Visualization Analysis of Kinesiophobia Research Field Based on VOSviewer
-
摘要:
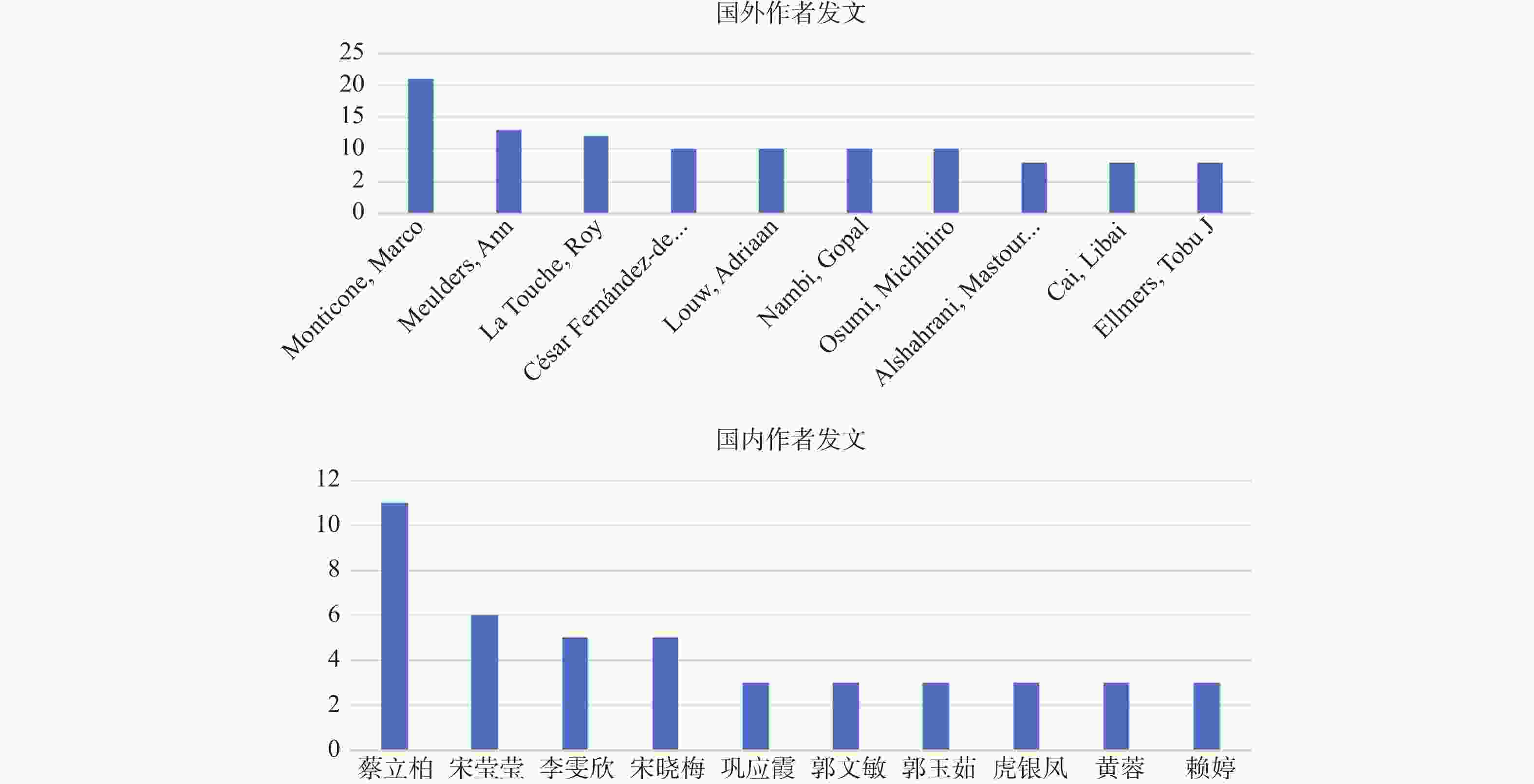
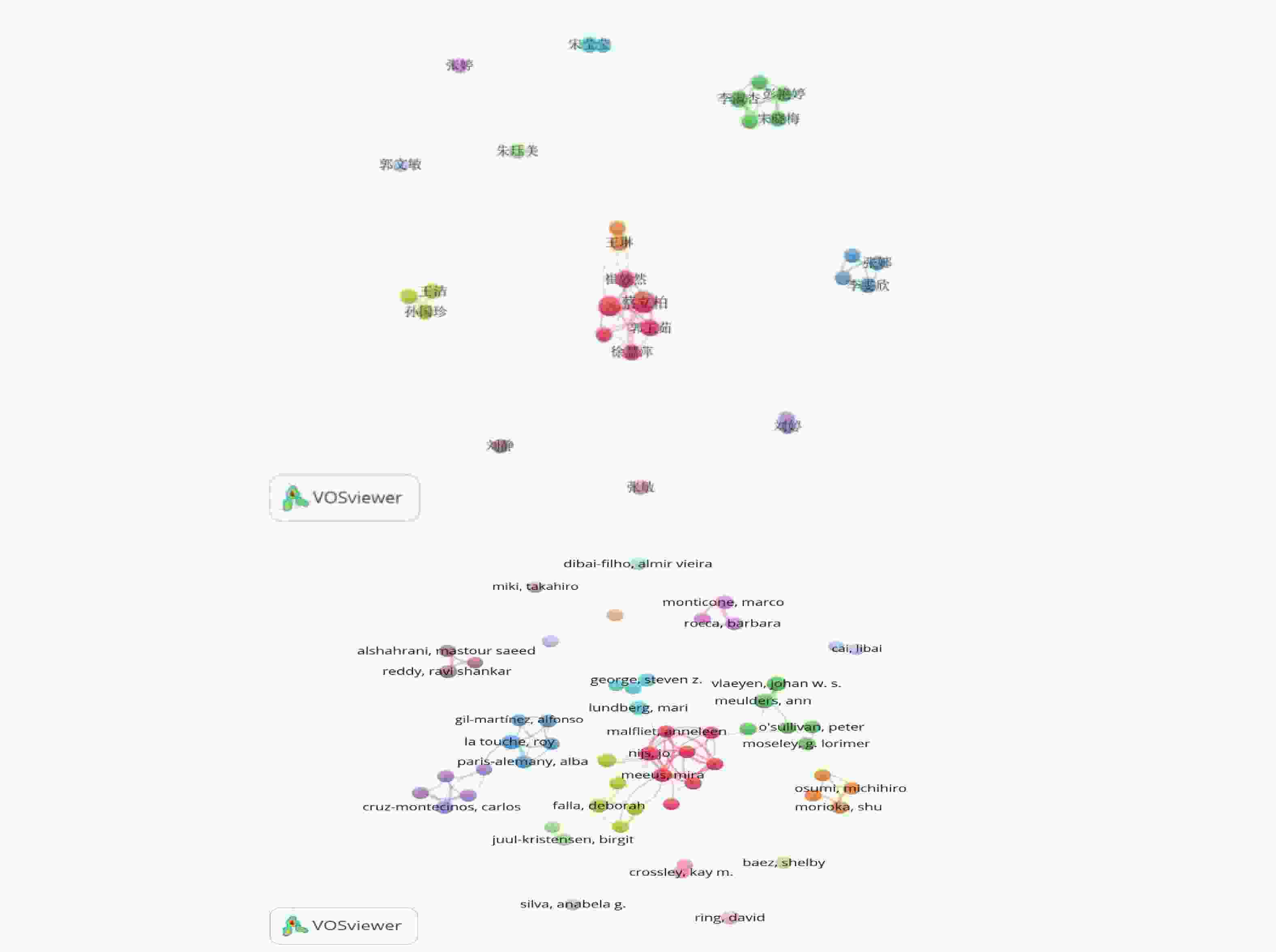
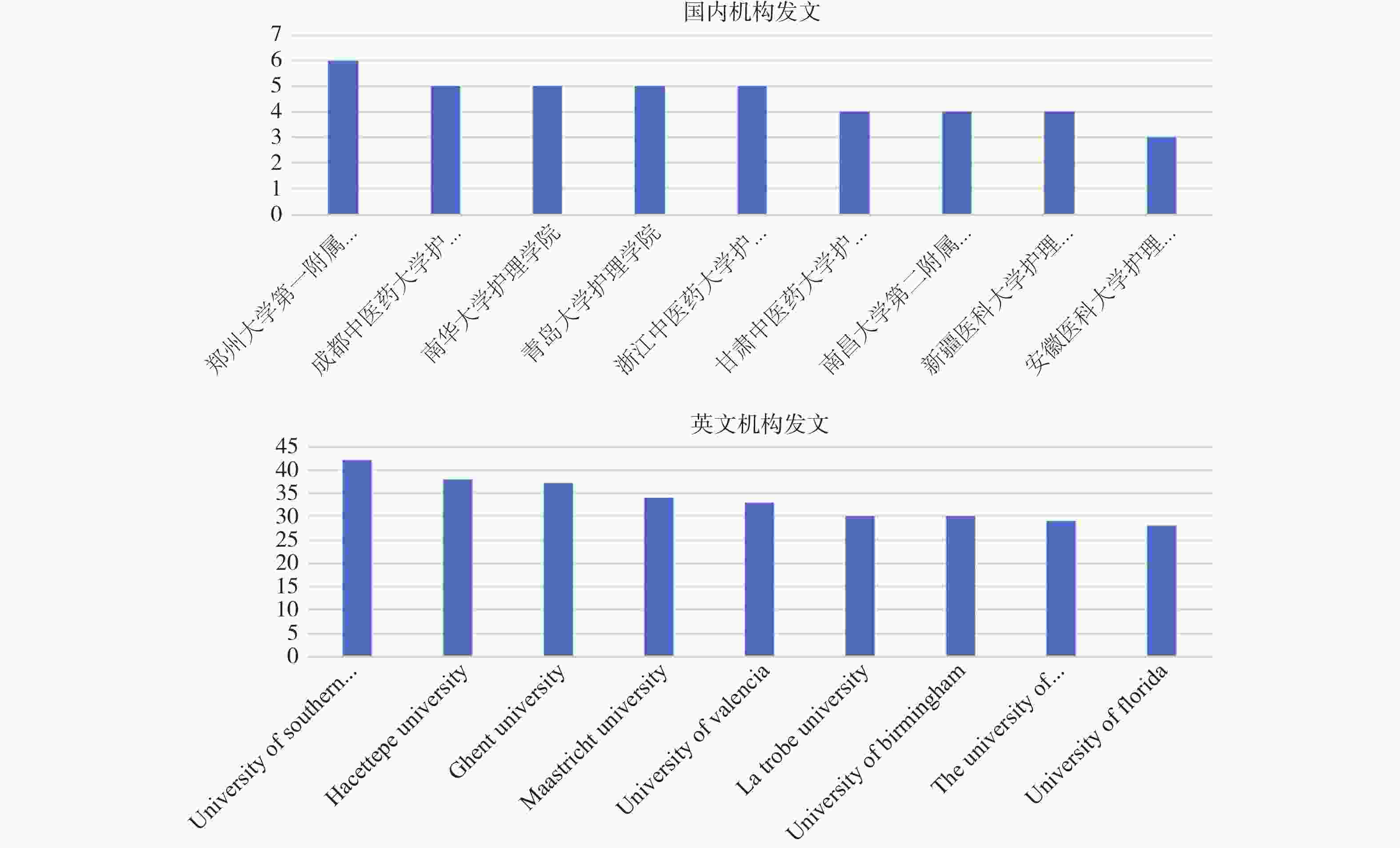
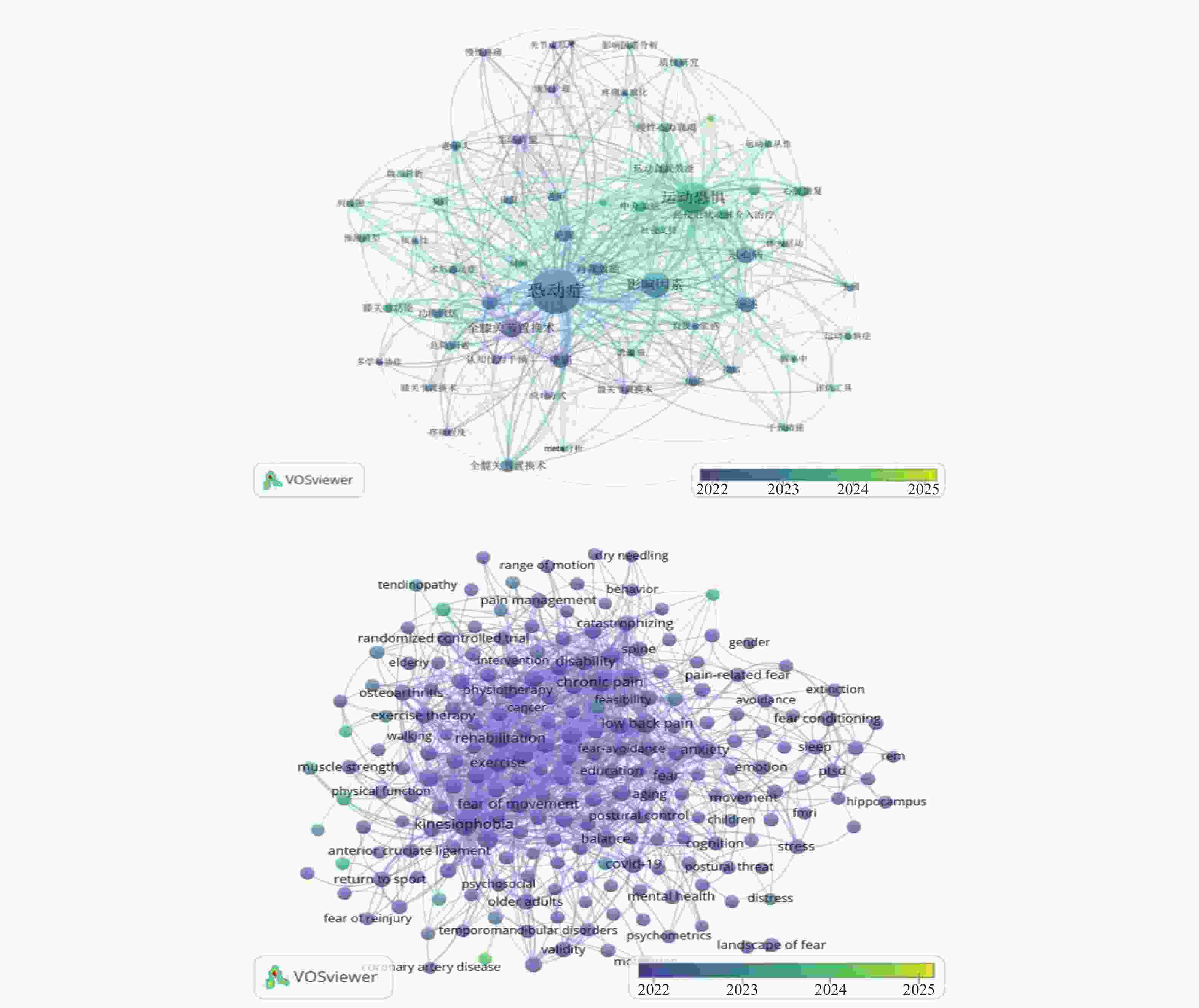
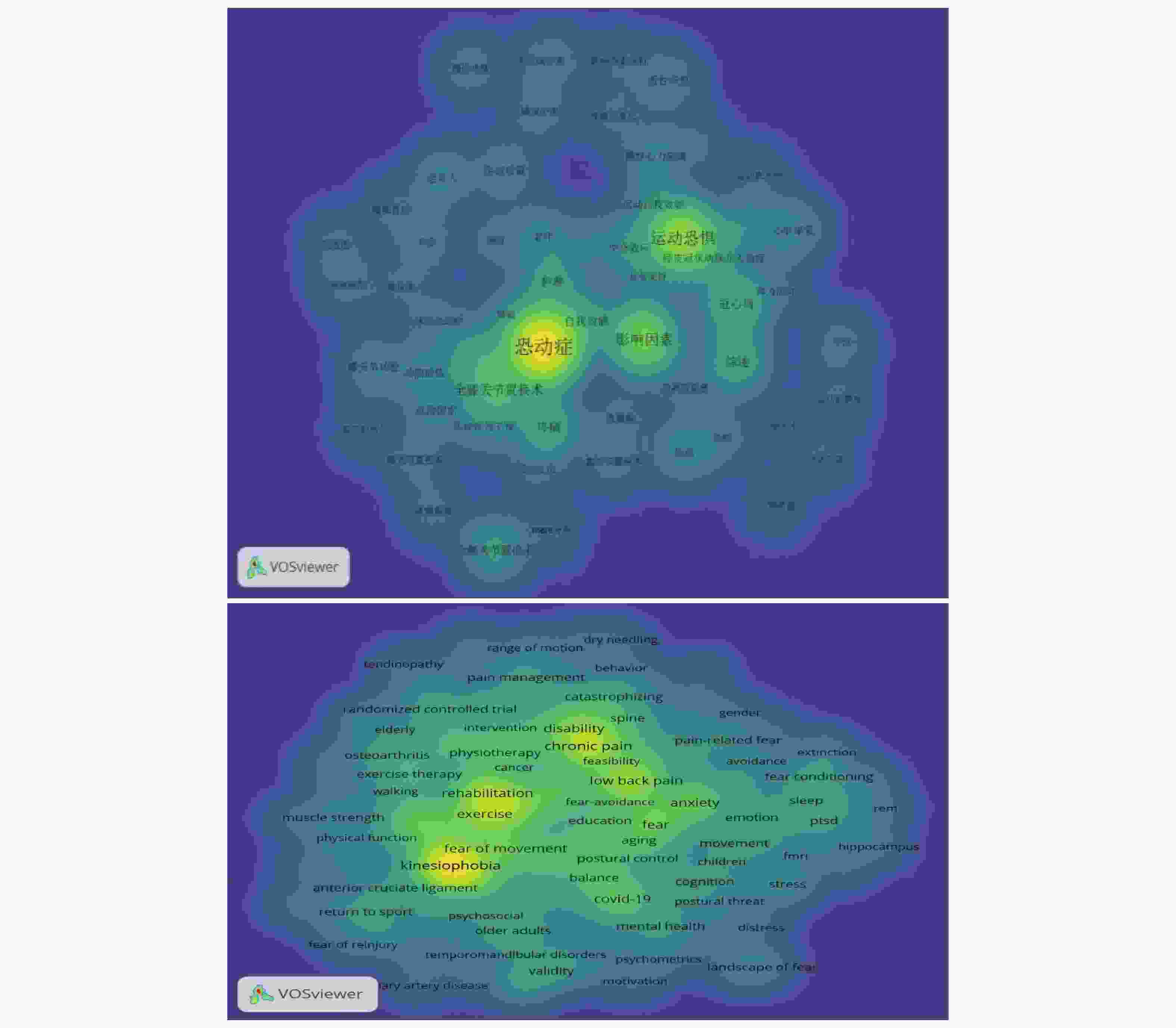
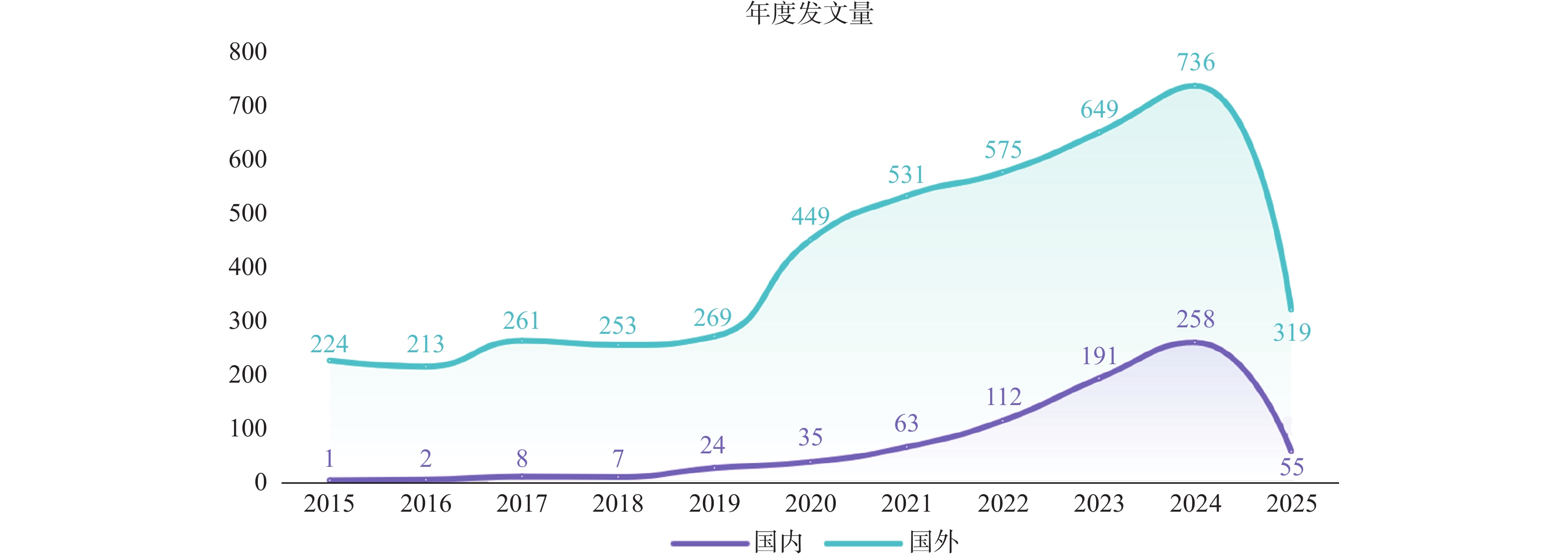
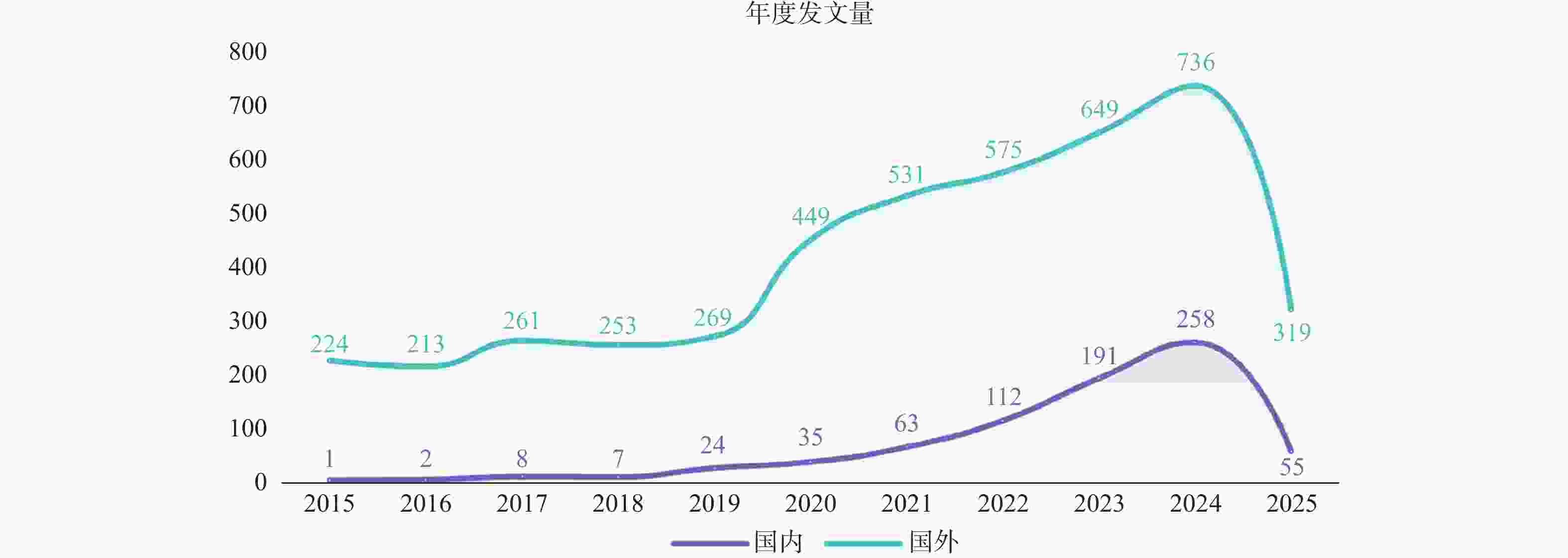
目的 基于VOSviewer软件,系统分析对比运动恐惧症现有的中英文研究的趋势和热点,旨在为临床干预及康复领域的研究提供参考。 方法 中文文献数据来源选用中国知网、万方、维普数据库,英文文献数据来源选用PubMed、Web of Science数据库,选取运动恐惧症相关主题文献,采用VOSviewer1.6.18软件中,分析文献基本信息材料,绘制图谱。 结果 中文文献共纳入760篇文献,英文文献共纳入 4491 篇文献。发文量高峰集中在2020 -2024年,国内在总体发文量、作者单人发文量、作者团队合作同国外相比较少;国内外研究共同高频关键词为“恐动症、疼痛、康复锻炼、残疾、焦虑”且关键词频率出现具有关联性和非随机性。结论 运动恐惧症的研究呈现上升趋势,国内外研究因发展侧重点不同,在研究方向具有异同点,国内研究可通过理论整合、技术转化、人群拓展、方法创新实现运动恐惧症的深入研究。 Abstract:Objective Based on the VOSviewer software, to systematically analyze and compare the trends and hotspots in existing Chinese and English research on kinesiophobia, aiming to provide references for research in the field of clinical intervention and rehabilitation. Methods Chinese literature data sources were selected from CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP databases, while English literature data sources were selected from PubMed and Web of Science databases.Relevant literature on kinesiophobia was selected, and the VOSviewer1.6.18 software was used to analyze the basic information materials of the literature and to draw maps. Results 760 Chinese literature articles and 4491 English literature articles were included. The peak of publication volume was concentrated between 2020 and 2024. Domestically, the overall publication volume, individual author publication volume, and team collaboration among authors were relatively lower compared to international standards. The common high-frequency keywords in both domestic and international research were "kinesiophobia, pain, rehabilitation exercise, disability, anxiety, " and the frequency of these keywords showed correlation and non-randomness.Conclusion Research on kinesiophobia is on an upward trend. Due to different development focuses, there are similarities and differences in research directions between domestic and international studies. Domestic research can achieve in-depth exploration of kinesiophobia through theoretical integration, technological transformation, population expansion, and methodological innovation. -
Key words:
- Kinesiophobia /
- VOSviewer /
- Bibliometric analysis
-
表 1 载文量排名前五的期刊
Table 1. Top 5 journals ranked by publication volume
序号 国内期刊 载文量 占比(%) 国外期刊 载文量 占比(%) 1 全科护理 34 5.19 PLOS ONE 97 2.16 2 心理月刊 25 3.81 BMC Musculoskelet Disord 67 1.49 3 护理学杂志 19 2.90 BMJ OPEN 61 1.35 4 中华护理杂志 16 2.44 Int J Environ Res Public Health 58 1.29 5 护理研究 14 2.13 J Clin Med 53 1.18 表 2 关键词χ2检验
Table 2. Keyword χ2 test
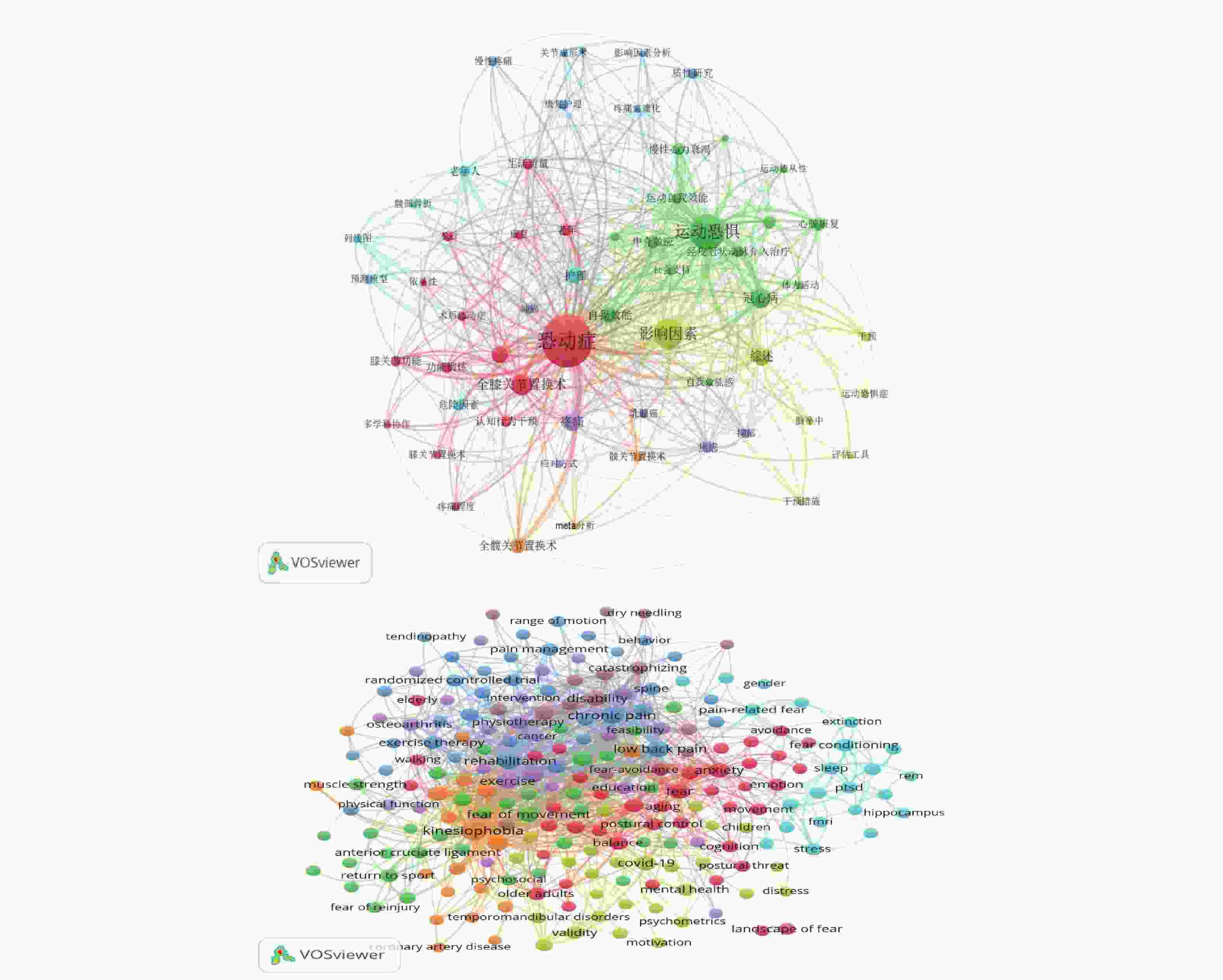
中文关键词 实际频率(次) 理论频率(次) 统计值 英文关键词 实际频率(次) 理论频率(次) 统计值 恐动症 673 32 0.000* Kinesiophobia 451 27 0.000* 影响因素 152 32 Chronic pain 227 27 全膝关节置换术 75 32 Low back pain 190 27 冠心病 64 32 Pain 173 27 综述 54 32 rehabilitation 180 27 疼痛 54 32 exercise 122 27 腰椎间盘突出 49 32 anxiety 120 27 护理 49 32 Fear 115 27 全髋关节置换术 39 32 Physical activity 112 27 自我效能 38 32 disability 105 27 *使用卡方检验,且关键词设定零假设即关键词的选择是随机的且均匀分布,则得出理论频率为24(总频率/总关键词),χ2对应的P值小于显著性水平(P < 0.05),则拒绝零假设,说明关键词的选择不是随机的。注:本次检验完整检验59个中文关键词、221个英文关键词,此表仅列出前10个。 表 3 中英文聚类词
Table 3. Chinese-English clustering terms
分类 中文关键词 英文关键词 #1 全膝关节置换术、依从性、功能锻炼、多学科协作、康复、术后、生活质量、膝关节功能、认知行为
干预Movement、movement disorders、movement ecology、multiple sclerosis、
older adults、older people、parkinson disease、parkinson's disease、
parkinson's disease、perception、physical fitness#2 中介效应、体力活动、心理弹性、
社会支持、自我效能、
运动依从性、运动自我效能avoidance behavior、extinction、fear conditioning、fear extinction、
fear generalization、fear memory、gender、hippocampus、
learning、memory、motor imagery、pain-related fear、pregnancy#3 关节成形术、康复护理、
影响因素分析、慢性疼痛、
疼痛灾难化、质性研究adolescent、anterior cruciate、ligament( reconstruction)、knee pain、Biomechanics(biopsychosocial)、Electromyography、fear avoidance(fear of reinjury)、Feasibility、Function(functional performance)kinematics、Knee、muscle strength、outcomes、patient-reportedoutcome measures、Prognosis Proprioception、Psychological(Psychology)、Qualitality、Return to play(sport)Treatment #4 干预、干预措施、影响因素、
综述、评估工具clinical trial、education、exercise、intervention、knee pain、meta-analysis、musculoskeletal、neuroscience、osteoarthritis、pain、patient education
physical exercise、physical function、physiotherapy、
primary care、randomised controllection#5 乳腺癌应对方式、抑郁、
焦虑、疼痛breast cancer、catastrophization、cognitive behavioral therapy、exercise therapy、
fear-avoidance model、pain education、pain management、pain neuroscience education、physical therapy、randomized controlled、Rehabilitation#6 列线图、危险因素、护理、老年人、预测模型、髋部骨折 Catastrophizingcentral sensitization、chronic musculoskeletal、
conditioned pain modulation、disability、dry needling、fear-avoidance beliefs、frozen shoulder、knee osteoarthritis、neck pain、pain intensity、
predictors、psychological factors psychosocial factors#7 meta分析、全髋关节置换术、
髋关节置换术ankylosing spondylitis、cardiac rehabilitation、coronary artery disease、depression、fatigue、haemophilia、health-related quality of influencing factors、physical activity、pilates、quality of life、rheumatoid arthritis、stroke、total knee arthroplasty -
[1] 医政司. 国家卫生健康委办公厅关于进一步推进加速康复外科有关工作的通知[EB/OL]. (2023-04-21)[2024-09-20]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7659/202304/3f9fb5d6eb304edfbf13dcfe28ce35a5.shtml. [2] 郑雯雯,罗家琴,余文文,等. 慢性肌肉骨骼疼痛患者体力活动的研究进展[J]. 中国护理管理,2023,23(2):293-297. [3] 徐榕璟,贺旭妍,贾守梅. 骨科老年患者术后运动恐惧的范围综述[J]. 中华护理杂志,2024,59(5):626-633. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2024.05.017 [4] 黄莉,杨旭,李芳芳,等. 髋、膝关节置换术后患者恐动症发生现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2023,16(11):1001-1007. [5] 宣沁,高红,姜嘉伟. 多学科协作下认知行为干预在慢性腰痛恐动症患者中的应用[J]. 中国护理管理,2021,21(10):1481-1486. [6] 宋晓梅,马素慧,安利杰,等. 冠心病心绞痛患者恐动症的危险因素分析[J]. 中国护理管理,2022,22(5):675-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2022.05.008 [7] 郑亚男,曹海娜,高东霞. 基于疼痛日记的早期量化康复训练对全膝关节置换术后患者恐惧回避信念、恐动症状缓解及膝关节功能的影响[J]. 国际移植与血液净化杂志,2024,22(2):5-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115399-20240125-02002 [8] Zhang Q,Zhang J,Ran W,et al. Effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy on kinesiophobia and oral health-related quality of life in patients with temporomandibular disorders,study protocol for a randomized controlled trial[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2020,99(47):e23295. [9] Lin L,Lin T,Chang K,et al. Pain neuroscience education for reducing pain and kinesiophobia in patients with chronic neck pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PAIN,2024,28(2):231-243. doi: 10.1002/ejp.2182 [10] 徐慧萍,张炎改,刘延锦,等. 全膝关节置换术后患者恐动症的影响因素研究[J]. 中华护理杂志,2021,56(10):1460-1465. [11] 朱世琴,邓波,罗欢,等. 护理预测研究文献热点与发展趋势[J]. 西南医科大学学报,2022,45(2):151-156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3351.2022.02.013 [12] 蔡立柏, 梁郝, 刘延锦, 等. 跌倒恐惧在全膝关节置换术后患者疼痛灾难化与恐动症的中介效应[J]. 护理学报,2024,31(7):63-67. [13] Monticone M, Cedraschi C, Ambrosini E, et al. Cognitive-behavioural treatment for subacute and chronic neck pain[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2015(5):CD010664. [14] 蔡立柏, 王琳, 刘延锦, 等. 基于回授法的健康教育在全膝关节置换术恐动症患者中的应用[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2022,28(8):986-991. [15] Murillo C, Gal á n-Mart í n MÁ, Montero-Cuadrado F, et al. Reductions in kinesiophobia and distress after pain neuroscience education and exercise lead to favourable outcomes: A secondary mediation analysis of a randomized controlled trial in primary care[J]. Pain,2023,164(10):2296-2305. [16] 吕振勇,纪晓蕾,黄丽,等. 疼痛恐惧对疼痛的影响及其认知机制[J]. 心理科学进展,2013(5):817-826. [17] 周阳,刘晓彤,黄颐殊,等. 意外创伤疼痛患者恐动症的影响因素及路径分析[J]. 中国护理管理,2023,23(10):1462-1466. [18] 石海宁,陈玲,周丽静,等. 乳腺癌患者术后早期恐动症现状、影响因素及其对策研究[J]. 现代临床护理,2023,22(8):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8283.2023.08.001 [19] 路仪,刘丽,张帅,等. 心力衰竭患者运动康复促进和障碍因素的系统评价[J]. 护理学杂志,2023,38(13):83-88. doi: 10.3870/j.issn.1001-4152.2023.13.083 [20] Osumi M,Sumitani M,Nishi Y,et al. Fear of movement-related pain disturbs cortical preparatory activity after becoming aware of motor intention[J]. BEHAVIOURAL BRAIN RESEARCH,2021,411:113379. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113379 [21] Bazancir-Apaydin Z,Sakizli Erdal E,Keser I,et al. The profile beyond leg pain: In basis of central sensitization,kinesiophobia,and body awareness in patients with chronic venous disease[J]. PHLEBOLOGY,2025,40(3):182-190. doi: 10.1177/02683555241286385 [22] Bonatesta L,Ruiz-Cardenas J D,Fernandez-Azorin L,et al. Pain science education plus exercise therapy in chronic nonspecific spinal pain: A systematic review and meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials[J]. J Pain,2022,23(4):535-546. doi: 10.1016/j.jpain.2021.09.006 [23] Haun J N,Fowler C A,Smith B M,et al. Benchmark findings from a veteran electronic patient-reported outcomes evaluation from a chronic pain management telehealth program[J]. BMC Health Serv Res,2024,24(1):2-15. doi: 10.1186/s12913-023-10159-6 [24] 杨娜. 老年全髋关节置换术患者康复运动恐惧的现况及其影响因素调查[J]. 护理实践与研究,2023,20(4):498-503. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9676.2023.04.006 [25] 黄蓉,丁梅,黄华华,等. 运动自我效能在冠心病患者运动恐惧和体育活动量间的中介作用[J]. 中华护理教育,2022,19(12):1119-1123. [26] 宋倩倩,覃勤,梁光梅,等. 脑卒中后肩手综合征病人运动恐惧现状及其影响因素[J]. 全科护理,2024,22(23):4537-4541. [27] 陈晓东,龚芬芬,陈隐. 鼻咽癌病人运动恐惧现状及影响因素调查研究[J]. 循证护理,2023,9(3):541-544. [28] Ferman B,Nyland J,Richards J,et al. Adolescent athletes with stronger athletic identity perceptions have weaker fear avoidance perceptions during musculoskeletal injury rehabilitation return to sports preparation[J]. J Pediatr Orthop,2024,44(8):489-496. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002723 [29] Koca T T,Ozer A. Low back pain and kinesiophobia in pregnant women[J]. Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation,2024,37(5):1373-1380. doi: 10.3233/BMR-240006 [30] Okan F,Ozsoy A Z,Sandalci T,et al. The relationship between kinesiophobia and physical activity levels,gestational weight gain,and musculoskeletal pain in pregnant women[J]. WOMEN & HEALTH,2023,63(7):551-561. [31] Yilmaz G G,Tanriverdi M,Onal G,et al. Understanding kinesiophobia in pediatric bone tumors: investigating its presence and predictive factors[J]. Eur J Pediatr,2025,184(3):2-11. [32] Griffin A,Wilson L,Feinstein A B,et al. Virtual reality in pain rehabilitation for youth with chronic pain: Pilot feasibility study[J]. JMIR Rehabil Assist Technol,2020,7(2):e22620. doi: 10.2196/22620 [33] 刘延锦,蔡立柏,徐秋露,等. 慢性疼痛患者恐动症的研究进展[J]. 中华护理杂志,2017,52(2):234-239. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2017.02.025 [34] 张莉,张子茹,张彩蕾,等. 全膝关节置换术患者恐动症水平变化轨迹及影响因素分析[J]. 护士进修杂志,2024,39(9):904-911. [35] 王亚欣,桑文凤,贾冠华,等. 首发急性心肌梗死患者运动恐惧现状及影响因素分析[J]. 中国护理管理,2022,22(1):63-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1756.2022.01.014 [36] U E. Ankylosing spondylitis and kinesiophobia[J]. PeerJ,2025,13:e19034. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19034 [37] Camalier C R,McHugo M,Zald D H,et al. The effect of deep brain stimulation therapy on fear-related capture of attention in parkinson's disease and essential tremor: A comparison to healthy individuals[J]. J Neurol Disord,2018,6(1):1000377. [38] 何玲,云洁,李宛霖,等. 骨关节疼痛病人恐动症影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 全科护理,2023,21(11):1472-1476. doi: 10.12104/j.issn.1674-4748.2023.11.008 [39] 郝丽丽,马艳秋,张正涛,等. 不同干预措施对经皮冠状动脉介入术后患者运动恐惧干预效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国实用护理杂志,2024,40(20):1542-1549. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn211501-20240102-00005 [40] 宋莹莹,邵丽芳,姜云龙,等. 普拉提疗法对慢性非特异性下腰痛恐动症患者干预效果的Meta分析[J]. 护理管理杂志,2024,24(3):242-246. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-315x.2024.03.012 [41] 雷梦迪,张倬萁,潘兰霞,等. 全膝关节置换术后病人恐动症列线图预测模型的构建[J]. 护理研究,2023,37(1):40-46. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2023.01.023 [42] Morales Tejera D,Nijs J,Malfliet A,et al. Effectiveness of pain neuroscience education,motivational interviewing and cognition targeted exercise therapy in patients with chronic neck pain: protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial (the COGMO-AP study)[J]. BMJ Open,2025,15(2):e87788. [43] Ozdemir F,Ari A,Kilcik M H,et al. Prediction of neuropathy,neuropathic pain and kinesiophobia in patients with type 2 diabetes and design of computerized clinical decision support systems by using artificial intelligence[J]. Medical Hypotheses,2020,143:110070. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110070 [44] 武满丽,汪张毅,郝淑云,等. 虚拟现实技术在慢性疼痛恐动症患者中的应用进展[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2024,30(4):545-549. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115682-20230725-00191 -





 下载:
下载: