The Interaction among Gene Polymorphisms of RANTES and Its Receptor CCR5 and Environmental Factors in the Development of T2DM in Kunming Han Nationality
-
摘要:
目的 探讨RANTES基因启动子区rs2280788位点、CCR5基因启动子区rs1799987位点多态性及环境因素在昆明地区汉族2型糖尿病(Type 2 diabetes mellitus, T2DM)的发生中是否存在交互作用。 方法 收集92例昆明地区汉族血糖正常者和97例T2DM患者的一般资料及外周静脉血,采用Taqman实时荧光定量PCR检测RANTES基因 rs2280788位点及其受体CCR5基因rs1799987位点的多态性,运用多因子降维法(multifactor dimensionality reduction, MDR)分析RANTES及其受体基因多态性与环境因素在昆明地区汉族T2DM的发生中是否存在交互作用。 结果 CCR5 rs1799987与RANTES rs2280788间存在交互作用(测试组平衡精度为0.5314,训练组平衡精度为0.5820,交叉验证一致性为10/10,P < 0.05,OR:2.0465,95%CI:1.1118~3.7672);高血压与中心性肥胖间存在交互作用(测试组平衡精度为0.7031,训练组平衡精度为0.7031,交叉验证一致性为10/10,P < 0.001,OR:8.1640,95%CI:3.8745~17.2026);未发现CCR5 rs1799987与环境因素、RANTES rs2280788与环境因素间存在交互作用(P > 0.05)。 结论 RANTES基因启动子区-28(rs2280788)与CCR5基因启动子区59029(rs1799987)SNP位点之间、高血压与中心性肥胖之间均存在交互作用,具有交互作用的因素同时存在会增加昆明地区汉族T2DM的患病风险。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the interaction among RANTES gene promoter region rs2280788 C/G polymorphism, CCR5 gene promoter region rs1799987 G/A polymorphism and environmental factors in the development of Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in the Han ethnic group in Kunming. Methods The general data and peripheral venous blood of 92 Han people with normal blood glucose and 97 Han T2DM patients in Kunming area were collected. Polymorphisms of RANTES gene rs2280788 and CCR5 gene rs1799987 were detected by TaqMan real-time quantitative PCR. Multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) was used to analyze the interaction among the gene polymorphisms of RANTES and its receptor and environmental factors in the occurrence of T2DM in Han nationality in Kunming. Results There was an interaction between CCR5 rs1799987 and RANTES rs2280788 (the testing balance accuracy was 0.5314, the training balance accuracy was 0.5820, and the cross validation consistency was 10/10, P < 0.05, OR: 2.0465, 95%CI: 1.1118-3.7672); There was an interaction between hypertension and central obesity (the testing balance accuracy was 0.7031, the training balance accuracy was 0.7031, the cross validation consistency was 10/10, P < 0.001, OR: 8.1640, 95%CI: 3.8745-17.2026); No interaction between CCR5 rs1799987 and environmental factors, as well as RANTES rs2280788 and environmental factors was found (P > 0.05). Conclusions There are interactions between the RANTES gene promoter region -28 (rs2280788) and the CCR5 gene promoter region 59029 (rs1799987) SNP, as well as between hypertension and central obesity, the co-existence of interacting factors will increase the risk of T2DM in Han nationality in Kunming. -
Key words:
- RANTES /
- CCR5 /
- Gene polymorphism /
- Type 2 diabetes /
- Interaction
-
2型糖尿病(type 2 diabetes mellitus, T2DM)是一种慢性代谢性疾病,遗传因素和环境因素在糖尿病的发生与发展中发挥重要作用。单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism, SNP)是人类遗传变异最常见的一种形式,被广泛应用于糖尿病、高血压的候选基因关联研究中。近年来随着全基因组关联研究(genome-wide association studies, GWAS)技术的发展,新的T2DM易感基因SNP位点被不断报道[1]。SNP与环境因素相互作用,共同影响个体的疾病易感性[2]。鉴于不同地区和种族人群易感基因SNP位点的分布不同,项目组检测了主要参与炎症反应的正常T细胞表达和分泌的活性调节蛋白(regulated upon activation normal T cell expressed and secreted, RANTES)基因启动子区-28(rs2280788)C/G多态性及其受体CCR5基因启动子区59029(rs1799987)A/G多态性,旨在探讨这2个SNP位点间以及2个SNP位点与环境因素间在T2DM的发生中是否存在交互作用,为T2DM的早期防治提供重要依据。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取在昆明医科大学第一附属医院就诊的189名汉族人作为研究对象,其中糖尿病组(DM组)97例(男57,女40),年龄(49.53±12.52)岁,均为确诊的T2DM患者;血糖正常组(NC组)92例(男43,女49),年龄(46.22±11.77)岁,均为体检中心体检后的血糖正常者且既往无糖尿病病史。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 一般资料收集
采用自编问卷收集研究对象的基本信息,包括年龄、性别、身高、体重、腰围、臀围、收缩压、舒张压、高血压史、吸烟史、饮酒史等;并计算体质指数(body mass index, BMI)和腰臀比(waist-to-hip ratio, WHR)。
1.2.2 生化指标检测
抽取研究对象的空腹静脉血,采用全自动生化分析仪检测空腹血糖(fasting plasma glucose, FPG)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol, TC)、甘油三酯(triglycerides, TG)、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, HDL-C)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C);采用高效液相色谱法检测糖化血红蛋白。
1.2.3 基因多态性检测
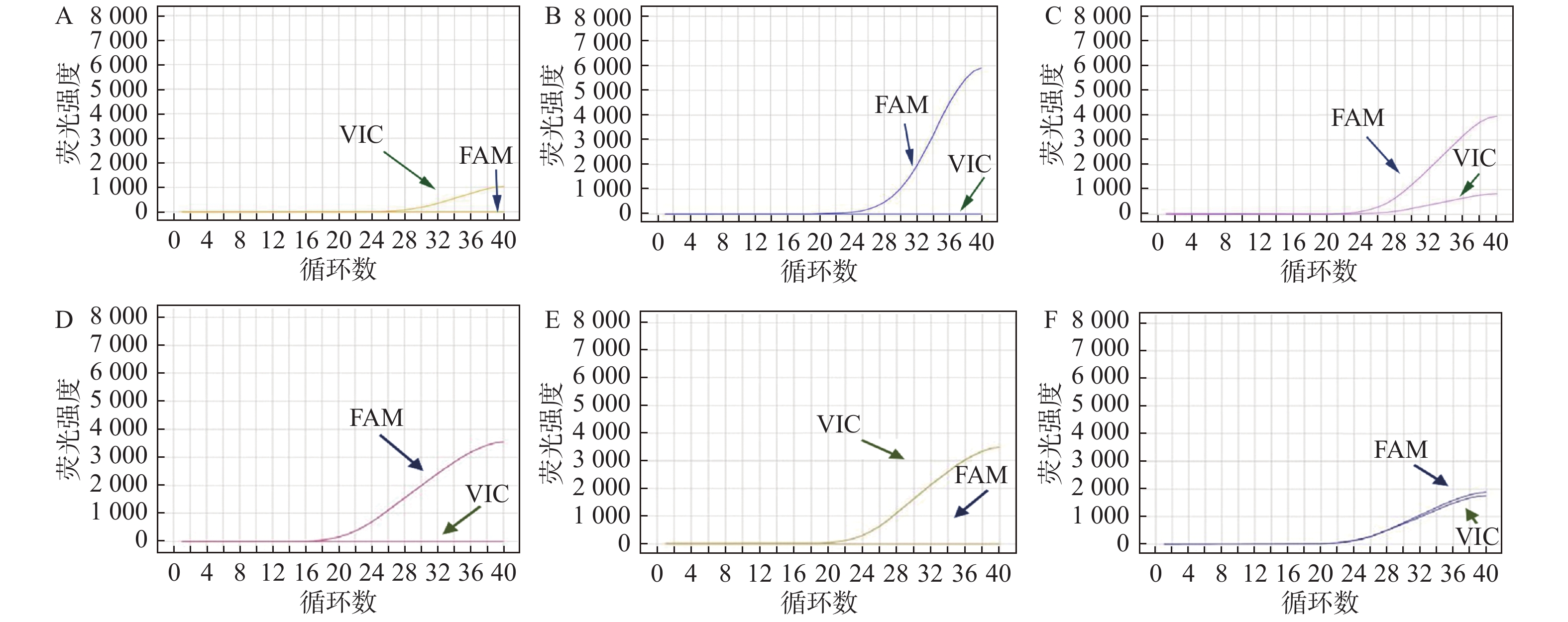
采用柱式小量全血基因组DNA快速提取试剂盒(北京博迈德科技发展有限公司)提取受试者外周静脉血DNA。使用北京擎科新业生物技术有限公司合成的RANTES基因rs2280788位点特异性片段引物及探针、ABI合成的CCR5基因rs1799987位点特异性片段引物及探针,采用Taqman实时荧光定量PCR法检测RANTES基因启动子区 -28(rs2280788)基因多态性及CCR5基因启动子区 59029(rs1799987)基因多态性。根据PCR产物熔解曲线进行基因分型,见图1。
1.3 诊断标准
1.3.1 糖尿病
参照世界卫生组织(world health organization, WHO)1999年诊断标准[3],典型糖尿病症状(多饮、多尿、多食、体重下降)加随机血糖 ≥ 11.1 mmol/L,或FPG ≥ 7.0 mmol/L,或口服葡萄糖耐量试验(oral glucose tolerance test, OGTT)2 h血糖 ≥ 11.1 mmol/L;或已确诊糖尿病并已进行治疗者。
1.3.2 高血压
参照《中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)》[4],在未使用降压药物的情况下,非同日3次测量诊室血压,收缩压 ≥ 140 mmHg 和(或)舒张压 ≥ 90 mmHg。既往有高血压史,目前正在使用降压药物,血压低于140/90 mmHg的患者仍诊断为高血压。
1.3.3 血脂异常
参照《中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)》[5],TG ≥ 1. 7 mmol /L,TC ≥ 5.2 mmol /L,LDL-C ≥ 3. 4 mmol /L,HDL-C ≤ 1.0 mmol/L,这四项血脂指标任何一项异常则诊断为血脂异常。
1.3.4 超重、肥胖、中心性肥胖
参照《中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南》[6],24 kg/m2 ≤ BMI < 28 kg/m2为超重,BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2为肥胖;男性腰围 ≥ 85 cm,女性腰围 ≥ 80 cm为中心性肥胖。
1.4 统计学处理
采用χ2拟合优度检验基因型分布是否符合 Hardy-Weinberg 遗传平衡定律。采用SPSS 26.0进行统计学分析,正态计量资料使用均数±标准差表示,非正态计量资料使用中位数(下四分位数,上四分位数)表示,计数资料采用率表示。两组间正态计量资料比较采用两独立样本t检验,非正态计量资料比较采用两独立样本秩和检验。采用多因子降维法(multifactor dimensionality reduction,MDR)3.0.2 软件分析各因素间的交互作用。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 一般资料比较
DM组的FPG、HbA1c、腰围、BMI、收缩压、TG高于NC组,TC、HDL低于NC组(P < 0.05),两组间年龄、性别、舒张压、LDL水平无统计学差异(P > 0.05),见表1。
表 1 研究对象的基线资料比较 ($\bar x \pm s$ )Table 1. Comparison of baseline data of the subjects ($ \bar x \pm s$ )特征 NC组
(n = 92)DM组
(n = 97)t/Z/χ2 P 年龄(岁) 46.22 ± 11.77 49.53 ± 12.52 −1.87 0.063 性别[n(%)] 女性 49(53.30) 40(41.20) 2.74 0.098 男性 43(46.70) 57(58.80) FPG (mmol/L) 5.03 ± 0.69 8.38 ± 2.95* −10.892 < 0.001 HbA1c (%) 5.58 ± 0.39 9.20 ± 2.21* −15.915 < 0.001 腰围 (cm) 83.83 ± 11.84 90.79 ± 10.09* −4.359 < 0.001 BMI (kg/m2) 24.02 ± 3.73 25.17 ± 3.85* −2.086 0.038 收缩压 (mmHg) 119.68 ± 16.92 130.65 ± 19.35* −4.138 < 0.001 舒张压 (mmHg) 79.38 ± 9.94 77.82 ± 11.44 0.996 0.321 TC (mmol/L) 4.99 ± 0.88 4.47 ± 1.13* 3.49 0.001 HDL (mmol/L) 1.34(1.11,1.64) 1.00(0.85,1.17) * −6.411 < 0.001 TG (mmol/L) 1.25(0.90,1.99) 1.61(1.07,2.31) * −2.148 0.032 LDL (mmol/L) 2.88(2.50,3.66) 3.08(2.32,3.45) −0.16 0.873 与NC组比较,*P < 0.05。 2.2 基因型频率和等位基因频率分布
经χ2拟合优度检验,DM组和NC组的CCR5 rs1799987基因多态性位点及RANTES rs2280788基因多态性位点的基因型分布均符合Hardy-Weinberg平衡定律(P > 0.05),所选样本具有群体代表性。DM组和NC组组间的CCR5 rs1799987基因型频率及A/G等位基因频率、RANTES rs2280788基因型频率及C/G等位基因频率差异统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表2。
表 2 DM组和NC组的CCR5 rs1799987及RANTES rs2280788基因型及等位基因频率 [n(%)]Table 2. Genotypes and allele frequencies of CCR5 rs1799987 and RANTES rs2280788 in DM and NC groups [n(%)]组别 基因型频率 等位基因频率 CCR5 rs1799987 AA AG GG A G NC组 19(20.70) 49(53.30) 24(26.10) 87(47.28) 97(52.72) DM组 18(18.60) 47(48.50) 32(33.00) 83(42.78) 111(57.22) RANTES rs2280788 CC + CG GG − C G NC组 20(21.70) 72(78.30) − 22(11.96) 162(88.04) DM组 23(23.70) 74(76.30) − 24(12.37) 170(87.63) 注:因RANTES rs2280788CC基因型仅3例,RANTES rs2280788 CG基因型40例,因此将这两个基因型合并到RANTES rs2280788 CC + CG组一起分析。 2.3 基因-基因交互作用与T2DM的相关性分析
以是否患T2DM(NC组 = 0,DM组 = 1)作为因变量,CCR5 rs1799987基因型(1 = AA,2 = AG,3 = GG)、RANTES rs2280788基因型(1 = CC,2 = CG,3 = GG)为自变量,将数据导入MDR软件,得到1~2阶交互模型,见表3。
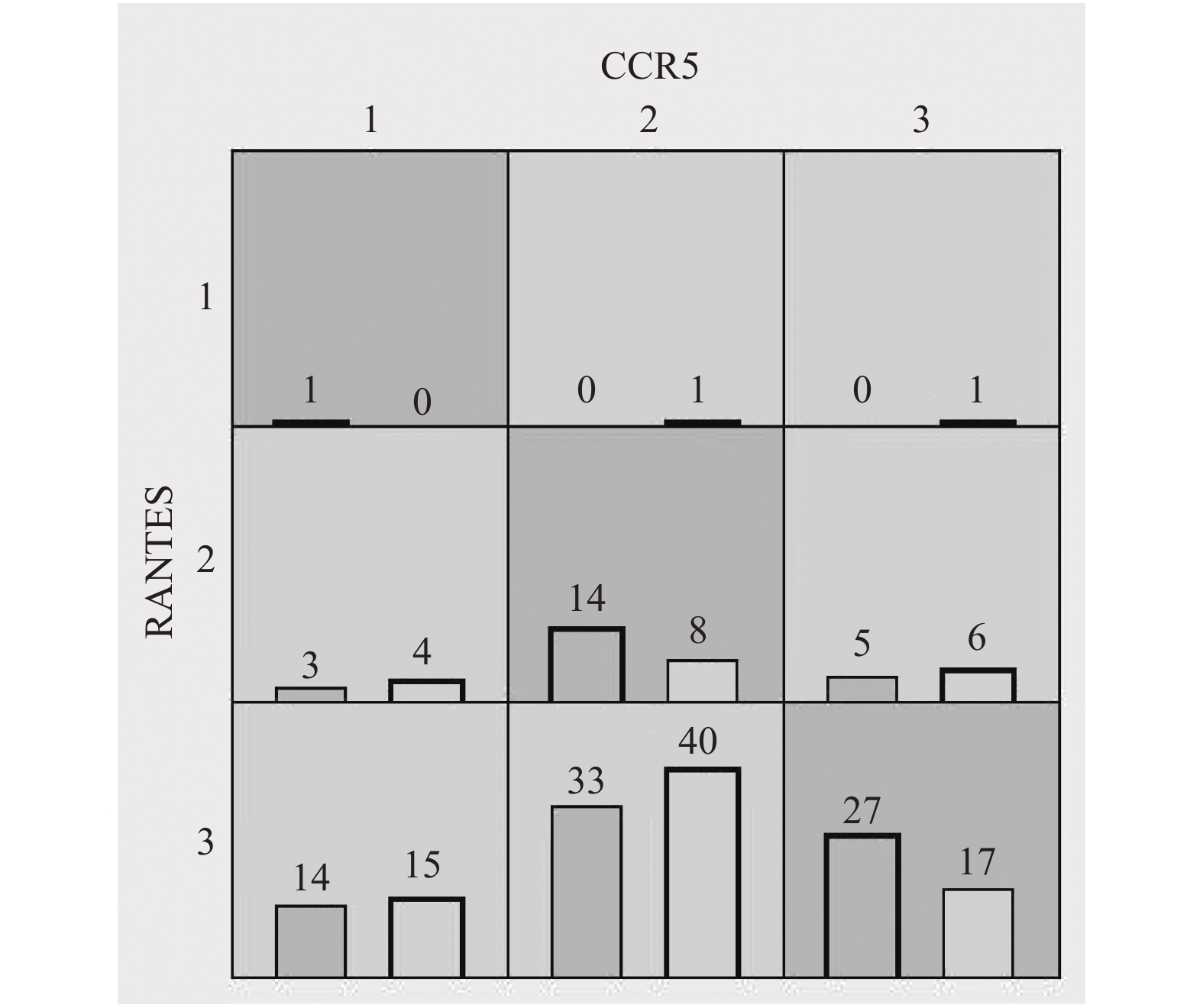
表 3 基因-基因交互作用的多因子降维法模型Table 3. MDR models of gene-gene interactions模型 训练组平衡精度 测试组平衡精度 交叉验证一致性 P值 OR 95%CI X1 0.5371 0.4338 7/10 0.2989 1.3949 0.7436~2.6166 X1、X2 0.5820 0.5314 10/10 0.0205 2.0465 1.1118~3.7672 X1:CCR5 rs1799987基因型;X2:RANTES rs2280788基因型。 经置换检验,一因素模型差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),二因素模型差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),即CCR5 rs1799987 -RANTES rs2280788交互模型为最佳模型,该模型的交叉验证一致性为10/10,测试组平衡精度为0.5314。两因素交互模型,见图2。
交互模型图解析:图中每个单元格里左侧的条形表示病例组,右侧的条形表示对照组,病例数 ≥ 对照数的单元格呈深灰色(提示该因素组合为高危组合),病例数 < 对照数的单元格呈浅灰色(提示该因素组合为低危组合)。图2显示:CCR5 rs1799987 AA及RANTES rs2280788 CC基因型携带者、CCR5 rs1799987 AG及RANTES rs2280788 CG基因型携带者、CCR5 rs1799987 GG及RANTES rs2280788 GG基因型携带者患T2DM风险明显增加。
表3所示,携带以上3种具有交互作用的任何一种基因型组合个体患T2DM的风险是未携带者的2.0465倍(OR 2.0465,95%CI 1.1118~3.7672)。
2.4 基因-环境交互作用与T2DM的相关性分析
以是否患T2DM(NC组 = 0,DM组 = 1)为因变量,CCR5 rs1799987基因型、RANTES rs2280788基因型、吸烟、饮酒、高血压、BMI、中心性肥胖、血脂为自变量,采用 MDR 分析各因素间的交互作用,赋值情况见表4。
表 4 MDR软件中各变量赋值情况Table 4. Variable assignment in MDR变量 赋值 CCR5 rs1799987基因型 1 = AA,2 = AG,3 = GG RANTES rs2280788基因型 1 = CC,2 = CG,3 = GG 吸烟 0 = 否,1 = 是 饮酒 0 = 否,1 = 是 高血压 0 = 否,1 = 是 BMI 0 = < 18.5,1 = 18.5-23.9,2 = ≥ 24.0 中心性肥胖 0 = 否,1 = 是 血脂 0 = 血脂正常,1 = 血脂异常 经分析得出1~3阶交互模型,见表5,经置换检验发现,3个模型均有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。其中高血压-中心性肥胖两因素模型的交叉验证一致性最大(10/10),且测试组平衡精度最高(0.7031),故两因素交互模型为最佳模型。两因素交互模型见图3。图3显示,患高血压的中心性肥胖人群发生T2DM的风险较无高血压和中心性肥胖人群明显增加。表5显示,患高血压的中心性肥胖人群发生T2DM的风险是无高血压和中心性肥胖人群的8.1640倍(OR:8.1640,95%CI:3.8745~17.2026)。未发现CCR5 rs1799987及RANTES rs2280788位点与环境因素间存在交互作用。
表 5 基因与环境因素交互作用的多因子降维法模型Table 5. MDR models of the interaction of genes and environmental factors模型 训练组平衡精度 测试组平衡精度 交叉验证一致性 P OR 95%CI X1 0.6748 0.6748 10/10 < 0.001 4.7143 2.4914-8.9206 X1、X2 0.7031 0.7031 10/10 < 0.001 8.1640 3.8745-17.2026 X1、X2、X3 0.7333 0.6691 6/10 < 0.001 9.5000 4.5822-19.6956 注:X1:高血压,X2:中心性肥胖;X3:饮酒。 3. 讨论
遗传因素在T2DM的发生中发挥重要作用,目前已报道超过100个基因位点与T2DM的患病风险相关[7]。不同的基因位点间可能存在交互作用,共同对T2DM的易感性产生影响[8]。本研究采用多因子降维法对CCR5 rs1799987、RANTES rs22807882个SNP位点在T2DM发病中的影响进行了分析,发现这2个SNP位点间存在交互作用,CCR5 rs1799987 AA基因型与RANTES rs2280788 CC基因型、CCR5 rs1799987 AG基因型与RANTES rs2280788 CG基因型、CCR5 rs1799987 GG基因型与RANTES rs2280788 GG基因型3种交互形式中任何一种的携带者发生T2DM的风险增加约1倍,这为早期筛查T2DM的高危人群提供了重要线索,为糖尿病的早期防治提供指导依据。
T2DM的发病是遗传和环境因素相互作用的结果,有报道TCF7L2 rs290487与饮酒和高血压[9]、IGF2BP2rs4402960与吸烟[10]、INAFM2 rs67839313与鸡蛋摄入量[11]、CDKN2A/CDKN2B rs10811661与BMI、腰围和腰臀比[12]等在T2DM发生中存在交互影响。而本研究未发现CCR5 rs1799987、RANTES rs22807882个SNP位点与环境因素吸烟、饮酒、高血压、BMI、中心性肥胖、血脂异常在昆明地区汉族T2DM的发病中存在交互作用,这与龙天柱[13]、许红霞等[14]的研究结论相似。T2DM的发病机制复杂,单一模型可能无法清楚的解释其中的因果关系,而且当纳入的分析因素较多,样本量不够大时,拟合降维分析的效能也会降低[15],这也可能是本研究未发现遗传与环境因素间存在交互作用的原因。因此,将来仍有必要扩大样本进一步深入研究。
另外,本研究发现高血压和中心性肥胖在昆明汉族T2DM的发病过程中存在交互作用,同时有高血压和中心性肥胖的人群发生T2DM的风险是无高血压和中心性肥胖人群的8.1640倍。也有多项研究报道高血压是糖尿病的危险因素之一[16-18],这可能与内皮功能障碍、炎性与抗炎性因子平衡的紊乱有关[19]。中心性肥胖个体多余脂肪在肝脏、肌肉等非脂肪组织中的积聚会导致胰岛素抵抗,在胰腺中的积聚会产生破坏性脂毒素、游离脂肪酸和炎性介质引起胰岛β细胞的破坏,从而导致糖尿病的发生[20-22]。但高血压和中心性肥胖之间的交互作用增加罹患 T2DM 的机制目前尚不清楚,有待深入研究。
综上所述,本研究发现在昆明地区汉族人群T2DM的发生中,RANTES基因启动子区-28(rs2280788)与CCR5基因启动子区59029(rs1799987)两个SNP位点间、高血压和中心性肥胖间存在交互作用,会使T2DM的发生风险增加。因此,针对交互作用的危险因素早期筛查糖尿病的高危人群,积极进行环境因素的干预可能对减少或延缓糖尿病的发生与发展具有重要指导意义。
-
表 1 研究对象的基线资料比较 (
$\bar x \pm s$ )Table 1. Comparison of baseline data of the subjects (
$ \bar x \pm s$ )特征 NC组
(n = 92)DM组
(n = 97)t/Z/χ2 P 年龄(岁) 46.22 ± 11.77 49.53 ± 12.52 −1.87 0.063 性别[n(%)] 女性 49(53.30) 40(41.20) 2.74 0.098 男性 43(46.70) 57(58.80) FPG (mmol/L) 5.03 ± 0.69 8.38 ± 2.95* −10.892 < 0.001 HbA1c (%) 5.58 ± 0.39 9.20 ± 2.21* −15.915 < 0.001 腰围 (cm) 83.83 ± 11.84 90.79 ± 10.09* −4.359 < 0.001 BMI (kg/m2) 24.02 ± 3.73 25.17 ± 3.85* −2.086 0.038 收缩压 (mmHg) 119.68 ± 16.92 130.65 ± 19.35* −4.138 < 0.001 舒张压 (mmHg) 79.38 ± 9.94 77.82 ± 11.44 0.996 0.321 TC (mmol/L) 4.99 ± 0.88 4.47 ± 1.13* 3.49 0.001 HDL (mmol/L) 1.34(1.11,1.64) 1.00(0.85,1.17) * −6.411 < 0.001 TG (mmol/L) 1.25(0.90,1.99) 1.61(1.07,2.31) * −2.148 0.032 LDL (mmol/L) 2.88(2.50,3.66) 3.08(2.32,3.45) −0.16 0.873 与NC组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 2 DM组和NC组的CCR5 rs1799987及RANTES rs2280788基因型及等位基因频率 [n(%)]
Table 2. Genotypes and allele frequencies of CCR5 rs1799987 and RANTES rs2280788 in DM and NC groups [n(%)]
组别 基因型频率 等位基因频率 CCR5 rs1799987 AA AG GG A G NC组 19(20.70) 49(53.30) 24(26.10) 87(47.28) 97(52.72) DM组 18(18.60) 47(48.50) 32(33.00) 83(42.78) 111(57.22) RANTES rs2280788 CC + CG GG − C G NC组 20(21.70) 72(78.30) − 22(11.96) 162(88.04) DM组 23(23.70) 74(76.30) − 24(12.37) 170(87.63) 注:因RANTES rs2280788CC基因型仅3例,RANTES rs2280788 CG基因型40例,因此将这两个基因型合并到RANTES rs2280788 CC + CG组一起分析。 表 3 基因-基因交互作用的多因子降维法模型
Table 3. MDR models of gene-gene interactions
模型 训练组平衡精度 测试组平衡精度 交叉验证一致性 P值 OR 95%CI X1 0.5371 0.4338 7/10 0.2989 1.3949 0.7436~2.6166 X1、X2 0.5820 0.5314 10/10 0.0205 2.0465 1.1118~3.7672 X1:CCR5 rs1799987基因型;X2:RANTES rs2280788基因型。 表 4 MDR软件中各变量赋值情况
Table 4. Variable assignment in MDR
变量 赋值 CCR5 rs1799987基因型 1 = AA,2 = AG,3 = GG RANTES rs2280788基因型 1 = CC,2 = CG,3 = GG 吸烟 0 = 否,1 = 是 饮酒 0 = 否,1 = 是 高血压 0 = 否,1 = 是 BMI 0 = < 18.5,1 = 18.5-23.9,2 = ≥ 24.0 中心性肥胖 0 = 否,1 = 是 血脂 0 = 血脂正常,1 = 血脂异常 表 5 基因与环境因素交互作用的多因子降维法模型
Table 5. MDR models of the interaction of genes and environmental factors
模型 训练组平衡精度 测试组平衡精度 交叉验证一致性 P OR 95%CI X1 0.6748 0.6748 10/10 < 0.001 4.7143 2.4914-8.9206 X1、X2 0.7031 0.7031 10/10 < 0.001 8.1640 3.8745-17.2026 X1、X2、X3 0.7333 0.6691 6/10 < 0.001 9.5000 4.5822-19.6956 注:X1:高血压,X2:中心性肥胖;X3:饮酒。 -
[1] Sayed S, Nabi A. Diabetes and genetics: A relationship between genetic risk alleles, clinical phenotypes and therapeutic approaches[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol,2021,1307:457-498. [2] Teng F, Qin R, Liu X, et al. Interaction between the rs9356744 polymorphism and metabolic risk factors in relation to type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Cardiometabolic Risk in Chinese (CRC) Study[J]. J Diabetes Complications,2021,35(4):107855. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2021.107855 [3] World Health Organization. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications: report of a WHO consultation, Part 1: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus[J]. Geneva: WHO, Diagnosis,1999:3-4. [4] 中国高血压防治指南(2018年修订版)[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2019, 24(1): 24-56. [5] 中国成人血脂异常防治指南修订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中国循环杂志,2016,31(10):937-950. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3614.2016.10.001 [6] 中国肥胖问题工作组. 中国成人超重和肥胖症预防与控制指南(节录)[J]. 营养学报,2004,26(1):1-4. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.2004.01.001 [7] Gaulton Kyle J. Mechanisms of Type 2 Diabetes Risk Loci[J]. Current diabetes reports,2017,17(9):72. doi: 10.1007/s11892-017-0908-x [8] Martínez-Ramírez O C, Salazar-Piña D A, De Lorena R M, et al. Association of NFκβ, TNFα, IL-6, IL-1β, and LPL Polymorphisms with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Biochemical Parameters in a Mexican Population[J]. Biochem Genet, 2021. doi: 10.1007/S10528-021-10047-W. [9] Qie R, Han M, Huang S, et al. Association of TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms, methylation, and gene-environment interaction with type 2 d iabetes mellitus risk: A nested case-control study in the Rural Chinese Cohort Study[J]. J Diabetes Complications,2021,35(3):107829. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107829 [10] Nfor O N, Ndzinisa N B, Tsai M H, et al. Interactive Effect of IGF2BP2 rs4402960 Variant, Smoking and Type 2 Diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes,2020,13(期?):5097-5102. [11] Wang X, Wang Z, Wu J, et al. Interactive associations of the INAFM2 rs67839313 variant and egg consumption with type 2 diabetes mellitus and fasting blood glucose in a Chinese population: A family-based study[J]. Gene,2021,770:145357. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145357 [12] Liu J, Wang L, Qian Y, et al. Analysis of the interaction effect of 48 SNPs and obesity on type 2 diabetes in Chinese Hans[J]. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care,2020,8(2):e001638. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001638 [13] 龙天柱. EIF2S1和MAPK1基因多态性与2型糖尿病患病风险关联研究[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学硕士论文, 2019. [14] 许红霞, 王发选, 赵燚, 等. 多因子降维法分析9个SNPs及环境因素与宁夏农村人群高血糖的相关性[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报,2019,41(11):1117-1121. [15] 王娜娜, 张毓洪, 杨泽. 应用多因子降维法MDR分析基因-基因的交互作用[J]. 中国老年保健医学,2012,10(06):31-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4860.2012.06.007 [16] Zhang H, Rogers K, Sukkar L, et al. Prevalence, incidence and risk factors of diabetes in Australian adults aged ≥ 45 years: A cohort study using linked routinely-collected data[J]. J Clin Transl Endocrinol,2020,22:100240. [17] Yu X, Duan F, Lin D, et al. Prevalence of Diabetes, Prediabetes, and Associated Factors in an Adult Chinese Population: Baseline of a Prediabetes Cohort Study[J]. Int J Endocrinol,2020,2020:8892176. [18] Alam M S, Dyck R, Janzen B, et al. Risk factors, incidence, and prevalence of diabetes among rural farm and non-farm residents of Saskat chewan, Canada; a population-based longitudinal cohort study[J]. J Diabetes Metab Disord,2020,19(2):1563-1582. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00693-z [19] 任青娟. 单纯性肥胖人群2型糖尿病发病相关危险因素分析[D]. 石家庄: 河北医科大学硕士论文, 2008. [20] Weber MB, Oza-Frank R, Staimez LR, et al. Type 2 diabetes in Asians: prevalence, risk factors, and effectiveness of behavioral intervention at individual and population levels[J]. Annu Rev Nutr,2012,32:417-439. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071811-150630 [21] Newell AM. Genetics for targeting disease prevention: diabetes[J]. Prim Care,2004,31(3):743-66. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2004.04.002 [22] Unger RH, Orci L. Diseases of liporegulation: new perspective on obesity and related disorders[J]. Faseb J,2001,15(2):312-321. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0590 -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:

