The Effectiveness of Liraglutide Combined with Metformin in Improving Glycolipid Metabolism and Hormonal Levels in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis
-
摘要:
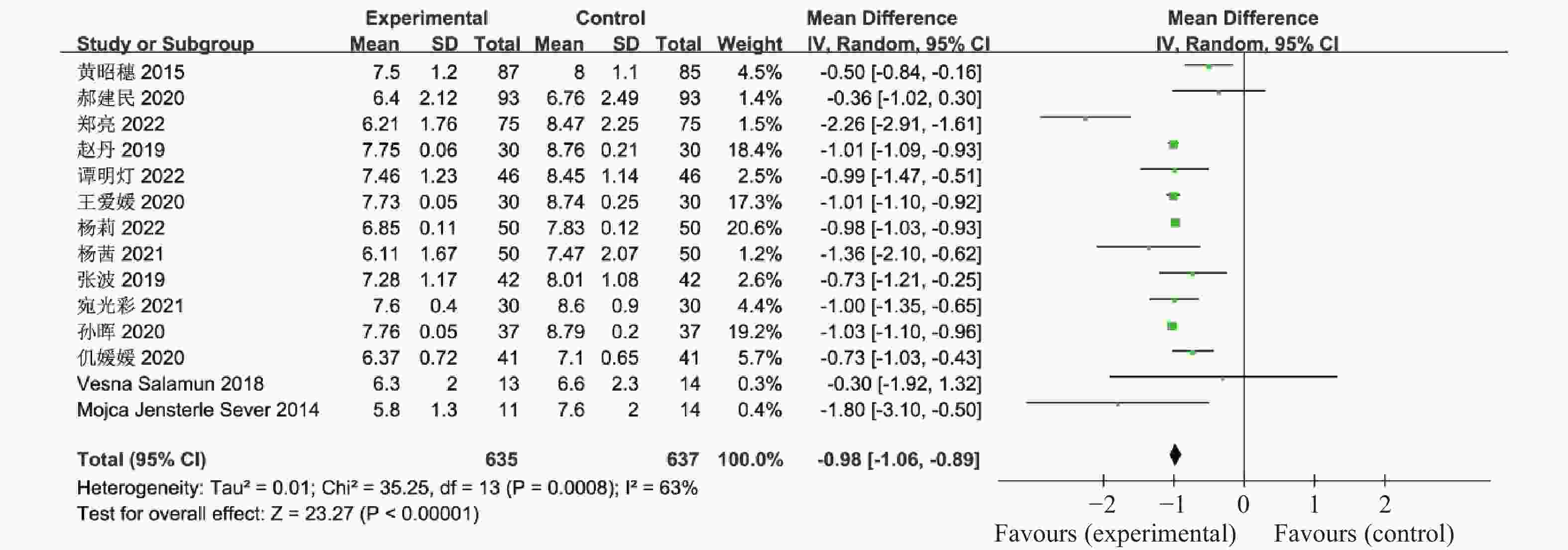
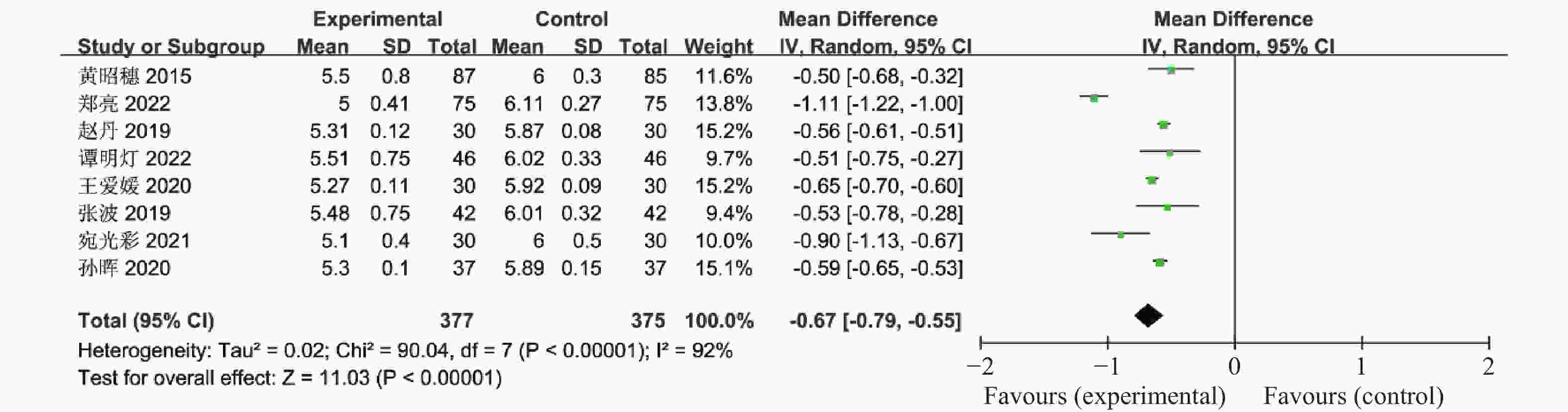
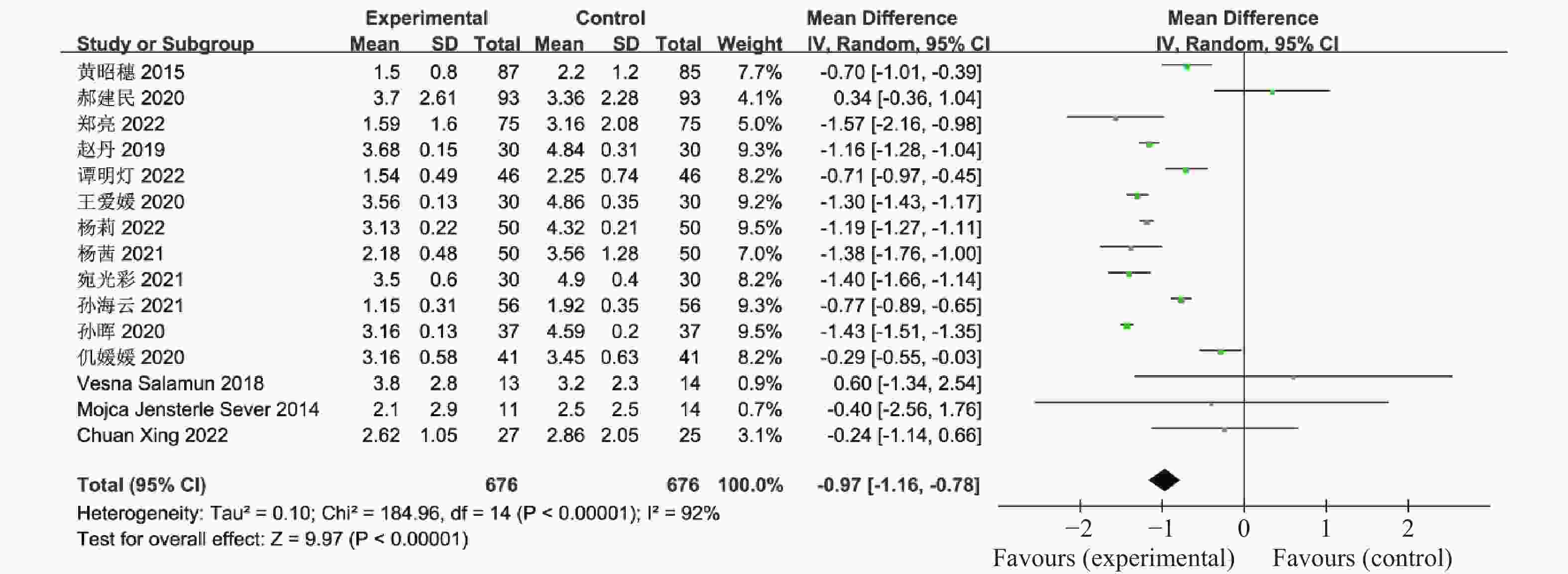
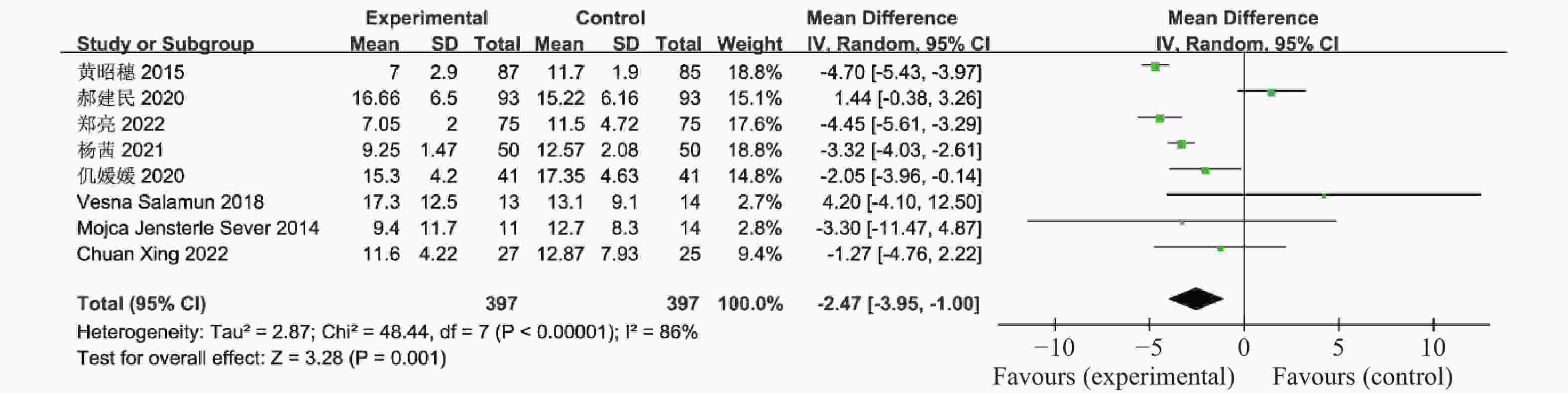
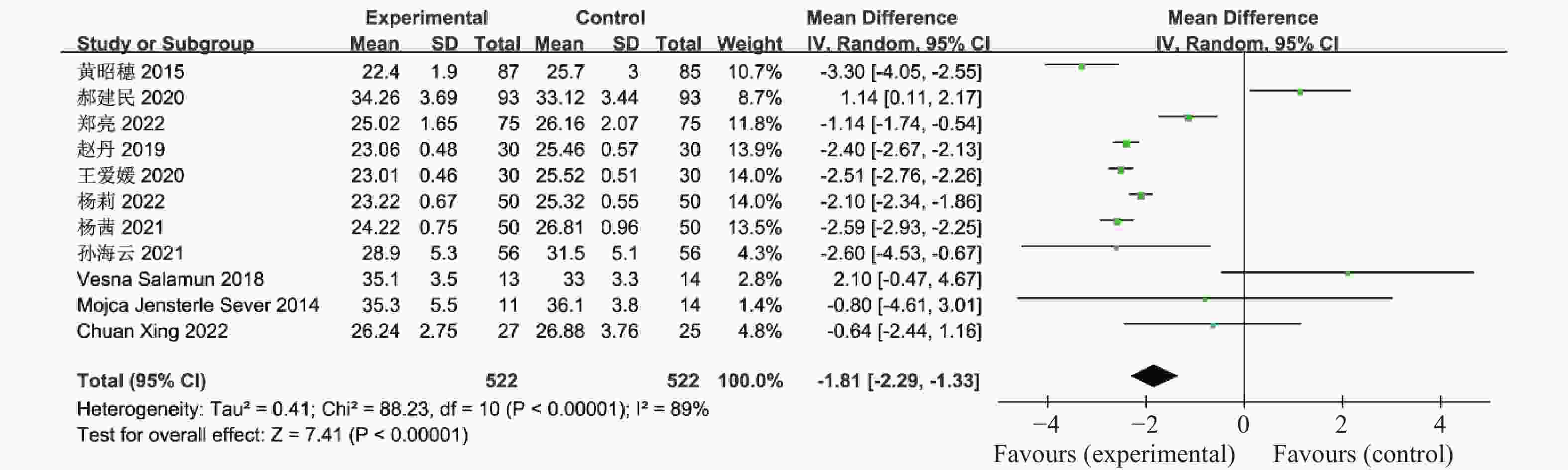
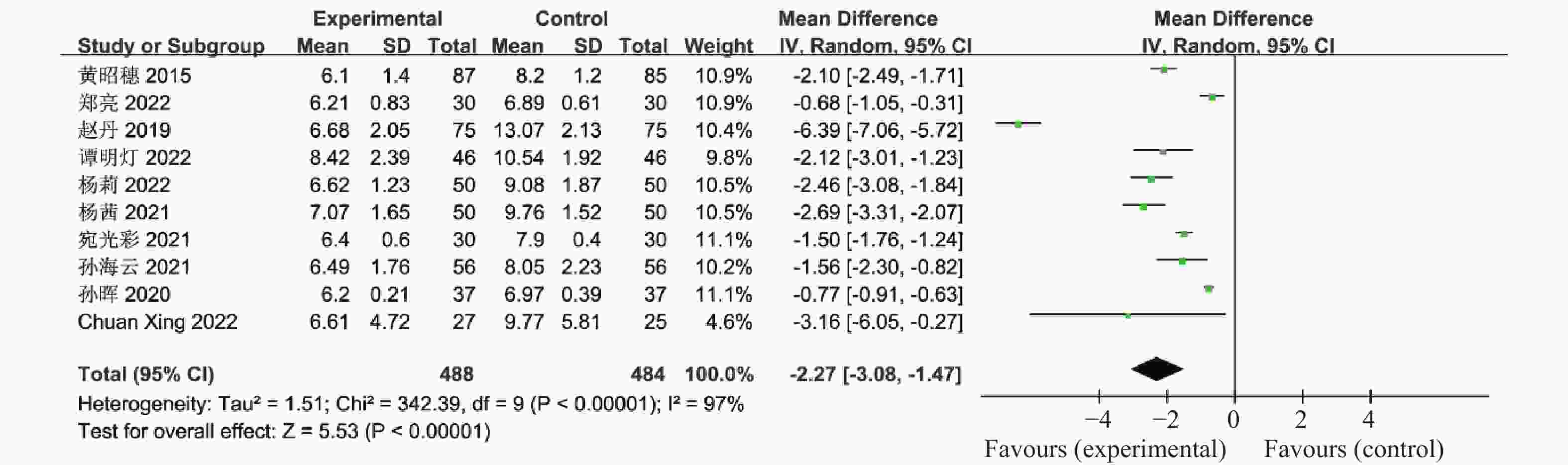
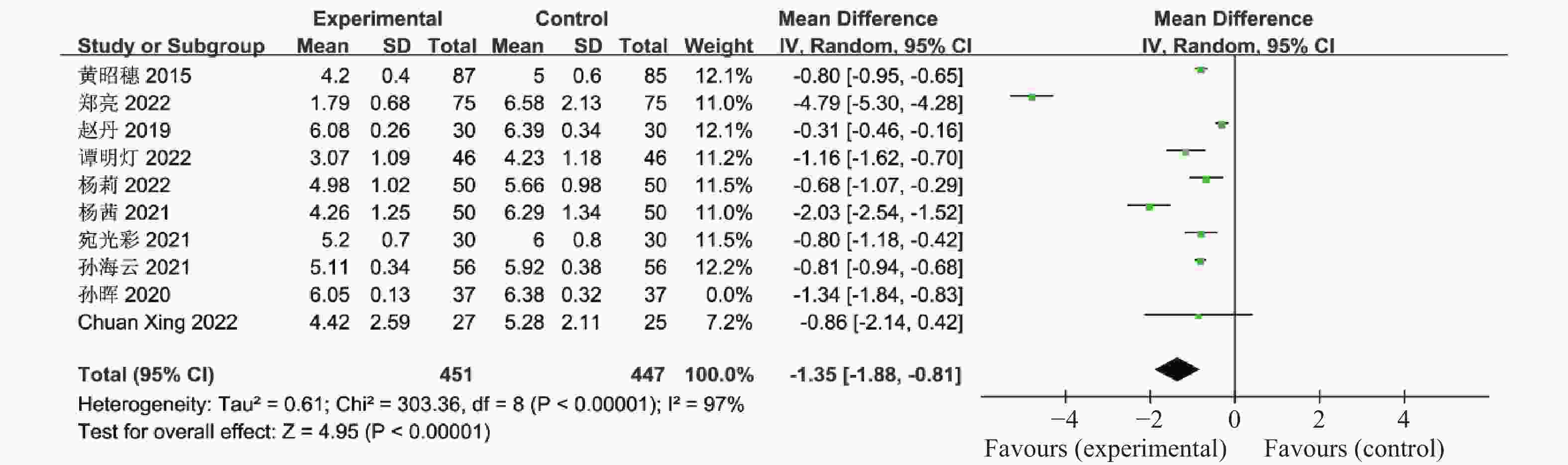
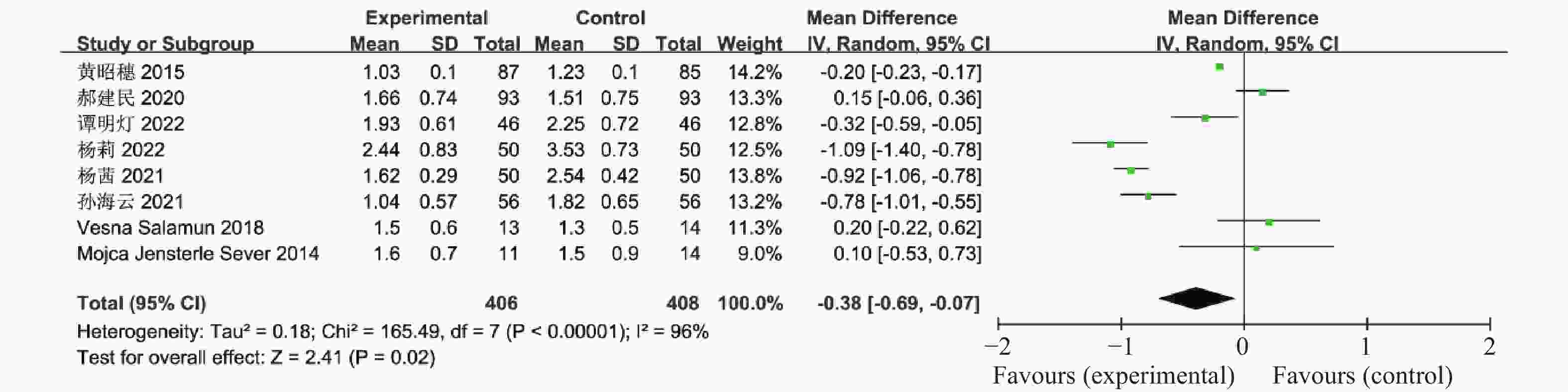
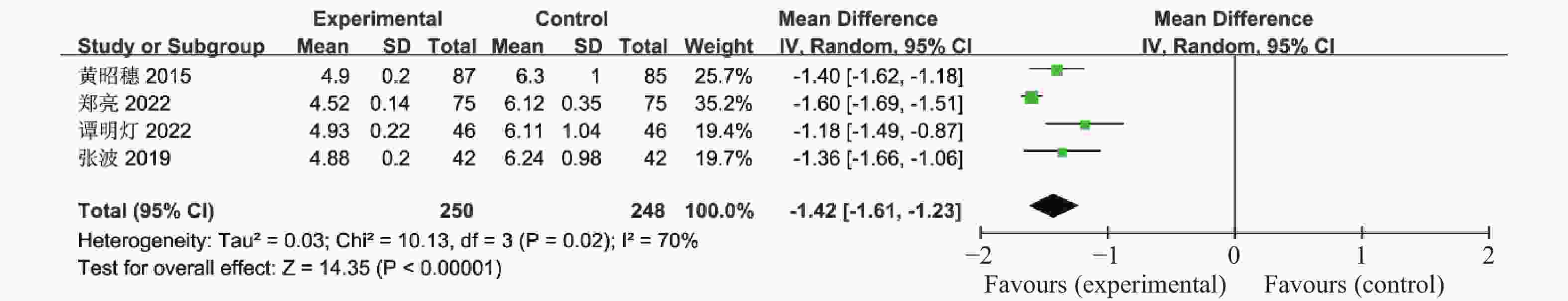
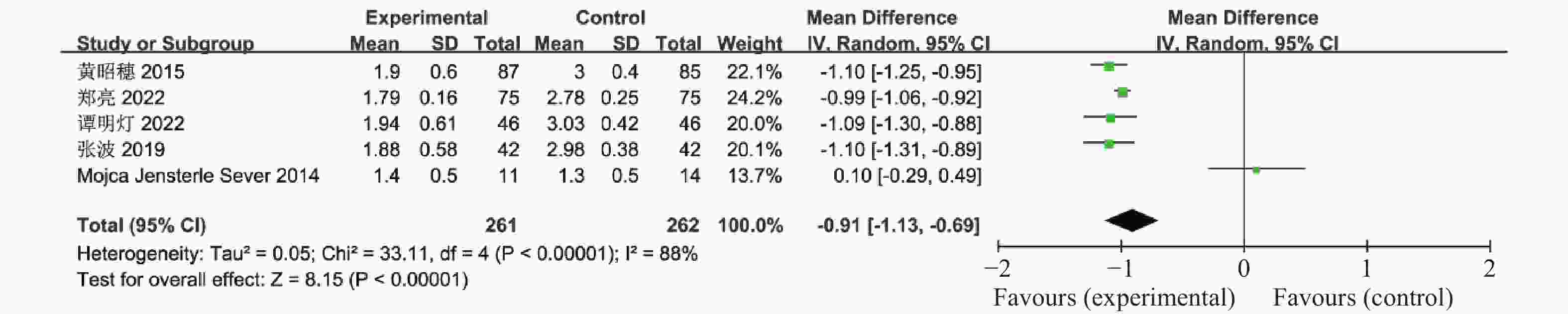
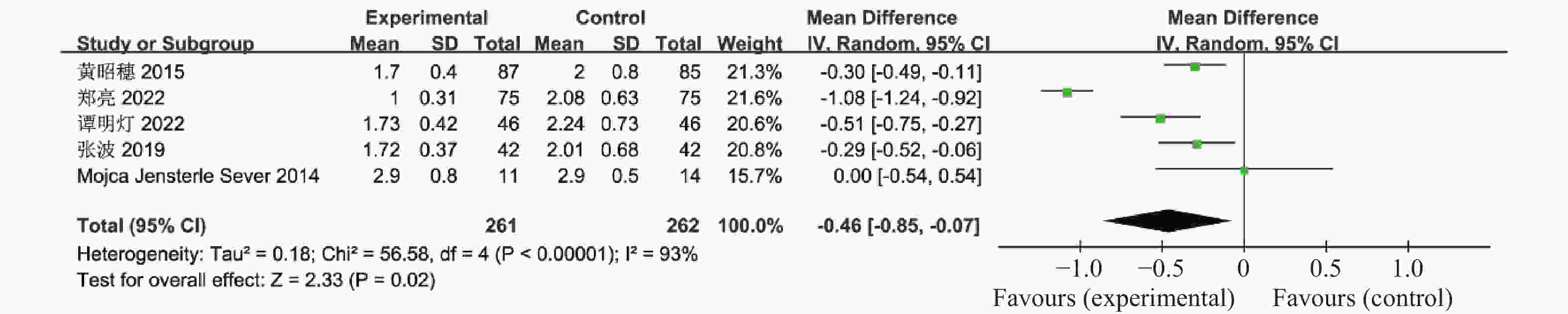
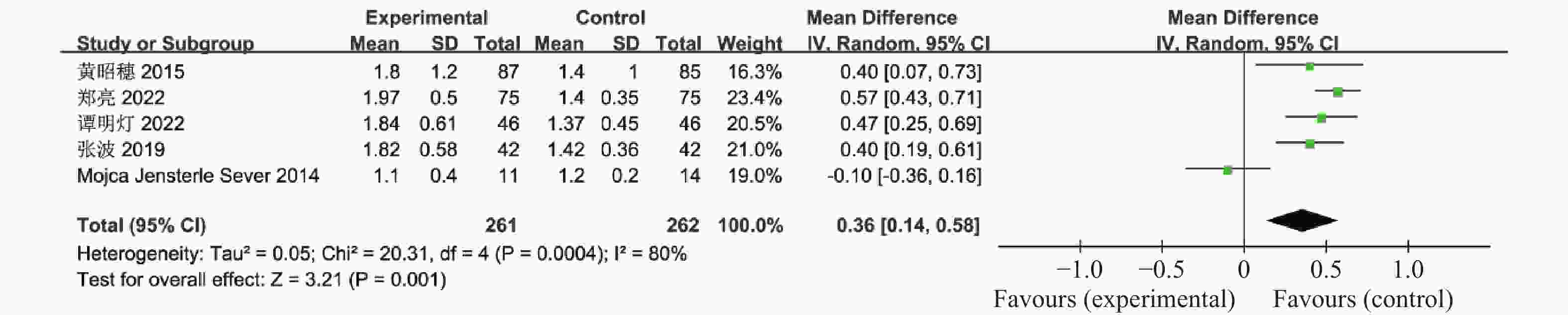
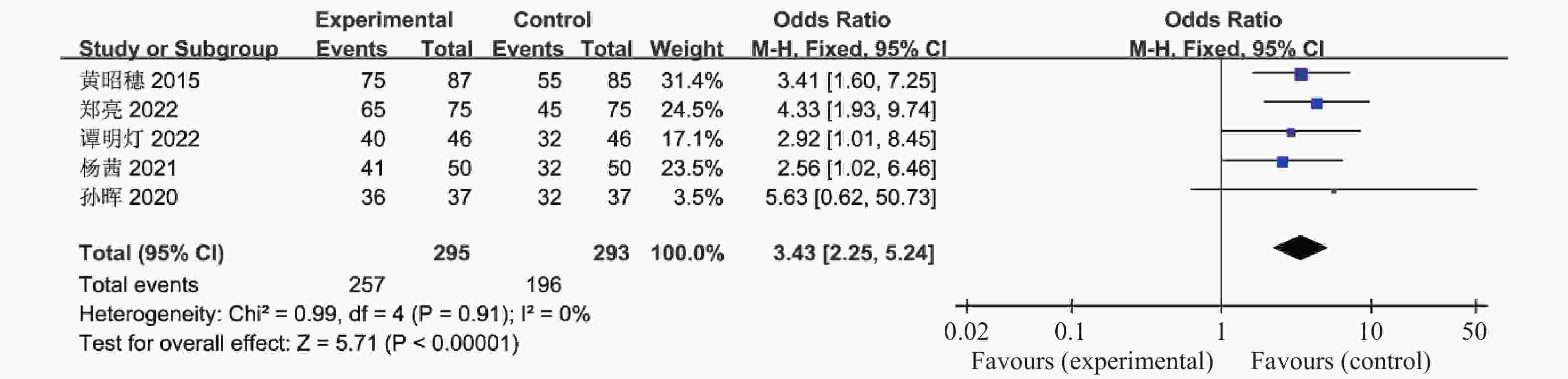
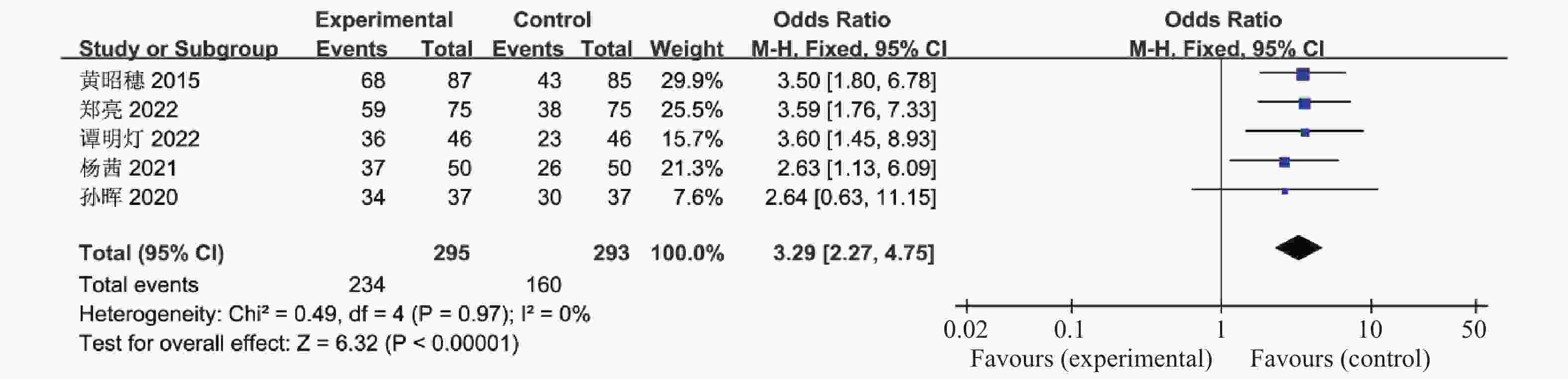
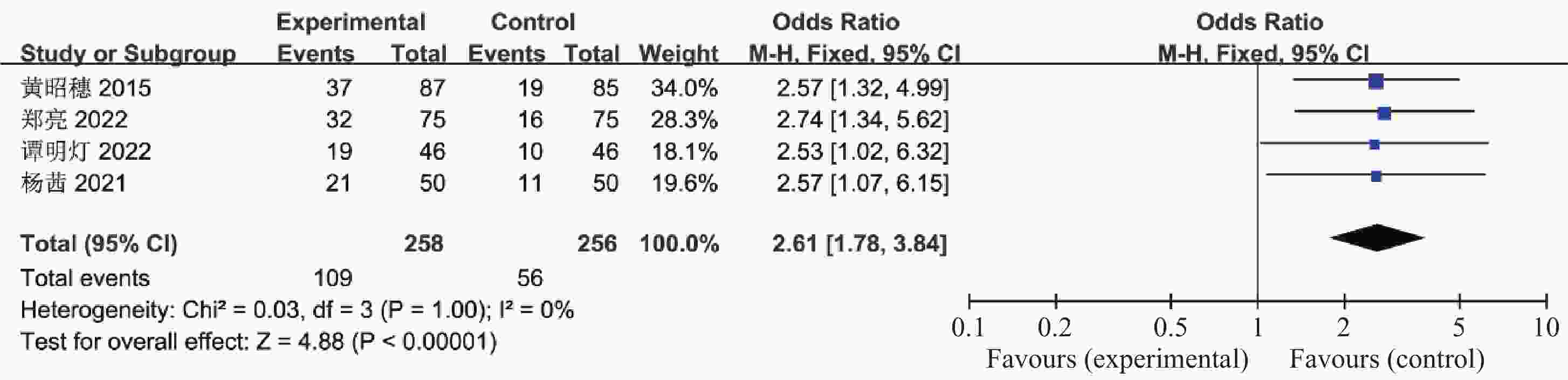
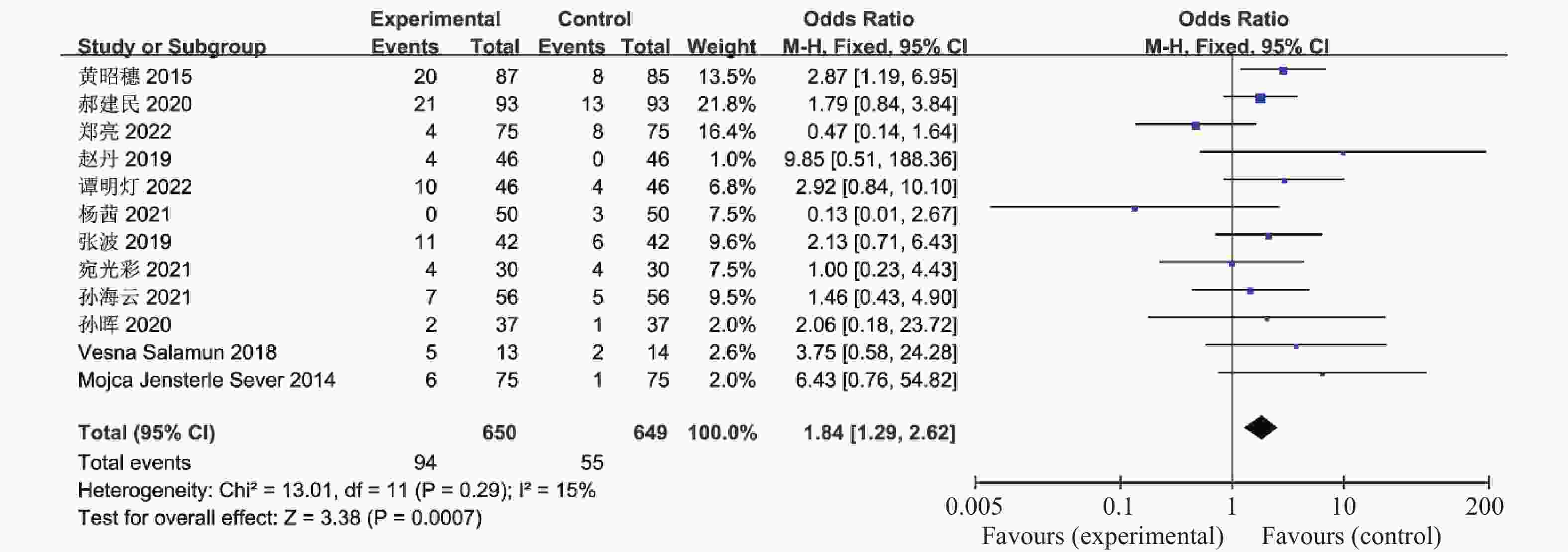
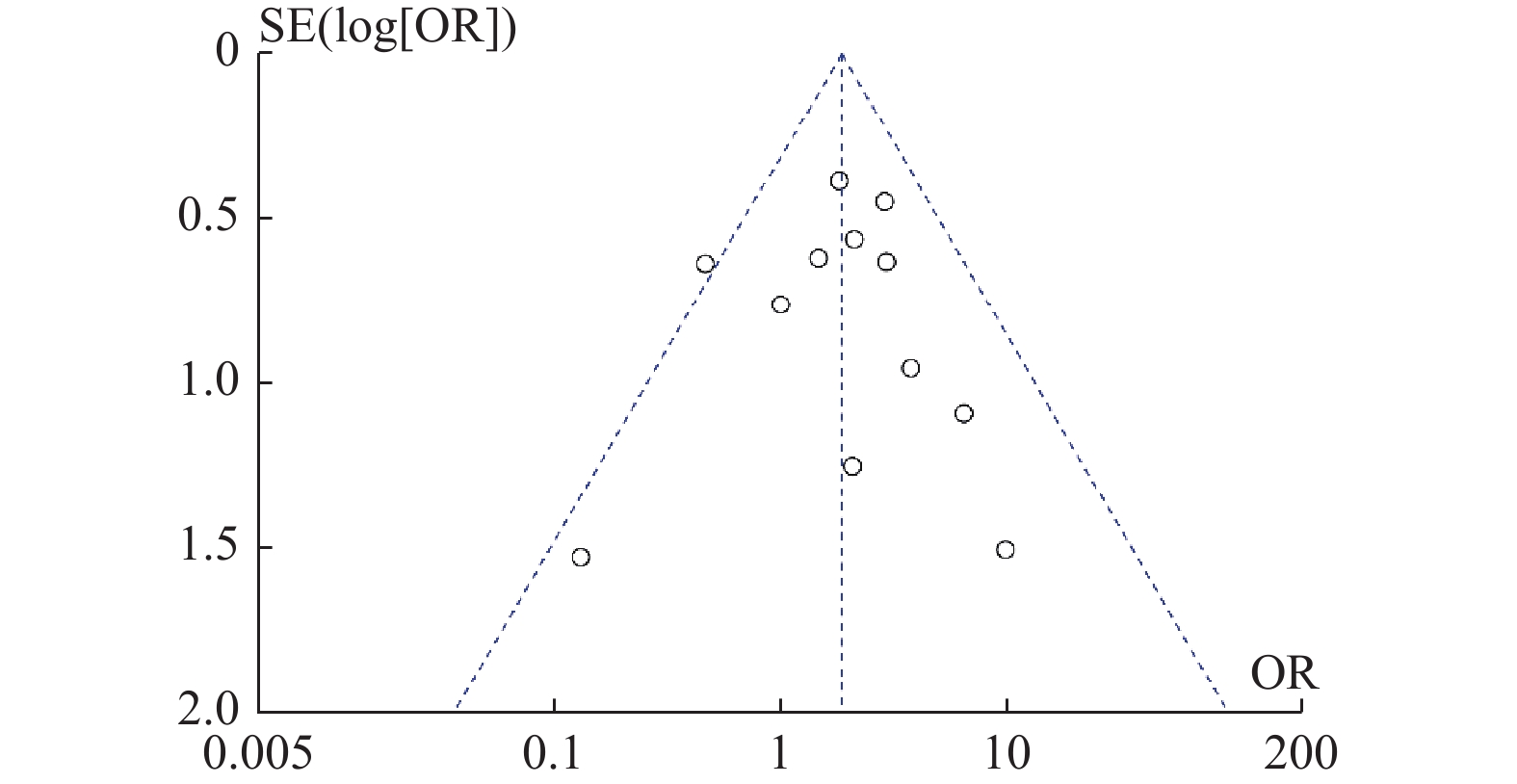
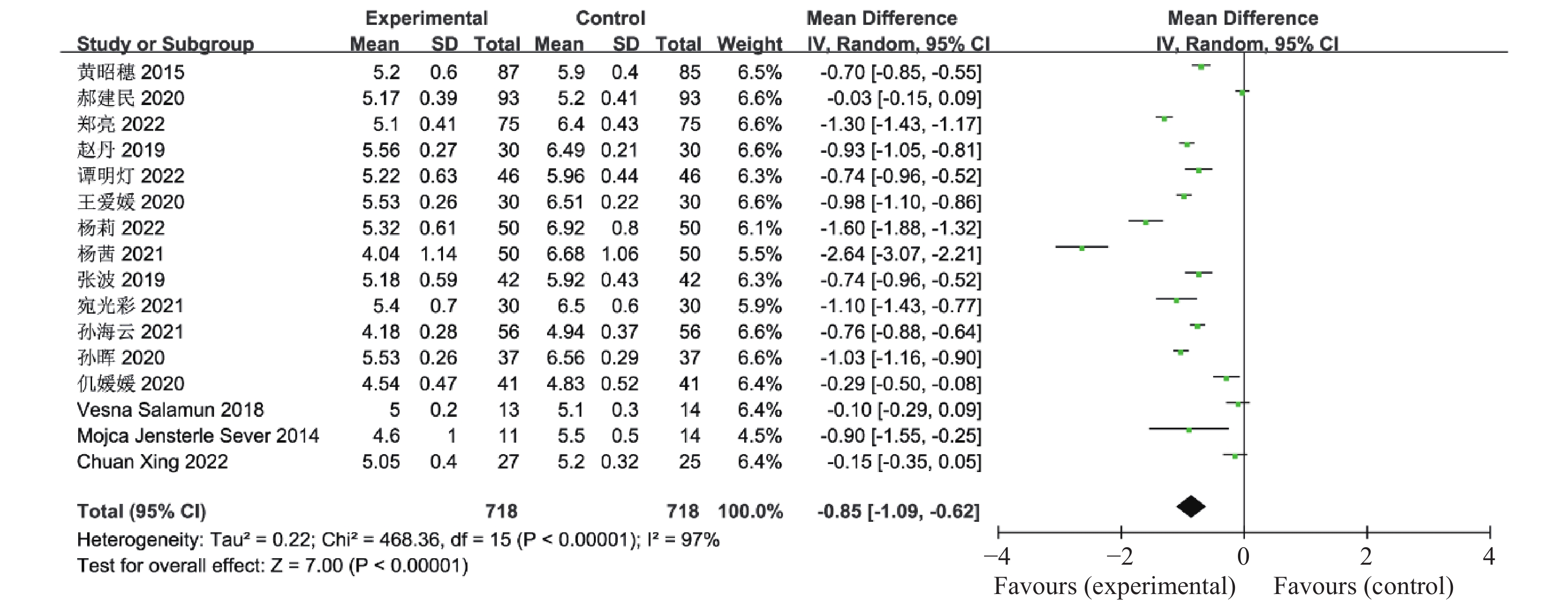
目的 系统性评价利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍对多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)患者糖脂代谢、性激素、生殖功能及胃肠道反应的影响。 方法 检索PubMed、万方医学网、万方数据库、CNKI中国知网、维普期刊等数据库,收集2011年1月至2022年8月公开发表的利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍治疗多囊卵巢综合征的随机对照研究,使用Revman5.4进行荟萃分析。 结果 共纳入16项病例对照研究,包括了 1436 例患者,与单用二甲双胍相比较,利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍可显著降低PCOS患者的空腹血糖、餐后2 h血糖、HbA1C、HOMA-IR、FINS、BMI及LH、FSH、总睾酮(P < 0.05),改善了PCOS患者的血脂水平、促使其月经周期的建立,提高了PCOS患者的正常排卵率、自然受孕率,但利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍组患者的胃肠道反应发生率明显增加,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍可改善多囊卵巢综合征(PCOS)患者的糖脂代谢,降低LH、FSH、总睾酮水平,促使月经周期的建立,提高排卵率及受孕率,但胃肠道反应明显增加。 Abstract:Objective To systematically evaluate the effects of liraglutide combined with metformin on glucose and lipid metabolism, sex hormones, reproductive function, and gastrointestinal reactions in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Methods We searched databases such as PubMed, WanFang Medical Network, WanFang Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure(CNKI), and VIP Journals to collect randomized controlled trials published from January 2011 to August 2022 on the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with liraglutide combined with metformin, using Revman 5.4 for the meta-analysis. Results A total of 16 case-control studies were included, involving 1436 patients. Compared to metformin alone, the combination of liraglutide and metformin significantly lowered fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood glucoseafter 2 hours, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, FINS, BMI, as well as LH, FSH, and total testosterone in patients with PCOS. It improved lipid levels, helped establish menstrual cycles, and increased the normal ovulation rate and natural conception rate in these patients. However, there was a significantly higher incidence of gastrointestinal reactions in the liraglutide plus metformin group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).Conclusion The combination of liraglutide and metformin can improve glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), reduce levels of LH, FSH, and total testosterone, help establish regular menstrual cycles, and increase ovulation and pregnancy rates, but it significantly increases gastrointestinal side effects. -
Key words:
- Liraglutide /
- Metformin /
- Polycystic ovary syndrome /
- Glycolipid metabolism
-
表 1 纳入荟萃分析的16篇文献资料
Table 1. 16 studies included in the meta-analysis
第一作者/发表年份 研究起始时间 联合治疗组
(n)对照组
(n)分组方法 治疗时间
(周)疗效指标 黄昭穗,2015[4] 2011.3-2014.3 87 85 随机数字表法 24 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨⑩⑪⑫⑬⑭⑮⑯⑰ 郝建民,2020[5] 2017.6-2018.12 93 93 随机数字表法 12 ①②④⑤⑥⑨⑰ 郑亮,2022[6] 2018.5-2020.12 75 75 随机抽签法 24 ①②③④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨⑩⑪⑫⑬⑭⑮⑯⑰ 赵丹,2019[7] 2015.1-2018.10 30 30 患者选择不同治疗方案 24 ①②③④⑥⑦⑧⑨⑰ 谭明灯,2022[8] 2018.11-2020.11 46 46 随机数字表法 16 ①②③④⑦⑧⑨⑩⑪⑫⑬⑭⑮⑯⑰ 王爱媛,2020[9] 2018.1-2020.2 30 30 奇偶数法 4 ①②③④⑥ 杨莉,2022[10] 2018.5-2020 .5 50 50 随机数字表法 24 ①②④⑥⑦⑧⑨ 杨茜,2021[11] 2017.3-2020.3 50 50 奇偶数法 12 ①②④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨⑭⑮⑯⑰ 张波,2019[12] 2017.1-2019.1 42 42 随机数字表法 16 ①②③⑩⑪⑫⑬⑰ 宛光彩,2021[13] 2018.1-2019.1 30 30 随机数字表法 24 ①②③④⑦⑧⑰ 孙海云,2021[14] 2019.3-2020.3 56 56 随机分组 16 ①④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨⑰ 孙晖,2020[15] 2018.1-2020.1 37 37 随机数字表法 24 ①②③④⑦⑧⑨⑭⑮⑰ 仉媛媛,2020[16] 2018.1-2019.6 41 41 随机分组 12 ①②④⑤⑨ Vesna Salamun,2018[17] 2014.9-2015.5 13 14 随机分组 12 ①②④⑤⑥⑨⑰ Mojca Jensterle
Sever,2014[18]2011.11-2012.5 11 14 随机分组 12 ①②④⑤⑥⑨⑪⑫⑬⑰ Chuan Xing,2022[19] 2021.1-2022.1 27 25 随机分组 12 ①④⑤⑥⑦⑧⑨ 联合治疗组:利拉鲁肽+二甲双胍;对照组:二甲双胍,疗效指标:①空腹血糖,②餐后2 h血糖,③糖化血红蛋白,④胰岛素抵抗指数,⑤空腹胰岛素,⑥BMI,⑦促黄体生成素,⑧促卵泡刺激素,⑨总睾酮,⑩总胆固醇,⑪甘油三酯,⑫低密度脂蛋白,⑬高密度脂蛋白,⑭建立月经周期,⑮正常排卵率,⑯自然受孕率,⑰胃肠道反应。 -
[1] Tzotzas T,Karras S N,Katsiki N. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists in the treatment of obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Curr Vasc Pharmacol,2017,15(3):218-229. doi: 10.2174/1570161114666161221115324 [2] Pani A,Gironi I,Di Vieste G,et al. From prediabetes to type 2 diabetes mellitus in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Lifestyle and pharmacological management[J]. International Journal of Endocrinology,2020,7(8):1-10. [3] Siamashvili M ,Davis S N. Update on the effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol,2021,14(9): 1081-1089. [4] 黄昭穗,栾丽丽,杨骄,等. 利拉鲁肽对多囊卵巢综合征合并糖耐量异常及肥胖患者的代谢及受孕的影响[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2015,7(7):437-441. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-5809.2015.07.009 [5] 郝建民,卢涛,邱娟,等. 利拉鲁肽提高肥胖不孕多囊卵巢综合征妇女临床妊娠率的研究[J]. 实用药物与临床,2020,23(1):51-58. [6] 郑亮,黎淑贞 ,林小玲. 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍治疗多囊卵巢综合征患者糖脂代谢紊乱及生殖功能异常[J]. 吉林医学,2022,43(9): 2442-2444. [7] 赵丹. 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍治疗2型糖尿病合并多囊卵巢综合征的临床效果观察[J]. 中国现代医生,2019,57(9):43-45,55. [8] 谭明灯,崔小平 ,陈平. 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍对肥胖型多囊卵巢综合征患者糖脂代谢及生殖功能的影响[J]. 中国计划生育和妇产科,2022,14(9): 74-78. [9] 王爱媛,吕月,卢雅丹,等. 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍治疗2型糖尿病合并多囊卵巢综合征的临床效果观察[J]. 实用妇科内分泌电子杂志,2020,7(35): 34-41. [10] 杨莉,邓赫男,谭琛,等. 利拉鲁肽辅助治疗多囊卵巢综合征的效果及对卵巢功能的影响[J]. 医学理论与实践,2022,35(10):1712-1714. [11] 杨茜,张海雄,韩雪梅,等. 利拉鲁肽治疗对肥胖多囊卵巢综合征患者生育功能的影响[J]. 川北医学院学报,2021,36(12):1634-1637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3697.2021.12.023 [12] 张波. 利拉鲁肽联合盐酸二甲双胍治疗多囊卵巢综合征伴糖脂代谢紊乱的临床效果[J]. 中国当代医药,2019,26(32):36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4721.2019.32.011 [13] 苑光彩. 利拉鲁肽治疗2型糖尿病合并多囊卵巢综合征的临床价值研究[J]. 糖尿病新世界,2021,24(1):14-16. [14] 孙海云,胡玉宏 ,徐水芳. 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍对多囊卵巢综合征患者卵巢功能的影响[J]. 现代药物与临床,2021,36(8): 1654-1658. [15] 孙晖. 利拉鲁肽联合二甲双胍对2型糖尿病合并多囊卵巢综合征患者代谢和内分泌参数的影响研究[J]. 实用妇科内分泌电子杂志,2020,7(3): 16,21. [16] 仉媛媛,韩晓璐,刘鸿丽,等. 应用利拉鲁肽对中心性肥胖和非中心性肥胖多囊卵巢综合征患者生殖内分泌及糖脂代谢的改善分析[J]. 饮食保健,2020,7(24):21-22. [17] Salamun V,Jensterle M,Janez A,et al. Liraglutide increases IVF pregnancy rates in obese PCOS women with poor response to first-line reproductive treatments: A pilot randomized study[J]. Eur J Endocrinol,2018,179(1):1-11. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0175 [18] Jensterle Sever M,Kocjan T,Pfeifer M,et al. Short-term combined treatment with liraglutide and metformin leads to significant weight loss in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and previous poor response to metformin[J]. Eur J Endocrinol,2014,170(3):451-459. doi: 10.1530/EJE-13-0797 [19] Xing C,Zhao H,Zhang J,et al. Effect of metformin versus metformin plus liraglutide on gonadal and metabolic profiles in overweight patients with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2022,8(17):421-429. [20] 柳丽佳,邵铜,方媛,等. 1990—2019年中国多囊卵巢综合征发病趋势分析[J]. 中国预防医学杂志,2023,24(3):259-263. [21] Del Olmo-Garcia M I,Merino-Torres J F. GLP-1 receptor agonists and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. J Diabetes Res,2018,4(2):492-503. [22] McCreight L J,Bailey C J ,Pearson E R. Metformin and the gastrointestinal tract[J]. Diabetologia,2016,59(3): 426-435. [23] Conway G,Dewailly D,Diamanti-Kandarakis E,et al. European survey of diagnosis and management of the polycystic ovary syndrome: Results of the ESE PCOS Special Interest Group's Questionnaire[J]. Eur J Endocrinol,2014,171(4):489-498. doi: 10.1530/EJE-14-0252 [24] Long X,Liu H,Xiong W,et al. Low dose of liraglutide combined with metformin leads to a significant weight loss in Chinese Han women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A retrospective study[J]. Gynecol Endocrinol,2023,39(1):648-657. [25] Jensterle M,Kravos N A,Goričar K,et al. Short-term effectiveness of low dose liraglutide in combination with metformin versus high dose liraglutide alone in treatment of obese PCOS: Randomized trial[J]. BMC Endocr Disord,2017,17(1):51-59. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0201-7 [26] Lim S S,Hutchison S K,Van Ryswyk E,et al. Lifestyle changes in women with polycystic ovary syndrome[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2019,3(3):506-512. [27] Glueck C J ,Goldenberg N. Characteristics of obesity in polycystic ovary syndrome: Etiology,treatment,and genetics[J]. Metabolism,2019,92(3): 108-120. [28] Sikirica M V,Martin A A,Wood R,et al. Reasons for discontinuation of GLP1 receptor agonists: data from a real-world cross-sectional survey of physicians and their patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes,2017,9(10):403-412. -





 下载:
下载: