Changes in Ang-2 Levels Before and after Microwave Ablation Treatment in High-Risk Pulmonary Nodule Patients and Its Impact on Postoperative Recurrence
-
摘要:
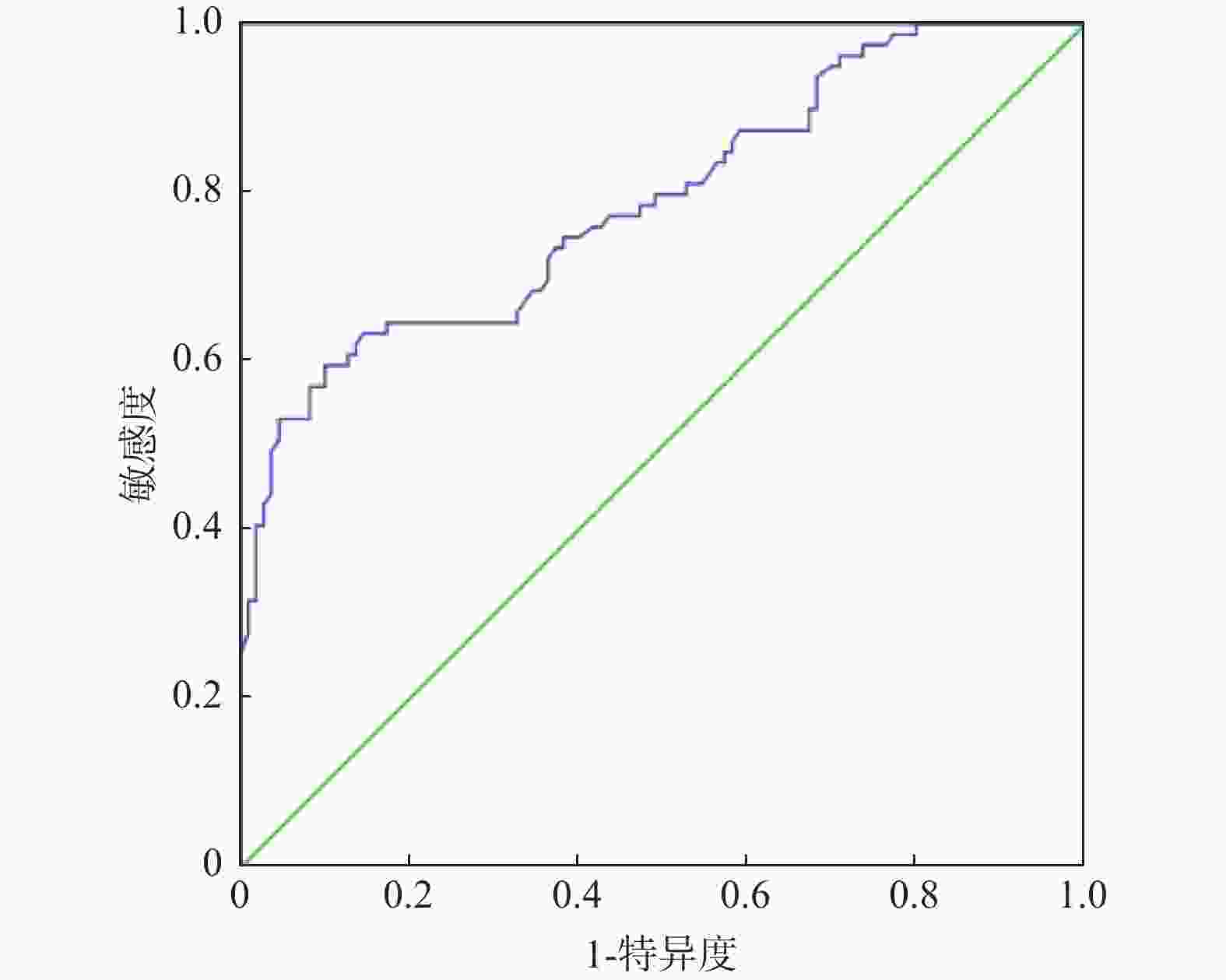
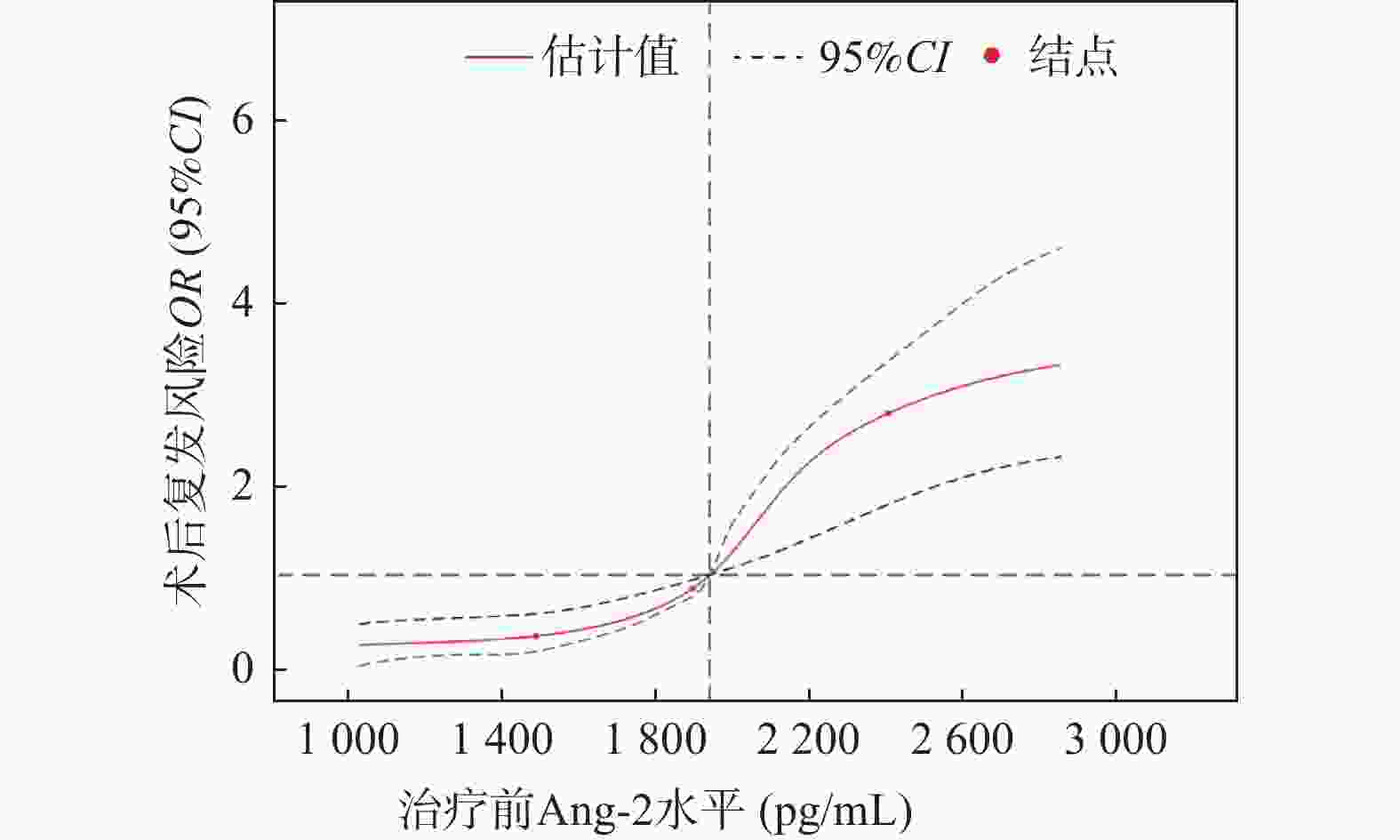
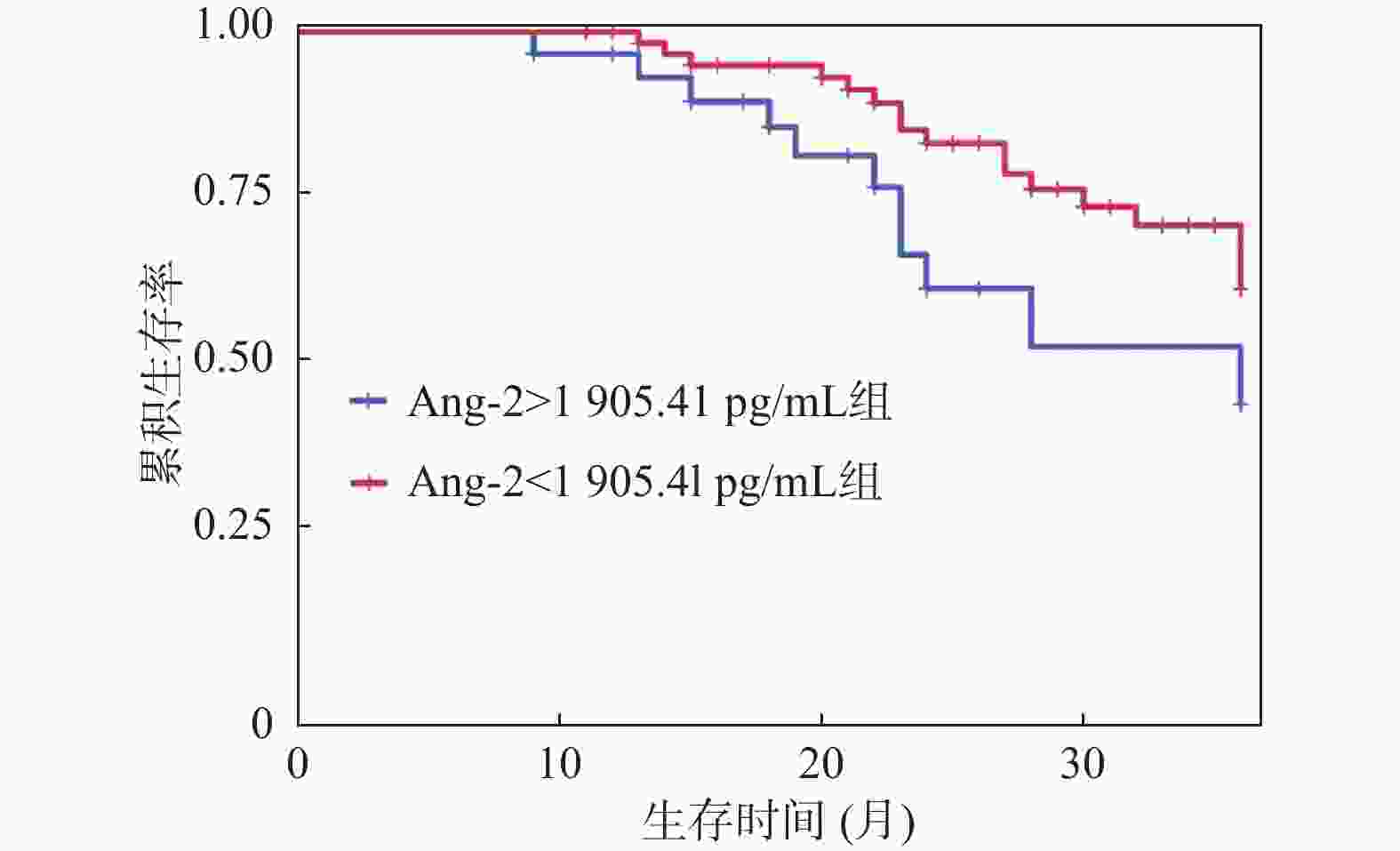
目的 分析高危肺结节微波消融(microwave ablation,MWA)术前后血管生成素-2(angiopoietin-2,Ang-2)水平变化及其对术后复发的影响。 方法 纳入2019年12月至2021年12月贵州航天医院94例高危肺结节患者,分为复发组(n = 30)和未复发组(n = 64)。比较两组患者临床资料。通过Pearson相关性分析治疗前Ang-2水平与CT参数的关联。通过Logistic回归模型、限制性立方样条及阈值效应、受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线分析治疗前Ang-2水平与术后复发的关系。采用Kaplan-Meier生存曲线分析不同水平Ang-2患者总生存期差异。利用COX回归模型分析影响患者生存期的因素。 结果 与同组治疗前相比两组Ang-2水平均明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Pearson相关性分析显示,治疗前Ang-2与BF、BV、PS、MTT均呈正相关。Ang-2水平与术后复发存在独立相关性。ROC结果显示,治疗前Ang-2对术后复发具有一定的预测价值(曲线下面积为0.789)。限制性立方样条分析显示,治疗前Ang-2与术后复发呈非线性剂量-反应关系(P < 0.05)。阈值效应分析显示,Ang-2影响复发的拐点为 1905.41 pg/mL。生存分析显示,Ang-2<1905.41 pg/mL组患者中位总生存期长于Ang-2≥1905.41 pg/mL组(P = 0.039)。且Ang-2≥1905.41 pg/mL是影响患者生存期的独立因素。结论 高危肺结节患者微波消融术治疗后Ang-2水平明显降低,治疗前Ang-2对术后复发具有一定预测价值。 Abstract:Objective To analyze the changes in angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) levels before and after microwave ablation (MWA) in patients with high-risk pulmonary nodule and its impact on postoperative recurrence. Method A total of 94 patients with high-risk pulmonary nodules admitted to Guizhou Aerospace Hospital from December 2019 to December 2021 were included and categorized into a recurrence group (n = 30) and a non-recurrence group (n = 64). Clinical data was compared between the two groups. Pearson correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between pre-treatment angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) levels and CT parameters. Logistic regression model, restricted cubic splines, threshold effect analysis, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve were used to analyze the relationship between pre-treatment Ang-2 levels and postoperative recurrence. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were used to analyze the differences in overall survival among patients with different Ang-2 levels. Cox regression model was used to analyze the factors affecting patients' survival. Result Compared to pre-treatment levels within the same group, Ang-2 levels in both groups decreased significantly, with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation analysis showed that pre-treatment Ang-2 levels were positively correlated with BF, BV, PS, and MTT. Ang-2 level was independently associated with postoperative recurrence. Results of ROC analysis indicated that pre-treatment Ang-2 had certain predictive value for postoperative recurrence (area under the curve=0.789). Restricted cubic spline analysis revealed a nonlinear dose-response relationship between pre-treatment Ang-2 and postoperative recurrence (P < 0.05). Threshold effect analysis identified that the inflection point of Ang-2 affecting recurrence as 1905.41 pg/mL. Survival analysis demonstrated that the median overall survival of patients in the Ang-2<1905.41 pg/mL group was longer than that in the Ang-2≥1905.41 pg/mL group (P = 0.039). Furthermore, Ang-2≥1905.41 pg/mL was an independent factor affecting patients' survival time.Conclusion The levels of Ang-2 decreased significantly in patients with high-risk pulmonary nodules after MWA, and pre-treatment Ang-2 level has certain predictive value for postoperative recurrence. -
表 1 两组患者一般资料对比[n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups [n(%)]
指标 复发组(n=30) 未复发组(n=64) χ2 P 年龄(岁) 2.396 0.122 <60 9(30.00) 30(46.88) ≥60 21(70.00) 34(53.12) 性别 1.691 0.193 男 14(46.67) 39(60.94) 女 16(53.33) 25(39.06) 吸烟 4.896 0.027* 是 20(66.67) 27(42.19) 否 10(33.33) 37(57.81) 饮酒 1.358 0.244 是 11(36.67) 16(25.00) 否 19(63.33) 48(75.00) 进行体育锻炼 5.591 0.018* 是 3(10.00) 21(32.81) 否 27(90.00) 43(67.19) 合并COPD 4.818 0.028* 是 8(26.67) 6(9.38) 否 22(73.33) 58(90.62) 合并肺纤维化 - 0.059 是 3(10.00) 1(1.56) 否 27(90.00) 63(98.44) 肺结核史 - 0.018* 是 4(13.33) 1(1.56) 否 26(86.67) 63(98.44) 高血压 3.650 0.056 是 15(50.00) 19(29.69) 否 15(50.00) 45(70.31) 糖尿病 1.490 0.222 是 9(30.00) 12(18.75) 否 21(70.00) 52(81.25) 结节位置 2.118 0.146 左肺 17(56.67) 26(40.62) 右肺 13(43.33) 38(59.38) 结节直径(mm) 1.608 0.205 ≤10 22(73.33) 54(84.38) >10 8(26.67) 10(15.62) 结节密度 1.408 0.235 实性结节 24(80.00) 57(89.06) 亚实性结节 6(20.00) 7(10.94) 分叶征 - 0.957 是 1(3.33) 2(3.13) 否 29(96.67) 62(96.87) 毛刺征 - 0.428 是 2(6.67) 2(3.13) 否 28(93.33) 62(96.87) 空泡征 - 0.491 是 0(0.00) 1(1.56) 否 30(100.00) 63(98.44) 胸膜凹陷征 - 0.166 是 3(10.00) 2(3.13) 否 27(90.00) 62(96.87) -:为Fisher精确概率;*P < 0.05。 表 2 两组患者的CT参数对比($\bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of CT parameters between the two groups ($\bar x \pm s $)
CT参数 复发组(n=30) 未复发组(n=64) t P BF[mL/(min·100 g)] 81.14 ± 21.92 53.43 ± 15.36 7.078 <0.001* BV(mL/100 g) 9.94 ± 3.69 5.21 ± 1.75 8.457 <0.001* PS[mL/(min·100 g)] 36.41 ± 15.15 22.49 ± 12.83 4.624 <0.001* MTT(s) 20.93 ± 7.73 11.05 ± 2.36 9.328 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 两组患者治疗前后的血液指标对比(pg/mL,$\bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of blood indices in the two groups before and after treatment (pg/mL,$\bar x \pm s $)
血液指标 复发组(n=30) 未复发组(n=64) t P Ang-2 治疗前 1936.50 ± 347.151474.31 ± 335.926.153 <0.001* 治疗后 894.73 ± 201.36a 566.29 ± 161.17a 8.490 <0.001* VEGF 治疗前 672.67 ± 32.41 570.36 ± 31.86 14.434 <0.001* 治疗后 451.49 ± 40.96a 343.81 ± 35.74a 12.990 <0.001* *P < 0.05;与同组治疗前相比,aP < 0.05。 表 4 治疗前Ang-2与CT参数的相关性
Table 4. Correlation between pre-treatment Ang-2 levels and CT parameters
变量 r P BF 0.812 0.001* BV 0.539 0.036* PS 0.657 0.017* MTT 0.648 0.020* *P < 0.05。 表 5 治疗前Ang-2水平与术后复发的独立相关性
Table 5. Independent correlation between pre-treatment Ang-2 level and postoperative recurrence
变量 模型1 模型2 模型3 Ang-2 1.136(0.789~1.529) 1.271(0.895~1.573) 1.302(1.014~1.628) Ang-2二分类 低Ang-2(≤ 1715.26 pg/mL)1 1 1 高Ang-2(> 1715.26 pg/mL)1.370(0.961~2.545) 1.395(1.054~1.986) 1.584(1.248~1.883) Ang-2五分位数组 Q1(≤ 1402.31 pg/mL)1 1 1 Q2( 1402.32 ~1589.77 pg/mL)1.329(0.876~2.005) 1.368(1.102~3.210) 1.405(1.069~2.458) Q3( 1589.78 ~1702.39 pg/mL)1.425(1.160~2.334) 1.488(1.182~2.539) 1.582(1.255~3.291) Q4( 1702.40 ~1958.54 pg/mL)1.536(1.285~3.002) 1.601(1.257~3.206) 1.628(1.134~2.259) Q5(≥ 1958.55 pg/mL)1.596(1.274~2.059) 1.638(1.280~2.604) 1.695(1.125~2.541) P趋势 0.002* 0.011* <0.001* 注:模型1:未校正混杂因素;模型2:吸烟、进行体育锻炼、合并COPD;模型3:在模型2的基础上调整BF、BV、PS;*P < 0.05。 表 6 治疗前Ang-2水平与术后复发的亚组分析
Table 6. Subgroup analysis of the relationship between pre-treatment Ang-2 levels and postoperative recurrence
指标 Ang-2五分位数组 P趋势 P交互 Q1(n=12) Q2(n=21) Q3(n=31) Q4(n=17) Q5(n=13) 吸烟 0.109 是 1 0.506(0.401~0.612) 0.524(0.411~0.637) 0.530(0.422~0.643) 0.553(0.439~0.630) 0.004* 否 1 0.410(0.302~0.516) 0.421(0.320~0.515) 0.436(0.319~0.528) 0.450(0.346~0.564) 0.026* 进行体育锻炼 0.174 是 1 0.506(0.433~0.621) 0.531(0.446~0.706) 0.625(0.512~0.734) 0.662(0.514~0.735) 0.003* 否 1 0.671(0.532~0.759) 0.698(0.576~0.805) 0.711(0.602~0.834) 0.733(0.635~0.826) 0.021* 合并COPD 0.126 是 1 0.611(0.518~0.712) 0.657(0.546~0.743) 0.702(0.622~0.862) 0.739(0.689~0.801) 0.001* 否 1 0.613(0.507~0.720) 0.628(0.509~0.713) 0.634(0.608~0.721) 0.656(0.562~0.762) 0.007* 肺结核史 0.089 是 1 0.514(0.401~0.618) 0.527(0.406~0.682) 0.529(0.461~0.645) 0.532(0.497~0.652) 0.006* 否 1 0.413(0.306~0.538) 0.425(0.314~0.521) 0.441(0.351~0.568) 0.459(0.396~0.517) 0.025* VEGF(pg/mL) 0.231 <534.58 1 0.714(0.614~0.822) 0.728(0.596~0.812) 0.740(0.664~0.847) 0.754(0.682~0.856) 0.023* ≥534.58 1 0.705(0.603~0.827) 0.724(0.616~0.838) 0.739(0.579~0.894) 0.752(0.649~0.840) 0.004* BF[mL/(min·100 g)] 0.154 <67.28 1 0.709(0.601~0.814) 0.720(0.613~0.838) 0.743(0.632~0.861) 0.767(0.645~0.856) 0.002* ≥67.28 1 0.701(0.605~0.810) 0.714(0.609~0.824) 0.737(0.642~0.825) 0.756(0.637~0.842) 0.012* BV(mL/100 g) 0.085 <7.57 1 0.497(0.394~0.605) 0.517(0.401~0.642) 0.529(0.416~0.638) 0.549(0.435~0.664) 0.014* ≥7.57 1 0.476(0.382~0.586) 0.518(0.407~0.620) 0.522(0.415~0.649) 0.531(0.438~0.657) 0.046* PS[mL/(min·100 g)] 0.066 <29.45 1 0.505(0.396~0.612) 0.528(0.431~0.609) 0.543(0.422~0.641) 0.564(0.463~0.621) 0.010* ≥29.45 1 0.517(0.404~0.611) 0.521(0.436~0.639) 0.527(0.419~0.642) 0.541(0.421~0.639) 0.034* MTT(s) 0.130 <15.99 1 0.521(0.407~0.625) 0.529(0.399~0.612) 0.534(0.447~0.643) 0.552(0.480~0.669) 0.008* ≥15.99 1 0.487(0.331~0.561) 0.504(0.415~0.653) 0.523(0.406~0.617) 0.537(0.450~0.629) 0.009* *P < 0.05。 表 7 治疗前Ang-2与术后复发的阈值效应分析
Table 7. Threshold effect analysis of pre-treatment Ang - 2 and postoperative recurrence
模型 项目 OR(95%CI) P 模型1 标准线性效应 1.005(1.004~1.007) <0.001* 模型2 Ang-2的拐点 1905.41 pg/mLAng-2< 1905.41 pg/mL0.986(0.979~0.998) <0.001* Ang-2≥ 1905.41 pg/mL1.009(1.007~1.010) <0.001* 效应差 1.012(1.010~1.015) <0.001* 对数似然比检验 - <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 8 患者生存期的影响因素分析结果
Table 8. Analysis of factors influencing patients' survival time
变量 单变量分析 多变量分析 HR 95%CI P HR 95%CI P 年龄(<60岁或≥60岁) 1.255 0.507~1.726 0.382 吸烟(否或是) 1.156 0.618~1.543 0.421 进行体育锻炼(是或否) 1.034 0.645~1.634 0.808 合并COPD(否或是) 1.892 1.150~3.074 0.012* 2.064 1.451~2.833 0.001* 肺结核史(否或是) 1.631 1.053~2.394 0.031* 1.232 0.861~1.672 0.387 Ang-2(< 1905.41 pg/mL或≥1905.41 pg/mL)1.761 1.245~2.482 0.017* 1.915 1.144~2.965 0.009* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Bade B C, Dela Cruz C S. Lung cancer 2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention[J]. Clin Chest Med, 2020, 41(1): 1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.10.001 [2] 史健, 王亚静, 侯冉, 等. 表皮生长因子受体酪氨酸激酶抑制剂联合化疗一线治疗表皮生长因子受体突变晚期非小细胞肺癌疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(11): 1383-1394. [3] Chen Y, Li J, Ma S, et al. The role of microwave ablation in combination with surgery in the management of multiple high-risk pulmonary nodules[J]. Clin Radiol, 2025, 81: 106707. doi: 10.1016/j.crad.2024.09.013 [4] Wang S, Meng F, Chen P, et al. Cell-free DNA assay for malignancy classification of high-risk lung nodules[J]. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2024, 168(5): e140-e175. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2024.04.026 [5] Cheng M, Ding R, Wang S. Diagnosis and treatment of high-risk bilateral lung ground-glass opacity nodules[J]. Asian J Surg, 2024, 47(7): 2969-2974. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2024.01.072 [6] Chan M V, Huo Y R, Cao C, et al. Survival outcomes for surgical resection versus CT-guided percutaneous ablation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(7): 5421-5433. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07634-7 [7] 洪子强, 金大成, 白向豆, 等. 热消融治疗肺癌的研究进展[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2024, 31(1): 166-172. [8] 辛少伟, 杨阳, 高峰, 等. 38例肺癌的CT引导下微波消融安全性及初步疗效临床总结[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2024, 24(23): 4444-4448. [9] Tsakogiannis D, Nikolakopoulou A, Zagouri F, et al. Update overview of the role of angiopoietins in lung cancer[J]. Medicina (Kaunas), 2021, 57(11): 1191. doi: 10.3390/medicina57111191 [10] Meder L, Orschel C I, Otto C J, et al. Blocking the angiopoietin-2-dependent integrin β-1 signaling axis abrogates small cell lung cancer invasion and metastasis[J]. JCI Insight, 2024, 9(10): e166402. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.166402 [11] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会肺癌学组, 中国肺癌防治联盟专家组. 肺结节诊治中国专家共识(2018年版)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2018, 41(10): 763-771. [12] Krieger J R, Lee F T, McCormick T, et al. Microwave ablation of renal cell carcinoma[J]. J Endourol, 2021, 35(s2): S33-S37. doi: 10.1089/end.2020.1078 [13] 李帅, 韩哲洙, 金秀颖, 等. 微波消融治疗肺癌的疗效及安全性[J]. 癌症进展, 2023, 21(17): 1888-1892. [14] Cao B, Liu M, Wang L, et al. Remodelling of tumour microenvironment by microwave ablation potentiates immunotherapy of AXL-specific CAR T cells against non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 6203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33968-5 [15] 张家豪, 张亚杰, 王洁, 等. 2021年V1版《NCCN非小细胞肺癌临床诊治指南》更新解读[J]. 中国胸心血管外科临床杂志, 2021, 28(3): 271-277. [16] Roos-Mattila M, Kaprio T, Mustonen H, et al. The possible dual role of Ang-2 in the prognosis of pancreatic cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 18725. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45194-0 [17] 徐文飞, 梅其杰, 郭锦荣, 等. 血管生成素-2表达与骨肉瘤预后关系的Meta分析[J]. 癌症进展, 2020, 18(18): 1853-1857+1931. [18] 焦策, 高丽萍, 杨敬芳, 等. Ang-2、TWIST表达水平及血小板分布宽度与宫颈癌患者预后的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2023, 43(8): 1819-1823. [19] 邹立君, 马建刚, 华菁. 超声成像参数联合血清Ang-2、PLAC1对非小细胞肺癌淋巴结转移的诊断价值[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2023, 28(10): 1479-1482. [20] Sha C, Li L, Rahman H, et al. Surgical outcomes of smoking and nonsmoking women with lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2025, 17(8): 5711-5719. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2025-280 [21] Devulder J V. Unveiling mechanisms of lung aging in COPD: A promising target for therapeutics development[J]. Chin Med J Pulm Crit Care Med, 2024, 2(3): 133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.pccm.2024.08.007 [22] 孙兴智, 栗鸿宝, 朱思毅, 等. 多层螺旋CT灌注参数联合外周血炎症复合指标对非小细胞肺癌患者纵隔淋巴结转移的预测价值[J]. 放射学实践, 2025, 40(3): 325-330. [23] 杨文魁, 周志刚, 张琼, 等. 经皮微波消融术前血清VEGF和Ang-2水平与Ⅰ期非小细胞肺癌患者预后的相关性[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2024, 53(3): 142-146. [24] 马逸超, 鲁燕, 贾永平. 血管生成素-Tie通路在冠心病中的作用机制及意义[J]. 中华全科医学, 2019, 17(8): 1379-1383. -





 下载:
下载: