Regulatory Role of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Hypertrophic Scar
-
摘要:
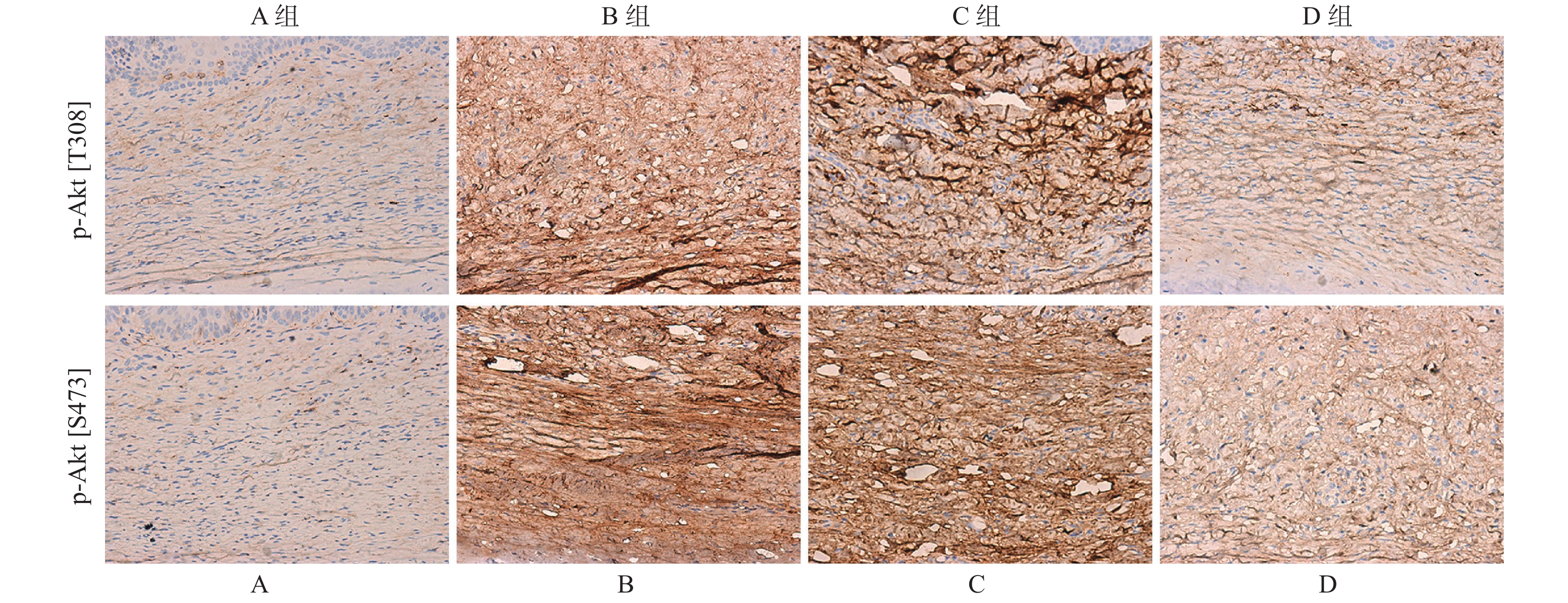
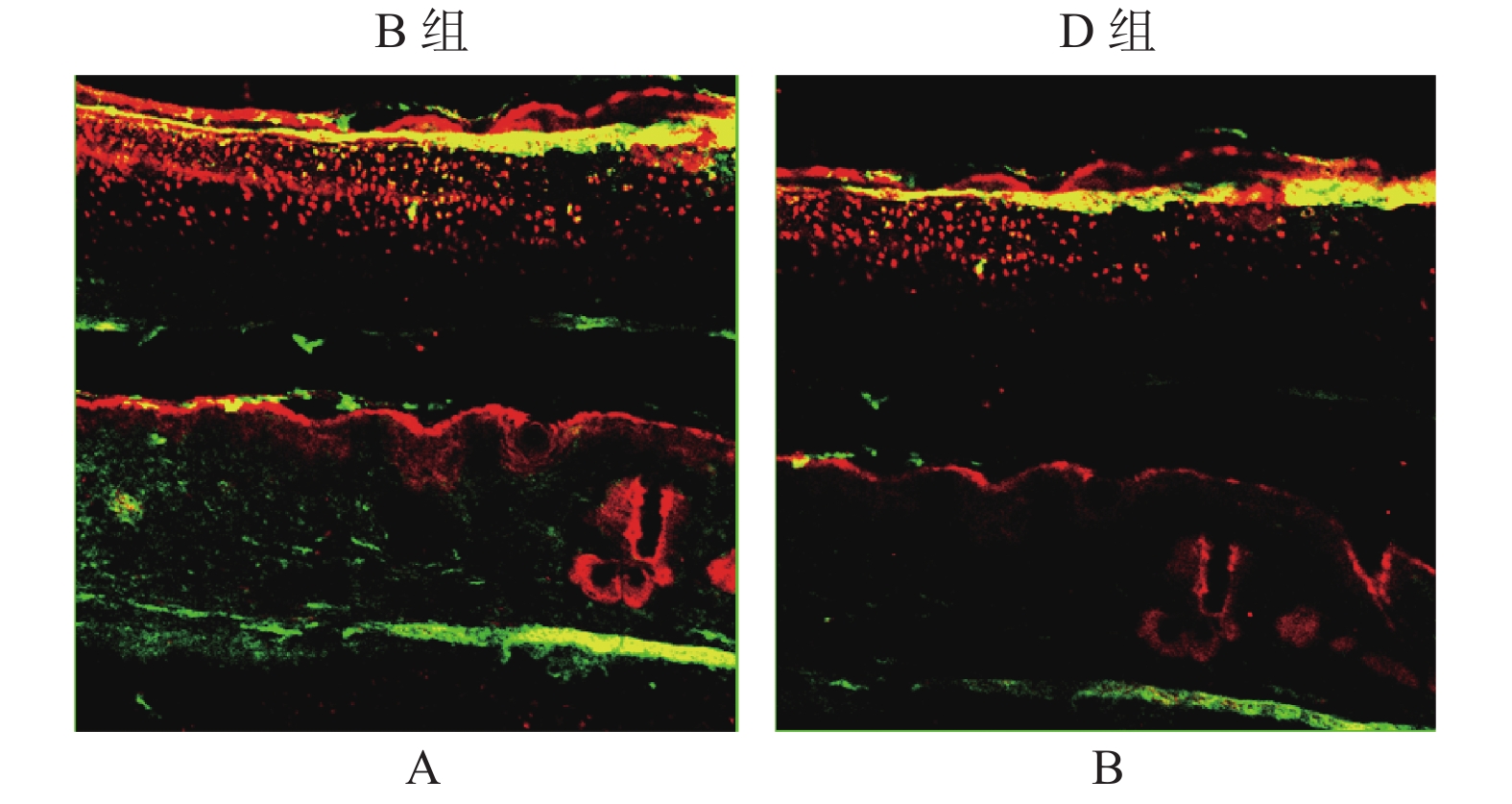
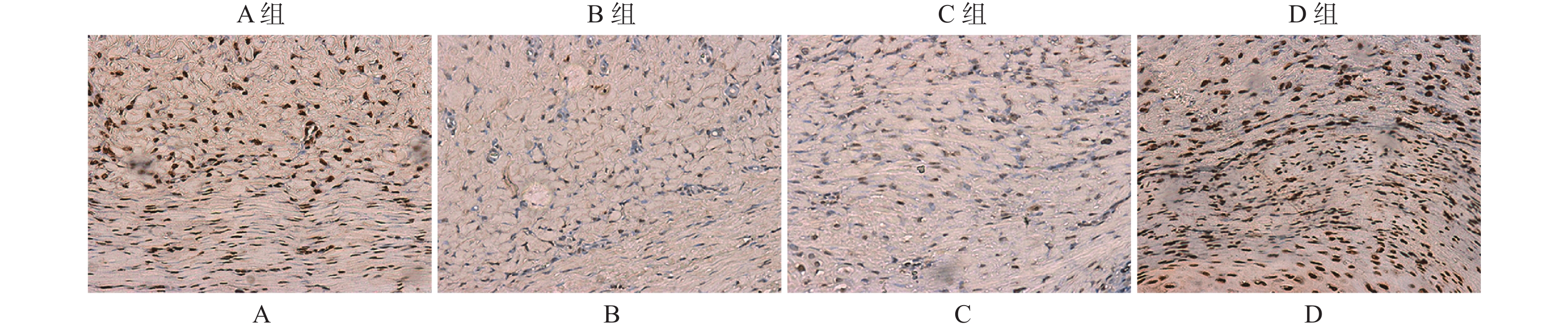
目的 探讨PI3K/AKT信号通路在增生性瘢痕中的调控作用。 方法 构建兔耳增生性瘢痕模型,并随机分为4组:正常兔耳皮肤组(A)、瘢痕模型组(B)、DMSO刺激模型组(C)、PI3K特异性抑制剂(LY294002)刺激模型组(D)。通过组织病理学观察兔耳瘢痕的形态学变化;免疫组化和Western blot检测p-Akt[S473]和p-Akt[T308]的表达量;免疫荧光双染色评估p-Akt[S473]和p-Akt[T308]的共定位情况;以及TUNEL评估皮肤组织中成纤维细胞的凋亡水平。 结果 D组中瘢痕厚度及成纤维细胞数明显高于B和C组。免疫组化和Western blot检测结果表明,p-Akt[T308]和p-Akt[S473]在B组中的表达量明显高于A组,但在D组中显著低于C组。免疫荧光表明,p-Akt[T308]和p-Akt[S473]主要定位于瘢痕组织中的细胞浆内,且在D组中的共表达量低于B组。TUNEL检测结果证实,与A组相比,B组皮肤组织中细胞凋亡水平明显下调,且D组中细胞凋亡水平高于C组(P < 0.01)。 结论 阻断PI3K/Akt信号通路可通过抑制Akt磷酸化,导致成纤维细胞凋亡水平上调,进而缓解瘢痕增生进程。 Abstract:Objective To explore the regulatory role of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in the hypertrophic scar. Methods The rabbit ear hypertrophic scar model was established and randomly divided into four groups, including normal rabbit ear skin group (A), hypertrophic scar model group (B), DMSO-stimulated hypertrophic scar model group (C), and PI3K-specific inhibitor (LY294002) stimulated model group (D). Morphological changes of rabbit ear scar were observed by histopathology. The expression of phosphorylation of Akt[S473] and Akt[T308] was examined by immunohistochemistry and western blot. Immunofluorescence double staining was performed to assess the co-localization of p-Akt[S473] and p-Akt[T308]. The TUNEL assay was used to detect the fibroblasts’ apoptosis in skin tissues. Results Scar thickness and fibroblast count were significantly higher in the D group than that in the B and C groups, but the difference was not statistically significant between the B group and the C group. The results of immunohistochemistry and western blot assay confirmed that the expression of p-Akt[T308] and p-Akt[S473] were significantly higher in the B group than in the A group, but significantly lower in the D group than in the C group. The expression of p-Akt[T308] and p-Akt[S473] was significantly enhanced in the B group compared with the C group. Immunofluorescence double staining showed that p-Akt[T308] and p-Akt[S473] were mainly co-localized in the cytoplasm in scar tissue, and their co-expression was lower in the D group than in the B group. TUNEL assay results confirmed that the apoptosis level of fibroblast was significantly downregulated in skin tissue in the B group compared with the A group, and the apoptosis level of fibroblast was higher in the D group than in the C (P < 0.01). Conclusion Blocking the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway can accelerate fibroblast apoptosis by inhibiting Akt phosphorylation, and then alleviate hypertrophic scar formation. -
Key words:
- Hypertrophic scar /
- LY294002 /
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase /
- Apoptosis
-
肝内胆管癌是一种具有高度侵袭性的恶性肿瘤[1],预后差,近年来,其发病率逐年升高[2]。腺苷酸激酶4(Adenylate kinase4,AK4)是腺苷酸激酶家族的一员,其分子量为25kDa,别称为AK3L1。多项研究显示AK4促进恶性肿瘤的发生发展[3-5]。但其对肝内胆管癌的作用尚无报道。本实验通过小干扰RNA手段,就AK4对肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1增殖、迁移能力的影响作出探究。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 细胞系
本实验所用肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1购自上海誉驰生物科技有限公司,该细胞已通过中国科学院昆明动物研究所鉴定明确。该细胞作为肝内胆管癌细胞株之一,常用于肿瘤增殖、迁移的研究。
1.2 小干扰RNA(Small interfering RNA,siRNA)转染细胞
本实验采用siRNA技术以沉默AK4。siRNA购自上海市吉玛基因生物技术有限公司,共计构建6条si-RNA序列,序列设计见表1。本次实验分组为空白对照组(CON)、阴性对照组(siRNA-NC)、阳性对照组(siRNA-GAPDH)、实验组1(siRNA-AK4-1),实验组2(siRNA-AK4-2),实验组3(siRNA-AK4-3)。转染试剂采用上海市吉玛基因生物技术有限公司GP-transfect-Mate。采用免疫印迹法(Western Blot,WB)对实验组1、实验组 实验组3进行si-RNA筛选,其中空白对照组不添加siRNA,阴性对照组基因序列与目的基因序列无同源性,阳性对照组基因序列与内参GAPDH同源。各组间其余实验操作步骤(转染方法、WB、EdU、细胞划痕实验)均一致。
表 1 si-RNA序列Table 1. Sequence of si-RNA built by siRNA technology组别 序列 Antisense Negative control 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ 5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3′ GAPDH Positive control 5′-UGACCUCAACUACAUGGUUTT-3′ 5′-AACCAUGUAGUUGAGGUCATT-3′ siRNA-AK4-1 5′-GCGGAAGGGUAUAUAACCUTT-3′ 5′-AGGUUAUAUACCCUUCCGCCT-3′ siRNA-AK4-2 5′-CAGGCUAAGACAGUACAAATT-3′ 5′-UUUGUACUGUCUUAGCCUGTT-3′ siRNA-AK4-3 5′-CACCUAUUCAGUCCAAAGATT-3′ 5′-UCUUUGGACUGAAUAGGUGTT-3′ 转染前1 d将HUCCT1细胞接种至6孔板中,以次日细胞融合度达到60%~80%为宜,用无抗生素的完全培养基进行培养。转染:(1)转染试剂室温备用;(2)按照每孔200 µL无血清培养基(1640培养基)加5~8 µL转染试剂配置转染试剂混合物。静置5 min;(3)按照每孔200 µL无血清培养基(1640培养基)加150/pmol siRNA配置siRNA混合物。静置5 min;(4)将转染试剂混合物滴加到siRNA混合物中,混匀,静置20 min;(5)20 min后将混合液均匀加至6孔板各孔中;(6)各孔另外加入1 600 µL无抗生素完全培养基;(7)孔板放入细胞培养箱中培养48 h,使用免疫印迹检测转染效率。
1.3 免疫印迹实验检测转染效率及siRNA筛选
(1)裂解细胞:使用PMSF(品牌:Beyotime,货号:ST506-2 PMSF)与RIPA裂解液(强)品牌:Beyotime,货号:P0013B)按照200∶1配置细胞裂解液。于冰上充分裂解细胞;(2)测蛋白浓度:取裂解产物于4 ℃离心机12000 r/min,离心30 min。吸取86 µL上清液,使用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(品牌:Beyotime,货号:P0012 500次)测定蛋白浓度;(3)取80 µL上清液加20 µL SDS-PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液(品牌:Beyotime,货号:P0015L)沸水加热15 min;(4)电泳:配置12%下层胶,5%上层胶,蛋白上样量为2.5 µg,上层胶60 V恒压电泳,下层胶100 V恒压电泳;(5)转膜:甲醇浸泡PVDF膜,胶、膜放置妥当后以300 mA恒流条件下湿转发转膜,时间为30 min;(6)封闭:PVDF膜置于5%脱脂牛奶中封闭,缓慢摇晃,室温封闭2 h;(7):孵育一抗:兔单克隆抗体[EPR7678] to AK3L1抗体,(1∶7000,品牌:Abcam,货号:ab131327)。一抗孵育过夜,4 ℃;(8):孵育二抗:山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)(品牌:Proteintech,货号:SA00001-2,1∶10000),室温孵育2 h;(9)显影:ECL化学发光液孵育1 min后,于成像仪中曝光显影。
1.4 增殖EdU实验
(1)转染细胞:6孔板培养细胞。免疫印迹实验已明确siRNA-AK4-3的沉默效果最好,故本次实验使用siRNA-NC及siRNA-AK4-3做细胞转染。分组亦同。转染完成24 h开始进行EdU实验。(2)工作液孵育:使用BeyoclickTM Edu-555配置2XEdU工作液后(品牌:Beyotime,货号:C0075s),与无抗生素完全培养基等体积加入六孔板中,孵育2 h。(3):固定、染色:每孔1 mL固定液固定15 min,洗涤后加入通透液孵育15 min,Click反应液孵育15 min,1X Hoechst 33342溶液孵育10 min。(4):荧光检测:洗涤液清洗后于倒置荧光显微镜观察。
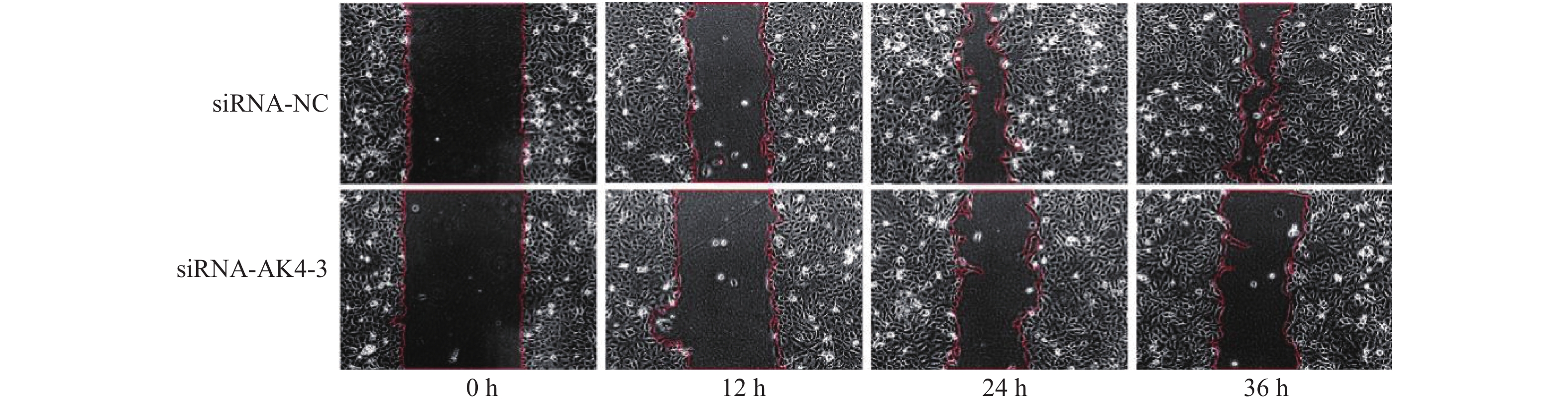
1.5 细胞划痕实验
(1)转染细胞:6孔板培养细胞。本次实验分组为siRNA-NC及siRNA-AK4-3。转染完成24 h开始细胞划痕实验。(2)画线:使用直尺于6孔板背面作横行画线。(3)划痕:待细胞融合度为95%~100%时,使用200 µL枪头沿直尺作垂直于画线的划痕。(4)冲洗:使用PBS冲洗孔板3次,动作轻柔,吸净PBS后,加入无血清1640培养液。(5)拍照:每孔以“十”字交叉处上下为定点,于0 h,12 h,24 h,36 h拍照,对比不同时间下各组细胞迁移能力,并进行统计分析。
1.6 统计学处理
数据分析使用GraphPad Prism 8及SPSS 26统计软件,计量资料采用(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),计数资料用t检验,3组及多组计量资料采用单因素方差分析。所有检验取两端。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 siRNA转染效率及筛选
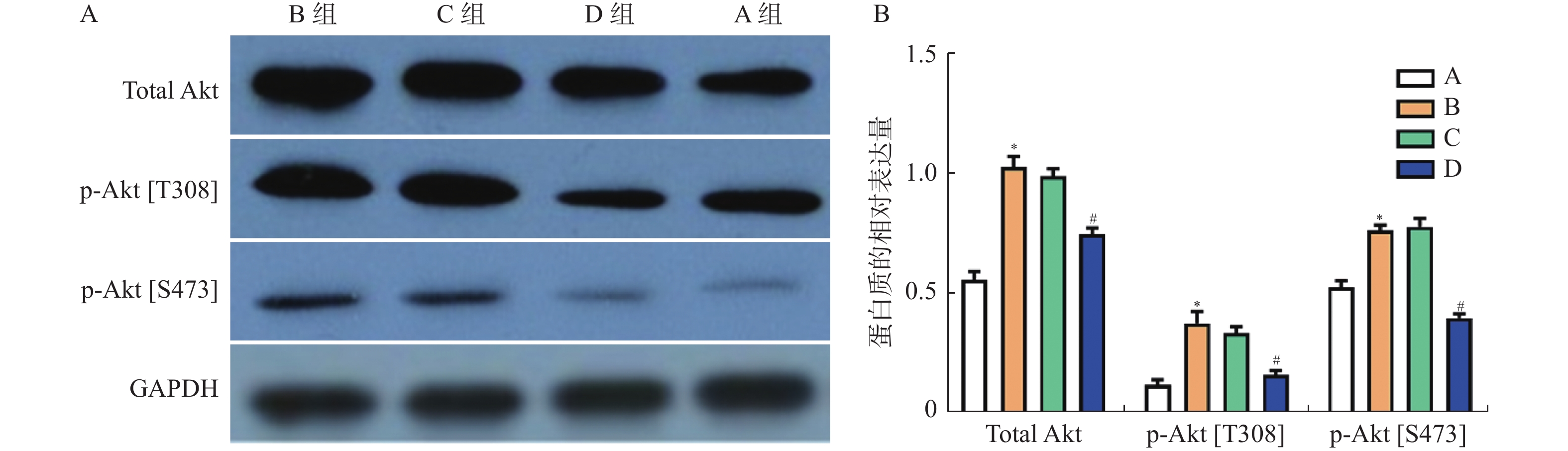
免疫印迹法检测各组后量化结果分别为:空白对照组(CON):(0.9±0.01,)阴性对照组(siRNA-NC):(0.92±0.01),阳性对照组(siRNA-GAPDH):(0.95±0.04),实验组1(siRNA-AK4-1):(0.74±0.08),实验组2(siRNA-AK4-2):(0.45±0.04),实验组3(siRNA-AK4-3):(0.24±0.02)。免疫印迹结果显示各组内参齐,沉默效果较好,其中阳性对照组对GAPDH的沉默效果显著。各siRNA组中siRNA-AK4-3对AK4的沉默效果最好,见图1,2。因此,后期实验使用siRNA-NC作为对照组,siRNA-AK4-3作为实验组。
2.2 增殖EdU实验
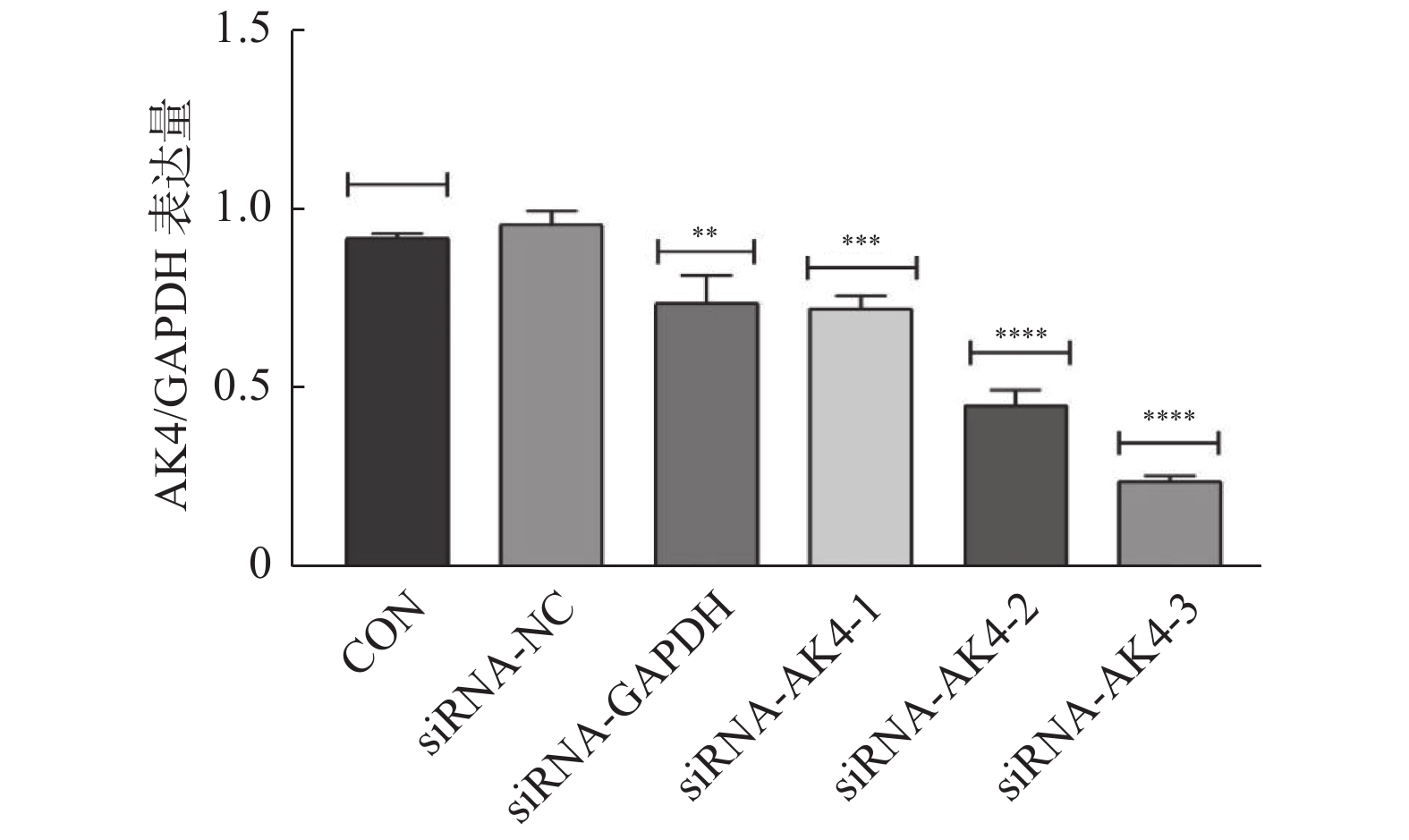
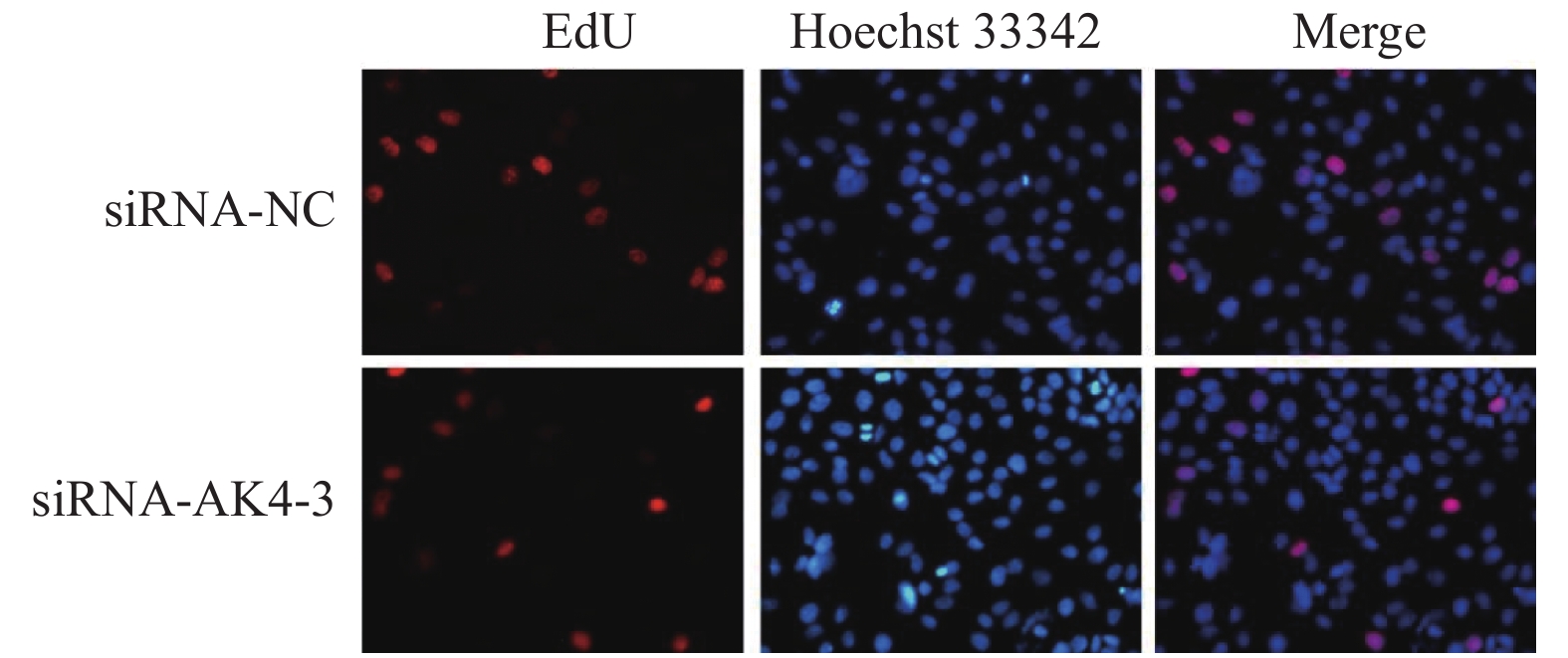
Edu实验结果显示:siRNA-NC组增殖细胞(15.9±4.4)/视野,细胞总数(110.9±22.4)/视野。siRNA-AK4-3组增殖细胞数目(12.8±5.0)/视野,细胞总数(116.7±22.1)/视野。两组增殖比率有差异,差异有统计学意义。siRNA-NC组增殖细胞多于siRNA-AK4-3组,AK4促进细胞增殖,见图3,4。
图3中EdU中增殖的HUCCT1细胞被标记为红色荧光,Hoechst 33342中蓝色荧光标记的为视野下所有活细胞,Merge图由EdU和Hoechst 33342图像合并后得到。
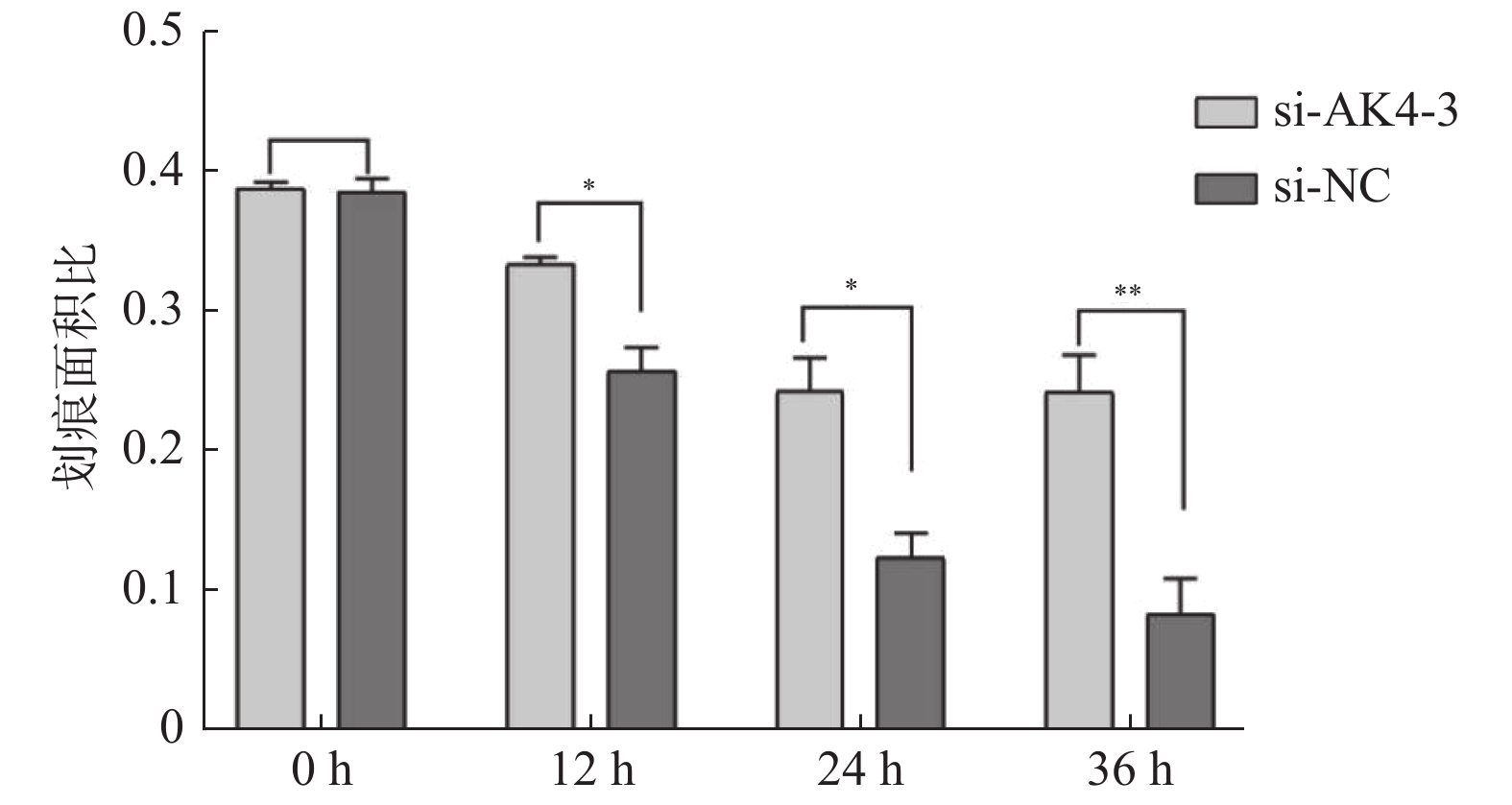
2.3 细胞划痕实验
划痕实验取划痕面积/视野总面积,各组面积比见表2,差异有统计学意义,见图5,6。siRNA-NC组细胞迁移面积较siRNA-AK4-3组更大,AK4促进细胞迁移。
表 2 划痕面积比Table 2. Scratch area ratio项目 0 h 12 h 24 h 36 h siRNA-NC 0.39 ± 0.01 0.26 ± 0.017 0.12 ± 0.017 0.08 ± 0.026 siRNA-AK4-3 0.39 ± 0.005 0.33 ± 0.001 0.24 ± 0.024 0.24 ± 0.027 3. 讨论
肝内胆管癌的手术治疗是极其重要的,目前全球范围内术后其平均无瘤生存时间( DFS) 为12 ~ 36 个月[6-7],但胆管癌起病隐匿,多数患者在发现疾病时已属晚期[8],据报道,肝内胆管癌的根治切除率为30%~40% ,其他肝胆恶性肿瘤均比此数据高[1,9]。肝内胆管癌的辅助化疗(吉西他滨联合铂类)在一定程度上实现肿瘤将期,从而获得手术机会[10-12],但其中位生存期仍然不到1 a时间[13-15]。根据Andrew X Zhu的RCT临床研究,靶向药物Ivosidenib使得患者有10.3个月的中位生存期,而安慰剂组仅有7.5个月[16],Abou-Alfa GK等学者也通过RCT实验研究了Ivosidenib在胆管癌中的作用,其结果是实验组的无病生存期为2.7个月(95% CI:1.6~4.2),而安慰剂组的无病生存期为1.4个月(95% CI:1.4~1.6)[17]。A Demols也在胆管癌的靶向治疗上进行了RCT研究,他研究了靶向药Regorafenib对胆管癌作用,最终得出实验组无病生存期为3.0个月(95% CI:2.3~4.9),而对照组无病生存期为1.5个月(95% CI:1.2~2.0),然而实验组的总生存时间和对照组的总生存时间并无统计学差异[18]。可以看出,靶向药能提高患者生存时间,但有研究显示部分靶向药并不能显著提升患者的总生存率[18, 19]。因此需寻找一个更有效的作用靶点。
1944年,美国学者Kalckar在实验中首次发现了肌苷酸[20]。在随后的科学实践中,更名为腺苷酸激酶AK。AK4定位于细胞线粒体基质内,在肝脏、心脏、脑、肾脏、胃肠道组织中富于表达[21],AK4在细胞能量代谢方面表现出特异性[22],因此他与肿瘤应该存在相关性。2012年由台湾地区学者Yi-Hua Jan完成了首例AK4与癌症关系论证的研究:体外试验中shRNA沉默肺癌细胞CL1-5和A549中的AK4后,两株细胞的侵袭能力下降约50%,从而证实AK4促进肺癌细胞的侵袭[3]。连云港市的学者MinMin HUANG在研究中显示AK4在人浆液性卵巢癌组织中高表达。在体内试验中,AK4敲低组的肿瘤体积明显减小,肿瘤重量明显减轻。这些试验均显示AK4促进了人浆液性卵巢癌的发生发展[4]。Jie Zhang等在Her-2阳性乳腺癌中的研究显示AK4的表达水平与肿瘤TNM分期(P = 0∶017)和淋巴结转移(P = 0∶046) 显著相关。体外试验中,MTT法、细胞划痕实验和Transwell试验都显示敲低AK4组的癌细胞增值、迁移、侵袭能力减弱。体外试验也显示敲低了AK4的肿瘤组织体积减小,重量减轻[5]。此后AK4与肿瘤的研究未曾断绝,田华等学者通过免疫组化等方法证实了AK4在肺腺癌中高表达[23]。李辰运的研究显示AK4在胰腺导管腺癌中高表达,并且与肿瘤分期、淋巴结转移、神经受侵、脉管内瘤栓有相关性(P < 0.05)[24]。李绍军等也证实AK4在食管鳞状细胞中高表达[25],夏林等也通过免疫组化的方式证实了AK4在胃癌中高表达[26],尽管我国的多数学者都明确了AK4在大多数肿瘤中的表达,但是很遗憾,仅有少数人通过体内、体外实验论证AK4对相关癌症的影响,无法将他们的研究进一步转化为临床制定治疗方案的依据。
本实验首次论证AK4对肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1增殖、迁移的影响。首先予siRNA沉默AK4的表达,再通过EdU检测细胞增殖能力,细胞划痕实验检测细胞迁移能力。本次实验的结论与前人的研究结论相似,即AK4促进肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1的增殖、迁移。本实验的不足在于,笔者尚未完成AK4对肝内胆管癌细胞其他生物学能力的影响,如EMT、侵袭等等。因此,笔者接下来即将完成其他细胞生物学行为实验,并且探究在机制方面的变化以及通过体内实验验证结论。本实验结论将为肝内胆管癌的临床分子靶向治疗提供基础实验数据,采用生物医学工程技术干预肝内胆管癌组织中AK4的表达,将有助于肿瘤的综合治疗。
-
图 3 Western blot检测总Akt、p-Akt[T308]、p-Akt[S473]蛋白在兔耳创面中的表达水平
A:Western blot检测总Akt、p-Akt[T308]、p-Akt[S473]蛋白;B:总Akt、p-Akt[T308]、p-Akt[S473]蛋白统计值; 与A组比较,*P < 0.05;与C组比较,#P < 0.05 。
Figure 3. The protein expression of total Akt,p-Akt[T308],p-Akt[S473] in the tissues of rabbit ear trauma was examined by western blot
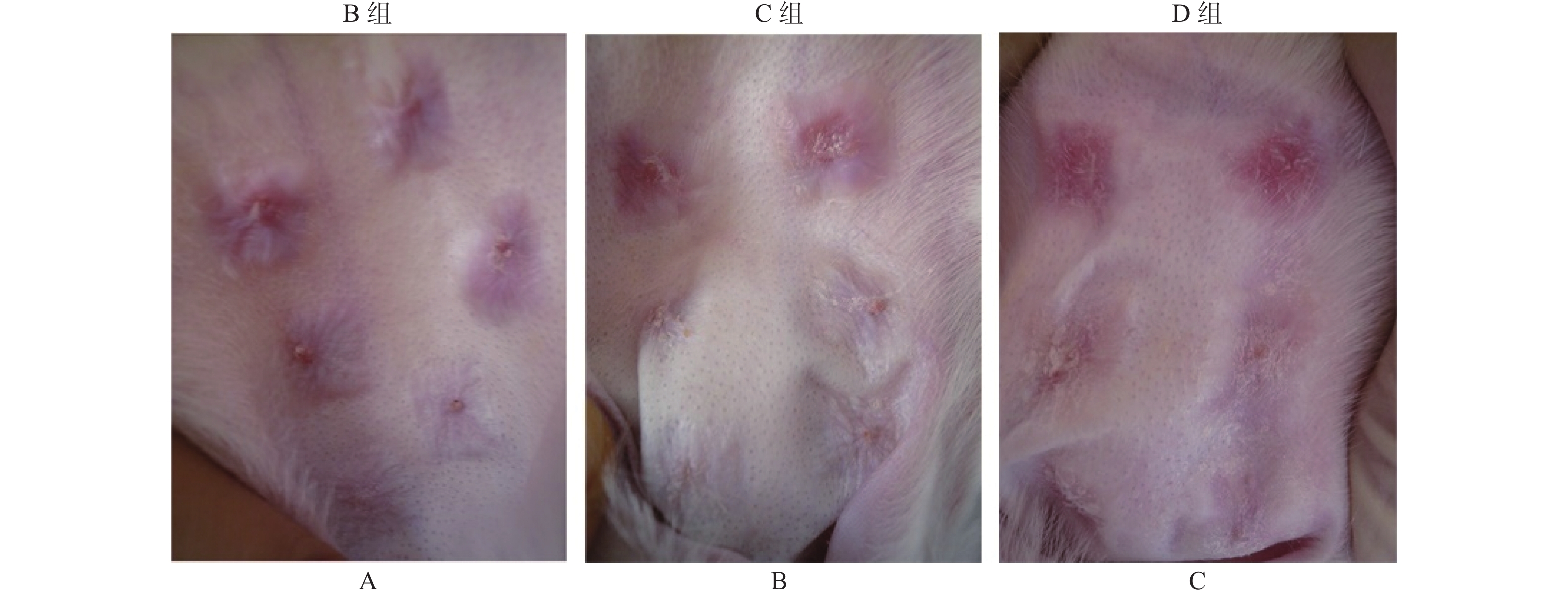
表 1 各组增生块相对增生厚度测量结果[n = 5,(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )]Table 1. The thickness of scar tissue in different groups [n = 5,(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )]组别 n 厚度(mm) F P B组 5 2.23 ± 0.38 1.177 0.37 C组 5 2.09 ± 0.10 D组 5 1.94 ± 0.08* 与C组相比,*P < 0.05。 表 2 各组凋亡指数的变化(n = 5,
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. Changes of fibroblast apoptosis index (n = 5,
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 凋亡率(%) F P A组 5 2.38 ± 0.41 16.357 < 0.001* B组 5 2.02 ± 0.16△ C组 5 2.05 ± 0.26 D组 5 3.66 ± 0.42##△△ *P < 0.05;与A组相比,△P < 0.05;与B组相比,##P < 0.01;与C组相比,△△P < 0.01。 -
[1] Ogawa R,Dohi T,Tosa M,et al. The latest strategy for keloid and hypertrophic scar prevention and treatment: The nippon medical school (NMS) protocol[J]. J Nippon Med Sch,2021,88(1):2-9. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2021_88-106 [2] Raktoe R S,van Haasterecht L,Antonovaite N,et al. The effect of TGFβRI inhibition on extracellular matrix structure and stiffness in hypertrophic scar-specific fibroblast-derived matrix models[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2021,559(6):245-251. [3] Mercurio L,Albanesi C,Madonna S. Recent updates on the involvement of PI3K/AKT/mTOR molecular cascade in the pathogenesis of hyperproliferative skin disorders[J]. Front Med (Lausanne),2021,8(4):665647. [4] Liu C,Chen K,Wang H,et al. Gastrin attenuates renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by a PI3K/Akt/bad-mediated anti-apoptosis signaling[J]. Front Pharmacol,2020,11(11):540479. [5] He T,Zhang Y,Liu Y,et al. MicroRNA-494 targets PTEN and suppresses PI3K/AKT pathway to alleviate hypertrophic scar formation[J]. J Mol Histol,2019,50(4):315-323. doi: 10.1007/s10735-019-09828-w [6] Tu T,Huang J,Lin M,et al. CUDC-907 reverses pathological phenotype of keloid fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo via dual inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling and HDAC2[J]. Int J Mol Med,2019,44(5):1789-1800. [7] Md Mokhtar A H,Malik I A,Abd Aziz N A A,et al. LY294002,a PI3K pathway inhibitor,prevents leptin-induced adverse effects on spermatozoa in sprague-dawley rats[J]. Andrologia,2019,51(3):e13196. doi: 10.1111/and.13196 [8] Long H Y,Wang C Y,Yang Y E. LY294002,a PI3K inhibitor,attenuates Tourette syndrome in rats[J]. Metab Brain Dis,2017,32(5):1619-1625. doi: 10.1007/s11011-017-0051-z [9] Luo L,Li J,Wu Y,et al. Adiponectin,but Not TGF-β1,CTGF,IL-6 or TNF-α,may be a potential anti-inflammation and anti-fibrosis factor in keloid[J]. J Inflamm Res,2021,14(3):907-916. [10] Wu X,Pu L,Chen W,et al. LY294002 attenuates inflammatory response in endotoxin-induced uveitis by downregulating JAK3 and inactivating the PI3K/Akt signaling[J]. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol,2022,44(4):510-518. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2055565 [11] Chen H,Xu K,Sun C,et al. Inhibition of ANGPT2 activates autophagy during hypertrophic scar formation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. An Bras Dermatol,2022,98(1):26-35. [12] Ma F, Shen J, Zhang H, et al. A novel lncRNA FPASL regulates fibroblast proliferation via the PI3K/AKT and MAPK signaling pathways in hypertrophic scar[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2022. http://doi.org/10.3724/abbs.2022122. [Online ahead of print]. [13] Zhi Y, Wang H, Huang B, et al. Panax Notoginseng Saponins suppresses TRPM7 via the PI3K/AKT pathway to inhibit hypertrophic scar formation in vitro. Burns, 2021, 47(4): 894-905. [14] Shi W,Wu Y,Bian D. p75NTR silencing inhibits proliferation,migration,and extracellular matrix deposition of hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by activating autophagy through inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway[J]. Can J Physiol Pharmacol,2021,99(4):349-359. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2020-0219 [15] Wu X,Wang Z,Wu G,et al. Tetramethylpyrazine induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of hypertrophic scar-derived fibroblasts via inhibiting the phosphorylation of AKT[J]. Front Pharmacol,2020,11(5):602. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载:
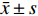

 下载:
下载: