Effects of Sanqi Oral Liquid on Glycolysis,Renal Cell Apoptosis,and Keap1-Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Nephropathy Rats
-
摘要:
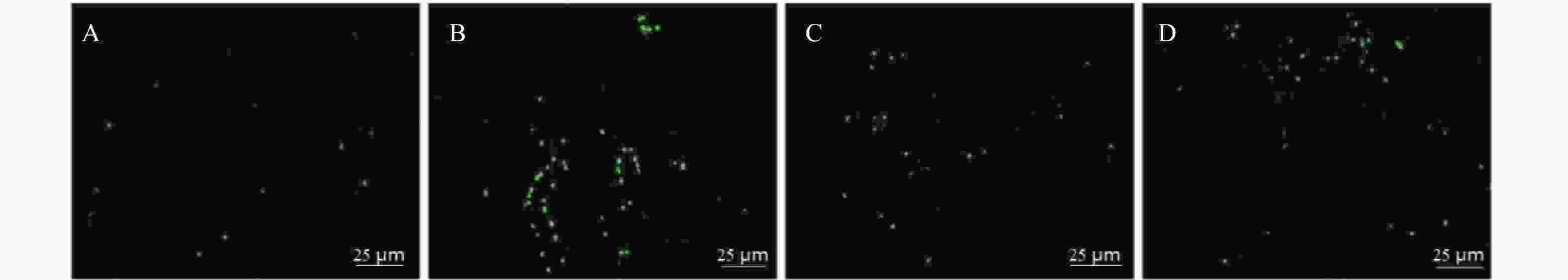
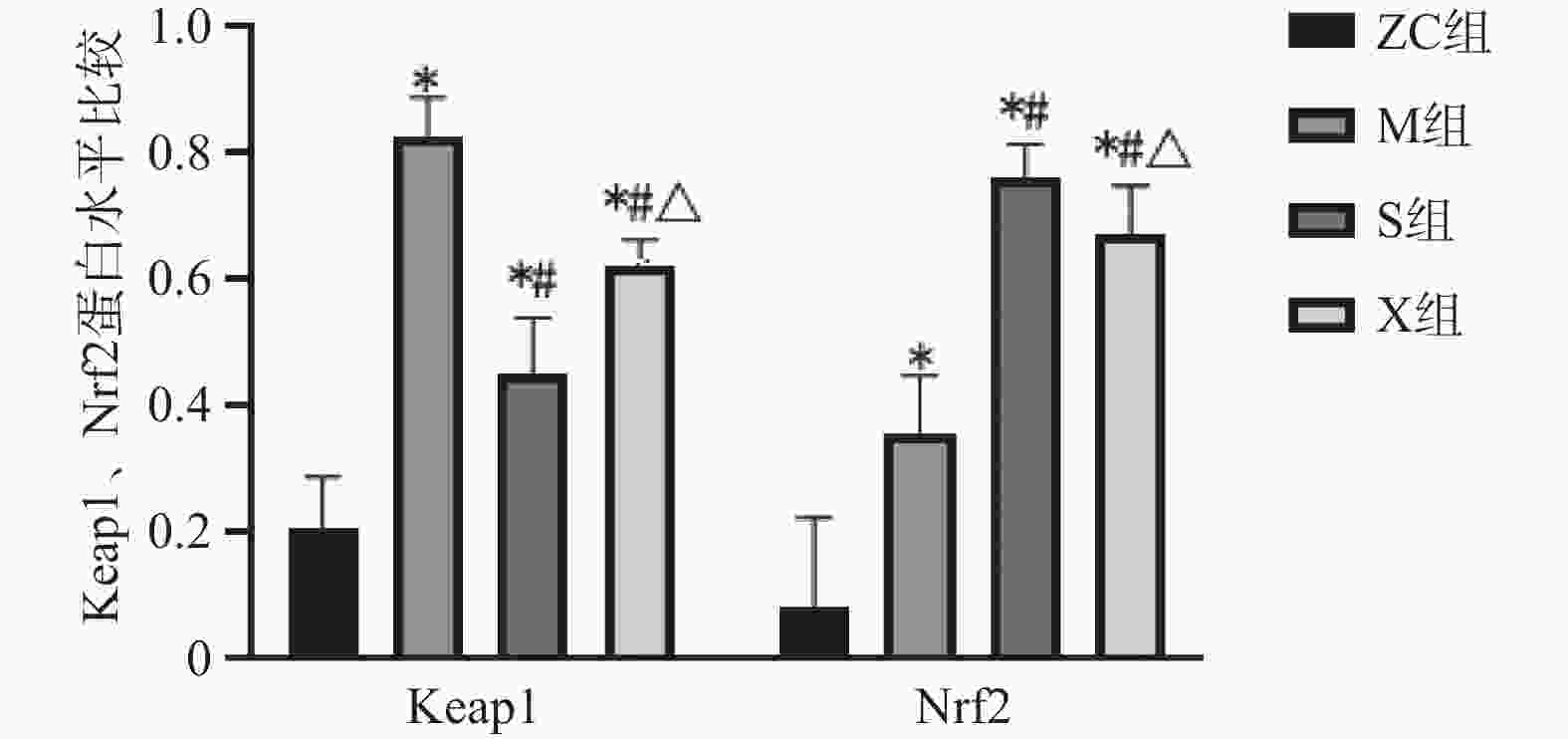
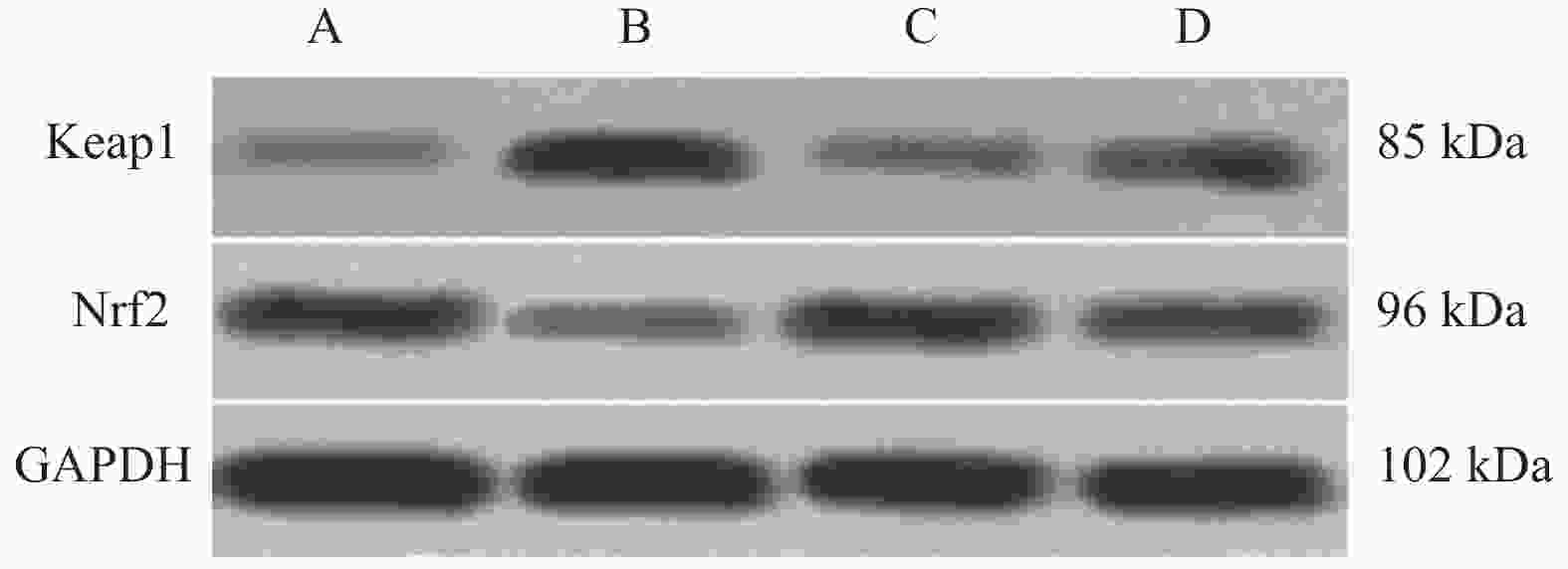
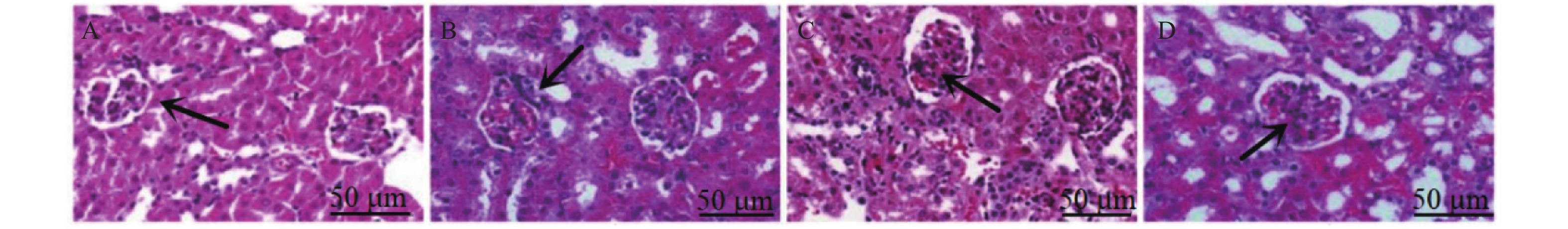
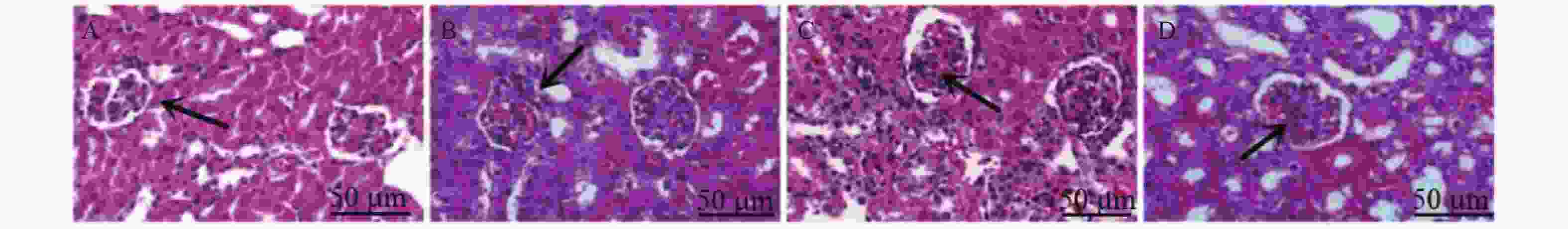
目的 探讨三芪口服液对糖尿病肾病大鼠糖酵解、肾脏细胞凋亡及Keap1-Nrf2 信号通路的影响。 方法 将SPF级雄性SD大鼠40只,分为正常组(ZC组)、模型组(M组)、三芪组(S组)、西药组(X组),10只/组。除ZC组外其余大鼠均建立糖尿病肾病(DN)模型,S组进行三芪口服液灌胃、X组进行缬沙坦灌胃,ZC组与M组灌胃等体积生理盐水。使用尿蛋白试剂盒、全自动生化分析仪测量各组小鼠空腹血糖、尿素氮以及肌酐含量,评估肾脏功能。使用ELISA法测定ATP、乳酸、葡萄糖含量;采用HE染色、TUNEL检测法观察肾组织病理程度及肾脏组织凋亡细胞分布及凋亡率情况;WesternBlot检测Keap1、Nrf2蛋白的表达。 结果 (1)与ZC组相比,M组24 h尿微量蛋白、空腹血糖、尿素氮、血肌酐、乳酸、Keap1蛋白升高(P < 0.05),ATP、葡萄糖、Nrf2蛋白降低(P < 0.05)。与M组相比,S组ATP、葡萄糖、Nrf2蛋白升高(P < 0.05),24 h尿微量蛋白、空腹血糖、尿素氮、血肌酐、乳酸、Keap1蛋白降低(P < 0.05)。与S组相比,X组Keap1蛋白升高、Nrf2蛋白下降(P < 0.05)。S组与X组各生化指标、各糖酵解指标对比无意义;(2)HE染色显示,M组明显肾小球系膜区增宽;S组、X组病变程度减轻,S组最佳;(3)与M组相比,各组肾组织细胞凋亡率下降(P < 0.05),S组最佳;(4)Pearson分析,Keap1与ATP、葡萄糖呈负相关性,与乳酸呈正相关性(P < 0.05) ;Nrf2与ATP、葡萄糖呈正相关性与与乳酸呈负相关性。 结论 三芪口服液可通过调控Keap1-Nrf2信号通路,改善DN大鼠的糖代谢紊乱与能量供应,最终达到延缓肾功能损伤、减少肾脏细胞凋亡的保护作用。 -
关键词:
- 三芪口服液 /
- 糖尿病肾病 /
- 糖酵解 /
- 肾脏细胞凋亡 /
- Keap1-Nrf2 信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of Sanqi oral liquid on glycolysis, renal cell apoptosis and Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy(DN) rats. Methods Forty SPF-grade male SD rats were divided into four groups: normal control group (ZC group), model group (M group), Sanqi group (S group), and Western medicine group (X group), with 10 rats per group. Except for the ZC group, all other rats were subjected to diabetic nephropathy model establishment. The S group received Sanqi oral liquid by gavage, the X group received valsartan by gavage, and the ZC and M groups received equivalent volumes of normal saline by gavage. Fasting blood glucose, blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine levels in each group were measured using urinary protein assay kits and a fully automated biochemical analyzer to assess renal function. ATP, lactate, and glucose levels were determined by ELISA. HE staining and TUNEL detection were used to observe renal tissue pathology and the distribution and apoptosis rate of apoptotic cells in renal tissue. Western blot was performed to detect the expression of Keap1 and Nrf2 proteins. Results Compared with the ZC group, the M group showed elevated 24-hour urinary microalbumin, fasting blood glucose, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, lactatic acid, and Keap1 protein (P < 0.05), while ATP, glucose, and Nrf2 protein were decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the M group, the S group showed elevated ATP, glucose, and Nrf2 protein (P < 0.05), while 24-hour urinary microalbumin, fasting blood glucose, blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine, lactate, and Keap1 protein were decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the S group, the X group showed elevated Keap1 protein and decreased Nrf2 protein (P < 0.05). There were no significant differences between the S and X groups in biochemical and glycolysis parameters. (2) HE staining showed obvious glomerular mesangial expansion in the M group; the S and X groups exhibited reduced pathological changes, with the S group showing the best improvement. (3) Compared with the M group, renal tissue cell apoptosis rates in all treatment groups decreased (P < 0.05), with the S group showing the best effect; (4) Pearson correlation analysis revealed that Keap1 was negatively correlated with ATP and glucose but positively correlated with lactate (P < 0.05); Nrf2 was positively correlated with ATP and glucose but negatively correlated with lactate. Conclusion Sanqi oral liquid can exert protective effects by regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway, improving glucose metabolism disorder and energy supply in DN rats, ultimately delaying renal function damage and reducing renal cell apoptosis. -
表 1 各组大鼠生化指标水平比较($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
Table 1. Comparison of Biochemical Index Levels among rats in each group($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
组别 24 h尿微量蛋白(mg/24 h) 空腹血糖(mmol/L) 尿素氮(mmol/L) 血肌酐(mmol/L) ZC组 17.29 ± 1.21 10.03 ± 4.51 8.29 ± 0.72 26.74 ± 2.76 M组 34.05 ± 3.28 38.16 ± 4.09 26.74 ± 1.56 38.58 ± 2.14 S组 23.42 ± 2.79 24.43 ± 4.45 15.61 ± 1.43 27.92 ± 1.27 X组 21.57 ± 1.62 24.39 ± 3.87 16.72 ± 1.64 26.83 ± 1.59 F 89.690 73.440 299.500 80.480 P <0.001* <0.001* <0.001* <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 2 各组大鼠糖酵解指标水平比较($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
Table 2. Comparison of Glycolytic Index Levels among rats in each group ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
组别 ATP(μmol/g) 乳酸(μmol/g) 葡萄糖(mmol/L) ZC组 1.05 ± 0.14 1.13 ± 0.16 0.98 ± 0.17 M组 0.42 ± 0.09 1.94 ± 0.21 0.46 ± 0.08 S组 0.86 ± 0.12 1.67 ± 0.18 0.64 ± 0.09 X组 0.48 ± 0.07 1.81 ± 0.17 0.55 ± 0.07 F 77.980 38.830 42.750 P <0.001* <0.001* <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 糖酵解与Keap1、Nrf2的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation Analysis of glycolysis with Keap1 and Nrf2
指标 ATP 乳酸 葡萄糖 r P r P r P Keap1 −0.517 <0.001 0.435 0.004 −0.429 0.006 Nrf2 0.423 0.008 −0.323 0.021 0.323 0.019 -
[1] Fang J, Luo C, Zhang D, et al. Correlation between diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 14: 1265711. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1265711 [2] 丁涵露, 罗昊军, 徐丹萍, 等. 重视糖尿病中慢性肾脏病的诊断[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021, 101(10): 687-690. [3] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会微血管并发症学组. 中国糖尿病肾脏疾病防治临床指南[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2019, 11(1): 15-28. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2019.01.004 [4] Li X, Zhang Y, Xing X, et al. Podocyte injury of diabetic nephropathy: Novel mechanism discovery and therapeutic prospects[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 168: 115670. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115670 [5] 张秀华, 曹式丽. 糖尿病肾病的发病机制研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2019, 25(6): 1212-1216. [6] Liu Q J, Yuan W, Yang P, et al. Role of glycolysis in diabetic atherosclerosis[J]. World J Diabetes, 2023, 14(10): 1478-1492. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i10.1478 [7] 乌日娜, 丁海东, 常宏, 等. 萝卜硫素通过调节ALOX5/NF-κB信号通路调控巨噬细胞糖酵解抑制糖尿病肾病进展[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2024, 59(3): 390-397. doi: 10.19405/j.cnki.issn1000-1492.2024.03.004 [8] Li X, Zhang Y, Xing X, et al. Podocyte injury of diabetic nephropathy: Novel mechanism discovery and therapeutic prospects[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 168: 115670. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115670 [9] 陈一洁, 全紫娇, 郑楠, 等. 芹菜素通过激活Keap1-Nrf2-ARE信号通路缓解高糖引起的肾脏细胞损伤和氧化应激[J]. 中国药师, 2024, 27(6): 975-983. doi: 10.12173/j.issn.1008-049X.202310076 [10] 侯海晶, 王立新, 杨霓芝. 三芪口服液对糖尿病肾病大鼠肾小球足细胞及其蛋白表达的影响[J]. 湖北中医杂志, 2012, 34(6): 20-22. [11] 吴平亚, 冯磊. 丹参素对糖尿病肾病大鼠MEK/ERK/Nrf2通路及肾脏纤维化的影响[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2021, 21(10): 1260-1264+1376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-3619.2021.10.006 [12] 方积乾, 陆盈. 现代医学统计学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2002: 690-695. [13] van Raalte D H, Bjornstad P, Cherney D Z I, et al. Combination therapy for kidney disease in people with diabetes mellitus[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2024, 20(7): 433-446. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00827-z [14] 王正, 刘蕊, 王培. 当归补血汤加味联合西医治疗糖尿病肾病的疗效及对足细胞损伤的影响[J]. 川北医学院学报, 2023, 38(5): 676-680. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2023.05.023 [15] 李文歌, 李平, 王明, 等. 糖尿病肾病中西医诊治的思路与方法[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2023, 24(9): 844-846. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2023.09.032 [16] 林嘉荣, 张蕾, 桂定坤, 等. 基于网络药理学三芪口服液治疗糖尿病肾病的作用机制[J]. 中国医药导报, 2019, 16(30): 130-135+190. [17] Zhu D, Ni Y, Chen C, et al. Geniposide ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetic mice by targeting AGEs-RAGE-dependent inflammatory pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156046. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156046 [18] Parwani K, Patel F, Bhagwat P, et al. Swertiamarin mitigates nephropathy in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end products[J]. Arch Physiol Biochem, 2024, 130(2): 136-154. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1987478 [19] 曾贵兴, 林嘉荣, 吴禹池, 等. 基于网络药理学探究三芪口服液治疗慢性肾小球肾炎的效应机制[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2020, 21(5): 397-402. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-587X.2020.05.006 [20] 邓太平. 三芪口服液联合缬沙坦治疗慢性肾小球肾炎的疗效及对肾功能的影响[J]. 临床合理用药, 2024, 17(1): 97-100. [21] Pająk B, Zieliński R, Priebe W. The impact of glycolysis and its inhibitors on the immune response to inflammation and autoimmunity[J]. Molecules, 2024, 29(6): 1298. doi: 10.3390/molecules29061298 [22] 邓文娟. 黄芪汤通过AMPK/Nrf2信号通路抑制氧化应激改善C57小鼠糖尿病肾病足细胞损伤[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2019. [23] 刘唐威, 伍伟锋, 冯震博, 等. 黄芪对小鼠病毒性心肌炎细胞凋亡及bcl-2/bax基因转录的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2003, 20(6): 823-825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-930X.2003.06.001 [24] 桂定坤, 汪年松. 黄芪甲苷肾保护作用机制[J]. 中华肾病研究电子杂志, 2013, 2(4): 39-41. [25] 徐莉莉, 戴世杰, 项晓骏. 三七总皂苷对糖尿病肾病小鼠TGF-β1及自噬相关蛋白Bax、Bcl-2、LC3I/LC3II表达的影响[J]. 中国中医药科技, 2022, 29(4): 560-565. [26] Chen J, Wang Q, Li R, et al. The role of Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway during the progress and therapy of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Life Sci, 2024, 338: 122386. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122386 [27] Yu Y, Li M, Lai W, et al. Shengqing Jiangzhuo capsule ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by improving Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2024, 76(9): 1149-1159. doi: 10.1093/jpp/rgae095 -





 下载:
下载: