Effects of Willed Movement on the Expression of GLUA2 and N-cadherin in Rats with Focal Cerebral Ischemia
-
摘要:
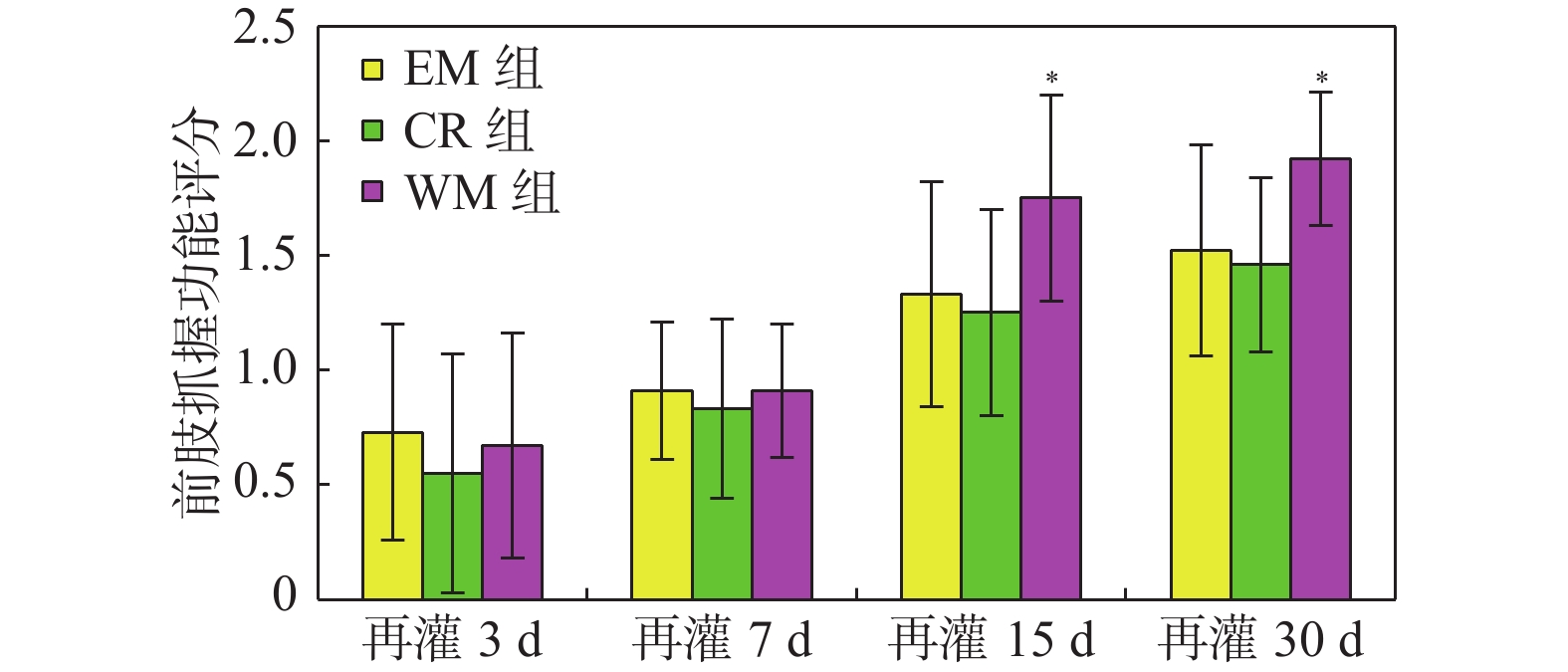
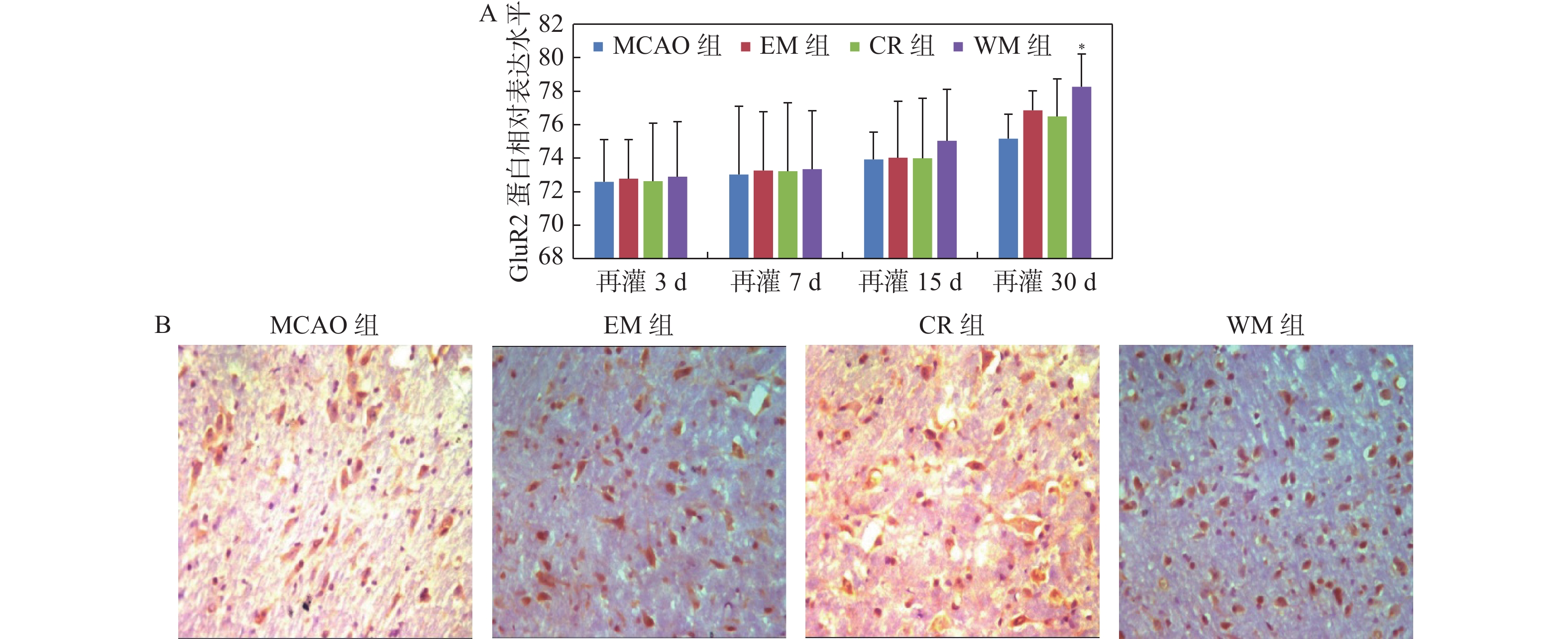
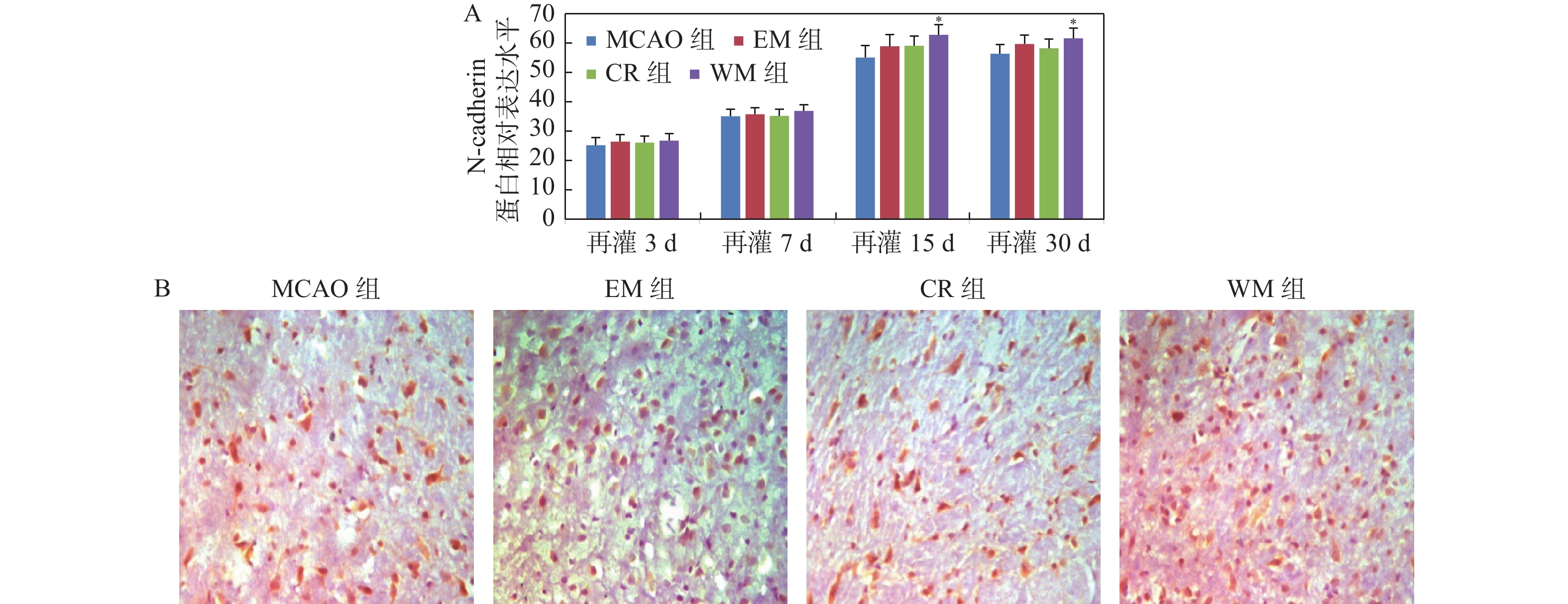
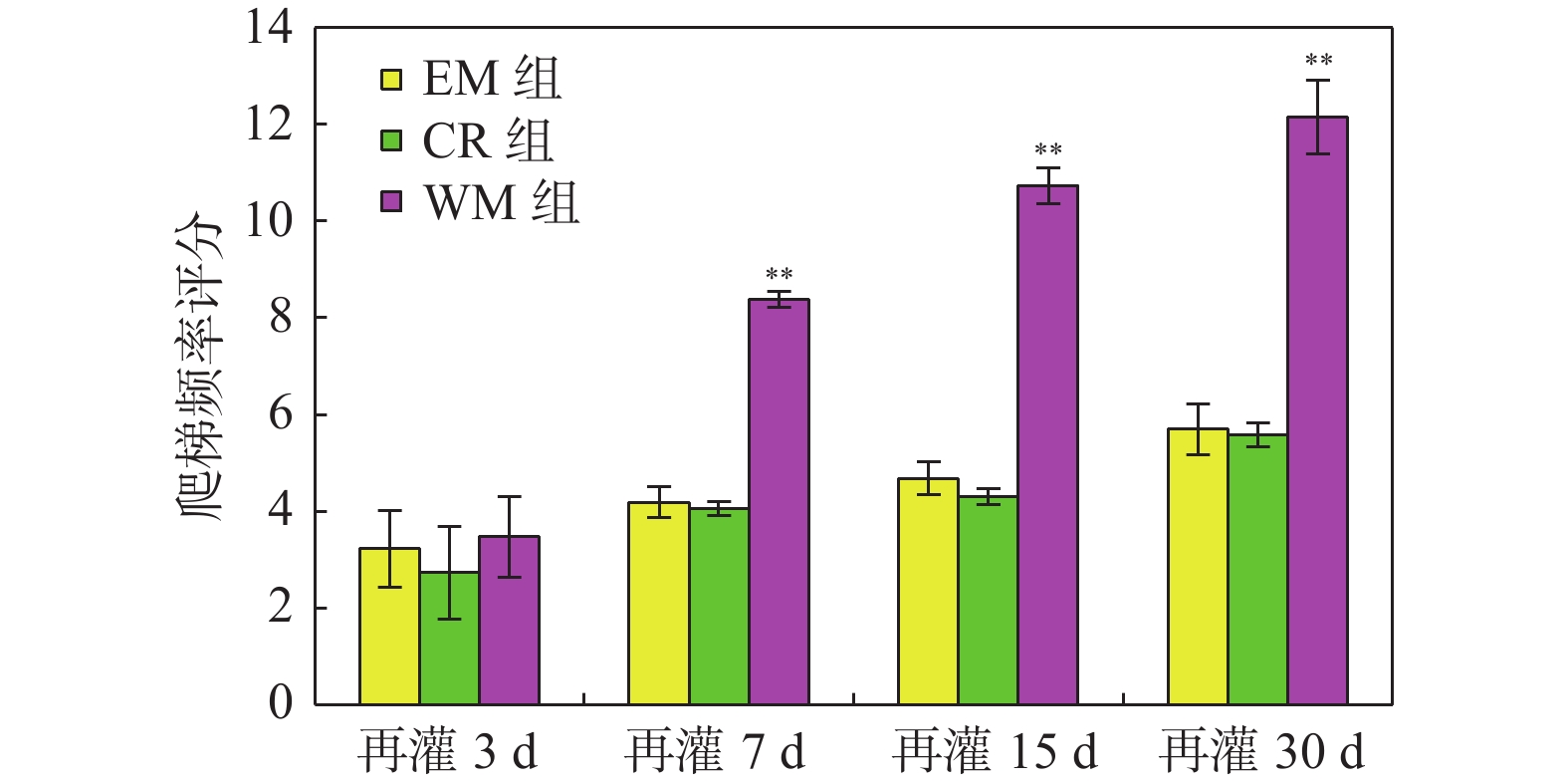
目的 研究意向性运动干预治疗对大脑局部缺血大鼠行为学及梗死灶周围组织中GluA2和N-cadherin表达的影响。 方法 利用鱼线栓堵法将大鼠制成大脑中动脉栓塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion,MCAO)模型共144只,随机分成模型(MCAO)组、生活环境变化(environment modification,EM)组、普通康复训练(control rehabilitstion, CR)组和意向性运动干预(willed movement,WM)组,每组根据术后时间划分为7 d、15 d、30 d 3个亚组。对各组研究对象的行为变化进行观察分析,通过免疫组化技术研究脑梗死灶周围组织中GluA2和N-cadherin蛋白水平。 结果 再灌7 d、15 d、30 d,意向性运动干预组的攀爬频率显著高于EM及CR组(P < 0.01);再灌30 d,和MCAO组相比,意向性运动干预组的神经功能缺损评分更低(P < 0.05 );而其缺血半暗带区域GLUA2、N-cadherin蛋白表达量都更高(P < 0.05)。 结论 对于大脑局部缺血所导致的神经功能障碍,意向性运动干预治疗可促进其恢复,这可能是因为该运动可激活缺血半暗带中GLUA2和N-cadherin的表达,提高突触可塑性。 -
关键词:
- 局灶性脑缺血 /
- 意向性运动 /
- 突触可塑性 /
- GLUA2 /
- N-cadherin
Abstract:Objective To explore effect of the Willed movement on behaviours of rats with focal cerebral ischemia and the expression of GluA2 and N-cadherin in the brain tissue around ischemia. Methods We selected clean-level healthy male SD rats, and prepared 144 middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) models by thread occlusion method, and randomly divided them into model (MCAO) group, environment modification (EM) group, control rehabilitstion (CR) group and Willed movement (WM) group, each group was divided into four subgroups of 7, 15, and 30 days according to the postoperative time. The behavioral changes of rats in each group were dynamically observed, and the expression changes of GluA2 and N-cadherin protein in the brain tissue around the ischemic area were observed by immunohistochemical staining. Results On 7, 15, and 30 days after reperfusion, the climbing frequency of rats which were treated by willed movement was obviously higher than EM and CR group (P < 0.01). After 30 days of reperfusion, the neurological deficits score of the intentional exercise intervention group was lower than MCAO rats (P < 0.05). Compare with MCAO rats, the expression levels of GLUA2 and N-cadherin were higher in ischemic penumbra (P < 0.05). Conclusions Willed movement can promote the recovery of damaged nerve function after focal cerebral ischemia, which may be related to up-regulating the expression of GLUA2 and N-cadherin in the brain tissue around the ischemic focus and enhancing synaptic plasticity. -
Key words:
- Focal cerebral ischemia /
- Willed movement /
- Synaptic plasticity /
- GLUA2 /
- N-cadherin
-
盐酸氨溴索注射液是常见的呼吸系统疾病临床用药[1],能有效祛痰、减少咳嗽,临床疗效好,无明显毒副作用。该品种应用人群广,是儿科甚至新生儿常用药物[2],因临床使用时直接进入血液系统,药物临床使用安全风险较高,被视为高风险注射剂。盐酸氨溴索注射液的含量测定结果是其有效性和安全性的重要指标,代表药品质量的好坏,因此客观评价结果的可靠性显得尤为重要[3]。通常可对测量结果的质量用不确定度给出定量说明,而目前未见盐酸氨溴索注射液含量测定不确定度评定的报道,为此,有必要对其进行研究。
在药物分析领域,目前国内暂未发布评定指南。2018—2020年期间国家药典委先后发布了征求意见稿《不确定度评定在药品检验中的应用》,可见不确定度评定在药品检验领域具有重要性和必要性[4]。当前的文献报道中,药品测量不确定度的评定主要是采用GUM法[5−7],未见TOP-DOWN法用于药品外标法含量测定的不确定度评定。GUM法评定是按照实际检验,分析各相关分量建立数学模型再评定,过程繁琐、复杂,要求细致,各分量不能重复也不能遗漏,评定质量取决于评定者对有贡献的影响量认识的程度。TOP-DOWN法是由美国人Horwitz提出的是自上而下或自顶向下的评定方法[8],评定原理是:在确保测量过程的偏倚和精密度受控的前提下,将影响检验结果的各因素利用实验室间再现性数据和实验室内重复性数据归纳为偏倚不确定度和期间精密度2个分量,再合成不确定度,该法较于GUM法,能全面反映实验室的质控状态和实验室间的偏倚[9]。
为确保药物的安全性和有效性,本文采用TOP-DOWN和GUM 2种方法对盐酸氨溴索注射液的含量测定进行不确定评定,GUM法为传统经典的不确定度评定方法,通过识别各个影响因素合成不确定度,除此之外,本实验还利用实验室长期积累的数据作为“期间精密度”分量和17家实验室间的实验数据作为“偏倚精密度”分量,建立TOP-DOWN法测量模型,该方法既包含了在GUM法中体现的各影响因素如称量、测量等,还包含了GUM法所不具备的环境变动、方法本身的误差等不容易识别的不确定度分量,更全面系统。本文首次在药品检验领域采用TOP-DOWN法评定药品含量测定的不确定度,为探索非GUM法评定药品的测量不确定度,提供了1种有价值的参考方法[10]。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验仪器
日本岛津LC-20A型高效液相色谱仪;梅特勒-托利多BP221S型电子分析天平;移液管和容量瓶均为天玻牌A级玻璃仪器。
1.2 实验材料
甲醇为色谱纯(美国赛默飞科技有限公司);盐酸氨溴索对照品(来源于中国食品药品检定研究院,批号:100599-202106);样品为盐酸氨溴索注射液(A企业,批号:2AA21203);实验其他所用试剂均为分析纯;实验用水为超纯水。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 盐酸氨溴索注射液含量测定
盐酸氨溴索注射液含量测定标准收载于《中国药典》2020年版二部[11],按照其规定的方法进行测定。
色谱柱:月旭 C18 5 μm,250×4.6 mm;流动相A和B分别为0.01 mol/L磷酸氢二铵溶液和乙腈,体积比为50∶50,检测波长:248 nm。对照品和供试品分别用流动相制成约30 μg/mL的试液。
1.3.2 TOP-DOWN法不确定度评定程序及数学模型
评定程序:参照《化学检测领域测量不确定度评定》RB/T 141–2018 [12]指南,确定测量不确定度的评定程序:(1)按照1.3.1中盐酸氨溴索注射液的含量测定方法,获取不同实验室间再现性数据(提交两组平行数据χ1和χ2)和一段时间内本实验室的重复性数据;(2)使用h/k检验确认再现性数据的偏倚是否受控;使用AD检验判断重复性数据的精密度是否处于期望范围内;(3)若偏倚和精密度均处于控制范围内,量化再现性估计值和精密度的不确定度,计算偏倚和精密度分量,合成不确定度。
数学模型为:
$$ {U}_{rel } = 2{u}_{c,\,\,rel} = 2\sqrt{{u}^{2}{}_{b,\,\,rel}+{u}^{2}{}_{R{'},\,\,rel}} $$ 式中:$ {u^2}_{b,\,\,rel} $ :偏倚不确定度分量;$ {u^2}_{R',\,\,rel} $:期间精密度不确定度分量
1.3.3 GUM法评定的数学模型
(1)不确定度识别及分析 根据对此次实验过程的分析,盐酸氨溴索注射液不确定度的主要的来源有以下几条:对照品的纯度、对照品称量引入的不确定度、对照品溶液和样品溶液配置定容所用的容量瓶、量取对照品溶液和样品溶液所用的移液管、由仪器性能引入的不确定度、在相同条件下被测量重复观测值的变化。以上各分量相互独立,其中第6项为A类不确定度,其余均为B类不确定度。(2)数学模型 盐酸氨溴索注射液含量以双对照高效液相色谱外标法按峰面积计算,根据上述不确定度来源分析确定数学模型为:
$$ X{ = }\frac{{A}_{X}\times {V}_{X2}\times 2}{{V}_{X1}\times 规格\times \left(\dfrac{{A}_{R1}\times {V}_{R1}}{{W}_{R1}\times {P}_{R}}+\dfrac{{A}_{R1}\times {V}_{R1-2}}{{W}_{R1}\times {V}_{R1-1}}\right)}\times 100\text{%}$$ 式中:X为按外标法计算得的盐酸氨溴索的标示百分含量;$ {A_X} $为样品峰面积,$ {V_{X1}} $为样品取样量(1 mL);$ {A_{R1}} $为对照品溶液①连续进样5针的平均峰面积,$ {V_{R1}} $为对照品溶液①的稀释体积,$ {W_{R1}} $为对照品①的取样量;$ {P_R} $为对照品纯度;$ {A_{R2}} $为对照品②连续进样3针的平均峰面积,$ {V_{R2}} $为对照品溶液②的稀释体积,$ {W_{R2}} $为对照品②的取样量;样品规格:7.5 mg/mL(2 mL:15 mg)。
1.4 TOP-DOWN法不确定度评定
1.4.1 偏倚不确定度分量
(1)实验室间再现性数据。向17家实验室同步发放1.2中同批次对照品和盐酸氨溴索注射液样品,按照1.3.1中实验方法,得到各个实验室的含量测定数据,每个实验室提交2次测量数据χ1和χ2(%),各个实验室数据统计,见表1。(2)判断偏倚受控。参照RB/T141-2018,接受测量系统一致性的假设可判断偏倚是否受控,即h/k检验。
表 1 实验室间再现性数据Table 1. Inter-laboratory reproducibility data序号 x1(%) x2(%) $ \overline {{x_i}} $(%) bi si h k 样品统计 1 100.82 100.20 100.51 0.51 0.44 0.10 1.88 ARV = 100.4%
X = 100.445%
$ {s_{\overline x }} $ = 1.08
sr = 0.2072 100.23 100.33 100.28 0.28 0.07 −0.11 0.30 3 100.80 100.85 100.83 0.82 0.04 0.39 0.15 4 101.70 101.95 101.83 1.83 0.18 1.32 0.76 5 99.48 99.61 99.55 −0.45 0.09 −0.79 0.39 6 100.30 100.80 100.55 0.55 0.35 0.14 1.52 7 98.40 98.20 98.30 −1.70 0.14 −1.94* 0.61 8 100.30 99.70 100.00 0.00 0.42 −0.37 1.82 9 101.48 101.23 101.36 1.36 0.18 0.88 0.76 10 99.01 99.15 99.08 −0.92 0.10 −1.22 0.42 11 101.32 101.33 101.33 1.32 0.00 0.85 0.03 12 100.28 100.06 100.17 0.17 0.16 −0.21 0.67 13 98.58 98.59 98.59 −1.41 0.01 −1.68 0.03 14 100.71 100.55 100.63 0.63 0.11 0.21 0.49 15 101.42 102.15 101.79 1.79 0.52 1.28 2.22* 16 100.99 100.92 100.96 0.95 0.05 0.51 0.21 17 101.77 101.92 101.85 1.85 0.11 1.33 0.46 注:标*为异常值。 h/k检验计算公式:
①$ h = \dfrac{{{b_i}}}{{{s_{\overline x }}}} $
式中:h为实验室间一致性统计量;bi为第i个实验室的单元偏倚(bi = $ \overline {{x_i}} $-ARV,$ \overline {{x_i}} $为各实验室的平均值,ARV的期望值为100.4%);$ {\mathrm{s}}_{\stackrel{-}{\mathrm{x}}} $$ {s_{\overline x }} $为样品水平下各实验室$ \overline {{x_i}} $的标准差。
②$ k = \frac{{{s_i}}}{{{s_r}}} $
式中:k为实验室内一致性统计量;si 为第i个实验室的单元标准差;sr为重复性标准差($ {s_r} = \sqrt {\frac{{\sum {{s_i}^2} }}{{{p_i}}}} $,pi为实验室总个数)。
查询95%和99%概率下的h/k临界表, h = 1.86,k = 1.93(95%);h = 2.32,k = 2.41(99%),实验室间的数据变异基本符合精密度要求。(3)计算偏倚不确定度分量。偏倚不确定度计算公式:
$$ {u^2}_{b,\,\,rel} = \sqrt {{b^2} + {u^2}_{c,\,\,ref}} = \sqrt {{{0.045}^2} + {{0.267}^2}} = 0.27 $$ 式中: $ {u^2}_{c,\,\,ref} = \frac{{{S_R}}}{{\sqrt L }} = 0.267 $ ,(SR为复现性标准差,L为实验室数量)
1.4.2 期间精密度不确定度分量
(1)获取实验室内重复性数据。室间变异并未涵盖室内所有误差源的贡献,因此,本实验室在半年内按时间顺序进行了一段时间稳定过程的期间精密度测量,以18个检验的含量测定数据$ x_i $(%)作为期间精密度重复性数据,最小值为99.4%,最大值为102.7%,均值为100.9%,相对标准偏差为0.88%。实验室内重复性数据,见表2。(2)判断期间精密度受控。参照RB/T141-2018标准中AD检验计算公式,对数据进行AD检验,分别检验$ A_S^{2*} $(正态性检验)和$ A_{MR}^{2*} $(独立性检验)。$ A_S^{2*} $检验结果为0.196,$ A_{MR}^{2*} $检验结果为0.272,AD检验结果均小于1.0[13],按照标准指南,表明该组数据在99%概率下接受测量系统的正态性和独立性假设,说明实验室数据处于统计受控状态。(3)期间精密度不确定度分量。实验室数据处于统计受控状态,期间精密度不确定度估计值为数据的相对标准偏差,即将$ {{S}}_{{{R}}^{{{'}}}} $视为期间精密度不确定度$ {u}_{R}{'} $,则$ {u^2}_{R',\,\,rel} $ = $ {{S}}_{{{R}}^{{{'}}}} $ = 0.88%。
表 2 实验室内重复性数据Table 2. Repeatability data within the laboratoryn 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 xi 99.9 100.2 100.6 100.7 101.1 100.3 101.9 100.5 102.7 101.4 n 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 $ \bar x $ SR’ xi 99.4 99.5 101.5 101.6 101.8 100.3 101.1 100.4 100.9 0.88% 1.5 GUM法不确定度评定
1.5.1 对照品纯度引入的相对不确定度urel(p)
盐酸氨溴索对照品说明书标示的纯度为p = 100.0%,标准品区间宽度a为±0.05%,按矩形分布计算,包含因子k = $ \sqrt{3} $:则urel (p) = $ \dfrac{\dfrac{a}{k}}{P} $ = $ \dfrac{\dfrac{0.05\mathrm{\%}}{\sqrt{3}}}{100\mathrm{\%}} $ = 2.9×10−4。
1.5.2 对照品称重引入的相对不确定度urel(m)
对照品称量所用的天平精度为十万分之一,不确定度来源分别为天平的示值误差和偏载误差。首先由天平校准证书提供的天平示值误差为±0.05 mg,区间半宽度为a = 0.05,按矩形分布计算(k = $ \sqrt{3} $),计算示值误差的标准不确定度u(m1) = a/$ k = 0.05/\sqrt{3} $ =
0.02887 mg;由天平偏载误差为±0.15 mg,区间半宽度为a = 0.15,按矩形分布计算(k = $ \sqrt{3} $),得出示值误差的标准不确定度u(m2) = a/$ \mathrm{k} = 0.15/\sqrt{3} $ =0.0866 mg,再合成天平的相对标准不确定度:u(m)$ = \sqrt{{u}^{2}\left({m}_{1}\right)+{u}^{2}\left({m}_{2}\right)} $ =0.0932 mg。 最后按照本次实验中实际称取的2份对照品称样量(15.37 mg、15.50 mg),计算由于天平称重引起的相对不确定度:urel(m) = $ \sqrt{{\left(\dfrac{0.0932}{15.37}\right)}^{2}+{\left(\dfrac{0.0932}{15.50}\right)}^{2}} $ = 8.5×10−3。1.5.3 容量瓶引入的不确定度分量urel(va)
在实际工作中,对照品及供试品的溶解过程均需要用到容量瓶玻璃仪器定容,容量瓶定容的不确定度来源主要有:容量允差和温度效应。(1)容量允差MPEurel(va1) 实验中涉及到的定容配置过程分别用到50、10、250 mL 的3种规格容量瓶,均为A 级。由容量允差(10 mL,±0.020 mL;50 mL,±0.05 mL;250 mL,±0.15 mL),以B 类不确定度中的三角分布(k = $ \sqrt{6} $),计算各容量允差的标准不确定度:10 mL:u(v1) = a/k = $ 0.02/\sqrt{6} $ = 0.00816 mL;50 mL:u(v2) = 0.0204 mL;250 mL:u(v3) = 0.0612 mL;带入实验中三次使用不同的容量瓶计算其相对标准不确定度:urel (va1) = $ \sqrt{{\left(\dfrac{0.00816}{10}\right)}^{2} + {\left(\dfrac{0.0204}{50}\right)}^{2} + {\left(\dfrac{0.0612}{250}\right)}^{2}} $ = 9.4×10−4。(2)温度效应urel(va2) 实际工作中,玻璃仪器的校正温度为20 ℃,水的体积膨胀系数为2.1×10−4 ℃−1,玻璃的体积膨胀系数为1.5×10−5 ℃−1,实验室实际温度为20±5 ℃,依照B 类不确定度评定规则,按均匀分布(k = $ \sqrt{3} $)计算,由各容量瓶引入的温度效应标准不确定度分别为10 mL :u (v1-1) = ∆V/k = $ \left({2.1\mathrm{*}10}^{-4}-{1.5\mathrm{*}10}^{-5}\right)\mathrm{*}10\mathrm{*}(25-20)/\sqrt{3} $ =
0.0056 mL;50 mL u (v2-1) = =0.0281 mL;250 mL:u (v3-1)=0.1407 mL;合并计算温度效应的相对标准不确定度urel (va2):$$ \begin{split} u_{ {rel }}\left(v_{\mathrm{a} 2}\right)=&\sqrt{\left(\frac{0.0056}{10}\right)^2+\left(\frac{0.0281}{50}\right)^2+\left(\frac{0.1407}{250}\right)^2}=\\&9.7 \times 10^{-4} 。 \end{split}$$ (3)由容量允差和温度效应合成得容量瓶引入的相对不确定度:
$$ u_{ {rel }}\left(v_{\mathrm{a}}\right)=\sqrt{u_{r e l}^2\left(v_{a 1}\right)+u_{r e l}^2\left(v_{a 2}\right)}=1.4 \times 10^{-3} 。 $$ 1.5.4 移液管引入的不确定度分量urel(vb)
实验中,对照品和样品的稀释过程中各用到1次1 ml的移液管,均为A 级。移液管作为玻璃仪器,其不确定度分量也包括容量允差urel (vb1)和温度效应u rel (v b2)。按照1.5.3计算方法,根据1ml移液管的容量允差(±0.007)和温度效应,合成移液管引入的相对不确定度:urel (va)$ =\sqrt{{{u}_{rel}}^{2}\left({v}_{\mathrm{b}1}\right)+{{u}_{rel}}^{2}\left({v}_{\mathrm{b}2}\right)} $ = 0.004。
1.5.5 仪器性能引入的不确定度分量u rel (r)
查询仪器的检定证书得知,高效液相色谱仪的整机性能中定量重复性误差为1.12%,则其相对扩展不确定度为1.12%,按分布均匀计算,包含因子k = $ \sqrt{3} $,则仪器的相对不确定度为:u rel (r)$ = 1.12\mathrm{\%}/\sqrt{3} $ = 6.5 × 10−3。
1.5.6 样品重复性引入的不确定度分量u rel (χ)
A类不确定度,平行取样品12份,按照标准处理后,注入液相色谱仪,结果含量χi分别为:100.8%,100.2%,100.1%,102.3%,99.1%,101.6%,101.6%,100.8%,100.5%,99.4%,101.0%,101.2%,相对标准偏差为
0.00926 %,平均值为100.7%,则重复性引入的标准不确定度:u (χ)= $ 0.00926/\sqrt{n} $=0.00267,相对标准不确定度:urel (χ)= $ \dfrac{u\left(x\right)}{100.7\mathrm{\%}} $ = 2.65 × 10−3。1.5.7 GUM法合成相对不确定度
根据1.3.3中数学模型和对实验过程的分析,明确盐酸氨溴索注射液不确定度的主要来源,按照实验室实际操作中涉及仪器的检定证书,按1.5.1~1.5.6计算各分量相对不确定度并汇总结果,见表3。 当各个分量之间相互独立时,可以将计算出的每一个相对不确定度分量进行综合,共同合成相对标准不确定度:
表 3 GUM法各分量相对不确定度结果汇总表Table 3. Summary of Relative Uncertainty Components Using the GUM Method分量 来源 影响因素 分布 分类 相对不确定度 urel (p) 对照品纯度 纯度 矩形 B 2.9×10−4 urel(m) 对照品称重 示值、偏载误差 矩形 B 8.5×10−3 urel(va) 容量瓶定容 容量允差MPE、温度效应 三角和矩形 B 1.4×10−3 urel(vb) 移液管量取 容量允差MPE、温度效应 三角和矩形 B 4.0×10−3 urel(r) 仪器性能 整机性能定量重复性 矩形 B 6.5×10−3 urel(x) 样品重复性测量 12份样品 正态 A 2.7×10−3 $$ u_{r d}(X)=\sqrt{u_{r d}{ }^2(p)+u_{r d}{ }^2(m)+u_{r d}{ }^2\left(v_a\right)+u_{r d}{ }^2\left(v_b\right)+u_{r d}{ }^2(r)+u_{r e l}{ }^2(x)}=1.18 \% $$ 2. 结果
2.1 TOP-DOWN法扩展不确定度及不确定度报告
按照评定的数学模型,由 1.4 中得到的2个分量值合为相对合成标准不确定度$ {u^2}_{c,rel} $,在置信度95%,包含因子(k取2)概率下求得扩展不确定度$ {U}_{rel } $。$ {U}_{rel } = 2{u}_{c,rel} = 2\sqrt{{u}^{2}{}_{b,rel}+{u}^{2}{}_{R{'},rel}}= 1.84\% $(95%,k = 2);由TOP-DOWN法评定的盐酸氨溴索含量表示为:(100.5±1.84)%,100.5%数值为本次实验笔者实验室内测定的样品含量数据。
2.2 GUM法扩展不确定度及不确定度报告
在95%的置信概率情况下,取包含因子k = 2,计算GUM法扩展不确定度U:U rel (X) = k· urel (X) = 2.36%。GUN法不确定度报告为:由GUM法评定的盐酸氨溴索含量为:(100.5±2.36)%,k = 2。
2.3 评定结果
TOP-DOWN法和GUM法两种方法评定盐酸氨溴索注射液含量,结果表示为(100.5±1.84)%和(100.5±2.36)%,即用扩展不确定度1.84%和2.36%分别来表征实验室含量测量数据100.5%的分散性,被不确定度表征后的数值在药品标示含量值以内(90.0%~110.0%),表明盐酸氨溴索注射液含量测定可靠,实验室质控较好,可持续保持,含量测定结果的可靠信进一步确保了药物的安全性和有效性。实验结果表明,TOP-DOWN法可有效评定药品外标法含量测定,在实际测量中,始终存在的客观事实是无论如何控制环境条件及控制各类对测量结果可能产生影响的因素,最终的测量结果总会存在一定的分散性,这些随机效应所造成的不确定度,包括尚未认识到的系统效应在评定中不可能被完全考虑到,导致了测量结果的误差。而该法的优势恰好在于能充分利用实验室内长期积累的数据和实验室间再现性数据,归纳为精密度和偏倚2个分量,更加系统、全面的评定不确定度。而GUM法是实验室根据实验过程分析,在各操作部分中可能引入的对结果产生影响的各种因素,识别其来源,建立数学模型,再量化各分量,最后根据不确定度传播规律合成、扩展得到扩展不确定度,使用GUM法评定必须熟悉整个检验流程,评定过程繁琐、复杂,要求细致,因素不能重复也不能遗漏。本次实验共识别出6种影响因素,对照品的纯度、对照品称量、溶液配置定容所用的容量瓶、量取溶液的移液管、由仪器性能引入的不确定度、在相同条件下被测量重复观测值的变化。以容量瓶、相同条件下被测量重复观测值的变化和移液管引入的分量贡献最大,因实验过程中使用到的容量瓶有3种,而重复观测值由实验室不同人员检验得到的不同结果,涉及的仪器、检验人员越多,GUM法评定时引入的不确定度分量越多,导致评定值越高,这是使用GUM法评定无法避免的情况。
3. 讨论
3.1 实验数据ARV值的来源依据
TOP-DOWN法应用时,数据受控是最重要的前提条件,h/k检验希望参加的实验室数量L越大越好[14-15],但h/k临界值参考表中L上限为15。由于h/k值随着L增大其可接受的h/k值范围越大,以表中L为15对应的h/k值判断本次实验数据(共17家实验室)是否受控。h或k超出95%的临界值为异常值,但仍在99%临界值范围内。通过调查发现,实验室操作没有任何程序问题,属于随机原因的正常变异,综合判断整体数据基本受控[12,14-16],并未剔除数据异常值(表1中带*号数据)。此外,ARV为接受参照值(即用作比较的经协商同意的标准值),本文使用的ARV值使用数据来源为本实验室自2020年至2023年检验的22批盐酸氨溴索注射液的含量平均值(100.4%)。
3.2 TOP-DOWN法可有效评定药品含量的不确定度
TOP-DOWN法已应用于食品等其他行业的不确定度评定中[17-19],本文利用TOP-DOWN法对药品含量测定结果进行不确定度评定,评定结果期间精密度的分量大于偏倚精密度的分量,说明期间精密度是影响不确定度数值的主要分量,则可通过加长期间精密度的时间和样本量来进一步验证期间精密度的贡献量。偏倚分量贡献较小,影响的变化不显著,而偏倚由实验室间的再现性数据提供,提示可以通过增加实验室及样本数量来验证偏倚分量的贡献大小。该法的优势在于能充分利用实验室内长期积累的实验数据,评定过程较传统的GUM法更全面,是一种客观、可靠的评定方法,为药品检验领域不确定度评定提供了新的方法。
3.3 TOP-DOWN法与GUM法在评定结果方面的对比分析
TOP-DOWN法和GUM法为两种不同的评定方法,评定结果 TOP-DOWN法评定结果(1.84%)小于GUM法(2.36%),可能的原因为:在TOP-DOWN法再现性评估中,偏倚分量贡献较小,影响的变化不显著,而偏倚由实验室间的再现性数据提供,因此,可以通过增加实验室及样本数量来验证偏倚分量的贡献大小。同时,通过结果比较,说明GUM的测量模型较为完整,但给出的各已知分量的估计值可能比TOP-DOWN法中直接观察到的方差大,导致该模型下的不确定度结果更为宽泛,可能过多的输入了不确定度影响因素,提示在用GUM法计算不确定度时应保守估计影响因素,否则容易造成结果偏大。既然不确定度有助于解释测量结果,则应注意弥补每种评估方法的不足,实际应用时,可以综合运用这两种方法,将两种方法融合[14−15],如本次盐酸氨溴索注射液含量测定值为100.5%,不确定度的2种评定方法结果不完全一致,分别为1.84%和2.36%,将2种方法融合后取平均值2.1%,产品测定结果均在药品标示含量值以内(90.0%~110.0%),2种方法分别评判或融合后均表明测定盐酸氨溴索注射液含量测定结果可靠。
3.4 对盐酸氨溴索注射液进行不确定度评定
盐酸氨溴索注射液作为高风险制剂,目前未见其含量测定不确定度评定的报道,本文对其不确定度进行研究,研究结果表明该药物含量测定数据可靠,能确保药物的安全性和有效性。
-
表 1 4组大鼠各时间点神经功能缺损评分比较 [n = 12,(
$\bar x \pm s $ )]Table 1. The comparison of neurologic impairment scores in four groups at different timing [n = 12,(
$\bar x \pm s $ )]组别 时间 再灌24 h 再灌3 d 再灌7 d 再灌15 d 再灌30 d MCAO组 2.15 ± 0.61 1.92 ± 0.19 1.75 ± 0.45 1.50 ± 0.52 1.33 ± 0.49 EM组 2.21 ± 0.45 1.83 ± 0.38 1.58 ± 0.51 1.33 ± 0.49 1.08 ± 0.79a CR组 2.15 ± 0.72 1.83 ± 0.38 1.67 ± 0.49 1.41 ± 0.51 1.17 ± 0.72a WM组 2.23 ± 0.45 1.75 ± 0.45 1.50 ± 0.52 1.25 ± 0.45 0.75 ± 0.62abc F 1.894 1.887 1.789 1.488 3.102 P 0.164 0.152 0.170 0.109 0.037* *P < 0.05;与MCAO组同时间点比较,aP < 0.05;与EM组同时间点比较,bP < 0.05;与CR组同时间点比较,cP < 0.05。 -
[1] Maigeng Zhou,Haidong Wang,Xinying,et al. Mortality,morbidity,and risk factors in China and its provinces,1990–2017:A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet,2019,394(17):102-104. [2] Jingjing Nie,Xiaosu Yang,Qingping Tang,et al. Willed-movement trainingreduces brain damage and enhances synaptic plasticity related proteins synt-hesisafter focal ischemia[J]. Brain Res Bull,2016,120(11):90-96. [3] Zhiwen Zhou,Qidong Yang,Qingping Tang,et al. Effect of willed movement training on neurorehabilitation after focal cerebral ischemia and on the neural plasticity-associated signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep,2018,17(1):1173-1181. [4] Qingping Tang,Qidong Yang,Zhongyang Hu,et a1. The effects of willed movement therapy on AMPA receptor properties for adult rat following focal cerebral ischemia[J]. Behav Brain Res,2007,181(2):254-261. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2007.04.013 [5] Parkinson Gabrielle T,Hanley Jonathan G. Mechanisms of AMPA ReceptorEndosomal Sorting[J]. Front Mol Neurosci,2018,11(2):440-441. [6] Surya P,Pandey,Rakesh Rai,Pankaj Gaur,et al. Development- and age-related alterations in the expression of AMPA receptor subunit GluR2 and its trafficking proteins in the hippocampus of male mouse brain[J]. Biogerontology,2015,16(3):17-28. [7] Parkinson Gabrielle T,Chamberlain Sophie E L,Jaafari Nadia,et al. Cortactin regulates endo-lysosomal sorting of AMPARs via direct interaction with GluA2 subunit[J]. Sci rep,2018,8(1):15-17. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-16936-8 [8] Zikai Zhou,An Liu,Shuting Xia,et al. Publisher correction:The C-terminal tails of endogenous GluA1 and GluA2 differentially contribute to hippoc-ampal synaptic plasticity and learning[J]. Nat neurosci,2018,4(10):11-15. [9] Zsombor Koszegi,Maria Fiuza,Jonathan G. Endocytosis and lysosomal de-gradation of GluA2/3 AMPARs in response to oxygen/glucose deprivation in hippocampal but not cortical neurons[J]. Sci Rep,2017,7(1):28-29. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00040-y [10] Hu Jian,Li Ce,Hua Yan,et al. Constraint-induced movement therapy imp-roves functional recovery after ischemic stroke and its impacts on synaptic-plasticity in sensorimotor cortex and hippocampus[J]. Brain Res Bull,2020,4(2):160-162. [11] Yamagata Masahito,Duan Xin,Sanes Joshua R. Cadherins interact with synaptic organizers to promote synaptic differentiation[J]. Front Mol N-eurosci,2018,4(1):11-13. [12] Cen Cheng,Luo Li-Da,Li Wen-Qi,et al. PKD1 promotes functional synapse formation coordinated with N-Cadherin in hippocampus[J]. J Neurosci,2018,38(1):28-31. [13] Elena Bacchelli,Fabiola Ceroni,Dalila Pinto,et al. A CTNNA3 compound heterozygous deletion implicates a role for αT-catenin in susceptibility to autism spectrum disorder[J]. J Neurodev Disord,2014,6(1):17. doi: 10.1186/1866-1955-6-17 [14] Tucci,Valter,Kleefstra,et al. Dominant β-catenin mutations cause intelle-ctual disability with recognizable syndromic features[J]. J Clin Invest,2014,124(4):1468-1482. doi: 10.1172/JCI70372 [15] Alejandro Uribe-Arias,Rafael Andrés Posada-Duque,Christian González‐Billault,et al. p120-catenin is necessary for neuroprotection induced by CDK5 silencing in models of Alzheimer’s disease[J]. J Neurochemistry,2016,138(4):115-118. [16] Heisler Frank F,Lee Han Kyu,Gromova Kira V,et al. GRIP1 interlinks N-cadherin and AMPA receptors at vesicles to promote combined cargo t-ransport into dendrites[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci,2014,111(13):224-226. [17] Xiaoying Wu,Shengqun Liu,Zhenhua Hu,et al. Enriched housing promo-tes post-stroke neurogenesis through calpain 1-STAT3/HIF-1α/VEGF signal-ing[J]. Brain Res Bull,2018,139(18):133-143. 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 颜晓睿,宫丽鸿,刘云褀,周锦涵,彭亮. 祛痰化瘀方对AF大鼠心房代谢重构的机制研究. 时珍国医国药. 2024(15): 3362-3369 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载: