Propofol Modulates the miR-142-3p/RAC1/NF-κB Axis to Influence Knee Osteoarthritis in Rats
-
摘要:
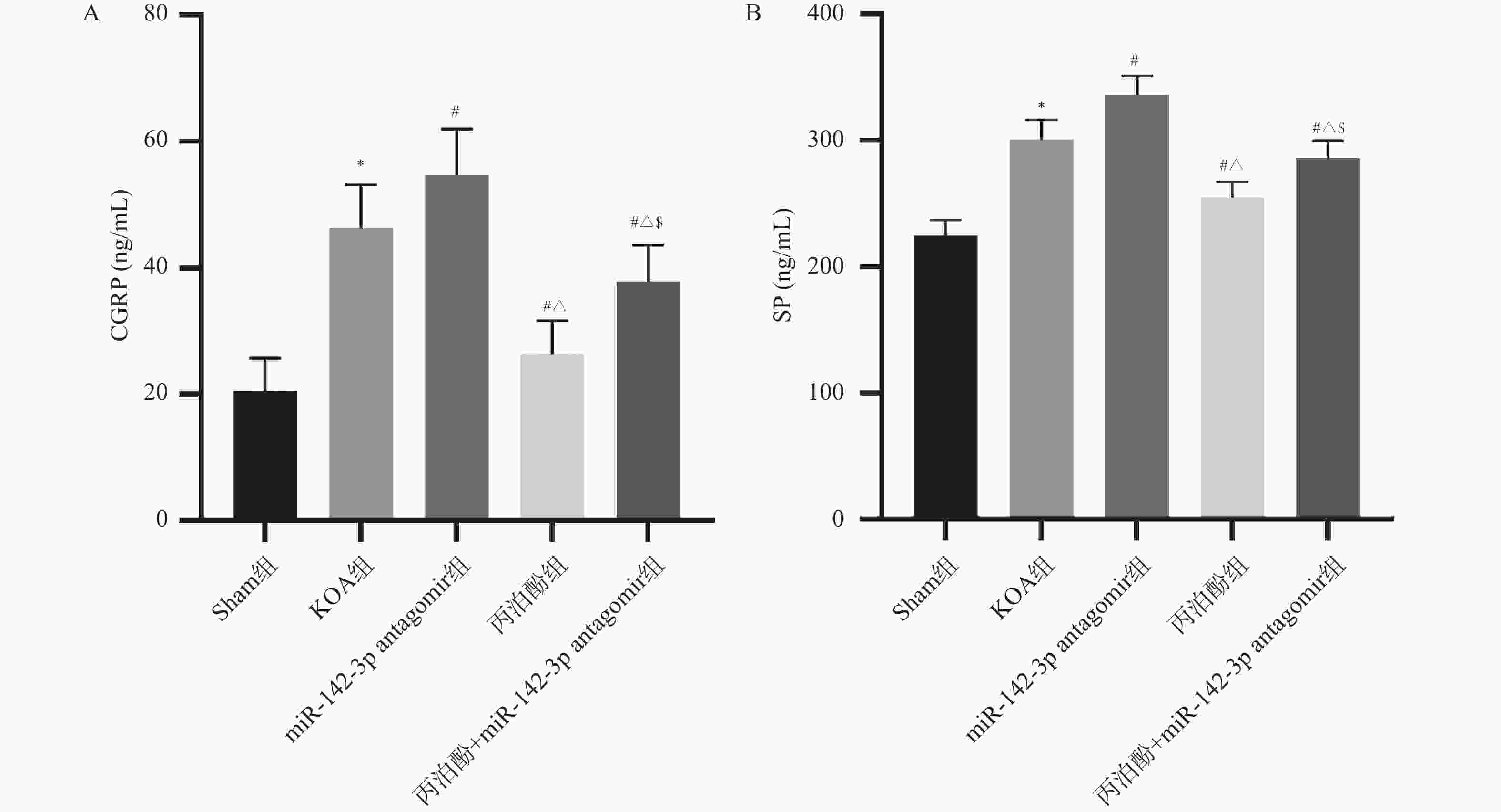
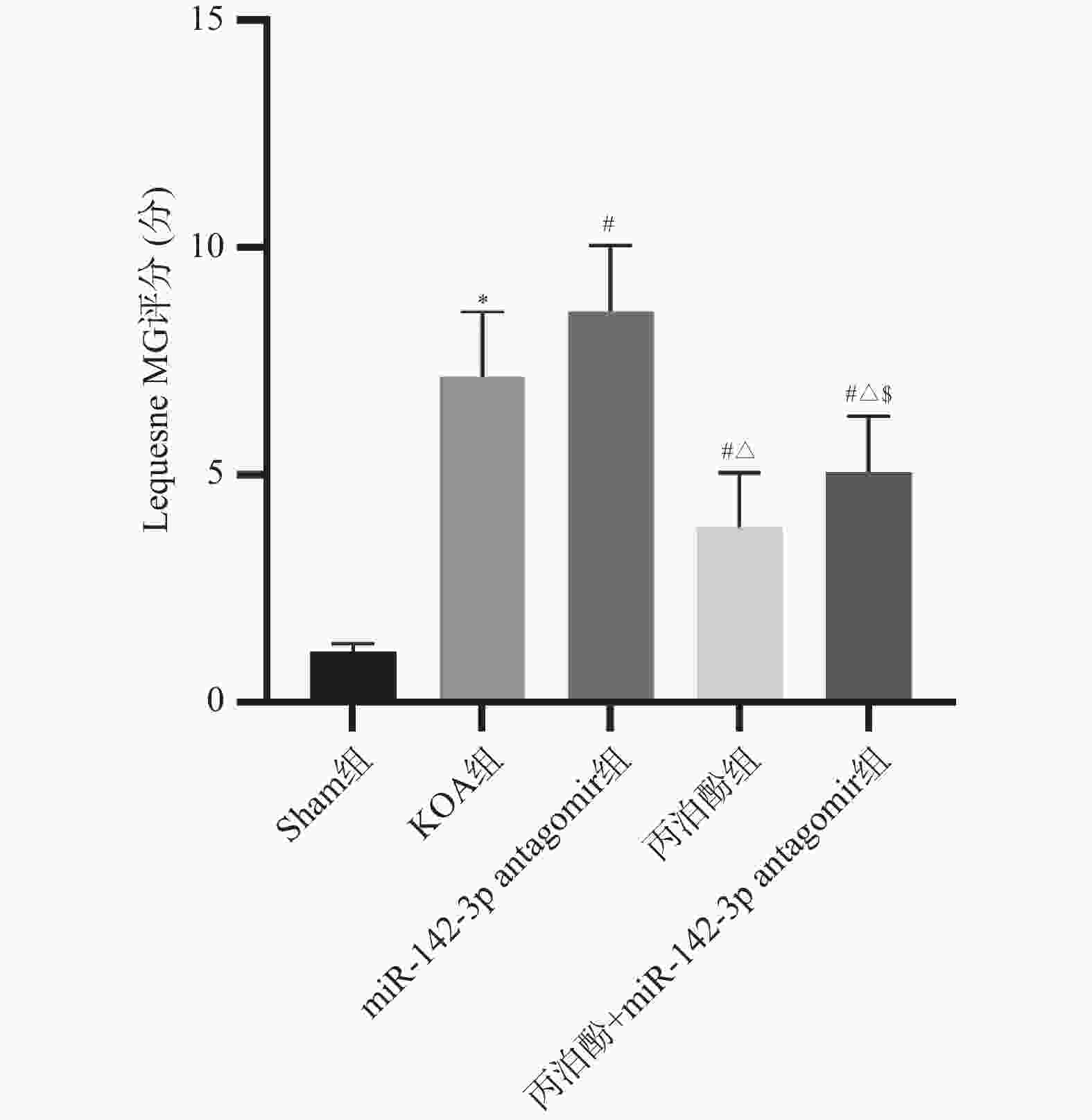
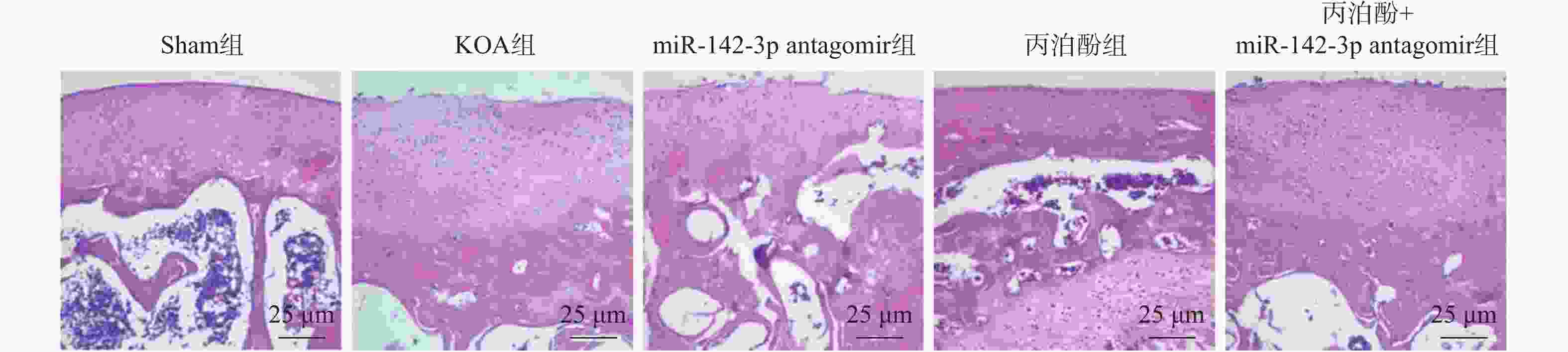
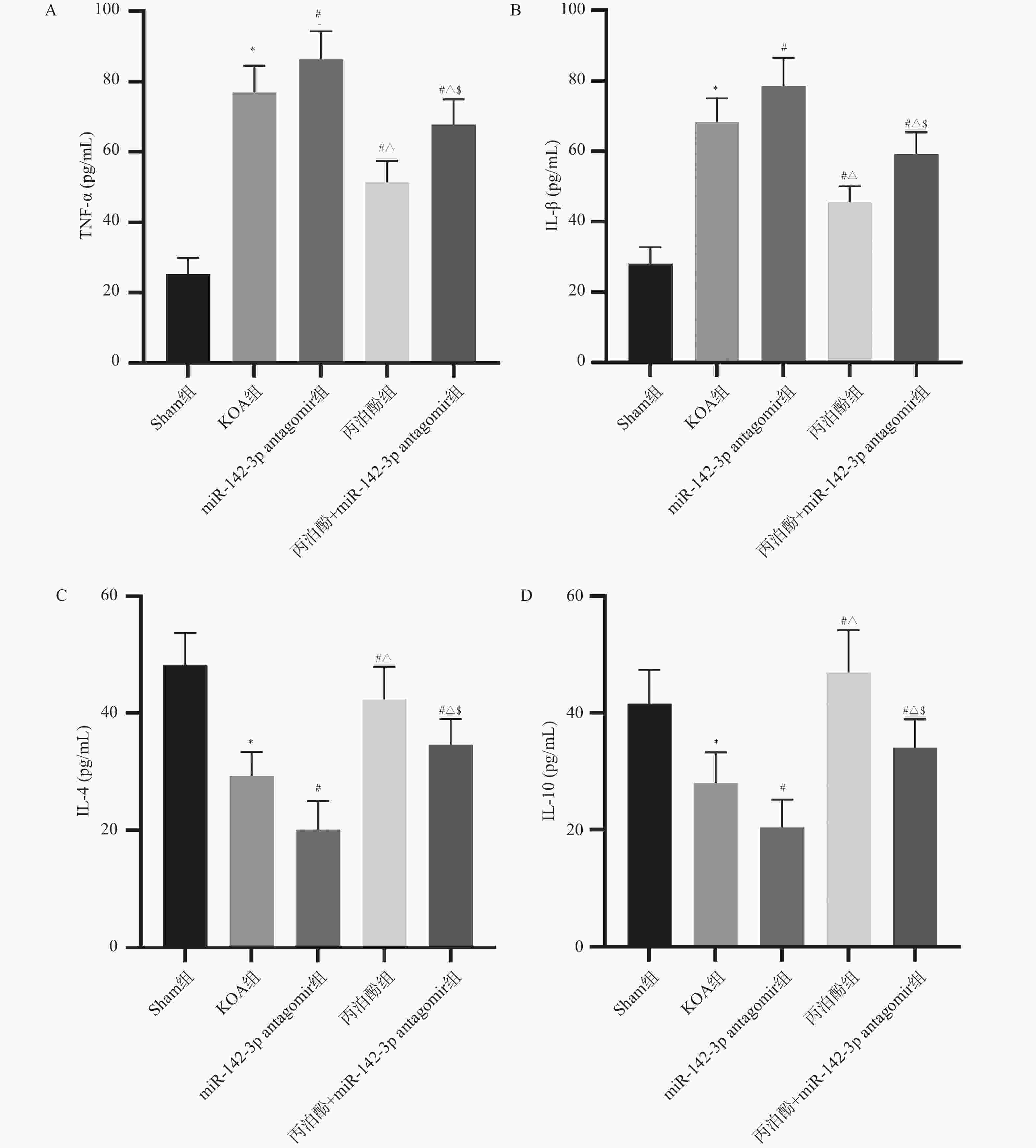
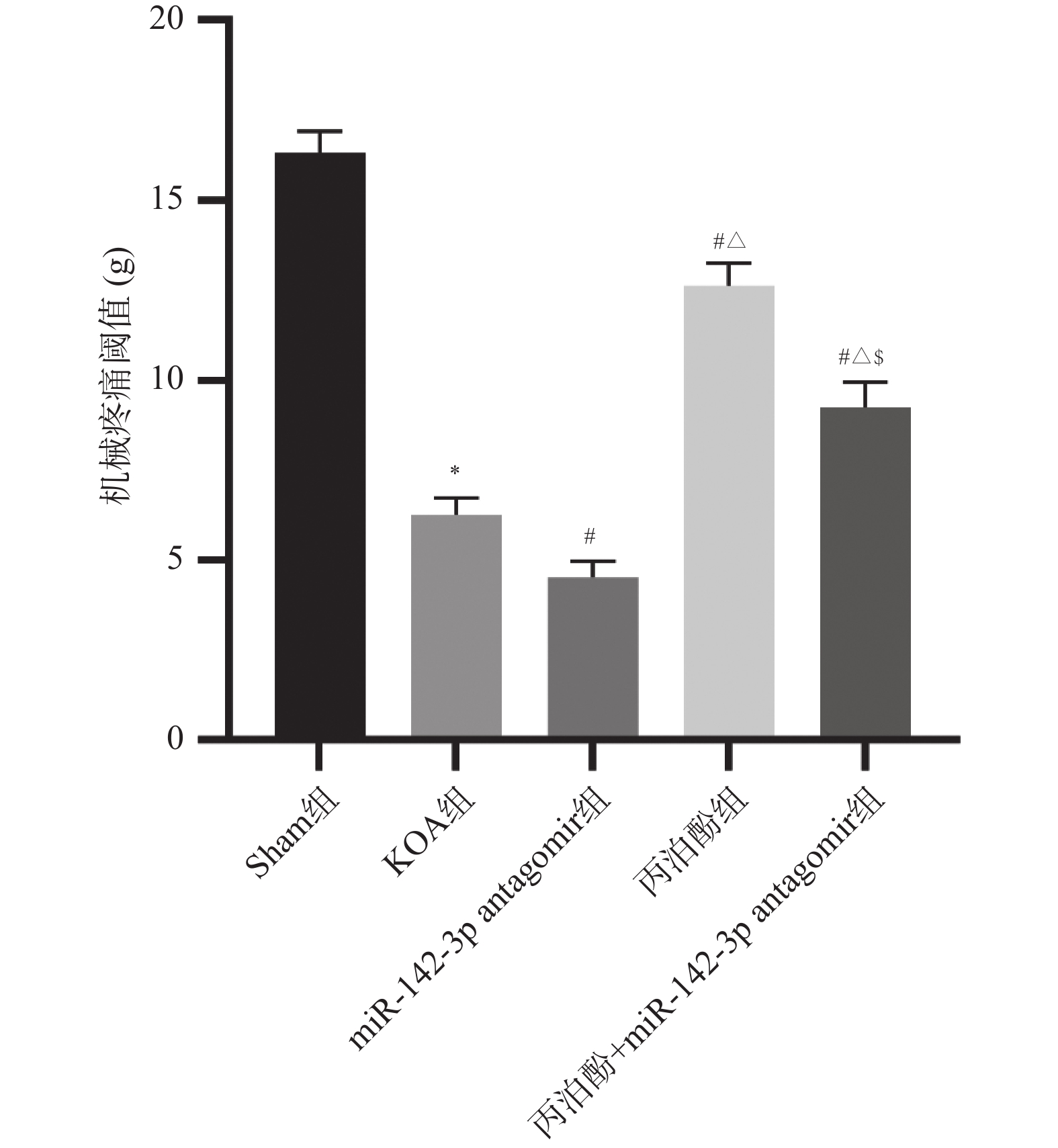
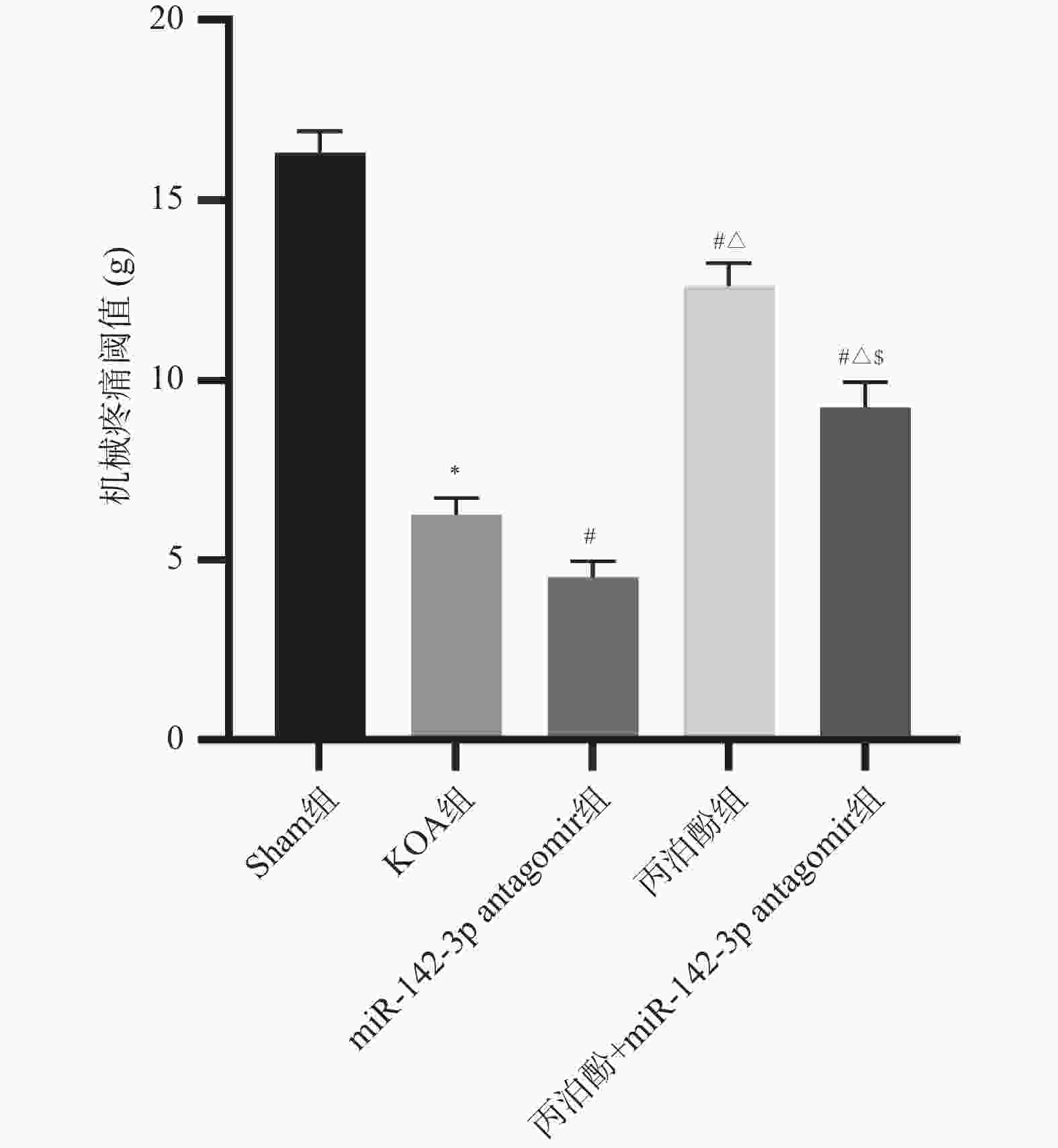
目的 探讨丙泊酚对膝骨关节炎(knee osteoarthritis,KOA)大鼠疼痛的改善作用及其对微小RNA-142-3p(miR-142-3p)/Ras相关C3肉毒素底物1(ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1,RAC1)/核因子-κB (nuclear factor-κB,NF-κB)轴的调控机制。 方法 采用手术离断前交叉韧带、内侧副韧带及内侧半月板的方法构建大鼠KOA模型,用miR-142-3p antagomir或丙泊酚干预。干预结束后,检测大鼠机械刺激缩足阈值;酶联免疫吸附法(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)检测大鼠血清中P物质(substance P,SP)、降钙素基因相关肽(calcitonin gene-related peptide,CGRP)和肿瘤坏死因子-α(tumour necrosis factor-α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素(interleukin,IL)-1β、IL-4、IL-10水平;改良Lequesne MG评分评估膝关节功能;免疫荧光检测脊髓组织中小胶质细胞活化标志物离子钙结合衔接分子1(ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1,IBA-1)表达;qRT-PCR测定脊髓组织中诱导型一氧化氮合酶(inducible nitric oxide synthase,iNOS)、精氨酸酶1(Arginase 1,Arg-1)、miR-142-3p相对表达水平;Western blot检测脊髓组织中RAC1、p-NF-κB p65和NF-κB p65蛋白表达水平。 结果 与KOA组相比,miR-142-3p antagomir组大鼠机械疼痛阈值降低(P < 0.05),Lequesne MG评分及血清SP、CGRP、TNF-α、IL-1β水平增加(P < 0.05),血清IL-4、IL-10水平和脊髓组织Arg-1、miR-142-3p表达水平降低(P < 0.05),脊髓组织IBA-1荧光强度、iNOS mRNA表达及RAC1、p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达增加(P < 0.05);丙泊酚组大鼠机械疼痛阈值增加(P < 0.05),Lequesne MG评分及血清SP、CGRP、TNF-α、IL-1β表达降低(P < 0.05),血清IL-4、IL-10水平和脊髓组织Arg-1、miR-142-3p表达增加(P < 0.05),脊髓组织IBA-1荧光强度、iNOS mRNA表达及RAC1、p-NF-κB p65蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05)。与miR-142-3p antagomir组相比,丙泊酚组和丙泊酚+miR-142-3p antagomir组大鼠的结果有明显改善(P < 0.05);miR-142-3p antagomir则部分逆转了丙泊酚对KOA大鼠的改善作用(P < 0.05)。 结论 丙泊酚可能通过调控miR-142-3p/RAC1/NF-κB轴,抑制小胶质细胞M1极化、促进M2型极化来纠正炎症因子失衡,从而缓解KOA大鼠疼痛症状。 -
关键词:
- 丙泊酚 /
- 微小RNA-142-3p /
- RAC1/NF-κB通路 /
- 膝骨关节炎 /
- 小胶质细胞极化
Abstract:Objective To explore the effect of propofol on pain relief in rats with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) and its regulatory mechanism on the microRNA-142-3p (miR-142-3p)/Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (RAC1)/nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) axis. Methods A rat knee osteoarthritis model was established by surgically transecting the anterior cruciate ligament, medial collateral ligament, and medial meniscus, with intervention by miR-142-3p antagomir or propofol. Following the conclusion of the intervention, the mechanical pain withdrawal threshold in rats was assessed. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) was employed to detect levels of substance P (SP), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-4 and IL-10 levels in rat serum. Modified Lequesne MG score for assessing knee joint function. Immunofluorescence detection of ionized calcium-binding adaptor molecule 1 (IBA-1) , an activational marker of microglia, in spinal cord tissue. Quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was employed to determine the relative expression levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), arginase 1 (Arg-1), and miR-142-3p in spinal cord tissue. Western blot analysis of RAC1, p-NF-κB p65 and NF-κB p65 protein expression levels in spinal cord tissue. Results Compared with the KOA group, rats in the miR-142-3p antagomir group exhibited a reduced mechanical pain threshold (P < 0.05), increased Lequesne MG scores and serum levels of SP, CGRP, TNF-α, and IL-1β (P < 0.05), serum IL-4 and IL-10 levels, and spinal cord tissue Arg-1 and miR-142-3p expression levels decreased (P < 0.05). Spinal cord tissue IBA-1 fluorescence intensity, iNOS mRNA expression levels, and RAC1 and p-NF-κB p65 protein expression levels increased (P < 0.05). The propofol group exhibited increased mechanical pain thresholds in rats (P < 0.05), reduced Lequesne MG scores and serum levels of SP, CGRP, TNF-α, and IL-1β (P < 0.05), serum IL-4 and IL-10 levels, and spinal cord tissue Arg-1 and miR-142-3p expression levels increased (P < 0.05). Spinal cord tissue IBA-1 fluorescence intensity, iNOS mRNA expression levels, and RAC1 and p-NF-κB p65 protein expression levels decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the miR-142-3p antagomir group, the propofol group and the propofol+miR-142-3p antagomir group demonstrated significant improvement in the aforementioned indicators in rats (P < 0.05). The miR-142-3p antagomir partially reversed the ameliorative effects of propofol in KOA rats (P < 0.05). Conclusion Propofol may inhibit the M1 polarization of microglia, promote the M2 polarization, exert anti-inflammatory effect and inhibit the pain response of KOA rats by regulating the miR-142-3p/RAC1/NF-κB axis. -
Key words:
- Propofol /
- MicroRNA-142-3p /
- RAC1/NF-κB pathway /
- Knee osteoarthritis /
- Microglial polarization
-
图 5 各组大鼠血清中炎症因子水平($\bar x \pm s $,n = 15)
A:各组大鼠血清中TNF-α水平;B:各组大鼠血清中IL-1β水平;C:各组大鼠血清中IL-4水平;D:各组大鼠血清中IL-10水平。与Sham组相比,*P < 0.05;与KOA组相比,#P < 0.05;与miR-142-3p antagomir组相比,△P < 0.05;与丙泊酚组相比,$P < 0.05。
Figure 5. Levels of inflammatory cytokines in the serum of rats from each group ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 15)
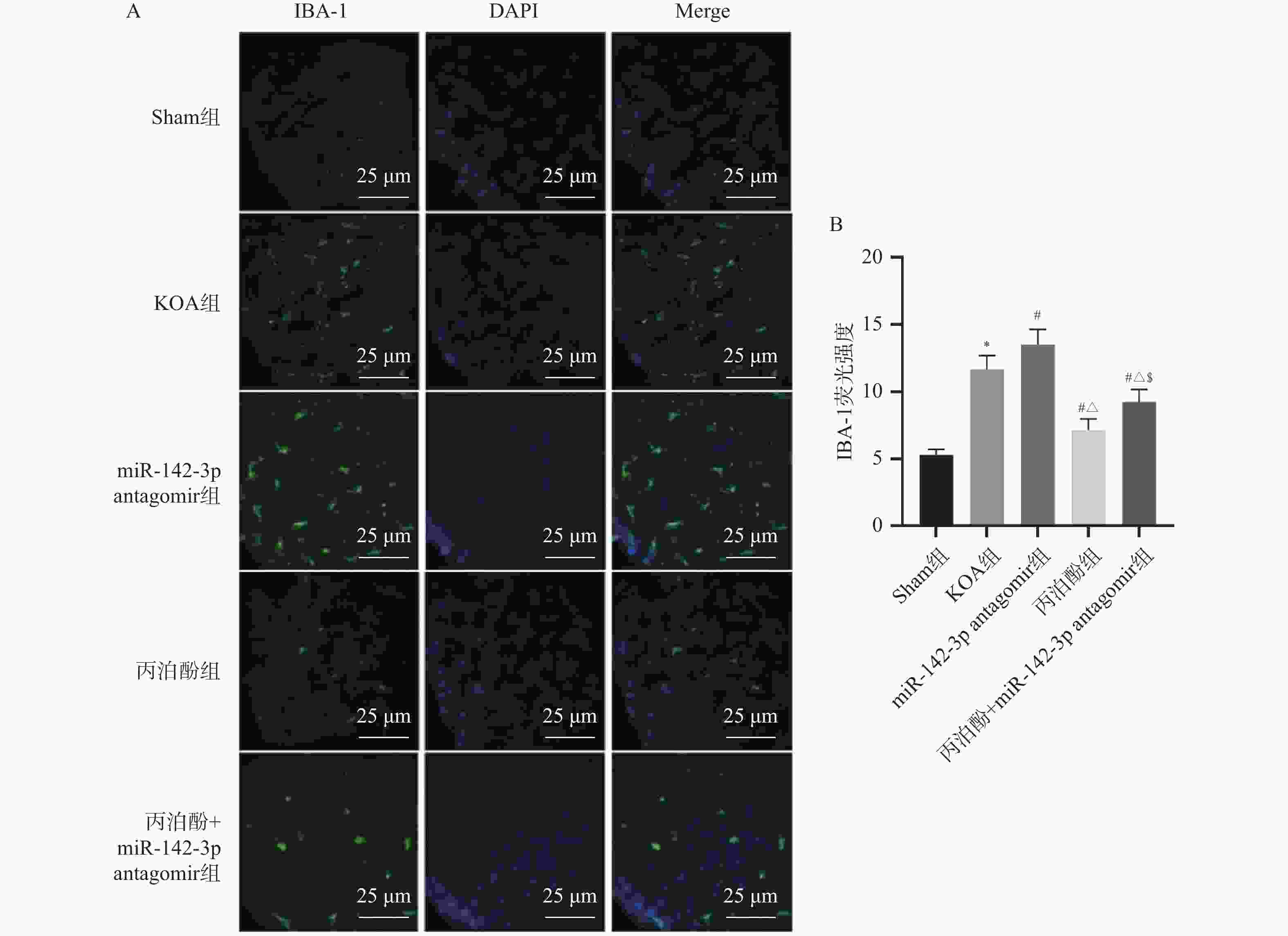
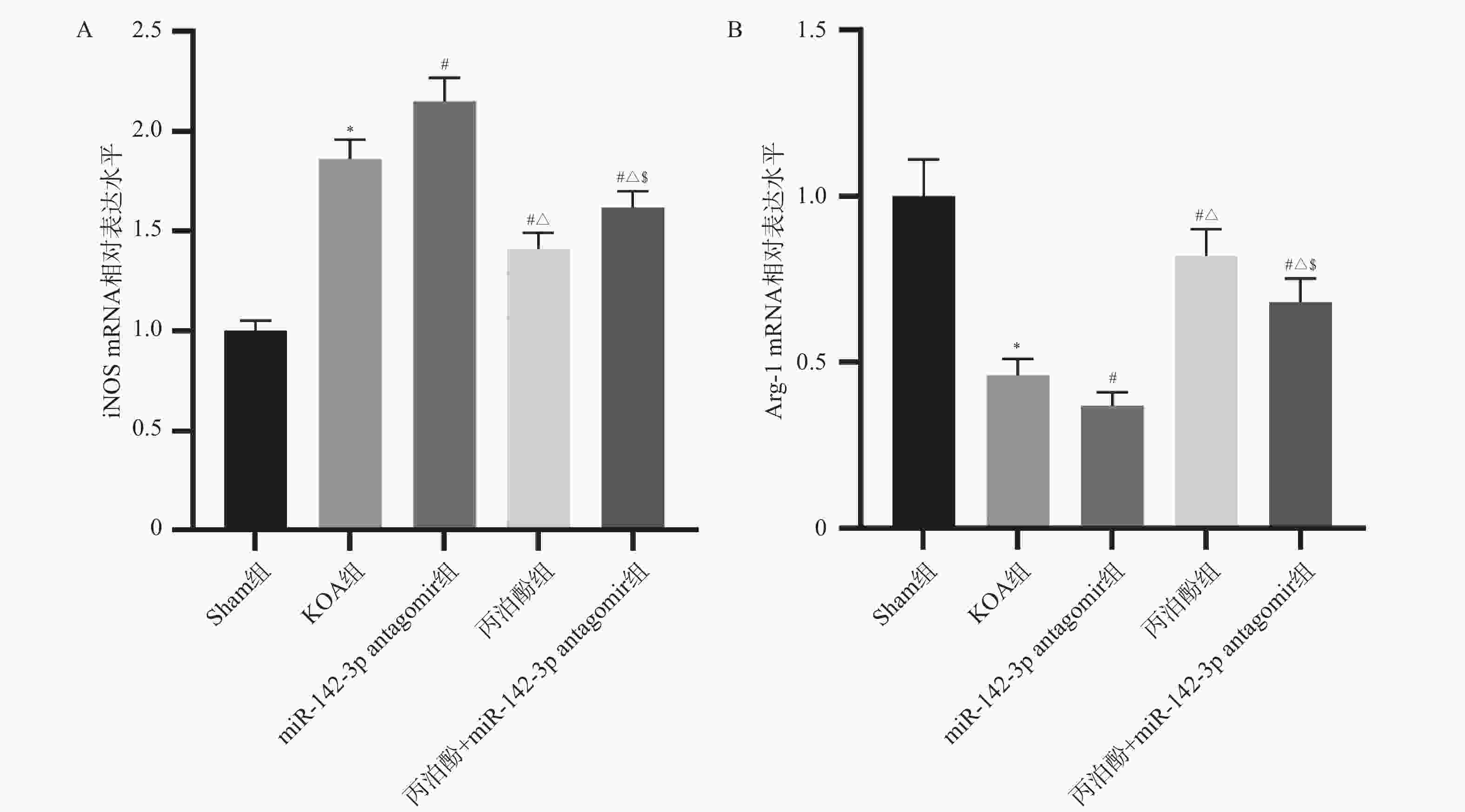
图 7 各组大鼠脊髓组织小胶质细胞极化标志物水平($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
A:各组大鼠脊髓组织iNOS mRNA水平;B:各组大鼠脊髓组织Arg-1 mRNA水平。与Sham组相比,*P < 0.05;与KOA组相比,#P < 0.05;与miR-142-3p antagomir组相比,△P < 0.05;与丙泊酚组相比,$P < 0.05。
Figure 7. Levels of glial cell polarisation markers in spinal cord tissue from rats in each group ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
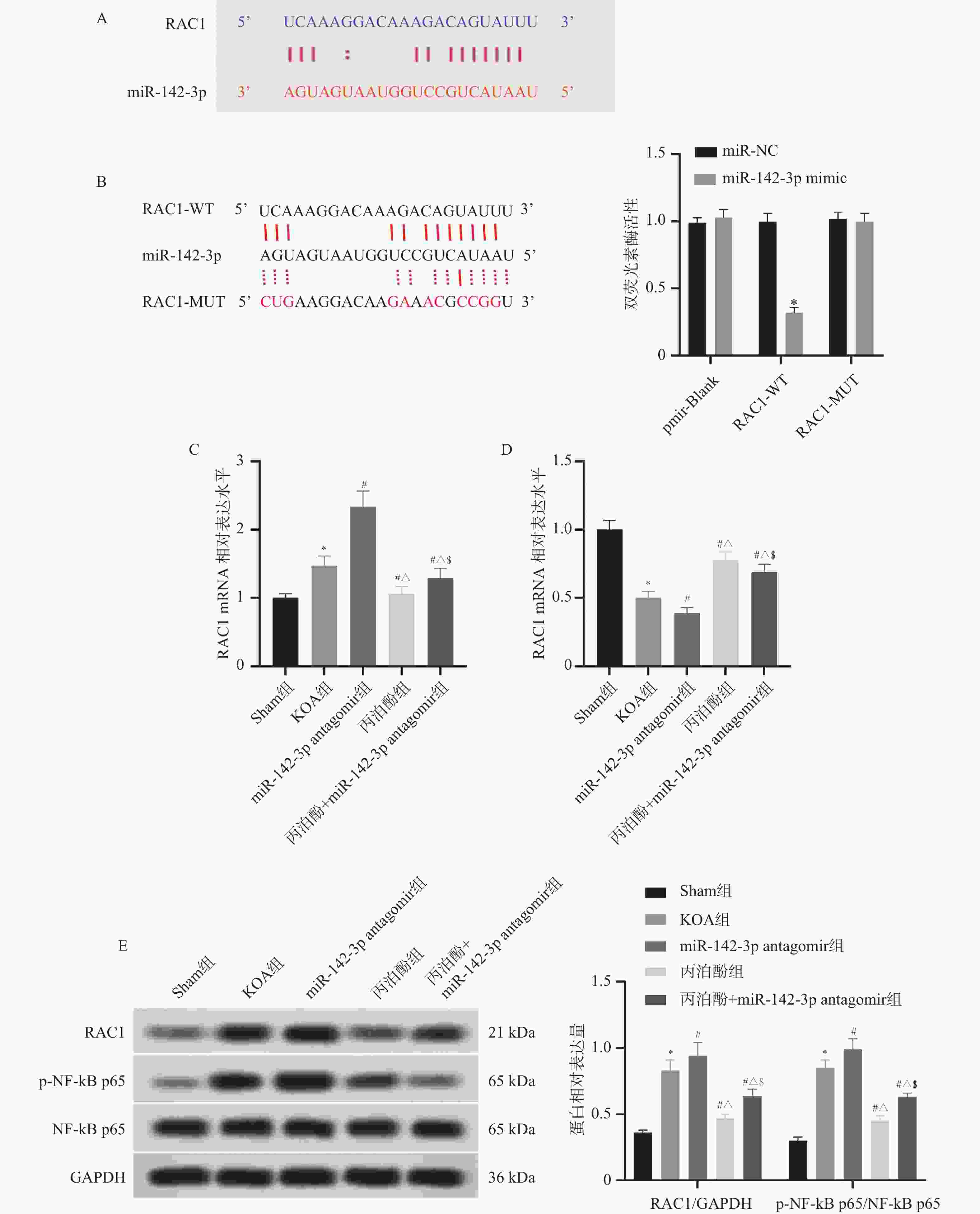
图 8 各组大鼠脊髓组织miR-142-3p、RAC1和p-NF-κB p65的表达($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
A:miR-142-3p和RAC1的结合位点预测;B:双荧光素酶报告基因测定miR-142-3p与RAC1的靶向关系;C:各组大鼠脊髓组织miR-142-3p相对表达水平;D:各组大鼠脊髓组织RAC1 mRNA相对表达水平;E:各组大鼠脊髓组织RAC1、p-NF-κB p65、NF-κB p65蛋白表达。与miR-NC相比,▲P < 0.05;与Sham组相比,*P < 0.05;与KOA组相比,#P < 0.05;与miR-142-3p antagomir组相比,△P < 0.05;与丙泊酚组相比,$P < 0.05。
Figure 8. Expression of miR-142-3p,RAC1 and p-NF-κB p65 in spinal cord tissue from each group of rats ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 10)
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences
基因 引物序列(5'-3') 引物长度(bp) miR-142-3p F:TGCTGCTGTGTAGTGTTTCCTACT 83 R:TATGGTTGTTCACGACTCCTTCAC U6 F:CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA 171 R:GCGAGCACAGAATTAATACGAC iNOS F:CGGAGAACAGCAGAGTTGG 122 R:GGAATAGCACCTGGGGTTT Arg-1 F:CAGTATTCACCCCGGCTA 198 R:CCTCTGGTGTCTTCCCAA GAPDH F:GTTACCAGGGCTGCCTTCTC 134 R:GGGTTTCCCGTTGATGACC -
[1] Amodeo G, Franchi S, Galimberti G, et al. Osteoarthritis pain in old mice aggravates neuroinflammation and frailty: The positive effect of morphine treatment[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(11): 2847. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112847 [2] Liu R, Zhu T, Chu X, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation alleviates chronic pain in knee osteoarthritis by modulating microglial and astrocytic polarization and neuroinflammation[J]. Life Sci, 2025, 376: 123753. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123753 [3] Chen Y, Dong S, Zeng X, et al. EZH2/miR-142-3p/HMGB1 axis mediates chondrocyte pyroptosis by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in knee osteoarthritis[J]. Chin Med J, 2025, 138(1): 79-92. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003186 [4] Li X, Wang S, Yang X, et al. miR-142-3p targets AC9 to regulate sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain by regulating the cAMP/AMPK signalling pathway[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 47(2): 561-572. [5] Glémain A, Néel M, Néel A, et al. Neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles induce endothelial inflammation and damage through the transfer of miRNAs[J]. J Autoimmun, 2022, 129: 102826. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102826 [6] Yin Y, Yan Y, Jin X, et al. Netrin-1 promotes M2 type activation and inhibits pyroptosis of microglial cells by depressing RAC1/nf-κB pathway to alleviate inflammatory pain[J]. Physiol Res, 2024, 73(2): 305-314. [7] Liu J, Ai P, Sun Y, et al. Propofol inhibits microglial activation via miR-106b/Pi3k/Akt axis[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2021, 15: 768364. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.768364 [8] 孙鼐, 宋琼, 张伟, 等. 丙泊酚对类风湿性关节炎大鼠炎症反应及滑膜细胞凋亡影响[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2020, 36(4): 574-577. doi: 10.11847/zgggws1121449 [9] 王歌, 潘富伟, 宋永达, 等. 温针灸改善膝骨关节炎大鼠症状和关节病理损伤的机制研究[J]. 海南医学, 2025, 36(12): 1673-1678. [10] 李帆, 祖丽娅提·阿热甫江, 陈红. 丙泊酚通过JAK激酶-信号转导及转录活化因子信号通路抑制类风湿关节炎大鼠炎症反应及滑膜细胞凋亡[J]. 安徽医药, 2022, 26(6): 1079-1083. [11] 郭文帆, 杨学钰, 郑雪君, 等. 茶黄素调节AMPK/SIRT1/NF-κB信号通路对膝骨关节炎大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 河北医学, 2023, 29(1): 42-49. [12] 王丽丽, 徐腾腾, 王潇潇, 等. 基于“病-证-症”结合研究策略探索膝骨关节炎大鼠湿热痹阻证的表征和特点[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2025, 50(7): 1861-1871. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20241212.701 [13] Codazza S, Ferrara PE, Gueli G, et al. The management of knee osteoarthritis in elderly: Results from a national survey compared to ESCEO guidelines[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 26(1): 24-32. [14] 潘炳, 周颖芳, 方芳, 等. 骨性关节炎的国内外研究现状及治疗进展[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2021, 27(5): 861-865. [15] 何宁, 唐晓巍, 朱玉, 等. 白杨素调控SDF-1/CXCR4轴对滑膜炎模型大鼠症状的改善作用[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2025, 45(14): 3531-3535. [16] Kuroo A, Murata K, Morishita Y, et al. Controlling joint instability reduces inflammatory pain in early knee osteoarthritis[J]. Cureus, 2025, 17(7): e87711. [17] Labastida-Ramírez A, Caronna E, Gollion C, et al. Mode and site of action of therapies targeting CGRP signaling[J]. J Headache Pain, 2023, 24(1): 125. [18] Zhang C, Yu M, Zhang L, et al. Exploring the analgesic effect of acupuncture on knee osteoarthritis based on MLT/cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2025, 18: 237-249. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S498202 [19] Chen G L, Sun K, Liu X Z, et al. Inhibiting tau protein improves the recovery of spinal cord injury in rats by alleviating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress[J]. Neural Regen Res, 2023, 18(8): 1834-1840. [20] 张畅, 万衍, 汪威廉. 丙泊酚通过调控p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路减轻大鼠术后疼痛的机制研究[J]. 实用临床医药杂志, 2025, 29(1): 18-22. doi: 10.7619/jcmp.20243770 [21] Ikuma Y, Sakai A, Sakamoto A, et al. Increased extracellular release of micro-RNAs from dorsal root ganglion cells in a rat model of neuropathic pain caused by peripheral nerve injury[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(1): e0280425. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280425 [22] 魏萌, 张英民, 康少英, 等. miR-142-3p靶向PERK/Bip信号通路对骨关节炎模型大鼠的干预作用[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2022, 31(5): 379-383. [23] Roblain Q, Louis T, Yip C, et al. Intravitreal injection of anti-miRs against miR-142-3p reduces angiogenesis and microglia activation in a mouse model of laser-induced choroidal neovascularization[J]. Aging, 2021, 13(9): 12359-12377. doi: 10.18632/aging.203035 [24] Xiang H, Yang J, Li J, et al. Citrate pretreatment attenuates hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cardiomyocyte injury via regulating microRNA-142-3p/Rac1 Aix[J]. J Recept Signal Transduct, 2020, 40(6): 560-569. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2020.1768548 [25] Hou W, Ye C, Chen M, et al. Excavating bioactivities of nanozyme to remodel microenvironment for protecting chondrocytes and delaying osteoarthritis[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6(8): 2439-2451. [26] Wang L, Xu P, Xu Y, et al. A discovery of clinically approved panlongqi tablet for repositioning to treat osteoarthritis by inhibiting PI3K/AKT activation[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 105: 154360. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154360 [27] Sun X, Li X, Zhou Y, et al. Up-regulating TIPE2 alleviates inflammatory pain by suppressing microglial activation-mediated inflammatory response via inhibiting Rac1/NF-κB pathway[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2021, 404(1): 112631. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2021.112631 -





 下载:
下载: