Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus with Pulmonary Mucormycosis
-
摘要:
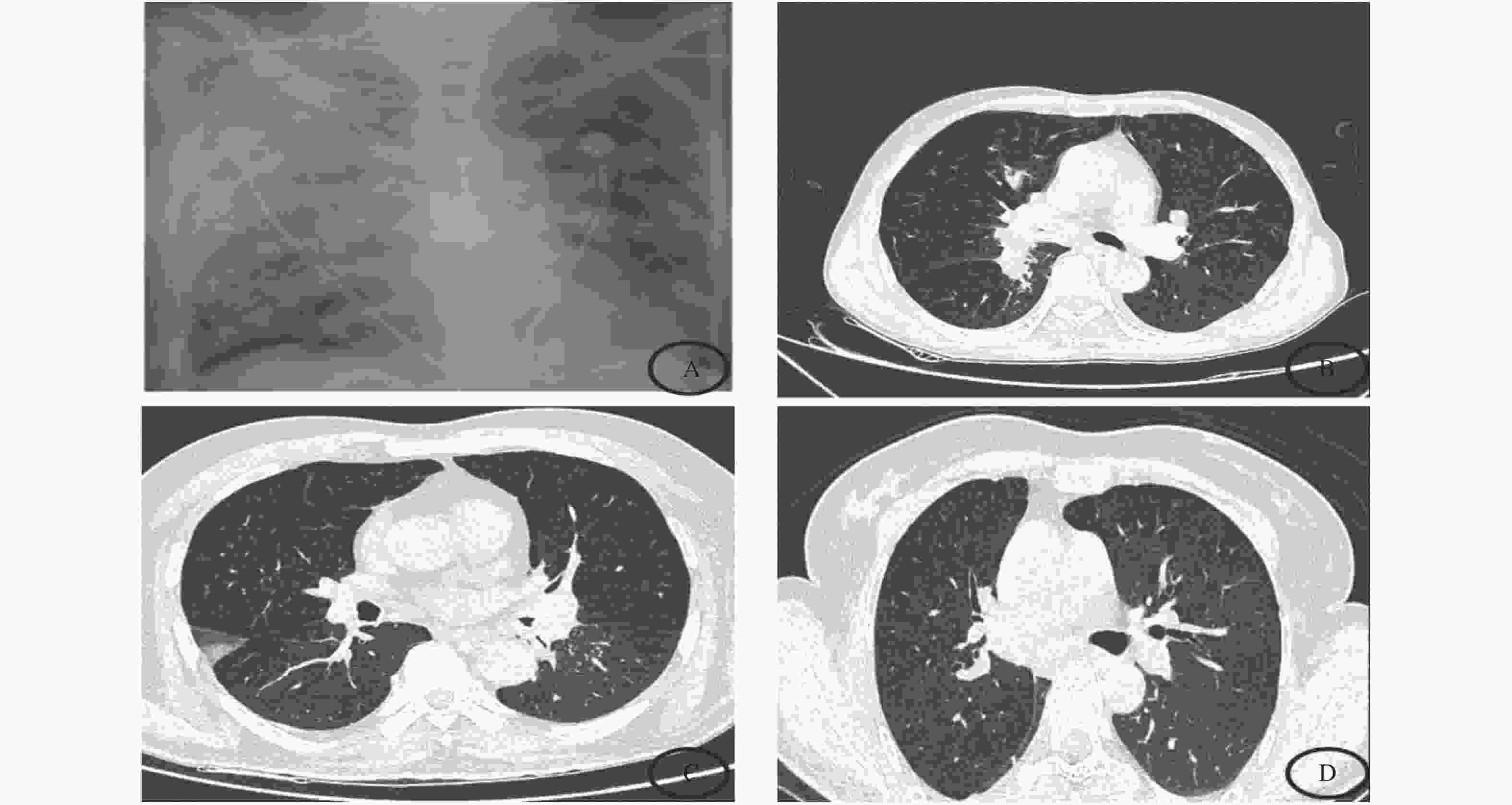
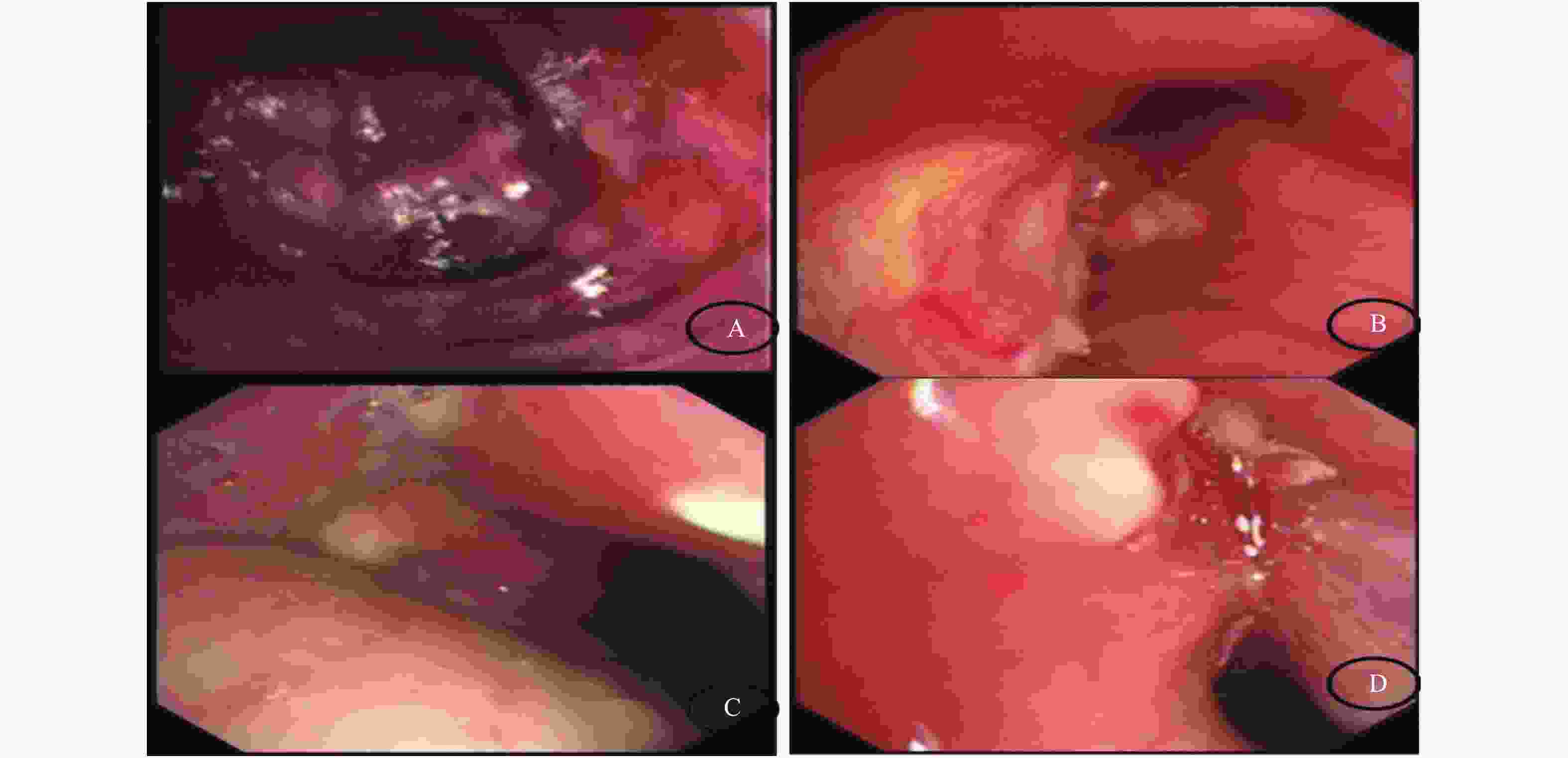
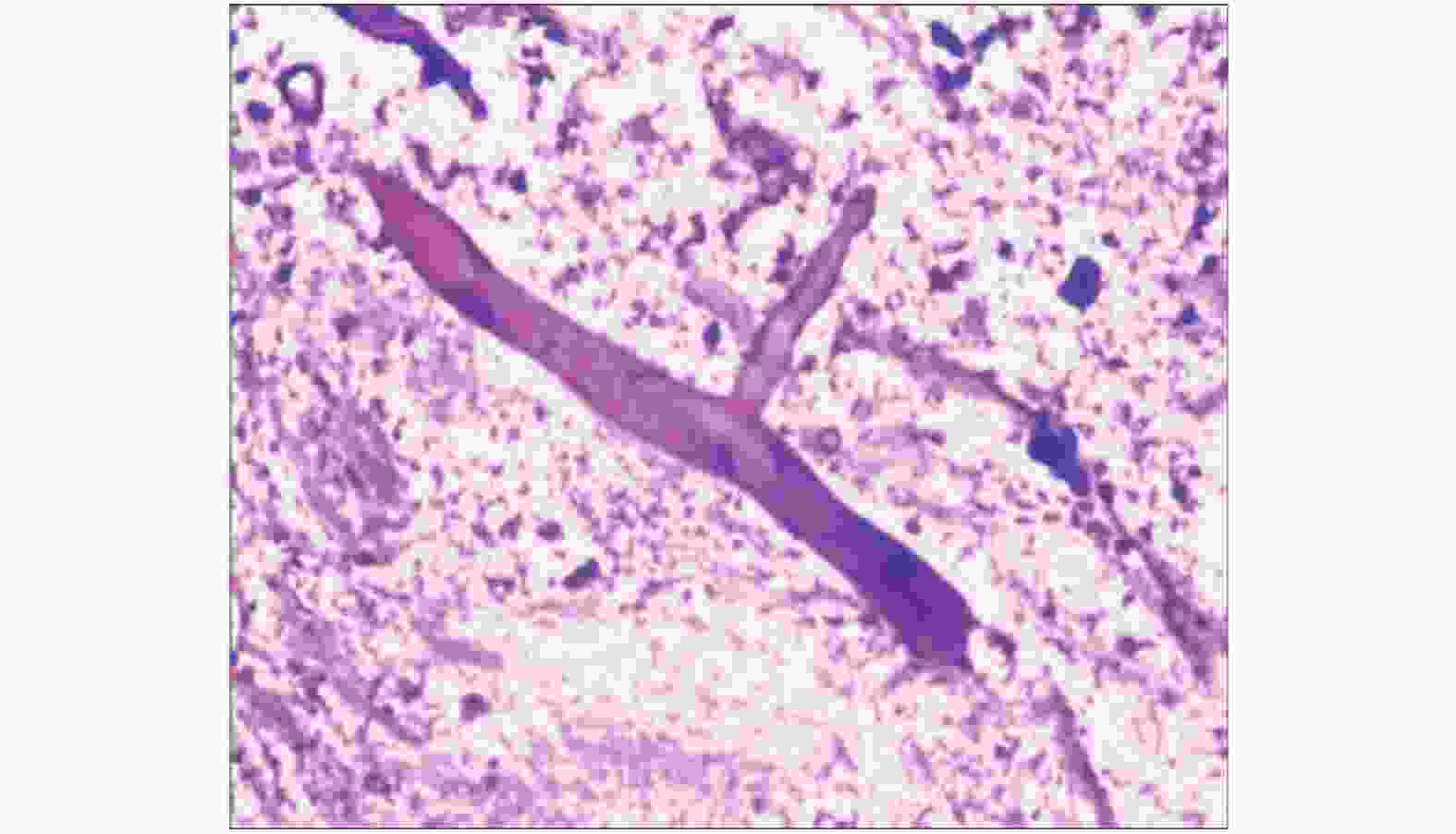
目的 探讨肺毛霉菌病(pulmonary mucormycosis,PM)的危险因素、临床表现和诊治方法,以期提高肺毛霉菌病的诊断率,降低死亡率。 方法 收集2011年1月至2021年8月在昆明市延安医院呼吸与危重症医学一科经病理确诊的PM患者4例,分析其临床特征、临床症状、影像学表现及诊治方法、预后情况。 结果 4例PM中女性2例,男性2例。4例均合并2型糖尿病,1例合并高血压,1例合并慢性肾功能衰竭、长期口服激素治疗。胸部CT表现主要为斑片状、片絮状高密度影、支气管管腔狭窄。4例PM患者均经组织病理学检查确诊。确诊后1例因大咯血死亡,2例给予全身使用抗真菌药物联合支气管镜介入治疗,1例因不耐受全身抗真菌治疗行支气管镜介入治疗。经治疗后3例临床症状明显改善。 结论 PM 为一种罕见的侵袭性真菌病,好发于糖尿病、肾功能衰竭、免疫功能低下患者。临床症状缺乏特异性,确诊主要依赖于病原学和组织学检查。临床经验提示,抗真菌药物联合支气管镜下介入治疗可改善患者预后,但仍需进一步扩大样本量观察其疗效确切性。 Abstract:Objective To explore the risk factors, clinical symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary mucormycosis (PM) so as to improve the diagnostic rate of PM and reduce the mortality. Methods 4 patients (2 females and 2 males) with pulmonary mucormycosis confirmed by pathology in the First Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine of Yan'an Hospital of Kunming City from January 2011 to August 2021 were collected and their clinical data, risk factors, clinical symptoms, imaging findings, treatment and prognosis were analyzed. Results All 4 patients were complicated with type 2 diabetes, 1 patient with hypertension, 1 patient with chronic renal failure and was treated with long-term oral hormone therapy. The main chest imaging findings were mainly patchy, patchy high-density shadows and bronchial lumen stenosis. All the 4 patients were diagnosed as PM by pathological biopsy. After the diagnosis, 1 patient died of massive hemoptysis, 2 patients were treated with systemic antifungal drugs combined with bronchoscopic intervention and 1 patient was treated with bronchoscopic intervention due to intolerance to systemic antifungal therapy. The clinical symptoms of the 3 patients were improved significantly after the treatment. Conclusion PM is a rare invasive fungal disease, which occurs frequently in patients with diabetes, renal failure and immune deficiency. The clinical symptoms are lack of specificity, and the diagnosis mainly depends on the etiology and histological examination. Our clinical experience suggests that antifungal drugs combined with bronchoscopic interventional therapy can improve the outcomes of patients with PM, but further expanded sample size is still needed to observe the efficacy of the treatment. -
Key words:
- Pulmonary mucormycosis /
- Clinical characteristics /
- Treatment
-
表 1 4例肺毛霉菌病患者的临床特征n(%)
Table 1. Clinical characteristics of 4 patients with PM n(%)
临床特征 占比 女性 2(50) 男性 2(50) 年龄(中位数)(岁) 54(48~61) 合并基础疾病情况 糖尿病 4(100) 慢性肾功能衰竭 1(25) 高血压 1(25) 表 2 肺毛霉菌病患者的临床表现、胸部影像学改变 n(%)
Table 2. Clinical features, computed tomographic presentation of patients with PM n(%)
临床表现+影像学改变 占比 咳嗽 4(100) 呼吸困难 3(75) 咳痰 2(50) 发热 1(25) 病变部位 中央型 3(75) 外周型 1(25) 左肺 3(75) 右肺 2(50) 上叶 3(75) 中叶 3(50) 下叶 4(75) -
[1] Guinea J,Escribano P,Vena A,et al. Increasing incidence of mucormycosis in a large Spanish hospital from 2007 to 2015:Epidemiology and microbiological characterization of the isolates[J]. PLos One,2017,12(6):e0179136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179136 [2] Kontoyiannis D P,Wessel V C,Bodey G P,et al. Zygomycosis in the 1990s in a tertiary-care cancer center[J]. Clin Infect Dis,2000,30(6):851-856. doi: 10.1086/313803 [3] Tedder M,Spratt J A,Anstadt M P,et al. Pulmonary mucormycosis:Results of medical and surgical therapy[J]. Ann Thorac Surg,1994,57(4):1044-1050. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)90243-7 [4] Chamilos G,Lewis R E,Kontoyiannis D P. Delaying amphotericin B-based frontline therapy significantly increases mortality among patients with hematologic malignancy who have zygomycosis[J]. Clin Infect Dis,2008,47(4):503-509. doi: 10.1086/590004 [5] Linden P K. Amphotericin B lipid complex for the treatment of invasive fungal infections[J]. Expert Opin Pharmacother,2003,4(11):2099-2110. doi: 10.1517/14656566.4.11.2099 [6] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会感染学组, 中华结核和呼吸杂志编辑委员会. 肺真菌病诊断和治疗专家共识[S]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2007, 30(11): 821-834. [7] 梁志欣, 金芬华, 余丹阳等. 5例病理确诊的肺毛霉菌病临床分析[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2012, 17(3): 418-420. [8] Cohen-Abbo A,Bozeman P M,Patrick C C. Cunninghamella infections:Review and report of two cases of Cunninghamella pneumonia in immunocompromised children[J]. Clin Infect Dis,1993,17(2):173-177. doi: 10.1093/clinids/17.2.173 [9] Rüping M J,Heinz W J,Kindo A J,et al. Forty-one recent cases of invasive zygomycosis from a global clinical registry[J]. J Antimicrob Chemother,2010,65(2):296-302. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp430 [10] Pozo Laderas J C,Pontes Moreno A,Pozo Salido C,et al. Disseminated mucormycosis in immunocompetent patient:A disease that also exsists[J]. Rev Iberoam Micol,2015,32(2):63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.riam.2014.01.006 [11] Farmakiotis D,Kontoyiannis D P. Mucormycoses[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am,2016,30(1):143-163. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2015.10.011 [12] Lee F Y,Mossad S B,Adal K A. Pulmonary mucormycosis:The last 30 years[J]. Arch Intern Med,1999,159(12):1301-1309. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.12.1301 [13] Feng J,Sun X. Characteristics of pulmonary mucormycosis and predictive risk factors for the outcome[J]. Infection,2018,46(4):503-512. doi: 10.1007/s15010-018-1149-x [14] Danion F,Aguilar C,Catherinot E,et al. Mucormycosis:New developments into a persistently devastating infection[J]. Semin Respir Crit Care Med,2015,36(5):692-705. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1562896 [15] Chitasombat M N,Kontoyiannis D P. Treatment of mucormycosis in transplant patients:Role of surgery and of old and new antifungal agents[J]. Curr Opin Infect Dis,2016,29(4):340-345. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000277 [16] 邓莉萍, 杨莹, 邓治平. 支气管镜下注入两性霉素B脂质体治疗肺毛霉菌病 [J]. Chinese Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2018, 17(4): 416-417. [17] Mihara T,Kakeya H,Izumikawa K,et al. Efficacy of aerosolized liposomal amphotericin B against murine invasive pulmonary mucormycosis[J]. J Infect Chemother,2014,20(2):104-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2013.09.002 [18] Panigrahi M K,Manju R,Kumar S V,et al. Pulmonary mucormycosis presenting as nonresolving pneumonia in a patient with diabetes mellitus[J]. Respiratory Care,2014,59(12):201-205. doi: 10.4187/respcare.03205 [19] Virally M L,Riveline J P,Virally J,et al. Pulmonary mucormycosis in a diabetic patient with HIV[J]. Diabetes Care.,2002,25(11):2105. doi: 10.2337/diacare.25.11.2105 -





 下载:
下载: