Expression of Cell Pyroptosis-Associated TLR4 Signalling Pathway During the Progression from Actinic Keratosis to Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma
-
摘要:
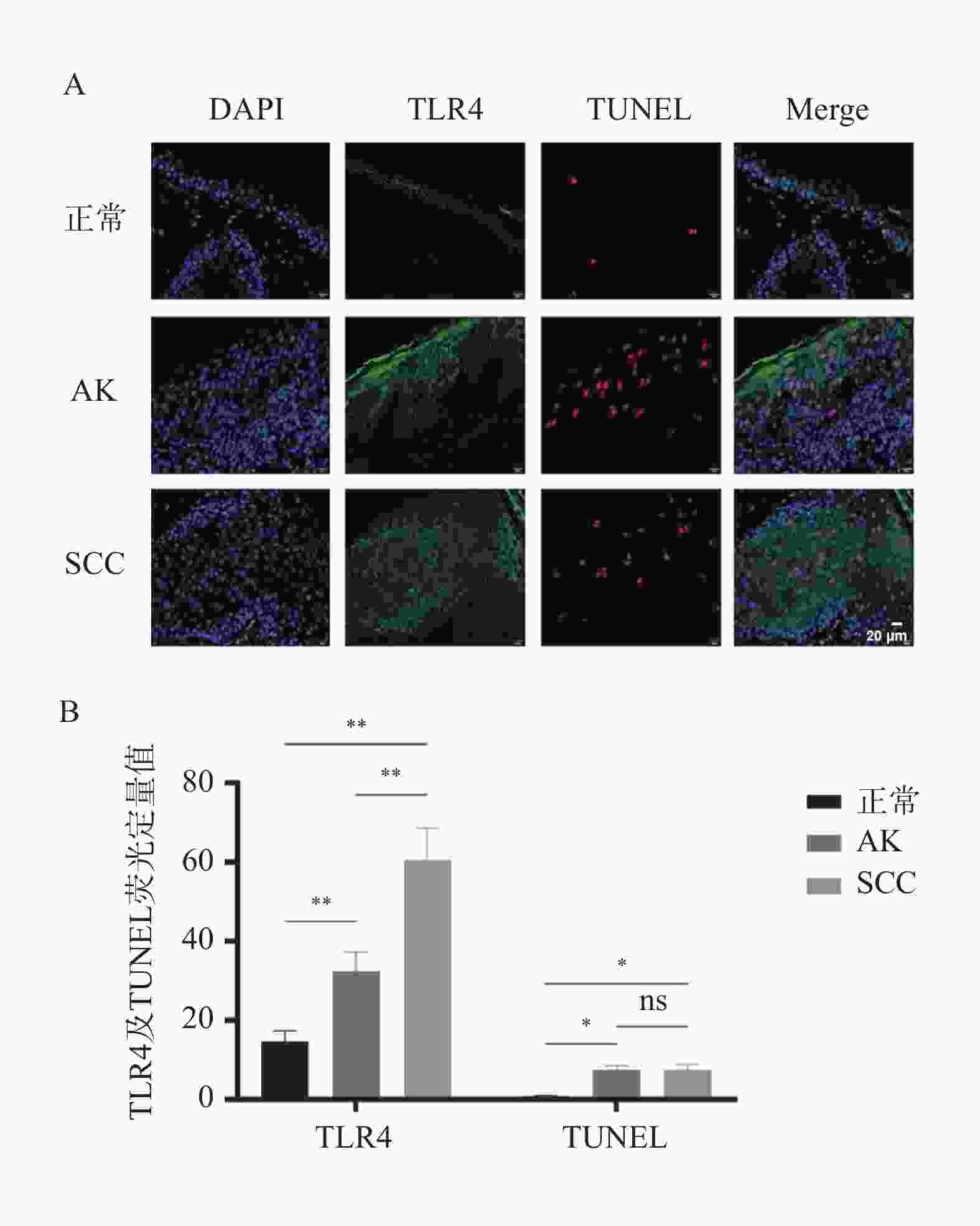
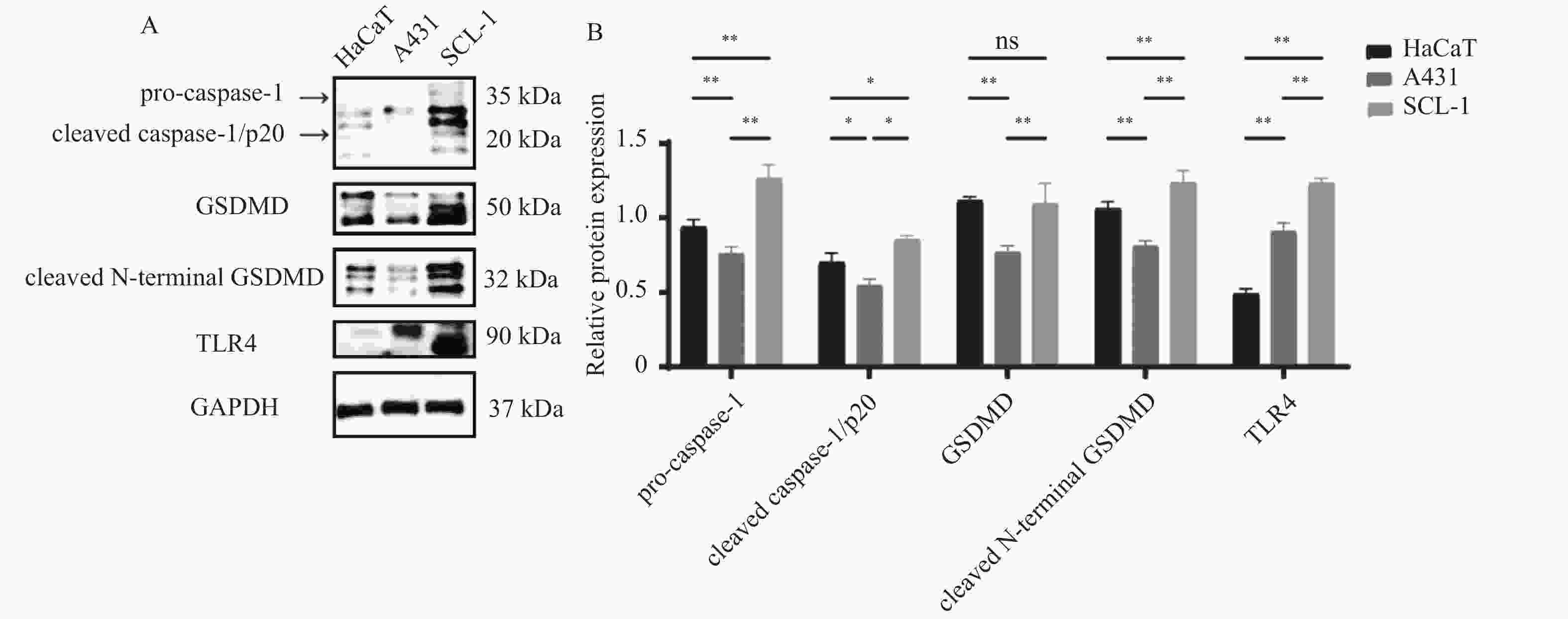
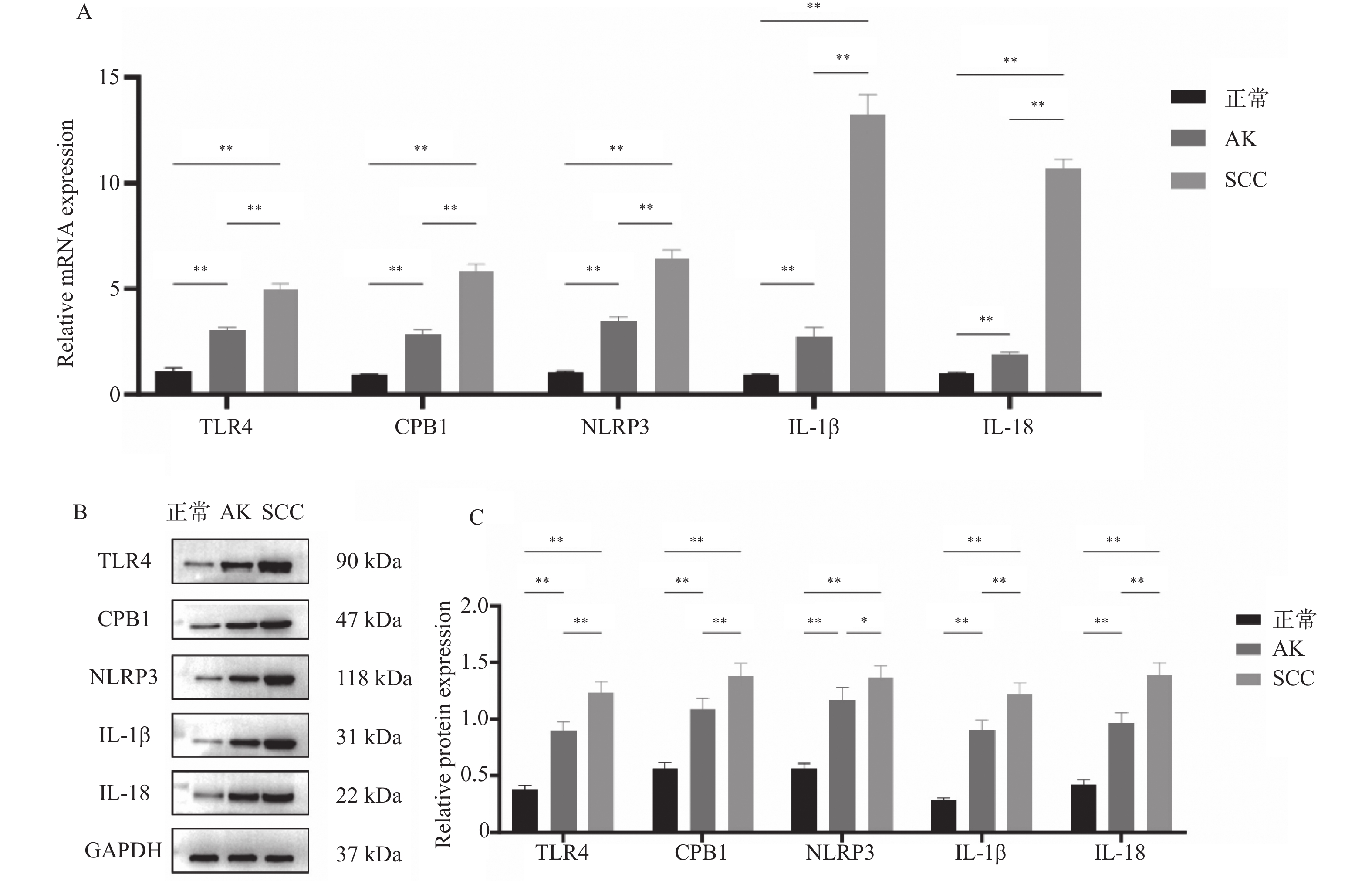
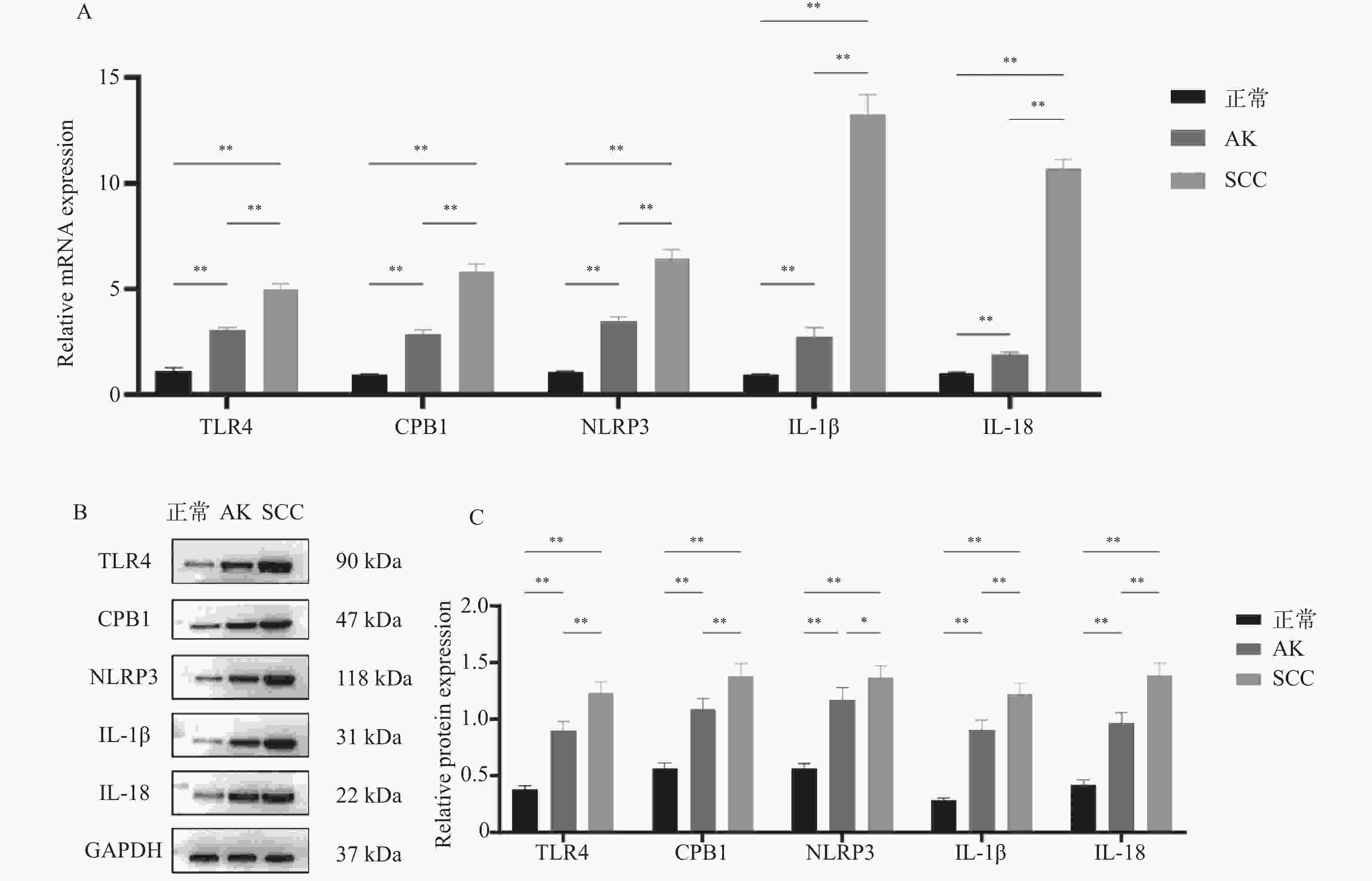
目的 探讨细胞焦亡相关TLR4信号通路是否影响光线性角化病(actinic keratosis,AK)向皮肤鳞状细胞癌(squamous cell carcinoma,SCC)恶性转化。 方法 收集昆明医科大学第一附属医院2020年8月至2021年8月AK、SCC患者病变组织样本各6例及健康受试者正常皮肤组织5例作为对照。采用定量PCR和Western blot检测TLR4信号通路相关因子TLR4、CPB1、NLRP3、IL-1β及IL-18的mRNA及蛋白表达水平;TLR4/TUNEL免疫荧光双染用于检测各组织中TLR4的表达及细胞焦亡水平。通过Western blot检测正常角质形成细胞系HaCaT及皮肤鳞状细胞癌细胞系A431、SCL-1中焦亡核心蛋白(pro-caspase-1、cleaved caspase-1/p20、GSDMD、cleaved N-terminal GSDMD)及TLR4的表达差异。 结果 定量PCR和Western blot结果显示,SCC组织中TLR4、CPB1、NLRP3、IL-1β及IL-18的mRNA及蛋白表达水平均显著高于AK和正常皮肤组织(P < 0.05)。TLR4/TUNEL免疫荧光双染结果显示,从正常皮肤到AK再到SCC,TLR4表达及细胞焦亡水平呈逐步升高趋势(P < 0.05)。此外,SCL-1细胞中pro-caspase-1、cleaved caspase-1/p20、cleaved N-terminal GSDMD及TLR4的表达升高(P < 0.05),而A431细胞中仅TLR4上调(P < 0.05),其他焦亡核心蛋白较HaCaT细胞下降(P < 0.05)。 结论 TLR4信号通路在AK及SCC中表达逐步升高,且不同皮肤鳞癌细胞系中该通路的活化状态存在差异。 Abstract:Objective To investigate whether the pyroptosis-related Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signaling pathway influences the malignant transformation of actinic keratosis (AK) into cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Methods A total of 6 lesion tissue samples each from patients with AK and SCC, as well as 5 normal skin tissue samples from healthy subjects as controls, were collected from the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University between August 2020 and August 2021. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) and Western blot analysis were performed to determine the mRNA and protein expression levels of TLR4 pathway–related factors, including TLR4, CPB1, NLRP3, IL-1β, and IL-18. TLR4/TUNEL double immunofluorescence staining was used to evaluate TLR4 expression and the level of cellular pyroptosis in tissue samples. In addition, Western blotting was performed to analyze the expression differences of pyroptosis-related core proteins (pro-caspase-1, cleaved caspase-1/p20, GSDMD, and cleaved N-terminal GSDMD) and TLR4 among the normal keratinocyte cell line HaCaT and SCC cell lines A431 and SCL-1. Results Quantitative PCR and Western blot results showed that the mRNA and protein expression levels of TLR4, CPB1, NLRP3, IL-1β, and IL-18 were significantly higher in SCC tissues than in AK and normal skin tissues (P < 0.05). TLR4/TUNEL double immunofluorescence results revealed a progressive increasing trend in TLR4 expression and pyroptosis levels from normal skin to AK and further to SCC (P < 0.05). Furthermore, in SCL-1 cells, the expression levels of pro-caspase-1, cleaved caspase-1/p20, cleaved N-terminal GSDMD, and TLR4 were significantly upregulated (P < 0.05), whereas in A431 cells, only TLR4 expression was increased (P < 0.05), and the levels of other pyroptosis-related proteins were downregulated compared to HaCaT cells (P < 0.05). Conclusion The expression of the TLR4 signaling pathway gradually increased from AK to SCC, and its activation status varied among different cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. -
Key words:
- Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma /
- Actinic keratosis /
- Cell pyroptosis /
- TLR4
-
表 1 定量PCR检测基因的引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences of genes detected by qPCR
基因 引物序列(5'-3') 产物长度(bp) TLR4 TCAGTGTGCTTGTAGTAT (F) 135 CCTGGCTTGAGTAGATAA (R) CPB1 CAGTTGACTTCCGTGTTA (F)
TTCTCAGGTTGCTTATCAG (R)99 NLRP3 CAAGAATCCACAGTGTAA (F) 101 TCTGATTAGTGCTGAGTA (R) IL-1β AATGACCTGAGCACCTTCT (F) 82 GCACATAAGCCTCGTTATCC (R) IL-18 GACCAAGTTCTCTTCATT (F) 143 ATAGTTACAGCCATACCT (R) GAPDH AAAGGGTCATCATCTCTG (F) 80 GCTGTTGTCATACTTCTC (R) -
[1] Lobl M B, Clarey D, Higgins S, et al. The correlation of immune status with ultraviolet radiation-associated mutations in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: A case-control study[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2020, 82(5): 1230-1232. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.10.069 [2] 陈雯婷, 钟欣妮, 李巍. DNA甲基化在紫外线相关皮肤病中的研究进展[J]. 皮肤性病诊疗学杂志, 2023, 30(6): 561-566. [3] Gutzmer R, Wiegand S, Kölbl O, et al. Actinic keratosis and cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2019, 116(37): 616-626. [4] Madani S, Marwaha S, Dusendang J R, et al. Ten-year follow-up of persons with Sun-damaged skin associated with subsequent development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma[J]. JAMA Dermatol, 2021, 157(5): 559-565. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.0372 [5] Zamyatina A, Heine H. Lipopolysaccharide recognition in the crossroads of TLR4 and caspase-4/11 mediated inflammatory pathways[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 585146. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.585146 [6] Pandey N, Chauhan A, Jain N. TLR4 polymorphisms and expression in solid cancers[J]. Mol Diagn Ther, 2018, 22(6): 683-702. [7] Nanz L, Keim U, Katalinic A, et al. Epidemiology of keratinocyte skin cancer with a focus on cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2024, 16(3): 606. doi: 10.3390/cancers16030606 [8] Que S K T, Zwald F O, Schmults C D. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Incidence, risk factors, diagnosis, and staging[J]. J Am Acad Dermatol, 2018, 78(2): 237-247. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2017.08.059 [9] Huerta-Brogeras M, Olmos O, Borbujo J, et al. Validation of dermoscopy as a real-time noninvasive diagnostic imaging technique for actinic keratosis[J]. Arch Dermatol, 2012, 148(10): 1159-1164. doi: 10.1001/archdermatol.2012.1060 [10] 王玲, 秦祥川, 李金秋, 等. CD147通过AIM2炎症小体介导宫颈癌细胞焦亡和增殖[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2024, 45(1): 15-21. [11] Xia X, Wang X, Cheng Z, et al. The role of pyroptosis in cancer: Pro-cancer or pro- “host”?[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(9): 650. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1883-8 [12] 于百莹, 惠雪, 赵曙, 等. 细胞焦亡及其与癌症的关系[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2022, 30(13): 2471-2475. [13] Zhou B, Zhang J Y, Liu X S, et al. Tom20 senses iron-activated ROS signaling to promote melanoma cell pyroptosis[J]. Cell Res, 2018, 28(12): 1171-1185. doi: 10.1038/s41422-018-0090-y [14] Li Pomi F, Borgia F, Custurone P, et al. Role of HMGB1 in cutaneous melanoma: State of the art[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(16): 9327. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169327 [15] Ye K, Wu Y, Sun Y, et al. TLR4 siRNA inhibits proliferation and invasion in colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ACAT1 expression[J]. Life Sci, 2016, 155: 133-139. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.05.012 [16] Zou Y, Qin F, Chen J, et al. sTLR4/MD-2 complex inhibits colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo by targeting LPS[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7(32): 52032-52044. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10496 [17] Burgueño J F, Fritsch J, González E E, et al. Epithelial TLR4 signaling activates DUOX2 to induce microbiota-driven tumorigenesis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 160(3): 797-808. e6. [18] Sasamori R, Sato Y, Nomura K, et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces CCL2 through TLR4 signaling and promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2024, 14(7): 3497-3512. doi: 10.62347/EIKE6128 [19] Sun Y, Wu C, Ma J, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 promotes angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2016, 347(2): 274-282. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.009 [20] Wang K, Wang J, Wei F, et al. Expression of TLR4 in non-small cell lung cancer is associated with PD-L1 and poor prognosis in patients receiving pulmonectomy[J]. Front Immunol, 2017, 8: 456. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00456 [21] Iotzova-Weiss G, Freiberger S N, Johansen P, et al. TLR4 as a negative regulator of keratinocyte proliferation[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10): e0185668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185668 [22] 胡新红, 曹天宇, 刘涛, 等. TLR4在皮肤鳞状细胞癌细胞的表达及其对细胞迁移和侵袭的影响[J]. 山西医科大学学报, 2022, 53(8): 928-934. [23] Yusuf N, Nasti T H, Meleth S, et al. Resveratrol enhances cell-mediated immune response to DMBA through TLR4 and prevents DMBA induced cutaneous carcinogenesis[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2009, 48(8): 713-723. doi: 10.1002/mc.20517 [24] Eiró N, Ovies C, Fernandez-Garcia B, et al. Expression of TLR3, 4, 7 and 9 in cutaneous malignant melanoma: Relationship with clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis[J]. Arch Dermatol Res, 2013, 305(1): 59-67. doi: 10.1007/s00403-012-1300-y [25] Kotrashetti V S, Nayak R, Bhat K, et al. Immunohistochemical expression of TLR4 and TLR9 in various grades of oral epithelial dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma, and their roles in tumor progression: A pilot study[J]. Biotech Histochem, 2013, 88(6): 311-322. doi: 10.3109/10520295.2013.785592 [26] Visioli F, Nunes J S, Pedicillo M C, et al. TLR4 expression in ex-lichenoid lesions-oral squamous cell carcinomas and its surrounding epithelium: The role of tumor inflammatory microenvironment[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(3): 385. doi: 10.3390/biom12030385 [27] Shi S, Xu C, Fang X, et al. Expression profile of Toll-like receptors in human breast cancer[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 21(2): 786-794. [28] Szczepanski M J, Czystowska M, Szajnik M, et al. Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor development and protects the tumor from immune attack[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69(7): 3105-3113. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3838 [29] Ju H, Hu Z, Lu Y, et al. TLR4 activation leads to anti-EGFR therapy resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2020, 10(2): 454-472. [30] Laikova K V, Oberemok V V, Krasnodubets A M, et al. Advances in the understanding of skin cancer: Ultraviolet radiation, mutations, and antisense oligonucleotides as anticancer drugs[J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(8): E1516. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081516 [31] Ahmad I, Simanyi E, Guroji P, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 deficiency enhances repair of UVR-induced cutaneous DNA damage by nucleotide excision repair mechanism[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2014, 134(6): 1710-1717. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.530 [32] Harberts E, Zhou H, Fishelevich R, et al. Ultraviolet radiation signaling through TLR4/MyD88 constrains DNA repair and plays a role in cutaneous immunosuppression[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 194(7): 3127-3135. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402583 [33] Song H J, Lee S H, Choi G S, et al. Repeated ultraviolet irradiation induces the expression of Toll-like receptor 4, IL-6, and IL-10 in neonatal human melanocytes[J]. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed, 2018, 34(2): 145-151. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12359 [34] Kirschnerova V, Vaishampayan P, Khawam M, et al. Abstract 2447: TLR4 expression as a determinant of EMT and stress response gene expression in UV exposed human keratinocytes[J]. Cancer Res, 2021, 81(13_Supplement): 2447. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.AM2021-2447 -





 下载:
下载: