Molecular Mechanism of the YAP1/ANXA2 Signaling Axis in Regulating Apoptosis and Migration of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
-
摘要:
目的 探讨Hippo信号通路核心效应分子YAP1在肾损伤中调控下游效应分子ANXA2的分子机制。 方法 构建YAP1过表达的人肾小管上皮细胞(human proximaltubular epithelial cell line,HK-2)模型,采用免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)联合质谱分析技术筛选YAP1相互作用蛋白;通过siRNA干扰技术敲低ANXA2表达,采用Transwell实验检测细胞迁移能力,流式细胞术(Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法)检测细胞凋亡水平;通过双荧光素酶报告基因实验验证YAP1对ANXA2启动子转录活性的调控作用。 结果 Co-IP与质谱分析表明,YAP1过表达可显著富集ANXA2并形成稳定复合物(P < 0.01)。功能实验显示,ANXA2沉默后细胞早期与晚期凋亡率显著升高(P < 0.001),细胞迁移数明显减少(P < 0.01)。双荧光素酶报告系统证实YAP1可直接激活ANXA2启动子转录活性(P < 0.001)。 结论 YAP1通过直接结合ANXA2启动子并增强其转录,进而抑制肾小管上皮细胞凋亡并促进迁移。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the molecular mechanism by which YAP1, the core effector of the Hippo pathway, regulates its downstream effector ANXA2 in renal injury, and to elucidate the role of the YAP1/ANXA2 axis in renal tubular epithelial cell repair. Methods A YAP1-overexpressing HK-2 cell model was established. Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) combined with mass spectrometry was used to screen for YAP1-interacting proteins. ANXA2 expression was knocked down using siRNA interference. Cell migration ability was assessed via Transwell migration assays, and apoptosis levels were detected by flow cytometry (Annexin V-FITC/PI staining). The regulatory effect of YAP1 on ANXA2 promoter transcriptional activity was verified using a dual-luciferase reporter gene assay. Results YAP1 overexpression significantly enriched ANXA2 and formed a stable complex (P < 0.01). Silencing of ANXA2 significantly increased the rates of early and late apoptosis (P < 0.001) and markedly reduced the number of migrating cells (P < 0.01). The dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed that YAP1 directly activates ANXA2 promoter and enhances its transcriptional activity (P < 0.001). Conclusion YAP1 directly binds to the ANXA2 promoter and enhances its transcription, thereby inhibiting apoptosis and promoting migration of renal tubular epithelial cells, highlighting the YAP1/ANXA2 axis as a critical regulator of renal injury repair. This study provides a novel potential target for mitigating renal fibrosis. -
Key words:
- YAP1 /
- ANXA2 /
- Renal injury /
- Apoptosis /
- Epithelial-mesenchymal transition /
- Transcriptional regulation
-
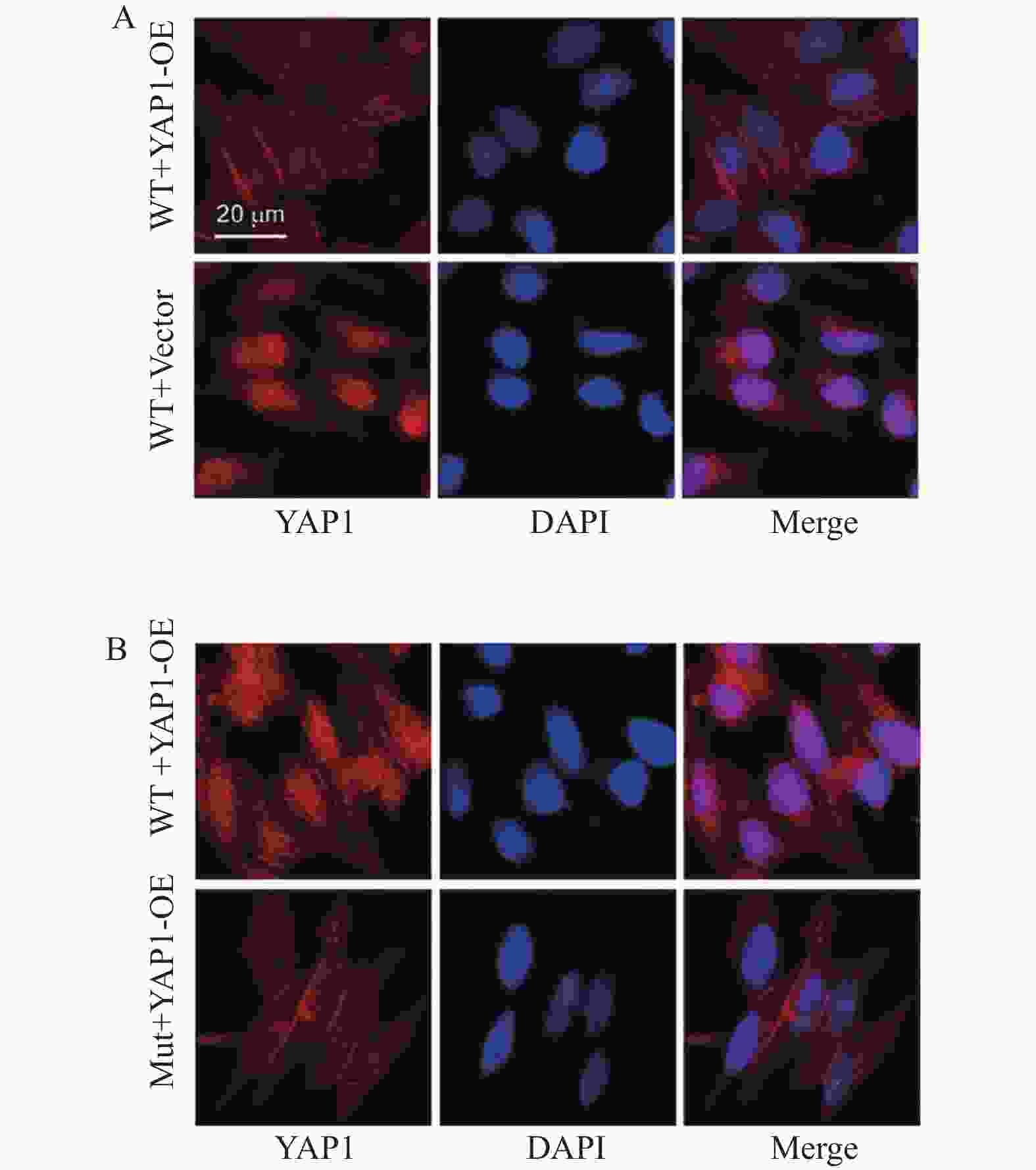
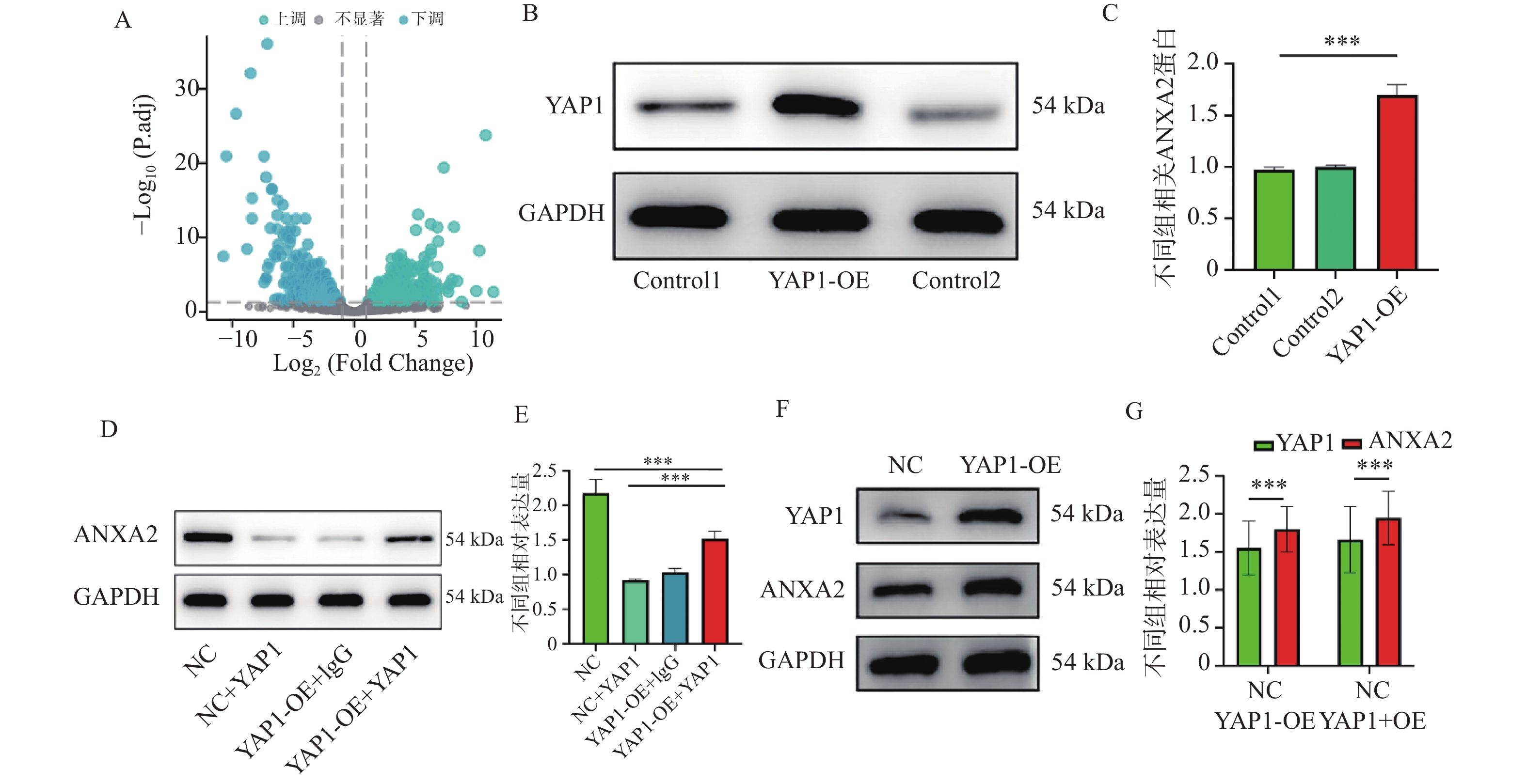
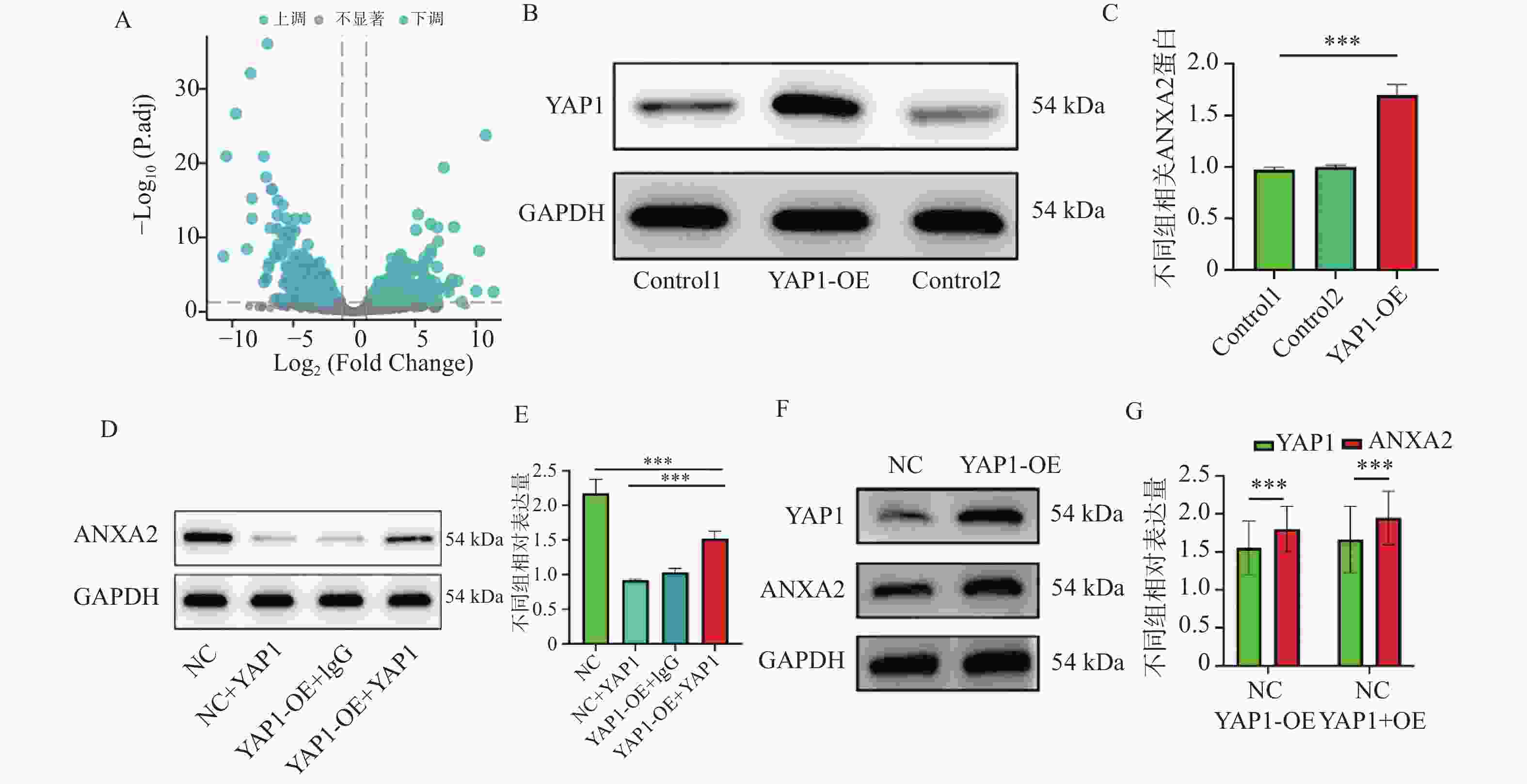
图 1 YAP1与ANXA2的相互作用及表达调控($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
A:差异基因火山图;B:YAP1 Western blot蛋白条带与统计柱状图;C:YAP1 Western blot统计柱状图;D:ANXA2 Western blot蛋白条带;E:ANXA2 Western blot蛋白统计柱状图;F:YAP1、ANXA2 Western blot蛋白条带与统计柱状图;G:YAP1、ANXA2 Western blot蛋白条带与统计柱状图。统计分析如下:(C) 采用Student's t检验进行两组比较;(D-E) 采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)结合Tukey事后检验进行多组比较。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001。
Figure 1. Interaction between YAP1 and ANXA2 and their expression regulation ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
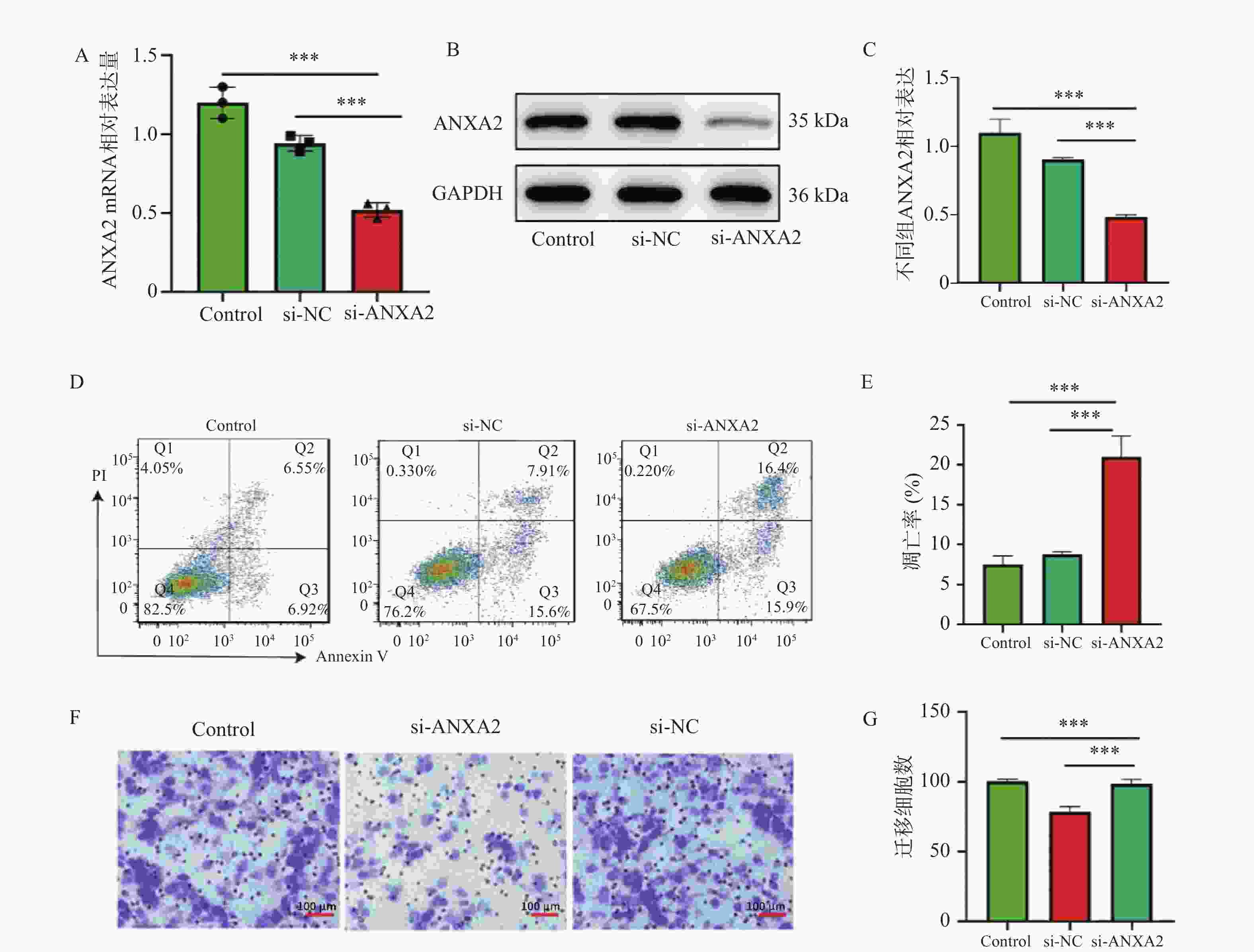
图 2 ANXA2沉默对YAP1调控的细胞功能影响($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
A:qRT-PCR显示si-ANXA2组中mRNA水平显著降低;B:Western blot显示si-ANXA2组中ANXA2蛋白水平显著降低;C:Western blot显示si-ANXA2组中ANXA2蛋白水平柱状图;D:ANXA2沉默组(si-ANXA2)总凋亡率;E:细胞凋亡统计柱状图;F:Transwell迁移实验结果;G:Transwell迁移实验统计柱状图。所有组间比较均采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)结合Tukey事后检验。*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01;***P < 0.001。
Figure 2. Effect of ANXA2 silencing on YAP1-regulated cellular functions ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
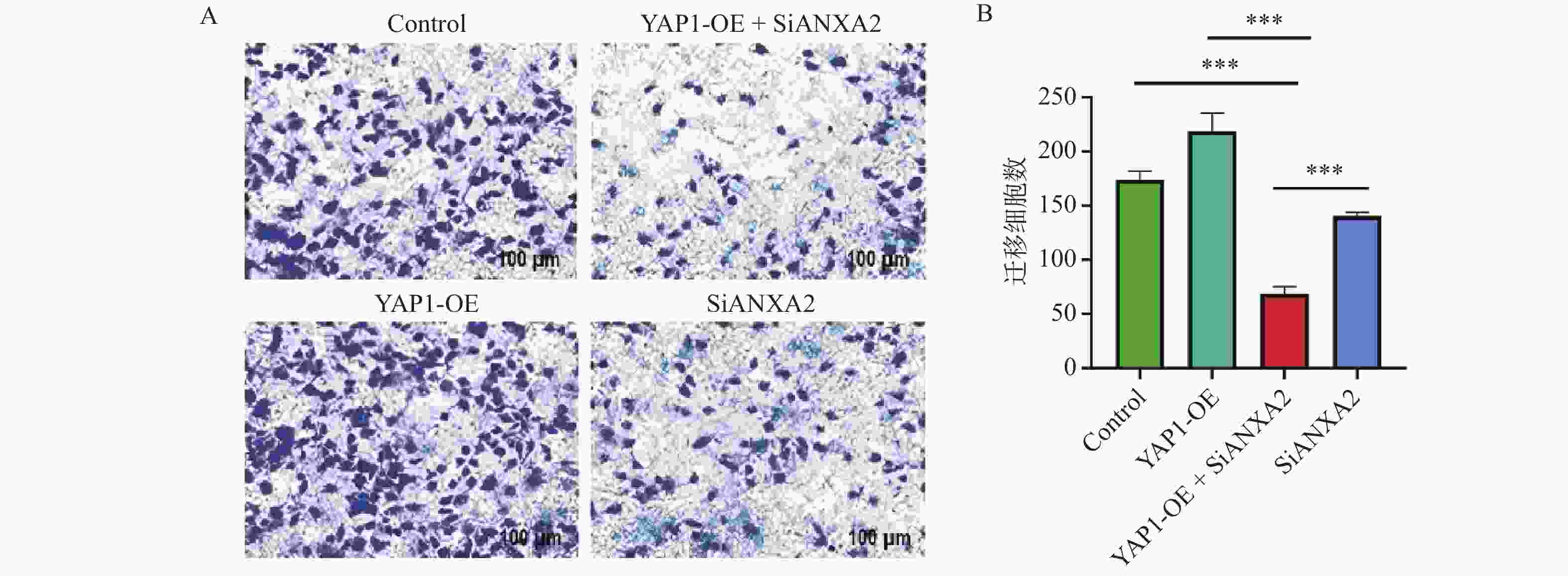
表 1 ANXA2沉默对细胞凋亡与迁移的影响($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
Table 1. Effect of ANXA2 silencing on cell apoptosis and migration ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
组别 总凋亡率(%) t P 迁移细胞数 (个/视野) t P si-NC 5.2 ± 0.8 - 220.0 ± 25.0 - si-ANXA2 25.8 ± 3.2 12.45 <0.001* 85.0 ± 15.0 8.91 0.003* YAP1-OE + si-NC 4.1 ± 0.6 0.89 0.425 350.0 ± 32.0 6.78 0.002* YAP1-OE + si-ANXA2 22.5 ± 2.9 10.93 <0.001* 98.0 ± 18.0 9.15 0.009* *P < 0.05。 表 2 YAP1对ANXA2启动子活性的调控作用 ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
Table 2. Regulatory effect of YAP1 on ANXA2 promoter activity ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
组别 相对荧光素酶活性 Vector + pGL3-Basic 1.00 ± 0.12* Vector + ANXA2-WT 1.15 ± 0.18* YAP1-OE + ANXA2-WT 3.42 ± 0.27 YAP1-OE + ANXA2-Mut 1.21 ± 0.15* 统计分析采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)与Tukey事后检验。ANXA2-Mut:YAP1结合位点突变型启动子。与YAP1-OE+ANXA2-WT组相比,*P < 0.001。 -
[1] Epstein M. Aging and the kidney[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 1996, 7(8): 1106-1122. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V781106 [2] Robert T, Tang E, Kervadec J, et al. Kidney injury and hair-straightening products containing glyoxylic acid[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390(12): 1147-1149. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2400528 [3] Foresto-Neto O, Menezes-Silva L, Leite J A, et al. Immunology of kidney disease[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2024, 42(1): 207-233. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-090122-045843 [4] Cui N, Liu C, Tang X, et al. ISG15 accelerates acute kidney injury and the subsequent AKI-to-CKD transition by promoting TGFβR1 ISGylation[J]. Theranostics, 2024, 14(11): 4536-4553. doi: 10.7150/thno.95796 [5] Matsuura R, Doi K, Rabb H. Acute kidney injury and distant organ dysfunction-network system analysis[J]. Kidney Int, 2023, 103(6): 1041-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.03.025 [6] Sui Y, Jiang R, Niimi M, et al. Gut bacteria exacerbates TNBS-induced colitis and kidney injury through oxidative stress[J]. Redox Biol, 2024, 72: 103140. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103140 [7] Chen J, Wang X, He Q, et al. Inhibition of transcriptional coactivator YAP Impairs the expression and function of transcription factor WT1 in diabetic podocyte injury[J]. Kidney Int, 2024, 105(6): 1200-1211. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2024.01.038 [8] Lv X, Liu J, Ruan J, et al. Targeting the disrupted Hippo signaling to prevent neoplastic renal epithelial cell immune evasion[J]. Nat Commun, 2025, 16(1): 2858. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57697-7 [9] Wang K, Ma F, Arai S, et al. WNT5a signaling through ROR2 activates the hippo pathway to suppress YAP1 activity and tumor growth[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(7): 1016-1030. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3003 [10] Edwards A C, Stalnecker C A, Jean Morales A, et al. TEAD inhibition overcomes YAP1/TAZ-driven primary and acquired resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(24): 4112-4129. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2994 [11] Blakely W J, Hatterschide J, White E A. HPV18 E7 inhibits LATS1 kinase and activates YAP1 by degrading PTPN14[J]. mBio, 2024, 15(10): e01811-24. [12] Zhang J, Chen W, Song K, et al. YAP activation in liver macrophages via depletion of MST1/MST2 enhances liver inflammation and fibrosis in MASLD[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(17): e70026. doi: 10.1096/fj.202400813RR [13] Guo Y, Cui Y, Li Y, et al. Cytoplasmic YAP1-mediated ESCRT-III assembly promotes autophagic cell death and is ubiquitinated by NEDD4L in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2023, 43(5): 582-612. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12417 [14] Claude-Taupin A, Terzi F, Codogno P, et al. Yapping at the autophagy door? The answer is flowing in the kidney proximal tubule[J]. Autophagy, 2024, 20(6): 1465-1466. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2319023 [15] Yoshimura K, Zou G, Fan Y, et al. HSP90 inhibitor AUY922 suppresses tumor growth and modulates immune response through YAP1-TEAD pathway inhibition in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2025, 610: 217354. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217354 [16] Koh M, Lim H, Jin H, et al. ANXA2 (annexin A2) is crucial to ATG7-mediated autophagy, leading to tumor aggressiveness in triple-negative breast cancer cells[J]. Autophagy, 2024, 20(3): 659-674. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2024.2305063 [17] 张星星, 王蓓, 白莎莎. 血清ANXA1、ANXA2在上皮性卵巢癌患者铂类化疗耐药中的评估价值及其与预后的关系[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2024, 45(23): 2862-2866+2872. [18] Chew C, Brand O J, Yamamura T, et al. Kidney resident macrophages have distinct subsets and multifunctional roles[J]. Matrix Biol, 2024, 127: 23-37. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2024.02.002 [19] Shen K, Miao J, Gao Q, et al. Annexin A2 plays a key role in protecting against cisplatin-induced AKI through β-catenin/TFEB pathway[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2022, 8(1): 430. doi: 10.1038/s41420-022-01224-w [20] Liu Y, Wang Y, Xu C, et al. Activation of the YAP/KLF5 transcriptional cascade in renal tubular cells aggravates kidney injury[J]. Mol Ther, 2024, 32(5): 1526-1539. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.02.031 [21] Ying X, Hu W, Huang Y, et al. A novel tsRNA, m7G-3' tiRNA LysTTT, promotes bladder cancer malignancy via regulating ANXA2 phosphorylation[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2024, 11(31): e2400115. doi: 10.1002/advs.202400115 [22] Partevian S A, Slominsky P A, Shadrina M I, et al. ANXA2 protein and its role in neurodegeneration processes[J]. Life (Basel), 2025, 15(3): 402. doi: 10.3390/life15030402 [23] 王心茹, 王心怡, 杨畅, 等. ANXA2调控YAP和p38 MAPK信号通路改善ATDC5软骨细胞炎症损伤[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2025, 41(03): 243-249. [24] Mitrofanova A, Merscher S, Fornoni A. Kidney lipid dysmetabolism and lipid droplet accumulation in chronic kidney disease[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2023, 19(10): 629-645. doi: 10.1038/s41581-023-00741-w [25] Gao Y, Wei G, Yu H, et al. Integrin β6/Annexin A2 axis triggers autophagy to orchestrate hepatocellular carcinoma radioresistance[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2025, 32(4): 689-701. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01411-5 -





 下载:
下载: