Erector Spinae Plane Block for Postoperative Analgesia in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
-
摘要:
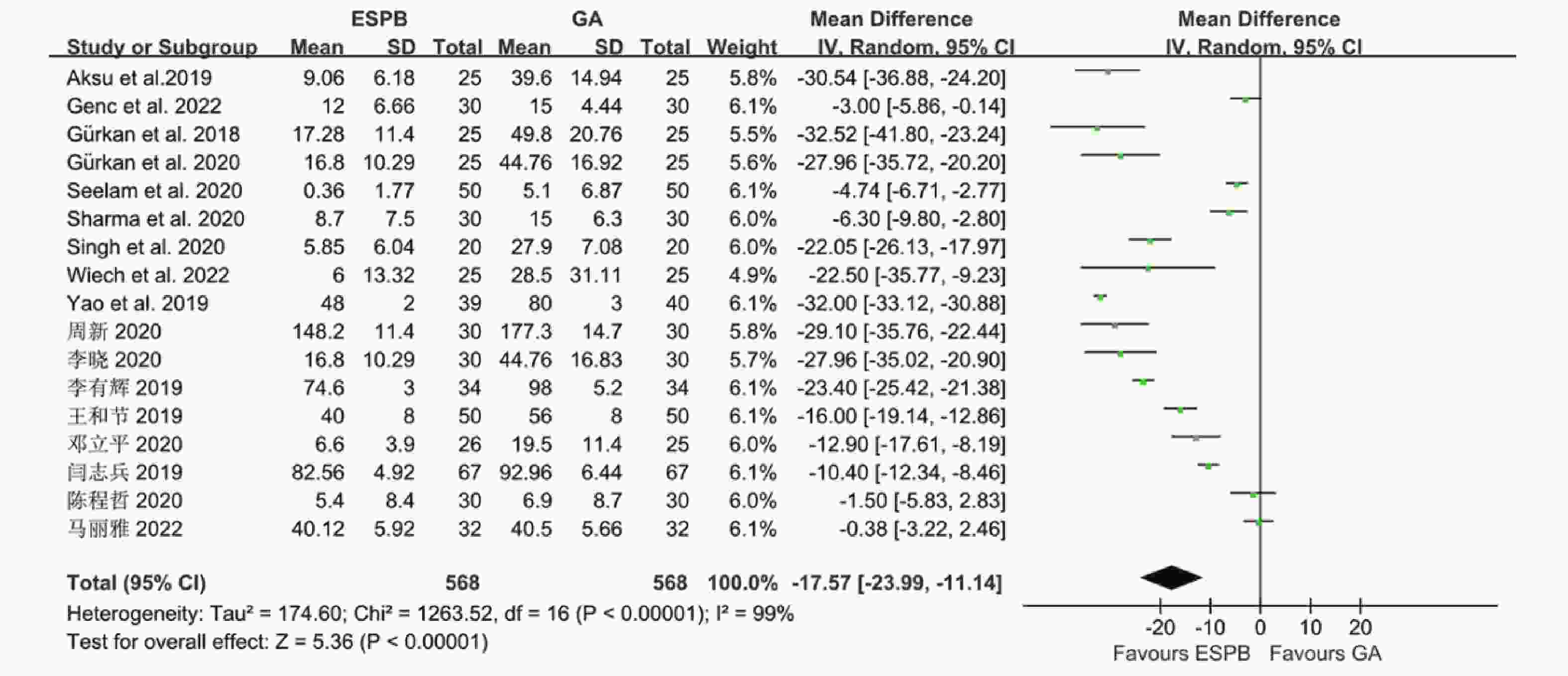
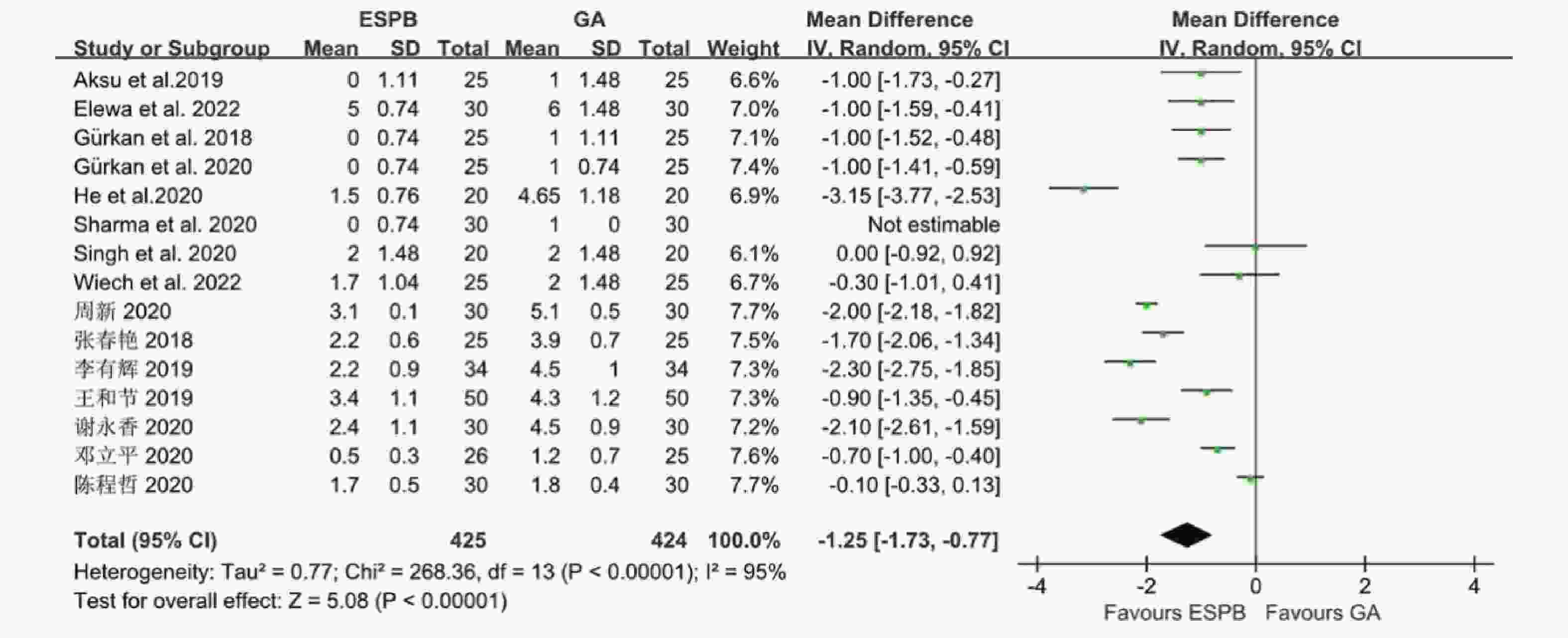
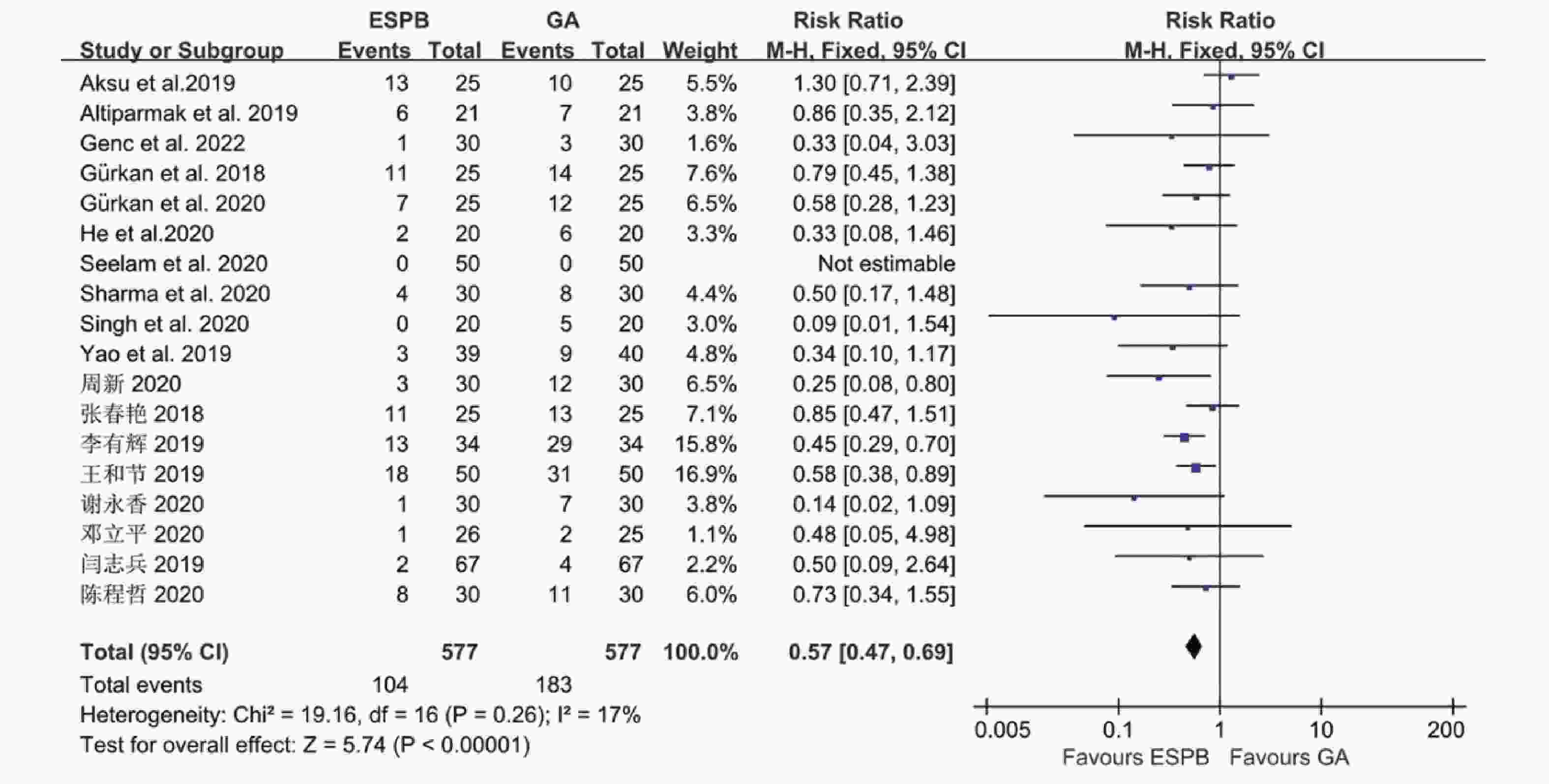
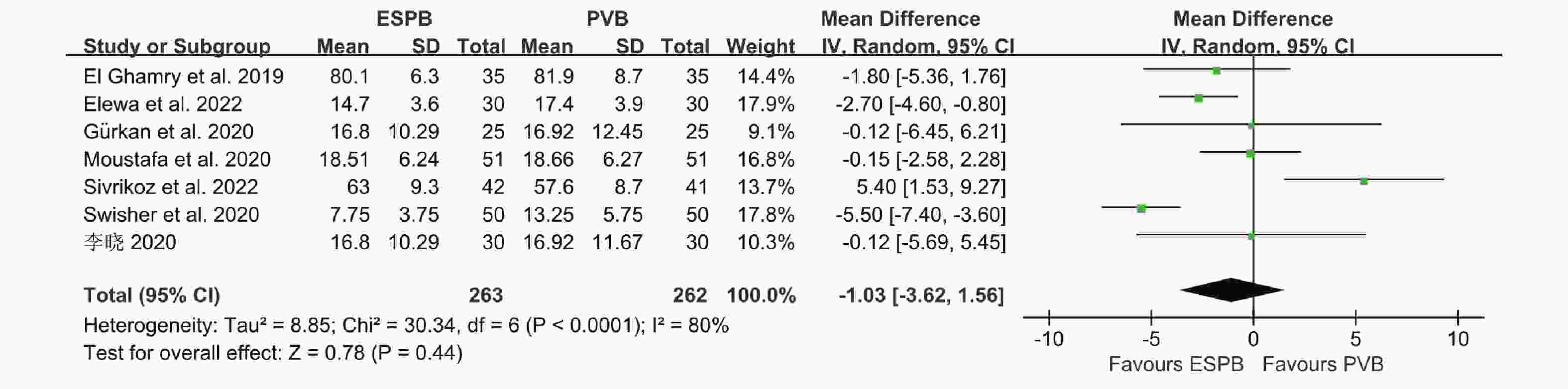
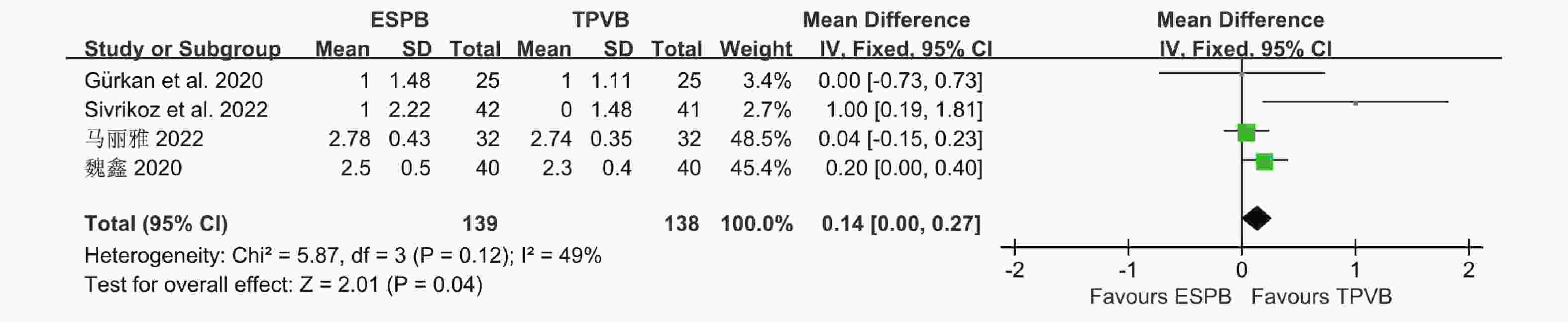
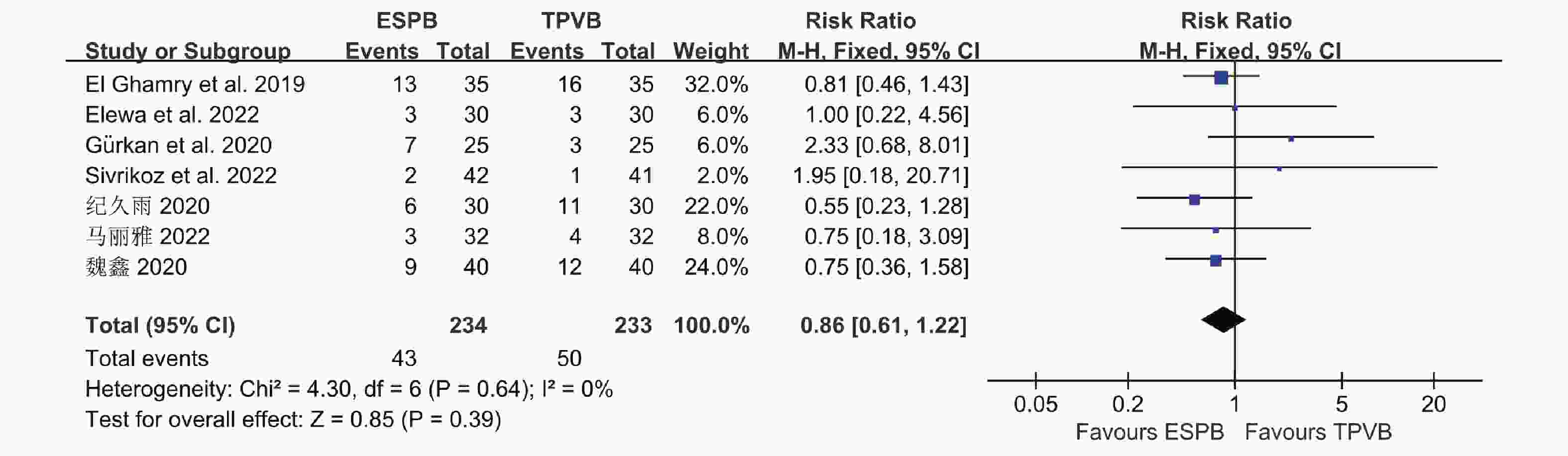
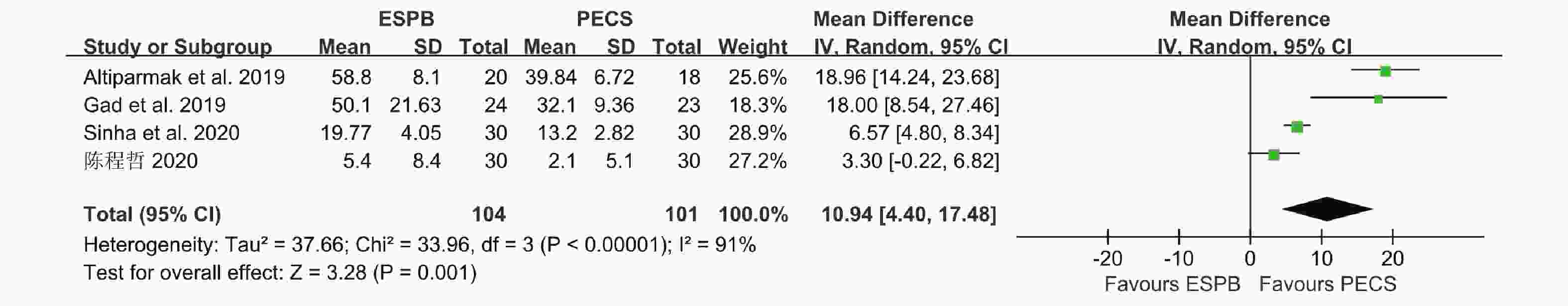
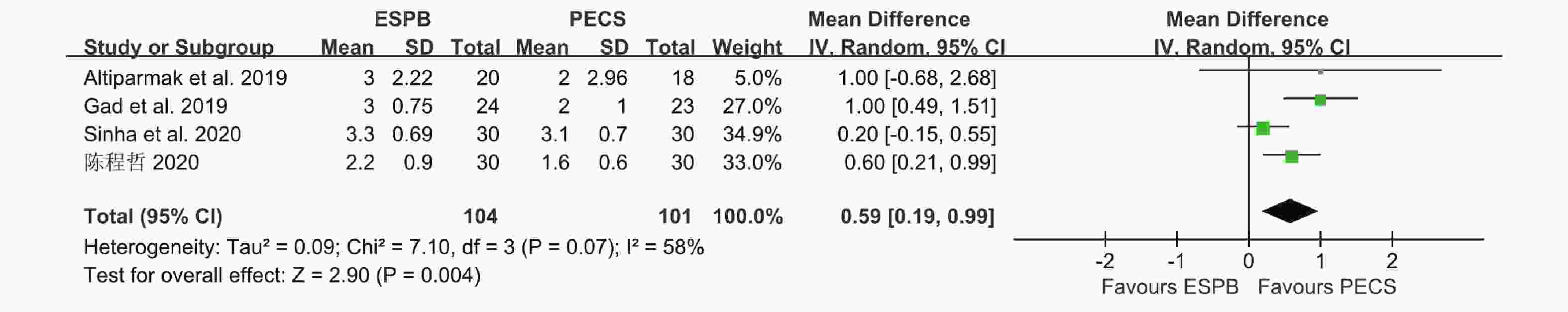
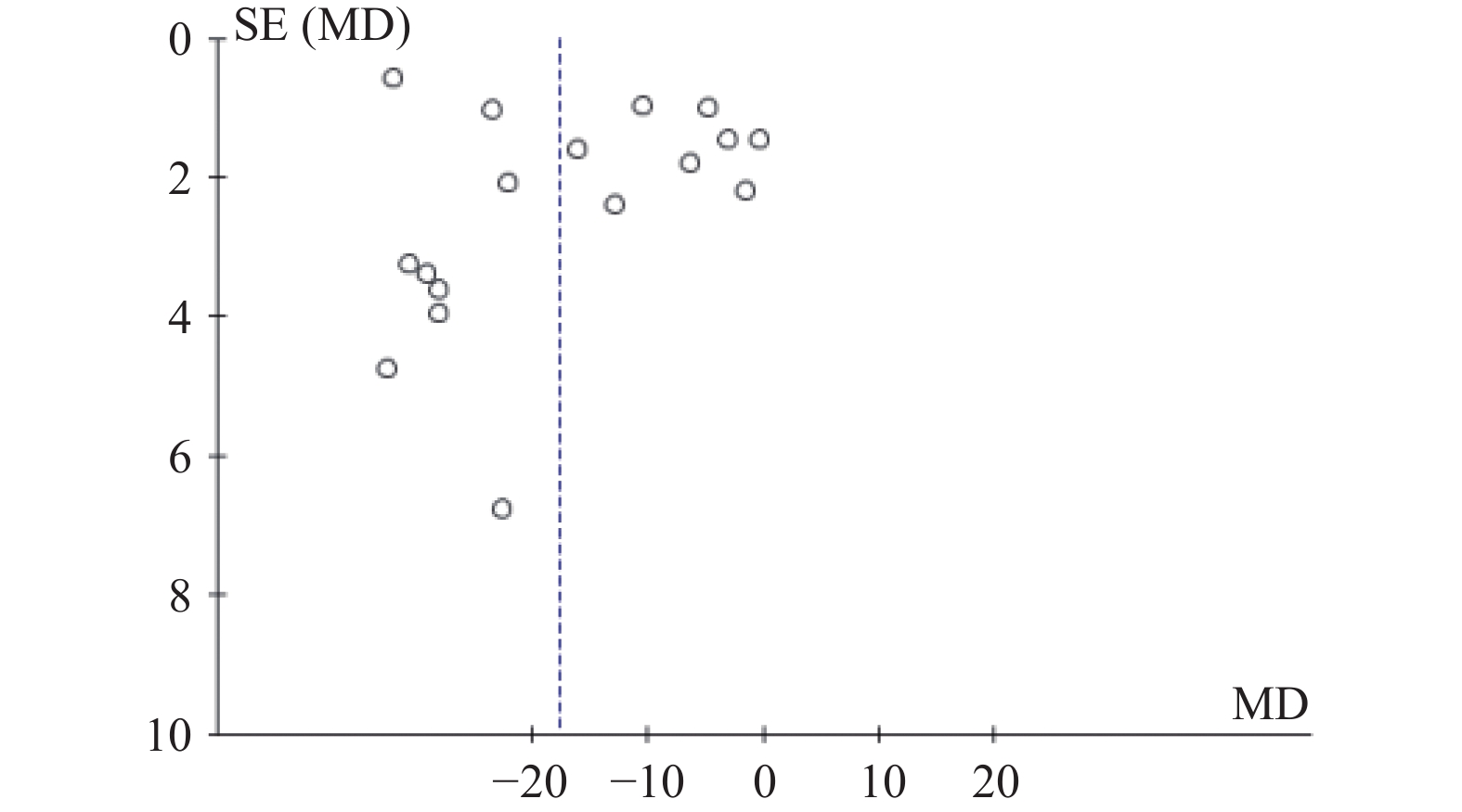
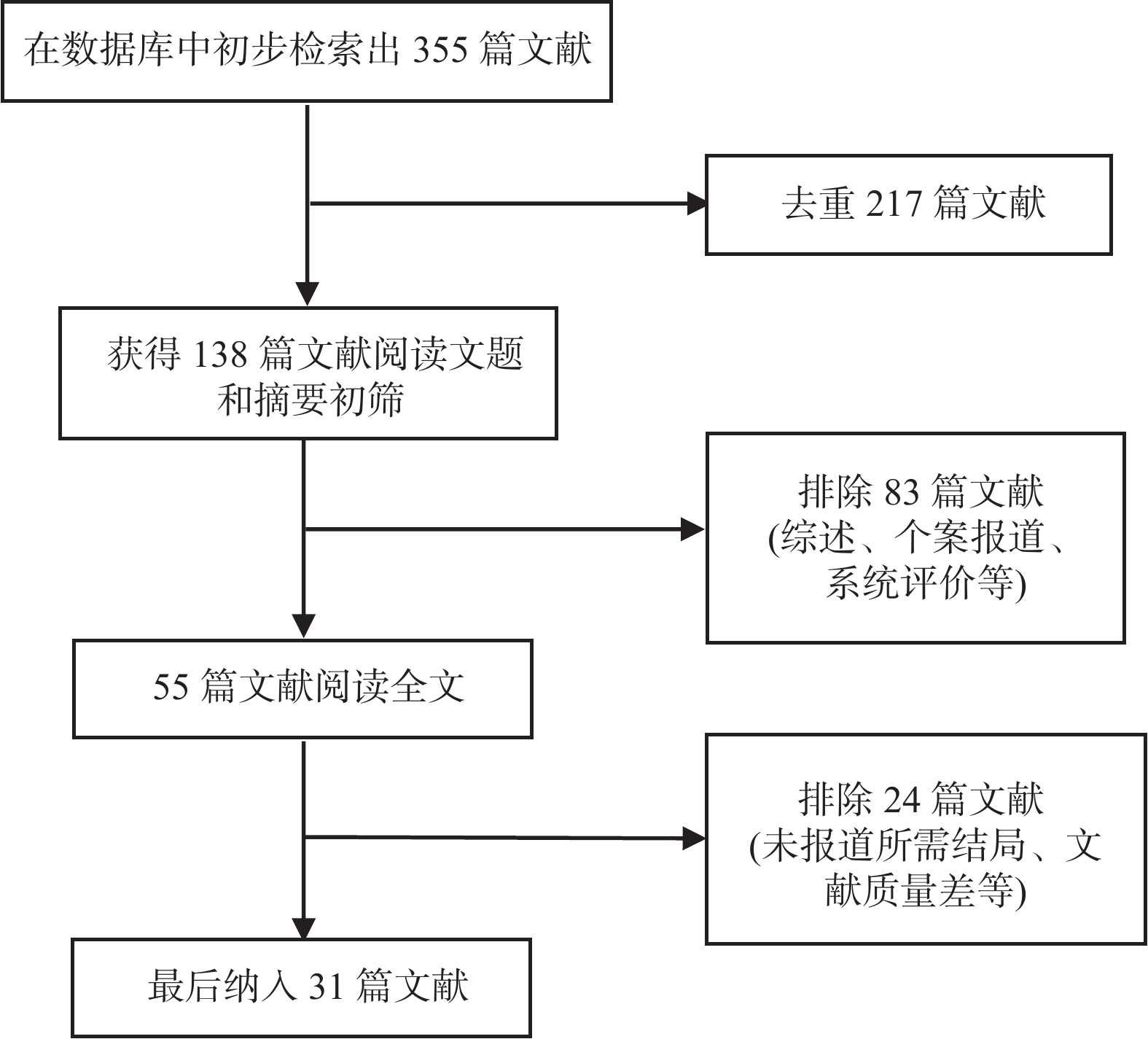
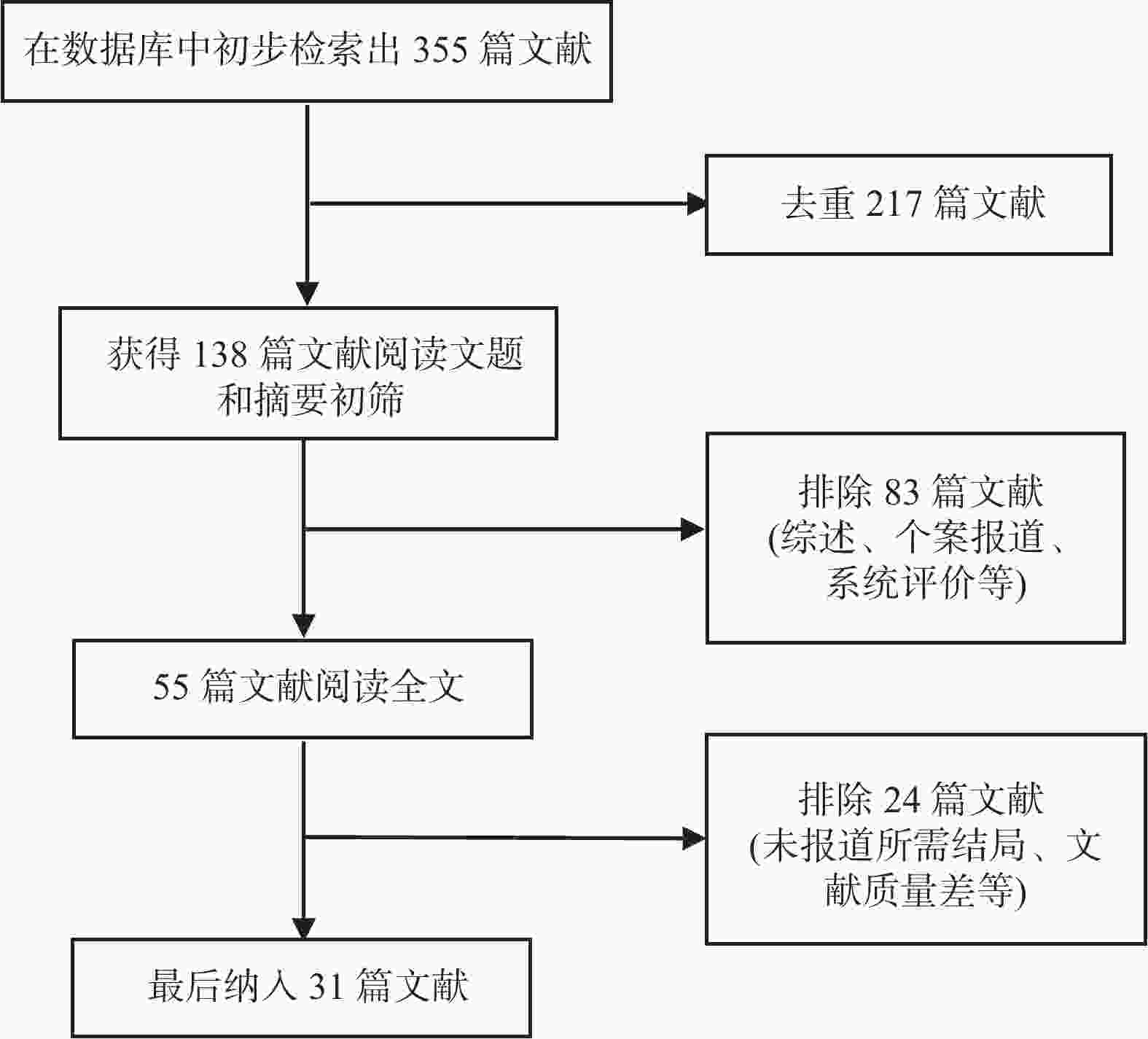
目的 分析竖脊肌平面阻滞(erector spinae plane block,ESPB)对乳腺癌患者术后镇痛药物消耗量、疼痛视觉模拟评分(visual analog scale,VAS)及术后恶心呕吐(postoperative nausea and vomiting,PONV)的影响,及其与单纯全身麻醉(general anesthesia,GA)、胸椎旁神经阻滞(thoracic paravertebral block,TPVB)、胸神经阻滞(pectoral nerves block,PECS)间的优劣,系统评价其临床应用。 方法 检索英文数据库Pubmed、Embase、Scopus、Cochrane library、Web of Science,中文数据库CNKI、万方、维普,纳入随机对照研究。使用Cochrane 偏倚评价工具进行偏倚风险评估,并使用RevMan 3.5软件进行Meta分析。 结果 共纳入31项随机对照研究, 2296 例患者。Meta分析结果显示ESPB组术后24 h吗啡消耗量低于GA组(MD -17.57,95%CI -23.99~-11.14,P < 0.05),术后2 h、6 h、12 h及24 h的VAS评分均低于GA组(P < 0.05),患者PONV的发生率降低(RR 0.57,95%CI 0.47~0.69,P < 0.05),差异均有统计学意义。ESPB组与TPVB组术后24 h吗啡消耗量无统计学意义,术后2 h、12 h及24 h时VAS比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),PONV的人数无统计学意义。PECS组术后24 h吗啡消耗低于ESPB组(MD 10.94,95%CI 4.40~17.48,P < 0.05),在术后12 h时,PECS组的VAS评分低于ESPB组(MD 0.59,95%CI 0.19~0.99,P < 0.05),差异有统计学意义,而其他时间点两组无统计学意义。结论 ESPB组术后镇痛效果优于GA组,与TPVB组相似,但差于PECS组。ESPB与GA组相比显著降低术后PONV发生率,与TPVB及PECS组相似。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the effects of erector spinae plane block (ESPB) on postoperative analgesic consumption, visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, and postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) in breast cancer patients, and to evaluate its advantages and disadvantages compared to general anesthesia (GA), thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB), and pectoral nerve block (PECS), providing a systematic review of its clinical application. Methods We searched English databases including PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science, as well as Chinese databases such as CNKI, Wanfang, and Weipu, including randomized controlled trials. The Cochrane bias risk assessment tool was used for bias risk evaluation, and RevMan 3.5 software was utilized for meta-analysis. Results A total of 31 randomized controlled trials involving 2296 patients were included. The meta-analysis results indicated that the morphine consumption in the ESPB group was lower than that in the GA group at 24 hours postoperative (MD -17.57, 95% CI -23.99 to -11.14, P < 0.05). VAS scores at 2, 6, 12, and 24 hours postoperative were also lower in the ESPB group compared to the GA group (P < 0.05), and the incidence of PONV in patients was reduced (RR 0.57, 95% CI 0.47 to 0.69, P < 0.05), with all differences being statistically significant. No statistically significant differences were found in morphine consumption at 24 hours postoperative between the ESPB and TPVB groups, nor in VAS scores at 2, 12, and 24 hours postoperative, and the number of PONV cases showed no statistically significant difference. The morphine consumption in the PECS group at 24 hours postoperative was lower than that in the ESPB group (MD 10.94, 95% CI 4.40 to 17.48, P < 0.05), and the VAS score at 12 hours postoperative in the PECS group was lower than that in the ESPB group (MD 0.59, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.99, P < 0.05), indicating statistical significance, while no significant differences were observed at other time points.Conclusions The analgesic effect of the ESPB group is superior to that of the GA group and similar to that of the TPVB group, but inferior to that of the PECS group. Compared to the GA group, ESPB significantly reduces the incidence of postoperative PONV, showing similarity with the TPVB and PECS groups. -
表 1 纳入研究的基本特征表
Table 1. The characteristics of the included studies
作者 年份 国家 总样
本量ESPB组
例数ESPB
平面阻滞药物 阻滞体位 干预对照组
例数GA组
例数结局
指标Abdella et al. 2022 Egypt 60 20 T4 0.25%布比卡因 俯卧位 高容量
ESPB:2020 ad Aksu et al. 2019 Turkey 50 25 T2、T4 0.25%布比卡因 俯卧位 25 abe Altıparmak et al. 2019 Turkey 38 20 T4 0.25%布比卡因 侧卧位 PECS:18 abcg Elewa et al. 2022 Egypt 90 30 T4 0.25%布比卡因 侧卧位 PVB:30 30 abefg El Ghamry et al. 2020 Egypt 70 35 T5 0.25%布比卡因 坐位 PVB:35 abcefg Gad et al. 2019 Egypt 47 24 T4 0.25%左旋布比卡因+
右美托咪定侧卧位 PECS:23 abcfg Genc et al. 2022 Turkey 90 30 T5 0.25%布比卡因 坐位 PSPB:30 30 abcef Gürkan et al. 2018 Turkey 50 25 T4 0.25%布比卡因 俯卧位 25 abe Gürkan et al. 2020 Turkey 75 25 T4 0.25%布比卡因 俯卧位 PVB:25 25 abe He et al. 2020 China 40 20 T3 0.5%罗哌卡因 未注明 20 abfg Moustafa et al. 2020 Egypt 102 51 T4 0.25%布比卡因 侧卧位 PVB:51 bf Seelam et al. 2020 India 100 50 T4 0.25%布比卡因 坐位 50 beg Sharma et al. 2020 India 60 30 T5 0.5%罗哌卡因 坐位 30 abefg Singh et al. 2020 India 40 20 T5 0. 5%布比卡因 坐位 20 abefg Sinha et al. 2020 India 60 30 T4 0.2%罗哌卡因 坐位 PECS:30 abdf Sivrikoz et al. 2022 Turkey 83 42 T4 0.375%布比卡因 未注明 PVB:41 abdef Swisher et al. 2020 USA 100 50 T3或T4 0.2%罗哌卡因+
肾上腺素坐位 PVB:50 abef Wiech et al. 2022 Poland 75 25 T4 0.375% 罗哌卡因 侧卧位 假ESP组:25 25 abf Yao et al. 2020 China 82 39 T4 0.5%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 假ESP组:40 abeg 周新等 2020 中国 60 30 T5 0.5%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 假ESP组:30 abeg 张春艳等 2018 中国 50 25 T5 0.5%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 25 abceg 李晓等 2020 中国 90 30 T3、T4、T5 0.25%布比卡因 侧卧位 PVB:30 30 abe 李有辉等 2019 中国 68 34 T5 0.33%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 34 abeg 王和节等 2019 中国 150 50 T5 0.375%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 SAPB:50 50 abcefg 纪久雨等 2020 中国 60 30 T4 0.375%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 PVB:30 aefg 谢永香等 2020 中国 90 30 T5 0.4%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 硬膜外:30 30 aefg 邓立平等 2020 中国 51 26 T5 0.5%罗哌卡因 未注明 25 abeg 闫志兵等 2019 中国 134 67 T5 0.5%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 67 bceg 陈程哲等 2020 中国 90 30 T5 0.25% 罗哌卡因 侧卧位 PECS:30 30 abcefg 马丽雅等 2022 中国 64 32 T5 0.375%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 PVB:32 abefg 魏鑫等 2020 中国 80 40 T6 0.5%罗哌卡因 侧卧位 PVB:40 acdeg A:术后VAS评分; b:术后镇痛药物消耗量;c:术中全麻药物消耗;d:阻滞范围;e:术后恶心呕吐发生率;f:术后补救镇痛;g:神经阻滞相关并发症 -
[1] Abdella A,Arida E,Megahed N A,et al. Analgesia and spread of erector spinae plane block in breast cancer surgeries: A randomized controlled trial[J]. BMC Anesthesiol,2022,22(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01860-w [2] Aksu C,Kus A,Yorukoglu H U,et al. Analgesic effect of the bi-level injection erector spinae plane block after breast surgery: A randomized controlled trial[J]. The Journal of the Turkish Society of Algology,2019,31(3):132-137. [3] Altiparmak B,Korkmaz Toker M,Uysal A I,et al. Comparison of the effects of modified pectoral nerve block and erector spinae plane block on postoperative opioid consumption and pain scores of patients after radical mastectomy surgery: A prospective,randomized,controlled trial[J]. J Clin Anesth,2019,54:61-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2018.10.040 [4] El Ghamry M R,Amer A F. Role of erector spinae plane block versus paravertebral block in pain control after modified radical mastectomy. A prospective randomised trial[J]. Indian J Anaesth,2019,63(12):1008-1014. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_310_19 [5] Elewa A M,Faisal M,Sjöberg F,et al. Comparison between erector spinae plane block and paravertebral block regarding postoperative analgesic consumption following breast surgery: A randomized controlled study[J]. BMC Anesthesiol,2022,22(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01724-3 [6] Gad M,Abdelwahab K,Abdallah A,et al. Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block compared to modified pectoral plane block for modified radical mastectomy operations[J]. Anesth Essays Res,2019,13(2):334-339. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_77_19 [7] Genc C,Kaya C,Bilgin S,et al. Pectoserratus plane block versus erector spinae plane block for postoperative opioid consumption and acute and chronic pain after breast cancer surgery: A randomized controlled trial[J]. J Clin Anesth,2022,79:110691. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2022.110691 [8] Gurkan Y,Aksu C,Kus A,et al. Erector spinae plane block and thoracic paravertebral block for breast surgery compared to IV-morphine: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia,2020,59:84-88. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2019.06.036 [9] Gurkan Y,Aksu C,Kus A,et al. Ultrasound guided erector spinae plane block reduces postoperative opioid consumption following breast surgery: A randomized controlled study[J]. J Clin Anesth,2018,50:65-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2018.06.033 [10] He W S,Wu Z Y,Zu L J,et al. Application of erector spinae plane block guided by ultrasound for postoperative analgesia in breast cancer surgery: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Cancer Commun,2020,40(2-3):122-125. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12013 [11] Moustafa M A,Alabd A S,Ahmed A M M,et al. Erector spinae versus paravertebral plane blocks in modified radical mastectomy: Randomised comparative study of the technique success rate among novice anaesthesiologists[J]. Indian J Anaesth,2020,64(1):49-54. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_536_19 [12] Seelam S,Nair A S,Christopher A,et al. Efficacy of single-shot ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia after mastectomy: A randomized controlled study[J]. Saudi J Anaesth,2020,14(1):22-27. doi: 10.4103/sja.SJA_260_19 [13] Sharma S,Arora S,Jafra A,et al. Efficacy of erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia in total mastectomy and axillary clearance: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Saudi J Anaesth,2020,14(2):186-191. doi: 10.4103/sja.SJA_625_19 [14] Singh S,Kumar G,Akhileshwar. Ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block for postoperative analgesia in modified radical mastectomy: A randomised control study[J]. Indian J Anaesth,2019,63(3):200-204. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_758_18 [15] Sinha C,Kumar A,Kumar A,et al. Pectoral nerve versus erector spinae block for breast surgeries: A randomised controlled trial[J]. Indian J Anaesth,2019,63(8):617-622. doi: 10.4103/ija.IJA_163_19 [16] Sivrikoz N,Turhan Ö,Ali A,et al. Paravertebral block versus erector spinae plane block for analgesia in modified radical mastectomy: A randomized,prospective,double-blind study[J]. Minerva Anestesiologica,2022,88(12):1003-1012. [17] Swisher M W,Wallace A M,Sztain J F,et al. Erector spinae plane versus paravertebral nerve blocks for postoperative analgesia after breast surgery: A randomized clinical trial[J]. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine,2020,45(4):260-266. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-101013 [18] Wiech M,Piwowarczyk P,Mieszkowski M,et al. The quality of recovery after erector spinae plane block in patients undergoing breast surgery: A randomized controlled trial[J]. BMC Anesthesiol,2022,22(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01760-z [19] Yao Y,Li H,He Q,et al. Efficacy of ultrasound-guided erector spinae plane block on postoperative quality of recovery and analgesia after modified radical mastectomy: Randomized controlled trial[J]. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine,2020,45:5-9. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2019-100983 [20] 陈程哲,李会芳,任益锋,等. 超声引导下胸神经阻滞和竖脊肌平面阻滞用于乳腺癌改良根治术后镇痛效果的比较[J]. 医学研究杂志,2020,49(4):108-112. [21] 邓立平,李长红,林少锋. 超声引导竖脊肌平面阻滞对乳腺肿物切除术后镇痛作用效果的研究[J]. 中国实用医药,2020,15(20):24-26. [22] 纪久雨,鲁学文,刘月江. 超声引导下竖脊肌平面阻滞和胸椎旁阻滞对行乳腺癌根治术患者术后恢复的影响[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版),2020,39(4):440-444. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6264.2020.04.007 [23] 李晓,唐栋梁,王洁,等. 超声引导竖脊肌间隙阻滞与胸椎椎旁神经阻滞治疗乳腺癌术后急性疼痛疗效观察[J]. 介入放射学杂志,2020,29(8):777-781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-794X.2020.08.008 [24] 李有辉,项余华,曹志得,等. 超声引导下竖脊肌平面阻滞对乳腺癌根治术后镇痛疗效评价[J]. 浙江临床医学,2019,21(3):398-400. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-7664.2019.03.044 [25] 马丽雅,原大江,赵丽,等. 超声引导下竖脊肌平面阻滞与胸椎旁神经阻滞用于乳腺癌根治术术后镇痛效果的比较[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2022,22(4):761-765. [26] 王和节,刘煜,戈文威,等. 超声引导下前锯肌平面和竖脊肌平面阻滞在乳腺癌根治术围术期应用的比较[J]. 中华医学杂志,2019,99(23):1809-1813. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2019.23.012 [27] 魏鑫,杨凯,高晓秋,等. 竖脊肌平面阻滞与胸椎旁神经阻滞用于乳腺癌根治术围术期镇痛效果的比较[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2020,36(9):871-875. doi: 10.12089/jca.2020.09.008 [28] 谢永香,刘妙惠,倪洪湖. 超声引导下竖脊肌平面阻滞联合自控静脉镇痛用于乳腺癌根治术后镇痛的研究[J]. 中国现代医药杂志,2020,22(8):37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9463.2020.08.008 [29] 闫志兵,许立新. 超声引导下竖脊肌平面阻滞在乳腺癌术后镇痛中的应用[J]. 广州医科大学学报,2019,47(4):69-71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-9664.2019.04.19 [30] 张春艳,李宁. 超声引导下竖脊肌平面阻滞对乳腺癌改良根治术患者术后疼痛的影响[J]. 中国实用医刊,2018,45(5):50-53. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-4756.2018.05.017 [31] 周新,胡胜红,王胜斌,等. 超声引导下单次竖脊肌平面阻滞对单侧乳腺癌根治术后患者恢复的影响[J]. 癌症进展,2020,18(5):479-481,488. [32] Woodworth G E,Ivie R M J,Nelson S M,et al. Perioperative breast analgesia: a qualitative review of anatomy and regional techniques[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med,2017,42(5):609-631. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000641 [33] Forero M,Adhikary S D,Lopez H,et al. The erector spinae plane block: a novel analgesic technique in thoracic neuropathic pain[J]. Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine,2016,41(5):621-627. doi: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000451 [34] Leong R W,Tan E S J,Wong S N,et al. Efficacy of erector spinae plane block for analgesia in breast surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Anaesthesia,2021,76(3):404-413. doi: 10.1111/anae.15164 [35] Hussain N,Brull R,Noble J,et al. Statistically significant but clinically unimportant: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the analgesic benefits of erector spinae plane block following breast cancer surgery[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med,2021,46(1):3-12. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2020-101917 [36] Altiparmak B,Korkmaz Toker M,Uysal A I,et al. Comparison of the efficacy of erector spinae plane block performed with different concentrations of bupivacaine on postoperative analgesia after mastectomy surgery: ramdomized,prospective,double blinded trial[J]. BMC Anesthesiol,2019,19(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0700-3 [37] Adhikary S D, Bernard S, Lopez H, et al. Erector spinae plane block versus retrolaminar block: A magnetic resonance imaging and anatomical study[J]. Reg Anesth Pain Med,2018,43(7):756-762. [38] ElHawary H, Abdelhamid K, Meng F Y, et al. Erector spinae plane block decreases pain and opioid consumption in breast surgery: Systematic review[J]. Prs-Glob Open,2019,7(11):8. -





 下载:
下载: