Interventional Effect and Mechanism of Saikosaponin A on Noise-induced Tinnitus in Mice
-
摘要:
目的 探究柴胡皂苷A对噪音诱发耳鸣(Tinnitus)小鼠模型的干预作用及机制。 方法 将50只小鼠随机分为对照组(Control组)、噪音诱发耳鸣小鼠模型组(BBN组)、BBN组基础上分别灌胃10 mg/kg、20 mg/kg、40 mg/kg柴胡皂苷A(SSA)的SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组,每组10只。检测小鼠耳鸣行为;通过旷场实验、高架十字迷宫实验和强迫游泳实验评估小鼠的抑郁样行为;ABR阈值测定小鼠听力;RT-qPCR和Western blot检测小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β mRNA和蛋白表达。 结果 和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠在噪声暴露2 h后3 d、14 d和28 d时GPIAS%值降低(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠在噪声暴露2 h后3 d、14 d和28 d时GPIAS%值升高,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05)。和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠进入中央区时间和距离、进入开放臂次数和时间均减少,不动时间及Click和8、16、32 kHz声刺激下ABR阈值均升高( P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠进入中央区时间和距离、进入开放臂次数和时间均增加,不动时间及Click和8、16、32 kHz声刺激下ABR阈值均降低( P < 0.05)。和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β mRNA和蛋白表达均升高( P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β mRNA和蛋白表达均降低( P < 0.05)。 结论 柴胡皂苷A可改善噪声诱导耳鸣小鼠抑郁行为和听力,其可能和抑制耳鸣小鼠听觉皮层炎症因子密切相关。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the intervention effect and mechanism of Saikosaponin A on noise-induced tinnitus in a mouse model. Methods Fifty mice were randomly divided into control group(Control group), noise-induced tinnitus mouse model group(BBN group), and SSA-L group, SSA-M group and SSA-H group based on BBN group with 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg of Caihu saponin A by gavage, respectively, 10 mice in each group. The tinnitus behavior of mice was detected; the depression-like behavior of mice was assessed by the open field experiment, elevated cross-maze experiment and forced swimming experiment; the hearing of mice was measured by ABR threshold; and IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β mRNA and protein expression in the auditory cortex of mice were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blotting. Results Compared with the Control group, mice in the BBN group had significantly lower GPIAS% values at 3 d, 14 d and 28 d after 2 h of noise exposure(P < 0.05); compared with the BBN group, mice in the SSA-L, SSA-M and SSA-H groups had significantly higher GPIAS% values at 3 d, 14 d and 28 d after 2 h of noise exposure in a dose-dependent manner( P < 0.05). Compared with the Control group, mice in the BBN group had significantly reduced time and distance to the central zone, number and time to the open arm, and significantly higher immobility time and ABR thresholds under Click and 8, 16 and 32 kHz acoustic stimulation( P < 0.05); compared with the BBN group, mice in the SSA-L, SSA-M and SSA-H groups had significantly higher time and distance to the central zone, and The number and time of entering the open arm were significantly increased, and the immobility time and Click and ABR thresholds under 8, 16 and 32 kHz acoustic stimulation were significantly decreased( P < 0.05). Compared with the Control group, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β mRNA and protein expression were significantly increased in the auditory cortex of mice in the BBN group( P < 0.05); compared with the BBN group, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β mRNA and protein expression were significantly decreased in the auditory cortex of mice in the SSA-L, SSA-M and SSA-H groups( P < 0.05). Conclusion Saikosaponin A can improve depressive behavior and hearing in noise-induced tinnitus mice, which may be closely related to the inhibition of inflammatory factors in the auditory cortex of tinnitus mice. -
Key words:
- Saikosaponin A /
- Tinnitus /
- Depressive behavior /
- Inflammatory response
-
耳鸣(Tinnitus)是指无相应的外界生源刺激下,患者却可以感受到耳内或颅内产生持续或间断性声音的主观感觉[1]。耳鸣的发生机理可以分为主观性耳鸣和客观性耳鸣。其中,客观性耳鸣较为少见,是由内部生物源性声音引起的,可以通过仪器检测或被其他人听到,这种耳鸣具有确切的生源,通常与中耳或脑部血管发育异常等相关;主观性耳鸣的发生率较高,是指缺乏相应生源的耳鸣,也是平常所指耳鸣,与中耳炎、噪声暴露、听觉通路肿瘤、神经系统疾病等相关[2]。耳鸣的患病率较高,国外数据统计显示成年人中约有10.1%的人患有耳鸣[3],而在我国成年人中约有11.4%的人患有耳鸣,且患病率随着年龄的增加而升高[4]。耳鸣可能导致患者出现注意力不集中、失眠、焦虑、易怒、抑郁、恐惧等严重的精神症状,甚至可能会引起自杀。这些负面情绪会进一步使患者对耳鸣更加敏感,形成恶性循环,导致患者出现精神和行为异常[5]。目前临床尚无有效治疗耳鸣的药物,因此探究耳鸣的发病机制对治疗耳鸣有重要意义。噪声是世界上公认的危害之一,其可通过损伤听觉系统等多个系统影响人的听觉和记忆能力等多方面的功能[6]。柴胡的主要有效成分之一是柴胡皂苷A(saikosaponin A,SSA),其具有多种药理活性,如抗炎、抗肿瘤、抗氧化等作用。近年对SSA的研究主要集中在抗癫痫、抗抑郁和抗炎等研究,而癫痫和抑郁的发病与炎症因子密切相关[7],体内研究发现SSA可通过抑制核因子κB(nuclear factor kappa B,NF-κB)信号通路发挥较强的抗炎活性[8],但目前关于SSA能否通过影响炎症因子对耳鸣小鼠发挥治疗作用鲜有报道,因此本研究从实践角度出发,用噪音诱导耳鸣小鼠模型探究,探究SSA对耳鸣小鼠的干预作用机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
1.1.1 实验动物
7~8周龄,50只听力正常的C57BL/6雄性小鼠,体质量18~20 g,动物均购自成都达硕实验动物实验公司,许可证号为:SCXK(川)2013-0024。小鼠均分笼饲养于统一的动物房内,温度21~25 ℃,相对湿度50%~60%,光照12 h/12 h昼夜交替,自由摄食饮水。本研究经保山市人民医院动物伦理委员会审批通过(20220012)。
1.1.2 试剂和仪器
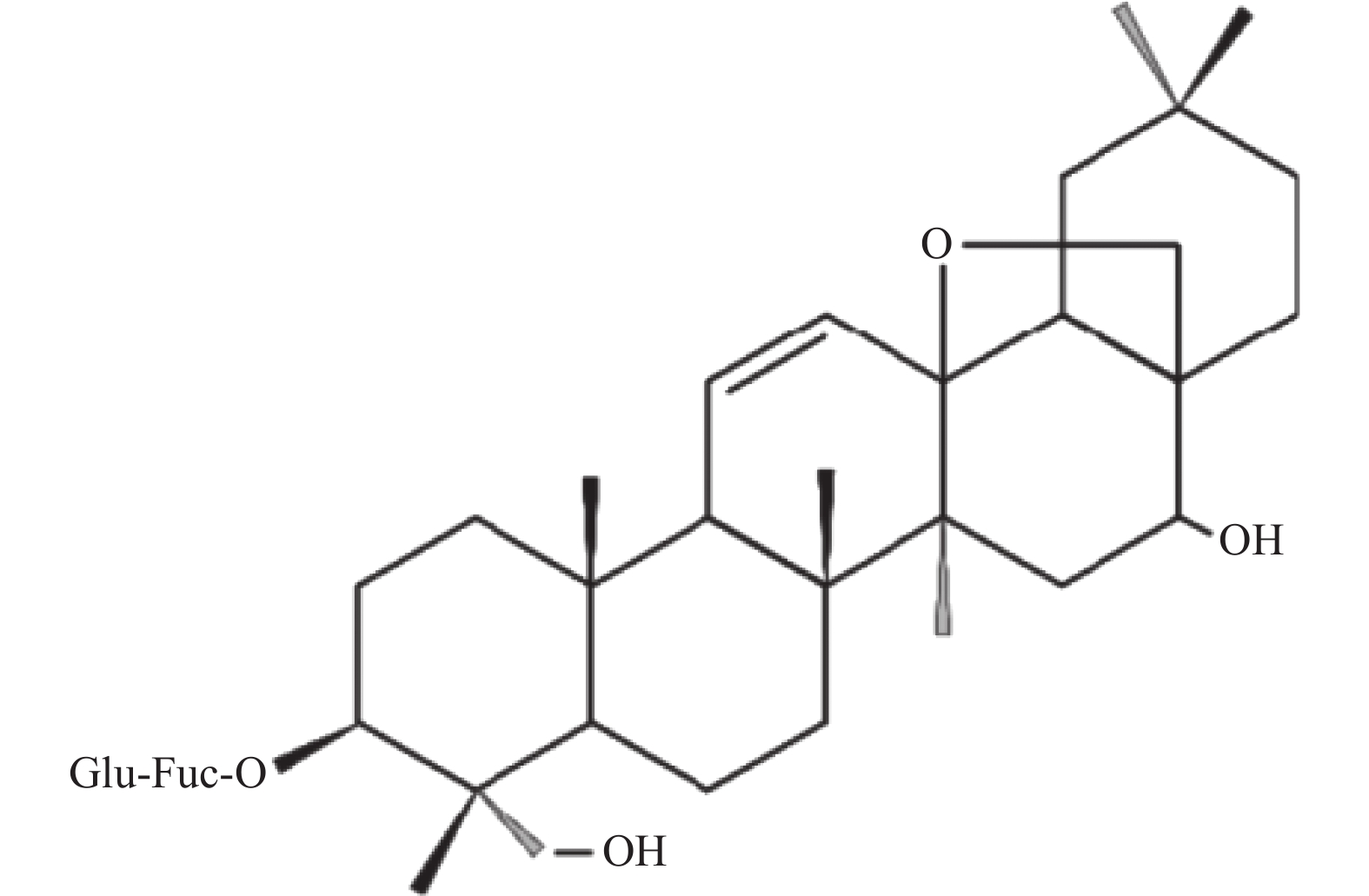
柴胡皂苷A(SSA化学结构见图1,质量分数 > 98%,批号:130301,美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α抗体(美国Cell signaling technology公司);惊跳反射实验系统(美国Med Associates公司);音响(HARMAN International公司);视频行为学分析系统(美国HAVARD APPARAUTUS panlab公司);超净工作台(新加坡艺思高科技有限公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 分组和模型制备[9]
将50只小鼠随机分为对照组(Control组)10只和造模组40只。将造模组40只小鼠制备噪音诱发耳鸣小鼠模型,将造模组小鼠均置于标准隔音室内,采用100 dB SPL的宽频带噪声(broadband noise,BBN)进行噪声单次暴露2 h;为了避免实验动物在暴露期间相互影响入耳声强以及相互撕咬,将小鼠分别放置在长4.5 cm、宽4.5 cm、高8 cm的铁丝笼内,在不影响声音传播的同时小鼠能自由活动。将音响放在笼子前方进行实验。造模成功标准:出现头部摇晃、耳朵抖动、耳朵摩擦等耳鸣行为。Control组小鼠置于相同的金属笼中,并于标准隔音室内放置2 h,但关闭扬声器。实验结束各组小鼠均分笼饲养并进行后续检测。
造模成功后将40只小鼠随机分为4组,即噪音诱发耳鸣小鼠模型组(BBN组)、BBN组基础上分别灌胃10 mg/kg、20 mg/kg、40 mg/kg的柴胡皂苷A干预,分别设为SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组,每组10只。Control组和BBN组小鼠均灌胃等量的生理盐水。各组小鼠均每次灌胃1次,连续灌胃28 d。
1.2.2 耳鸣行为学检测
各组小鼠分别于噪声暴露2 h后3 d、14 d、28 d时进行耳鸣行为学测定。在进行前间隙抑制听觉惊跳反应(gap prepulse inhibition of acoustic startle response,GPIAS)实验之前,需要先让小鼠在透明盒子中适应10 min。实验过程中,将每只小鼠放置在一个透明盒子中,并将盒子放置在灵敏的压电传感器上。通过检测小鼠肌肉动作幅度的波形,自动计算出相应的波幅,以进行实验。GPIAS实验包括30次有间隙试验(gap试验)和30次无前间隙试验(no gap试验)采用随机配对法消除有前间隙试验和无前间隙试验偏差。耳鸣行为学检测以GPIAS抑制率作为检测指标,即
$$ \begin{split} \text{GPIAS抑制率} ({\text{%}}) = \frac{\text{无前间隙的刺激所引出反应} \text{的波幅(no gap)}- \text{有间隙额} \text{刺激所引出反应的幅度gap}} {\text{无前间隙额刺激所引出反应}\text{的幅度(no gap)}} \times {100\text{%}} \end{split}$$ (1) 1.2.3 焦虑抑郁样行为评估[10]
每只小鼠于给药后1 d,分别采用旷场实验、高架十字迷宫实验、强迫游泳实验来评估各组小鼠的焦虑抑郁情绪。实验前1 h将测试小鼠单笼单只放置于测试室内以适应环境,全部行为测定结束后将小鼠放回原始笼中。
(1)旷场实验:制备5个相同大小、内壁及底部均为白色的矿场箱,长宽均为45 cm,高为30 cm。将矿场仪器放于灯的正下方,面向箱壁将小鼠放于不同的矿场箱内中央与周围区交界处,让小鼠在矿场内自由活动10 min。取出测定后的小鼠放回笼内,将小鼠的排泄物清理干净。矿场箱底部为25个正方形,中间9个正方形为中央区,采用视频行为学系统采集并记录小鼠进入中央区时间及在中央区距离。
(2)高架十字迷宫实验:高架十字迷宫由2条开放臂、2条闭合臂和1个联合4条臂的中央区平台组成,形状呈十字形,各面均为白色。每个臂和平台的距离为50 cm。为确保亮度相等,高架被置于灯的正下方,避免阴影。在测试中,将小鼠背对实验员放置在中央区,面对其中一条开放臂。然后,让小鼠在高架内自由活动5 min。测试结束后,将小鼠放回笼子中,并清理高架上的分泌物。在进行下一轮测试前,使用酒精擦拭干净高架各部分。记录小鼠进入开放臂次数及在开放臂的时间。
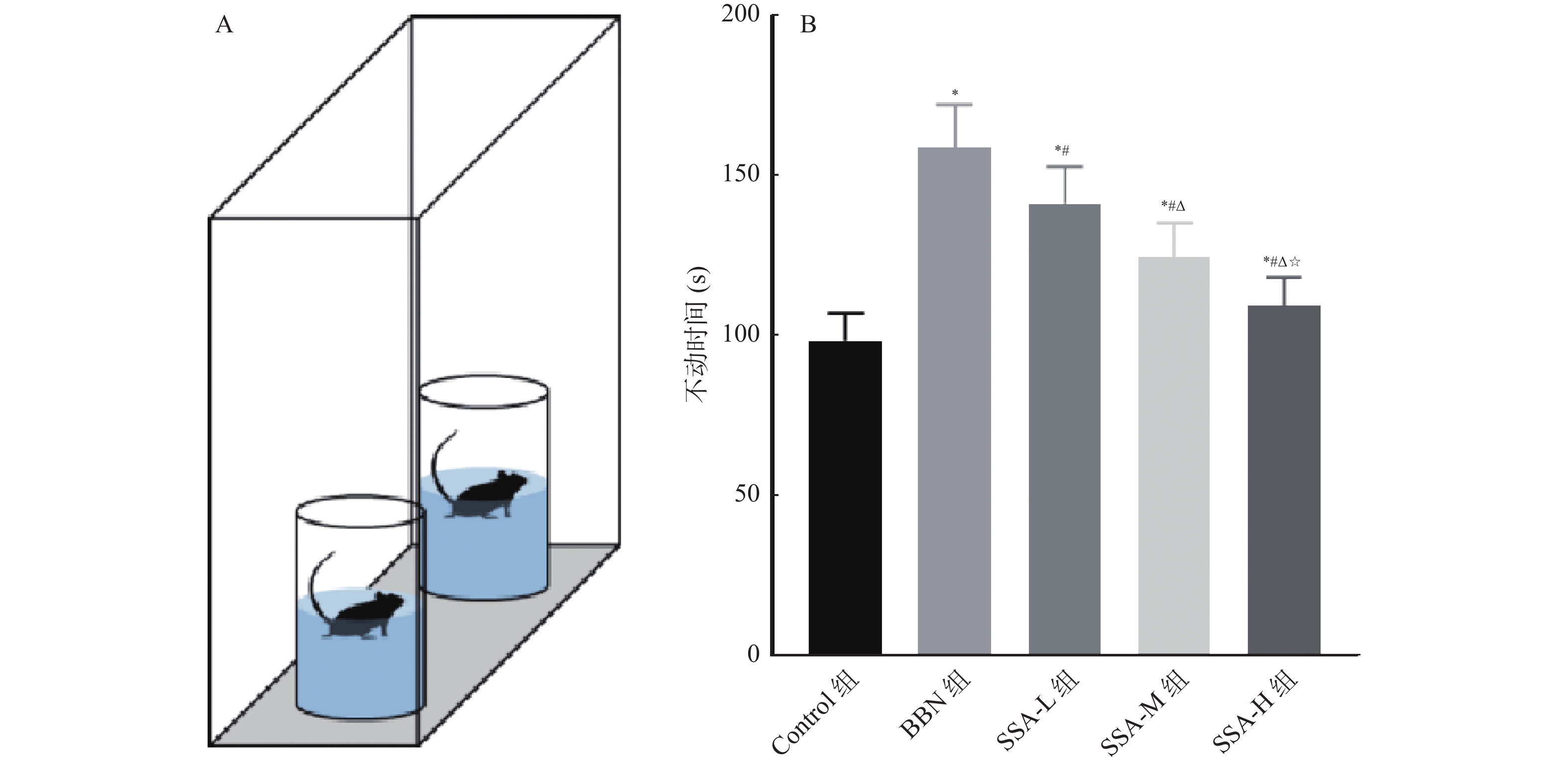
(3)强迫游泳实验:进行小鼠强迫游泳测试时,需要使用直径为16 cm、高为30 cm的2个玻璃烧杯,并在每个杯子加入温度为28 ℃的水,深度达20 cm。然后将小鼠放置在其中1个烧杯内,确保小鼠可以直立在水中,但尾巴不触及杯底。观察小鼠是否漂浮或摆动,并保持其头部浮在水面,仅单下肢微颤状态。借助手动计数器,在5 min内记录小鼠的不动时间。测试结束后将小鼠擦拭干净后放回笼中。
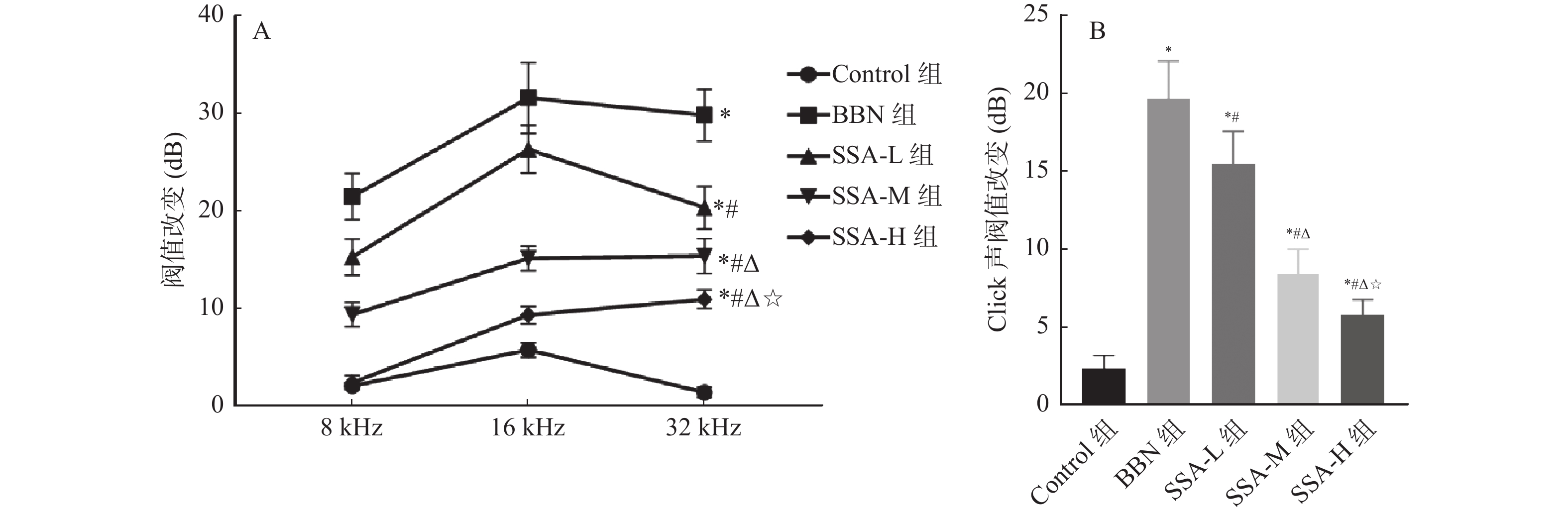
1.2.4 ABR阈值测定
各组小鼠于药物干预结束后36 h测定听力。进行小鼠ABR阈值测试时,先在麻醉状态下将记录电极放置于颅顶皮下、参考电极放置在右耳乳突部皮肤下,接地电极放置在左耳同一位置。然后使用耳机依次刺激click声、8 kHz、16 kHz和32 kHz的纯音,从70 dB开始每降低10 dB,并在阈值附近改为5 dB递减。测定前五个波中最后一个消失的波确定阈值,并将被消失时的声强数值与上一个仍有波的声强数值取平均值作为阈值。在测定过程中要保持小鼠体温并确保其舒适度。
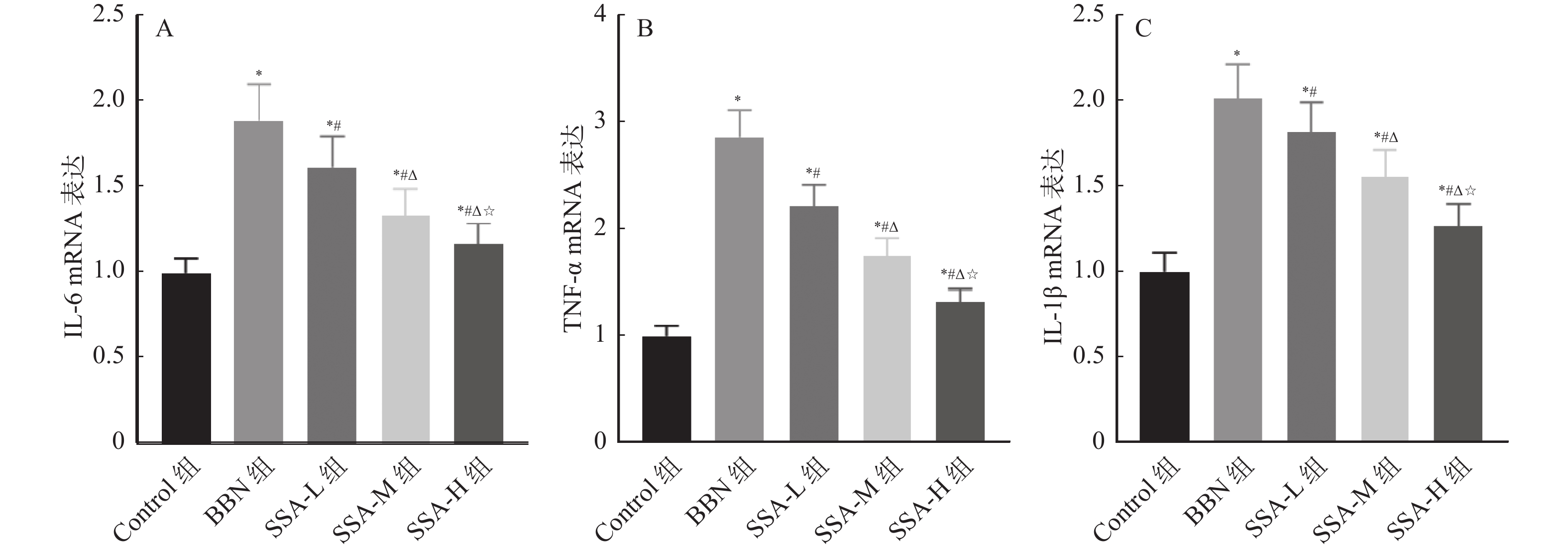
1.2.5 RT-qPCR检测小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β mRNA表达
3%戊巴比妥钠腹腔注射30 mg/kg麻醉小鼠,断头处死小鼠,取听觉皮层组织研磨,加入1 mL TRIzol裂解液裂解,提取裂解后细胞和组织中总RNA,提取步骤按照试剂盒说明书进行。根据逆转录试剂盒说明书将总RNA逆转录为cDNA。瞬时离心各引物(引物序列见表1),在引物中加入去离子水并制成100 μmol/L的液体,稀释引物终浓度为10 μmol/L。按照以下条件扩增引物,预变性95 ℃ 5 min;变性95 ℃ 10 s;退火60 ℃ 20 s;延伸72 ℃ 10 min;共30个循环。用2-△△CT法分析表达量。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Primer sequence基因 引物序列 扩增长度 IL-6 F:5'-ATTGTATGAACAGCGATGATGCAC-3' 400 bp R:5'-CCAGGTAGAAACGGAACTCCAGA-3' TNF-α F:5'-TCAGTTCCATGGCCCAGAC-3' 150 bp R:5'-GTTGTCTTTGAGATCCATGCCATT-3' IL-1β F:5'-CCAGCTGGAGAGTGGATCC-3' 300 bp R:5'-AGCTGTCGGAGATTCGTAGC-3' GAPDH F:5'-GGCACAGTCAAGGCTGAGAATG-3' 150 bp R:5'-ATGGTGGTGAAGACGCCAGTA-3' 1.2.6 Western blot检测小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β蛋白表达
麻醉并处死小鼠,取听觉皮层组织,提取组织中总蛋白,用BCA法检测总蛋白浓度。将蛋白溶液的终浓度配制为2 μg/mL,将蛋白溶液置于热水中煮沸10 min,后保存在-20 ℃冰箱中。将30 μg的蛋白样品用200 V电压电泳,通过电转的方式将SDS-PAGE分离胶中的蛋白质转移到PVDF膜上,用5%脱脂奶粉封闭PVDF膜1 h,将一抗IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β(1∶
1000 )加入到PVDF膜上,4 ℃孵育过夜;将PVDF膜冲洗干净后加入二抗(1∶1000 ),室温孵育2 h。ECL发光液加入到细胞中,曝光显影后用Image Lab软件分析条带灰度值。1.3 统计学处理
实验数据使用Graphpad priam 8.0软件进行统计学分析,并用均数±标准差( $ \bar x \pm s $)表示计量资料。针对不同组间的数据,采用单因素方差(one-way ANOVA)分析来进行统计学比较。同时使用LSD-t检验来比较组间两两比较的差异。根据实验结果,若P < 0.05,则表示差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 各组小鼠耳鸣行为学比较
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠在噪声暴露2 h后3 d、14 d和28 d时GPIAS%值降低(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠在噪声暴露2 h后3 d、14 d和28 d时GPIAS%值升高,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05),见 表2。
表 2 各组小鼠噪声暴露2 h后不同时间节点中GPIAS%值比较( $ \bar x \pm s $,n = 10)Table 2. Comparison of GPIAS% values at different time points after 2-hour noise exposure in each group of mice( $ \bar x \pm s $,n = 10)组别 3 d 14 d 28 d Control组 28.69 ± 2.31 37.58 ± 3.15 40.31 ± 3.20 BBN组 19.34 ± 1.52 18.17 ± 1.28 17.23 ± 1.35 SSA-L组 21.53 ± 1.45▲# 22.62 ± 1.31▲# 20.65 ± 1.69▲# SSA-M组 24.09 ± 1.33▲#△ 28.39 ± 1.57▲#△ 27.19 ± 2.01▲#△ SSA-H组 27.15 ± 1.24#△☆ 32.66 ± 2.09▲#△☆ 33.87 ± 5.64▲#△☆ F 57.080 148.700 87.790 P < 0.001 *< 0.001 *< 0.001 **P < 0.05;与Control组相比, ▲P < 0.05;与BBN组相比, #P < 0.05;与SSA-L组相比, △P < 0.05;与SSA-M组相比, ☆P < 0.05。 2.2 各组小鼠进入中央区时间和进入中央区距离比较
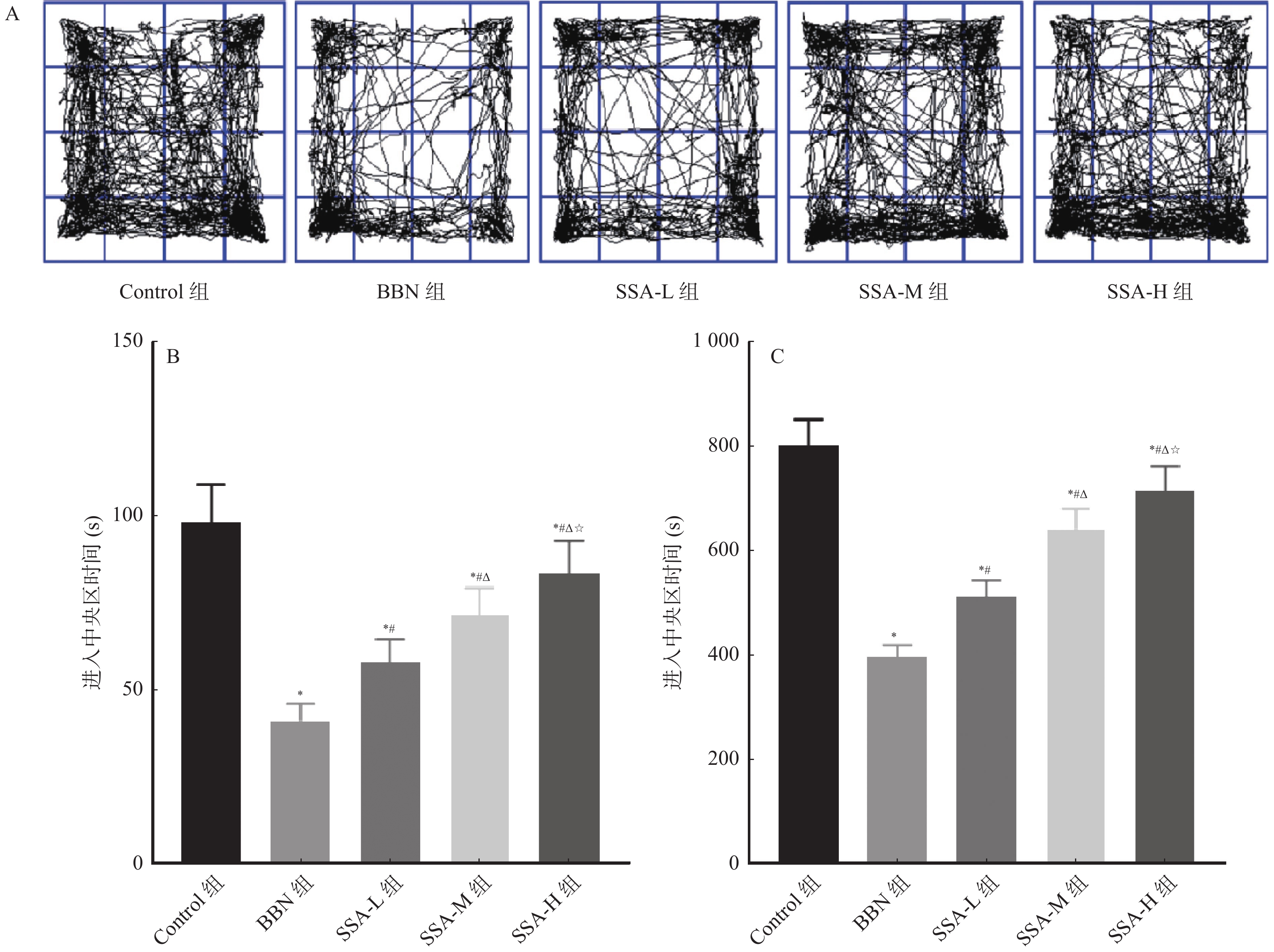
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠进入中央区时间和进入中央区距离均缩短(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠进入中央区时间和进入中央区距离均增加,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05),见 图2。
2.3 各组小鼠进入开放臂次数及进入开放臂的时间比较
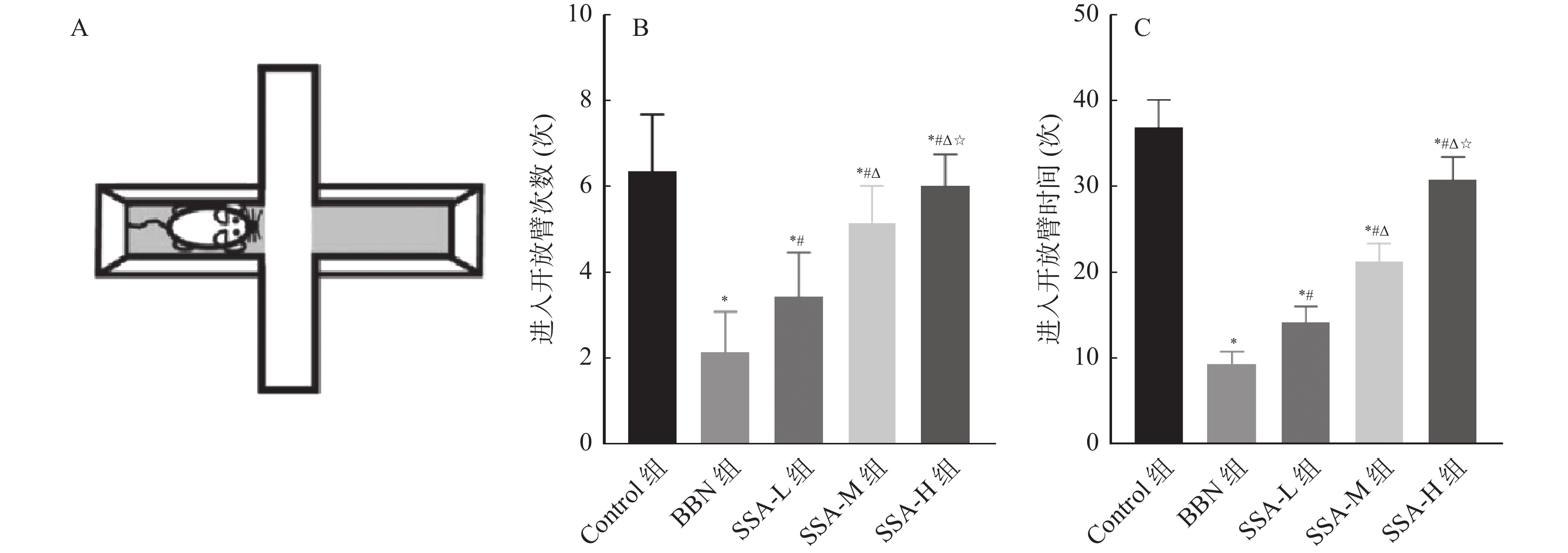
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠进入开放臂次数和时间均减少(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠进入开放臂次数和时间均增加,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05),见 图3。
2.4 各组小鼠强迫游泳实验不动时间比较
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠不动时间增加(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠不动时间均减少,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05),见 图4。
2.5 各组小鼠ABR阈值改变比较
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠在Click和8、16、32 kHz声刺激下ABR阈值均升高(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠在Click和8、16、32 kHz声刺激下ABR阈值均降低( P < 0.05),见 图5。
2.6 各组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β mRNA表达比较
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β mRNA表达均升高(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β mRNA表达均降低,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05),见 图6。
2.7 各组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β蛋白表达比较
和Control组相比,BBN组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05);和BBN组相比,SSA-L组、SSA-M组和SSA-H组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β蛋白表达均降低,且呈剂量依赖( P < 0.05),见 图7。
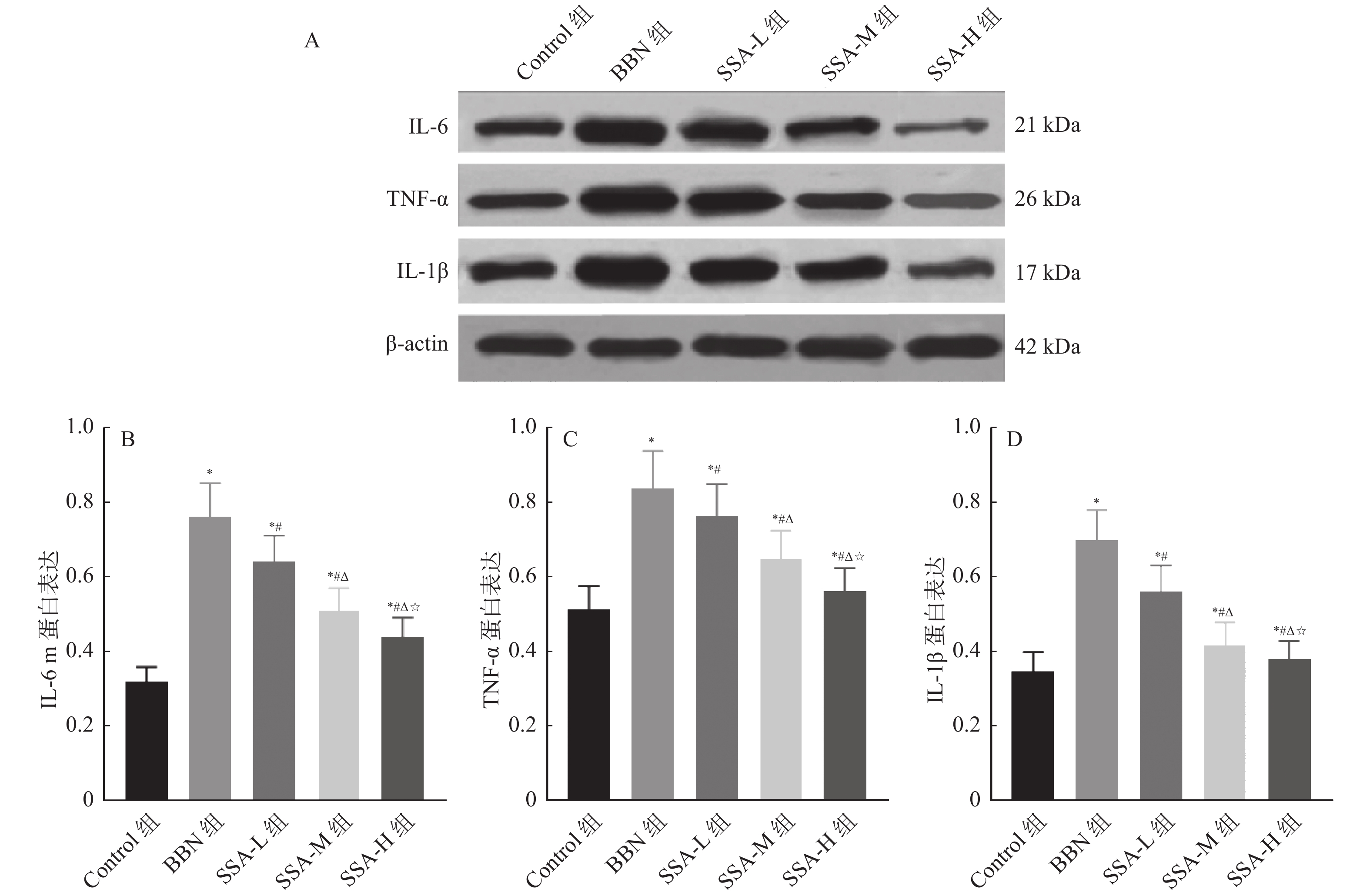 图 7 各组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β蛋白表达比较A:各组小鼠IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β蛋白电泳图;B:小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6蛋白表达比较;C:小鼠听觉皮层中TNF-α蛋白表达比较;D:小鼠听觉皮层中IL-1β蛋白表达比较。与Control组相比,*P < 0.05;与BBN组相比,#P < 0.05;与SSA-L组相比,△P < 0.05;与SSA-M组相比,☆P < 0.05。Figure 7. IL-6 and TNF in the auditory cortex of mice in each group- α、 IL-1 β Comparison of protein expression
图 7 各组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β蛋白表达比较A:各组小鼠IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β蛋白电泳图;B:小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6蛋白表达比较;C:小鼠听觉皮层中TNF-α蛋白表达比较;D:小鼠听觉皮层中IL-1β蛋白表达比较。与Control组相比,*P < 0.05;与BBN组相比,#P < 0.05;与SSA-L组相比,△P < 0.05;与SSA-M组相比,☆P < 0.05。Figure 7. IL-6 and TNF in the auditory cortex of mice in each group- α、 IL-1 β Comparison of protein expression3. 讨论
耳鸣是由多种因素共同作用的一种疾病,其患病率较高,目前临床的治疗方案效果不显著且治愈率较低,严重影响患者的心理健康和生活质量[11]。目前,噪声已成为导致青少年和大学生出现耳鸣的常见因素之一。宽频白噪声是人们日常生活中接触最多的一种噪声类型,因其以较均匀分布的能量播放所有频率而备受关注。利用噪声诱导耳鸣动物模型结合GPIAS检测方式,可更有效地模拟人类耳鸣,降低训练时间成本,同时不对动物造成损伤,因此该方法可相对可靠地反应动物是否出现耳鸣行为[12]。本研究中采用了100 dB SPL白噪声环境中单次暴露2 h后,发现了小鼠在3 d、14 d和28 d时间节点时GPIAS%值较Control组均降低,提示造模成功。100 dB SPL宽频噪声诱发的耳鸣行为更显著,可在毛细胞和听觉中枢上产生明显变化,从造模角度证明这类噪声有利于构建稳定、便捷的耳鸣动物模型,同时可有效节约时间。唐薇等[13]研究证实,100 dB SPL宽频带白噪声可能更适合高效、便捷地构建噪声性耳鸣动物模型,且噪声可能通过上调GAP-43表达介导耳鸣的发生发展。
作为中国传统中药材之一,柴胡历史悠久,并可根据形状分为南柴胡和北柴胡。其具有多种功效,如和解少阳、疏肝解郁、热血入室等。柴胡主要药理活性成分包括柴胡皂苷A、B、C、D,其中柴胡皂苷A具有较好的抗癫痫、抗抑郁和抗炎作用[14]。近年来发现[15],尽管耳鸣的发病率较高,但只有少数患者(不到20%)会对其适应不良而严重影响生活质量,导致焦虑和抑郁等精神情绪障碍。本研究通过旷场实验、高架十字迷宫实验、强迫游泳实验来评估小鼠的焦虑抑郁情绪,结果发现耳鸣小鼠有明显的抑郁行为且听力受到明显损伤,柴胡皂苷A干预后发现,小鼠的GPIAS%值、进入中央区时间、进入中央区距离、进入开放臂次数和时间均增加,小鼠不动时间及在Click和8、16、32 kHz声刺激下ABR阈值均减少,提示柴胡皂苷A可明显改善耳鸣小鼠的抑郁行为,保护耳鸣小鼠听力。研究发现[16],柴胡皂苷A可以抑制利血平诱导的抑郁小鼠表现出的怠倦和上睑下垂的现象。吴启洋等[17]在强迫游泳实验和悬尾实验中发现,SSA可以明显改善表现绝望行为的抑郁小鼠,从而缓解其抑郁症状。
炎症是一种免疫反应,通常是身体对伤害或感染的反应,其可导致身体产生一系列化学物质,包括炎症因子,如细胞因子、趋化因子和炎症介质。这些炎症因子会引发免疫反应,促使白细胞和其他免疫细胞进入炎症部位,以清除病原体或修复受损组织。近年来研究发现[18],炎症因子与耳鸣的发病机制可能存在一定的关联。炎症反应可以引发神经炎症,导致神经元的损伤或异常兴奋,可能会引起耳鸣的发生。此外,一些研究表明,炎症因子的产生和释放可能与听觉系统的功能失调相关。Tetteh等[19]在对一项慢性耳鸣患者的研究发现,放松训练可显著减少患者的焦虑抑郁和耳鸣,这些症状的减轻和血清中TNF-α、IL-6等减少密切相关。目前,对于柴胡皂苷A治疗抑郁的机制研究主要关注于其对神经炎症的抑制以及对脑源性神经营养因子、神经递质和神经内分泌的调节。在抑郁过程中,抗炎性细胞因子和前炎性细胞因子都对其产生影响。其中,前炎性细胞因子如IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α等,在抑郁发病中起着重要的作用。研究表明[20],SSA可通过抑制海马区IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α等表达发挥抗抑郁作用,表明SSA抗抑郁的机制可能是通过介导围绝经期海马的神经炎症介导的。本研究结果显示,耳鸣小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β mRNA和蛋白表达均升高,提示耳鸣小鼠存在神经炎症,和上述研究结果一致;经过柴胡皂苷A干预后发现,耳鸣小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β mRNA和蛋白表达均降低,提示柴胡皂苷A可抑制耳鸣小鼠神经炎症,进而改善耳鸣小鼠抑郁行为。
综上所述,柴胡皂苷A可改善耳鸣小鼠抑郁行为,对耳鸣发挥治疗作用,其可能和抑制耳鸣小鼠听觉皮层炎症因子密切相关。由于时间和成本等因素,本研究未能给予阳性药物进行干预,仅设置了和对照组比较,使文章的结果可能存在一定的局限性,在今后的研究中会增加相关的阳性对照分组,从而为临床治疗提供更真实有效的实验依据。
-
图 7 各组小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β蛋白表达比较
A:各组小鼠IL-6、TNF-α和IL-1β蛋白电泳图;B:小鼠听觉皮层中IL-6蛋白表达比较;C:小鼠听觉皮层中TNF-α蛋白表达比较;D:小鼠听觉皮层中IL-1β蛋白表达比较。与Control组相比,*P < 0.05;与BBN组相比,#P < 0.05;与SSA-L组相比,△P < 0.05;与SSA-M组相比,☆P < 0.05。
Figure 7. IL-6 and TNF in the auditory cortex of mice in each group- α、 IL-1 β Comparison of protein expression
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequence
基因 引物序列 扩增长度 IL-6 F:5'-ATTGTATGAACAGCGATGATGCAC-3' 400 bp R:5'-CCAGGTAGAAACGGAACTCCAGA-3' TNF-α F:5'-TCAGTTCCATGGCCCAGAC-3' 150 bp R:5'-GTTGTCTTTGAGATCCATGCCATT-3' IL-1β F:5'-CCAGCTGGAGAGTGGATCC-3' 300 bp R:5'-AGCTGTCGGAGATTCGTAGC-3' GAPDH F:5'-GGCACAGTCAAGGCTGAGAATG-3' 150 bp R:5'-ATGGTGGTGAAGACGCCAGTA-3' 表 2 各组小鼠噪声暴露2 h后不同时间节点中GPIAS%值比较( $ \bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
Table 2. Comparison of GPIAS% values at different time points after 2-hour noise exposure in each group of mice( $ \bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
组别 3 d 14 d 28 d Control组 28.69 ± 2.31 37.58 ± 3.15 40.31 ± 3.20 BBN组 19.34 ± 1.52 18.17 ± 1.28 17.23 ± 1.35 SSA-L组 21.53 ± 1.45▲# 22.62 ± 1.31▲# 20.65 ± 1.69▲# SSA-M组 24.09 ± 1.33▲#△ 28.39 ± 1.57▲#△ 27.19 ± 2.01▲#△ SSA-H组 27.15 ± 1.24#△☆ 32.66 ± 2.09▲#△☆ 33.87 ± 5.64▲#△☆ F 57.080 148.700 87.790 P < 0.001 *< 0.001 *< 0.001 **P < 0.05;与Control组相比, ▲P < 0.05;与BBN组相比, #P < 0.05;与SSA-L组相比, △P < 0.05;与SSA-M组相比, ☆P < 0.05。 -
[1] Malfatti T,Ciralli B,Hilscher M M,et al. Decreasing dorsal cochlear nucleus activity ameliorates noise-induced tinnitus perception in mice[J]. BMC Biology,2022,20(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01288-1 [2] Yan W,Zhu H,Yu B,et al. Effects of two inhibitors of metabolic glutamate receptor 5 on expression of endogenous homer scaffold protein 1 in the auditory cortex of mice with tinnitus[J]. Bioengineered,2021,12(1):7145-7153. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1979354 [3] Longenecker R J,Gu R,Homan J,et al. Development of tinnitus and hyperacusis in a mouse model of tobramycin cochleotoxicity[J]. Front Mol Neurosci,2021,14:715952. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.715952 [4] Adcock K,Vanneste S. Neuroinflammation in tinnitus[J]. Curr Otorhinolaryngol Rep,2022,10(3):322-328. doi: 10.1007/s40136-022-00411-8 [5] Brüggemann P,Sória M G,Brandes-Schramm J,et al. The influence of depression,anxiety and cognition on the treatment effects of ginkgo biloba extract egb 761® in patients with tinnitus and dementia: A mediation analysis[J]. J Clin Med,2021,10(14):3151. doi: 10.3390/jcm10143151 [6] Koch L,Gaese B H,Nowotny M. Strain comparison in rats differentiates strain-specific from more general correlates of noise-induced hearing loss and tinnitus[J]. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol,2022,23(1):59-73. doi: 10.1007/s10162-021-00822-2 [7] Sui C,Han W J,Zhu C R,et al. Recent progress in saikosaponin biosynthesis in Bupleurum[J]. Curr Pharm Biotechnol,2021,22(3):329-340. doi: 10.2174/1389201021999200918101248 [8] Wang X,Ming Y,Li Q,et al. Saikosaponin a alleviates rat liver fibrosis by inhibiting Hedgehog signaling pathway-mediated autophagy and NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Trop J Pharm Res,2023,22(4):741-747. doi: 10.4314/tjpr.v22i4.5 [9] Marinos L,Kouvaros S,Bizup B,et al. Transient delivery of a KCNQ2/3-specific channel activator 1 week after noise trauma mitigates noise-induced tinnitus[J]. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol,2021,22(2):127-139. doi: 10.1007/s10162-021-00786-3 [10] Aliomrani M,Mesripour A,Sayahpour Z. AChR is partly responsible in mice depressive-like behavior after Phosalone exposure[J]. Neurotoxicol Teratol,2021,84:106957. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2021.106957 [11] Hao J,Xia L,Yang X. The latest research progress of tinnitus related treatment[J]. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi,2021,35(12):1141-1144. [12] Henton A,Tzounopoulos T. The neuroscience and the treatment of tinnitus[J]. Hear J,2021,74(6):16-17. [13] 唐薇,凌赛泳,向澎,等. 不同强度白噪声建立噪声性耳鸣动物模型效果比较及对听皮层生长相关蛋白-43表达的影响[J]. 右江民族医学院学报,2023,45(2):259-262,286. [14] Sun C,Gao M,Qiao M. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine compound" Xiaochaihu Decoction" in the treatment of depression[J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2023,159:114249. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114249 [15] Labree B,Hoare D J,Gascoyne L E,et al. Determining the effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on tinnitus,depression,and anxiety: A systematic review[J]. Brain Sci,2022,12(4):484. doi: 10.3390/brainsci12040484 [16] 赵慧源,田诗琪,翟春影,等. 柴胡皂苷a对抑郁模型大鼠脑内神经递质及行为学的影响[J]. 中国医学创新,2021,18(34):28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.34.007 [17] 吴启洋,刘纪明,谢华,等. 柴胡皂苷a药理作用及其作用机制的研究进展[J]. 赣南医学院学报,2022,42(11):1143-1150. [18] 惠林娜,宋勇莉,查定军. 急性耳鸣预后及影响因素研究进展[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2022,46(6):357-360. [19] Tetteh H,Lee M,Lau C G,et al. Tinnitus: Prospects for pharmacological interventions with a seesaw model[J]. Neuroscientist,2018,24(4):353-367. doi: 10.1177/1073858417733415 [20] 郭旭彤,安继东,梅建强. 柴胡皂苷A对抑郁症大鼠Treg和Th17免疫平衡的影响[J]. 海南医学院学报,2020,26(22):1686-1690. doi: 10.13210/j.cnki.jhmu.20200508.003 -






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:

