Efficacy of Dapagliflozin on Early Diabetic Nephropathy and Its Effect on Serum MCP-1 and IL-6
-
摘要:
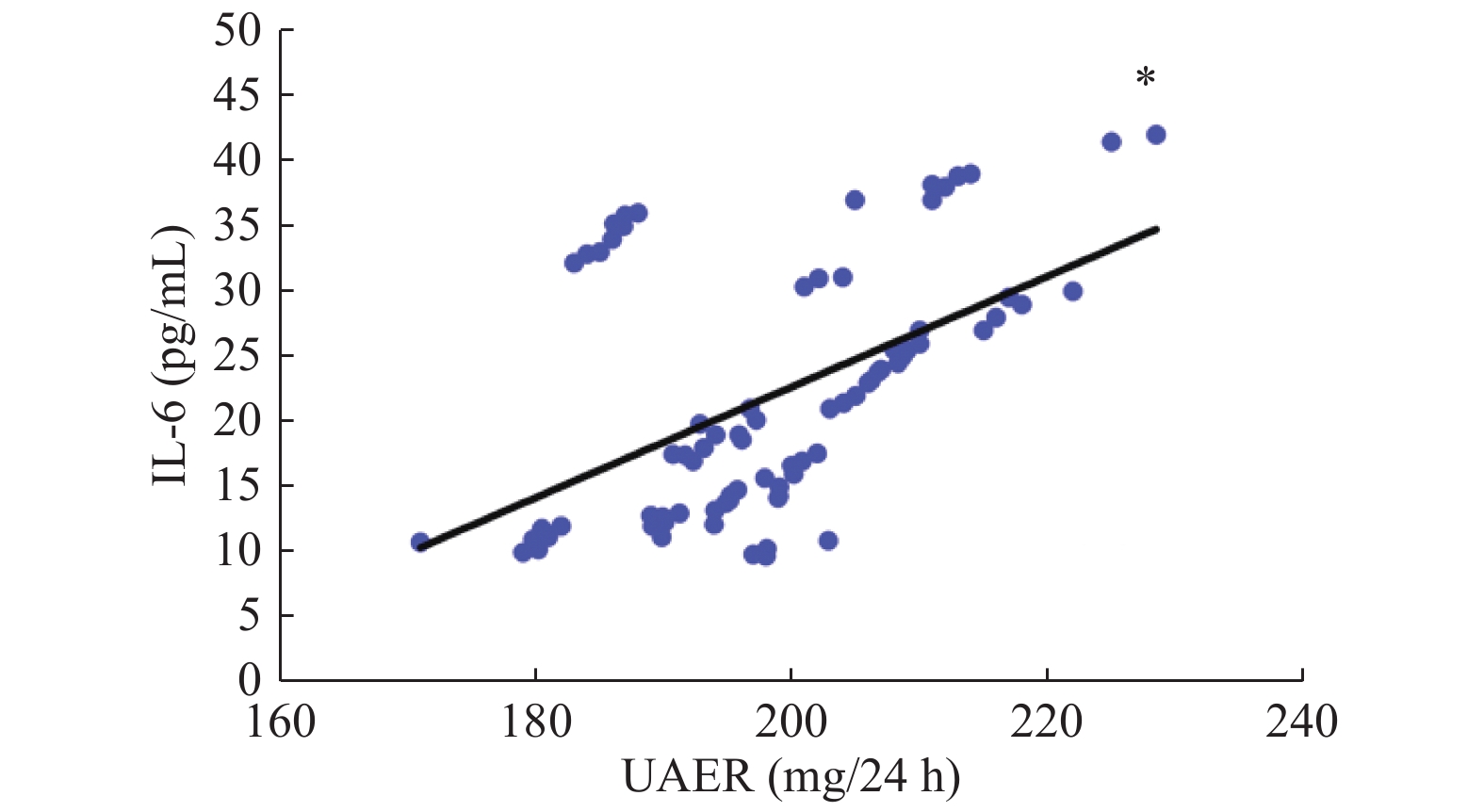
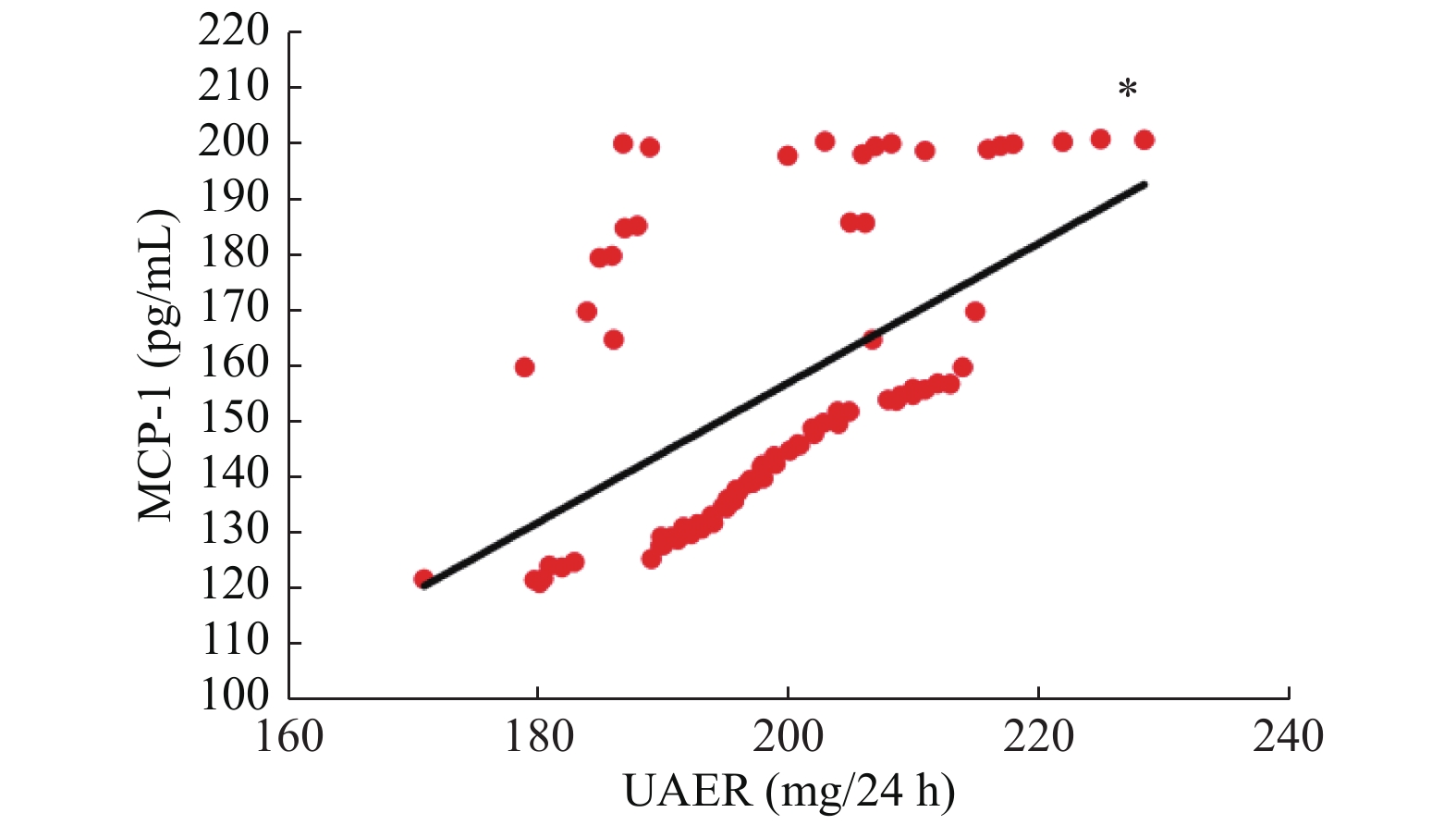
目的 探讨达格列净治疗早期糖尿病肾病的疗效及对血清单核细胞趋化因子-1(MCP-1)、白细胞介素-6(IL-6)水平的影响。 方法 选择昆明医科大学第二附属医院于2019年1月至2020年1月期间收治的78例早期糖尿病肾病患者为研究对象,随机分为观察组与对照组,每组39例,2组均接受厄贝沙坦等常规治疗,对照组患者予二甲双胍降糖,观察组患者则应用达格列净降糖,疗程为12周。比较2组患者治疗前后血肌酐、空腹血糖(FBG)、餐后2 h血糖(2 h PG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、尿白蛋白排泄率(UAER)以及血清MCP-1、IL-6水平的变化。 结果 治疗后,2组FBG、2 h PG及HbA1c均明显降低,且观察组均明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);治疗后,2组UAER较治疗前明显降低,且观察组低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);2组患者治疗前后血肌酐水平均无明显变化(P > 0.05);治疗后,2组患者血清MCP-1、IL-6水平均较治疗前明显下降,且观察组明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Peason相关性分析表明,早期糖尿病肾病患者UAER与血清MCP-1、IL-6水平均呈正相关性(P < 0.05)。 结论 达格列净应用于早期糖尿病肾病的治疗,不仅可以有效控制患者的血糖,还可以降低血清MCP-1、IL-6水平,减少尿蛋白的漏出,进而保护患者的肾功能。 -
关键词:
- 糖尿病肾病 /
- 达格列净 /
- 单核细胞趋化因子-1 /
- 白细胞介素-6 /
- 尿白蛋白排泄率
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of Dapagliflozin in the treatment of early diabetic nephropathy and its effect on serum MCP-1 and IL-6. Methods 78 cases of patients with early diabetic nephropathy treated in our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were randomly divided into observation group and control group, with 39 cases in each group. Both groups received irbesartan and other conventional treatment. In addition, patients in the control group were treated with metformin, and patients in the observation group were treated with dagaglidine for 12 weeks. The changes of serum creatinine, fasting blood glucose (FBG), 2 h postprandial blood glucose (2 h PG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), urinary albumin excretion rate (UAER) and serum McP-1 and IL-6 levels in 2 groups were compared before and after treatment. Results After treatment, FBG, 2hPG and HbA1c in the two groups were significantly decreased, and the observation group was significantly lower than the control group (P < 0.05). After treatment, UAER in both groups was significantly lower than before treatment, and the observation group was lower than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant change in serum creatinine level in 2 groups before and after treatment (P > 0.05). After treatment, the serum LEVELS of McP-1 and IL-6 in 2 groups were significantly decreased compared with before treatment, and the observation group was significantly lower than the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that UAER was positively correlated with serum MCP-1 and IL-6 in early diabetic nephropathy patients (P < 0.05). Conclusion The application of Dapagliflozin in the treatment of early diabetic kidney disease can not only effectively control the blood glucose, but also reduce the serum MCP-1 and IL-6, reduce the leakage of urine protein, and then protect the renal function. -
随着影像学学科的飞速发展,通过对影像技术的灵活运用可以对骨骼表面软骨进行更好的观察和测量,其中超声与MRI可对软骨进行测量[1-2]。二者无辐射,安全无害,但大量影像循证医学研究表明MRI在真实软骨测量准确性方面好于超声,是间接观察软骨的最佳选择[3]。随着MRI检查手段和系统的不断升级,可以很好的利用其对关节软骨损伤和病变检测,1.5T磁共振T1WI TSE成像技术可以测量出真实的软骨厚度[4]。对于踝关节损伤患者,除了考虑骨折和韧带损伤,软骨的损伤也逐渐得到骨科医生的关注,许多研究表明软骨厚度通常小于2 mm,然而软骨厚度也会因地方、性别、和个体的不同而表现出很大的差异[5]。因此对距骨软骨厚度测量将帮助骨科医生预测需要修复的软骨量,并以合理的成本进行治疗,而不会过度侵犯患者,在距骨解剖假体的设计过程中也要考虑软骨存在[6-8]。Giannicola等[9]研究发现软骨厚度分布与骨骼长短、粗细均不相关,即我们不能简单从骨骼CT和X光片显像中预测出软骨厚度。当前国内尚未有对距骨关节面软骨厚度测量的相关文献报道,因此应用MRI测量成人正常距骨表面软骨厚度,构建国内成人正常距骨表面软骨厚度参数势在必行。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选取2021年01月至2021年11月在云南省中医医院MRI室行检查的踝关节无关节炎、无外伤史的成人100例,其中男性、女性各50例,年龄18~60岁,中位年龄37岁,签署知情同意告知书,对踝关节进行扫描,如实记录体重、身高与年龄。已通过医院伦理委员会审批。
1.2 仪器与方法
使用荷兰飞利浦1.5T磁共振仪。扫描线圈:SENSE-FLEX-M-COIL,C1-COIL,C3-COIL,T/R HEAD COIL KNEE/FOOT COIL。扫描序列:冠状位T1WI TSE ,矢状位T2WI TSE,矩阵512×512,FOV 16 cm,层厚为3 mm,层距为1 mm。扫描体位:取仰卧位,足部先进,沙袋固定足部于中立位。
1.3 测量方法
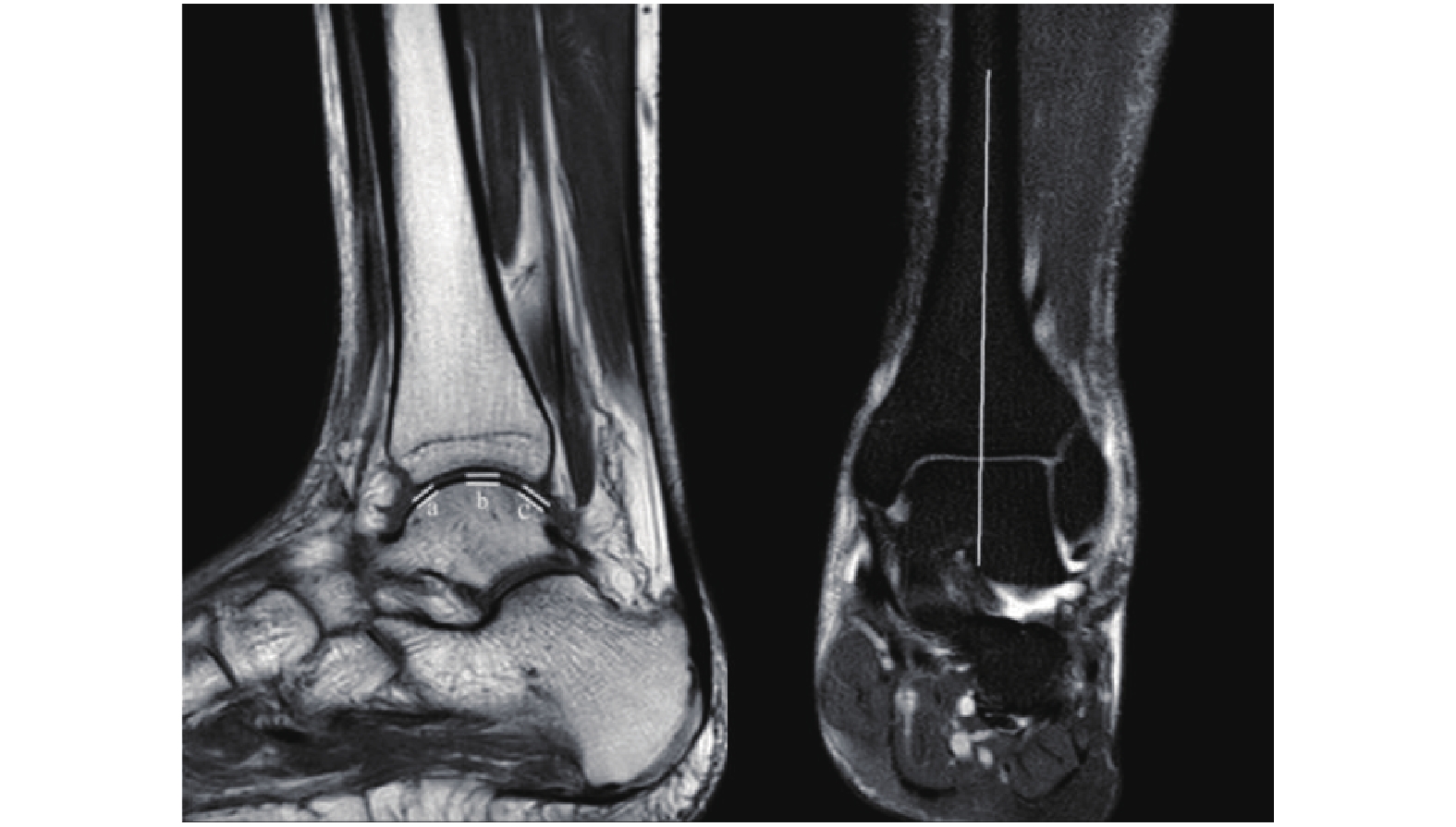
选择在冠状位通过距骨关节面中垂线的矢状位图像作为测量图像,以胫距关节面前、中、后3个点作为测量点,各测量点垂直于相应的关节面,测量软骨厚度为关节软骨低信号的垂直高度,得出软骨厚度a、b、c(图1)。所有图片均放大3倍,由3名骨科医师独立分别完成3个测量点测量,每个点取3者所得平均值作为最终结果,测量精度为0.01 mm。
软骨测量点的选择:选择在冠状位通过距骨关节面中垂线的矢状位图像作为测量图像,以胫距关节面前、中、后3个点作为测量点,各测量点垂直于相应的关节面,测量软骨厚度为关节软骨低信号的垂直高度,得出软骨厚度a、b、c。
1.4 统计学处理
采用SPSS25.0统计学软件包进行统计学分析,基本描述正态分布计量资料采用均数据±标准差表示,正态分布计量资料两组间比较采用两独立样本t检验,相关性分析采用Pearson相关性分析,P < 0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 性别与前、中、后距骨关节面软骨厚度的关系
男性前、中、后距骨关节面软骨厚度分别为(1.00±0.18)mm、(1.40±0.21)mm、(0.87±0.18)mm;女性前、中、后距骨关节面软骨厚度分别为(0.96±0.19)mm、(1.29±0.20)mm、(0.86±0.15)mm;男性和女性距骨前、后关节软骨面厚度差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),距骨中关节面软骨厚度,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表1。
表 1 男、女性各指标比较Table 1. Comparison of male and female indicators指标 男性 女性 t P a(mm) 1.00 ± 0.18 0.96 ± 0.19 1.342 0.183 b(mm) 1.40 ± 0.21 1.29 ± 0.20 2.715 0.008* c(mm) 0.87 ± 0.18 0.86 ± 0.15 0.089 0.930 年龄(岁) 37.00 ± 11.96 41.42 ± 14.10 −1.680 0.096 身高(m) 1.70 ± 0.06 1.64 ± 0.06 5.194 < 0.001* 体重(Kg) 67.61 ± 6.29 58.04 ± 4.47 8.707 < 0.001* a:前关节面软骨厚度;b:中关节面软骨厚度;c:后关节面软骨厚度。*P < 0.05。 2.2 身高、体重、年龄与距骨前、中、后关节面软骨厚度的关系
男性与女性年龄差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),男性身高、体重均大于女性,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),考虑为男女差异。经Pearson相关性分析男、女性身高、体重、年龄与距骨前、中、后关节面软骨厚度均无相关性(P > 0.05),见表2、表3、表4。
表 2 身高与各指标相关性分析Table 2. Correlation analysis between height and various indexes指标 r P a(mm) 0.11 0.297 b(mm) 0.05 0.600 c(mm) −0.03 0.764 a:前关节面软骨厚度;b:中关节面软骨厚度;c:后关节面软骨厚度。 表 3 体重与各指标相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis between body weight and various indexes指标 r P a(mm) 0.08 0.429 b(mm) 0.17 0.099 c(mm) 0.06 0.588 a:前关节面软骨厚度;b:中关节面软骨厚度;c:后关节面软骨厚度。 表 4 年龄与各指标相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis between age and various indicators指标 r P a(mm) −0.14 0.182 b(mm) −0.09 0.389 c(mm) −0.15 0.131 a:前关节面软骨厚度;b:中关节面软骨厚度;c:后关节面软骨厚度。 3. 讨论
在磁共振成像中使用各同向性体素进行厚度测量,来自各同向性体素的MRI数据结果表明,在关节间隙宽度和软骨厚度的测量值的位置准确测量软骨厚度是体素大小的2倍或更大是科学合理的,因此本研究所有测量图像均放大3倍;通过与3个模型、5个正常尸体髋部标本和9个骨关节炎患者的实验结果进行比较,验证了该模拟方法的有效性。MRI提供了软骨和软骨下骨厚度的良好表征,支持其在骨软骨结构和改变的研究和临床诊断中的应用[10-11],也正是如此为本研究MRI测量软骨厚度提供了研究基础。
虽然超声与MRI可对软骨进行测量,二者无辐射,安全无害,超声可以作为评估股骨中、后股骨区域相对软骨厚度的可行临床工具。然而,在软骨厚度 < 2 mm时,超声在相关测量值之间的绝对一致性较差,由于更多的基于MRI测量,超声测量的绝对有效性受到同行质疑[12]。而CT需要通过造影技术对软骨进行测量,有创且辐射大,不适于对人体进行研究,但动物研究可考虑CT造影技术;目前来说,相对于超声、CT测量软骨厚度,MRI测量更为准确、安全、敏感,因此本研究选择了MRI测量。
近年来关节软骨损伤越来越受到骨科医生所关注,距骨软骨面损伤是踝关节最常见的软骨损伤[13],主要表现为踝部肿痛、关节异物感、活动受限,多见于青壮年男性。X线片是踝关节扭伤后需拍摄的常规影像学检查,以前是距骨软骨面损伤的主要诊断依据,但X线片会忽略50%以上的软骨病变。MRI敏感度高,可清晰显示距骨软骨病变、骨髓水肿范围,是软骨损伤最佳无创检查[14];关节软骨损伤的患者日益受到重视,准确的诊断软骨损伤显得更为重要,而X线片误诊率较高,并不利于疾病的诊疗,因此目前MRI检查更有意义。当然,本研究只是起了一个抛砖引玉的作用,而且由于各方面的原因存在一定的局限性,本研究纳入的样本量有限,研究的还不够深入,由于选择健康志愿者进行检查成本高,实施难度大,本研究对象根据病情需要选择踝关节无关节炎、无外伤史的门诊就诊成人,节约成本,也能代表正常距骨软骨厚度,下一步将对运动前后、踝关节损伤后距骨软骨厚度的变化进行探索,希望更多的学者加入进一步更加全面的研究。
通过MRI对距骨表面软骨厚度测量研究发现,成人后距骨表面软骨厚度趋于稳定,与身高、体重、年龄均无相关性,负重区距骨软骨厚度明显大于非负重区,且负重区软骨厚度男性大于女性。展望未来,对于这一现象相信随着影像学学科的不断前进,笔者能更好的对不同区域的软骨进行更深入的研究。
-
表 1 2组患者基线临床资料的比较(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. Comparison of clinical baseline data between two groups (
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 n 年龄
(岁)性别
(男/女)BMI
(kg/m2)病程
(a)血肌酐(μmol/L) 观察组 39 48.82 ± 7.46 22/17 24.42 ± 2.10 8.72 ± 2.31 91.65 ± 15.44 对照组 39 49.71 ± 8.54 25/14 23.78 ± 1.56 9.06 ± 3.43 89.94 ± 20.17 t/χ2 0.490 0.482 1.528 0.514 0.420 P 0.625 0.488 0.131 0.609 0.675 表 2 2组患者治疗前后的血糖指标的比较(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. Comparison of blood glucose between two groups before and after treatment (
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 n FBG(mmol/L) 2hPG(mmol/L) HbA1c(%) 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 观察组 39 8.21 ± 2.19 5.02 ± 1.38* 14.29 ± 3.74 7.09 ± 1.94* 8.79 ± 1.38 4.78 ± 1.11* 对照组 39 8.34 ± 2.75 6.79 ± 1.54* 13.72 ± 4.01 9.16 ± 2.17* 8.52 ± 1.43 6.07 ± 1.70* t 0.231 5.3446 0.649 4.441 0.849 3.968 P 0.818 < 0.001 0.518 < 0.001 0.399 < 0.001 与本组治疗前比较,*P < 0.05。 表 3 2组患者治疗前后UAER及血肌酐水平的比较(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. Comparison of UAER and Creatine between two groups before and after treatment (
$ \bar x \pm s $ )组别 n UAER(mg/24 h) 血肌酐(μmol/L) 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 观察组 39 195.42 ± 52.44 112.51 ± 33.26* 91.65 ± 15.44 87.54 ± 12.43 对照组 39 201.73 ± 67.35 154.52 ± 34.28* 89.94 ± 20.17 88.61 ± 14.56 t 0.462 5.429 0.420 0.349 P 0.646 < 0.001 0.675 0.728 与本组治疗前比较,*P < 0.05。 表 4 2组患者治疗前后血清MCP-1、IL-6水平的比较[(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )pg/mL]Table 4. Comparison of MCP-1,IL-6 between two groups before and after treatment [(
$ \bar x \pm s $ )pg/mL]组别 n MCP-1 IL-6x 治疗前 治疗后 治疗前 治疗后 观察组 39 153.97 ± 50.06 69.16 ± 19.82* 22.79 ± 5.67 13.28 ± 4.13* 对照组 39 156.21 ± 47.45 94.54 ± 24.23* 21.34 ± 6.25 16.36 ± 4.44* t 0.203 5.063 1.073 3.172 P 0.840 < 0.001 0.287 0.002 与本组治疗前比较,*P < 0.05。 -
[1] 金莹,童林萍,沈培红. 糖尿病肾病进展机制及血糖波动、氧化应激状况的研究[J]. 中国基层医药,2017,24(13):1954-1958. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-6706.2017.13.009 [2] 刘蕊,戴岳. 糖尿病肾病发病机制的研究进展[J]. 药学与临床研究,2018,26(3):202-205. [3] Lin Y C,Chang Y H,Yang S Y,et al. Update of pathophysiology and management of diabetic kidney disease[J]. J Formos Med Assoc,2018,117(8):662-675. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2018.02.007 [4] Haiyan Fu,Silvia Liu,Sheldon I Bastacky,et al. Diabetic kidney diseases revisited: A new perspective for a new era[J]. Molecular Metabolism,2019,30:250-263. [5] Gurley S B,Coffman T M. The Renin-Angiotensin System and Diabetic Nephropathy[J]. Seminars in nephrology,2007,27(2):144-152. [6] Scheen André J. Sodium-glucose cotransporter type 2 inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nature reviews Endocrinology,2020,16(10):555-577. [7] Dhillon S. Dapagliflozin:A review in type 2 diabetes[J]. Drugs,2019,79(10):1135-1146. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01148-3 [8] 张倩倩,叶启宝,陈丽,等. 达格列净治疗2型糖尿病肾病患者的临床疗效观察[J]. 医学理论与实践,2019,32(22):3591-3593. [9] 中华医学会糖尿病分会. 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志,2018,38(4):292-344. [10] GuariguataL,Whiting D,Hambleton I,et al. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2014,103(2):137. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2013.11.002 [11] 况磊,陆菁. 糖尿病肾病的危险因素分析及血压的控制[J]. 中国实用医刊,2016,43(2):115-116. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-4756.2016.02.065 [12] Shin S J,Chung S,Kim S J,et al. Effect of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor,Dapagliflozin,on Renal Renin-Angiotensin System in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes[J]. Plos One,2016,11(11):e0165703. [13] 魏志敏,马瑞霞,刘丽秋. 糖尿病肾病病理分型和肾组织内血管紧张素2表达的相关性分析[J]. 临床肾脏病杂志,2016,16(8):466-470. [14] Doshi S M,Friedman A N. Diagnosis and management of type 2 diabetic kidney disease[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol,2017,12(8):1366-1373. doi: 10.2215/CJN.11111016 [15] Ele Ferrannini,Silvia Jimenez Ramos,Afshin Sals,et al. Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise:A randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled,phase 3 trial[J]. Diabetes Care,2010,33(10):2217-2224. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0612 [16] Johnston R,Uthman O,Cummins E,et al. Canagliflozin,dapagliflozin and empagliflozin monotherapy for treating type 2 diabetes:Systematic review and economic evaluation[J]. Health Technol Assess,2018,21(2):219-220. [17] 张伟华,李志龙,邱伟林,等. 达格列净对2型糖尿病伴代谢综合征患者血压、血糖和胆固醇的影响[J]. 黑龙江医学,2019,43(7):732-734. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775.2019.07.011 [18] Navarro J F,Mora C,Muros M,et al. Urinary tumour necrosis factor-alpha excretion independently correlates with clinical markers of glomerular and tubulointerstitial injury in type 2 diabetic patients[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant,2006,21(12):3428-3434. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl469 [19] Abdelrahman A M,A l Suleimani Y,Shalaby A,et al. Effect of tocilizumab,an interleukin-6 inhibitor,on early stage streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol,2019,392(8):1005-1013. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01655-w [20] Krystallenia Alexandraki,Christina Piperi,Christos Kalofoutis,et al. Inflammatory process in type 2 diabetes:The role of cytokines[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci,2006,1084(1):89-117. doi: 10.1196/annals.1372.039 [21] 阳皓,谭巧灵,王岑,等. 达格列净对早期2型糖尿病肾病患者尿微量白蛋白和促炎症因子的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版),2019,48(4):400-404. [22] Naoto Terami,Daisuke Ogawa,Hiromi Tachibana,et al. Long-term treatment with the sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor,dapagliflozin,ameliorates glucose homeostasis and diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(6):100777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100777 [23] Hatanaka Takashi,Ogawa Daisuke,Tachibana Hiromi,et al. Inhibition of SGLT2 alleviates diabetic nephropathy by suppressing high glucose-induced oxidative stress in type 1 diabetic mice[J]. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives,2016,4(4):00239. [24] H J L Heerspink,E Johnsson,I Gause-Nilsson,et al. Dapagliflozin reduces albuminuria in patients with diabetes and hypertension receiving renin-angiotensin blockers[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab,2016,18(6):590-597. doi: 10.1111/dom.12654 [25] Christoph Wanner,Silvio E Inzucchi,John M Lachin,et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in Type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med,2016,375(4):323-334. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1515920 -






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载: