Effect of rhTGF-β1 on Osteoclast Formation via the BMP2/Smad1 Pathway in Rats during Orthodontic Tooth Movement
-
摘要:
目的 基于大鼠骨形态发生蛋白2(bone morphogenetic protein2,BMP2)/ Smad家族成员1(smad family member 1,Smad1)通路,探究重组人转化生长因子-β1(recombinant human transforming growth factor-β1,rhTGF-β1)对正畸牙移动(orthodontic tooth movement,OMT)大鼠破骨细胞形成的影响。 方法 将40只雄性SD大鼠随机分为5组(n = 8/组):对照组(Con)、OTM模型组(Model)、BMP2抑制剂组(Noggin)、rhTGF-β1治疗组(rhTGF-β1)、rhTGF-β1+Noggin组。构建大鼠OTM模型,采用显微CT(Micro-CT)分析测定OTM的距离;通过抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶(tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase,TRAP)染色评估压力侧破骨细胞活性;苏木精-伊红(hematoxylin and eosin,HE)染色评估压力侧组织形态学特征,免疫组化(immunohistochemistry,IHC)染色和蛋白质印迹(Western blot)测定相关蛋白表达水平。 结果 与正常组相比,Model组大鼠OTM距离增加(P < 0.01),牙周间隙明显变窄并出现吸收陷窝,压力侧的基质金属蛋白酶-9(matrix metalloproteinases-9,MMP-9)、核因子κB受体活化因子配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand,RANKL)增加(P < 0.01)、骨保护素 (osteoprotegerin,OPG)表达降低(P < 0.01),BMP2/Smad1信号通路被激活(P < 0.01)。经BMP2抑制剂Noggin处理后,与Model组相比,BMP2、p-Smad1表达显著降低(P < 0.01),OTM距离显著降低(P < 0.01),且压力侧的TRAP、MMP-9及RANKL表达均显著降低(P < 0.01),OPG升高(P < 0.01)。经rhTGF-β1处理的大鼠中,较Model组OTM距离显著增加(P < 0.01),TRAP阳性多核细胞数量升高(P < 0.01),压力侧的MMP-9及RANKL表达均显著升高(P < 0.05)、OPG表达显著降低(P < 0.01),且BMP2、p-Smad1表达上调(P < 0.01)。此外,rhTGF-β1+Noggin组部分逆转了rhTGF-β1组大鼠的破骨细胞数量的增加效应(P < 0.01)。 结论 正畸力可促进破骨细胞形成,且rhTGF-β1可通过BMP2/Smad1信号通路增强OTM过程中破骨细胞的形成。 -
关键词:
- rhTGF-β1 /
- BMP2/Smad1通路 /
- 正畸牙移动 /
- 破骨细胞
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of recombinant human transforming growth factor-β1 (rhTGF-β1) on osteoclast formation during orthodontic tooth movement (OTM) in rats, based on the bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2)/smad family member 1(Smad1) pathway. Methods 40 male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly assigned to 5 groups (n = 8 per group): Control group (Con), OTM model group (Model) , BMP2 inhibitor group (Noggin) , rhTGF-β1 treatment group (rhTGF-β1), and rhTGF-β1 + Noggin group. The rat OTM model was established, and the distance of OTM was measured using micro-computed tomography (Micro-CT) analysis. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining was performed to assess osteoclast activity on the pressure side. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was used to evaluate histomorphological characteristics on the pressure side. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot analysis were conducted to determine the protein expression levels of related markers. Results Compared with the normal group, the OTM distance was increased in the Model group (P < 0.01), the periodontal ligament space was significantly narrowed with the presence of resorption lacunae, the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand (RANKL) on the pressure side was increased (P < 0.01), the expression of osteoprotegerin (OPG) was decreased (P < 0.01), and the BMP2/Smad1 signaling pathway was activated (P < 0.01). The differences were statistically significant (P < 0.01). After Noggin treatment to inhibit BMP2, compared with the Model group, the expression of BMP2 and p-Smad1 was significantly decreased (P < 0.01), the OTM distance was significantly reduced (P < 0.01), and the expression of TRAP, MMP-9, and RANKL on the pressure side was significantly decreased while OPG was increased (P < 0.01). In rats treated with rhTGF-β1, compared with the Model group, the OTM distance was significantly increased (P < 0.01), the number of TRAP-positive multinucleated cells was higher (P < 0.01), the expression of MMP-9, and RANKL on the pressure side was significantly increased (P < 0.01), OPG expression was significantly decreased (P < 0.01), and the expression of BMP2 and p-Smad1 was up-regulated (P < 0.01). Furthermore, the rhTGF-β1 + Noggin group partially reversed the increase in osteoclast number induced by rhTGF-β1 alone (P < 0.01). Conclusion Orthodontic force can promote osteoclast formation, and rhTGF-β1 can increase osteoclast formation during OTM via the BMP2/Smad1 signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- rhTGF-β1 /
- BMP2/Smad1 pathway /
- orthodontic tooth movement /
- osteoclast
-
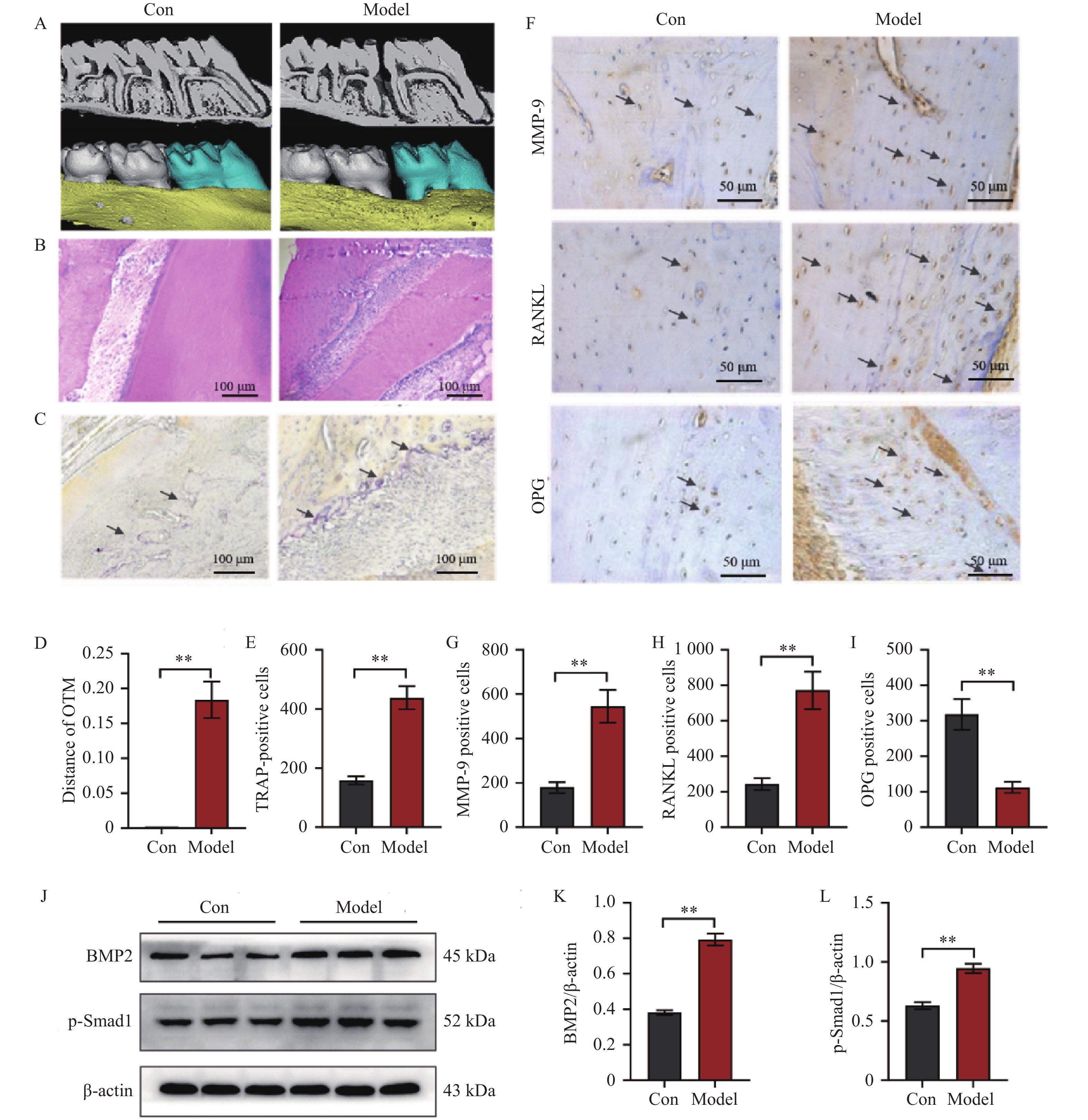
图 1 BMP2/Smad1信号通路在OTM过程中被激活并促进破骨细胞形成($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 8)
A:上颌磨牙的显微CT视图;B:上颌第一磨牙压力侧HE染色结果;C:上颌第一磨牙压力侧TRAP染色结果图;D:正畸牙移动距离;E:上颌第一磨牙压力侧TRAP染色定量分析结果;F~I:上颌第一磨牙压力侧MMP-9、RANKL和OPG免疫组化染色结果图与定量分析结果;J~L:Western blot结果图与定量分析结果。Model组与Con组比较,**P < 0.01。
Figure 1. BMP2/Smad1 signaling pathway is activated and promotes osteoclast formation during OTM($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 8)
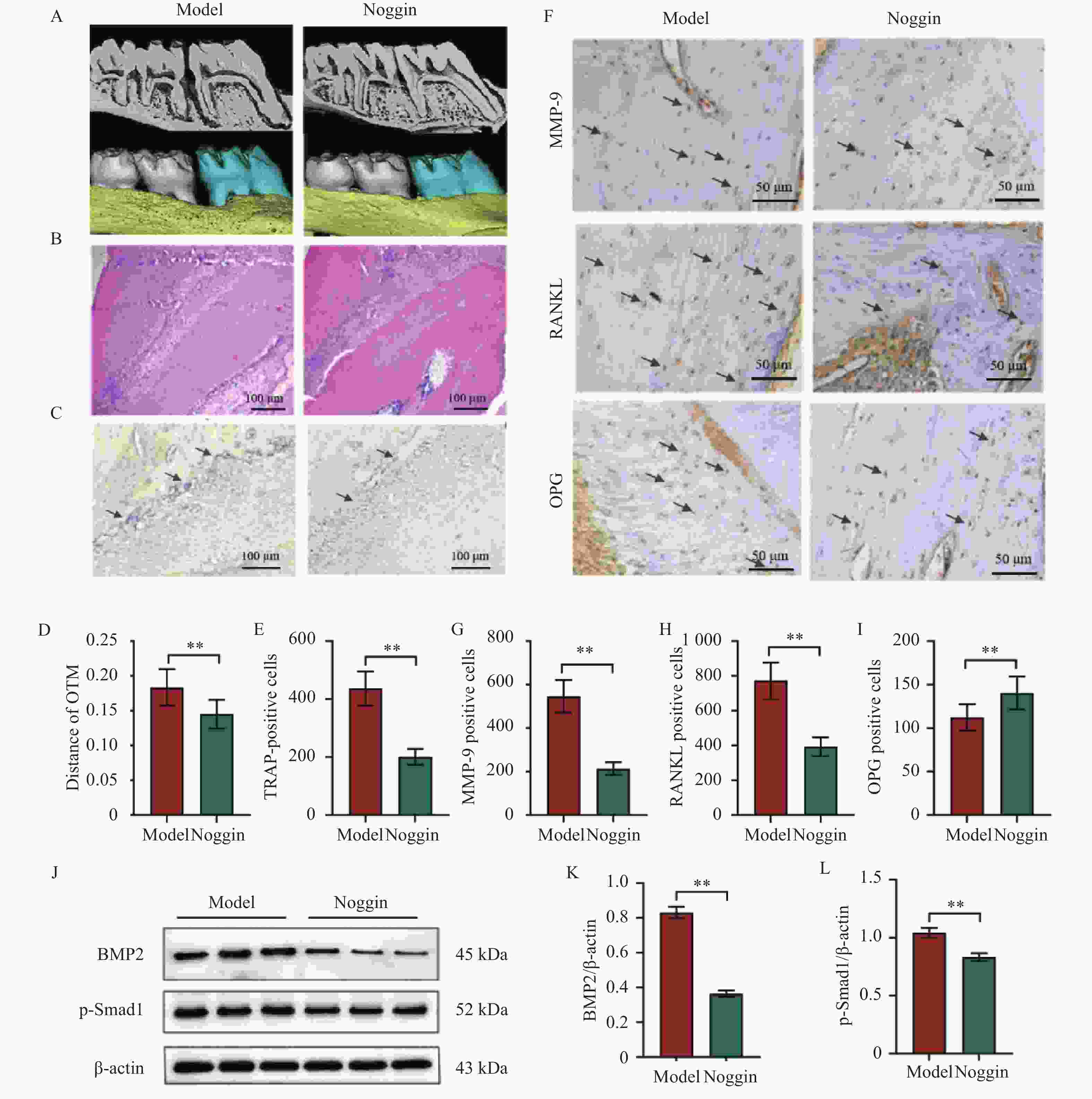
图 2 抑制BMP2/Smad1通路可减少破骨细胞的形成($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 8)
A:上颌磨牙的显微CT视图;B:上颌第一磨牙压力侧HE染色结果;C:上颌第一磨牙压力侧TRAP染色结果图;D:正畸牙移动距离;E:上颌第一磨牙压力侧TRAP染色定量分析结果;F~I:上颌第一磨牙压力侧MMP-9、RANKL和OPG免疫组化染色结果图与定量分析结果;J~L:Western blot结果图与定量分析结果。Noggin组与Model组比较,**P < 0.01。
Figure 2. Inhibition of the BMP2/Smad1 pathway reduces osteoclast formation($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 8)
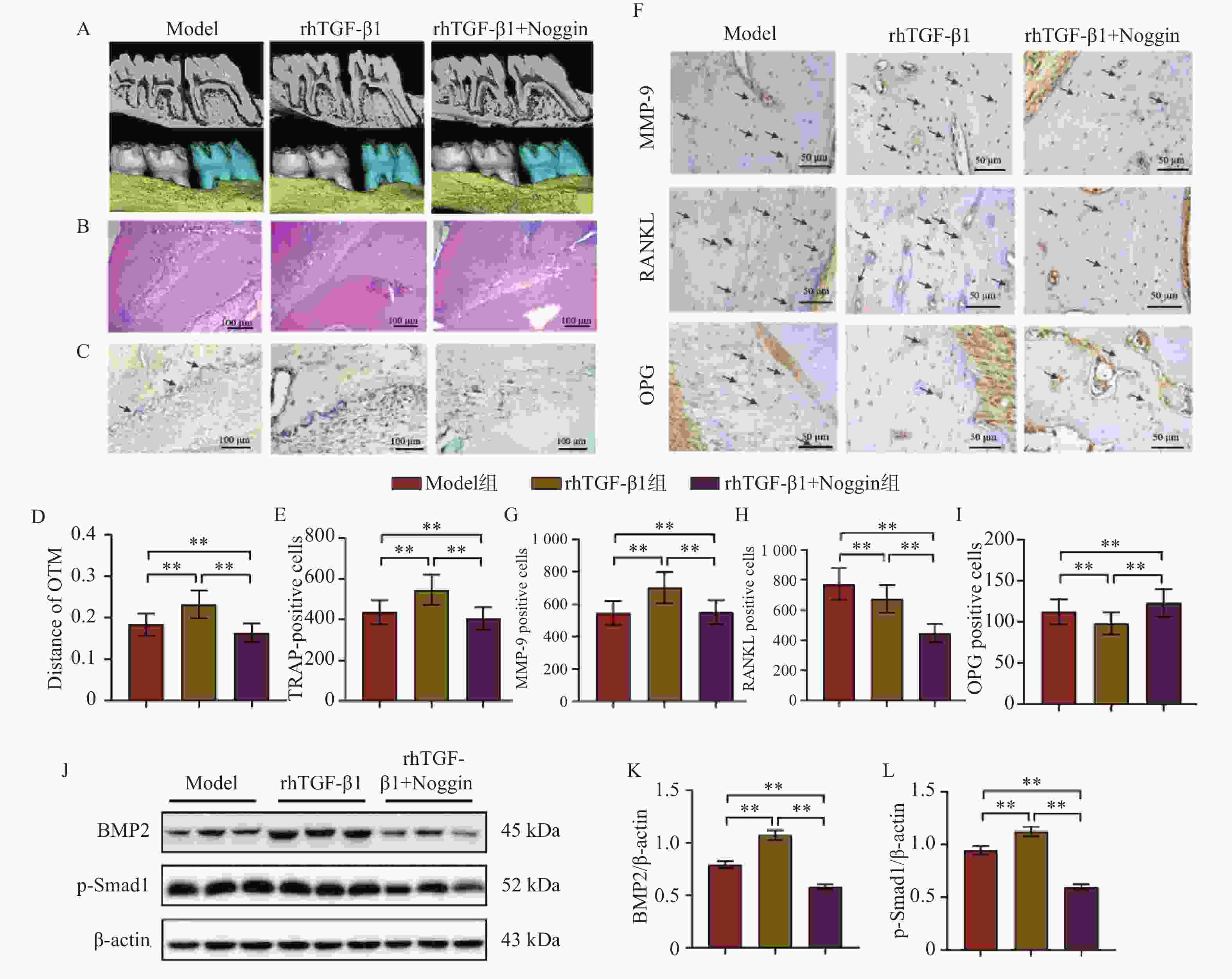
图 3 rhTGF-β1通过BMP2/Smad1信号通路促进OTM过程中的破骨细胞形成($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 8)
A:上颌磨牙的显微CT视图;B:上颌第一磨牙压力侧HE染色结果;C:上颌第一磨牙压力侧TRAP染色结果图;D:正畸牙移动距离;E:上颌第一磨牙压力侧TRAP染色定量分析结果;F~I:上颌第一磨牙压力侧MMP-9、RANKL和OPG免疫组化染色结果图与定量分析结果;J~L:Western blot结果图与定量分析结果。rhTGF-β1组与Model组比较以及rhTGF-β1+Noggin组与rhTGF-β1组比较,**P < 0.01。
Figure 3. rhTGF-β1 promotes osteoclast formation during OTM via the BMP2/Smad1 signaling pathway($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 8)
-
[1] 刘洁, 彭金枫, 陆萍, 等. 物理方式加速正畸牙移动的研究进展[J]. 口腔生物医学, 2023, 14(03): 141-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8603.2023.03.001 [2] Schröder A, Käppler P, Nazet U, et al. Effects of compressive and tensile strain on macrophages during simulated orthodontic tooth movement[J]. Mediat Inflamm, 2020, 2020: 2814015. [3] Ruiz-Heiland G, Yong J W, von Bremen J, et al. Leptin reduces in vitro cementoblast mineralization and survival as well as induces PGE2 release by ERK1/2 commitment[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2021, 25(4): 1933-1944. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03501-3 [4] Sasaki K, Takeshita N, Fukunaga T, et al. Vibration accelerates orthodontic tooth movement by inducing osteoclastogenesis via transforming growth factor-β signalling in osteocytes[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2022, 44(6): 698-704. doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjac036 [5] 林维龙, 吴晓沛, 何薇薇, 等. 重组人转化生长因子-β1对大鼠正畸牙移动模型成骨细胞分化及ERK/MAPK信号通路的影响[J]. 口腔医学研究, 2023, 39(2): 118-123. [6] 王凯, 宋敏, 文皓楠, 等. 转化生长因子-β在骨代谢中作用机制的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2020, 26(2): 308-312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2020.02.032 [7] 袁熳. rhPDGF-BB与rhTGF-β1联合使用对大鼠正畸牙牙周组织改建及RAS蛋白影响的研究[D]. 遵义医科大学, 2021. [8] Mai Z H, Huang J H, Peng Z L, et al. miR-20a: A key regulator of orthodontic tooth movement via BMP2 signaling pathway modulation[J]. Connect Tissue Res, 2024, 65(4): 304-312. doi: 10.1080/03008207.2024.2365201 [9] Heubel B, Nohe A. The role of BMP signaling in osteoclast regulation[J]. J Dev Biol, 2021, 9(3): 24. doi: 10.3390/jdb9030024 [10] Peng J, Mao Z, Liu Y, et al. 12-Epi-Napelline regulated TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway mediated by BMSCs paracrine acceleration against osteoarthritis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 113: 109307. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109307 [11] Mo L, Zhu J, Li M, et al. Smads and AP-1 activation of TGF-β signaling upregulate transcription of osteoprotegerin in cementoblasts to inhibit osteoclastogenesis[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(22): e70171. doi: 10.1096/fj.202401551R [12] 郭晓峰, 杜艳锋, 张晶, 等. 木犀草素对正畸牙移动模型大鼠骨改建及BMP2/Smad1信号通路的影响[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2024, 32(3): 179-183. doi: 10.20049/j.bjkqyx.1006-673X.2024.03.005 [13] Lee S H, Cha J Y, Choi S H, et al. Effect of nicotine on orthodontic tooth movement and bone remodeling in rats[J]. Korean J Orthod, 2021, 51(4): 282-292. doi: 10.4041/kjod.2021.51.4.282 [14] Yao X W, Liu H D, Ren M X, et al. Aloe polysaccharide promotes osteogenesis potential of adipose-derived stromal cells via BMP-2/Smads and prevents ovariectomized-induced osteoporosis[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2022, 49(12): 11913-11924. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-08003-x [15] Ren X, Wang Q, Liu C, et al. Osteogenic ability using porous hydroxyapatite scaffold-based delivery of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2021, 22(4): 1091. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10525 [16] Tan K, Wang J, Su X, et al. KAT6A/YAP/TEAD4 pathway modulates osteoclastogenesis by regulating the RANKL/OPG ratio on the compression side during orthodontic tooth movement[J]. Prog Orthod, 2024, 25(1): 29. doi: 10.1186/s40510-024-00530-6 [17] Liu Y Y, Ding Y F, Sui H J, et al. Pilose antler (Cervus elaphus Linnaeus) polysaccharide and polypeptide extract inhibits bone resorption in high turnover type osteoporosis by stimulating the MAKP and MMP-9 signaling pathways[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 304: 116052. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.116052 [18] 唐丁炫, 梅梅, 张疆弢. 正畸牙移动过程中转化生长因子β1的作用及其研究进展[J]. 海南医学, 2021, 32(11): 1472-1475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2021.11.030 [19] 庄新晨, 苏佳灿. 转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路在破骨细胞分化发育中的研究进展[J]. 海军军医大学学报, 2023, 44(5): 622-626. doi: 10.16781/j.CN31-2187/R.20230131 [20] Wald S, Leibowitz A, Aizenbud Y, et al. γδT cells are essential for orthodontic tooth movement[J]. J Dent Res, 2021, 100(7): 731-738. doi: 10.1177/0022034520984774 [21] Nakai Y, Praneetpong N, Ono W, et al. Mechanisms of osteoclastogenesis in orthodontic tooth movement and orthodontically induced tooth root resorption[J]. J Bone Metab, 2023, 30(4): 297-310. doi: 10.11005/jbm.2023.30.4.297 -





 下载:
下载: