Comparison of Two Surgical Managements for the Delayed Ankles Fracture Combined with Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Injuries
-
摘要:
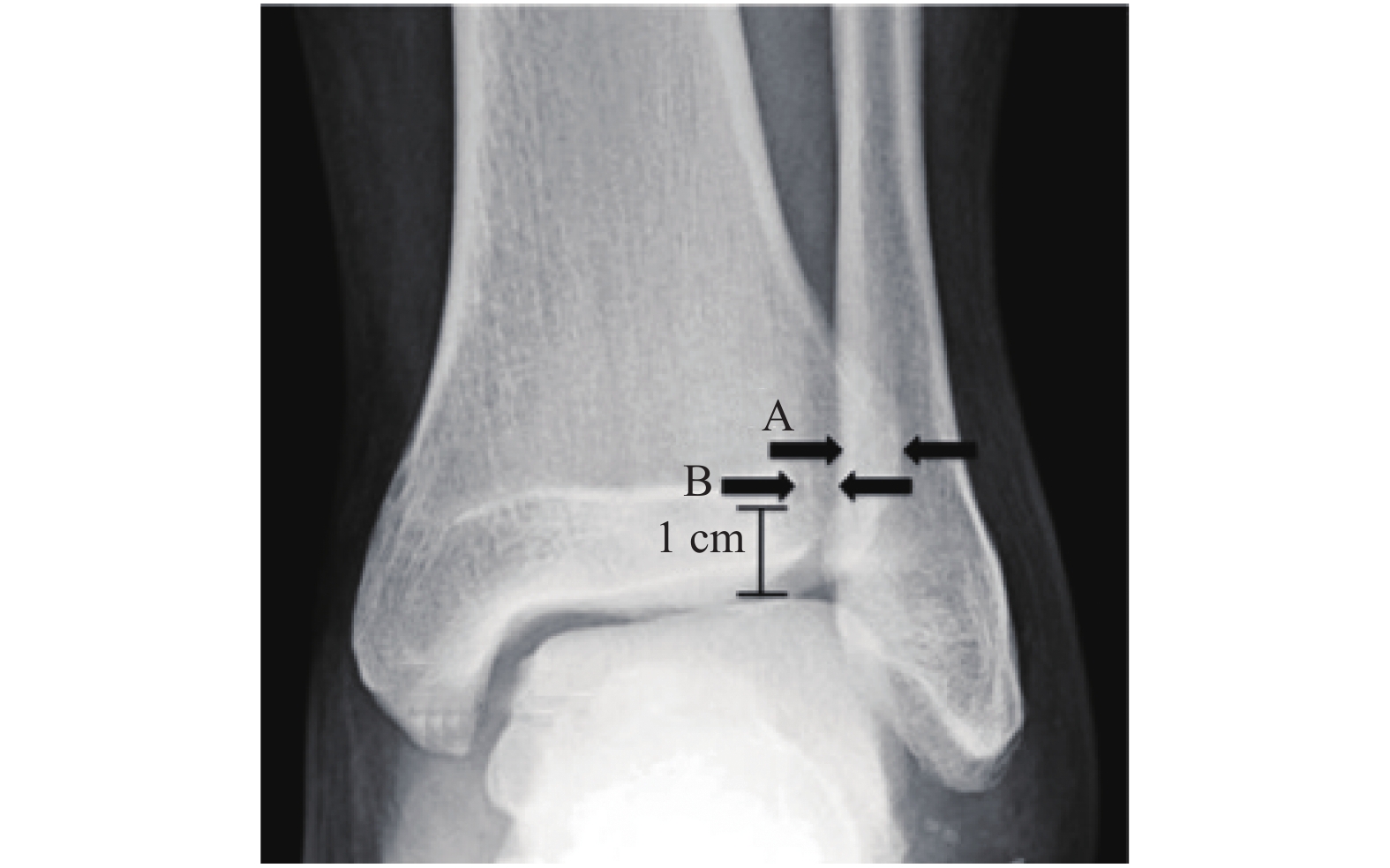
目的 探讨陈旧性踝关节骨折合并下胫腓联合韧带损伤(ankles fracture combined with distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injuries,AFTSI)的手术治疗效果。 方法 回顾性分析38例陈旧性AFTSI手术疗效,患者受伤至手术时间28~196 d,平均53 d。其中切开复位内固定 + 下胫腓联合Tighttrope袢钢板弹性固定18例(A组,n = 18),切开复位内固定 + 下胫腓联合螺钉固定20例(B组,n = 20),术后美国足踝外科学会评分、手术前后下胫腓间隙及下胫腓重叠阴影差值,平均住院时间,手术时间,术中失血量,术后开始完全负重时间用于评价疗效。所有患者均接受平均18个月随访,下胫腓联合螺钉于术后2~3月取出。 结果 所有患者均未出现切口感染、骨性关节炎、内固定断裂及踝穴增宽情况;术后AOFAS评分A组高于B组,术后开始完全负重时间A组早于B组(P < 0. 05);平均手术时间,术中失血量,平均住院时间,手术前后下胫腓重叠阴影差值及下胫腓间隙差值2组差异无统计学意义(P > 0. 05)。 结论 陈旧性AFTSI使用Tightrope袢钢板弹性固定患者可以早期负重,较传统的螺钉内固定具有更好的疗效。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of surgical treatments for delayed ankles fracture combined with distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injuries (AFTSI). Methods A retrospective study the operative effects of 38 cases of delayed AFTSI treated with open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) + Tightrope fixation (group A, n = 18) or ORIF + screw fixation (group B, n = 20) for syndesmosis injuries. AOFAS (Ankle-Hindfoot Score system), hospital stay, operative time, introperative blood loss, full weightbearing time, difference value between preoperative and postoperative tibiofibular clear space (TFCS) and tibiofibular overlap (TFO) were used to evaluate the postoperative curative effect. All patients were received a follow-up with an average of 18 months, and the syndesmosis screws were removed 2-3 months after operations. Results AOFAS score was higher in group A than in group B, postoperative onset time of full weightbearing was earlier in group A than in group B statistically (P < 0. 05), while no statistics difference were found between 2 groups in the factors of hospital stay, operative time, introperative blood loss, and the difference value between preoperative and postoperative time on TFCS together with TFO. Conclusion Tightrope syndesmosis fixation is a better options to enable early weight bearing for the delayed AFTSI compared with the traditional screws fixation. -
Key words:
- Delayed ankle fracture /
- Syndesmosis injury /
- Surgical management /
- Dynamic stabilization
-
表 1 患者一般资料(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. General information of patients (
$\bar x \pm s $ )组别 A组(下胫腓弹性固定,n = 18) B组(下胫腓螺钉固定,n = 20) P 病例数(n) 18 20 - 性别(男/女,n) 14/4 16/4 0.867 年龄(岁) 41.78 ± 13.65 39.5 ± 12.04 0.588 损伤至手术时间(d) 48.56 ± 33.78 57.1 ± 38.49 0.474 受伤机制(高坠/车祸/扭伤)(n) 6/5/7 7/4/9 0.846 Lauge-Hansen分型[10](旋后外旋/旋后内收型/
旋前外旋型/旋前外展型/垂直跖屈型)(n)7/4/4/2/1 9/5/3/2/1 0.982 骨折解剖分型(双踝/三踝)(n) 10/8 14/6 0.357 一般资料中年龄及损伤至手术时间2组比较采用独立样本t检验,其余指标卡方检验,显著水平设定成0.05。 表 2 AOFAS评分,术后完全负重、平均手术、住院时间,术中失血量,手术前后下胫腓-重叠阴影差值及间隙差值比较
Table 2. Comparison of AOFAS score,complete weight-bearing and average operative time,intraoperative blood loss,hospital stay,difference of pre- and post-operative tibiofibular clear space and overlap
项目 A组 B组 P F 例数 18 20 术后AOFAS评分 81.11 ± 8.49# 73.65 ± 12.68 < 0.05 3.52 开始完全负重时间(周) 8.44 ± 2.15# 11 ± 1.5 < 0.05 0.16 平均手术时间(h) 3.06 ± 0.75 3.23 ± 0.62 > 0.05 0.84 术中失血量(mL) 323.17 ± 49.62 347.7 ± 62.59 > 0.05 3.91 平均住院时间(d) 15.61 ± 2.43 16.55 ± 3.55 > 0.05 1.15 手术前后下胫腓重叠阴影差值(mm) 2.6 ± 0.49 2.49 ± 0.68 > 0.05 1.73 手术前后下胫腓间隙差值(mm) 2.84 ± 0.582 3.01 ± 0.74 > 0.05 2.17 与B组比较,#P < 0.05。 -
[1] Han S M,Wu T H,Wen J X,et al. Radiographic analysis of adult ankle fractures using combined danis-weber and lauge-hansen classification systems[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):7655. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-64479-2 [2] Baumbach S F,Braunstein M,Herterich V,et al. Arthroscopic repair of chronic lateral ankle instability[J]. Operative Orthopadie und Traumatologie,2019,31(3):201-210. doi: 10.1007/s00064-019-0595-7 [3] Cammas C,Ancion A,Detrembleur C,et al. Frequency and risk factors of complications after surgical treatment of ankle fractures:a retrospective study of 433 patients[J]. Acta Orthopaedica Belgica,2020,86(3):563-574. [4] Hamam A W,Chohan M B Y,Tieszer C,et al. Anatomic repair vs closed reduction of the syndesmosis[J]. Foot & Ankle International,2021,107(11):72. [5] Mandel J,Behery O,Narayanan R,et al. Single- vs 2-screw lag fixation of the medial malleolus in unstable ankle fractures[J]. Foot & Ankle International,2019,40(7):790-796. [6] Wu K,Lin J,Huang J,et al. Evaluation of transsyndesmotic fixation and primary deltoid ligament repair in ankle fractures with suspected combined deltoid ligament injury[J]. Journal of Foot & Ankle Surgery,2018,57(4):694-700. [7] Lee D O,Yoo J H,Choi W Y. Optimal screw fixation of syndesmosis using a targeting drill guide:a technical note[J]. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery,2020,59(1):206-209. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2019.05.005 [8] Song L,Liao Z,Kuang Z,et al. Comparison of tendon suture fixation and cortical screw fixation for treatment of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis injury:A case-control study[J]. Medicine,2020,99(34):e21573. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021573 [9] Rder B W,Figved W,Madsen J E,et al. Better outcome for suture button compared with single syndesmotic screw for syndesmosis injury:five-year results of a randomized controlled trial[J]. Bone and Joint Journal,2020,102-B(2):212-219. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.102B2.BJJ-2019-0692.R2 [10] Shariff S S,Nathwani D K. Lauge-hansen classification-A literature review[J]. Injury-international Journal of the Care of the Injured,2006,37(9):888-890. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2006.05.013 [11] Hermans J J,Wentink N,Beumer A,et al. Correlation between radiological assessment of acute ankle fractures and syndesmotic injury on MRI[J]. Skeletal Radiology,2012,41(7):787-801. doi: 10.1007/s00256-011-1284-2 [12] 苏琰,李振东,薛剑锋,等. 经腓骨截骨复位内固定治疗中老年累及后踝陈旧性踝关节骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2020,36(4):315-320. [13] Blom R P,Meijer D T,de Muinck Keizer R J O,et al. Posterior malleolar fracture morphology determines outcome in rotational type ankle fractures[J]. Injury,2019,50(7):1392-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2019.06.003 [14] Grambart S T,Prusa R D,Ternent K M. Revision of the Chronic Syndesmotic Injury[J]. Clinics in Podiatric Medicine and Surgery,2020,37(3):577-592. doi: 10.1016/j.cpm.2020.03.011 [15] Ju D G,Debbi E M,Neustein A Z,et al. Fibular lengthening osteotomy with revision syndesmotic repair for ankle fracture malunion[J]. Journal of orthopaedic trauma,2019,33(Suppl1):S38-S39. [16] Lemmers D H L,Lubberts B,Stavenuiter R,et al. Factors associated with adverse events after distal tibiofibular syndesmosis fixation[J]. Injury,2020,51(2):542-547. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2019.12.011 [17] Mosca M,Buda R,Ceccarelli F,et al. ,Vocale E,Massimi S,Benedetti MG,Grassi A,Caravelli S,Zaffagnini S. Ankle joint re-balancing in the management of ankle fracture malunion using fibular lengthening:prospective clinical-radiological results at mid-term follow-up[J]. International Orthopaedics,2021,45(2):411-417. doi: 10.1007/s00264-020-04690-y [18] Burton C A,Arthur R J,Rivera M J,et al. The Examination of Repeated Self-Mobilizations With Movement and Joint Mobilizations on Individuals With Chronic Ankle Instability[J]. Journal of Sport Rehabilitation,2020,30(3):458-466. [19] Kapadia B H,Sabarese M J,Chatterjee D,et al. Evaluating success rate and comparing complications of operative techniques used to treat chronic syndesmosis injuries[J]. Journal of Orthopaedics,2020,22:225-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.04.011 [20] Sanders D,Schneider P,Taylor M,et al. Improved reduction of the tibio-fibular syndesmosis with tightrope compared to screw fixation:results of a randomized controlled study[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma,2019,33(11):531-537. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001559 [21] McKenzie A C,Hesselholt K E,Larsen M S,et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis on treatment of ankle fractures with syndesmotic rupture:suture-button fixation versus cortical screw fixation[J]. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery,2019,58(5):946-953. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2018.12.006 -






 下载:
下载: