Association of Serum magnesium and Phosphorus with Vascular Calcification and Cardiovascular Events in Hemodialysis Patients
-
摘要:
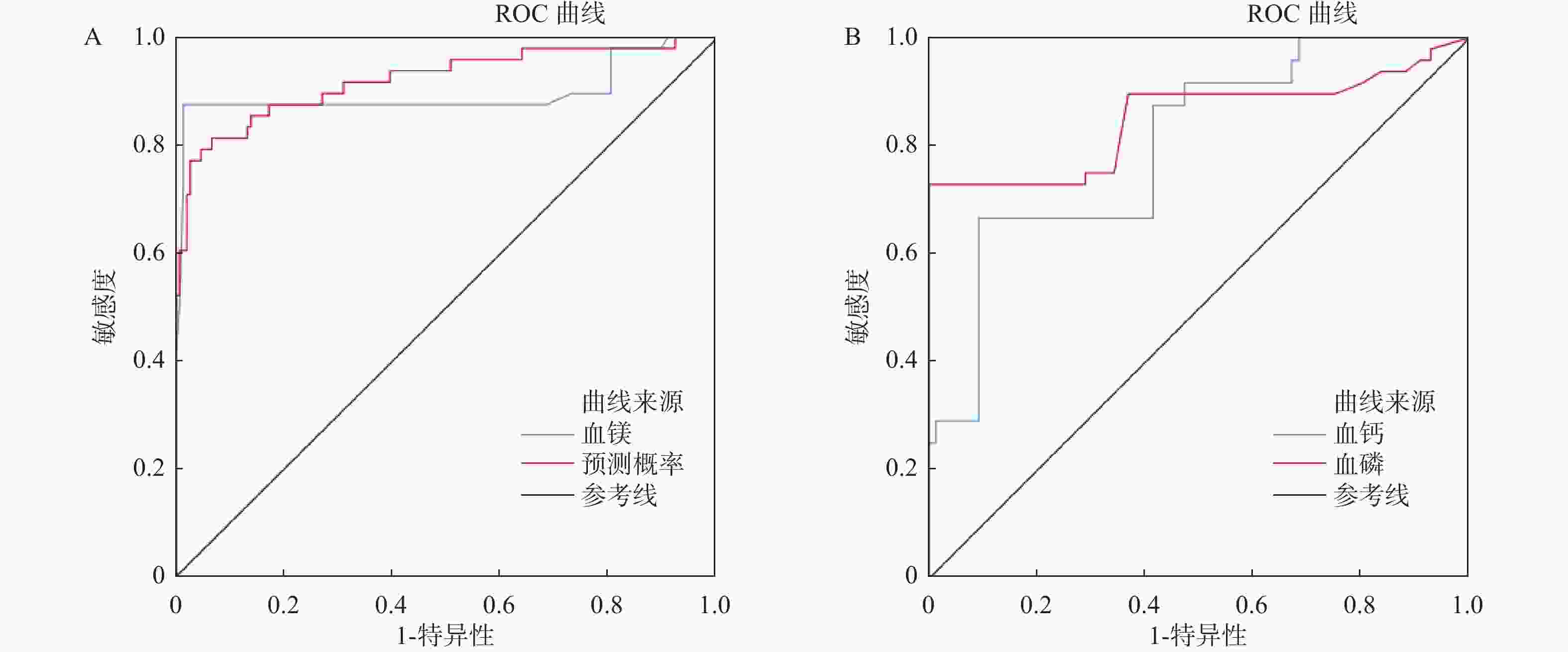
目的 探究维持性血液透析患者血镁水平、血清磷浓度与血管钙化及心血管疾病死亡的关联性预测研究。 方法 选取南京鼓楼医院2020年5月至2022年5月收治的200例维持性血液透析患者展开研究,另选取该院同期健康体检者200例为对照;比较两组间生化指标的差异;分析其之间相关性,采用二元 Logistic 回归分析维持性血液透析患者血镁、血磷水平与血管钙化及心血管事件的独立影响因素,并利用 ROC 曲线评估血镁、血磷对血管钙化或心血管事件的预测价值。 结果 研究组患者的血磷、钙磷乘积、iPTH、AACS、25-(OH)-VitI均显著高于对照组,其血镁、BMP-7均显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。皮尔逊相关性显示,血镁与血钙、血磷、钙磷乘积、25-(OH)-VitI、BMP-7互呈正相关(r = 0.385、0.183、0.141、0.131、0.458,P < 0.05);血钙与血磷、钙磷乘积、iPTH、AACS、25-(OH)-VitI、BMP-7互呈正相关(r = 0.318、0.311、0.098、0.170 、0.277、0.485,P < 0.05);血磷与钙磷乘积、iPTH、AACS、25-(OH)-VitI互呈正相关(r = 0.362、0.506、0.367、0.461,P < 0.05);钙磷乘积与iPTH、AACS、25-(OH)-VitI互呈正相关(r = 0.542、0.373、0.434,P < 0.05);iPTH与AACS、25-(OH)-VitI互呈正相关(r = 0.553、0.616,P < 0.05)与BMP-7互呈负相关(r = -0.373,P < 0.05);AACS与25-(OH)-VitI互呈正相关(r = 0.402,P < 0.05)与BMP-7互呈负相关(r = -0.155,P < 0.05),差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);两组年龄、糖尿病、血镁、血钙、血磷、钙磷乘积、25-(OH)-VitI、hs-CRP差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。Logistic回归分析显示,年龄、血镁、血钙、血磷、钙磷乘积、25-(OH)-VitI、均为MHD患者CVD死亡的危险因素(P < 0.05)。ROC曲线分析显示,血镁、血钙、血磷预测MHD患者CVD死亡的AUC为0.895、0.802、0.851,敏感度,特异度分别为:87.5%/98.7%、66.7%/90.8%、72.9%/100%;联合预测在MHD患者CVD死亡中的AUC为0.921,敏感度、特异度为81.3%、93.4%。 结论 MHD患者血镁水平低,血清磷浓度及钙磷乘积升高,且指标间存在复杂关联。年龄、血镁、血钙、血磷均与CVD死亡相关。ROC曲线分析显示,血镁、血钙、血磷单独及联合预测CVD死亡风险具有较高价值。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the predictive association between serum magnesium levels, serum phosphorus concentrationconcentrations, vascular calcification, and cardiovascular disease mortality in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Methods This study enrolled 200 hemodialysis patients admitted to Nanjing Drum Tower Hospital from May 2020 to May 2022 as subjects, with an additional 200 healthy individuals from the same period selected as a control group. The biochemical indicators between the two groups were compared; their correlations were analyzed. Binary logistic regression was used to investigate the independent factors of serum magnesium and phosphorus levels in relation to vascular calcification and cardiovascular events in maintenance hemodialysis patients. ROC curve analysis was employed to assess the predictive value of serum magnesium and phosphorus for vascular calcification and cardiovascular events. Results The research group's patients exhibited significantly elevated levels of blood phosphorus, calcium-phosphorus product, iPTH, AACS, and 25-(OH)-VitD compared to the control group. In contrast, their blood magnesium and BMP-7 levels were notably lower than those of the control group, with statistical significance (P < 0.05). Pearson correlation showed positive correlations between serum magnesium and serum calcium, phosphorus, calcium-phosphorus product, 25-(OH)-VitI, and BMP-7 (r = 0.385, 0.183, 0.141, 0.131, 0.458, P < 0.05); between serum calcium and serum phosphorus, calcium-phosphorus product, iPTH, AACS, 25-(OH)-VitI, and BMP-7 (r = 0.318). correlation (r = 0.318, 0.311, 0.098, 0.170 , 0.277, 0.485, P < 0.05); between serum phosphorus and calcium-phosphorus product, iPTH, AACS, 25-(OH)-VitI (r = 0.362, 0.506, 0.367, 0.461, P < 0.05); between calcium-phosphorus product and iPTH, AACS, 25-(OH)-VitI (r = 0.542, 0.373, 0.434, P < 0.05); between iPTH and AACS, 25-(OH)-VitI showing positive correlations (r = 0.553, 0.616, P < 0.05) and a negative correlation with BMP-7 (r = -0.373, P < 0.05); between AACS and 25-(OH)-VitI showing a positive correlation (r = 0.402, P < 0.05), and a negative correlation with BMP-7 (r = -0.155, P < 0.05), with statistically significant differences (P < 0.05). Statistically significant differences were noted between the two groups in age, diabetes, serum magnesium, serum calcium, serum phosphorus, calcium-phosphorus product, 25-(OH)-VitI, and hs-CRP (P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that age, serum magnesium, serum calcium, serum phosphorus, calcium phosphate product, 25- (OH) -vitamin I were all risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) mortality in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients (P <0.05). ROC curve analysis showed that serum magnesium, serum calcium, and serum phosphorus had predictive areas under the curve (AUC) of 0.895, 0.802, and 0.851 for CVD mortality in MHD patients, with sensitivities and specificities of 87.5%/98.7%, 66.7%/90.8%, and 72.9%/100%, respectively. The combined prediction for CVD mortality in MHD patients showed an AUC of 0.921, with a sensitivity of 81.3% and specificity of 93.4%. Conclusion MHD patients exhibit low blood magnesium levels, elevated serum phosphorus concentrations, and increased calcium-phosphorus product, with complex correlations among these biomarkers. Age, magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus levels were all associated with CVD mortality. ROC curve analysis demonstrates that magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus, both individually and in combination, have high predictive value for CVD mortality risk. -
表 1 两组生化指标比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 1. Comparison of two groups of biochemical indexes($ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 血镁
(mmol/L)血钙
(mmol/L)血磷
(mmol/L)钙磷
乘积iPTH
(pg/mL)AACS
(分)25-(OH)-VitI
(ng/mL)BMP-7
(ng/mL)研究组 1.32 ± 0.37 2.41 ± 0.48 1.65 ± 0.52 3.48 ± 1.16 44.64 ± 10.73 1.95 ± 0.93 23.30 ± 7.54 1192.58 ± 103.35对照组 1.47 ± 0.44 2.49 ± 0.44 1.24 ± 0.34 2.46 ± 0.60 7.77 ± 2.41 1.12 ± 0.32 15.52 ± 4.58 1346.67 ± 125.21t 3.805 1.745 9.253 11.048 47.462 11.989 12.465 13.422 P <0.001*** 0.082 <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** ***P < 0.001。 表 2 两组生化指标相关性($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Correlation between the two sets of biochemical indexes($ \bar x \pm s $)
皮尔逊相关性 血镁 血钙 血磷 钙磷乘积 iPTH AACS 25-(OH)-VitI BMP-7 血镁 相关系数(r) − 0.385 0.183 0.141 −0.08 0.088 0.131 0.458 P(双尾) − <0.001*** <0.001*** 0.005** 0.112 0.08 0.009** <0.001*** 血钙 相关系数(r) 0.385 − 0.318 0.311 0.098 0.170 0.277 0.485 P(双尾) <0.001*** − <0.001*** <0.001*** 0.049 0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** 血磷 相关系数(r) 0.183 0.318 − 0.362 0.506 0.367 0.461 0.097 P(双尾) <0.001*** <0.001*** − <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** 0.053 钙磷乘积 相关系数(r) 0.141 0.311 0.362 − 0.542 0.373 0.434 0.019 P(双尾) 0.005** <0.001*** <0.001*** − <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** 0.711 iPTH 相关系数(r) −0.08 0.098 0.506 0.542 − 0.553 0.616 −0.373 P(双尾) 0.112 0.049* <0.001*** <0.001*** − <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** AACS 相关系数(r) 0.088 0.17 0.367 0.373 0.553 − 0.402 −0.155 P(双尾) 0.08 0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** − <0.001*** 0.002** 25-(OH)-VitI 相关系数(r) 0.131 0.277 0.461 0.434 0.616 0.402 − −0.005 P(双尾) 0.009** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** <0.001*** − 0.922 *P < 0.05;**P < 0.01;***P < 0.001。 表 3 MHD患者CVD死亡单因素分析($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Single factor analysis of CVD mortality in MHD patients($ \bar x \pm s $)
项目 CVD 死亡组
(n = 48)CVD 存活组
(n=152)t/χ2 P 年龄(岁) 65.96 ± 7.32 58.92 ± 5.41 7.183 <0.001*** BMI(kg/m2) 23.62 ± 3.93 23.30 ± 3.79 0.506 0.614 性别(男/女) 男 25(52.08) 88(57.89) 0.501 0.479 女 23(47.92) 64(42.11) 高血压 有 28(58.33) 75(49.34) 1.181 0.277 无 20(41.67) 77(50.66) 高血脂 有 31(64.58) 89(58.55) 0.553 0.457 无 17(35.42) 63(41.45) 糖尿病 有 30(62.5) 61(40.13) 7.361 0.007** 无 18(37.5) 91(59.87) 血镁(mmol/L) 0.99 ± 0.27 1.42 ± 0.34 7.876 <0.001*** 血钙(mmol/L) 2.80 ± 0.41 2.29 ± 0.44 7.125 <0.001*** 血磷(mmol/L) 2.09 ± 0.37 1.51 ± 0.49 7.546 <0.001*** 钙磷乘积(百分毫克) 4.48 ± 0.75 3.19 ± 1.10 7.620 <0.001*** iPTH(pg/mL) 42.69 ± 10.98 45.26 ± 10.60 1.451 0.148 AACS(分) 1.81 ± 0.94 1.99 ± 0.92 1.424 0.158 25-(OH)-VitI(ng/mL) 16.53 ± 4.19 25.44 ± 7.10 8.257 <0.001*** BMP-7(ng/mL) 1181.17 ± 148.331196.79 ± 84.690.877 0.381 血清白蛋白(g/L) 30.41 ± 5.85 31.16 ± 4.45 0.944 0.346 血红蛋白(g/L) 84.23 ± 10.83 86.41 ± 12.23 1.105 0.271 hs-CRP(mg/L) 7.74 ± 2.63 5.42 ± 1.49 7.662 <0.001*** **P < 0.01;***P < 0.001。 表 4 MHD患者CVD死亡影响因素Logistic回归分析
Table 4. Logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for CVD mortality in MHD patients
变量 B S.E Wald P OR 95%CI 下限 上限 年龄 −0.256 0.107 5.667 0.017* 0.774 0.627 0.956 有糖尿病 −0.327 0.902 0.132 0.717 0.721 0.123 4.224 hsCRP −0.387 0.206 3.528 0.060 0.679 0.454 1.017 血镁 4.466 1.559 8.202 <0.001*** 86.994 4.094 1848.408 血钙 −2.756 1.061 7.000 0.009** 0.064 0.000 0.508 血磷 −2.654 1.105 5.773 0.016* 0.07 0.008 0.613 钙磷乘积 −1.573 0.510 9.518 0.002** 0.207 0.076 0.563 25-(OH)-VitI 0.281 0 .000 9.139 0.003** 1.324 1.104 1.588 常量 26.667 8.333 10.241 0.001** 381.178 *P < 0.05;**P < 0.01;***P < 0.001。 表 5 血镁、血钙、血磷联合预测MHD患者CVD死亡的价值
Table 5. Predictive value of serum magnesium,calcium,and phosphorus combined for cardiovascular death in maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients
变量 AUC S.E P 95%CI cut-off值 约登指数 敏感度(%) 特异度(%) 下限 上限 血镁 0.895 0.039 <0.001*** 0.820 0.971 0.965 0.862 87.5 98.7 预测概率 0.921 0.027 <0.001*** 0.867 0.974 0.595 0.747 81.3 93.4 血钙 0.802 0.036 <0.001*** 0.732 0.873 2.805 0.575 66.7 90.8 血磷 0.851 0.041 <0.001*** 0.770 0.932 2.195 0.729 72.9 100 ***P < 0.001。 -
[1] Bansal N, Artinian N T, Bakris G, et al. Hypertension in patients treated with in-center maintenance hemodialysis: Current evidence and future opportunities: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association[J]. Hypertension, 2023, 80(6): e112-e122. [2] Bossola M, Hedayati S S, Brys A D H, et al. Fatigue in patients receiving maintenance hemodialysis: A review[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2023, 82(4): 464-480. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.02.008 [3] 李大勇, 袁新科, 刘冠兰, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清Irisin、BMP-7水平与血管钙化及钙磷代谢指标的相关性研究[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2019, 29(15): 41-46. [4] 陈燕文, 陈都, 甘春蕾, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清BMP-2和BMP-4水平与血管钙化的关系[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2021, 34(8): 91-95. [5] 汪嘉莉, 王松, 李芫酶, 等. 维持性非卧床腹膜透析患者血清镁与颈动脉钙化的关系[J]. 广东医学, 2019, 40(5): 685-688+693. [6] 中华医学会肾脏病学分会. 慢性肾脏病患者评估与管理指南(2021年)[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志, 2021, 37(9): 755-803. [7] 李慧敏. 尿酸/高密度脂蛋白胆固醇比值与CKD患者CVD的相关性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2025. [8] Kang B, Kwon Y S. Benign convulsion with mild gastroenteritis[J]. Korean J Pediatr, 2014, 57(7): 304-309. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2014.57.7.304 [9] Liu Y, Du Q, Jiang Y. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in maintenance hemodialysis patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sleep Med, 2024, 114: 15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2023.11.1138 [10] Schaar B, Thys S, Hoppe B. Endurance training during maintenance hemodialysis in pediatric and adolescent patients-theory and best practice suggestions[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2020, 35(4): 595-602. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-4182-1 [11] 李富强, 吕晶, 熊礼娟. 维持性血液透析与腹膜透析患者中血清碱性磷酸酶、超敏肌钙蛋白I的表达水平及对心脏结构的影响[J]. 海南医学, 2022, 33(6): 711-713. [12] 周自英, 张颖, 冯锦红, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清镁与腹主动脉钙化及矿物质代谢的关系[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020, 40(5): 860-863. [13] 单婧, 耿燕秋, 刘东, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清碱性磷酸酶对心脏病变的评估价值[J]. 武警医学, 2021, 32(11): 925-928+932. [14] 江玉波, 王少清, 赖玮婧. 维持性血液透析患者冠状动脉钙化关联因素分析[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(5): 428-432. [15] 张宪, 邓薇, 周海洋, 等. 维持性血液透析合并恶性肿瘤患者血清碱性磷酸酶水平对心血管疾病死亡率的影响[J]. 肿瘤预防与治疗, 2024, 37(3): 226-230. [16] 蔡士铭, 李月红, 武向兰. 维持性血液透析患者透析超滤率与透析前后生化指标变化率的相关性[J]. 临床内科杂志, 2020, 37(10): 699-702. [17] 沈英, 梁世凯. 维持性血液透析患者发生骨质疏松的关联因素及其与血清钙、磷、甲状旁腺素的关系[J]. 中华全科医学, 2017, 15(11): 1901-1903. [18] 周自英, 张颖, 冯锦红, 等. 维持性血液透析患者血清镁与腹主动脉钙化及矿物质代谢的关系[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志, 2020, 40(5): 860-863. [19] 鲁晓涵, 林海霞, 耿明慧, 等. 联合检测血清碱性磷酸酶和甲状旁腺激素对维持性血液透析患者全因及心血管事件死亡风险的预测价值[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2020, 59(8): 634-637. [20] 向元兵, 胡耀. 糖尿病肾病患者血清TRPM7、Sirtuin-1与钙磷代谢、颈动脉钙化的相关性[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2023, 33(12): 86-91. [21] 黄梦娣, 陈卫东, 刘磊. 维持性血液透析患者血清碱性磷酸酶与钙磷代谢及炎症指标相关性分析[J]. 中华全科医学, 2023, 21(4): 611-614. -





 下载:
下载: