Expression Characteristics of COX2 and CDX2 in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Their Prognostic Values in Patients with Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
摘要:
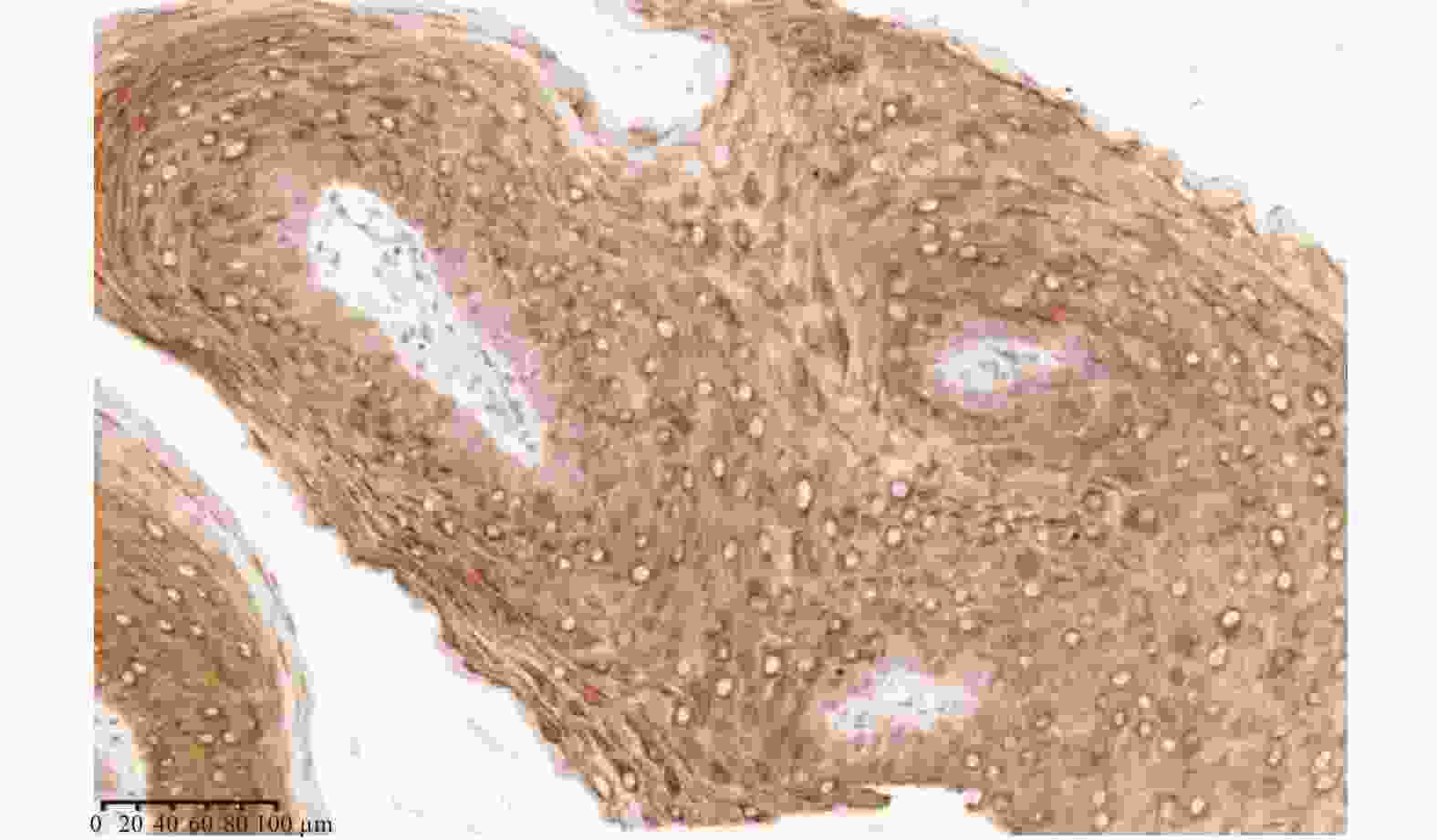
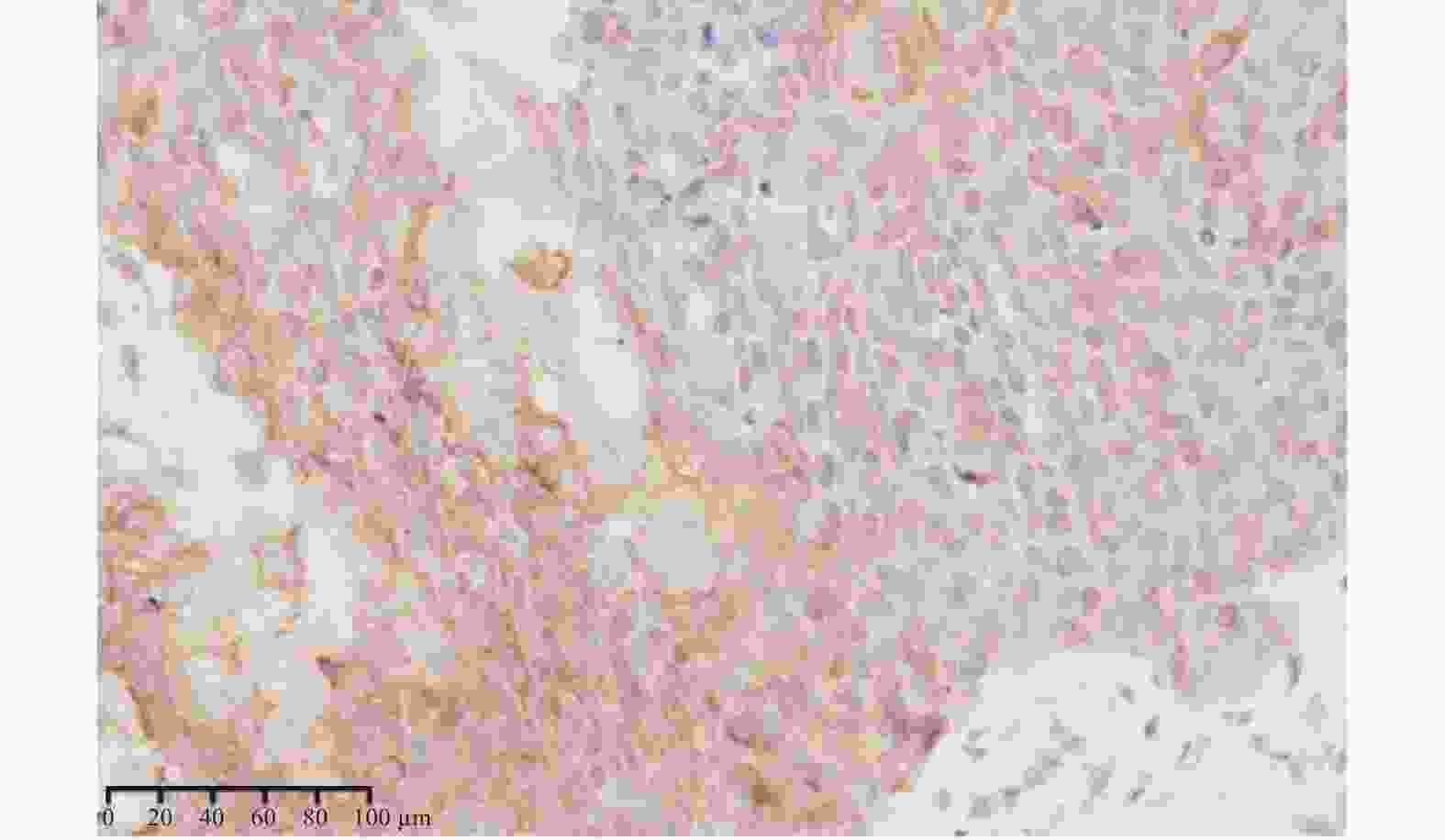
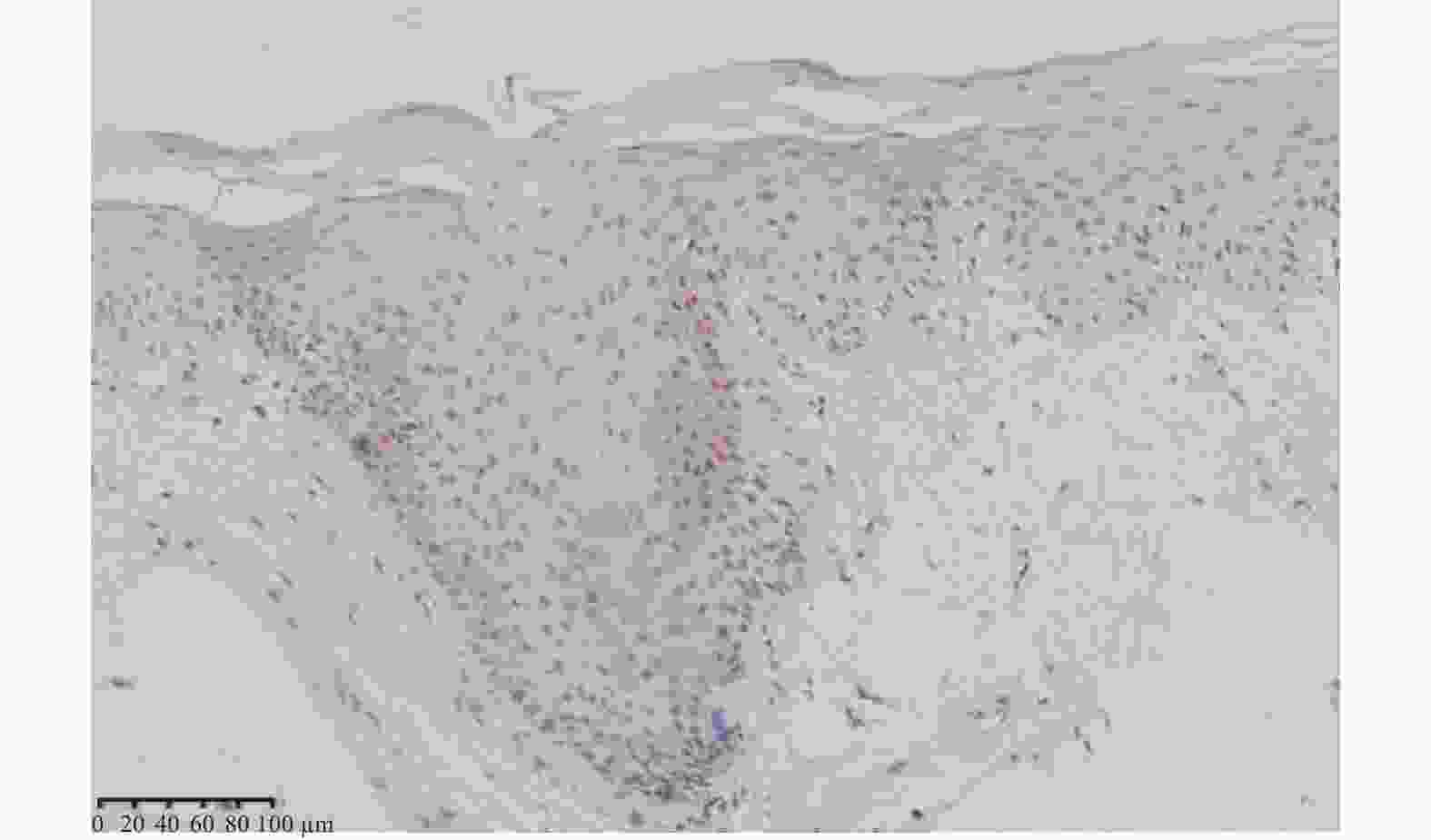
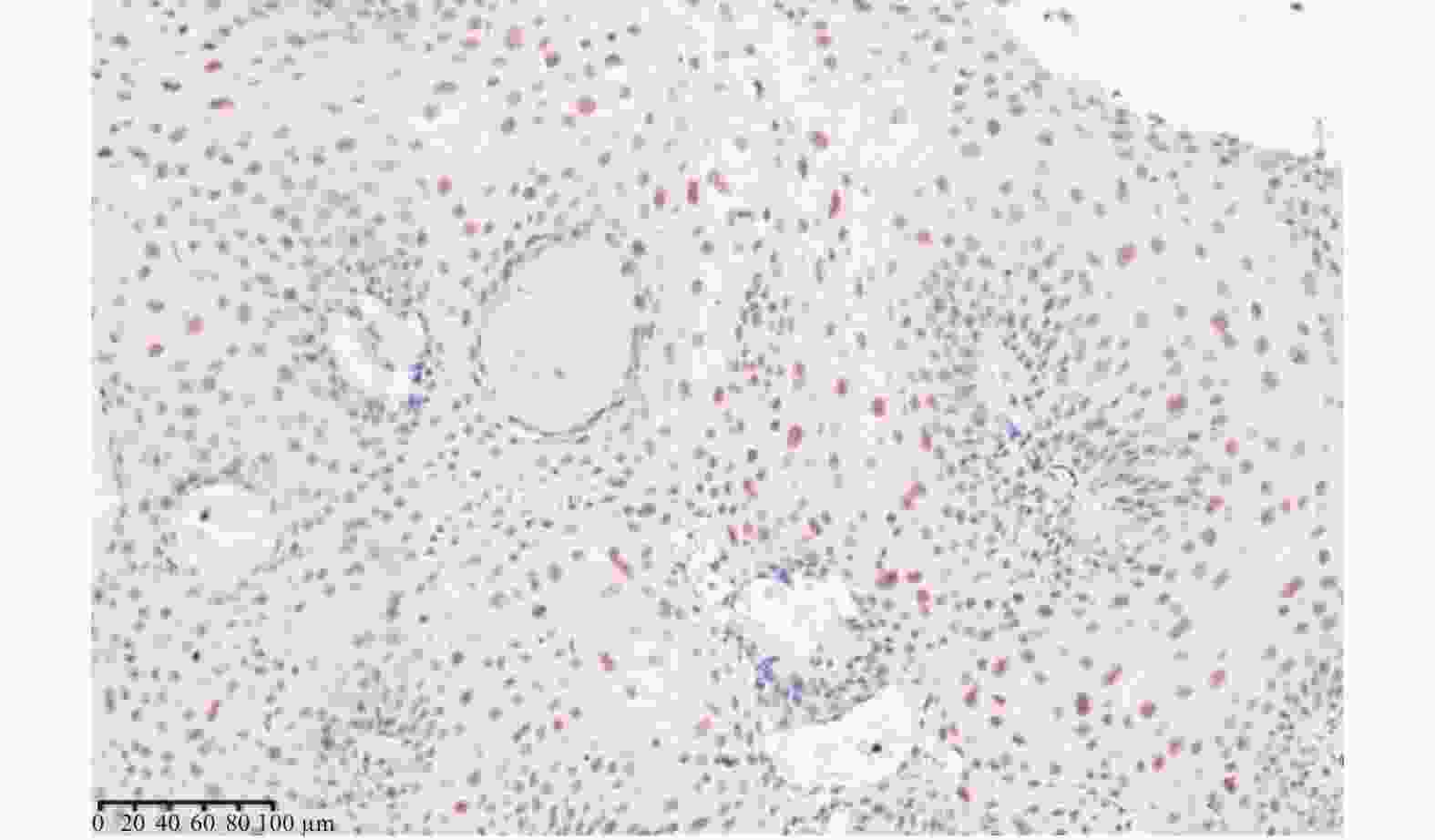
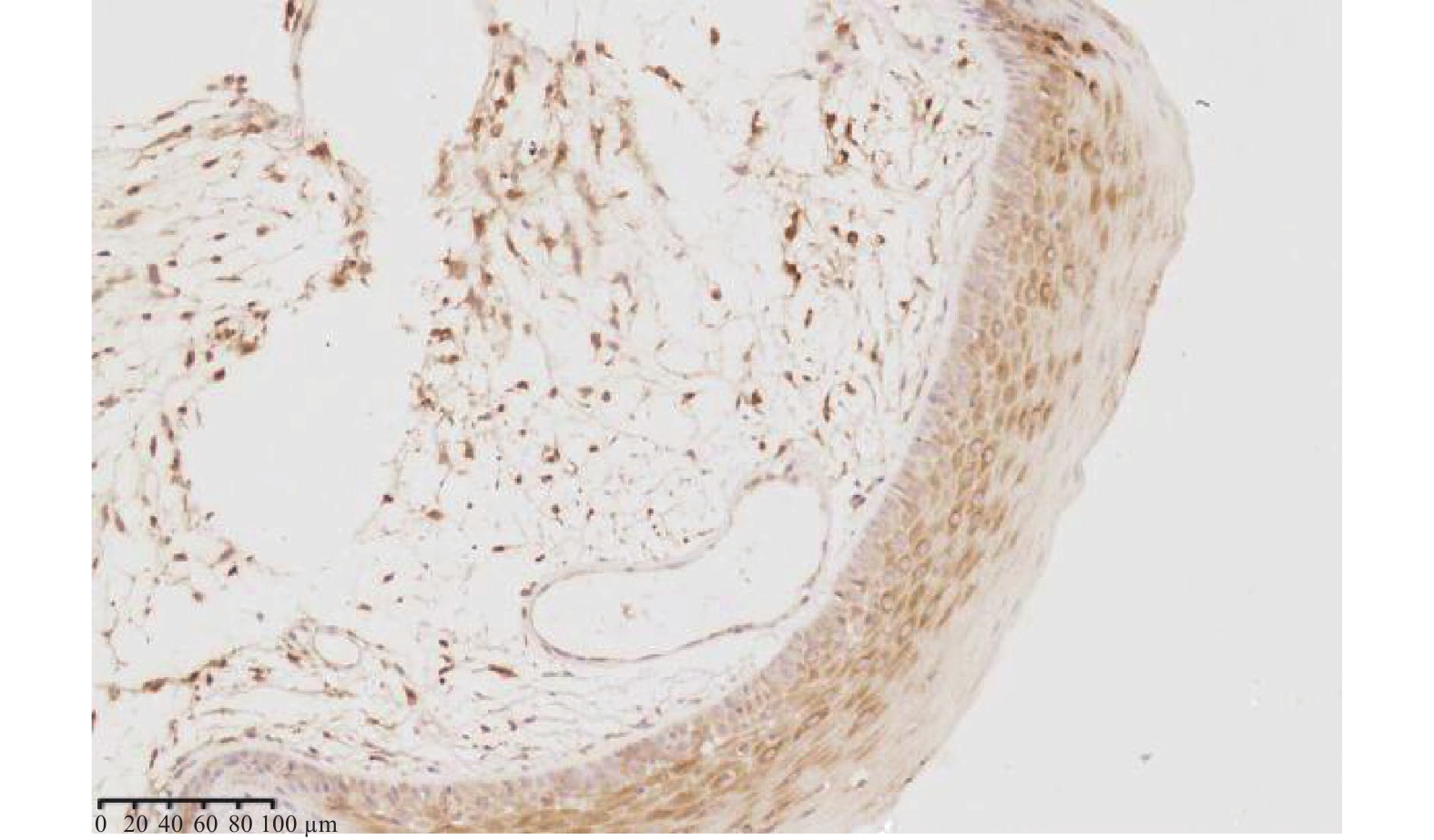
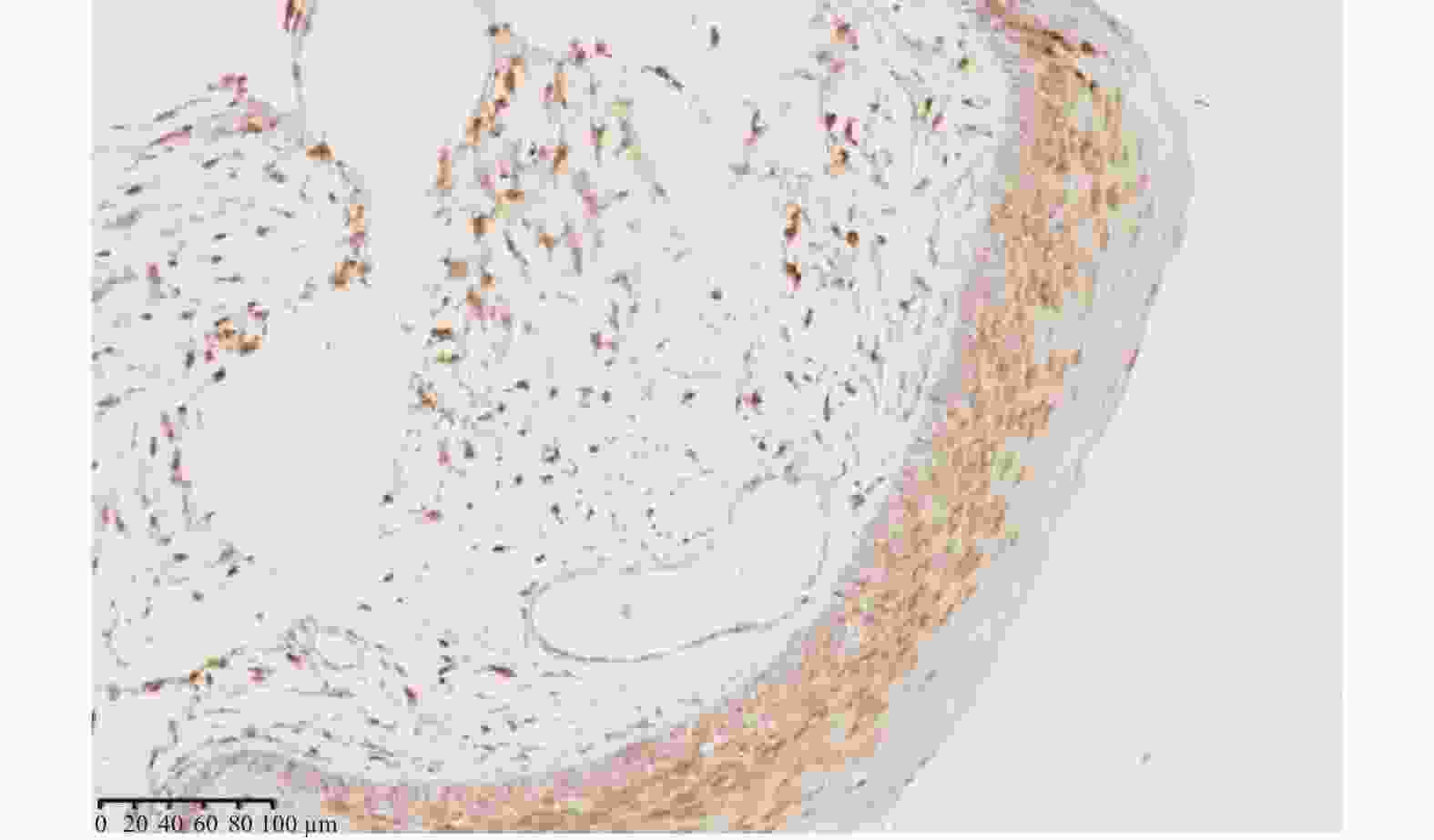
目的 研究COX2和CDX2在喉鳞癌发生发展过程中的表达特点及其与喉鳞癌患者预后的关系。 方法 采用免疫组化和计算机图像分析技术,观察喉息肉、喉乳头状瘤及喉鳞癌中COX2和CDX2的表达特点,并对其中的25位喉鳞癌患者进行随访以期了解COX2和CDX2对患者预后的影响。 结果 (1)COX2在喉鳞癌中的表达低于喉息肉(P = 0.004)和喉乳头状瘤(P = 0.001),T3-T4期喉鳞癌COX2表达比T1-T2期高,差异有统计学意义(P = 0.001);有淋巴结转移喉鳞癌组高于无淋巴结转移喉鳞癌组,低、中、高分化喉鳞癌中的表达逐渐升高,但差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05);(2)CDX2在喉息肉、喉乳头状瘤中表达均较弱,在喉鳞癌中不表达,且差异无统计学意义( P > 0.05);(3)COX2蛋白表达阳性或阴性对患者的预后无影响。 结论 (1)COX2低表达可能与喉鳞癌的发生有关,但不能预测喉鳞癌患者的预后;(2)CDX2可能不是喉鳞癌的危险因素。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression characteristics of COX2 and CDX2 in the development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and their relationship with the prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Methods The expression characteristics of COX2 and CDX2 in laryngeal polyps, laryngeal papilloma and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma were detected at their protein levels by immunohistochemistry (IHC) and image analysis (IA) techniques in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Twenty-five cases with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma were followed up to understand the patient prognostic effects of COX2 and CDX2. Results 1. The expression of COX2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma was lower than that of laryngeal polyps (P = 0.004) and laryngeal papilloma (P = 0.001). The expression of COX2 in T3-T4 stage laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma was higher than that in T1-T2 stage, and the difference was statistically significant (P = 0.001). The expression of COX2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma with lymph node metastasis was higher than that in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma without lymph node metastasis, the expression of COX2 increased gradually in low, medium and high differentiated laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, but the differences were not statistically significant (P > 0.05). 2. The expressions of CDX2 protein was weakly positive in laryngeal polyp and laryngeal papilloma, and the expressions of CDX2 protein was negative in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, and the difference was not statistically significant ( P > 0.05). 3. Positive or negative expression of COX2 protein had no effect on the prognosis of patients. Conclusion 1. Low expression of COX2 may be associated with the development of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma, but cannot predict the prognosis in patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. 2. CDX2 may not be a risk factor for laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. -
表 1 COX2在喉息肉、喉乳头状瘤和喉鳞癌中的表达(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. The expression of COX2 in laryngeal polyps,laryngeal papilloma and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 n COX2表达 P 阳性单位(PU) 喉息肉 15 20.5987 ± 6.1766 1.000,0.004▲ 喉乳头状瘤 11 23.0000 ± 2.4537 0.001▲ 喉鳞癌 25 11.3664 ± 10.4782 与喉鳞癌比较,▲P < 0.05。 表 2 COX2在喉鳞癌中的表达与临床病理参数之间的关系(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. The relationship between the expression of COX2 and clinicopathologic parameters in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (
$\bar x \pm s $ )临床病理参数 n COX2表达 P 阳性单位(PU) 临床分期 T1~T2 16 6.6875 ± 8.9408 0.001 T3~T4 9 19.5778 ± 7.6142 颈淋巴结转移 (+) 8 13.1500 ± 10.9172 0.571 (−) 17 10.5294±10.5008 分化程度 高分化 8 15.2275 ± 9.6195 1.000,0.169 中分化 11 12.3945±9.9813 0.381 低分化 6 4.3333±10.6145 表 3 CDX2在喉息肉、喉乳头状瘤和喉鳞癌中的表达(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. The expression of CDX2 in laryngeal polyps,laryngeal papilloma and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 n CDX2表达 P 阳性单位(PU) 喉息肉 15 8.73 ± 1.20 0.455,0.052 喉乳头状瘤 11 5.01 ± 0.05 0.132 喉鳞癌 25 0 表 4 COX2的表达与喉鳞癌患者预后的关系
Table 4. Relationship between expression of COX2 and prognosis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma patient
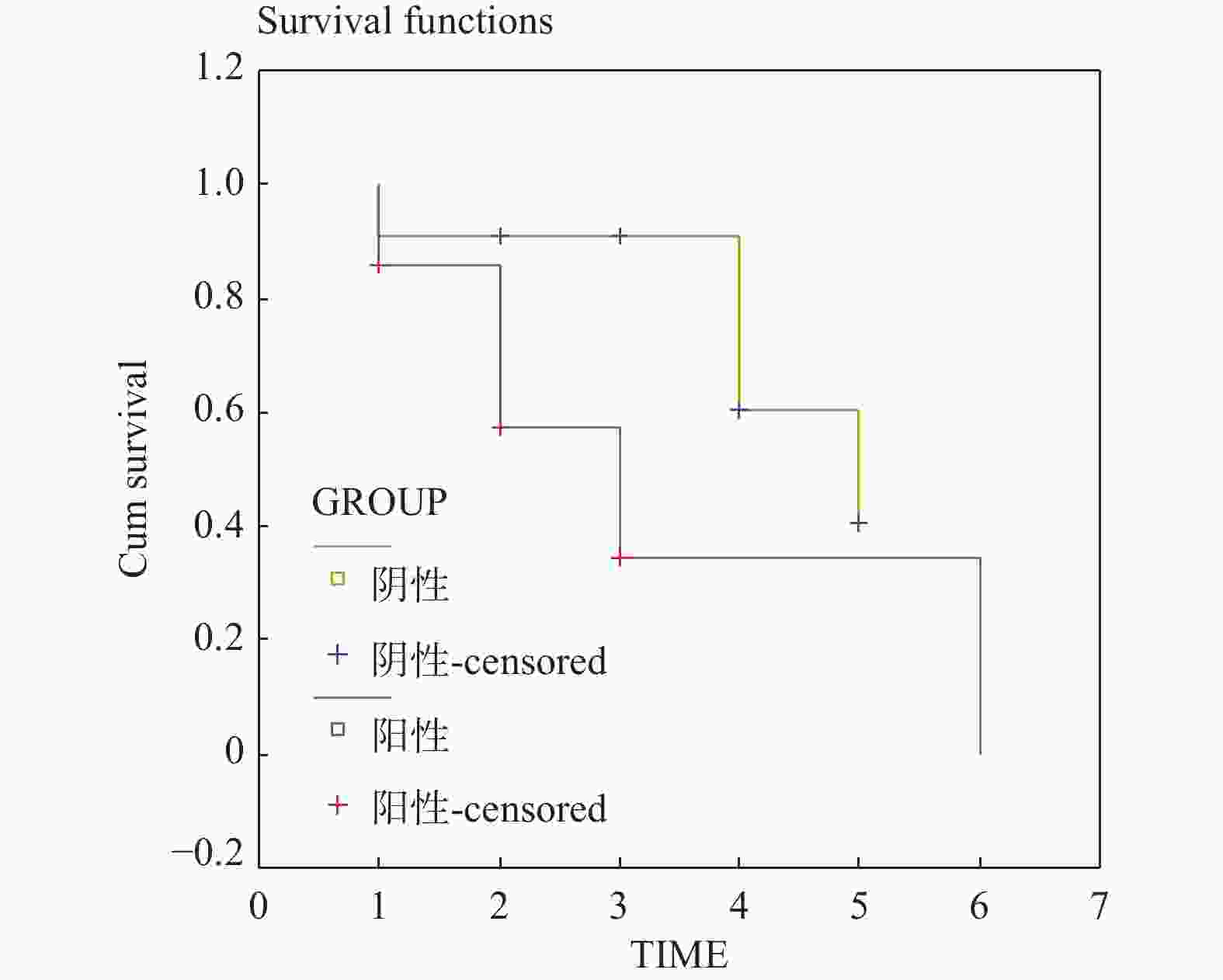
COX2表达 年生存率(%) 中位生存期 1 a 3 a 5 a 95%可信区间 P (+) 85.71 34.29 34.29 1.70~4.30 0.078 (−) 90.91 90.91 40.40 3.00~7.00 -
[1] Mohankumar K,Francis A P,Pajaniradje S,et al. Synthetic curcumin analog: Inhibiting the invasion,angiogenesis,and metastasis in human laryngeal carcinoma cells via NF-kB pathway[J]. Mol Biol Rep,2021,48(8):6065-6074. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06610-8 [2] Xia C F,Dong X S,Li H,et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States,2022:Profiles,trends,and determinants[J]. Chin Med J,2022,135(5):584-590. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002108 [3] 李惠萍,崔秀娟,关超,等. 喉癌前病变100例分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志,1995,30(5):302-304. [4] 柴丽萍,梁伟英,王章锋,等. 诱导型一氧化氮合酶在喉乳头状瘤中的表达及意义[J]. 中国肿瘤,2005,14(12):51-53. [5] 鹿道湿. 耳鼻咽喉科学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 1998: 360-361. [6] EI-Naggar A K, Chan J K C, Grandis J R, et al. World health organization classification of tumors//WHO classification of head and neck tumors[M]. 4th Edition . Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2017: 7. [7] 方静怡,朱正鹏,李凯,等. PDC-E2抗体在自身免疫性肝病的表达研究[J]. 肝脏,2017,22(1):34-37. [8] Escalante P,Barría T,Cancino M,et al. Genetic polymorphisms as non-modifiable susceptibility factors to laryngeal cancer[J]. Biosci Rep,2020,40(5):BSR20191188. doi: 10.1042/BSR20191188 [9] 王兴鹏. 环氧合酶、脂氧合酶与肿瘤[M]. 上海: 第二军医大学出版社, 2006: 14-16. [10] Cattaruzza M S,Maisonneuve P,Boyle P P. Epidemiology of laryngeal cancer[J]. Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol,1996,32B(5):293-305. [11] Sung M W,Roh J L,Park B J,et al. Bile acid induces cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in cultured human pharyngeal cells: A possible mechanism of carcinogenesis in the upper aerodigestive tract by laryngopharyn geal reflux[J]. Laryngoscope,2003,113(6):1059-1063. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200306000-00027 [12] Lima-Rodrigues M,Valle-Fernandes A,Lamas N,et al. A new model of laryngitis:Neuropeptide,cyclooxygenase and cytokine profile[J]. Laryngoscope,2008,118(1):78-86. doi: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e3181492400 [13] Chan G,Boyle J O,Yang E K,et al. Cyclooxygense-2 expression is up-regulated in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck[J]. Cancer Res,1999,59(5):991-994. [14] Ranelletti F O,Almadori G,Rocca B,et al. Prognotic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Int J Cancer,2001,95(6):343-349. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(200002)9999:9999<::AID-IJC1060>3.0.CO;2-0 [15] 孙希才,葛荣明,董庆汉,等. 环氧化酶-2在喉鳞状细胞癌中的表达及其与微血管密度的关系[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2005,19(21):967-970. [16] Höing B,Kanaan O,Altenhoff P,et al. Stromal versus tumoral inflammation differentially contribute to metastasis and poor survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget,2018,9(9):8415-8426. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23865 [17] Takatori H,Natsugoe S,Okumura H,et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is related to prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol,2008,34(4):397-402. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2007.04.011 [18] Gallo O,Masini E,Bianchi B,et al. Prognostic significance of cyclooxygenase-2 pathway and angiogenesis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Hum Pathol,2002,33(7):708-714. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2002.125376 [19] Goto R,Hoshikawa H,Fujii T,et al. Clinicopathological significance of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oncol Rep,2008,19(3):645-650. [20] Kyzas P A,Stefanou D,Agnantis N J. COX-2 expression correlates with VEGF-C and lymph node metastases in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Mod Pathol,2005,18(1):153-160. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800244 [21] 方义湖,来茂德. 结直肠肿瘤的新标记-CDX2[J]. 国际遗传学杂志,2006,29(4):311-316. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4386.2006.04.017 [22] Saller J,Al Diffalha S,Neill K,et al. CDX-2 expression in esophageal biopsies without goblet cell intestinal metaplasia may be predictive of Barrett's Esophagus[J]. Dig Dis Sci,2020,65(7):1992-1998. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05914-x [23] Chang Y T,Hsu C,Jeng Y M,et al. Expression of the caudal-type homeodomain transcription factor CDX2 is related to clinical outcome in biliary tract carcinoma[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol,2007,22(3):389-394. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04487.x [24] Matsumoto K,Mizoshita T,Tsukamoto T,et al. CDX2 expression in pancreatic tumors: Relationship with prognosis of invasive ductal carcinomas[J]. Oncol Rep,2004,12(6):1239-1243. [25] Gao N,White P,Kaestner K H. Establishment of intestinal identity and epithelial-mesenchymal signaling by CDX2[J]. Dev Cell,2009,16(4):588-599. [26] Gross I,Duluc I,Benameur T,et al. The intestine-specific homeobox gene CDX2 decreases mobility and antagonizes dissemination of colon cancer cells[J]. Oncogene,2008,27(1):107-115. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210601 [27] Zeng H A,Cartun R,Andrew Ricci Jr. Potential diagnostic utility of CDX-2 immunophenotyping in extramammary Paget’s disease[J]. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol,2005,13(4):342-346. doi: 10.1097/01.pai.0000163989.12896.d2 [28] Xia X P,Xu E P,Quan S,et al. No association between the polymorphisms in CDX2 coding regions and colorectal cancer in Chinese[J]. Mol Cell Biochem,2009,331(1-2):27-30. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0141-2 [29] 王超,周小鸽. 探讨CDX2在胃肠道腺癌诊断中的病理学价值[J]. 中华病理学杂志,2006,35(4):228-231. -





 下载:
下载: