Mechanism of miR-21-5p in Promoting Osteoarthritis Progression through Inhibition of the SIRT2/AKT Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
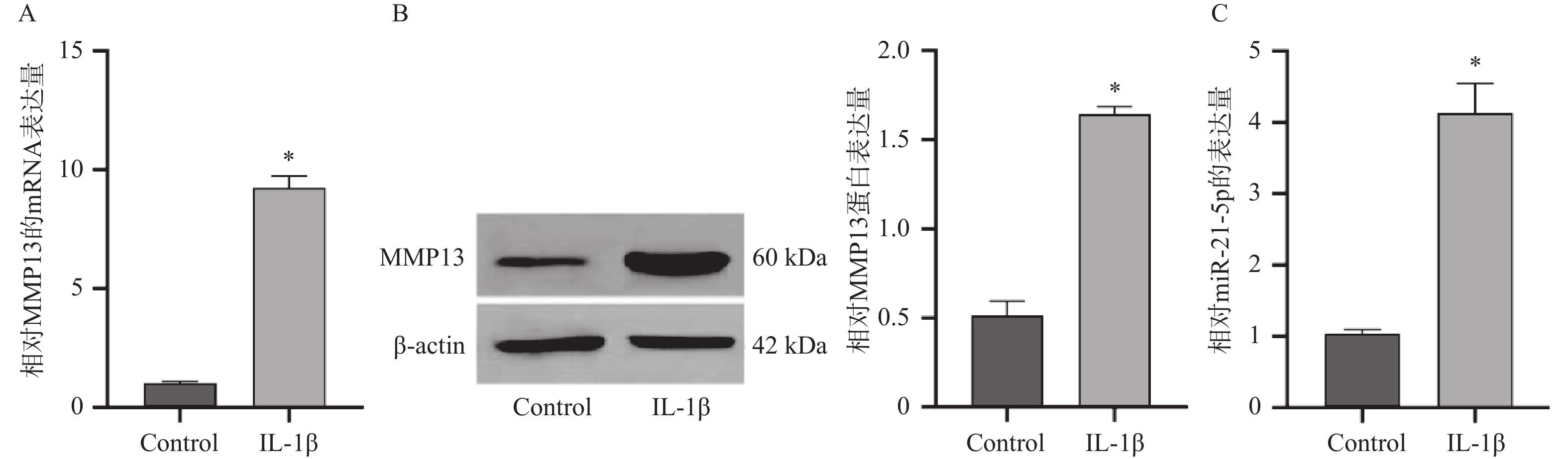
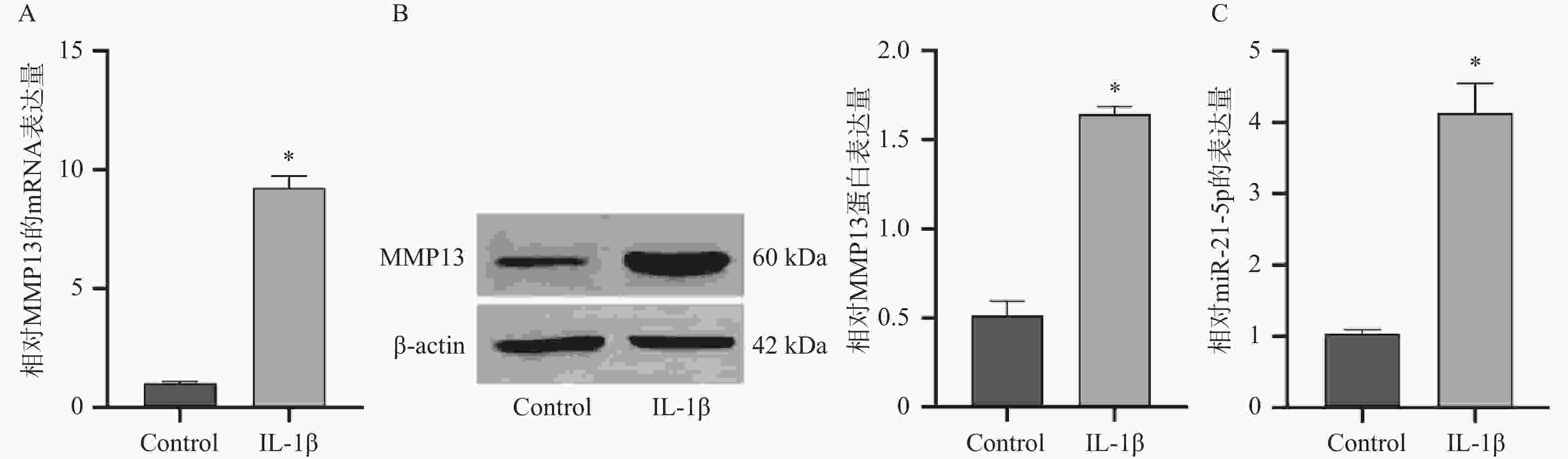
目的 探究miR-21-5p通过调控SIRT2/AKT信号轴在骨关节炎(osteoarthritis,OA)进展中的作用机制。 方法 采用10 ng/mL IL-1β诱导人软骨细胞系CP-H107构建OA体外模型。实验分组包括:IL-1β+阴性对照模拟物(NC mimic)组、IL-1β+miR-21-5p模拟物(mimic)组、IL-1β+阴性对照抑制物(NC inhibitor)组、IL-1β+miR-21-5p抑制物(inhibitor)组及IL-1β+miR-21-5p mimic+oe SIRT2组。通过RT-qPCR、Western blot(WB)、免疫荧光检测MMP13、SIRT2、AKT及p-AKT表达水平,Annexin V-FITC/PI流式细胞术分析细胞凋亡,ELISA检测IL-6、TNF-α、IL-10水平。双荧光素酶报告实验验证miR-21-5p与SIRT2的靶向结合。 结果 IL-1β刺激后,CP-H107细胞中miR-21-5p及MMP13表达显著升高(P < 0.05)。miR-21-5p过表达可促进MMP13表达、细胞因子(IL-6、TNF-α、IL-10)分泌及细胞凋亡(P < 0.05),而抑制miR-21-5p可产生相反效果(P < 0.05)。双荧光素酶实验证实miR-21-5p可直接靶向SIRT2。miR-21-5p过表达显著下调SIRT2及p-AKT/AKT比值(P < 0.05)。进一步实验显示,SIRT2过表达可部分逆转miR-21-5p过表达所致的MMP13上调、炎症因子释放及凋亡增加(P < 0.05)。 结论 miR-21-5p通过靶向抑制SIRT2,阻断其对AKT通路的调控作用,促进软骨细胞分解代谢、炎症反应及凋亡,加速OA进展。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the mechanism of miR-21-5p in promoting osteoarthritis (OA) progression by regulating the SIRT2/AKT signaling pathway. Methods An in vitro OA model was established by inducing human chondrocyte cell line CP-H107 with 10 ng/mL IL-1β. Experimental groups included: IL-1β + NC mimic, IL-1β + miR-21-5p mimic, IL-1β + NC inhibitor, IL-1β + miR-21-5p inhibitor, and IL-1β + miR-21-5p mimic + oe SIRT2. Expression levels of MMP13, SIRT2, AKT, and p-AKT were detected by RT-qPCR, Western blot (WB), and immunofluorescence. Cell apoptosis was analyzed by Annexin V-FITC/PI flow cytometry. IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 levels were measured by ELISA. The direct interaction between miR-21-5p and SIRT2 was validated by a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Results Following IL-1β stimulation, miR-21-5p and MMP13 expression in CP-H107 cells were significantly elevated (P < 0.05). miR-21-5p overexpression promoted MMP13 expression, cytokine (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10) secretion, and cell apoptosis (P < 0.05), while miR-21-5p inhibition produced opposite effects (P < 0.05). Dual-luciferase reporter assays confirmed that miR-21-5p directly targets SIRT2. Overexpression of miR-21-5p significantly downregulated SIRT2 expression and reduced the p-AKT/AKT ratio (P < 0.05). Further experiments demonstrated that SIRT2 overexpression partially reversed the MMP13 upregulation, inflammatory factor release, and increased apoptosis induced by miR-21-5p overexpression (P < 0.05). Conclusion miR-21-5p promotes chondrocyte catabolism, inflammatory response, and apoptosis by targeting and inhibiting SIRT2, thereby blocking its regulatory effect on the AKT pathway and accelerating OA progression. -
Key words:
- miR-21-5p /
- SIRT2 /
- AKT /
- Osteoarthritis
-
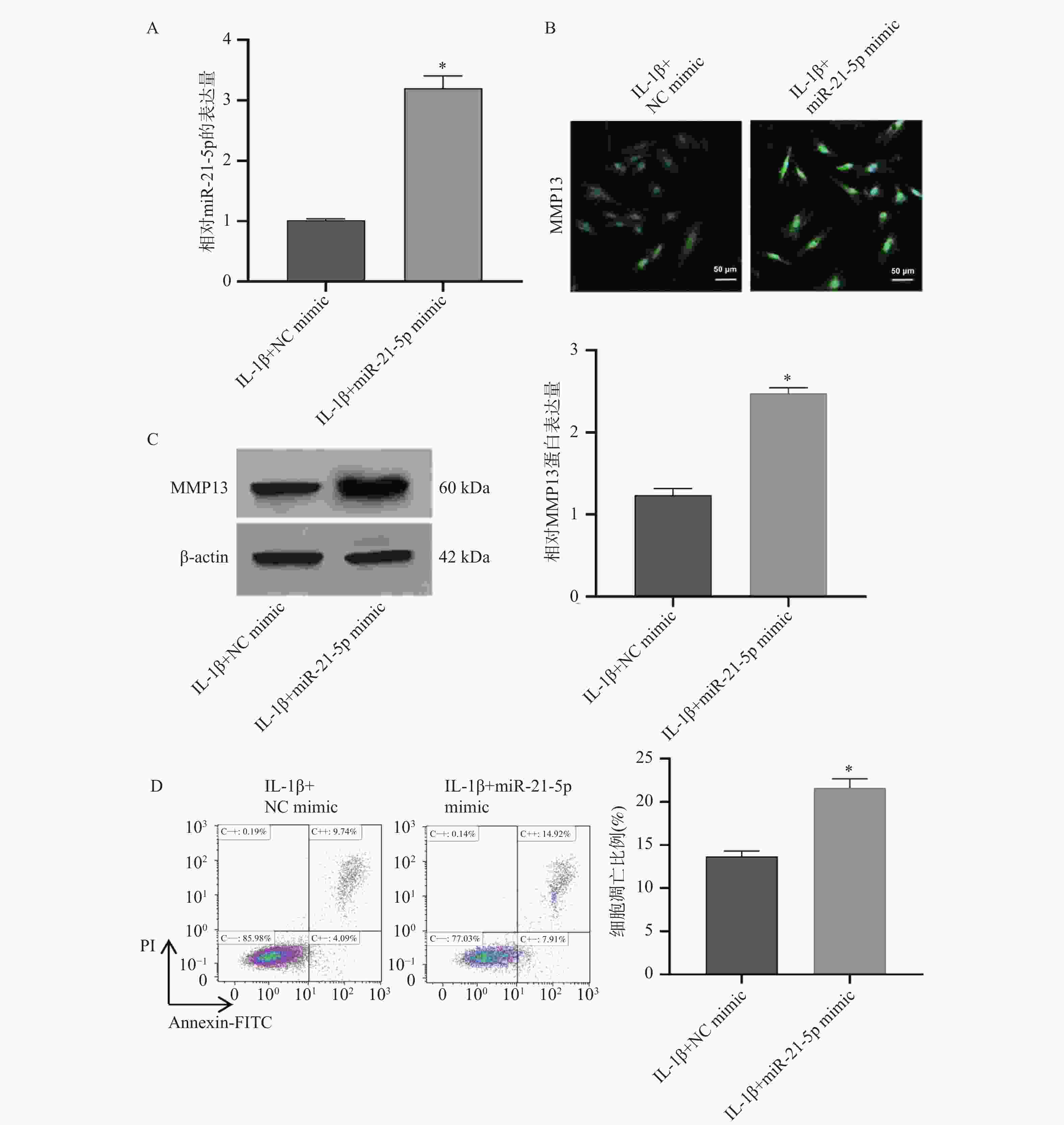
图 2 miR-21-5p过表达对MMP13水平及CP-H107细胞凋亡比例的影响($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
A:RT-qPCR检测miR-21-5p mimics转染效率;B:免疫荧光检测MMP13的表达;C: Western blot检测各组细胞中MMP13蛋白的表达水平;D:Annexin/PI双染实验检测CP-H107细胞凋亡比例;*P < 0.05。
Figure 2. Effects of miR-21-5p overexpression on MMP13 levels and apoptosis ratio in CP-H107 cells ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
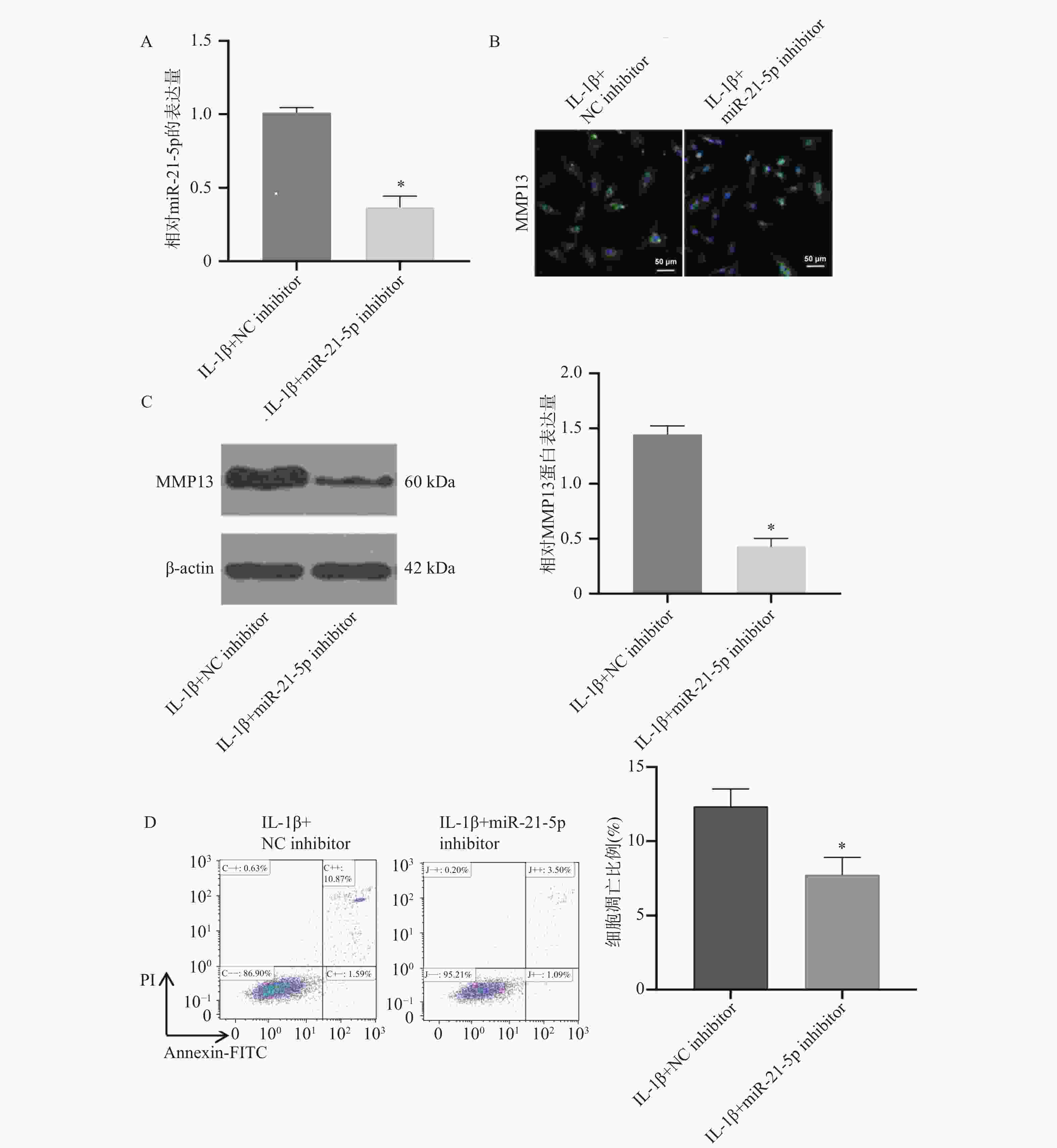
图 3 沉默miR-21-5p对MMP13水平及CP-H107细胞凋亡比例的影响($\bar x \pm s $,n = 5)
A:RT-qPCR检测miR-21-5p mimics转染效率;B:免疫荧光检测MMP13的表达;C: Western blot检测各组细胞中MMP13蛋白的表达水平;D:Annexin/PI双染实验检测CP-H107细胞凋亡比例;*P < 0.05。
Figure 3. Effects of miR-21-5p silencing on MMP13 expression and apoptosis ratio in CP-H107 cells ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 5)
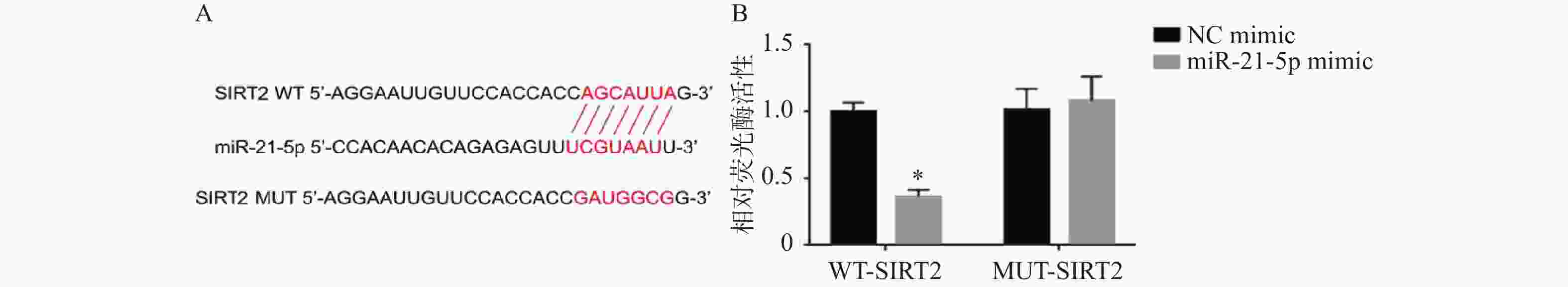
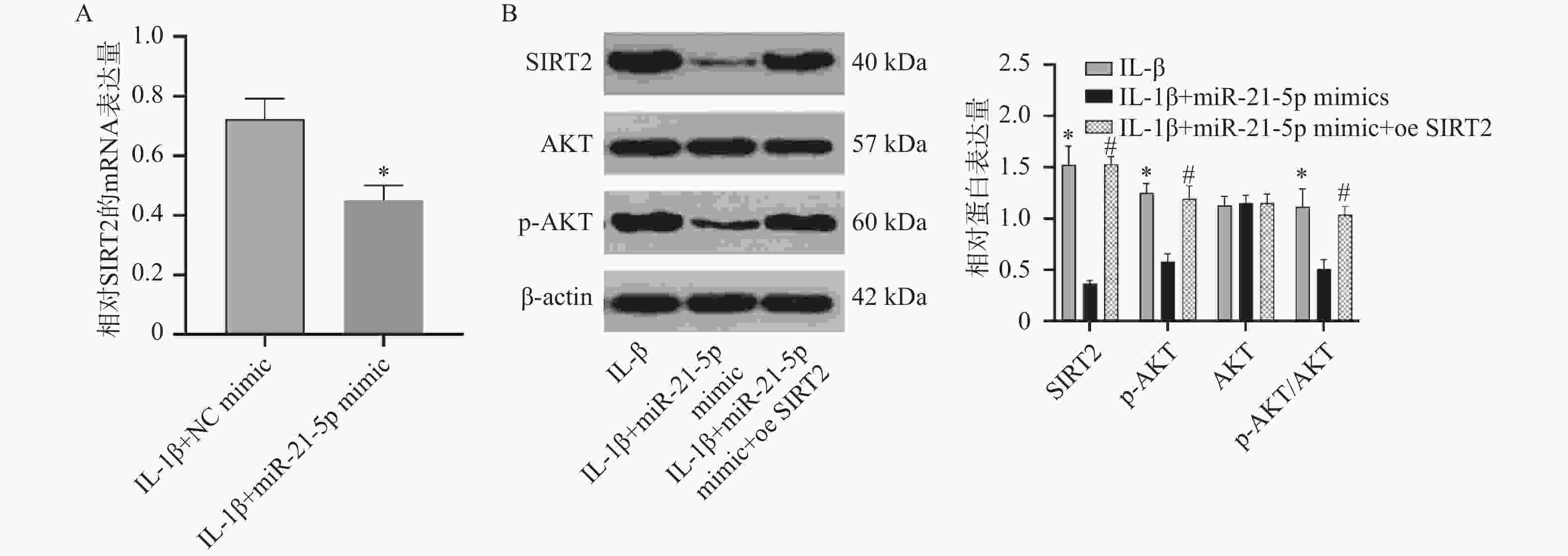
图 6 RT-qPCR和Western blot检测miR-21-5p过表达对CP-H107细胞中SIRT2、AKT和p-AKT的影响($\bar x \pm s $,n = 5)
A:RT-qPCR检测IL-1β+NC mimic组和IL-1β+miR-21-5p mimics组SIRT2 mRNA水平;B:Western blot检测IL-1β+NC mimic组、IL-1β+miR-21-5p mimics组及IL-1β+miR-21-5p mimic+oe SIRT2组SIRT2、AKT和p-AKT的蛋白表达;C:各组相对蛋白表达量;与IL-1β相比,*P < 0.05;与IL-1β+miR-21-5p mimic+oe SIRT2组相比,#P < 0.05。
Figure 6. Effects of miR-21-5p overexpression on SIRT2,AKT,and p-AKT expression in CP-H107 cells detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 5)
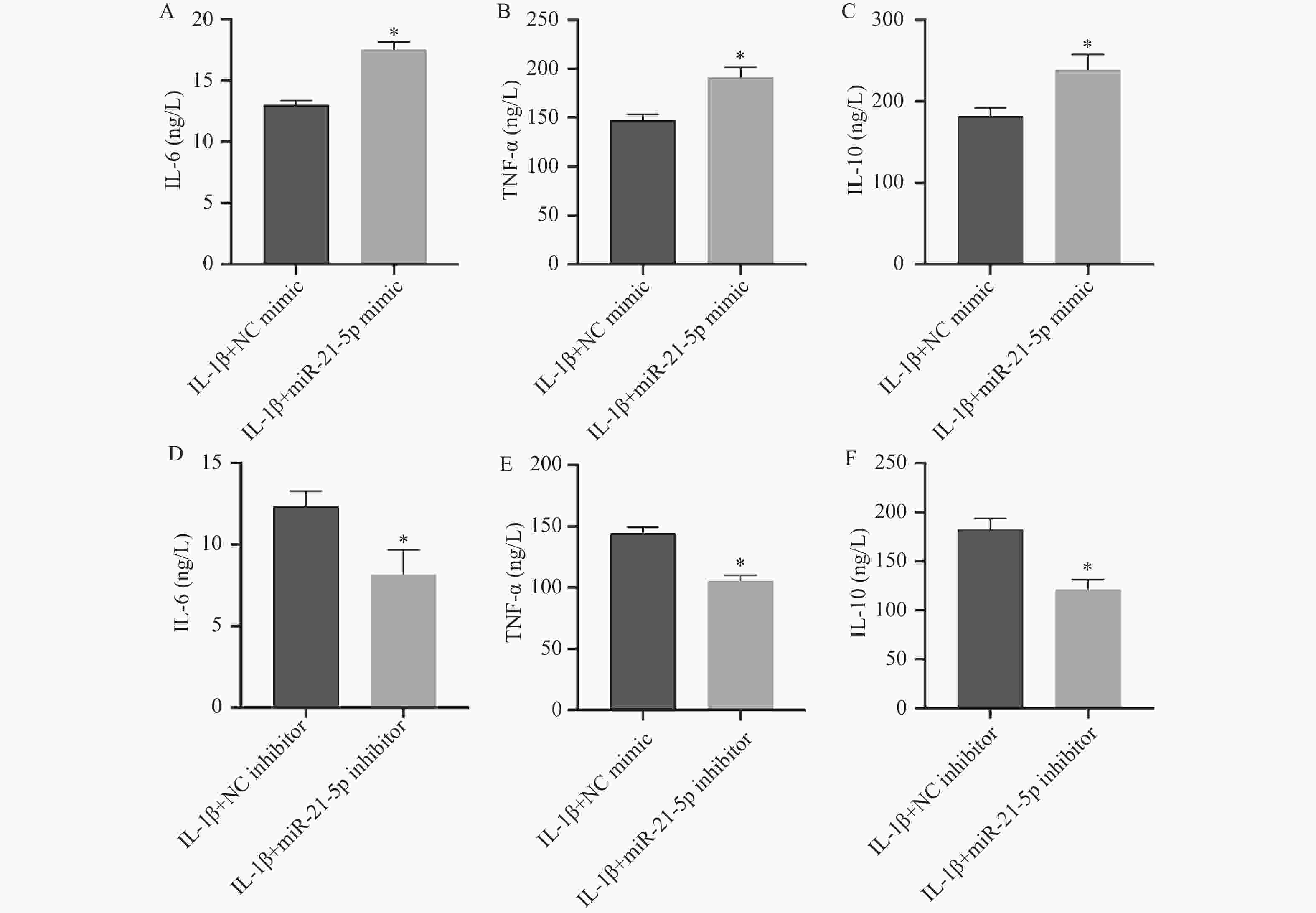
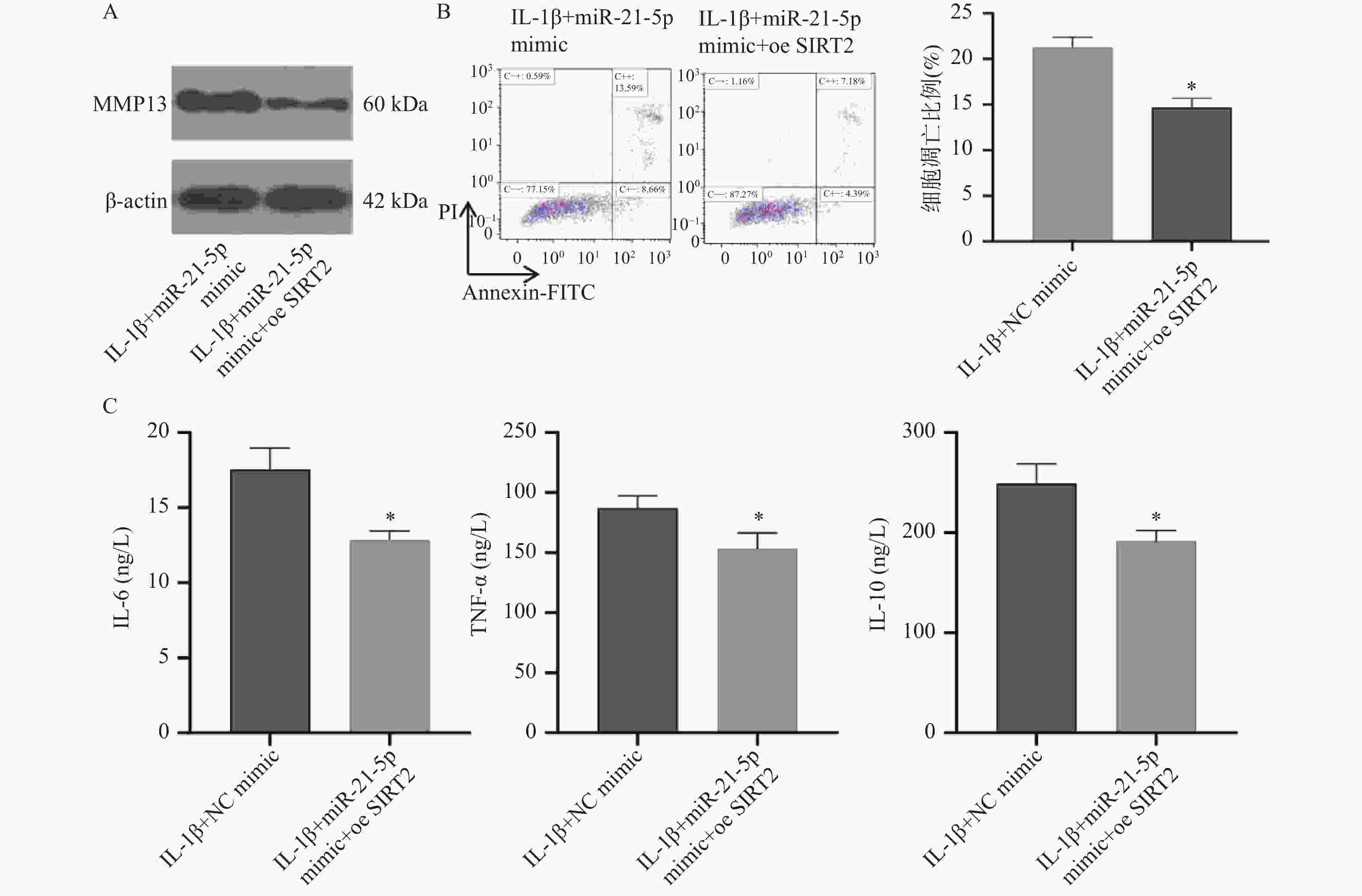
图 7 SIRT2过表达对miR-21-5p过表达软骨细胞凋亡及炎症反应的影响($\bar x \pm s $,n = 5)
A:Western blot检测MMP-13蛋白表达;B:Annexin V-FITC/PI双染流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡率;C:ELISA检测IL-6、TNF-α及IL-10的分泌水平;*P < 0.05。
Figure 7. Effects of SIRT2 overexpression on apoptosis and inflammatory response in chondrocytes overexpressing miR-21-5p ($\bar x \pm s $,n = 5)
表 1 PCR所需引物
Table 1. Primer sequences for PCR
基因名称 引物序列(5'-3') miR-21-5p 正向:5'-CTTACTTCTCTGTGTGATTTCTGTG-3'
反向:5'-ACAACCTTTCCAAAATCCATGAGGC-3'MMP13 正向:5'- AGA AGTGTGACCCAGCCCTA-3'
反向:5'-GGTCACGGGATGGATGTTCA -3'SIRT2 正向:5'-GGTGAACCAGTTGTGTTGTC-3'
反向:5'-CCGTCCTTTCCAGCAGTC-3'GAPDH 正向:5'-CCTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTA-3'
反向:5′-TCATACCAGGAAATGAGCTTGAC-3′U6 正向:5'-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3'
反向:5'-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3' -
[1] 赵奎, 潘润桑, 蓝奉军, 等. 骨关节炎中自噬与凋亡相互作用的分子机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(18): 2912-2917. doi: 10.12307/2024.058 [2] Xia B, Di C, Zhang J, et al. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis: A review of molecular mechanisms[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2014, 95(6): 495-505. doi: 10.1007/s00223-014-9917-9 [3] Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y. The Functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA Decay and Translational Repression[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2015, 25(11): 651-665. [4] Luan J, Che G, Man G, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng attenuates monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting miR-21-5p/FGF18-mediated inflammation[J]. J Food Biochem, 2022, 46(10): e14340. [5] Ma S, Zhang A, Li X, et al. miR-21-5p regulates extracellular matrix degradation and angiogenesis in TMJOA by targeting Spry1[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2020, 22(1): 99. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-2145-y [6] Qin L, Yang J, Su X, et al. The miR-21-5p enriched in the apoptotic bodies of M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles alleviates osteoarthritis by changing macrophage phenotype[J]. Genes Dis, 2022, 10(3): 1114-1129. [7] Zhu H, Yan X, Zhang M, et al. miR-21-5p protects IL-1β-induced human chondrocytes from degradation[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2019, 14(1): 118. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1160-7 [8] Qu Z A, Ma X J, Huang S B, et al. SIRT2 inhibits oxidative stress and inflammatory response in diabetic osteoarthritis[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2020, 24(6): 2855-2864. [9] Yang Q, Zhou Y, Cai P, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-23b-3p alleviates IL-1β-induced injury in chondrogenic CHON-001 cells[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2019, 13: 2503-2512. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S211051 [10] Shen K, Wang X, Wang Y, et al. miR-125b-5p in adipose derived stem cells exosome alleviates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells ferroptosis via Keap1/Nrf2/GPX4 in sepsis lung injury[J]. Redox Biol, 2023, 62: 102655. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102655 [11] Kong R, Ji L, Pang Y, et al. Exosomes from osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes promote cartilage ferroptosis and damage via delivering microRNA-19b-3p to target SLC7A11 in osteoarthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1181156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181156 [12] Liu B, Xian Y, Chen X, et al. Inflammatory fibroblast-like synoviocyte-derived exosomes aggravate osteoarthritis via enhancing macrophage glycolysis[J]. Adv Sci, 2024, 11(14): 2307338. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307338 [13] Zhang A, Ma S, Yuan L, et al. Knockout of miR-21-5p alleviates cartilage matrix degradation by targeting Gdf5 in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2020, 9(10): 689-700. doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.910.BJR-2020-0140.R1 [14] Mrosewski I, Jork N, Gorte K, et al. Regulation of osteoarthritis-associated key mediators by TNFα and IL-10: Effects of IL-10 overexpression in human synovial fibroblasts and a synovial cell line[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2014, 357(1): 207-223. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1868-y [15] Rodrigues P M, Afonso M B, Simão A L, et al. miR-21-5p promotes NASH-related hepatocarcinogenesis[J]. Liver Int, 2023, 43(10): 2256-2274. doi: 10.1111/liv.15682 [16] Xue J, Liu J, Xu B, et al. miR-21-5p inhibits inflammation injuries in LPS-treated H9c2 cells by regulating PDCD4[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(10): 11450-11460. [17] 庾珊, 肖林, 龚东平, 等. 抑制miR-153-3p通过调控Nrf2延缓椎间盘退变的调节机制[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2025, 46(5): 21-29. doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20250503 [18] Hu Q, Ecker M. Overview of MMP-13 as a promising target for the treatment of osteoarthritis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4): 1742. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041742 [19] Gan D, Tao C, Jin X, et al. Piezo1 activation accelerates osteoarthritis progression and the targeted therapy effect of artemisinin[J]. J Adv Res, 2024, 62: 105-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.09.040 [20] Zhuang H, Ren X, Jiang F, et al. Indole-3-propionic acid alleviates chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via the AhR/NF-κB axis[J]. Mol Med, 2023, 29(1): 17. doi: 10.1186/s10020-023-00614-9 [21] Zhang Y, Wang X, Li X K, et al. Sirtuin 2 deficiency aggravates ageing-induced vascular remodelling in humans and mice[J]. Eur Heart J, 2023, 44(29): 2746-2759. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad381 [22] Hu Z, Xu W, Yang X, et al. SIRT2 inhibition attenuates the vasculopathy and vision impairment via Akt signaling in retinopathy of prematurity[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2023, 233: 109547. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2023.109547 [23] Piracha Z Z, Saeed U, Kim J, et al. An alternatively spliced sirtuin 2 isoform 5 inhibits hepatitis B virus replication from cccDNA by repressing epigenetic modifications made by histone lysine methyltransferases[J]. J Virol, 2020, 94(16): e00926. [24] Ma J, Li X, Li Q, et al. Niacin regulates glucose metabolism and osteogenic differentiation via the SIRT2-C/EBPβ-AREG signaling axis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 180: 117447. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.117447 [25] Qian B, Yang Y, Tang N, et al. M1 macrophage-derived exosomes impair beta cell insulin secretion via miR-212-5p by targeting SIRT2 and inhibiting Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin pathway in mice[J]. Diabetologia, 2021, 64(9): 2037-2051. doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05489-1 [26] Yuan K, Wu Q, Yao Y, et al. Deacetylase SIRT2 inhibition promotes microglial M2 polarization through axl/PI3K/AKT to alleviate white matter injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Transl Stroke Res, 2025, 16(4): 1075-1093. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01282-5 -





 下载:
下载: