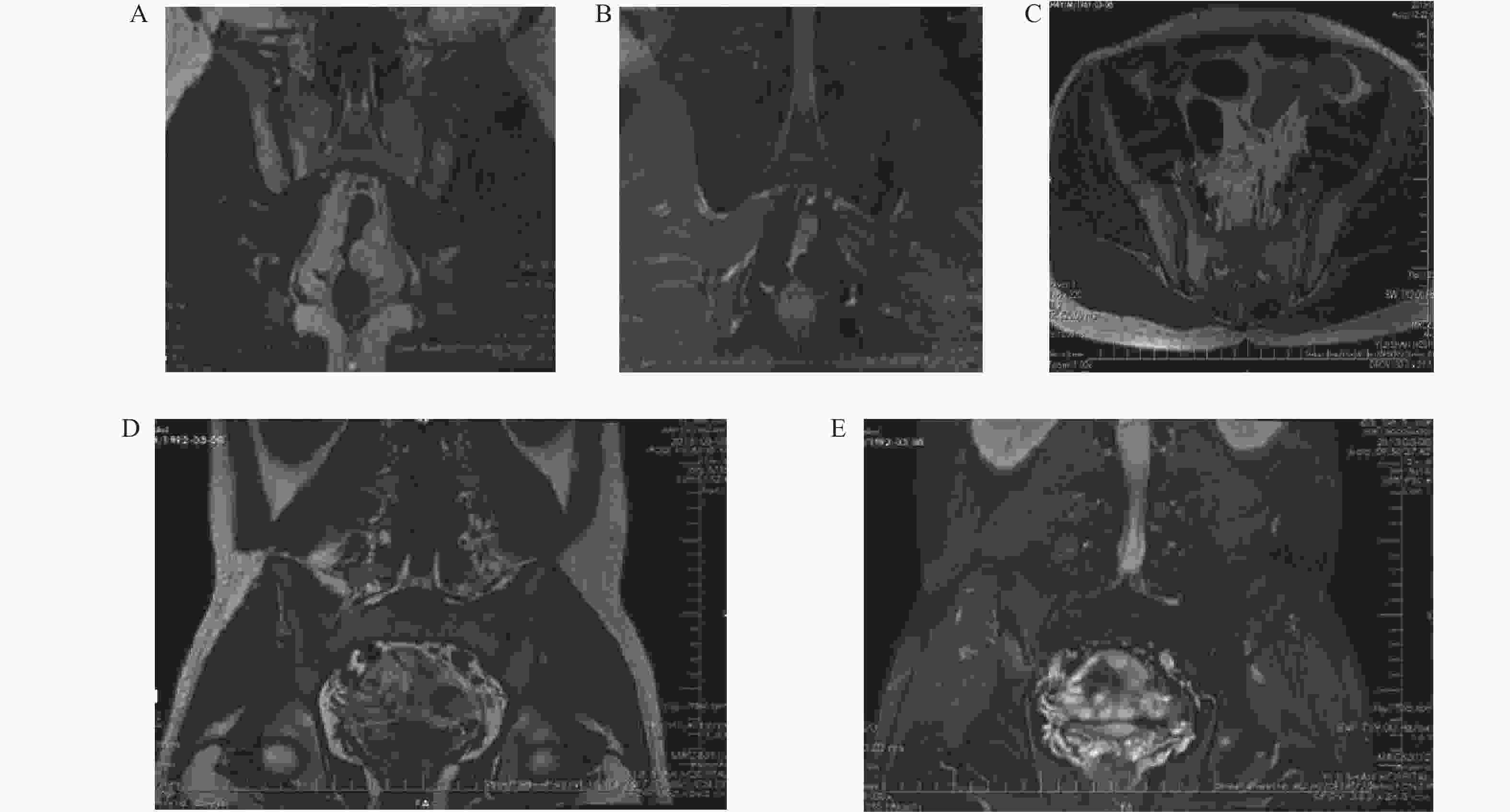
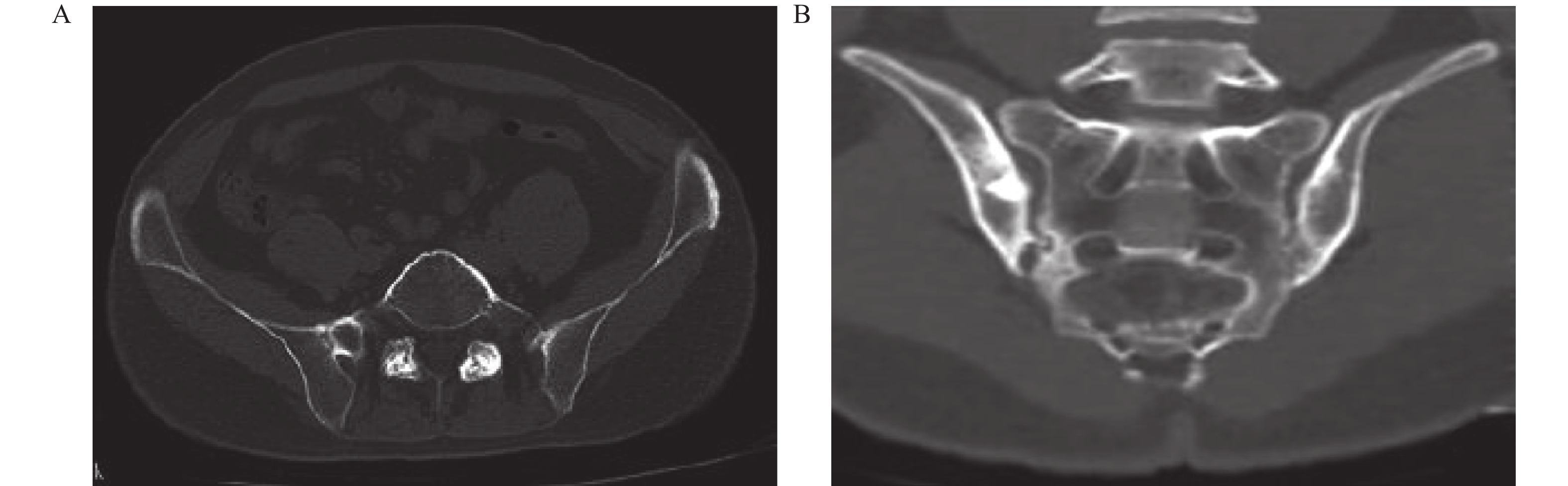
Clinical Diagnostic Value of CT Combined with MR in Grading Sacroiliac Joint Lesions in Ankylosing Spondylitis
-
摘要:
目的 探讨CT联合MRI(以下简称联合诊断)诊断强直性脊柱炎(ankylosing spondylitis,AS)骶髂关节病变的价值。 方法 回顾性选择2021年1月至2023年7月间海南省海口市第三人民医院收治的102例AS骶髂关节病变患者的CT、MRI检查资料,比较CT、MRI、联合诊断对AS骶髂关节病变分级以及各种征象检出率。 结果 MRI对Ⅰ~Ⅱ级AS骶髂关节病变检出率、骨髓水肿、肌腱韧带附着点炎症、关节面下软骨破坏、滑膜增厚、关节面下脂肪沉积检出率高于CT(P < 0.05),相较于MR,CT在检出关节面硬化、关节面骨下侵蚀/破坏以及关节面增生方面具有更高的准确率(P < 0.05)。联合诊断对AS骶髂关节病变分级、AS骶髂关节病变征象检出率均高于单独MRI和CT诊断(P < 0.05)。 结论 MRI对AS早期骶髂关节病变具有较高检出率,CT对关节面增生、硬化、侵蚀和破坏具有较高敏感性,联合诊断效能优于单独MRI和CT。 Abstract:Objective To explore the value of CT combined with MRI (hereinafter referred to as combined diagnosis) in diagnosing sacroiliac joint lesions in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Methods A retrospective study selected CT and MRI examination data from 102 AS patients with sacroiliac joint lesions admitted to the Third People's Hospital of Haikou, Hainan Province between January 2021 and July 2023. The study compared the grading and detection rates of various signs using CT, MRI, and combined diagnosis. Results MRI showed higher detection rates for AS sacroiliac joint lesions in grades I-II, bone marrow edema, tendon and ligament attachment point inflammation, subchondral cartilage destruction, synovial thickening, and subchondral fat deposition compared to CT (P < 0.05). In contrast, CT demonstrated higher accuracy in detecting joint surface sclerosis, subchondral bone erosion/destruction, and joint surface hyperplasia compared to MRI (P < 0.05). Combined diagnosis showed significantly higher grading and detection rates of AS sacroiliac joint lesion signs compared to MRI or CT alone (P < 0.05). Conclusion MRI has high detection rates for early AS sacroiliac joint lesions, CT exhibits high sensitivity for joint surface hyperplasia, sclerosis, erosion, and destruction, and combined diagnosis demonstrates superior efficacy compared to MRI or CT individually. -
Key words:
- CT /
- Magnetic resonance imaging /
- Ankylosing spondylitis /
- Sacroiliac joint lesions /
- Bone marrow edema
-
表 1 CT、MRI、联合诊断对AS骶髂关节病变分级检出率比较 [n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of detection rates for AS sacroiliac joint lesions by CT,MRI,and combined diagnosis [n(%)]
组别 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 CT 11(10.78) 15(14.71) 22(21.57) 6(5.88) MRI 19(18.63) 31(29.25) 22(20.75) 6(5.66) CT+MRI 23(22.55)a 35(34.31)a 27(26.47) 8(7.84) 三种方法
比较χ25.112 11.283 0.917 0.428 三种方法
比较P0.078 0.004b 0.632 0.807 联合诊断与CT单独诊断比较,aP < 0.05;三种方法比较,bP < 0.05。 表 2 CT、MRI、联合诊断对AS骶髂关节病变分级指标比较
Table 2. Comparison of grading indicators for sacroiliac joint lesions in ankylosing spondylitis using CT,MRI,and combined diagnosis
组别 Ⅰ级 Ⅱ级 Ⅲ级 Ⅳ级 CT组AUC值 0.712 0.692 0.893 0.833 MRI组AUC值 0.865 0.897 0.893 0.833 CT+MRI组AUC值 0.942 0.949 0.982 0.944 CT组敏感度 0.423 0.385 0.795 0.667 MRI 组敏感度 0.731 0.795 0.786 0.668 CT+MRI 组敏感度 0.885 0.874 0.964 0.889 CT组特异度 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 MRI组特异度 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 CT+MRI组特异度 1.000 1.000 1.000 1.000 CT组Kappa值 0.522 0.436 0.785 0.785 MRI组Kappa值 0.802 0.827 0.842 0.785 CT+MRI组Kappa值 0.920 0.915 0.975 0.936 表 3 CT、MRI、联合诊断对AS骶髂关节病变征象检出率比较[n(%)]
Table 3. Comparison of detection rates for AS sacroiliac joint lesions by CT,MRI,and combined diagnosis [n(%)]
组别 关节面下软骨破坏 肌腱韧带附着点炎 骨髓水肿 滑膜增厚 脂肪沉积 关节面增生硬化 关节面骨下侵蚀/破坏 CT 6(5.88)a 5(4.90)ab 3(2.94)ab 6(5.88)ab 9(8.82)ab 29(28.43)ae 35(34.31)ae MRI 15(14.71)f 29(28.43)f 15(14.71)f 27(26.47)f 26(25.49)f 10(9.80)c 12(11.76)c CT+MRI 19(18.63) 39(38.24) 21(20.59) 38(37.25) 35(34.31) 42(41.18) 45(44.12) 三种方法
比较χ27.650 32.959 14.811 29.807 19.375 29.377 26.702 三种方法
比较P0.022d < 0.001d 0.001d < 0.001d < 0.001d < 0.001d < 0.001d CT单独诊断与MRI单独诊断比较,aP < 0.05;联合诊断与CT单独诊断比较,bP < 0.05;联合诊断与MRI单独诊断比较,cP < 0.05;三种方法比较,dP < 0.05;联合诊断与CT单独诊断比较,eP > 0.05;联合诊断与MRI单独诊断比较,fP > 0.05。 -
[1] 郭洪録, 郭晓利, 李力毅, 等. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸对强直性脊柱炎大鼠Th1/Th2免疫平衡, 软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2020, 55(5): 676-681. [2] 余晴, 陈悦宁, 刘宏潇. 中国强直性脊柱炎人群工作能力现状及影响因素分析[J]. 海军军医大学学报, 2025, 46(4): 488-496. [3] Xu J, Deng Y, Yu C Y, et al. Efficacy of wIRA in the treatment of sacroiliitis in male patients with ankylosing spondylitis and its effect on serum VEGF levels[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2019, 14(1): 313. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1322-7 [4] 郑顺科, 张和平, 林炜盛. X线及CT诊断对强直性脊柱炎的诊断效果和影像学特点[J]. 智慧健康, 2022, 8(26): 18-21+40. [5] 陈慧鸽. X线、CT与MRI联合诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的价值[J]. 河南医学研究, 2020, 29(14): 2647-2649. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2020.14.074 [6] 赖苑威, 罗宏杰, 许军, 等. 青壮年活动性骶髂关节强直性脊柱炎CT与MRI表现及与炎性因子水平相关性研究[J]. 颈腰痛杂志, 2022, 43(6): 810-814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7234.2022.06.008 [7] 王邦彦, 王久存, 文少卿. 古代强直性脊柱炎的诊断标准及国内研究回顾[J]. 人类学学报, 2023, 42(3): 422-434. [8] 卢玉洁. 基于CT分级的强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变证素分布特点研究[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2023. [9] 薛三宝. MRI诊断强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的影像学价值[J]. 医学信息, 2022, 35(22): 142-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2022.22.034 [10] Korotaeva T, Dina O, Holdsworth E, et al. Investigating diagnosis, treatment, and burden of disease in patients with ankylosing spondylitis in Central Eastern Europe and the United States: A real-world study[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2021, 40(12): 4915-4926. [11] Lee Y H. Comparative efficacy and safety of Janus kinase inhibitors and secukinumab in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Pharmacology, 2022, 107(11-12): 537-544. doi: 10.1159/000525627 [12] Svedbom A, Dal é n J, Ivergård M, et al. The value of persistence in treatment with subcutaneous TNF-alpha inhibitors for ankylosing spondylitis[J]. Eur J Health Econ, 2020, 21(1): 45-54. doi: 10.1007/s10198-019-01110-w [13] 展晓梅. MRI、CT、X线联合诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的价值分析[J]. 中国社区医师, 2023, 39(30): 107-109. [14] 赵晓飞. X线、CT及MRI检查诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的价值研究[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2022, 6(18): 176-178. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3807.2022.18.060 [15] 宋炜, 徐晓军. MRI与CT检查对强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变的诊断价值比较[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2023, 8(24): 122-125. [16] 岳昌明, 雷文亭, 黄依莲. CT与MRI在诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变中的临床意义[J]. 河南医学研究, 2022, 31(16): 3040-3043. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2022.16.045 [17] 王琴. 早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变应用X线、CT和MRI的诊断价值[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2022, 6(7): 134-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-3807.2022.07.045 [18] 王国庆. MRI脂肪抑制技术STIR序列应用于强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节检测的价值[J]. 黑龙江医学, 2024, 48(22): 2735-2737. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2024.22.014 [19] 李筱倩, 朱建忠, 赵鲁平, 等. 磁共振DWI联合DCE序列诊断早期强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节改变[J]. 放射学实践, 2015, 30(6): 679-682. [20] 李成, 王妮, 王喆, 等. 骶髂关节融合断层显像(SPECT/CT)在强直性脊柱炎骶髂关节病变分期中的价值及临床观察[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2017, 27(12): 2365-2367. -





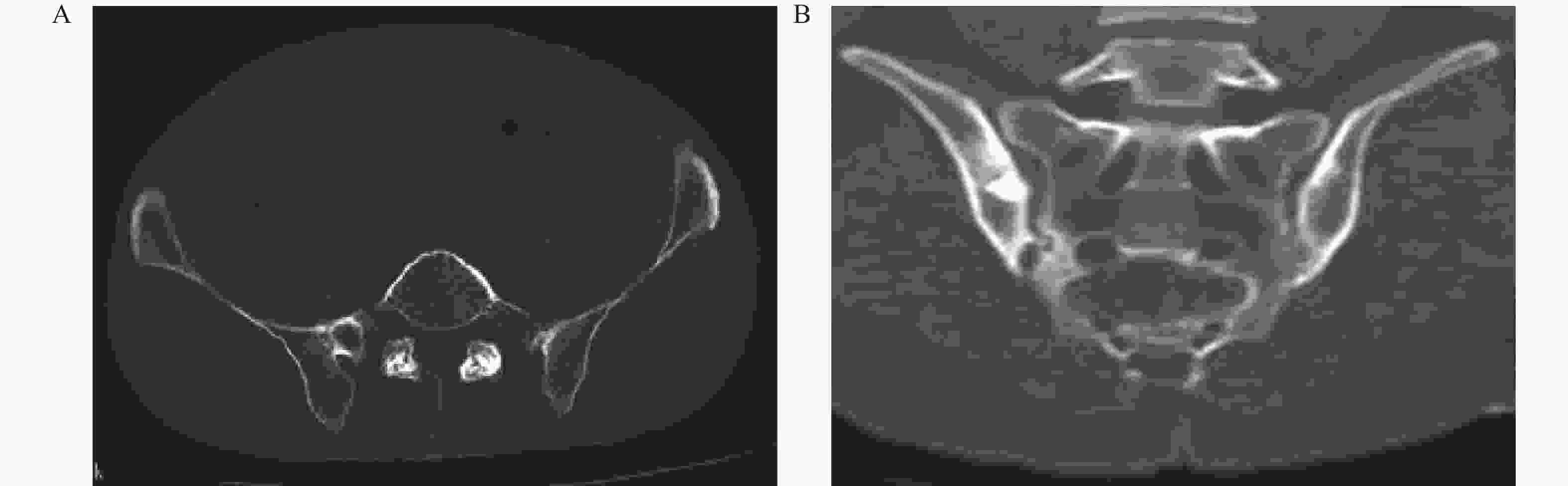
 下载:
下载: