Effect of TLR4/MyD88/NF- κB Signal Pathway on the Hippocampus of Methamphetamine-dependent CPP Rats
-
摘要:
目的 研究TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路对甲基苯丙胺(methamphetamine,MA)依赖的条件性位置偏好(conditioned place preference,CPP)大鼠海马的影响,同时采用特异性抑制剂TAK-242抑制Toll样4受体(Toll-like receptor 4,TLR4),减轻MA依赖诱导的海马神经炎症。 方法 建立MA(10 mg/kg,ip,14 d)依赖大鼠CPP模型,分别为生理盐水组、MA组、TAK-242组、MA+TAK-242组。TAK-242组和MA+TAK-242组先分别腹腔注射抑制剂TAK-242(3 mg/kg),1h后MA+TAK-242组再腹腔注射MA(10 mg/kg)。采用Western Blot实验和采用荧光定量PCR实验检测MA依赖CPP大鼠海马中TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6、IκB-α、p-IκB-α、NF-κBp65、p-NF-κBp65蛋白的表达和mRNA表达。 结果 与生理盐水组相比,MA组TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6、NF-κBp65的蛋白和mRNA表达均升高(P < 0.001或P < 0.01),IκB-α的蛋白和mRNA表达下降(P < 0.01),p-IκB-α、p-NF-κBp65的表达升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6、NF-κBp65的蛋白和mRNA表达均下降(P < 0.001、P<0.01或P < 0.05),IκB-α的蛋白和mRNA表达升高(P < 0.01),p-IκB-α、p-NF-κBp65表达下降(P < 0.01或P < 0.05)。 结论 MA依赖可通过激活TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路,诱导CPP大鼠海马神经炎症的发生,采用特异性TLR4抑制剂可以减轻MA诱导的神经炎症。 -
关键词:
- 甲基苯丙胺依赖 /
- 条件性位置偏爱 /
- 海马 /
- TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号转导通路
Abstract:Objective To study the effect of TLR4/MyD88/NF- κB signal pathway on the hippocampus of methamphetamine (MA) dependent conditioned place preference (CPP) rats, and inhibition of Toll like receptor 4 (TLR4) by specific inhibitor TAK-242, thereby reducing MA induced hippocampal neuroinflammation. Methods We established a model of MA (10 mg/kg, ip, 14 d) dependent CPP in rats. Rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: normal saline group, MA group, TAK-242 group, and MA+TAK-242 group. TAK-242 group and MA+TAK-242 group were intraperitoneally injected with inhibitor TAK-242 (3 mg/kg), and MA+TAK-242 group was intraperitoneally injected with MA (10 mg/kg) one hour later. Protein and mRNA expression of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, IκB- α, p-IκB- α, NF- κ B p65, p-NF-Κb p65 in hippocampus of MA dependent CPP rats were tested by Western Blot test and fluorescent quantitative PCR, respectively. Results Compared with normal saline group, the expression of protein and mRNA of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, NF- κBp65 in MA group increased (P < 0.001 or P < 0.01).The protein of IκB- α and mRNA expression of lactamase decreased (P < 0.01), the expression of p-IκB- α and p-NF- κBp65 increased (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05). Compared with MA group, the protein and mRNA expression of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, NF- κBp65 in MA+TAK-242 group decreased (P < 0.001, P < 0.01 or P < 0.05) . The expression of IκB- α protein and mRNA was increased (P < 0.01), the expression of p-IκB- α and p-NF- κBp65 decreased (P < 0.01 or P < 0.05). Conclusions MA dependency can be achieved by activating TLR4/MyD88/NF- κ B signal pathway, which can induce neuroinflammation on the hippocampus of methamphetamine-dependent CPP rats. The use of specific TLR4 inhibitors can attenuate MA induced neuroinflammation. -
甲基苯丙胺( methamphetamine,MA) ,属于苯丙胺类兴奋剂,可进入血脑屏障导致大脑的结构和功能的改变[1],其滥用诱发大脑多个脑区发生不同程度的神经损伤,从而诱导中枢神经系统神经毒性的产生[2]。研究发现[3]MA依赖引起的神经毒性损伤海马脑区损伤有重要联系。MA诱导海马神经毒性的产生与单胺类神经递质释放增加[4-5]、ROS和NOS的产生、大脑免疫细胞的激活、凋亡与自噬[6]和神经炎症[7]等有关。Toll样受体(Toll like receptors,TLR),能够调控免疫及炎症反应[8],主要在小胶质细胞中表达[9]。TLR4细胞内信号通路分为髓样分化因子88 (myeloid differentiation factor 88,MyD88)依赖性和β干扰素TIR结构域衔接蛋白(TIR-domain-containing adaptor inducing interferon-β,TRIF)依赖性通路。在MyD88依赖途径中当外界因素触发后,细胞表面的刺激信号通过TLR4-MyD88-TRAF6-IκB-PIκB-NF-κB分子传递到细胞核,从而调节相关炎症因子的转录[10]。颅脑外伤可以诱导神经元凋亡和神经炎症,从而导致严重的神经元损害和行为障碍[11],其中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的激活是造成中枢神经系统损伤的关键原因。在体外实验中脂多糖损伤的 BV2 小胶质细胞和神经炎症损伤的原代皮层神经元中采用TLR4 抑制剂 TAK-242所产生的抗神经炎症作用主要是与 TLR4 介导的 MyD88/NF-κB 信号通路的调节有关[12]。Li B等[13]的体外实验表明阻断 TLR4 介导的信号转导,TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 和 MAPK 通路的激活便会受到影响,从而抑制 BV-2 小胶质细胞中脂多糖刺激所产生神经炎症。TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB作为一条经典的炎性通路,在MA诱导的海马神经炎症中具有较大的研究价值。本研究旨在探究研究TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路对甲基苯丙胺CPP大鼠海马的影响,同时采用特异性抑制剂TAK-242抑制TLR4,在改善MA依赖海马神经炎症中的作用,为药物干预甲基苯丙胺依赖提供新的科学证据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料
实验动物:健康雄性SD大鼠40只,选择体重在180~200 g,购于昆明医科大学实验动物学中心[动物使用许可证编号:SCXK(滇)K2015-002]。
药品试剂:实验所用甲基苯丙胺,由云南省公安厅禁毒技术公安部重点实验室合法提供,纯度在98%以上。BestarTMqPCR RT Kit、荧光定量试剂盒(DBI Bioscience);引物合成(擎科生物科技有限公司);TLR4 受体抑制剂(TAK-242,A3850,Apexbio公司MyD88抗体(ab2064,Abcam公司);TRAF6抗体(66494,Proteintech公司);IκB-α 抗体(9242,CST公司);p-IκB-α抗体(2859,CST公司);NF-κB p65抗体(8142s,CST公司);p-NF-κB p65抗体(sc-136548,Santa Cruz Biotechnology公司);TLR4抗体(sc-293072,Santa Cruz Biotechnology公司);β-actin抗体(ab6276,购自美国Abcam公司)。
主要仪器:大鼠 CPP 实验箱(XR-XT401,上海欣软信息有限公司);酶标仪(Touch 2,美国BioTek公司);普通PCR仪、荧光定量 PCR 仪(T100TM Thermal Cycler、C1000 Touch TM Thermal Cycler,美国Bio-Rad 公司);垂直电泳仪、半干转膜仪(552BR、221BR,美国Bio-Rad 公司)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验动物分组及给药
健康雄性SD大鼠40只,随机分配为4组,包括生理盐水组:腹腔注射(生理盐水(10 mg/kg,qd,14 d);MA 实验组:给药 MA(10 mg/kg,ip,qd,14 d),大鼠形成MA依赖,CPP模型建模成功;TAK-242 组:给药 TAK-242(3 mg/kg,ip,qd,14 d);MA + TAK-242 组:给药 TAK-242(3 mg/kg,ip,qd,14 d)后 1 h给予 MA(10 mg/kg,ip,qd,14 d)。
1.2.2 条件性位置偏爱模型(CPP)
连续3 d将随机分组的大鼠放入实验检测的黑白箱中以适应检测环境,第4天检测每只大鼠的天然偏好时间;连续14 d对大鼠以10 mg/kg的MA进行腹腔注射给药,使得大鼠产生依赖,再进行CPP检测。
1.2.3 Western
Blot实验 用 10%的水合氯醛 ,按0.3 m L/100 g麻醉后迅速水合氯醛麻醉大鼠 , 用0.9%的氯化钠注射液对大鼠心脏灌注,将脑血管中的血液冲洗干净断头,取出全脑,分离大鼠海马组织解剖大鼠,取大鼠海马组织,匀浆,测定蛋白浓度。配制10%和12%的分离胶;上样、电泳,转膜、孵育一抗(β-actinantibody Anti-TLR4、Anti-Myd88、Anti-TRAF6、Anti-IκB-α、Anti-pIκB-α、Anti-NF-κBp65、Anti-P- NF-κBp65均按照1∶1000配制),放入4 ℃过夜,1xTBST 漂洗3次,温室孵育二抗(2 h),再次漂洗,采用ECL显影。 Image Pro Plus 图像分析软件分析目的条带与对应内参(β-actin)条带二者平均光密度比值,最后进行统计学分析。
1.2.4 荧光定量PCR实验
取海马组织80 mg,放入 EP 管中,匀浆,用酶标仪测定RNA浓度;按照说明书逆转录合成cDNA;荧光实时定量PCR仪,经94 ℃ 5 min预变性、94 ℃变性、58 ℃退火、72 ℃延伸,此循环进行40次,采用2-ΔΔCt法计算目的基因的相对表达量,荧光定量PCR引物序列见表1。
表 1 荧光定量PCR引物序列Table 1. Fluorescence quantitative PCR primer sequence基因名称 引物序列信息 温度 TLR4 上游引物:5'-TGCCTGAGACCAGGAAGCTTG 3'
下游引物:5'-CTTAAGATCTTCAGGGGGTTG3'54 ℃ Myd88 上游引物:5'-TGAGAAAAGGTGTCGTCGCA3'
下游引物:5'-GGGTCCAGAACCAGGACTTG'54 ℃ TRAF6 上游引物:5'-GCCCATGCCGTATGAAGAGA 3'
下游引物:5'-CGTGACAGCCAAACACACTG3'54 ℃ NF-κB p65 上游引物:5'-GAGACCTGGAGCAAGCCATT3'
下游引物:5'-AGTTCCGGTTTACTCGGCAG3'54 ℃ IKB-α 上游引物:5'-GAATCCTGACCTGGTCTCGC'
下游引物:5'-CACAGTCATCGTAGGGCAACT3'55 ℃ β-actin 上游引物:5'-AGACAGCCGCATCTTGT-3'
下游引物:5'-CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT-3'55 ℃ 1.3 统计学处理
采用 SPSS 19.0进行数据分析,数值代表均数±标准差(
$\bar x \pm s $ )表示,用于统计分析的Prism软件5.0作图(GraphPad software),组内给药前后比较采用配对 t 检验;组间多组比较采用多因素方差分析(Multi-factor analysis of variance),多重比较方法采用 Tukey-HSD,P < 0.05 为差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 甲基苯丙胺依赖CPP大鼠海马中TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6、IκB-α、p-IκB-α、NF-κBp65、p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达
TLR4蛋白变化:图1A结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组TLR4蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组TLR4的蛋白表达下降(P < 0.01)。
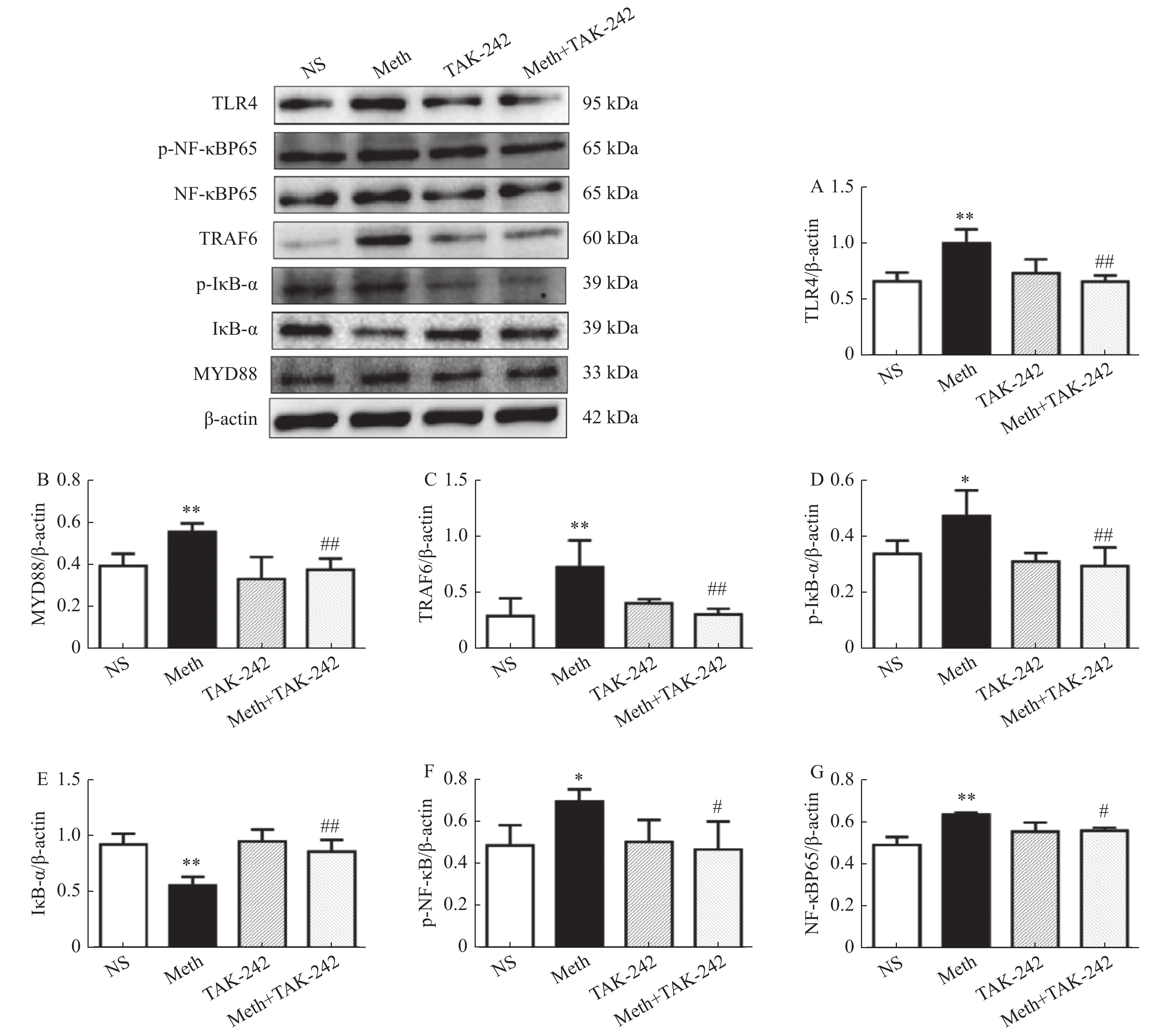 图 1 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路蛋白表达水平变化。A:海马中TLR4的表达水平;B:海马中MyD884的表达水平;C:海马中TRAF6的表达水平;D:海马中p-IκB-α的表达水平;E:海马中IκB-α的表达水平;F:海马中p-NF-κBp65的表达水平;G:海马中NF-κBp65的表达水平。与对照组进行比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01;与MA组比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01 。Figure 1. The protein expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus of rats
图 1 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路蛋白表达水平变化。A:海马中TLR4的表达水平;B:海马中MyD884的表达水平;C:海马中TRAF6的表达水平;D:海马中p-IκB-α的表达水平;E:海马中IκB-α的表达水平;F:海马中p-NF-κBp65的表达水平;G:海马中NF-κBp65的表达水平。与对照组进行比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01;与MA组比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01 。Figure 1. The protein expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus of ratsMyD88蛋白变化:图1B结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组MyD88蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组MyD88蛋白表达下降(P < 0.01)。
TRAF6蛋白变化:图1C结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组TRAF6的蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组TRAF6的蛋白表达下降(P < 0.01)。
p-IκB-α蛋白变化:图1D结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组p-IκB-α蛋白表达升高p-IκB-α蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组p-IκB-α蛋白表达下降(P < 0.01)。
IκB-α蛋白变化:图1E结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组IκB-α蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组IκB-α蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01)。
p-NF-κBp65蛋白变化:图1F结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组的p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05)。
NF-κBp65蛋白变化:图1G结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组NF-κBp65蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组的NF-κBp65蛋白表达下降(P < 0.05)。
上述结果提示MA可通过TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路诱导MA依赖CPP大鼠海马发生神经炎症。
2.2 甲基苯丙胺依赖CPP大鼠海马中TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6、IκB-α、NF-κBp65mRNA表达
TLR4 mRNA表达变化见表2和图2A,结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组TLR4mRNA表达上升(P < 0.01);与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组TLR4mRNA表达下降(P < 0.01)。
表 2 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路的mRNA表达(n = 6,$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. The mRNA expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus of rats (n = 6,$\bar x \pm s $ )因子 组别 生理盐水组 Meth组 TAK-242组 Meth+TAK-242 组 TLR4 0.82 ± 0.10 1.16 ± 0.20 ** 0.80 ± 0.22 0.83 ± 0.11 ## MyD88 0.90 ± 0.08 1.17 ± 0.13 ** 0.83 ± 0.15 0.86 ± 0.08 ## TRAF6 0.98 ± 0.27 1.62 ± 0.47 ** 0.84 ± 0.29 0.92 ± 0.25 ## IκB-α 1.04 ± 0.17 0.69 ± 0.11 ** 0.98 ± 0.14 1.00 ± 0.13 ## NF-κBp65 0.88 ± 0.12 1.14 ± 0.10 *** 0.89 ± 0.06 0.92 ± 0.16 ### 与对照组进行比较,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;与MA组进行比较,##P < 0.05 ,###P < 0.001。 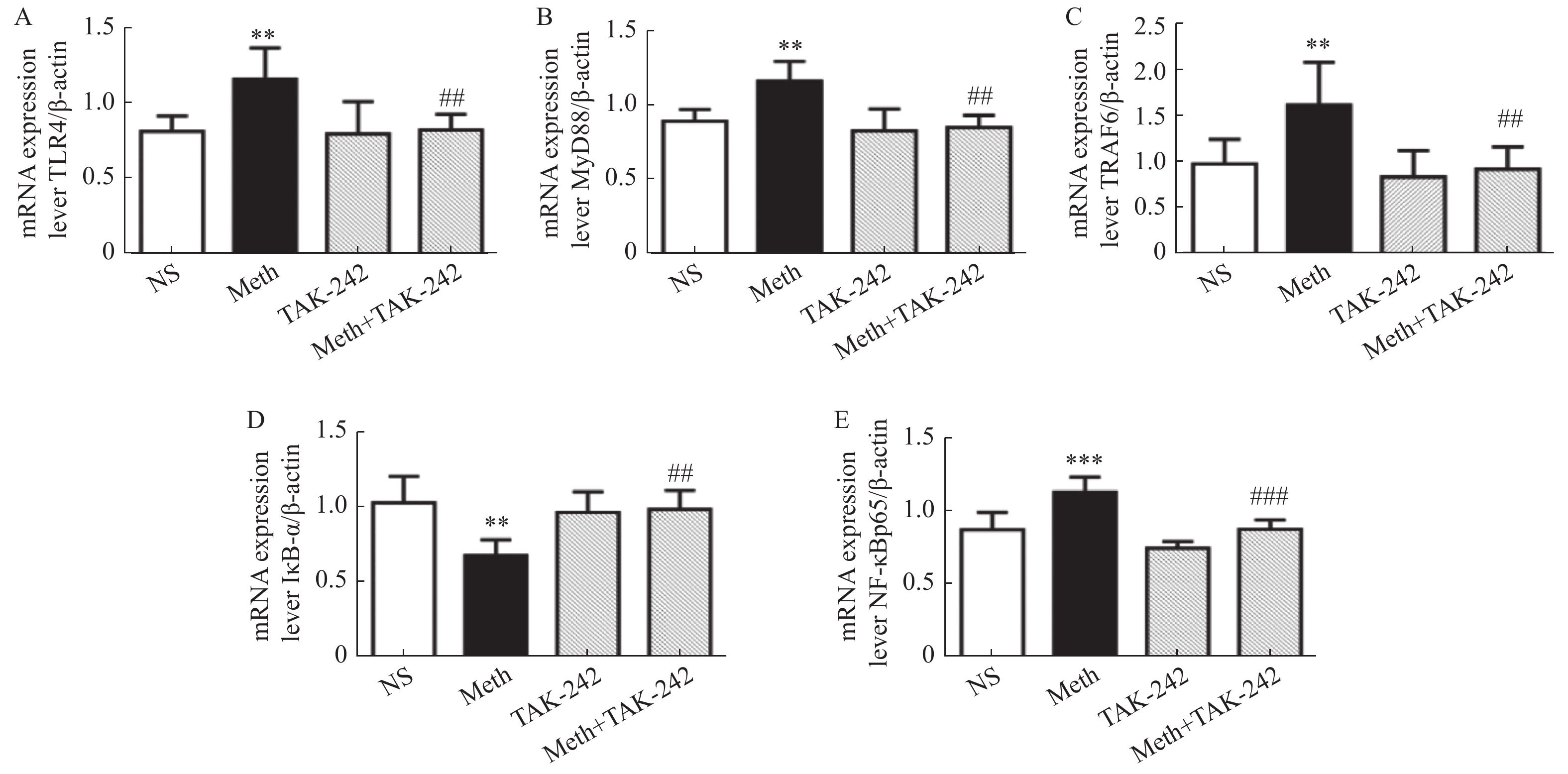 图 2 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路的mRNA表达 水平统计结果A:海马中TLR4的mRNA表达水平;B:海马中MyD884的mRNA表达水平;C:海马中TRAF6的mRNA表达水平;D:海马中IκB-α的mRNA表达水平;E:海马中NF-κBp65的mRNA表达水平。与对照组进行比较,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;与MA组进行比较,##P < 0.05 , ###P < 0.001。Figure 2. The mRNA expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus
图 2 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路的mRNA表达 水平统计结果A:海马中TLR4的mRNA表达水平;B:海马中MyD884的mRNA表达水平;C:海马中TRAF6的mRNA表达水平;D:海马中IκB-α的mRNA表达水平;E:海马中NF-κBp65的mRNA表达水平。与对照组进行比较,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;与MA组进行比较,##P < 0.05 , ###P < 0.001。Figure 2. The mRNA expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampusMyD88 mRNA表达变化:表2和图2B结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组MyD88mRNA表达上升(P < 0.01);与M组相比,MA+TAK-242组MyD88mRNA表达下降(P < 0.01)。
TRAF6 mRNA表达变化:表2和图2C结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组TRAF6mRNA表达上升(P < 0.01),与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组TRAF6mRNA表达下降(P < 0.01)。
IκB-α mRNA表达变化:表2和图2D结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组IκB-α mRNA表达下降(P < 0.01),与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组IκB-α mRNA表达上升(P < 0.01)。
NF-κBp65 mRNA表达变化:表2和图2E结果显示与生理盐水组相比,MA组NF-κBp65 mRNA表达上升(P < 0.001),与MA组相比,MA+TAK-242组NF-κBp65 mRNA表达下降(P < 0.001)。
3. 讨论
已有研究表明,MA依赖诱导海马神经炎症,造成了神经系统的损害。炎性因子过渡累积就会对机体产生严重的危害,其中与损害最为严重的海马脑区为例。本研究发现MA依赖的CPP大鼠激活了海马脑区TLR4/MYD88/NF-κB信号通路,诱导了海马神经炎症的发生。
TLR4作为天然免疫识别受体,通过Myd88通路发挥作用[14,15]。本研究表明:与对照组相比,MA组TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6蛋白和mRNA表达均增加。Xie等[16]的研究发现,在MA中毒大鼠模型中,MA可使大鼠纹状体中 TLR4,MyD88,TRAF6 蛋白表达增加;Du等的研究在 MA中毒小鼠模型中, MA也可使中脑和纹状体中TLR4 蛋白表达增加[8, 17],上述结果均与与本研究结果一致,但是本研究对于海马脑区的检测不仅包含上述因子蛋白水平的变化,还在mRNA水平进一步验证了MA依赖可通过激活TLR4/MyD88信号通路,诱导海马神经炎症发生。Qing-Peng Hu等[18]的研究表明,组蛋白乙酰化调节抑制剂(histone deacetylase inhibitor,HDACI)可抑制TLR4/MYD88信号通路中TLR4的表达,从而抑制小胶质细胞激活和神经元凋亡,这就表明阻断TLR4对神经炎症诱导的脑损伤具有潜在的神经保护作用。本研究采用TLR4受体抑制剂TAK-242预处理,特异性地抑制了海马脑区TLR4的表达,减少了MyD88、TRAF6的蛋白及mRNA的表达。
研究发现多种分子机制可以介导炎症过程,其中最显著的机制是通过核因子NF-κB信号通路[19],磷酸化的NF-κB抑制因子(inhibitor of NF-κB,IκB),使IKB降解,进而激活NF-κB,其中p65是NF-κB的主要活性亚单位[20]。本研究采用Western blot检测MA依赖CPP大鼠海马中p-IκB-α、NF-κBp65、p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达均增加,IκB-α的蛋白表达下降。Liu X等发现[21],苦碟子注射液(KDZ)可通过下调TLR4 依赖性 NF-κB信号通路,降低TRAF6、NF-κBp65和p-IκBα/IκBα的蛋白表达,保护大脑免受缺血性损伤。Long H等也发现[22],在大鼠Tourette综合征(TS)模型中,TS大鼠纹状体中IκB-α蛋白表达降低,p-IκB-α蛋白表达升高,结果均与本研究一致。不同的是本研究采用特异性TLR4拮抗剂TAK-242预处理后,p-IκB-α、NF-κBp65、p-NF-κBp65蛋白表达降低,IκB-α蛋白表达增加。此外,本研究发现IκB-αmRNA表达降低、NF-κBp65 mRNA表达增加,结果与蛋白水平一致。采用TLR4受体抑制剂(TAK-242)预处理,特异性地抑制了海马脑区TLR4的表达,减少了的NF-κB通路关键蛋白及mRNA的表达,从而减轻MA依赖大鼠海马脑区的神经炎症。
综上所述,TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路参与了MA依赖大鼠CPP效应的形成,该信号通路的激活可以诱导MA依赖大鼠海马神经炎症的发生。采用特异性的TLR4抑制剂可以改变TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路相关的因子的表达,减轻MA依赖的海马神经炎症。
-
图 1 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路蛋白表达水平变化。
A:海马中TLR4的表达水平;B:海马中MyD884的表达水平;C:海马中TRAF6的表达水平;D:海马中p-IκB-α的表达水平;E:海马中IκB-α的表达水平;F:海马中p-NF-κBp65的表达水平;G:海马中NF-κBp65的表达水平。与对照组进行比较,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01;与MA组比较,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01 。
Figure 1. The protein expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus of rats
图 2 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路的mRNA表达 水平统计结果
A:海马中TLR4的mRNA表达水平;B:海马中MyD884的mRNA表达水平;C:海马中TRAF6的mRNA表达水平;D:海马中IκB-α的mRNA表达水平;E:海马中NF-κBp65的mRNA表达水平。与对照组进行比较,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;与MA组进行比较,##P < 0.05 , ###P < 0.001。
Figure 2. The mRNA expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus
表 1 荧光定量PCR引物序列
Table 1. Fluorescence quantitative PCR primer sequence
基因名称 引物序列信息 温度 TLR4 上游引物:5'-TGCCTGAGACCAGGAAGCTTG 3'
下游引物:5'-CTTAAGATCTTCAGGGGGTTG3'54 ℃ Myd88 上游引物:5'-TGAGAAAAGGTGTCGTCGCA3'
下游引物:5'-GGGTCCAGAACCAGGACTTG'54 ℃ TRAF6 上游引物:5'-GCCCATGCCGTATGAAGAGA 3'
下游引物:5'-CGTGACAGCCAAACACACTG3'54 ℃ NF-κB p65 上游引物:5'-GAGACCTGGAGCAAGCCATT3'
下游引物:5'-AGTTCCGGTTTACTCGGCAG3'54 ℃ IKB-α 上游引物:5'-GAATCCTGACCTGGTCTCGC'
下游引物:5'-CACAGTCATCGTAGGGCAACT3'55 ℃ β-actin 上游引物:5'-AGACAGCCGCATCTTGT-3'
下游引物:5'-CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT-3'55 ℃ 表 2 大鼠海马中TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB 信号转导通路的mRNA表达(n = 6,
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 2. The mRNA expression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal transduction pathway in the hippocampus of rats (n = 6,
$\bar x \pm s $ )因子 组别 生理盐水组 Meth组 TAK-242组 Meth+TAK-242 组 TLR4 0.82 ± 0.10 1.16 ± 0.20 ** 0.80 ± 0.22 0.83 ± 0.11 ## MyD88 0.90 ± 0.08 1.17 ± 0.13 ** 0.83 ± 0.15 0.86 ± 0.08 ## TRAF6 0.98 ± 0.27 1.62 ± 0.47 ** 0.84 ± 0.29 0.92 ± 0.25 ## IκB-α 1.04 ± 0.17 0.69 ± 0.11 ** 0.98 ± 0.14 1.00 ± 0.13 ## NF-κBp65 0.88 ± 0.12 1.14 ± 0.10 *** 0.89 ± 0.06 0.92 ± 0.16 ### 与对照组进行比较,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001;与MA组进行比较,##P < 0.05 ,###P < 0.001。 -
[1] 石晶晶,吴宁,李锦. 苯丙胺类兴奋剂成瘾的治疗药物研究现状[J]. 中国药物依赖性杂志,2016,25(2):145-150. doi: 10.13936/j.cnki.cjdd1992.2016.02.001 [2] Veschsanit N,Yang J L,Ngampramuan S,et al. Melatonin reverts methamphetamine-induced learning and memory impairments and hippocampal alterations in mice[J]. Life Sciences,2021,7(3):265-274. [3] Zhang S,Jin Y,Liu X,et al. Methamphetamine modulates glutamatergic synaptic transmission in rat primary cultured hippocampal neurons[J]. Brain Research,2014,40(2):1-11. [4] 张莉,布胡丽倩木·伊买尔江,马瑞佳,等. 1-(2-氯)苯基-9-丁基-β-咔啉对小鼠的神经毒性作用[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(9):879-883. doi: 10.13286/j.1001-5213.2022.09.01 [5] 魏姗姗. 虫草素对谷氨酸诱导的兴奋性神经毒性的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 江西科技师范大学学报,2020,25(2):1-52. [6] 杨根梦,曾晓锋,张冬先,等. Nupr1/ERS/NLRP3炎性小体在甲基苯丙胺诱导的神经毒性中的作用[J]. 中国药理学通报,2020,36(3):297-300. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2020.03.001 [7] Shaerzadeh F,Streit W J,Heysieattalab S,et al. Methamphetamine neurotoxicity,microglia,and neuroinflammation[J]. Journal of Neuroinflammation,2018,15(1):341-363. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1385-0 [8] Fernández-Arjona M D M,Grondona J M,Fernández-Llebrez P,et al. Microglial activation by microbial neuraminidase through TLR2 and TLR4 receptors[J]. Journal of Neuroinflammation,2019,16(1):245-261. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1643-9 [9] Azam S,Jakaria M,Kim I S,et al. Regulation of Toll-Like Receptor (TLR) Signaling Pathway by Polyphenols in the Treatment of Age-Linked Neurodegenerative Diseases: Focus on TLR4 Signaling[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2019,10(1):432-447. [10] Chang J,Wang L,Zhang M,et al. Glabridin attenuates atopic dermatitis progression through downregulating the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Genes & Genomics,2021,43(8):847-855. [11] Jiang H,Yang X,Wang Y,et al. Vitamin D Protects against Traumatic Brain Injury via Modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB Pathway-Mediated Microglial Polarization and Neuroinflammation[J]. Biomed Research International,2022,15(7):336-339. [12] Chen H,Zhong J,Li J,et al. PTP70-2,a novel polysaccharide from Polygala tenuifolia,prevents neuroinflammation and protects neurons by suppressing the TLR4-mediated MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,194(1):546-555. [13] Li B,Wang M,Chen S,et al. Baicalin Mitigates the Neuroinflammation through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in LPS-Stimulated BV-2 Microglia[J]. Biomed Research International,2022,10(1):326-344. [14] Qu H,Liu R,Chen J,et al. Aerobic Exercise Inhibits CUMS-Depressed Mice Hippocampal Inflammatory Response via Activating Hippocampal miR-223/TLR4/MyD88-NF-κB Pathway[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2020,17(8):2676. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17082676 [15] Cui Y,Wang Y,Zhao D,et al. Loganin prevents BV-2 microglia cells from Aβ(1-42) -induced inflammation via regulating TLR4/TRAF6/NF-κB axis[J]. Cell Biology International,2018,42(12):1632-1642. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11060 [16] Xie X L,Zhou W T,Zhang K K,et al. METH-Induced Neurotoxicity Is Alleviated by Lactulose Pretreatment Through Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in Rat Striatum[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience,2018,12(2):802-809. [17] Du S H,Qiao D F,Chen C X,et al. Toll-Like Receptor 4 Mediates Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation through Caspase-11 Signaling Pathway in Astrocytes[J]. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience,2017,10(1):409-421. [18] Hu Q P,Mao D A. Histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA attenuates post-seizure hippocampal microglia TLR4/MYD88 signaling and inhibits TLR4 gene expression via histone acetylation[J]. BMC Neuroscience,2016,17(1):22-45. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0264-9 [19] 贺春香,于文静,杨苗,等. 黄芩苷通过TREM2/TLR4/NF-κB信号通路抑制脂多糖/干扰素γ诱导的BV2细胞炎症反应[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,47(6):1603-1610. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20211103.401 [20] 房尚萍,李海源,丁磊,等. 通过调节NF-κB通路中的IκBα抑制乳腺癌的研究进展[J]. 锦州医科大学学报,2021,42(1):104-128. [21] Liu X,Zhang X,Wang F,et al. Improvement in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the TLR4/NF-κB pathway after Kudiezi injection in rats[J]. Life Sciences,2017,191(1):132-140. [22] Long H,Ruan J,Zhang M,et al. Rhynchophylline Attenuates Tourette Syndrome via BDNF/NF-κB Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro[J]. Neurotoxicity Research,2019,36(4):756-763. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00079-x 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘洋,李岱株,孙春意,卿清,杨莹莹,周红林. hTERC基因和C-MYC基因在宫颈病变筛查和诊断中的应用. 昆明医科大学学报. 2019(07): 36-40 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载:
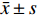
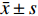
 下载:
下载:

