Application of miR-132,BDNF and NRG-1 in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of AI-related Vascular Dementia
-
摘要:
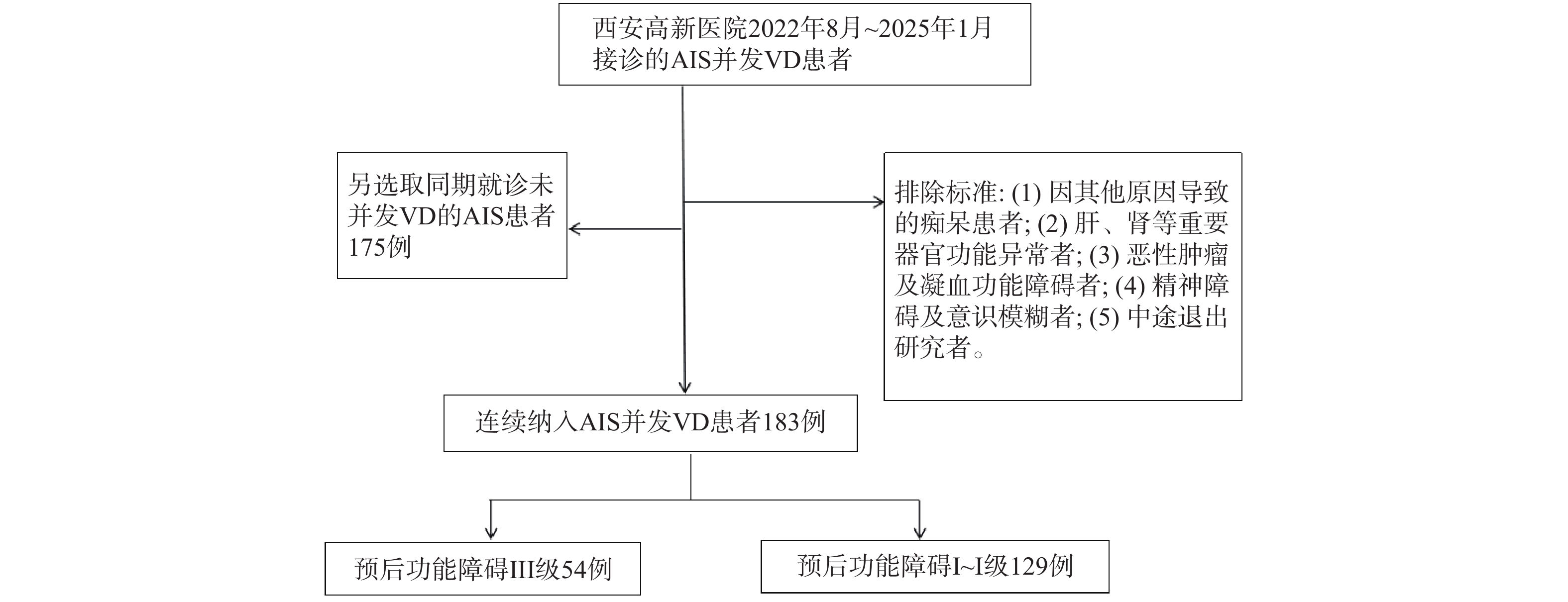
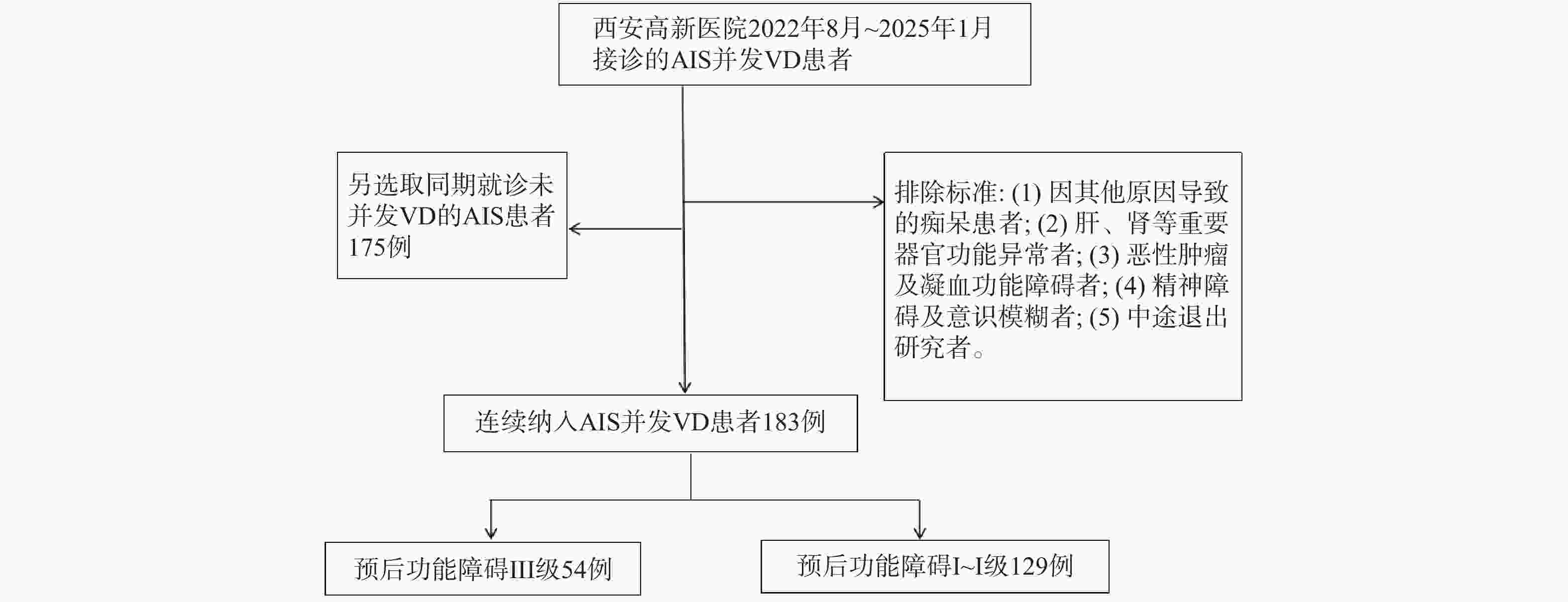
目的 探讨血清微小RNA-132(microRNA-132,miR-132)联合脑源性神经营养因子(brain-derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)、神经调节蛋白-1(neuroregulatory protein-1,NRG-1)在急性缺血性脑卒中(acute ischemic stroke,AIS)相关血管性痴呆(vascular dementia,VD)诊断及预后评估中的应用。 方法 连续纳入西安高新医院2022年8月至2025年1月接诊的AIS并发VD患者183例为VD组,对其随访6个月根据预后情况分为不良组(n = 54)、良好组(n = 129)。另选取同期就诊的未并发VD的AIS患者175例为非VD组。分析AIS并发VD患者预后不良的影响因素及血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1水平预测AIS并发VD患者预后不良的效能。 结果 VD组血清miR-132、BDNF水平均低于非VD组(P < 0.05)。血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1是AIS并发VD的影响因素(P < 0.05)。三者联合诊断AIS并发VD的AUC(0.860)高于单独诊断的AUC(0.796、0.758、0.713)(P < 0.05)。与良好组相比,不良组入院MMSE评分≤20分占比较高,血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1水平降低(P < 0.05)。血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1是AIS并发VD患者预后的影响因素(P < 0.05)。联合预测AIS并发VD患者预后的曲线下面积(AUC)(0.920)显著高于各指标单独预测的AUC(0.806、0.788、0.850)。 结论 AIS并发VD患者血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1水平均降低,三者联合检测在AIS相关VD诊断及预后评估中可能具有一定的应用价值。 Abstract:Objective To discuss the application of serum microRNA-132 (miR-132) jointed with brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neuregulin-1 (NRG-1) in the diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of acute ischemic stroke (AIS)-related vascular dementia (VD). Methods A total of 183 patients with AIS and complicated VD admitted to Xi'an Gaoxin Hospital from August 2022 to January 2025 were included as the VD group. They were followed up for 6 months and separated into adverse group (n = 54) and good group (n = 129) based on their prognosis. Another 175 AIS patients who did not have complicated VD during the same period were included as the non VD group. In addition, the influencing factors of poor prognosis in patients with AIS and complicated VD and the predictive efficacy of serum miR-132, BDNF, and NRG-1 levels for poor prognosis in patients with AIS and complicated VD were discussed. Results The levels of serum miR-132, BDNF and NRG-1 in the VD group were all lower than those in the non-VD group (P < 0.05). Serum miR-132, BDNF and NRG-1 were the influencing factors of AIS complicated with VD (P < 0.05). The AUC (0.860) of the jointed diagnosis for AIS complicated with VD was higher than that of the individual diagnosis (0.796, 0.758, 0.713) (P < 0.05). Compared with the good group, the poor group had a higher proportion of admission MMSE scores ≤ 20, and lower levels of serum miR-132, BDNF, and NRG-1 (P < 0.05). Serum miR-132, BDNF, and NRG-1 were prognostic factors in patients with AIS and complicated VD (P < 0.05). The AUC of the jointed prediction (0.920) for the prognosis of patients with AIS and complicated VD was obviously higher than that of the individual predictions of each indicator (0.806, 0.788, 0.850). Conclusion Serum miR-132, BDNF, and NRG-1 are all reduced in patients with AIS and complicated VD. The combined detection of these three markers may have certain application value in the diagnosis and prognosis evaluation of AIS-related vascular disease. -
Key words:
- MicroRNA-132 /
- Brain-derived neurotrophic factor /
- Neuregulin-1 /
- Acute ischemic stroke /
- Vascular dementia /
- Prognosis
-
表 1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences of qRT-PCR
基因 上游引物5’-3’ 引物长度(nt) 下游引物5’-3’ 引物长度(nt) miR-132 GCCGATAACAGTCTACAGC 19 CAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT 18 U6 CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA 17 AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT 20 表 2 两组基线资料及血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1水平比较[($\bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of baseline data and serum levels of miR-132, BDNF, and NRG-1 between the two group [($\bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
类别 VD组(n=183) 非VD组(n=175) χ2/t P 性别 0.516 0.472 男 104(56.83) 106(60.57) 女 79(43.17) 69(39.43) 年龄(岁) 64.70 ± 11.13 63.81 ± 10.96 0.762 0.447 BMI(kg/m2) 23.19 ± 2.34 22.86 ± 2.29 1.348 0.179 受教育程度 0.763 0.382 高中及以上 93(50.82) 97(55.43) 高中以下 90(49.18) 78(44.57) 高血压 71(38.80) 62(35.43) 0.435 0.510 糖尿病 66(36.07) 58(33.14) 0.338 0.561 高血脂 59(32.24) 52(29.71) 0.267 0.605 吸烟史 70(38.25) 64(36.57) 0.108 0.743 饮酒史 89(48.63) 86(49.14) 0.009 0.923 miR-132 0.86±0.18 1.03±0.26 7.219 <0.001* BDNF(pg/mL) 57.91 ± 16.20 71.54 ± 18.36 7.456 <0.001* NRG-1(pg/mL) 278.41 ± 56.98 314.53 ± 62.03 6.854 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 AIS并发VD的影响因素
Table 3. Influencing factors of AIS complicated with VD
影响因素 赋值方式 B SE Wald P OR 95%CI miR-132 连续变量 −0.736 0.315 5.460 0.019* 0.479 0.258~0.888 BDNF 连续变量 −0.642 0.293 4.808 0.028* 0.526 0.296~0.934 NRG-1 连续变量 −1.112 0.528 4.433 0.035* 0.329 0.117~0.926 *P < 0.05。 表 4 对AIS并发VD的诊断效能
Table 4. Diagnostic efficacy for AIS complicated with VD
变量 AUC(95%CI) 最佳截断值 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 约登指数 miR-132 0.796(0.750~0.836) 0.95 87.43 61.14 0.486 BDNF 0.758(0.711~0.802) 59.85 pg/mL 61.75 77.71 0.395 NRG-1 0.713(0.664~0.760) 292.79 pg/mL 65.03 71.43 0.365 联合 0.860(0.819~0.894) − 75.41 84.00 0.594 Z联合-miR-132/P 2.541/0.011* Z联合-BDNF/P 4.305/<0.001* Z联合-NRG-1/P 5.252/<0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 5 临床资料及miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1水平比较[($\bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 5. Comparison of clinical data and levels of miR-132, BDNF and NRG-1 [($\bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
临床资料 不良组(n=54) 良好组(n=129) χ2/t P 性别 0.572 0.449 男 33(61.11) 71(55.04) 女 21(38.89) 58(44.96) 年龄(岁) 65.48 ± 10.85 64.37 ± 11.23 0.616 0.539 BMI(kg/m2) 23.25 ± 2.39 23.16 ± 2.35 0.235 0.814 受教育程度 0.627 0.428 高中及以上 25(46.30) 68(52.71) 高中以下 29(53.70) 61(47.29) 高血压 23(42.59) 48(37.21) 0.465 0.495 糖尿病 21(38.89) 45(34.88) 0.265 0.607 高血脂 18(33.33) 41(31.78) 0.042 0.838 痴呆家族史 8(14.81) 17(13.18) 0.086 0.769 吸烟史 25(46.30) 45(34.88) 2.099 0.147 饮酒史 30(55.56) 59(45.74) 1.469 0.225 空腹血糖(mmol/L) 5.74 ± 1.26 5.42 ± 1.13 1.688 0.093 糖化血红蛋白(%) 6.18 ± 0.89 5.93 ± 0.84 1.785 0.076 入院MMSE评分(分) 13.051 <0.001* >20 8(14.81) 55(42.64) ≤20 46(85.19) 74(57.36) miR-132 0.71 ± 0.13 0.92 ± 0.21 6.816 <0.001* BDNF(pg/mL) 48.49±9.75 61.85±12.16 7.163 <0.001* NRG-1(pg/mL) 237.64 ± 38.96 295.47 ± 49.24 7.679 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 6 AIS并发VD患者预后的影响因素
Table 6. Influencing factors of prognosis in patients with AIS complicated by VD
影响因素 赋值方式 B SE Wald P OR 95%CI 模型1 miR-132 连续变量 −0.794 0.321 6.119 0.013* 0.452 0.241~0.848 BDNF 连续变量 −0.559 0.236 5.603 0.018* 0.572 0.360~0.908 NRG-1 连续变量 −0.270 0.127 4.536 0.033* 0.763 0.595~0.979 入院MMSE评分 >20=1,≤20=0 −0.770 0.317 5.901 0.015* 0.463 0.249~0.862 模型2 miR-132 连续变量 −0.826 0.345 5.726 0.017* 0.438 0.223~0.861 BDNF 连续变量 −0.322 0.145 4.919 0.027* 0.725 0.546~0.963 NRG-1 连续变量 −0.960 0.373 6.620 0.010* 0.383 0.184~0.796 模型1表示未校正;模型2表示校正入院MMSE评分后,*P < 0.05。 表 7 血清miR-132、BDNF、NRG-1水平预测AIS并发VD患者预后不良的效能
Table 7. Efficacy of serum levels of miR-132,BDNF,and NRG-1 in predicting poor prognosis in patients with AIS complicated with VD
变量 最佳截断值 AUC 95%CI 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 约登指数 P miR-132 0.84 0.806 0.741~0.861 77.78 74.42 0.522 <0.001* BDNF 53.96 pg/mL 0.788 0.722~0.845 66.67 78.29 0.450 <0.001* NRG-1 276.90 pg/mL 0.850 0.790~0.899 88.89 67.44 0.563 <0.001* 联合 − 0.920 0.870~0.955 85.19 86.05 0.712 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Rost N S, Brodtmann A, Pase M P, et al. Post-stroke cognitive impairment and dementia[J]. Circ Res, 2022, 130(8): 1252-1271. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.319951 [2] Wang X X, Zhang B, Xia R, et al. Inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy as critical players in vascular dementia[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(18): 9601-9614. [3] Custodero C, Ciavarella A, Panza F, et al. Role of inflammatory markers in the diagnosis of vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Geroscience, 2022, 44(3): 1373-1392. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00556-w [4] Huang H, Cui G, Tang H, et al. Relationships between plasma expression levels of microRNA-146a and microRNA-132 in epileptic patients and their cognitive, mental and psychological disorders[J]. Bioengineered, 2022, 13(1): 941-949. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2015528 [5] Wang C S, Kavalali E T, Monteggia L M. BDNF signaling in context: From synaptic regulation to psychiatric disorders[J]. Cell, 2022, 185(1): 62-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.12.003 [6] Shi L, Bergson C M. Neuregulin 1: An intriguing therapeutic target for neurodevelopmental disorders[J]. Transl Psychiatry, 2020, 10(1): 190. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-00868-5 [7] 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国急性缺血性脑卒中诊治指南2018[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 666-682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6731.2019.11.015 [8] 中国痴呆与认知障碍指南写作组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(一): 痴呆及其分类诊断标准[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(13): 965-970. [9] 赵元萍, 丁睿, 谢红. 中国版日常生活活动能力量表编制与信效度验证[J]. 实用老年医学, 2022, 36(12): 1215-1219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9198.2022.12.008 [10] Deng X, Zhao M, Zhang E, et al. New insights into acute ischemic stroke from the perspective of spatial omics[J]. Theranostics, 2025, 15(15): 7902-7924. [11] Martha S R, Pen A Y, McGuire L S, et al. Lipidomics, acute ischemic stroke, symptoms, and outcomes: Observational study protocol[J]. Nurs Res, 2023, 72(4): 326-333. [12] Zhang M, Bian Z. Alzheimer’s disease and microRNA-132: A widespread pathological factor and potential therapeutic target[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 687973. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.687973 [13] Penning A, Snoeck S, Garritsen O, et al. NACC2, a molecular effector of miR-132 regulation at the interface between adult neurogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 21163. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72096-6 [14] Wang Y, Zhao J, Guo Q, et al. Neural stem cell-derived exosomes improve neurite outgrowth and cognitive function through transferring miR-132-3p[J]. Exp Neurol, 2025, 388: 115224. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2025.115224 [15] 张柏扬, 步婷婷, 王利东. 急性缺血性脑卒中患者血清miR-132、sFasL及IL-1β水平与血管性痴呆的相关性[J]. 脑与神经疾病杂志, 2024, 32(8): 509-513. [16] Gao L, Zhang Y, Sterling K, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Alzheimer’s disease and its pharmaceutical potential[J]. Transl Neurodegener, 2022, 11(1): 4. doi: 10.1186/s40035-022-00279-0 [17] 郭冠玲. 急性脑梗死患者血清Lp-PLA2、BDNF对并发血管性痴呆的预测价值[J]. 黑龙江医学, 2025, 49(3): 266-269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2025.03.003 [18] Song J. BDNF signaling in vascular dementia and its effects on cerebrovascular dysfunction, synaptic plasticity, and cholinergic system abnormality[J]. J Lipid Atheroscler, 2024, 13(2): 122-138. [19] 段新飞, 贾俊栋, 胡科, 等. 血管性痴呆患者血清HDAC6和BDNF表达与患者认知功能及预后的相关性分析[J]. 四川医学, 2024, 45(8): 848-852. doi: 10.16252/j.cnki.issn1004-0501-2024.08.007 [20] Wang X, Zhang F, Ma W, et al. Increased levels of serum neuregulin 1 associated with cognitive impairment in vascular dementia[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020: 6683747. doi: 10.1155/2020/6683747 [21] 张晗, 何明利. 急性脑梗死合并血管性痴呆患者认知功能与血清NRG-1、Lp-PLA2水平的相关性分析[J]. 中国急救复苏与灾害医学杂志, 2024, 19(9): 1157-1159, 1165. [22] 沈俊, 李坪, 袁迎曦, 等. Nrg-1/ErbB信号通路在脊髓损伤修复中作用的研究进展[J]. 中国临床神经科学, 2021, 29(6): 690-695. [23] 杜磊, 雷晶, 何丹, 等. 血清CLU、NRG-1水平与血管性痴呆患者认知功能障碍严重程度的关系及对预后的价值分析[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2024, 24(11): 2068-2072. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2024.11.012 -





 下载:
下载: