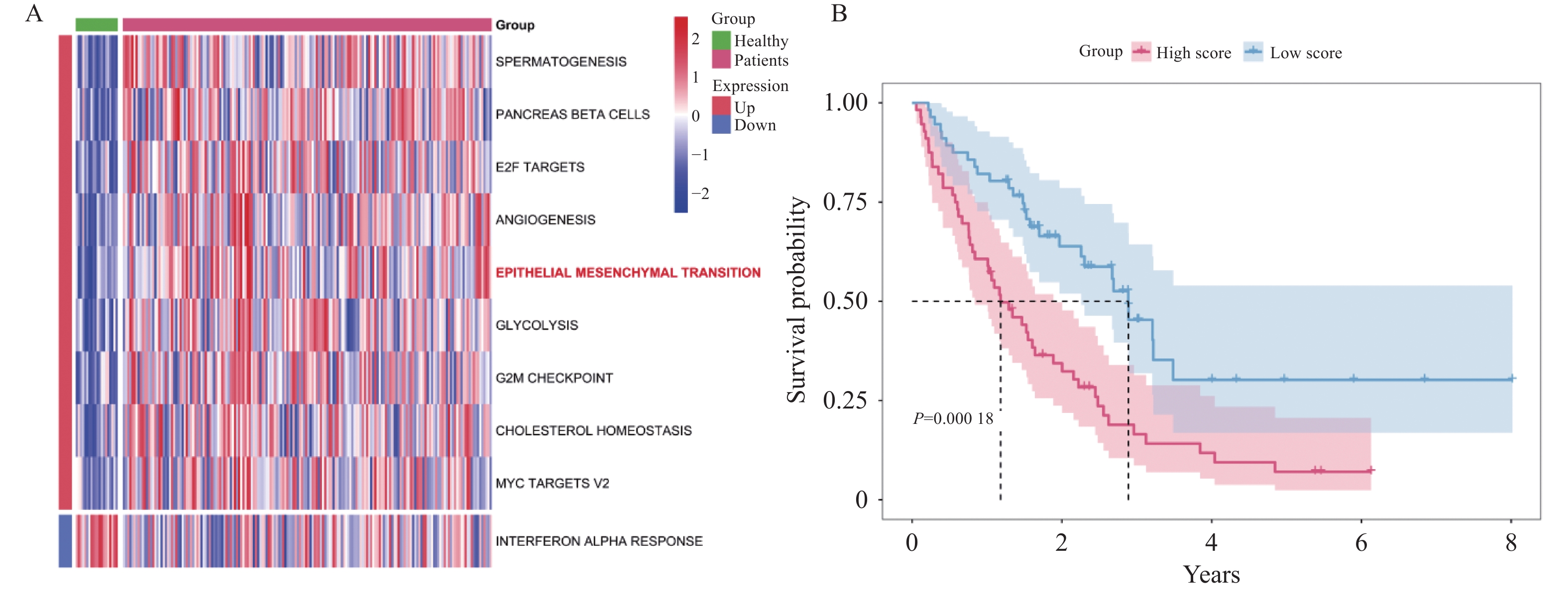
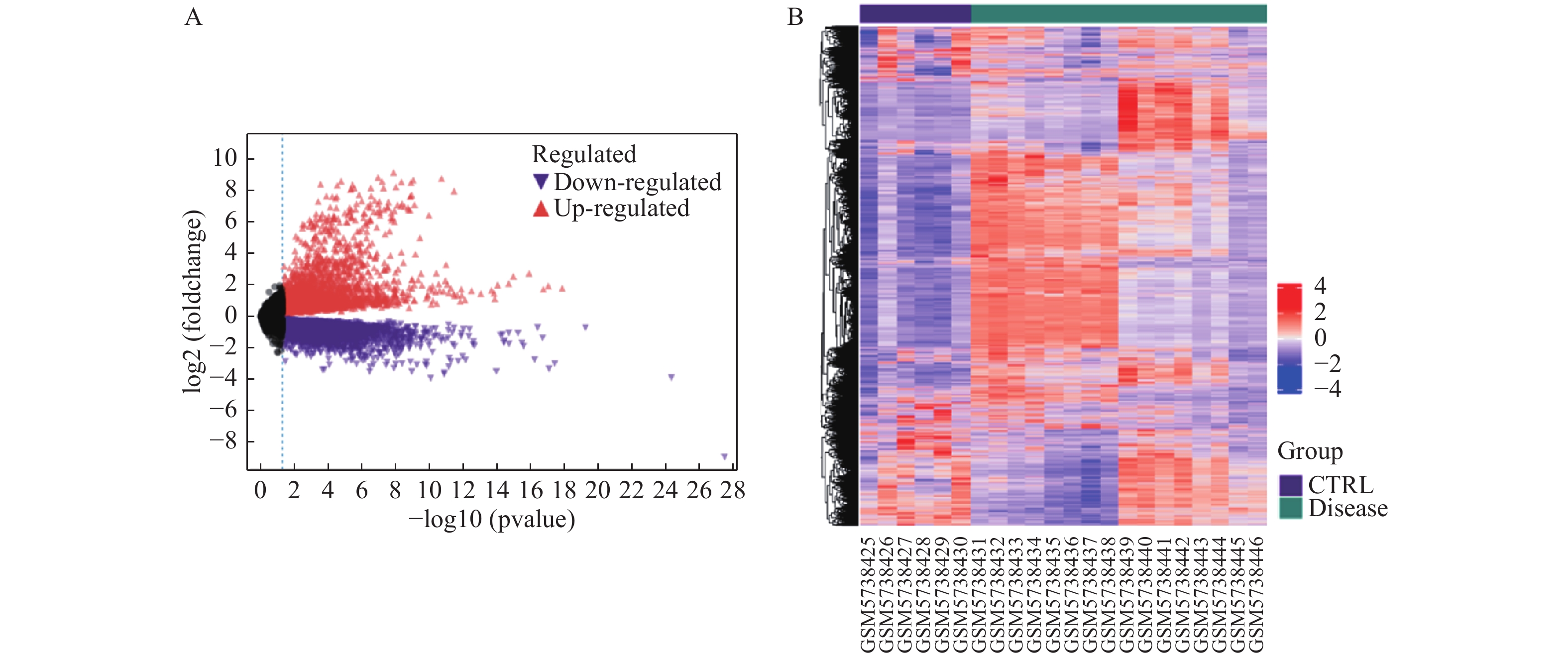
Objective To investigate the role of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), the key gene of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, in silicosis fibrosis progression, and to preliminarily explore its regulatory mechanisms. Methods Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) was employed on GSE70866 and GSE49072 from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database to assess the activity of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene set. LRP1 was screened via Venn diagram intersection. A multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model (adjusted for age and sex) was constructed to validate the independent prognostic value of LRP1. Patients were grouped based on LRP1 expression, and its function mechanisms in pulmonary were explored through differential analysis, enrichment analysis, correlation analysis, and immune infiltration analysis. The silicosis model was established by a single intratracheal injection of 10 mg SiO2 suspension in C57BL/6J mice, with 100 μL of 0.9% saline administered as the control group. Pathological changes were assessed by hematoxylin-eosin staining in lung tissues. EMT model was induced in A549 cells by TGF-β1 at varying time points. LRP1 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR in lung tissues and A549 cells of TGF-β1-induced EMT model. Protein expression of LRP1, E-Cadherin, α-SMA, collagen I, p-PI3K, PI3K, p-mTOR and mTOR were detected by Western blot in lung tissues and A549 cells. Results The epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene set score was significantly higher in patients than in healthy control, with high-score patients showing reduced survival time (P < 0.01). Bioinformatics analysis revealed that LRP1 primarily acts through the mTOR signaling pathway. Immune infiltration analysis demonstrated enhanced activities of activated dendritic cells, effector memory CD4+ T cells, and Th17/Th2 cells in LRP1 high-expression patients, suggesting its potential regulatory role in adaptive immune responses. Histopathological observation confirmed obvious silica nodule formation in lung tissues of mouse silicosis model. RT-qPCR and Western blot analyses showed that the expression levels of LRP1 mRNA and protein were significantly downregulated in both silicosis mouse lungs and A549 cells (P < 0.05). E-cadherin protein expression was downregulated, while α-SMA and collagen I expression were upregulated (P < 0.05). Furthermore, the phosphorylation ratios of PI3K (p-PI3K/PI3K) and mTOR (p-mTOR/mTOR) were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Conclusion LRP1 downregulation may activate the PI3K/mTOR signaling pathway, promoting the EMT process and fibrosis in silicosis. Targeting LRP1 regulation might become a new therapeutic strategy for silicosis.
2025, 46(5): 75-88.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250509
Abstract:
Objective To predict and preliminarily validate potential shared key genes involved in cardiac complications caused by influenza A virus (IAV) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections. Methods Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with cardiac complications were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. A hierarchical intersection strategy was applied. First, cardiac complication related DEGs were overlapped with 2 independent virus related gene sets: 3 454 human genes linked to IAV infection in GeneCards and 333 human protein-coding genes interacting with SARS-CoV-2 in the Human Protein Atlas. The 2 overlap results were then intersected to yield 22 hub genes. Lasso regression, random forest (RF) and support vector machine algorithms (SVM) were employed to refine this list. Predicted genes were validated in vitro in H1N1-infected human cardiomyocyte AC16 cells and in vivo in IFITM3 knockout mice challenged with H1N1, assessing transcriptional changes. Results A total of 22 hub genes were identified through integrative bioinformatics analysis. Application of the 3 machine learning algorithms resulted in 5 common key genes: ACE2, TBK1, NUP210, PUSL1, and MEPCE. In vitro infection of AC16 cells with H1N1 revealed dynamic transcriptional changes in all 5 genes post-infection (P < 0.05). In vivo experiments using H1N1-infected IFITM3 knockout mice confirmed the dynamic mRNA expression changes of these 5 genes, consistent with the in vitro results (P < 0.05). Conclusion By combining multilayered bioinformatics analysis with 3 machine learning approaches, 5 common key genes are identified: ACE2, TBK1, NUP210, PUSL1 and MEPCE. Validation in H1N1 infection models confirms their relevance to IAV-induced cardiac complications.
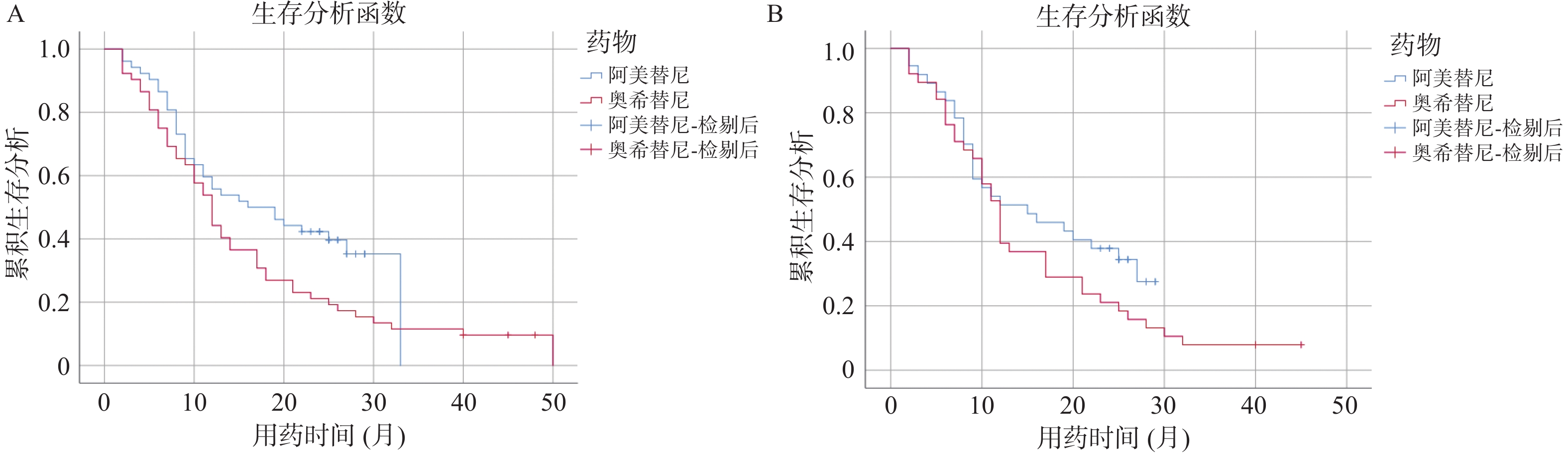
2025, 46(5): 89-95.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250510
Abstract:
Objective To compare the efficacy and safety of osimertinib and aumolertinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation. Methods A total of 139 patients with EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC treated in the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January, 2019 to December, 2022 were retrospectively collected. After screening by that row of criteria, 104 patients were included in this study. According to the treatment drugs, they were divided into osimertinib group and aumolertinib group, with 52 cases in each group. The osimertinib group received osimertinib mesylate tablets 80 mg once daily, and the aumolertinib group received aumolertinib mesylate tablets 110 mg once daily. The disease control rate (DCR), objective remission rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) of the two groups were observed. PFS and overall survival (OS) were evaluated. The Cox regression model was used to analyze the key factors affecting patient survival. Results The ORR of aumolertinib group was significantly higher than that of osimertinib group. The median progression-free survival (mPFS) of aumolertinib group was significantly longer than that of osimertinib group (P = 0.045). Cox regression model showed that clinical stage Ⅲ(HR = 2.25, 95%Cl 1.28~3.95, P = 0.005), no brain metastasis (HR = 0.59, 95%Cl 0.35~0.98, P = 0.040), third generation TKI type aumolertinib (HR = 1.82, 95%CI 1.15~2.87, P = 0.011). Conclusion Aumolertinib and osimertinib have similar clinical efficacy in the treatment of advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation. However, in terms of long-term efficacy, aumolertinib has significantly better median PFS and overall OS, and higher safety than osimertinib.
2025, 46(5): 96-100.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250511
Abstract:
Objective To study the effect of intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) in the therapy of ST-segment-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients complicated with ventricular septal rupture (VSR). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 35 STEMI patients complicated with VSR. Those patients were admitted in Yan’ an Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from January 2019 to June 2023.Patients were divided into the combine-treated group (20 cases) and the drug-treated group (15 cases) according to the therapeutic strategies. The combine-treated group received IABP implantation and drug therapy, and the drug-treated group only received drug therapy. The clinical characteristics, hemodynamic and cardiac function improvement and mortality were evaluated. Hemodynamic and cardiac function improvement were compared between the two groups. Results There were no statistically significant differences in age, male proportion and size of VSR between the two groups (P > 0. 05) . In the combine-treated group, the average heart rate, the average arterial blood pressure, central venous pressure, the LVEF value of cardiac ultrasound, pleural effusion, B-Line of lung, the level of B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP), the level of serum creatinine and the level of serum lactic acid were improved at 72 h after IABP use (all P < 0. 05). All these indicators got worse in the drug-treated group. The mortality rate of the combine-treated group was markedly lower than that of the drug-treated group (P < 0.05). The mortality rate of patients who received IABP implantation within 72 h after VSR was lower than that of patients who received IABP implantation beyond 72 h after VSR. Conclusion For patients with AMI complicated with VSR, implantation of IABP can significantly improve hemodynamics, cardiac function and reduce mortality.
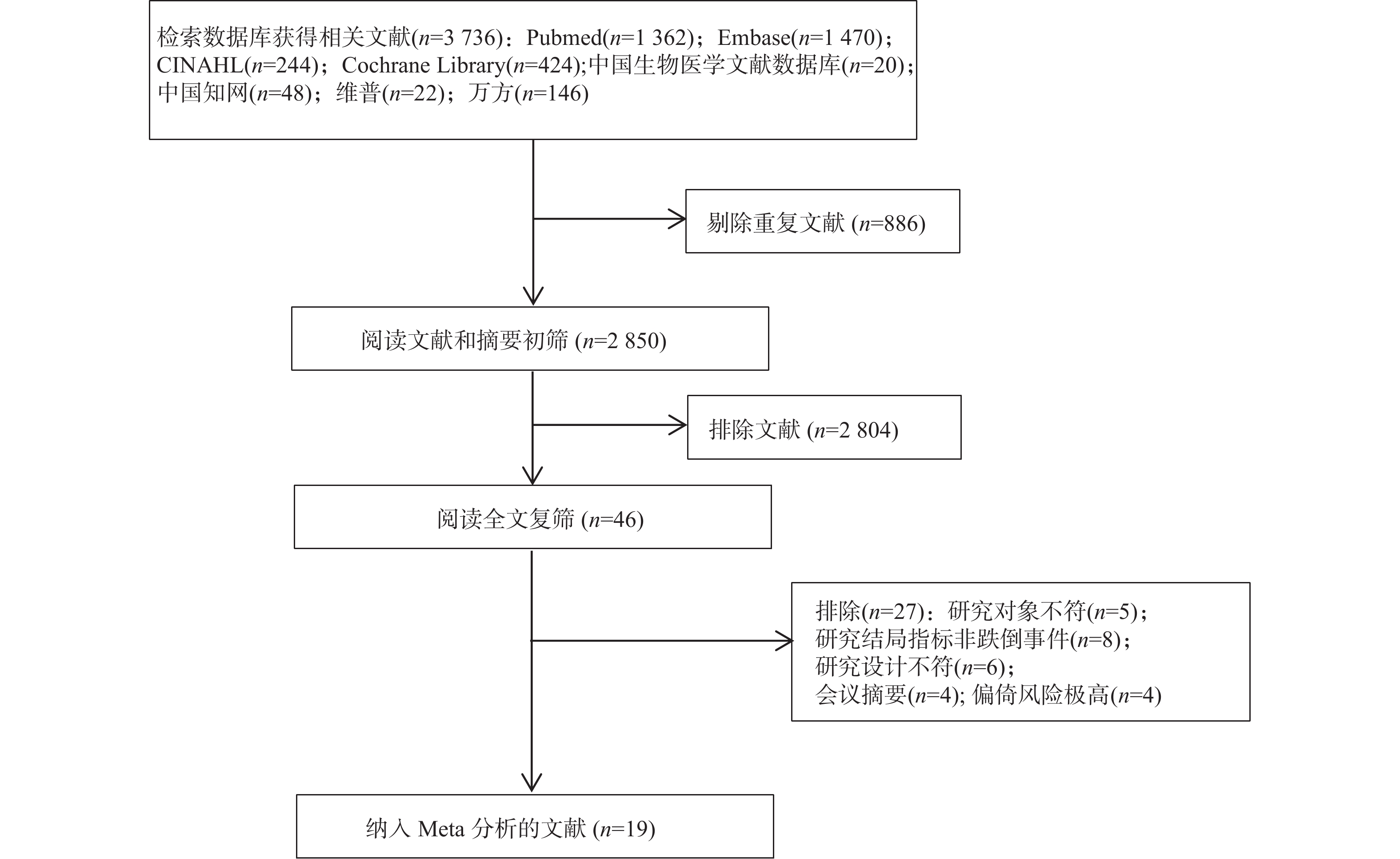
2025, 46(5): 101-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250512
Abstract:
Objective To systematically evaluate the incidence and influencing factors of falls in adult cancer patients, and provide evidence support for early identification and prevention of falls. Methods Eight Chinese and English databases, including PubMed, Embase, CNKI, and Wanfang Database, were searched by computer. The databases were established until January 2024 and included in cross-sectional, cohort, and case-control studies based on the incidence and/or influencing factors of falls in adult cancer patients. Two researchers independently screened and reviewed literature, evaluated literature quality, and extracted data before conducting meta-analysis using RevMan 5.4 software. Results A total of 19 articles were incorporated into the research, with a total sample population size of 70508 cases. The results showed that the incidence of comorbid falls in adult tumor patients was 23.0% (95%CI 0.23, 0.24). Age, female, low education level, fall history, fall fear, middle and late stage of tumor, tumor type (breast cancer, reproductive system tumor, prostate cancer), comorbidity, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, multiple drugs (n ≥ 5), drugs (antidepressants, antipsychotics, sedatives and hypnotics), related symptoms (fever, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, depression), malnutrition, low weight, cognitive dysfunction, balance disorders, gait abnormalities, and low ability of daily living were the influencing factors for falls of adult tumor patients. Conclusion Cancer professionals should identify the influencing factors of falls early and take targeted measures to reduce the occurrence of falls.
2025, 46(5): 110-117.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250513
Abstract:
Objective To explore the correlation between glycolysis related indexes of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) [glucose transporter 1(GLUT1), fructose-2, 6-diphosphatase 3(PFKFB3) and lactate kinase M2(PKM2)] and intracranial pressure and clinical prognosis of patients with hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage (HICH) who broke into the ventricle. Methods 85 HICH patients hospitalized in our hospital from January 2021 to June 2022 were retrospectively collected as the research participants. The levels of PKM2, GLUT1 and PFKFB3 in PBMCs were analyzed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit. Six months after the onset of HICH, the short-term outcome was evaluated by modified Rankin scale (mRS), and the patients were divided into good prognosis (mRS score ≤2) and poor prognosis (mRS score ≥3). Results The levels of PKM2, PFKFB3 and GLUT1 in PBMCs of HICH patients with ventricular rupture were further lower than those of the patients without ventricular rupture (P < 0.05). Six months after discharge, 8 patients (22.9%) with HICH in non-ventricular rupture group had poor prognosis, while 28 patients (56.0%) with HICH in ventricular rupture group had poor prognosis, and the difference was statistically significant (χ2=9.263, P = 0.002). Compared with the group with good prognosis, the levels of PKM2 and GLUT1 in PBMCs of HICH patients with poor prognosis were lower (P < 0.05). Compared with the good prognosis group, the levels of PKM2 and GLUT1 in PBMCs of HICH patients with poor prognosis group were lower in HICH patients with ventricular rupture (P < 0.05). In HICH patients who broke into the ventricle, the AUC of PKM2 and GLUT1 in predicting the poor prognosis of HICH patients were 0.879 (95%CI: 0.807~0.951) and 0.897 (95%CI: 0.831~0.963), respectively. Conclusion The levels of PKM2 and GLUT1 in PBMCs of patients with HICH breaking into ventricles decrease significantly, and are negatively correlated with intracranial pressure, which can be used to predict the short-term prognosis of the patients.
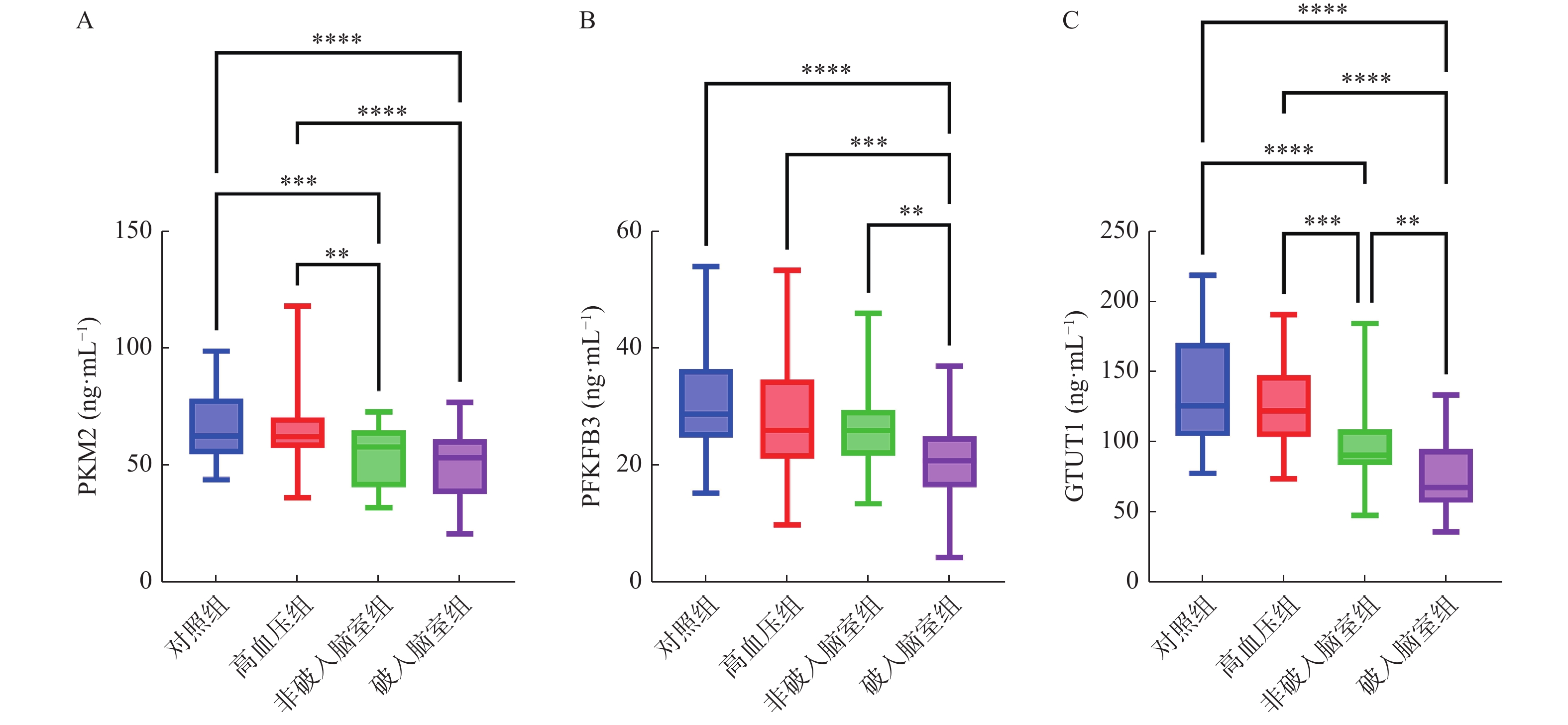
2025, 46(5): 118-125.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250514
Abstract:
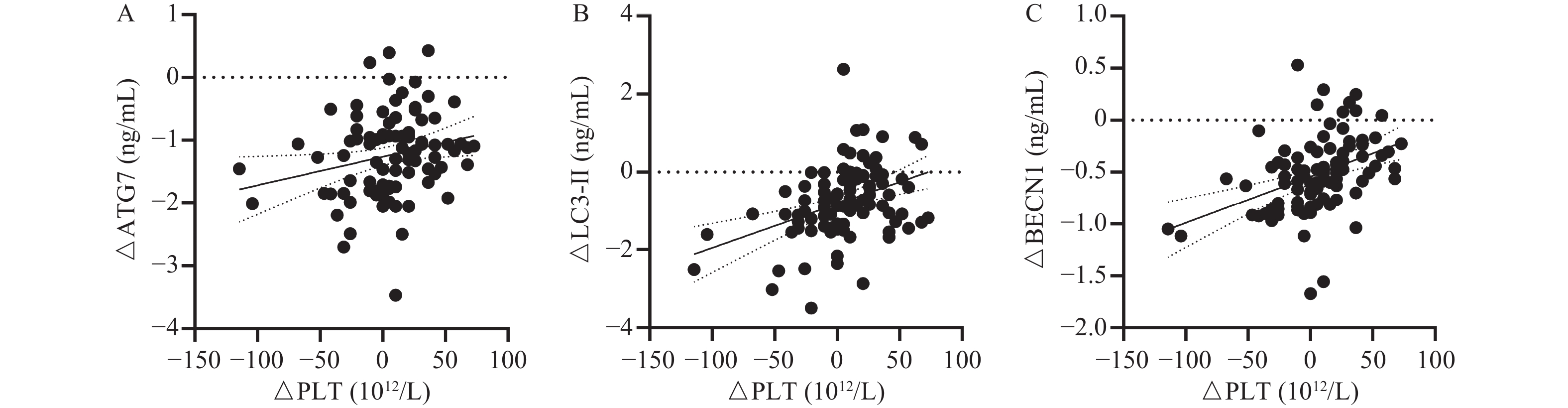
Objective To investigate the correlation between the level of platelet autophagy related factors and the neurological impairment and prognosis of the patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (aSAH). Methods From July 2020 to March 2023, 90 aSAH patients admitted to the intensive care unit of neurosurgery department of our hospital were analyzed retrospectively. Based on mRS score 3 months after discharge, patients with aSAH (n = 46, mRS 0-2) were divided into the good prognosis group, while those with mRS 3-5 (n = 44) as the poor prognosis group. Platelets of all the participants were collected, and the levels of autophagy-associated protein 7(ATG7), benzalkonium chloride 1(BECN1), microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3(LC3) and sequestosome 1(p62) were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results Compared with the good prognosis group, the mechanical ventilation time, ICU stay, cases of early brain injury, vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia in the poor prognosis group increased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared with the good prognosis group, the ΔPLT in the poor prognosis group decreased significantly (P < 0.05), and ΔLC3-Ⅱ and ΔATG7 increased significantly (P < 0.05). Spearman correlation analysis showed that ΔPLT was positively correlated with ΔATG7, ΔLC3-Ⅱ and ΔBECN1 (r = 0.239, 0.389 and 0.487, all P < 0.05). Platelet ΔLC3-Ⅱ in patients with vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia was higher than that in patients without vasospasm and delayed cerebral ischemia (P < 0.05). ICU stay (OR = 1.187, 95%CI = 1.045~1.349, P = 0.008), ΔPLT(OR = 0.972, 95%CI = 0.947~0.998, P = 0.034) and ΔLC3-Ⅱ (OR = 2.840, 95%CI = 1.049~7.694, P = 0.040) were independent influencing factors for the poor prognosis of aSAH patients. The combination of ICU stay, ΔPLT and ΔLC3-Ⅱ had the greatest ability to predict the poor prognosis of aSAH patients, with AUC of 0.921, sensitivity of 86.4% and specificity of 84.8%. Conclusion The decrease of platelet count and LC3-Ⅱ improvement in early treatment of aSAH patients can be regarded as the independent influencing factors of adverse outcomes.
2025, 46(5): 126-132.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250515
Abstract:
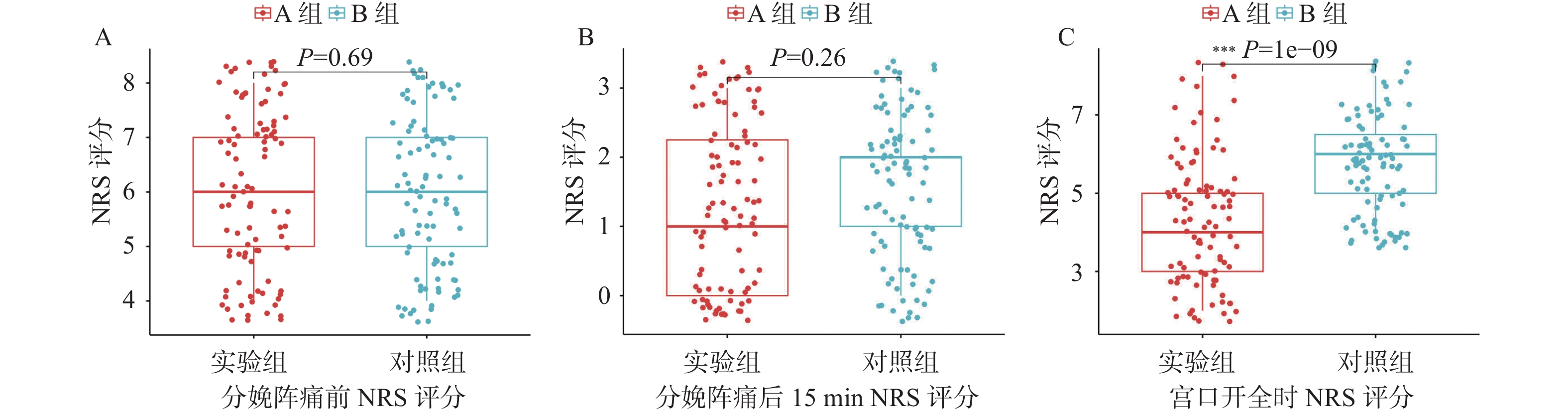
Objective To evaluate the effect difference between intelligent information management system and traditional management mode in labor analgesia, and to discuss its influence on labor pain control and clinical application. Methods The study included 200 eligible pregnant women admitted to Xiamen Humanity Maternity Hospital from April 2022 to April 2023, who were randomly divided into an experimental group (Group A) and a control group (Group B), with 100 patients in each group. Group A utilized an intelligent information management system (REHN I analgesia pump system), while Group B employed a traditional electronic analgesia pump. The primary outcomes included Numerical Rating Scale (NRS) scores before analgesia, 15 minutes after analgesia, and at full cervical dilation, as well as the proportion of patients with NRS ≥7. Secondary outcomes included the number of pump presses, the number of effective presses, the proportion of active versus passive rescue measures, adverse reactions, and maternal satisfaction. Results Compared with Group B, Group A had significantly lower NRS scores at full cervical dilation (P < 0.05), and a significantly lower proportion of patients with NRS ≥7[10 cases (10.4%)vs 24 cases (25.2%), P < 0.05]. Group A also showed a higher proportion of active rescue measures (P < 0.05) and significantly more effective presses (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of adverse reactions and maternal satisfaction (P > 0.05). Conclusion The intelligent information management system can significantly enhance the effectiveness of labor analgesia, decrease the incidence of severe maternal pain, reduce the frequency of active interventions by anesthesiologists, and improve the efficiency of analgesic management. Its application holds substantial value and potential for promotion.
2025, 46(5): 133-140.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250516
Abstract:
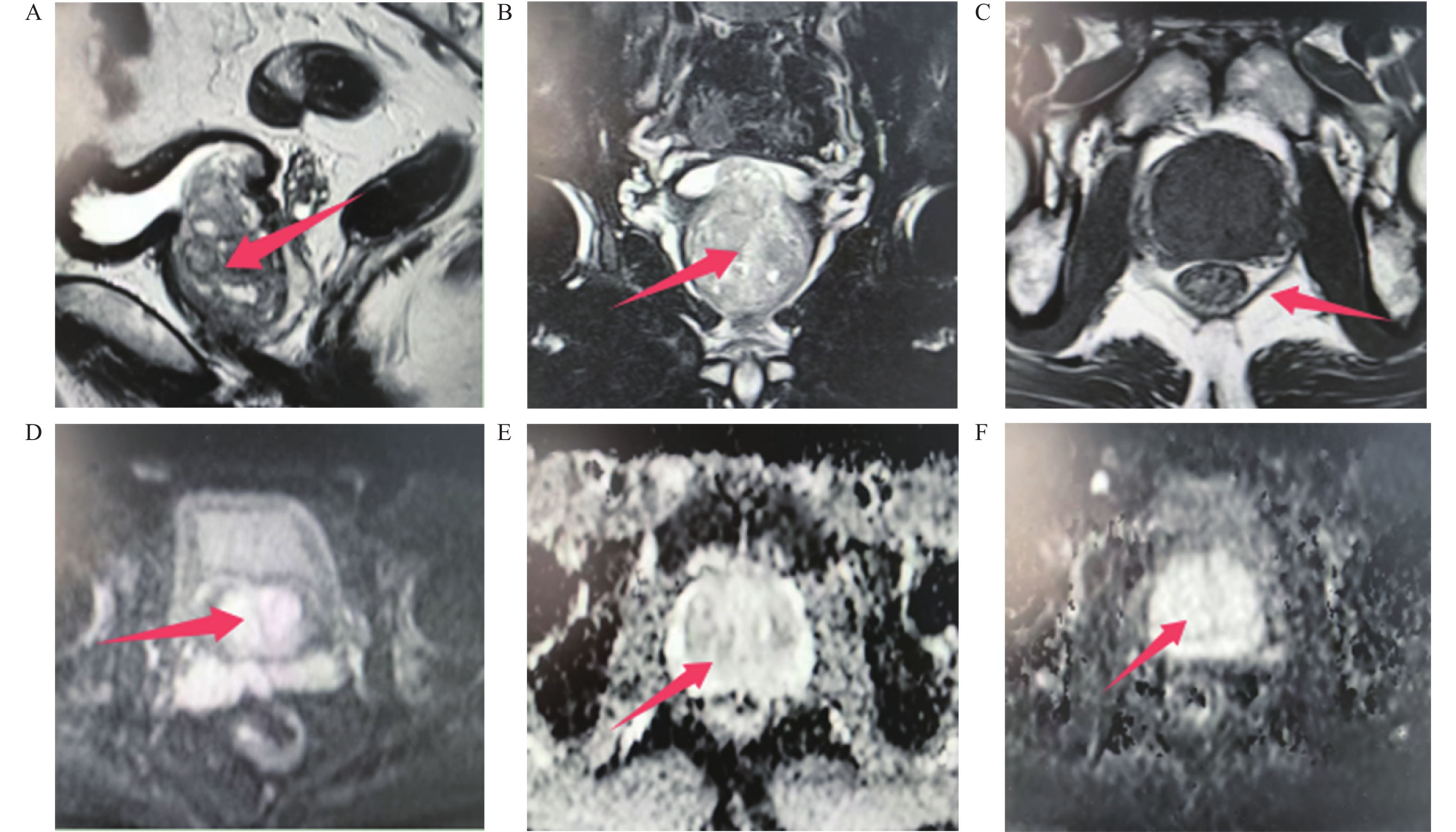
Objective To analyze the qualitative efficacy of MRI multi-sequence scanning combined with fPSA/tPSA in benign and malignant prostate lesions. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on the clinical data of 118 patients with suspected prostate cancer who visited Hebei Provincial First Veterans Hospital from January 2021 to November 2023. All the patients underwent DWI and DCE-MRI examinations. They were divided into the benign group (n = 39) and the malignant group (n = 39) based on the pathological results of partial prostatectomy or ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy. The DWI parameters, DCE-MRI parameters, PI-RADS scores, and fPSA/tPSA of the two groups were compared to analyze the factors influencing benign and malignant prostate lesions. ROC curves were drawn to analyze the diagnostic value of each index for benign and malignant prostate lesions. Results Among 118 suspected prostate cancer patients, 118 lesions were detected through biopsy at our hospital or initial diagnosis at Hebei Provincial First Veterans Hospital followed by surgical and biopsy pathological examinations at external medical institutions. Of these lesions, 79 (66.95%) were malignant and 39 (33.05%) were benign; the Rmax and SImax of the malignant group were higher than those of the benign group, and the Tmax and ADC values were lower than those of the benign group (P < 0.05); the PI- RADS scores were higher than the benign group, and fPSA/tPSA was lower than the benign group (P < 0.05); Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that Rmax [OR: 1.374 (95%CI: 1.211~1.560)], SImax [OR: 6.849 (95%CI: 2.573~18.230)], and PI-RADS score [OR: 4.689 (95%CI: 2.646~8.309)] were the risk factors for malignant prostate lesions (P < 0.05), while Tmax [OR: 0.906 (95%CI: 0.873~0.941)], ADC value [OR: 0.930 (95%CI: 0.905~0.955)], and fPSA/tPSA [OR: 0.859 (95%CI: 0.812~0.908)] were protective factors (P < 0.05); the ROC curve revealed that the AUC (95%CI) of Rmax, SImax, Tmax, ADC value, fPSA/tPSA, and PI-RADS score for the diagnosis of benign and malignant prostate lesions were 0.827 (0.747~0.906), 0.752 (0.660~0.844), 0.851 (0.773~0.930), 0.845 (0.765~0.925), 0.813 (0.722~0.905), 0.844 (0.768~0.920), and 0.940 (0.883~0.997). Conclusion DCE-MRI and DWI combined with PI-RADS score and fPSA/tPSA can improve the qualitative diagnostic accuracy of malignant prostate lesions, and provide reference for clinical identification of benign and malignant lesions.
2025, 46(5): 141-148.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250517
Abstract:
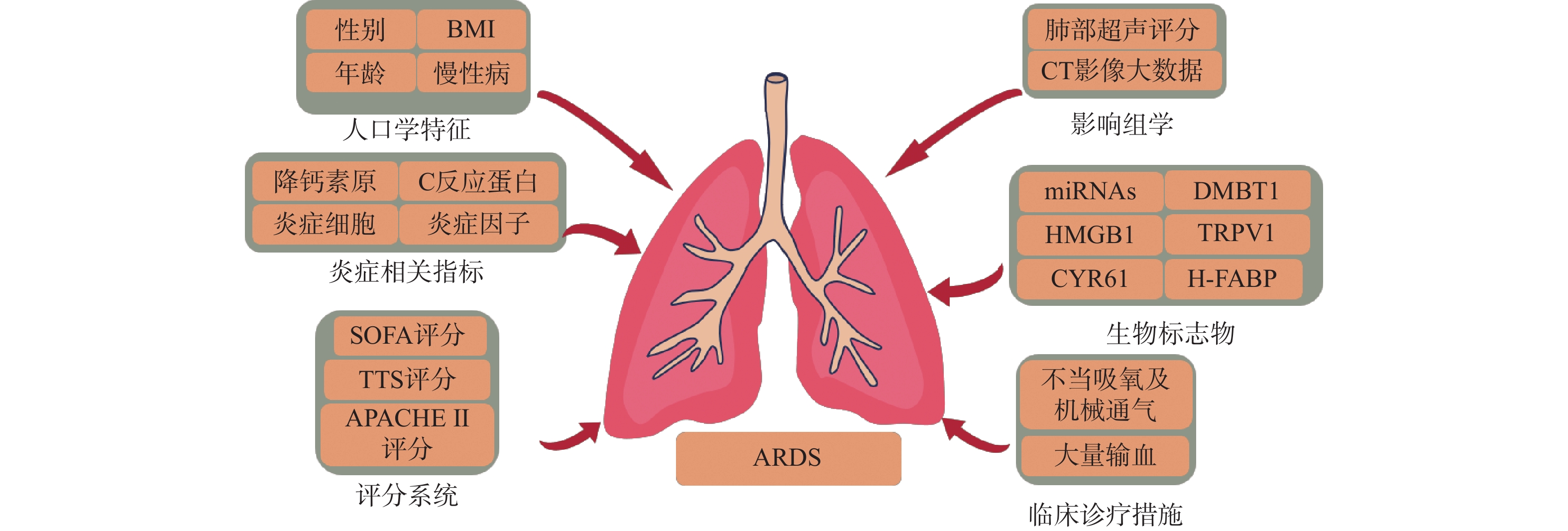
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a key disease in the field of clinical critical illness diagnosis and treatment. Its incidence and mortality rate have always remained high. Due to its high heterogeneity of the cause, specific biomarkers are still lacking in clinical diagnosis, and targeted treatment strategies for its core pathological links still have significant limitations. In view of this, the construction of an ARDS risk prediction model based on multi-dimensional risk factors can provide key evidence-based guidance for clinical medical staff to identify high-risk groups at ARDS in the early stage. This paper aims to review the research progress of ARDS risk factors and prediction models, in order to provide new ideas and references in building more accurate prediction models for ARDS.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a key disease in the field of clinical critical illness diagnosis and treatment. Its incidence and mortality rate have always remained high. Due to its high heterogeneity of the cause, specific biomarkers are still lacking in clinical diagnosis, and targeted treatment strategies for its core pathological links still have significant limitations. In view of this, the construction of an ARDS risk prediction model based on multi-dimensional risk factors can provide key evidence-based guidance for clinical medical staff to identify high-risk groups at ARDS in the early stage. This paper aims to review the research progress of ARDS risk factors and prediction models, in order to provide new ideas and references in building more accurate prediction models for ARDS.
2025, 46(5): 149-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250518
Abstract:
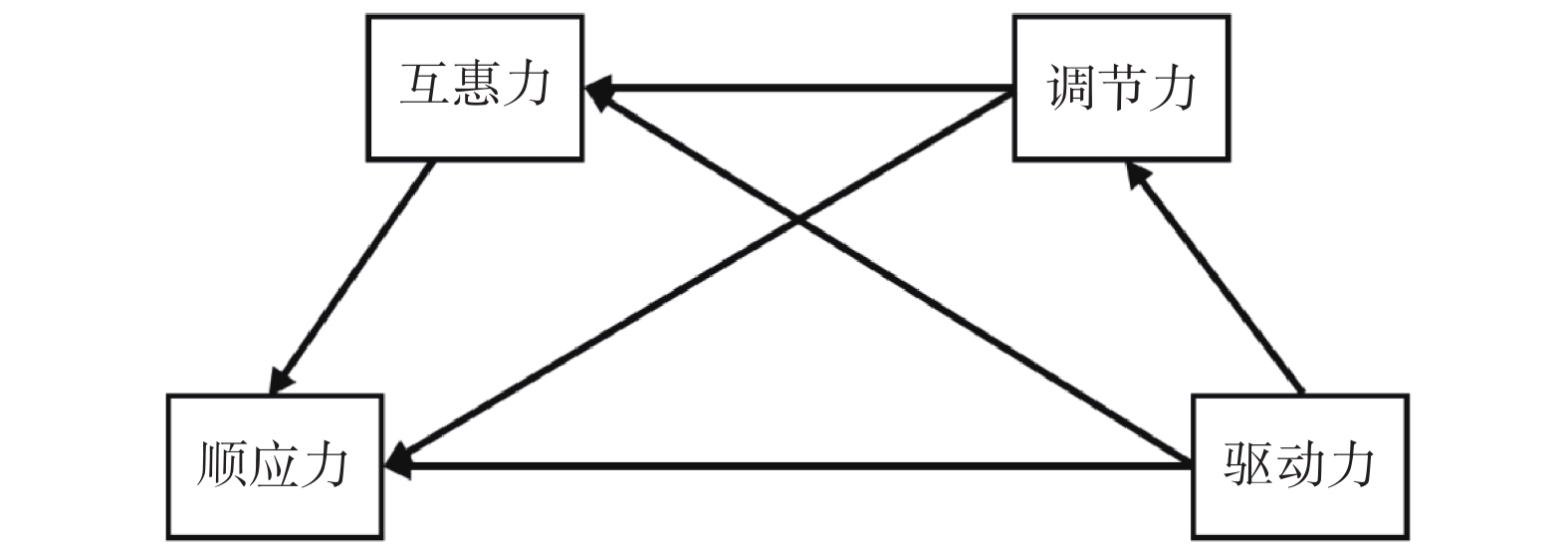
Objective To explore the interaction mechanisms among different dimensions of online learning competence in undergraduates, providing scientific evidence for optimizing software design and online education strategies. Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted with 347 undergraduates from Kunming Medical University via an online questionnaire in October 2024. Reliability testing and exploratory factor analysis were performed using SPSS 26.0, while structural equation modeling was constructed with Amos 24.0. Results Driving force directly and positively influenced regulatory force (β = 0.778, P < 0.001) and reciprocal force (β = 0.302, P = 0.003), but had no significant direct effect on adaptive force (β = 0.131, P = 0.182). Regulatory force and reciprocal force both exerted direct positive effects on adaptive force (β = 0.262, P = 0.022; β = 0.410, P < 0.001). The indirect effect of driving force on adaptive force accounted for 78.1% of the total effect (P = 0.007), with regulatory force showing a significant mediating role (β = 0.178, P = 0.023), while reciprocal force alone did not (β = 0.108, P = 0.060). A chain mediating effect (driving force→regulatory force→reciprocal force→adaptive force) was confirmed (β = 0.124, P = 0.004). Conclusion Driving force serves as the core of online learning competence, and adaptive capacity is enhanced through regulatory and reciprocal forces. To promote knowledge internalization and adaptability, it is required to optimize feedback mechanisms and deepen interactive designs in online learning platforms.
Objective To explore the interaction mechanisms among different dimensions of online learning competence in undergraduates, providing scientific evidence for optimizing software design and online education strategies. Methods A cross-sectional study was conducted with 347 undergraduates from Kunming Medical University via an online questionnaire in October 2024. Reliability testing and exploratory factor analysis were performed using SPSS 26.0, while structural equation modeling was constructed with Amos 24.0. Results Driving force directly and positively influenced regulatory force (β = 0.778, P < 0.001) and reciprocal force (β = 0.302, P = 0.003), but had no significant direct effect on adaptive force (β = 0.131, P = 0.182). Regulatory force and reciprocal force both exerted direct positive effects on adaptive force (β = 0.262, P = 0.022; β = 0.410, P < 0.001). The indirect effect of driving force on adaptive force accounted for 78.1% of the total effect (P = 0.007), with regulatory force showing a significant mediating role (β = 0.178, P = 0.023), while reciprocal force alone did not (β = 0.108, P = 0.060). A chain mediating effect (driving force→regulatory force→reciprocal force→adaptive force) was confirmed (β = 0.124, P = 0.004). Conclusion Driving force serves as the core of online learning competence, and adaptive capacity is enhanced through regulatory and reciprocal forces. To promote knowledge internalization and adaptability, it is required to optimize feedback mechanisms and deepen interactive designs in online learning platforms.
2025, 46(5): 157-161.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250519
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application of Mini-CEX oriented by nurses' core competencies in the clinical teaching of intern nursing students. Methods A total of 50 students, interning in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 1, 2023 to April 30, 2024, were randomly divided into experimental group and control group, with 25 students in each group. The control group was taught by traditional clinical teaching methods, and the experimental group by Mini-CEX. The data indicators of the two groups of intern nursing students were analyzed and compared at entry into and exit from the department, respectively. Results The scores of the two groups were higher than those at entry into the department (P < 0.05), and the intern nursing students in the experimental group had excellent scores in nursing consultation, nursing examination, nursing diagnosis, nursing measures, humanistic care, organizational effectiveness, health consultation, and overall evaluation, and the scores were higher than those of the control group (P < 0.05). The improvement in all the scores was also better than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Mini-CEX, which is oriented to the nurse’ core competencies of nurses, can improve the clinical nursing abilities of intern nursing students and enhance the cultivation effect of clinical practice skills.
2025, 46(5): 162-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250520
Abstract:
Objective To explore the current status of oncology nurses' medical narrative competence and to analyze its influencing factors. Methods 931 nurses from the oncological departments of 17 3A grade hospitals in Yunnan Province were selected from June to August 2023 and were surveyed using the Medical Narrative Competence Scale, the General Self-Efficacy Scale, and the Humanistic Care Scale. Results The score of medical narrative competence of oncology nurses was (151.52±14.61). The results of multiple linear regression showed that general self-efficacy, humanistic competence, years of experience, department, peer support, family support, familiarity with medical narratives, and job satisfaction were the factors influencing oncology nurses' competence in medical narratives(P < 0.05), which explained 38.0% of the total variation. Conclusion The medical narrative competence of oncology nurses, moderately level, is influenced by multiple factors.
2025, 46(5): 170-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250521
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application value of a holistic nursing model based on the Delphi method in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Methods A total of 110 AMI patients treated at Diqing Shangri-La People's Hospital in Yunnan Province from January 2019 to January 2020 were enrolled and divided into a control group and an observation group, with 55 patients in each, based on their admission order. The control group received routine nursing care, while the observation group received holistic nursing model intervention based on Delphi in addition to the routine nursing care. After 6 months of nursing, the left ventricular end-diastolic volume (LVEDV), left ventricular end-systolic volume (LVESV), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), general self-efficacy scale (GSES) score, complications, and changes in nursing satisfaction were compared and analyzed between the two groups. Results (1) After nursing, the LVEF significantly increased and the LVEDV and LVESV significantly decreased in both groups; the increase in LVEF was more significant, and the decrease in LVEDV and LVESV was more pronounced in the observation group (P < 0.05); (2) The GSES scores of patients in both groups improved compared to before nursing, with a more significant improvement in the observation group(P < 0.05); (3) The incidence of adverse events during hospitalization was lower in the observation group than in the control group (P < 0.05); (4) The satisfaction rate was higher in the observation group than in the control group after nursing (P < 0.05). Conclusion The application of a holistic nursing model based on Delphi in AMI patients can effectively improve cardiac function and self-management efficacy, reduce the incidence of complications, and enhance nursing satisfaction, demonstrating high feasibility.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS