2024 Vol. 45, No. 11
2024, 45(11): 1-8.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241122
Abstract:
Food safety is a major public health problem in the world. Foodborne pathogens are the main factors threatening human health and food safety. Rapid and accurate detection of foodborne pathogens is of great significance to ensure food safety and prevent foodborne diseases. Traditional detection methods of pathogenic microorganisms are cumbersome and time-consuming, and can not detect pathogens in food in time. With the rapid development of biotechnology, its application in the detection of foodborne pathogens is more and more extensive, which provides a strong technical support for the prevention of the occurrence and spread of foodborne diseases. In this paper, the harm of common foodborne pathogens and the principle, application, advantages and disadvantages of rapid detection methods were reviewed, in order to provide reference for food safety risk assessment and foodborne disease monitoring.
Food safety is a major public health problem in the world. Foodborne pathogens are the main factors threatening human health and food safety. Rapid and accurate detection of foodborne pathogens is of great significance to ensure food safety and prevent foodborne diseases. Traditional detection methods of pathogenic microorganisms are cumbersome and time-consuming, and can not detect pathogens in food in time. With the rapid development of biotechnology, its application in the detection of foodborne pathogens is more and more extensive, which provides a strong technical support for the prevention of the occurrence and spread of foodborne diseases. In this paper, the harm of common foodborne pathogens and the principle, application, advantages and disadvantages of rapid detection methods were reviewed, in order to provide reference for food safety risk assessment and foodborne disease monitoring.
Expression Analysis of WDR36 and WRN Genes of Borrelia Burgdorferi in HMC3 Cell Line Infection Model
2024, 45(11): 9-15.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241102
Abstract:
Objective The aim is to explore the molecular mechanism of neurological Lyme disease, particularly by identifying two differentially expressed genes WDR36 and WRN associated with Burkholderia infection through transcriptome analysis. Secondly, to verify their association in the pathogenesis of Borrelia burgdorferi infection and demonstrate their potential therapeutic targets. Methods By establishing a non-human primate model and utilizing high-throughput sequencing technology to obtain transcriptomic data. Through GO enrichment analysis, two differentially expressed genes with research value, WDR36 and WRN, were identified. To further validate the role of these two genes in Bb infection of Lyme disease, the HMC3 cell line of human glial cells was used as a model. The experimental group cells received Bb inoculation with different MOI (1 and 10), and cell suspensions were collected at 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h after infection. Extract RNA using the triazol method and determine the relative mRNA expression levels of WDR36 and WRN genes using qPCR. Result It was found that Bb MOI=1 was the appropriate infection concentration in HMC3 cells infected with Bb. The results showed that the expression level of WDR36 was significantly upregulated at 24 h and 12 h, and the gene expression content of the 6 h PBS group increased but not significantly compared to the experimental group. The increase was significant at 12 h and 24 h, and there was a significant statistical difference with P < 0.01. The expression level of WRN was significantly upregulated at 24 h and 12 h, and the gene expression content of the 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h experimental groups showed an upward trend compared to their PBS group, and there was a significant statistical difference with P < 0.01. Conclusion The upregulation of WDR36 and WRN may be associated with the neuropathological processes of LNB. These findings provide a new perspective for further studying the molecular mechanisms of LNB and may provide potential molecular targets for developing novel treatment strategies for Bb infection.
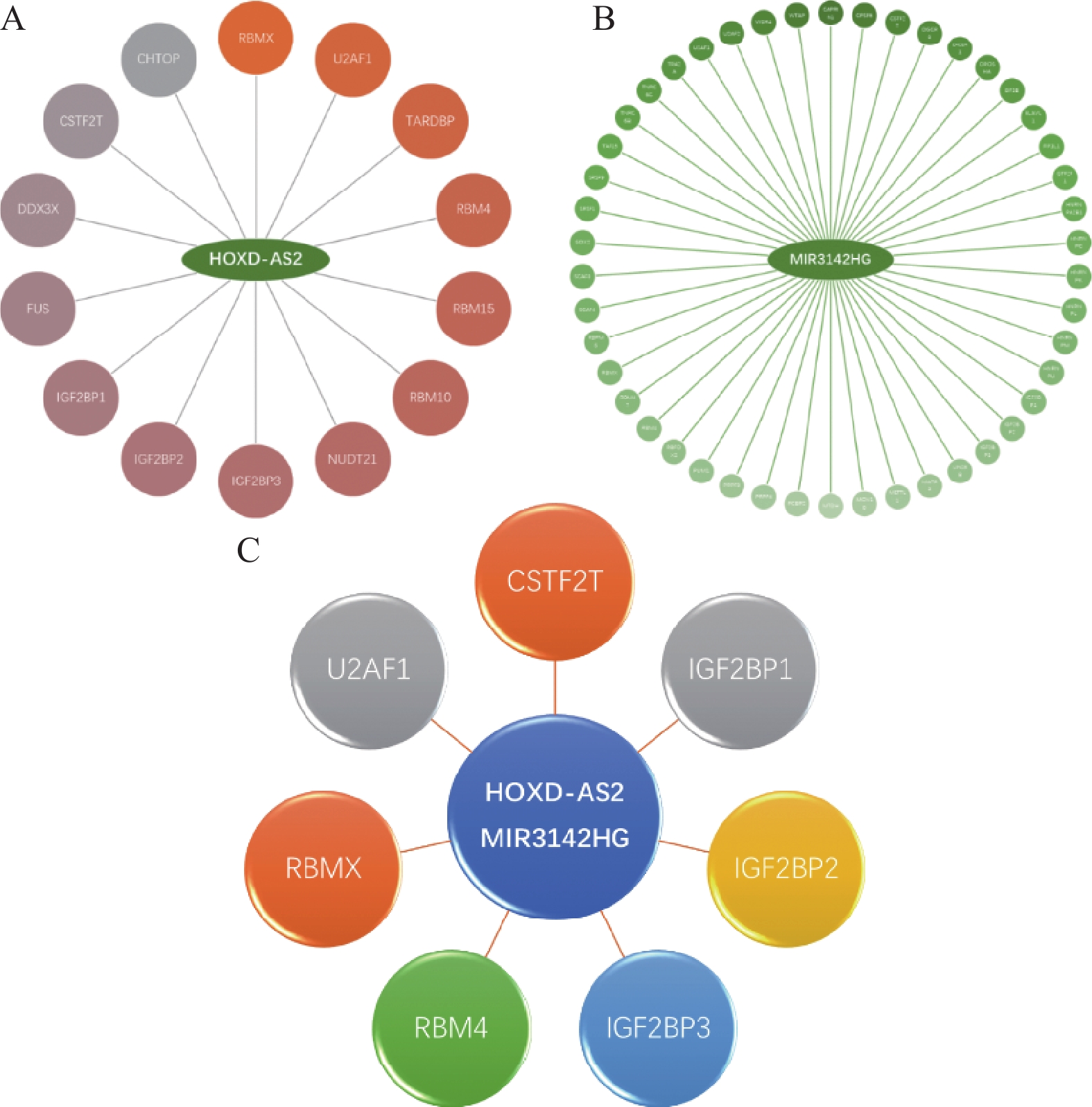
The Association of HOXD-AS2 and MIR3142HG Gene Polymorphisms with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
2024, 45(11): 16-21.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241103
Abstract:
Objective To explore the association of HOXD-AS2 and MIR3142HG gene polymorphism with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Methods Two single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) located in HOXD-AS2 (rs1348808) and located in MIR3142HG (rs2431099) were selected using bioinformatics tools. The two candidate SNPs were genotyped in 976 healthy individuals and 419 patients with CIN using the TaqMan probe method for genotyping, and the association with CIN were analyzed. Results rs1348808 C allele might be the protective factor for CIN3 as well as the progression from CIN2 to CIN3 (OR = 0.77, 95%CI: 0.63~0.94; OR = 0.57, 95%CI: 0.37~0.90). Similarly, rs2431099 A allele might be the protective factor of CIN2 (OR = 0.50, 95%CI: 0.31~0.80). Conclusion HOXD-AS2 and MIR3142HG gene polymorphisms might be associated with CIN.
2024, 45(11): 22-30.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241104
Abstract:
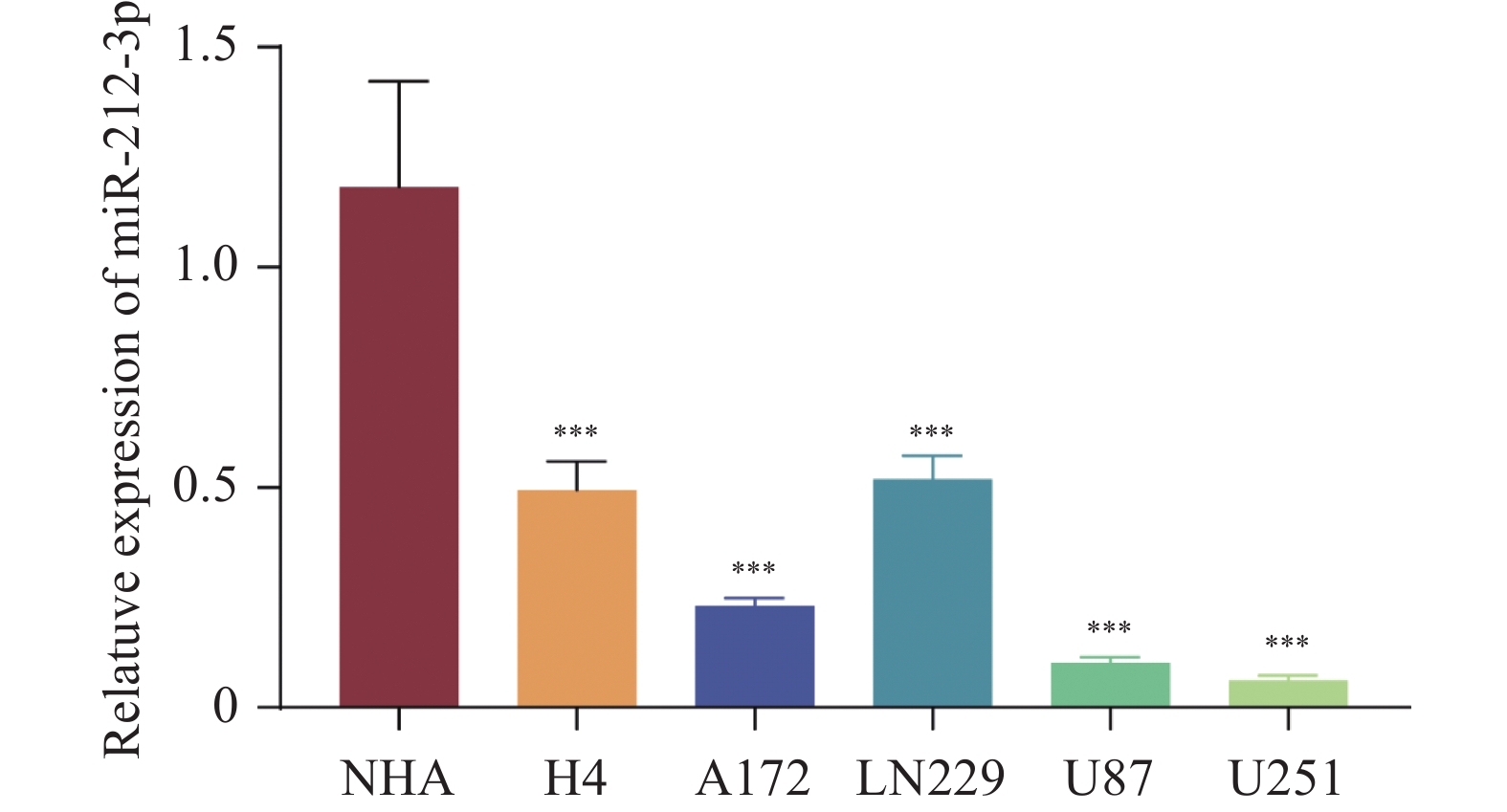
Objective To explore the molecular mechanism of miR-212-3p in glioma cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Methods The expression of miR-212-3p and NAP1L1 were detected by RT-qPCR in glioma cells. NC mimic, miR-212-3p mimic, oe-NC and oe-NAP1L1 were built and transfected in cells. CCK-8, Transwell and wound healing assay were used to evaluate the cell biological behaviour. Western blot was used to detect the expression of EMT-related biomarkers. The relationship between miR-212-3p and NAP1L1 was confirmed by the dual-luciferase reporter gene and AgO2-RIP assay. Results miR-212-3p was lowly expressed in glioma cells (P <0.0001 ). miR-212-3p mimic significantly inhibited the glioma cell proliferation (P <0.0001 ), invasion (P =0.0011 ) and migration (P <0.0001 ), and reduced the expression of EMT-related biomarkers N-cadherin (P =0.000861 ) and Vimentin (P =0.007430 ), while upregulating the expression of E-cadherin (P <0.0001 ). miR-212-3p targeted and negatively regulated the NAP1L1 expression. Overexpression of NAP1L1 reversed the inhibitory effects of miR-212-3p on glioma cell proliferation (P <0.0001 ), migration (P <0.0001 ), and EMT (P <0.0001 ). Conclusion miR-212-3p inhibits the glioma cell proliferation, migration and EMT by targeting the negative regulation of NAP1L1 expression.
2024, 45(11): 31-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241105
Abstract:
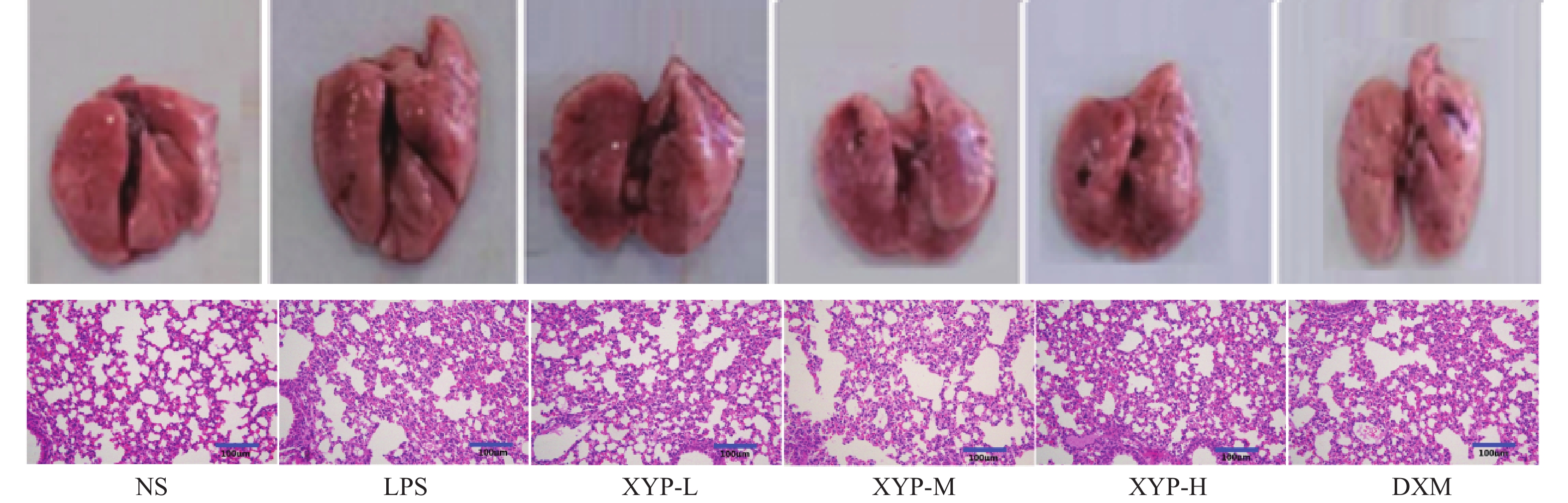
Objective To explore the protective effects of Xiyanping injection against lipopolysaccharide (lipopolysaccharide, LPS)-induced acute lung injury (acute lung injury, ALI)in mice, and preliminarily investigate its mechanism. Methods The mice were randomly divided into the normal control group (NS), ALI model group (LPS), Xiyanping injection low dosage group (XYP-L, 18.96 mg/kg), medium dosage group (XYP-M, 37.92 mg/kg), and high dosage group (XYP-H, 75.83 mg/kg) and dexamethasone positive drug group (DXM, 3.03 mg/kg), with 20 in each group. Each group was injected intraperitoneally with the corresponding drug, once a day at the same time for 3 consecutive days. the NS and LPS groups were given the same 0.9% sodium chloride injection volume. Except for NS group, LPS was instilled into the trachea to induce the acute lung injury in mice 1 hour after the last administration of the above drugs. The lung tissue samples and broncho alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples were collected 24 hours after the intratracheal instillation of LPS. The lung coefficient was calculated. The pathological and morphological changes of lung tissue were observed macroscopically and microscopially. The total cell count in BALF was calculated under the microscope. The concentration of total protein in BALF was measured using the BCA (bicin-choninic acid) method. The content of inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α), interleukin-1β(IL-1β), and interleukin-8 (IL-8)in BALF was detected using the ELISA (enzyme linked immunosorbent assay) method. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in mouse lung tissue were measured using MDA and SOD assay kits. Results Compared with the NS group, the LPS group showed severe pathological damage in the lung tissue, increased lung coefficient, total cell count, total protein concentration, and elevated levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8 in BALF (P < 0.01). The LPS group also exhibited the higher levels of MDA in the lung tissue (P < 0.001), decreased SOD activity (P < 0.001). The treatment groups showed the improvements in the lung tissue damage compared to the LPS group. The treatment groups exhibited the decreased lung coefficient, total cell count, total protein concentration, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-8 levels in BALF (P < 0.05), reduced MDA content in lung tissue (P < 0.001), and increased SOD activity (P < 0.05). Conclusions Xiyanping injection has a certain protective effect on LPS-induced ALI in mice, and its mechanism is related to anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. It can alleviate the lung inflammation through inhibiting the release of downstream inflammatory factors and oxidative stress in the lung tissue caused by LPS through antioxidant effects.
2024, 45(11): 38-45.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241106
Abstract:
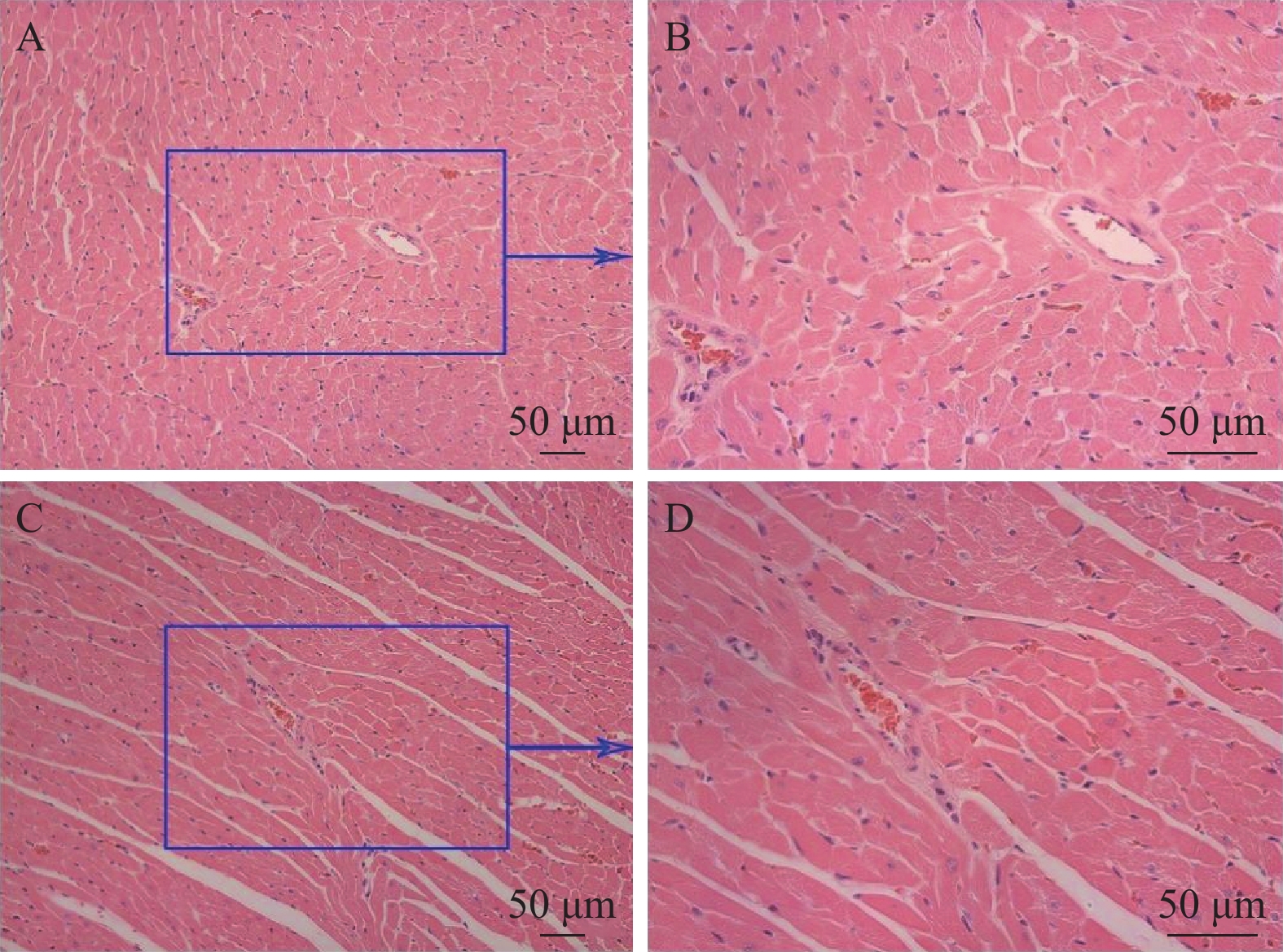
Objective To establish in vivo rat ischemic myocardial injury and in vitro cardiac microvascular endothelial cell (CMEC) hypoxia models so as to investigate the structural and biological changes and probe the angiogenesis basis of coronary microcirculation. Methods In vivo rat myocardial ischemia model was established using the 1/3 ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery and myocardial tissue structure and ultrastructure were detected using HE, Masson staining, and transmission electron microscopy, respectively. In vitro time-gradient hypoxia model of rat CMECs (hypoxia times set at 0 h, 4 h, 8 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, 72 h) was established using a hypoxic incubator. An inverted phase-contrast microscope was used to observe the morphological and growth characteristics of CMECs. The proliferation rate was determined by CCK-8 method, and the survival rate was determined by counting method. The expression of inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α) and angiogenic factors (VEGF, Ang-2) were detected using ELISA method. Results After 72 hours of coronary artery ligation, HE and MASS staining indicated the successful establishment of a rat model of myocardial ischemia and hypoxia. The transmission electron microscopy revealed the ischemic and hypoxic changes in the ultrastructure of cells. . CMECs exhibited the distinct morphological characteristics and adhered to the surface. With the prolonged hypoxia time, the proliferation rate significantly decreased after 48 h (P = 0.0426 ), and the survival rate significantly decreased after 24 h (72.8%). Long-term hypoxia led to significantly higher release levels of IL-1β (24~72 h, P = 0.0007 , 0.0007 , 0.001), IL-6 (24~72 h, P = 0.0015 , 0.0005 , 0.0007 ), and TNF-α (24~72 h, P = 0.0015 , 0.0063 , 0.0008 respectively) compared to short-term hypoxia IL-1β (4~12 h, P = 0.007, 0.0034 , 0.0009 respectively), IL-6 (4~12 h, P = 0.0026 , 0.0013 , 0.0045 respectively), and TNF-α (12 h, P = 0.0087 ). In addition, the expression of angiogenic factor VEGF began to increase 8 hours after hypoxia (P < 0.0001 ), decreased at 12-24 hours (P < 0.0001 respectively), and then increased rapidly (P < 0.01); The expression of Ang-2 decreased from 4-12 hours (P < 0.05), and gradually increased from 24 hours (P < 0.01). Conclusions Myocardial tissues and CMECs exhibit the different biological changes at different ischemia-hypoxia time points with inflammatory reactions beginning in the early stages and angiogenesis reactions occurring in the late stages. These findings contribute to elucidating the key cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying ischemic myocardial injury.
2024, 45(11): 46-51.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241107
Abstract:
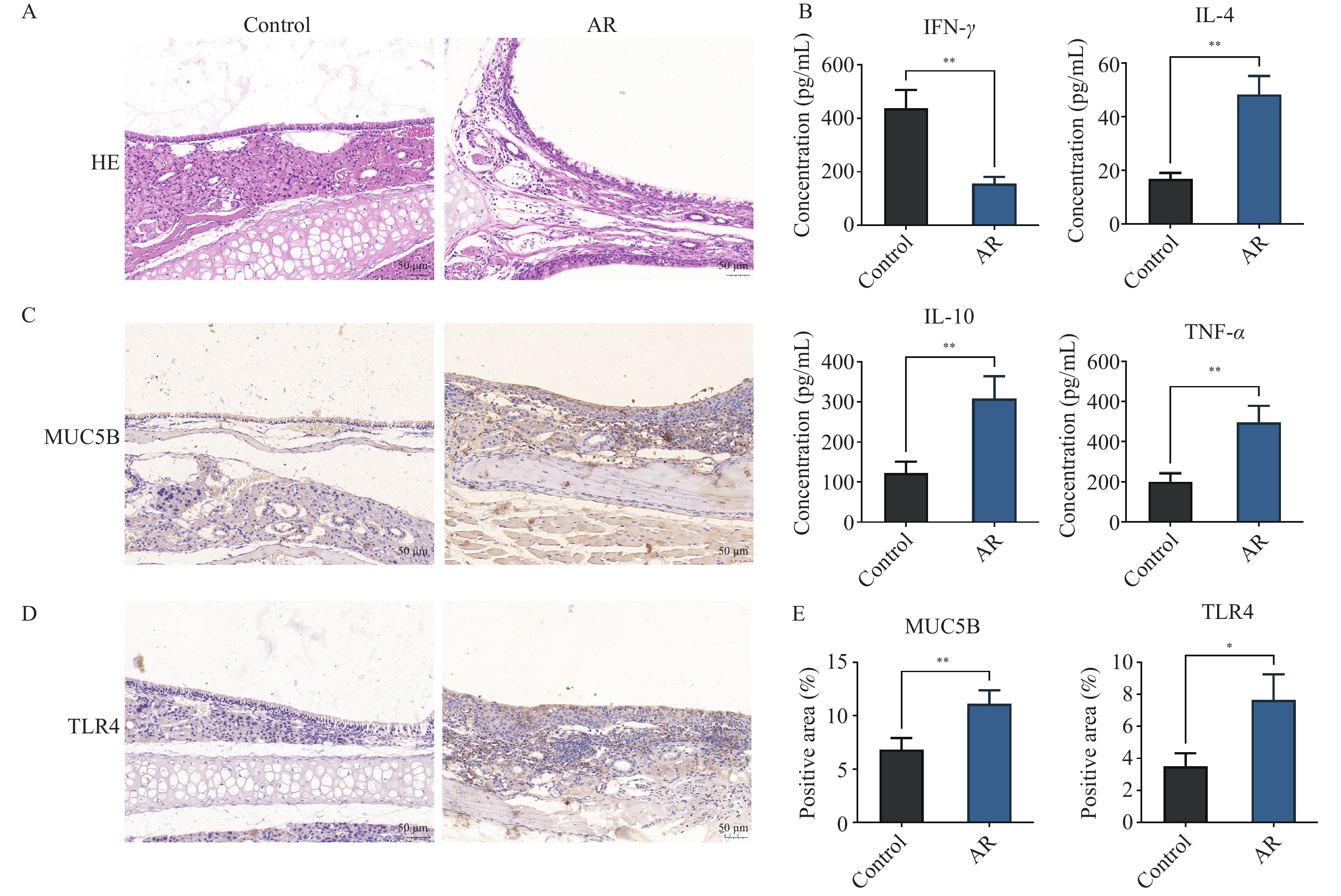
Objective To explore the regulatory mechanism of TLR4/NF-κB/MUC5B in allergic rhinitis. Methods A mouse model of allergic rhinitis was established to observe the changes in pathological characteristics of the model and to detect the expression of TLR4 and MUC5B. By reducing the expression of TLR4 by intranasal administration, the histopathological changes of TLR4, the expression of MUC5B and the concentration of inflammatory factors were observed. An in vitro cell model was established to detect the expression of MUC5B as well as to observe the changes of NF-κB and phosphorylated NF-κB (p-NF-κB) after knockdown of TLR4 by cell transfection. Results (1) TLR4 and MUC5B were highly expressed in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis (P < 0.05); (2) Lowering the expression of TLR4 could reduce the expression of MUC5B and inflammatory factors, as well as alleviated allergic rhinitis (P < 0.05); (3) In vitro, knockdown of TLR4 could reduce the expression of p-NF-κB and MUC5B (P < 0.05). Conclusion The regulatory mechanism of TLR4/NF-κB/ MUC5B in allergic rhinitis provides the new ideas for the treatment of allergic rhinitis.
2024, 45(11): 52-58.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241108
Abstract:
Objective The purpose of the study is to understand the exposure of rural women to pyrethroid pesticides during each pregnancy stage. Methods From December 2014 to December 2016, 216 pregnant and postpartum women with the average age between 24.81±5.256 years old were recruited from 2 townships in Xuanwei rural area. Results In this study, the majority of pregnant women were still engaged in farming during pregnancy and self-reported no active exposure to pesticides during pregnancy. The self-reporting exposure rates among the three trimesters were no more than 1.4%. However, Laboratory testing found that the exposure rates of pyrethroid pesticides among the three trimester of pregnancy were exceed 90.0%, and the total of 67.1% of women exposed to pyrethroid pesticides in every trimester of gestation. Women exposure rates of pyrethroid by laboratory detection were significantly higher than those by questionnaire. In the first, the second and the third trimester, the medians of urine pyrethroid metabolites 3-PBA were 3.61 ng/ml、3.60 ng/ml、3.57 ng/ml, respectively, and the medians of urine cis/trans-DCCA, pyrethroid metabolites, distributed 49.10 ng/ml、45.45 ng/ml、47.45 ng/ml, respectively. The pregnancy exposure to pyrethroid pesticides was in the middle level of domestic research, but exceeded the level of most foreign reports. The result of women who exposed to pyrethroid pesticides in each trimester of gestation by Repeated Measures Define Factor(s) showed that address, education and family income had interaction with the three trimester pyrethroid metabolites amount (F gestation×address=3.183, F gestation×education=2.731, P<0.05), and the amount by laboratory test in the first trimester and the second trimester were higher than that in the third trimester(LSD, P < 0.05). Chi-square test indicated that there were no significant differences in the amounts of pyrethroid exposure among women age groups, between the minority and the majority, among different education levels, between on work and stopping work, between the two towns, across different family income and among the four seasons. Conclusion Rural pregnancy women are with low awareness of pesticide in Xuan wei. The vast majority of pregnancy women are exposed to pyrethroid pesticides in varying degrees and in the middle level of domestic research. Pyrethroid exposure in the third trimester is likely less serious than the other trimesters. The address, education and family income affect the pyrethroid exposure level. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen health education and improve the health consciousness of pregnant women to reduce pyrethroids pesticides exposure as much as possible in rural areas.
2024, 45(11): 59-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241109
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the research hotspots and frontiers of symptom clusters of hepatocarcinoma patients. Methods The relevant literatures on liver cancer symptom cluster research collected by CNKI since 1987 were searched, and a total of 100 relevant articles were visually analyzed by using CiteSpace software, including the main authors, publishers, keyword co-occurrence and clustering. Results A total of 100 literatures were included. The number of publications in this field is generally on the rise, reaching its peak with 14 articles published in 2020. The main author group is composed of Invalid, and there is no cooperation network between various research institutions, and it is an independent research branch. Among the top 20 keywords, quality of life and qualitative research were more frequently mentioned. Keywords burst analysis from 2021 to 2023, qualitative research has the highest strength at 1.45. A growing focus on the population segmentation and self-management both domestically and internationally . Conclusion The main research hotspots of this topic have changed with the passage of time, and quality of life, symptom clusters, population segmentation, self-management, and evidence-based nursing are becoming cutting-edge research hotspots. However, at present, there is still a lack of strong evidence for the intervention research on management strategies, and it is necessary to further explore the relevant biological mechanisms, and it is urgent to carry out multi-center and multidisciplinary exchanges and cooperation in clinical nursing, in order to optimize more popular research conclusions and symptom cluster management programs.
2024, 45(11): 67-72.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241110
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the factors influencing physician job burnout. Methods A multistage stratified random sampling method was adopted to select a total of 1190 physicians from 10 public general hospitals above the second level in 5 regions of Yunnan Province. Self-filled questionnaire and MBI-GS were used for the investigation, and a multi-level regression model was used to fit the relationship between the physician burnout score and the related influencing factors. Results The incidence of physician burnout in the investigated area was 45.3%.The scores of the emotional exhaustion, work attitude and sense of achievement were lower than the norm. The two-level model analysis found that the physician job burnout scores were clustered at the department level, and the intra-group correlation coefficient (ICC = 0.1181 ). The influencing factors included working hours per week, working pressure, occupational satisfaction, sleep, health status and leisure time. Conclusion Physician job burnout is affected by many factors and should be intervened. Because of the aggregation of physician burnout at the department level, it is also of practical significance to eliminate adverse factors from within the department.
2024, 45(11): 73-80.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241111
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the current situation of medical cooperation and nurses' work engagement of dental specialty nurses in Yunnan province, and to explore the impact of medical cooperation on the work engagement of dental specialty nurses. Methods A total of 251 dental nurses in Yunnan province were investigated by convenience sampling from January to March 2024 with the general information questionnaire, the medical cooperation scale (NPCS) and the Utrecht work engagement scale (UWES). Results The total score of the medical cooperation scale for dental specialty nurses in Yunnan province was (85.09 ± 15.14), the total average score of each item was (4.052 ± 0.02), the total average score of the communication dimension of patient information was (4.16 ± 0.66), the decision dimension of joint participation in the treatment or nursing was (3.97 ± 0.83), and the relationship dimension between nurses and doctors was (4.05 ± 0.91). The scores decreased in order of the communication of patient information, the relationship between nurses and doctors, and the decision dimension of joint participation in the treatment or nursing. The total score of nurses' work engagement scale was (50.75 ± 15.69), and the total average score was (3.906 ± 0.123). The average score of the dedication dimension was (4.04 ± 1.30), the average score of focus dimension was (3.89 ± 1.22), and the average score of the vitality dimension was (3.83 ± 1.21). The score decreased in turn from the dimension of dedication, focus and vitality. Pearson correlation analysis showed that medical cooperation was moderately positively correlated with the work engagement of dental specialty nurses (r = 0.574, P < 0.001), and all the dimensions of the scale were moderately and positively correlated with the work engagement (r = 0.502-0.574, P < 0.001). Single factor analysis showed that gender, position and income had an impact on the work engagement score of dental specialty nurses. Multiple linear regression analysis showed that nurses with more than 5 years of service scored significantly higher in medical cooperation than those with less than 5 years of service (P < 0.05), the monthly income of nurses positively affected the work engagement score (P < 0.05), and the communication of patient information between doctors and nurses had a significant positive impact on the work engagement score (P < 0.05). Conclusion The medical cooperation of dental specialty nurses in Yunnan province is at a high level, and the work engagement is at a medium level. The higher the level of medical cooperation of dental specialty nurses, the greater the degree of the work engagement. Oral specialty nursing managers should consider various measures that can promote the medical cooperation, build a united and harmonious medical cooperation relationship in their work, pay attention to the factors that affect nurses' work engagement, and take corresponding measures to promote the level of work engagement of oral specialist nurses and improve the quality of oral medical care service.
2024, 45(11): 81-86.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241112
Abstract:
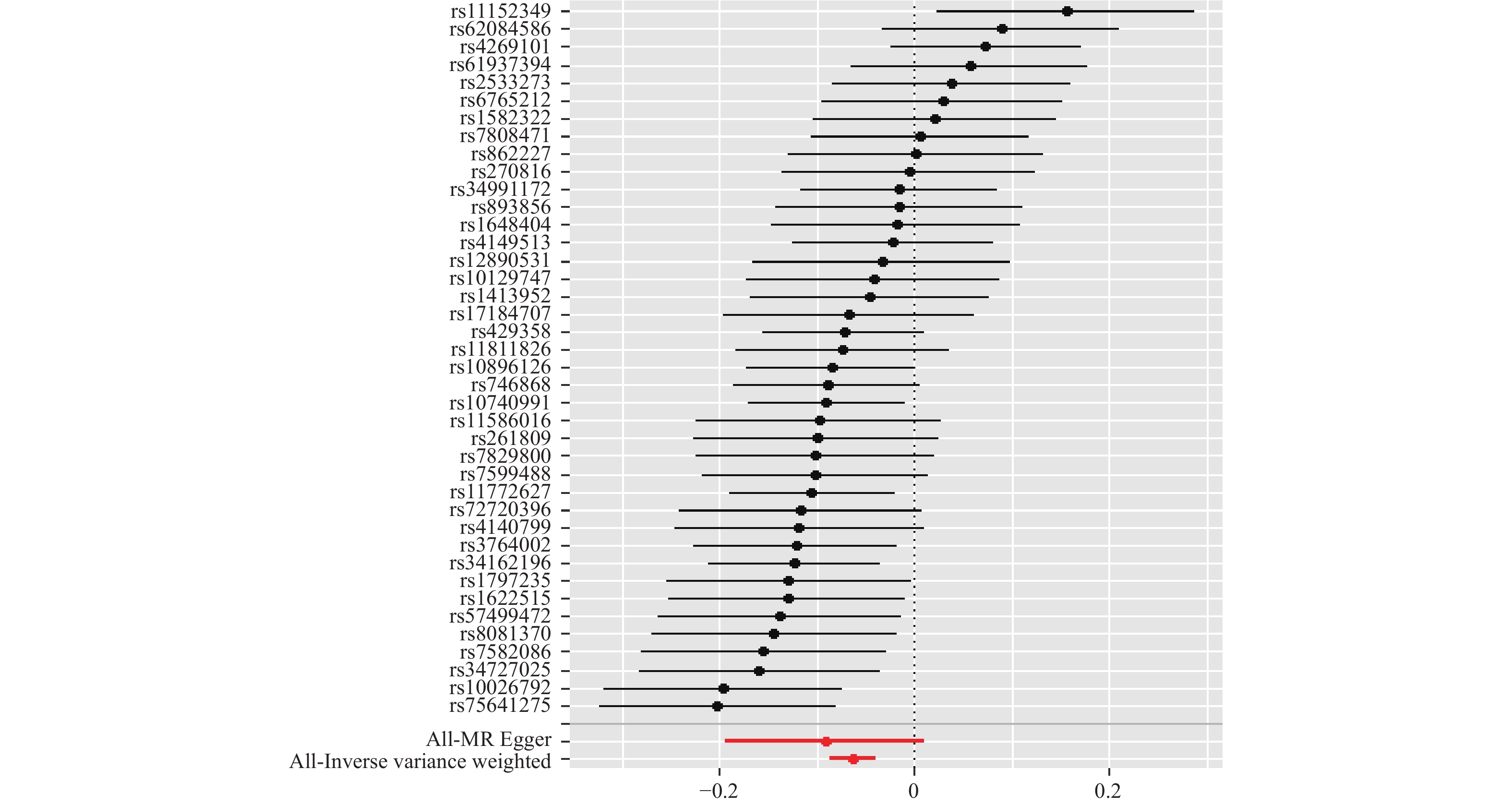
Objective To explore the causal relationship between nut intake and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by two-sample Mendelian randomization method. Methods SNP loci closely related to nut intake was extracted from the summarized large sample open GWAS database as instrumental variables, and Mendelian randomization analysis was performed using MR-Egger regression, weighted median, inverse variance weighting, Simple mode and Weighted mode respectively. OR value and 95%CI were used to evaluate whether there was a causal relationship between nut intake and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The mr_pleiotropy_test method was used to test the level of pleiotropy, and the leave-one-out method was used for sensitivity analysis. Results A total of 49 SNPS were extracted from the ukb-b-16576 data set as instrumental variables. The OR values and 95% confidence intervals were calculated by MR-Egger regression, weighted median, inverse variance weighting method, Simple mode, and Weighted mode, respectively [0.91, 95%CI (0.82~1.01), P = 0.084], [0.92, 95%CI (0.89~0.95), P = 0.001], [0.94, 95%CI (0.92~0.96), P = 0.001], [0.91, 95%CI (0.85~0.95), P = 0.001], [0.91, 95%CI (0.86~0.96), P = 0.001]. All b values were less than 0. Due to the heterogeneity (Q = 67.36, P = 0.012 ), the random effect IVW model was concerned. The mr_pleiotropy_test showed that the MR-Egger intercept was 3.50E-04, the intercept was close to 0, P = 0.591, and the selected instrumental variables did not have horizontal pleiotropy. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis did not find SNP loci that had a significant effect on the results, suggesting that the results were stable and reliable. Conclusion The two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis shows a negative causal relationship between nut intake and the risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, but larger sample size and data of people with different ethnic backgrounds are needed for further verification.
2024, 45(11): 87-94.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241113
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the risk factors of EB virus (EBV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections in patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and their relationship with drug efficacy. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on clinical data from 280 patients diagnosed with UC at the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University between January 1, 2018, and December 31, 2022. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to identify the factors associated with EBV infections and univariate analyses was performed to identify the factors associated with CMV infections. Results Univariate analysis indicated that older age, severe disease activity, elevated C-reactive protein(CRP), increased platelet count(PLT), erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR), fibrin degradation products(FDP), D-dimer(D-D), fibrinogen(FIB), calprotectin(CAL), higher Mayo endoscopic scores (MES)index, decreased albumin(ALB), and corticosteroid use were linked to EBV infection (The average p value was < 0.05). For CMV infection, significant factors included older age, severe disease activity, decreased hemoglobin (HB), ALB, elevated CRP (The average p value was < 0.05). Multivariate analysis confirmed that older age and severe disease activity were risk factors for EBV infection (The average p value was < 0.05). EBV-infected patients showed a higher likelihood of steroid resistance, ineffective immunosuppressants, and loss of response to biological therapies, while CMV-infected patients also faced challenges with the treatment response. Conclusion Older age and severe disease activity are the significant risk factors for EBV infection in UC patients. UC patients infected with EBV and CMV are more prone to immune suppressant ineffectiveness and biological agent failure to respond. People infected with EBV are also prone to hormone resistance.
2024, 45(11): 95-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241114
Abstract:
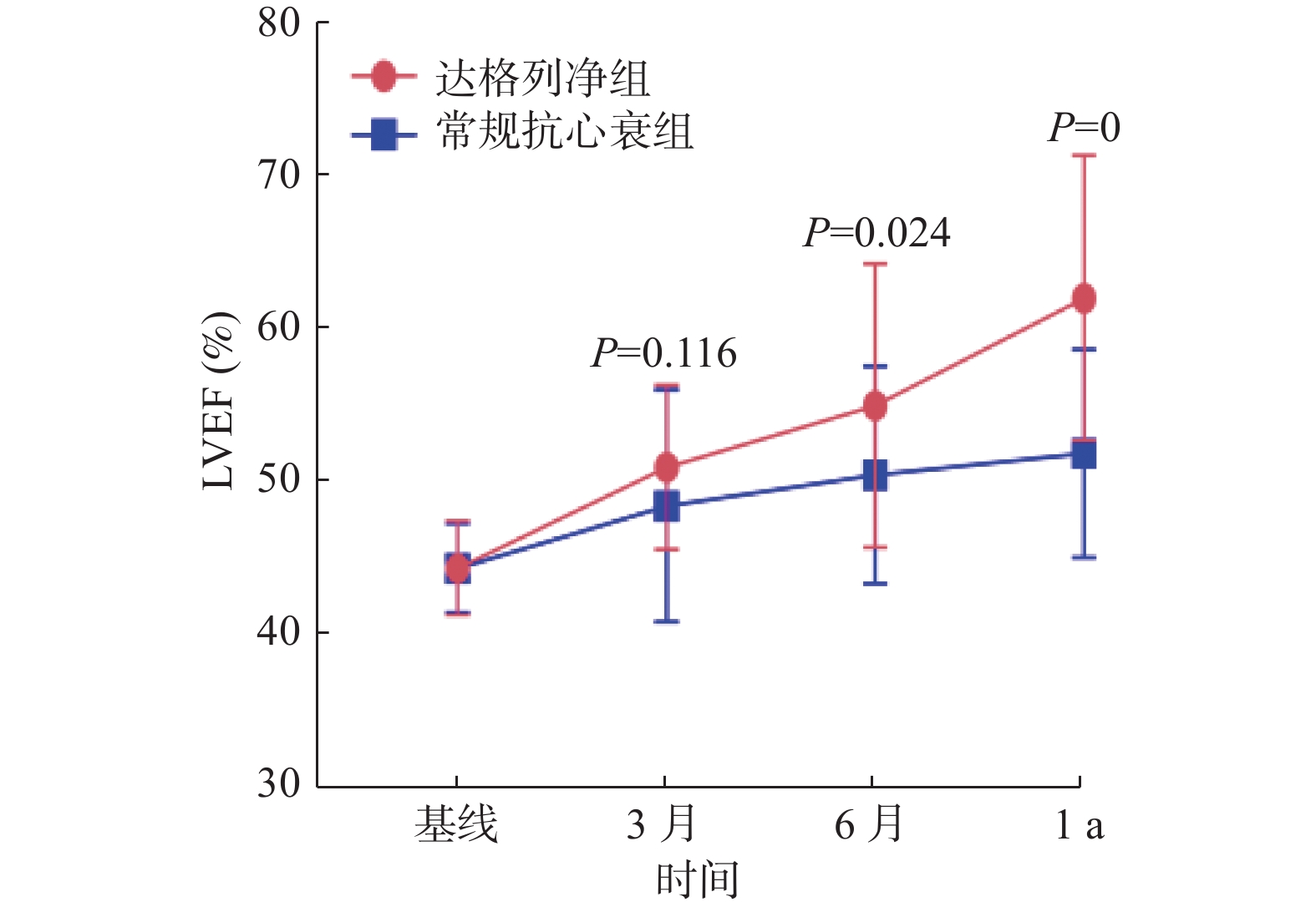
Objective To investigate the effects of dapagliflozin on cardiac structure and function in patients with heart failure due to mildly reduced ejection fraction. Methods Patients diagnosed with heart failure due to mildly reduced ejection fraction in the outpatient department and inpatient department of the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from November 1, 2021 to December 31, 2022 were selected and divided into the conventional anti-heart failure group and dapagliflozin group according to whether they were taking dapagliflozin or not. The conventional anti-heart failure group received the conventional anti-heart failure treatment (loop diuretics, ACEI/ARB/ARNI, spironolactone, β-blocker), and the dapagliflozin group was given oral dapagliflozin on the basis of conventional anti-heart failure treatment. The improvement of cardiac function, LVEDD (left ventricular end-diastolic diameter), LVESD (left ventricular end-systolic diameter), LVEF (left ventricular ejection fraction), IVST (ventricular septum thickness), LVPWT (left ventricular posterior wall thickness), LAD (left atrial diameter) and the incidence of adverse events after the treatment within 3 months, 6 months and 1 year were observed in both groups. Results 33 patients in the dapagliflozin group and 37 patients in the conventional anti-heart failure group completed the follow-up. (1)After 3 months, 6 months and 1 year of thefollow-up, the NYNH cardiac function grade of the two groups was improved compared with that before the treatment and the total effective rate of the dapagliflozin group was significantly higher than that of the conventional anti-heart failure group(P < 0.05).(2)LVEF increased compared with the baseline in both groups, while LVEDD, LVESD, LAD, IVST and LVPWT decreased compared with the baseline(P < 0.05).(3)After 3 months of treatment , there was no significant difference between LVEF, LVEDD, LVESD, LAD and IVST at 3 months(P > 0.05)and the decrease of LVPWT in dapagliflozin group was significantly higher than that in conventional anti-heart failure group. (4)After 6 months and 1 year of the treatment, the increase of LVEF and the decrease of LAD, IVST and LVPWT in dapagliflozin group were significantly higher than those in conventional anti-heart failure group (P < 0.05).There was no significant difference in the decrease degree of LVEDD and LVESD between the two groups at 6 months after the treatment(P > 0.05) and the difference was significant at 1 year after the treatment(P < 0.05). Conclusion On the basis of standardized anti-heart failure drug therapy, the combination of dapagliflozin can further improve the cardiac remodeling and function of patients with heart failure due to mildly reduced ejection fraction.
2024, 45(11): 103-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241128
Abstract:
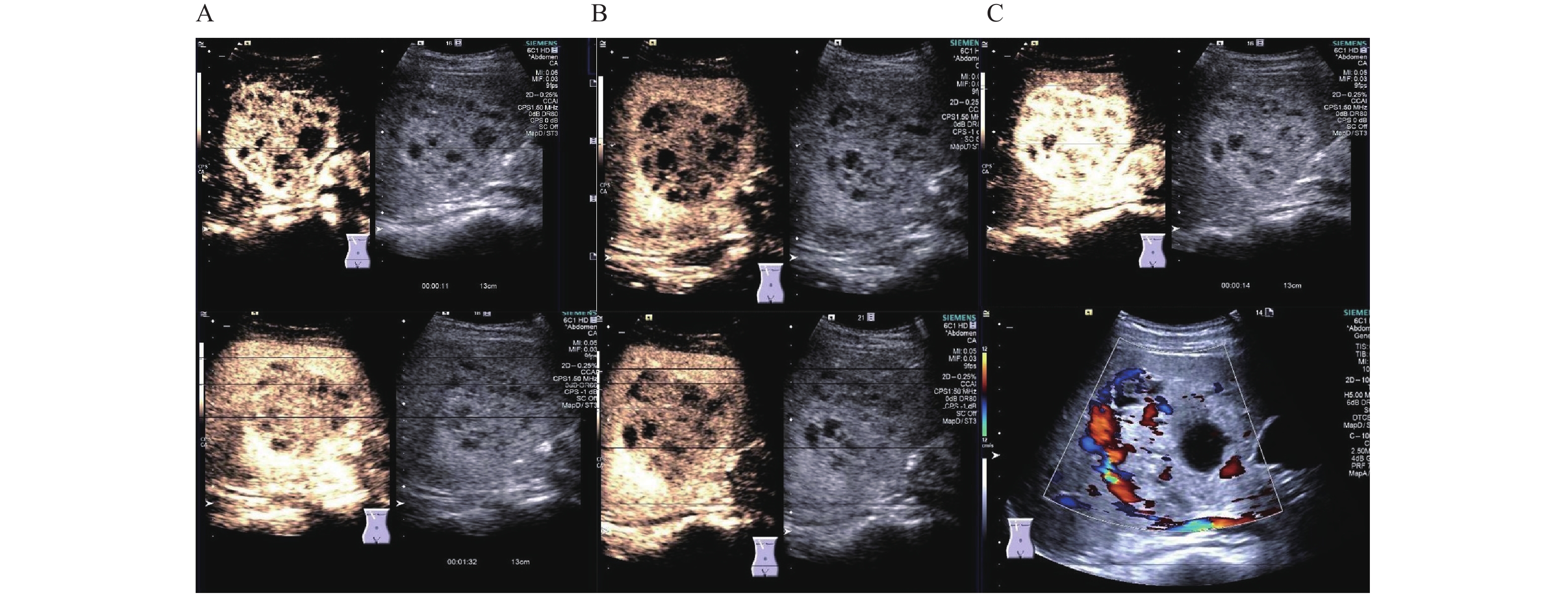
Objective To summarize the case data of patients with primary liver neuroendocrine tumors (PHNET) and analyze their clinical characteristics, imaging manifestations, pathological characteristics, and diagnosis and treatment status so as to improve the clinical diagnosis and treatment. Methods 11 PHNET patients (7 females and 4 males with the age ranged from 24 to 68 and the median age being 65 ) treated in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 1, 2016 to May 9 were selected and the clinical manifestations, laboratory examinations, imaging features, pathological findings, diagnosis and treatment process, and prognosis were retrospectively analyzed. Results Abdominal pain was the main symptom of the patients, including 5 cases of abdominal pain, 1 case of abdominal distension and the remaining 5 cases without obvious clinical symptoms. AFP, CEA and HBsAg were all negative, and CA-199 was elevated in only 2 patients. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound images of 7 cases showed “fast in and fast out” model. 256-slice CT enhanced scan of 6 cases revealed the obvious enhancement in arterial phase and enhancement decline in venous phase and equilibrium phase. Five cases of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed the cluster distribution or large focal area with subfocal area and T1WI sequence showed the low signal in 4 cases and mixed high and low signal in 1 case. T2WI sequence showed the high signal, and diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) displayed marginal interval enhancement of lesion. All patients were NET by histopathological examination, including 2 cases of G1 phase and 9 cases of G2 phase. The positive rates of CgA, Ki-67, CD-56 and Syn were 72.73% (8/11), 100.00% (11/11), 81.82% (9/11) and 100.00% (11/11) respectively. 9 patients underwent the radical hepatectomy, and 2 patients underwent the puncture biopsy without follow-up treatment. During the follow-up period of 6.0-37.0 months, 6 patients survived, 2 patients died, and 3 patients were lost to follow-up. There were 5 cases of postoperative recurrence, including 4 cases treated with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) and 1 case treated with TACE+oral targeted drug sulfatinib, and finally 4 cases survived. Conclusion PHNET lacks the characteristic clinical manifestations and imaging characteristics and the diagnosis depends on the histopathological examination and the exclusion of other lesions. Early detection and combined treatment are important strategies to improve the prognosis of patients.
2024, 45(11): 110-116.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241115
Abstract:
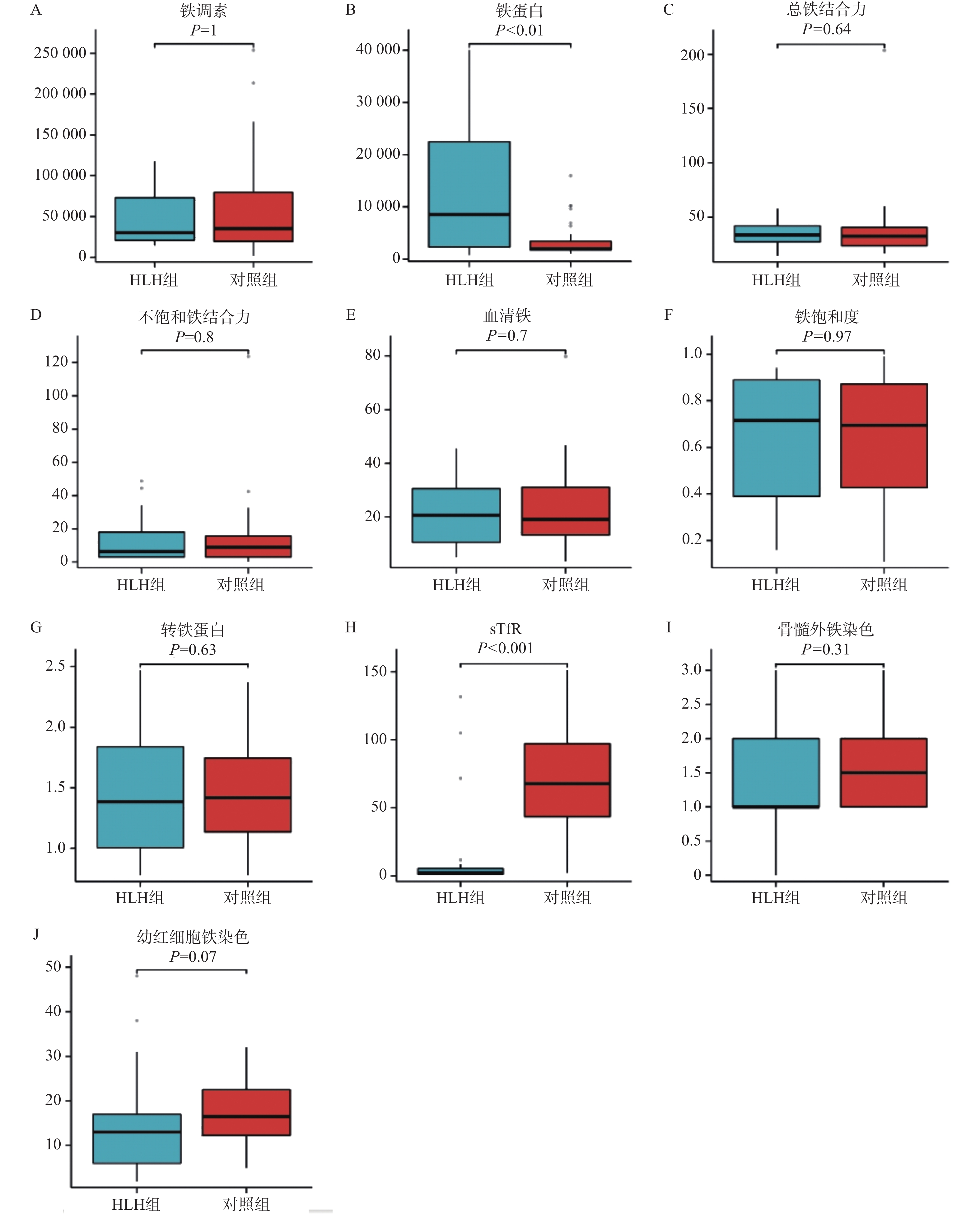
Objective To investigate preliminarily the causes of elevated ferritin in patients with hemophagocytic syndrome by analyzing the iron metabolism indexes, liver function and cytokine levels. Methods 41 patients with the hemophagocytic syndrome and another 41 non-hemophagocytic syndrome patients with the elevated ferritin levels (as the control group) admitted to the First People’ s Hospital of Yunnan Province from September 2021 to May 2024 were recruited for iron metabolism, cytokine and liver function tests, and the differences between these indexes and their relationship with the ferritin were analyzed. Results Patients with the hemophagocytic syndrome had the significantly higher levels of ferritin and lower levels of soluble transferrin receptor compared to the control group. Cytokines IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, IL-1 β, IL-2, IFN - γ, TNF - α, TNF - β, IL-17A, and IL-17F were significantly higher than those in the control group, while transaminase, bilirubin, and lactate dehydrogenase were significantly higher than those in the control group. There was no significant correlation between ferritin and iron metabolism indicators, but it was negatively correlated with cytokine IL-4, positively correlated with IL-8 and IL-10, and positively correlated with LDH, ALT, and AST. Conclusion The ferritin of patients with hemophagocytic syndrome is significantly increased, but the iron metabolism process is not significantly different from that of the control group, and there are obvious inflammatory reactions and liver damage at the onset of the disease.The increase of ferritin is not correlated with iron metabolism indexes, but is related to the inflammation and liver damage.
2024, 45(11): 117-124.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241116
Abstract:
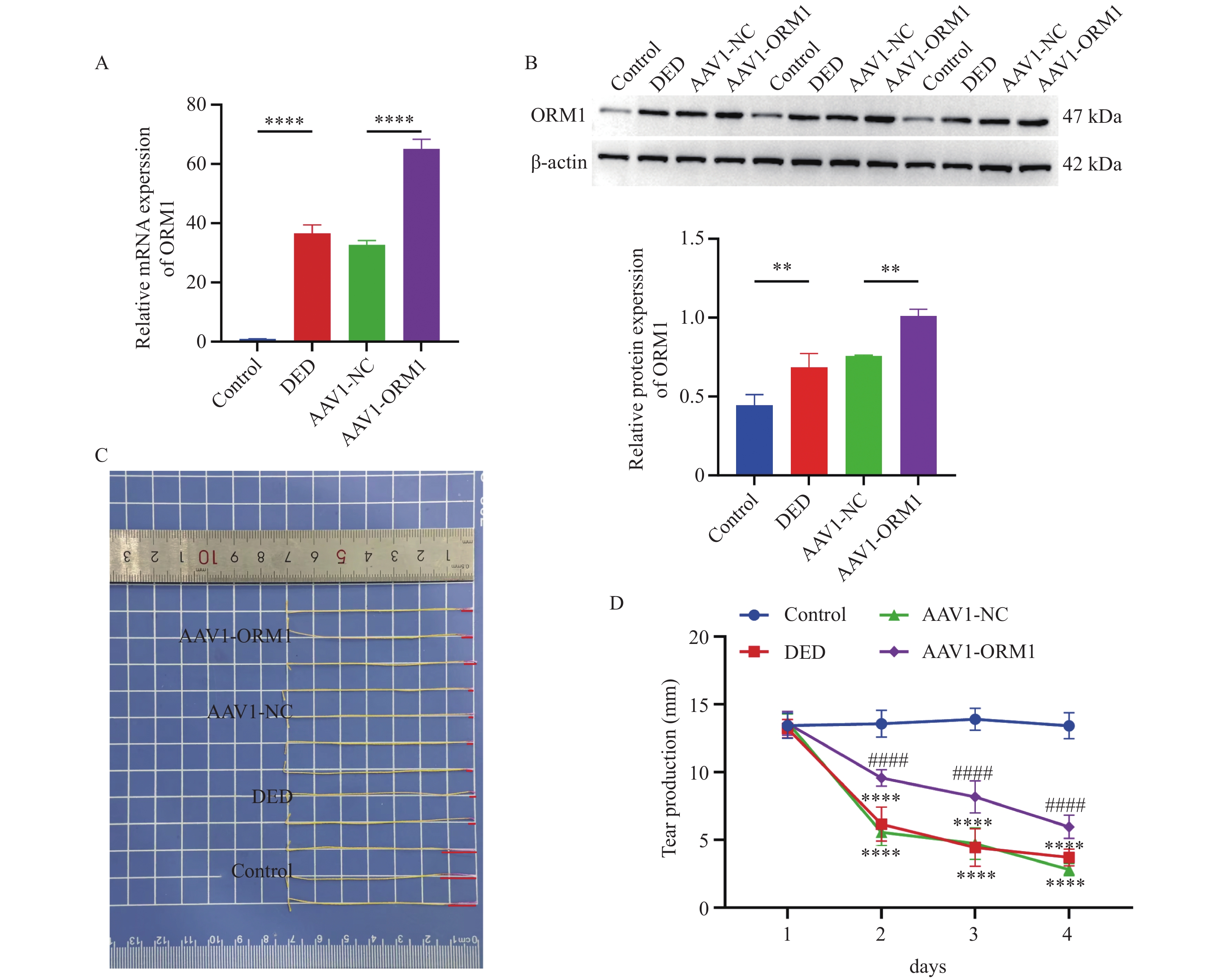
Objective To study the effect of ORM1 on sphingolipid metabolism in dry eye via SPTLC1 so as to provide a new research direction for the pathogenesis of dry eye. Methods By the subcutaneous injection of scopolamine hydrobromide (SCOP), a dry eye model was constructed, and adeno-associated virus overexpressing ORM1 was injected through the lens. Tear secretion assay, goblet number, corneal fluorescein staining, lacrimal gland rupture time, and HE assay were performed to assess the corneal conjunctival damage, tear quality, and histopathological changes. Ceramide and sphingomyelin content were detected by biochemical kits, and the expression of ORM1 and SPTLC1 was detected by qPCR and WB. Results (1) ORM1 increased tear secretion in the dry eye model (P < 0.0001 ); (2) ORM1 increased the stability of the lacrimal gland on the ocular surface in the dry eye model (P < 0.0001 ); (3) ORM1 improved the corneal epithelial damage in the dry eye model (P < 0.0001 ); (4) ORM1 increased the number of goblet in the corneal tissue in the dry eye model (P < 0.0001 ); (5) After the overexpression of ORM1, the epithelium of the corneal tissue became thicker and the cells of the basal lamina were more closely arranged. cell layers became more numerous and vacuoles were reduced; (6) ORM1 inhibited the inflammatory gene expression in a dry eye model (P < 0.01); (7) ORM1 promoted the total ceramide and sphingomyelin content (P < 0.01); (8) ORM1 promoted the rise of mRNA and protein expression of SPTLC1 (P < 0.001). Conclusion ORM1 can participate in the regulation of sphingolipid metabolism in dry eye disease through the regulation of SPTLC1, which provides new perspectives for exploring the mechanism of the development of dry eye disease and searching for effective and safe therapeutic options.
The Effects of NLR,PLR,and FRA in Peripheral Blood on Normal Bone Mass and Bone Loss after Fractures
2024, 45(11): 125-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241117
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio, platelet/lymphocyte ratio, and fibrin/albumin ratio in systemic inflammatory markers on bone loss and normal bone function after fractures. Methods A retrospective study was conducted from January 2023 to September 2023 on the medical records of 2652 postoperative fracture patients publicly available in the electronic case system of the 1st Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. According to the results of bone density testing, patients were divided into two groups: 141 patients with the reduced bone mass and 79 patients with the normal bone mass. According to the collected data, the relevant information of each group, including NLR, PLR, FAR, gender, age, triglycerides, blood glucose, blood pressure, etc, was analyzed using SPSS 25.0 software. Results There was no significant statistical difference in NLR, PLR, and FAR between the two groups(P > 0.05). There were statistical differences in BMI , age and gender(P < 0.05). Conclusion The inflammatory response of bone loss after the fracture may be different from the inflammatory factors of female osteoporosis.
2024, 45(11): 130-136.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241118
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the relationship between the biochemical indexes of bone metabolism and gender, age and season in adult residents. Methods The data of 6462 cases of physical examination in the physical examination center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2021 to April 2024 were retrospectively analyzed. Gender, age, 25-hydroxyvitamin D(25-OH-VD), calcitonin (CT), n-terminal osteocalcin (N-MID), and β-collagen degradation products (Beta-CrossLaps, β-CTX) of all subjects were collected. The data were grouped according to the reference value range, gender, age and season of biochemical indicators of bone metabolism. SPSS29.0 software was used to conduct the overall level distribution statistics of the data, compare the differences in the level of biochemical indicators of bone metabolism between groups, analyze the correlation between the level of biochemical indicators of bone metabolism, and explore the influencing factors of biochemical indicators of bone metabolism. Results The overall median levels of biochemical indices were 25-OH-VD 61.93 (49.17, 77.12) nmol/L, CT1.43 (.53, 3.01) pg/mL, N-MID16.0 (12.8, 20.2) ng/mL, β-CTX397.0 (295.0, 527.0) pg/mL. N-MID was significantly positively correlated with β-CTX (rs = 0.748). The effects of gender, age and season on 25-OH-VD and N-MID were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The overall median 25-OH-VD levels in this study population are lower than the normal reference range, and vitamin D levels are generally insufficient and more common in the younger study population, suggesting that vitamin D supplementation may be an general public health issue. The overall median CT, N-MID and β-CTX levels are in the normal reference range, indicating that the population is in good health on these indicators. Gender and age are significant factors affecting 25-OH-VD, CT and N-MID levels. Age is a significant factor affecting 25-OH-VD and N-MID levels. Season is a significant factor affecting the levels of 25-OH-VD, N-MID and β-CTX. N-MID and β-CTX may have a close biological relationship.
2024, 45(11): 137-143.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241119
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical features, independent risk factors, and antibiotic selection in children with acute leukemia complicated by multidrug-resistant (multiple resistant bacteria, MDR) bloodstream infections. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 101 children with acute leukemia complicated by bacterial bloodstream infections and treated at Kunming Children's Hospital from January 2015 to December 2023. Based on blood culture results, patients meeting the criteria for multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), and pandrug-resistant (PDR) were included in the multidrug-resistant group (n = 47), while the remaining patients were included in the non-multidrug-resistant group (n = 54). Clinical features, laboratory indicators, and antibiotic selection were recorded for both groups, and the risk factors influencing MDR infections were analyzed. Results The proportion of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and the percentage of patients with neutropenia lasting≥7 days before the induction chemotherapy were both higher in the MDR group compared to the non-MDR group. Additionally, the levels of hemoglobin (Hb) and platelets (PLT) before fever in the MDR group were lower than those in the non-MDR group, and there was statistically significant difference (P < 0.05).The results indicated that acute myeloid leukemia, neutropenia lasting≥7 days before induction chemotherapy, Hb < 79 g/L before and after the infection, and PLT < 20×109/L before the infection were independent risk factors for MDR infections (P < 0.05). Microbiological analysis showed that Gram-negative bacteria were the primary pathogens, with a high resistance rate but sensitivity to carbapenems. Gram-positive bacteria were sensitive to specific antibiotics but showed high resistance to erythromycin. Furthermore, the levels of procalcitonin (PCT) and C-reactive protein (CRP) in the MDR group were higher than those in the non-MDR group, and the proportion of patients transferred to the ICU was significantly higher in the MDR group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Acute myeloid leukemia, neutropenia lasting≥7 days before the induction chemotherapy, hemoglobin < 70 g/L, and PLT < 20×109/L are independent risk factors for multidrug-resistant (MDR) bloodstream infections in children and the factors affecting the prognosis. Escherichia coli is identified as the primary resistant pathogen. Children with MDR infections exhibited the elevated levels of procalcitonin (PCT) and C-reactive protein (CRP), along with a low recovery rate. Therefore, effective preventive measures should be implemented for high-risk factors, and treatment plans should be promptly adjusted based on antibiotic susceptibility results to improve the efficacy.
2024, 45(11): 144-148.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241120
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effect of the delay of myopia in children wearing composite multi-point optical defocusing lens. Methods A total of 52 cases (n = 104) of monocal lens wearers were selected as the control group, and 78 cases (n = 156) of compound multi-point optical distrocal lens wearers were selected as the experimental group. The effect of myopic control between two groups was compared before and after wearing glasses at 3, 6, 9 and 12 months, during which the changes of equivalent spherical lens and eye axis length were mainly observed. Results The equivalent spherical degree of the two groups before and after wearing glasses had different degrees of change and the treatment effect between the control group and the experimental group was statistically significant (F = 13.80, P < 0.001). After 6 months of wearing glasses, the diopter of the control group was significantly lower than that of the experimental group, and the longer the wearing time, the greater the difference between the two groups. The axial length of the eyes of the two groups also changed to different degrees before and after wearing glasses, but there was no statistical significance in the treatment effect between the control group and the experimental group (F = 0.028, P = 0.876), suggesting that there was no statistical significance in the influence of the two lenses on the axial of the eyes. Conclusion Compared with the single-focus lenses, composite multi-point optical defocus lenses can effectively delay the progression of myopia in children.
2024, 45(11): 149-154.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241121
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the current status of metabolic syndrome (MS) in ART patients and analyze its influencing factors. Methods Data from 1972 ART patients were collected and the prevalence of MS was determined according to the diagnostic guidelines. T-tests, chi-square tests, and rank-sum tests were used to compare the differences in the related factors, and the logistic regression was used to analyze the influencing factors. Results Among these patients, 495 (25.05%) met the diagnostic criteria for MS. The risk of MS in males was 2.045 times higher than that in females (P = 0.001). Patients with elementary or lower education had a higher risk of MS than those with the secondary (P = 0.001) or higher education (P < 0.001). The risk of developing MS for those over 40 years old was 8.819 times higher than those under 40 years old(P < 0.001). Smokers had a 1.565 times higher risk of MS compared to non-smokers (P < 0.001). Patients with BMI≥25 kg/m2 (P < 0.001), fasting glucose≥6.1 mmol/L (P < 0.001), TG≥1.7 mmol/L (P < 0.001), HDL-C<1.04 mmol/L (P < 0.001), and blood pressure≥130/85 mmHg (P < 0.001) were at the higher risk of MS. Pairwise comparisons of the patients using different ART regimens showed that those using integrase inhibitors had a higher incidence of MS (χ2 = 17.278, P < 0.001). Conclusion The prevalence of metabolic syndrome is high among the patients undergoing antiretroviral therapy for AIDS. More interventions and recommendations should be provided to actively reduce and prevent the occurrence of metabolic syndrome. Lifestyle interventions should be a critical part of managing AIDS patients. The focus is on monitoring the blood pressure, blood sugar, and lipid abnormalities, and taking corresponding measures for individualized treatment and management so as to minimize the occurrence of metabolic syndrome.
2024, 45(11): 155-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241101
Abstract:
Diabetes often coexists with cardiovascular complications, which are also a common cause of death in diabetes patients. Therefore, in addition to improving glucose metabolism, it is also necessary to control cardiovascular complications in diabetes patients. Sacubitril valsartan is a novel compound with dual actions of inhibiting neprilysin and angiotensin receptor, and it is commonly used as a heart failure drug in clinical practice. Recent studies suggest that sacubitril valsartan may also have potential metabolic benefits, improving cardiac function while improving glycemic control in diabetes patients, and it is expected to become a drug that can be used routinely in diabetes, bringing cardiovascular and metabolic benefits. This review focuses on the clinical efficacy and metabolic benefits of sacubitril valsartan in the treatment of diabetes patients with cardiovascular diseases.
Diabetes often coexists with cardiovascular complications, which are also a common cause of death in diabetes patients. Therefore, in addition to improving glucose metabolism, it is also necessary to control cardiovascular complications in diabetes patients. Sacubitril valsartan is a novel compound with dual actions of inhibiting neprilysin and angiotensin receptor, and it is commonly used as a heart failure drug in clinical practice. Recent studies suggest that sacubitril valsartan may also have potential metabolic benefits, improving cardiac function while improving glycemic control in diabetes patients, and it is expected to become a drug that can be used routinely in diabetes, bringing cardiovascular and metabolic benefits. This review focuses on the clinical efficacy and metabolic benefits of sacubitril valsartan in the treatment of diabetes patients with cardiovascular diseases.
2024, 45(11): 161-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241123
Abstract:
With the deepening development of molecular biology, people's understanding of the mechanisms of cancer occurrence is becoming increasingly profound. In recent years, DDX46 has been found to be overexpressed in various cancers such as colorectal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and gastric cancer. It can promote the proliferation of various malignant tumor cells, activate invasion and migration, resist cell apoptosis, and participate in the cell cycle. Therefore, it may become a potential target and biomarker for anti-tumor drugs. To provide a more intuitive understanding of the role of DDX46 in cancer, we systematically describe its functions and related mechanisms in various aspects of tumorigenesis and development. It provides a new idea for the research and development of DDX46 targeted drugs.
With the deepening development of molecular biology, people's understanding of the mechanisms of cancer occurrence is becoming increasingly profound. In recent years, DDX46 has been found to be overexpressed in various cancers such as colorectal cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and gastric cancer. It can promote the proliferation of various malignant tumor cells, activate invasion and migration, resist cell apoptosis, and participate in the cell cycle. Therefore, it may become a potential target and biomarker for anti-tumor drugs. To provide a more intuitive understanding of the role of DDX46 in cancer, we systematically describe its functions and related mechanisms in various aspects of tumorigenesis and development. It provides a new idea for the research and development of DDX46 targeted drugs.
2024, 45(11): 166-173.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241124
Abstract:
Objective To explore the intervention effect of an evaluation index system based on the comprehensive evaluation (CE) on undergraduate academic mentorship. Methods Delphi method and Analytic Hierarchy Process were used to determine the evaluation indicators and weights. 80 undergraduate academic supervisors from four schools of Kunming Medical University were randomly selected as the research subjects according to an equal proportion of 55%. The research subjects were randomly divided into a control group and an experimental group, with 40 in each group. More than 600 teachers and students familiar with the guidance work of academic supervisors from the corresponding colleges were selected to evaluate the teaching effectiveness of the two groups of academic supervisors. The evaluation index system based on CE was used to evaluate the teaching effectiveness of the two groups of academic supervisors, and the evaluation results were promptly fed back to the experimental group. The evaluation results were not fed back to the control group. Six months later, the same set of evaluation indicators and the same group of evaluators were used again to evaluate the teaching effectiveness of two groups of academic mentors, and the teaching effectiveness of the two groups of academic mentors was compared. Results After the intervention, the total score of student evaluation and other four dimensions in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group. The total score of college evaluation, peer evaluation, and other three dimensions were also higher than those in the control group. The differences in the most dimension indicators, such as student evaluation total score, college evaluation total score, peer evaluation total score, academic planning guidance, professional learning guidance, fulfilling responsibilities, work effectiveness, and student outcomes, were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion The evaluation index system based on CE can effectively improve the teaching effectiveness of academic supervisors and the comprehensive quality of students.
2024, 45(11): 174-180.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241125
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of health education under the guidance of cognitive behavioral therapy in the virtual community care of patients with colorectal cancer chemotherapy intermittent. Methods 74 colorectal cancer patients who underwent the chemotherapy in the Department of Oncology of Kunming Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from January 2024 to May 2024 and were in the chemotherapy interval were randomly divided into a control group and an observation group, with 37 cases in each group. The disease cognition, self-management efficacy and quality of life of the two groups were compared before and after the intervention using the Mini-Impairment Disease Awareness Scale (B-IPQ), Cancer Self-Management Efficacy Scale(C-SUPPH) and Colorectal Cancer Quality of Life Measurement Scale (FACT-C). Results After the intervention, the B-IPQ score in the observation group was significantly lower (t = -4.529, P < 0.001), and the scores of C-SUPPH, FACT-C and their dimensions were significantly higher (Z = 9.664, 12.941, -4.774, -4.330, -6.739, -5.360, -3.162, P < 0.05) compared with the control group. Conclusion The application of the health education based on cognitive-behavioral therapy in virtual community nursing for patients with colorectal cancer during the chemotherapy intervals can effectively improve patients' negative cognition of the disease and enhance their self-management efficiency and quality of life.
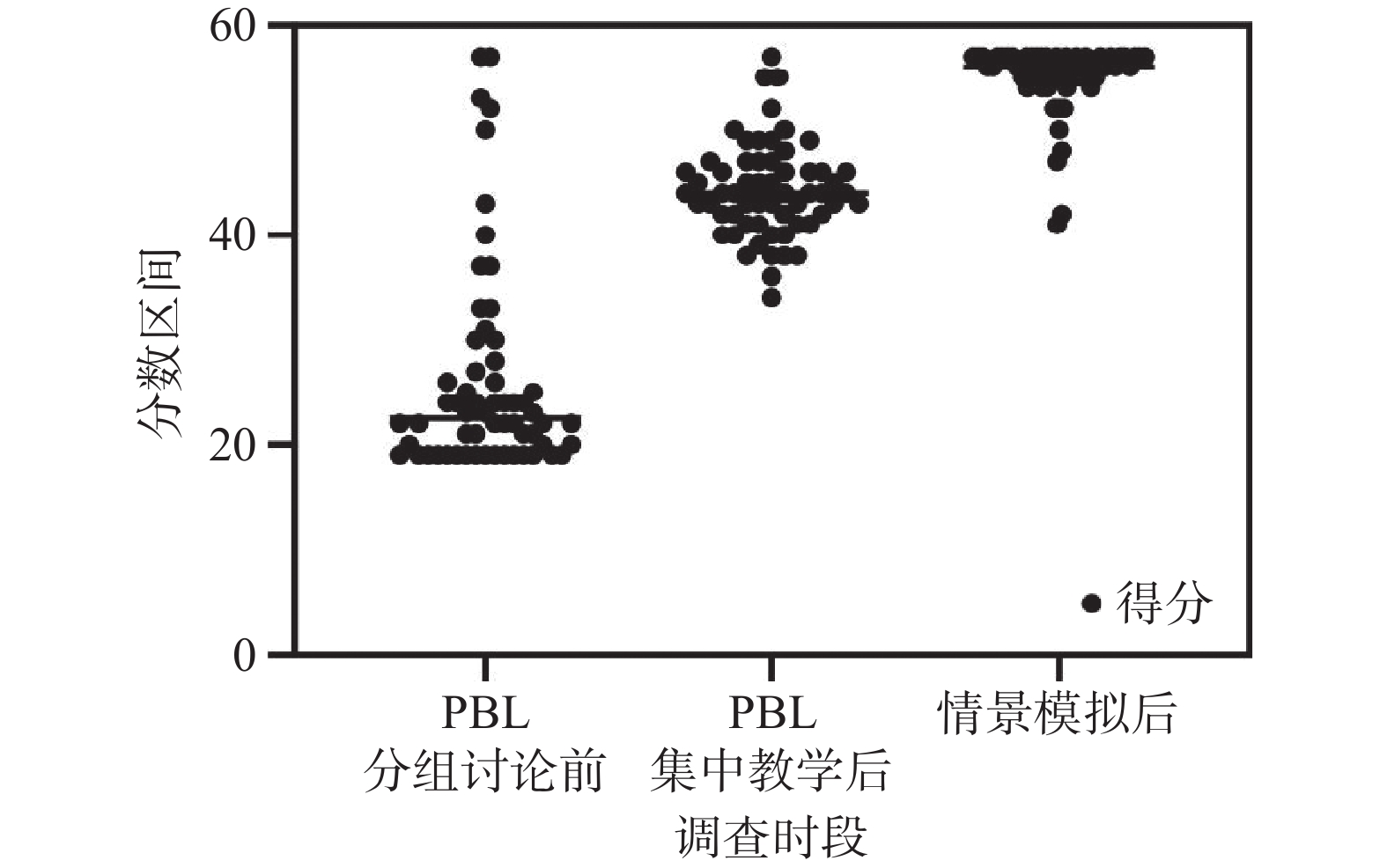
2024, 45(11): 181-185.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241126
Abstract:
Objective To study the construction and application effect of PBL teaching model combined with the scenario simulation teaching method in the nursing first aid course for generalized tonic-clonic seizure (GTCS) attacks. Methods A total of 120 nursing students who entered the Neurosurgery Department of Yunnan Cancer Hospital for nursing practice and rotation from October 2022 to March 2024 were selected as the research objects. The SPSS software was used to randomly divide the same batch of nursing students into an observation group and a control group according to the investigation time. PBL teaching method was used in the observation group for group discussions respectively before the training, after the PBL centralized teaching, and after the scenario simulation. The "SET-M Revised Version of the Scenario Simulation Effect Evaluation Form" was used to statistically compare and analyze the feelings of nursing students towards the four dimensions of pre-simulation introduction, learning, confidence, and guided feedback at each time period. The control group was trained using the traditional PPT explanation combined with basic nursing operation routine exercises. Results During the training process of the observation group, the scores of each dimension in different stages were improved, and the comparison before and after the training was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The observation group had the higher scores in the theoretical exam, practical exam, and course satisfaction than the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion The PBL teaching model combined with the scenario simulation teaching method constructed in this study has a significant teaching effect in the application of the nursing first aid course for generalized tonic-clonic seizure (GTCS) attacks among nursing students. Nursing students have a high degree of recognition that this course can effectively improve their theoretical knowledge and clinical practice ability.
2024, 45(11): 186-190.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20241127
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effect of parallel medical record writing in practice teaching of nursing students. Methods From September 2021 to February 2022, 58 nursing students who practiced in a Grade A hospital in Xiangyang City were selected as the control group. 56 nursing students who practiced in the hospital from September 2022 to February 2023 were selected as the experimental group, and the training mode of parallel medical record writing was adopted. The nurses' job esteem scale, critical thinking scale and caring ability evaluation scale were used at four time points before the practice, 1, 3 and 6 months after the practice. Results There were statistically significant differences in the scores of job esteem , critical thinking ability and humanistic care ability of nursing students in the two groups in the time effect, inter-group effect and interaction effect (P < 0.05). Conclusions Parallel medical record writing training mode can effectively improve the level of job esteem, critical thinking ability and humanistic care ability of nursing students.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS