Mechanism by Which T Cell Immune Structural Proteins Promote the Role of the Hippo Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Preeclampsia
-
摘要:
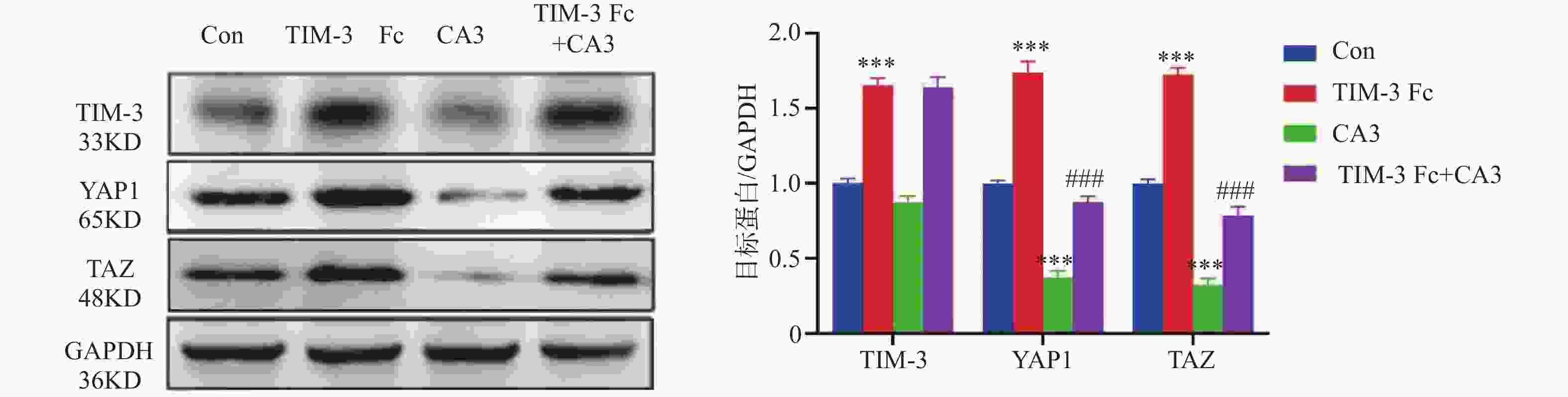
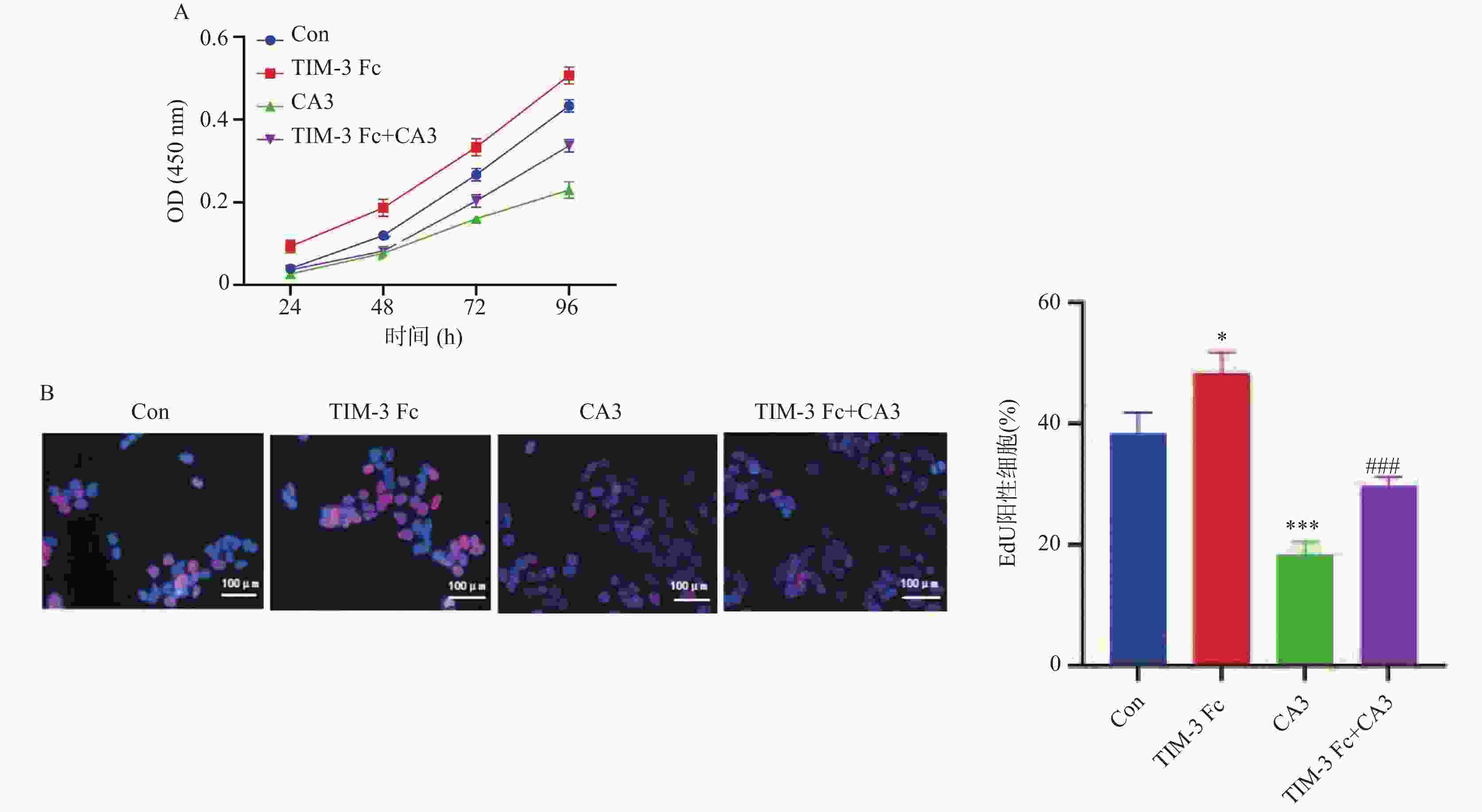
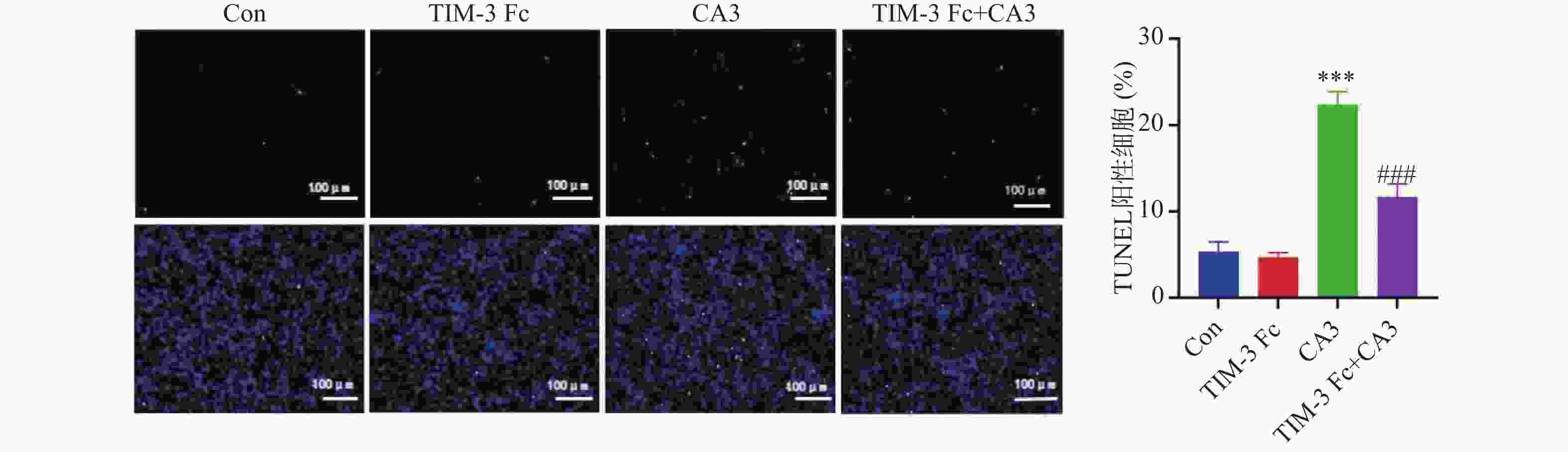
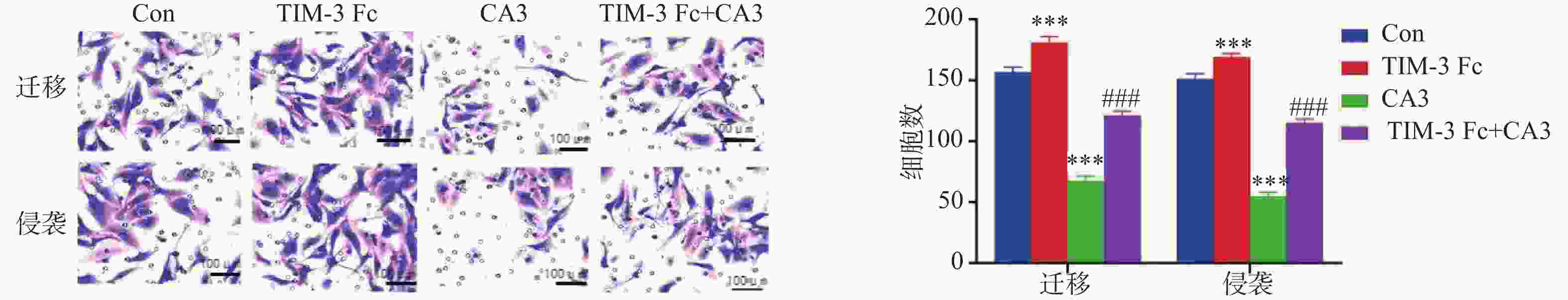
目的 探讨T细胞免疫球蛋白结构域和粘蛋白结构域3(TIM-3)促进河马(Hippo)通路在子痫前期发病中的作用机制。 方法 将HTR-8/Svneo细胞分为对照组(Con)、重组人Tim-3蛋白(Tim-3 Fc)组、YAP1抑制剂组CA3组和Tim-3 Fc+CA3组。分别通过5-乙炔基-2′-脱氧尿苷(EdU)分析细胞的增殖能力,Transwell分析评估细胞的侵袭和迁移能力,末端脱氧核苷酸转移酶dUTP缺口末端标记(TUNEL)分析细胞凋亡。通过Western blot检测HTR-8/SVneo细胞中TIM-3、Hippo通路蛋白表达。 结果 与Con组相比,TIM-3 Fc组HTR-8/SVneo滋养层细胞中TIM-3、YAP1、TAZ蛋白表达上调(P < 0.05)。与TIM-3 Fc组相比,TIM-3 Fc+CA3组滋养层细胞中YAP1、TAZ蛋白表达下调(P < 0.05)。与Con组相比,TIM-3 Fc组滋养层细胞中EdU阳性细胞率增加(P < 0.05)。与TIM-3 Fc组相比,TIM-3 Fc+CA3组HTR-8/SVneo滋养层细胞中EdU阳性细胞率、凋亡细胞数降低(P < 0.05)。与Con组相比,TIM-3 Fc组滋养层细胞的迁移、侵袭细胞数增加(P < 0.05)。与TIM-3 Fc组相比,TIM-3 Fc+CA3组滋养层细胞的迁移、侵袭细胞数降低(P < 0.05)。 结论 Tim-3通过与滋养层细胞的YAP1相互作用激活Hippo通路,进而促进细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移能力。 -
关键词:
- T细胞免疫球蛋白结构域和粘蛋白结构域3 /
- 先兆子痫 /
- Hippo通路 /
- 滋养层细胞
Abstract:Objective To explore the mechanism by which T cell immunoglobulin and mucin domain-3 (TIM-3) promotes the Hippo signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Methods HTR-8/Svneo cells were divided into a control group (Con), a recombinant human Tim-3 protein (Tim-3 Fc) group, a YAP1 inhibitor CA3 group and a Tim-3 Fc+CA3 group. Cell proliferation was analyzed by 5- ethynyl-2 ′-deoxyuridine (EdU). Cell invasion and migration were evaluated by Transwell assay, and cell apoptosis was analyzed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Protein expression levels of TIM-3 and Hippo pathway components in HTR-8/SVneo cells were detected by Western blot. Results Compared to the Con group, protein expression levels of TIM-3, YAP1 and TAZ were up-regulated in HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells of the TIM-3 Fc group(P < 0.05). Compared to the TIM-3 Fc group, protein expression levels of YAP1 and TAZ were down-regulated in trophoblast cells of the TIM-3 Fc+CA3 group (P < 0.05). Compared to the Con group, the rate of EdU positive cells in HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells in TIM-3 Fc group was increased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared to the TIM-3 Fc group, the rate of EdU positive cells and the number of apoptotic cells in HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells of the TIM-3 Fc+CA3 group were decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared to the Con group, the numbers of HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells in TIM-3 Fc group were increased significantly (P < 0.05). Compared to the TIM-3 Fc group, the number of HTR-8/SVneo trophoblast cells in TIM-3 Fc+CA3 group were decreased significantly (P < 0.05). Conclusions Tim-3 activates the Hippo pathway by interacting with YAP1 in trophoblast cells, thus promoting cell proliferation, invasion and migration. -
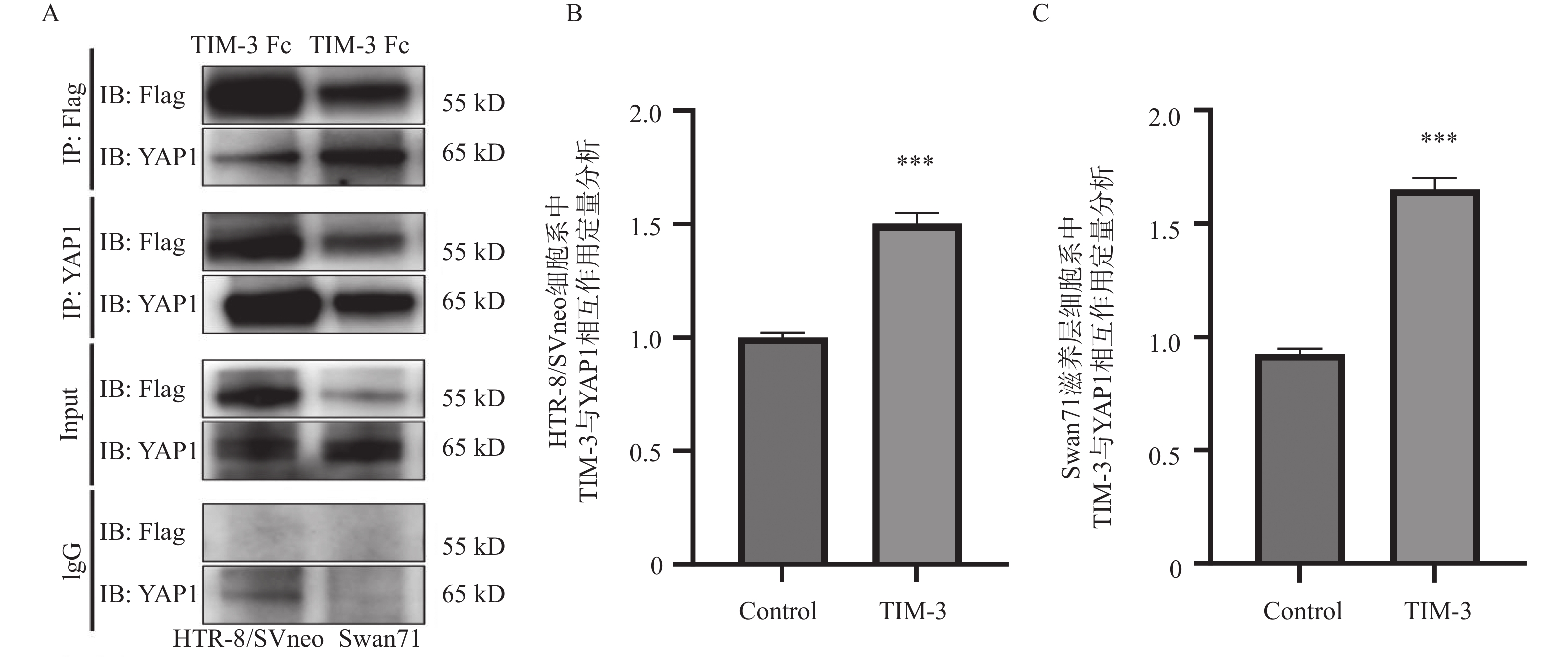
图 1 co-IP分析HTR-8/SVneo,Swan71滋养层细胞系中TIM-3与YAP1相互作用及定量分析
注:A:co-IP分析HTR-8/SVneo,Swan71滋养层细胞系中TIM-3与YAP1相互作用图;B: HTR-8/SVneo滋养层细胞系中TIM-3与YAP1相互作用的定量分析;C:Swan71滋养层细胞系中TIM-3与YAP1相互作用的定量分析。与control组相比,***P < 0.001。
Figure 1. Co-IP analysis of the interaction between TIM-3 and YAP1 and quantitative analysis in HTR-8/SVneo,Swan71 trophoblast cell lines
-
[1] Wheeler S M, Myers S O, Swamy G K, et al. Estimated prevalence of risk factors for preeclampsia among individuals giving birth in the US in 2019[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(1): e2142343. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.42343 [2] Chang K J, Seow K M, Chen K H. Preeclampsia: Recent advances in predicting, preventing, and managing the maternal and fetal life-threatening condition[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2023, 20(4): 2994. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20042994 [3] Roberts J M, King T L, Barton J R, et al. Care plan for individuals at risk for preeclampsia: Shared approach to education, strategies for prevention, surveillance, and follow-up[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2023, 229(3): 193-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2023.04.023 [4] Tassi A, Sala A, Mazzera I, et al. Long-term outcomes of patients with preeclampsia, a review of the literature[J]. Hypertens Pregnancy, 2023, 42(1): 2217448. doi: 10.1080/10641955.2023.2217448 [5] Megli C J, Coyne C B. Infections at the maternal-fetal interface: An overview of pathogenesis and defence[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2022, 20(2): 67-82. doi: 10.1038/s41579-021-00610-y [6] Li M, Sun F, Qian J, et al. Tim-3/CTLA-4 pathways regulate decidual immune cells-extravillous trophoblasts interaction by IL-4 and IL-10[J]. FASEB J, 2021, 35(8): e21754. [7] Lin Q, Cao J, Yu J, et al. YAP-mediated trophoblast dysfunction: The common pathway underlying pregnancy complications[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 21(1): 353. [8] Sun K, Zhang X D, Liu X Y, et al. YAP1 is a prognostic biomarker and correlated with immune cell infiltration in pancreatic cancer[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 625731. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.625731 [9] 杜晓晓, 王萍, 孙丽娜, 等. 母胎界面巨噬细胞在子痫前期发病机制中的作用[J]. 现代免疫学, 2023, 43(4): 351-355. [10] Moffett A, Shreeve N. Local immune recognition of trophoblast in early human pregnancy: Controversies and questions[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2023, 23(4): 222-235. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00777-2 [11] Joo J S, Lee D, Hong J Y. Multi-layered mechanisms of immunological tolerance at the maternal-fetal interface[J]. Immune Netw, 2024, 24(4): e30. doi: 10.4110/in.2024.24.e30 [12] Wang S, Chen C, Sun F, et al. Involvement of the tim-3 pathway in the pathogenesis of pre-eclampsia[J]. Reprod Sci, 2021, 28(12): 3331-3340. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00675-3 [13] Sun Y, Wu S, Zhou Q, et al. Trophoblast-derived interleukin 9 mediates immune cell conversion and contributes to maternal-fetal tolerance[J]. J Reprod Immunol, 2021, 148: 103379. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2021.103379 [14] Zhu W, Tan Y Q, Wang F Y. Tim-3: An inhibitory immune checkpoint is associated with maternal-fetal tolerance and recurrent spontaneous abortion[J]. Clin Immunol, 2022, 245: 109185. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109185 [15] Li M, Sun F, Xu Y, et al. Tim-3+ decidual Mφs induced Th2 and Treg bias in decidual CD4+T cells and promoted pregnancy maintenance via CD132[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(5): 454. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04899-2 [16] Ning J, Zhang M, Cui D, et al. The pathologic changes of human placental macrophages in women with hyperglycemia in pregnancy[J]. Placenta, 2022, 130: 60-66. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2022.11.004 [17] Zych M, Kniotek M, Roszczyk A, et al. Surface immune checkpoints as potential biomarkers in physiological pregnancy and recurrent pregnancy loss[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(17): 9378. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179378 [18] Huang B, Zhao Y, Zhou L, et al. PADI6 regulates trophoblast cell migration-invasion through the hippo/YAP1 pathway in hydatidiform moles[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2021, 14: 3489-3500. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S313422 [19] Chen L, Dai F, Huang Y, et al. Mechanisms of YAP1-mediated trophoblast ferroptosis in recurrent pregnancy loss[J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2024, 41(6): 1669-1685. doi: 10.1007/s10815-024-03096-8 [20] Basak T, Ain R. Molecular regulation of trophoblast stem cell self-renewal and giant cell differentiation by the Hippo components YAP and LATS1[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13(1): 189. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02844-w [21] Du X, Liu H, Shi J, et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway regulates decidual macrophage polarization and may participate in preeclampsia[J]. J Reprod Immunol, 2024, 164: 104258. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2024.104258 -





 下载:
下载: