The Mechanism of miR-23 Regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway to Improve Myocardial Angiogenesis in Hypertensive Heart Failure Rats
-
摘要:
目的 探讨微小RNA-23(microRNA-23,miR-23)通过调控磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶B/哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin,PI3K/AKT/mTOR)信号通路对高血压性心力衰竭(heart failure,HF)大鼠心肌重构、纤维化及血管生成的影响机制。 方法 将40只大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、阴性对照组(antagomir-NC组)和miR-23抑制组(antagomir-23组),每组10只。采用高盐饮食诱导HF模型,并通过尾静脉注射antagomir-23进行干预。检测各组大鼠的心功能指标、心肌组织纤维化程度、细胞凋亡水平及血小板内皮细胞黏附分子-1(cluster of differentiation 31,CD31)、血管内皮生长因子(Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor,VEGF)和碱性成纤维生长因子(basic fibroblast growth factor,bFGF)等血管生成相关蛋白的表达,同时评估PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路活性;并通过双荧光素酶报告实验验证miR-23对PI3K的靶向调控。 结果 抑制miR-23可显著改善高血压性HF大鼠心功能,减少心肌纤维化与细胞凋亡,增强CD31、VEGF及bFGF的表达,并激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路(均P < 0.05)。双荧光素酶实验证实miR-23可负向调控PI3K的表达。 结论 抑制miR-23能够通过激活PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路,促进血管生成,减轻心肌损伤,从而延缓高血压性心力衰竭的进展。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the mechanisms by which miR-23 regulates the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to influence myocardial remodeling, fibrosis, and angiogenesis in hypertensive heart failure (HF) rats. Methods Forty rats were randomly divided into five groups (n = 10 per group): control group, model group, antagomir-NC group, and antagomir-23 group. The HF model was established using a high-salt diet, and intervention was performed via tail vein injection of antagomir-23. Cardiac function parameters, the degree of myocardial fibrosis, cell apoptosis levels, and the expression of angiogenesis-related proteins including CD31, VEGF, and bFGF were measured in each group. Concurrently, the activity of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway was assessed. A dual-luciferase reporter assay was conducted to confirm that miR-23 targets PI3K. Results Inhibition of miR-23 significantly improved cardiac function in hypertensive HF rats, reduced myocardial fibrosis and apoptosis, and enhanced the expression of CD31, VEGF, bFGF, and activated the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in hypertensive HF rats (all P < 0.05). The dual-luciferase assay confirmed that miR-23 negatively regulates PI3K expression. Conclusion Inhibition of miR-23 can activate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway, promote angiogenesis, reduce myocardial damage, thereby delaying the progression of hypertensive heart failure. -
Key words:
- Hypertension /
- Heart failure /
- miR-23 /
- Myocardial remodeling /
- Fibrosis /
- Angiogenesis
-
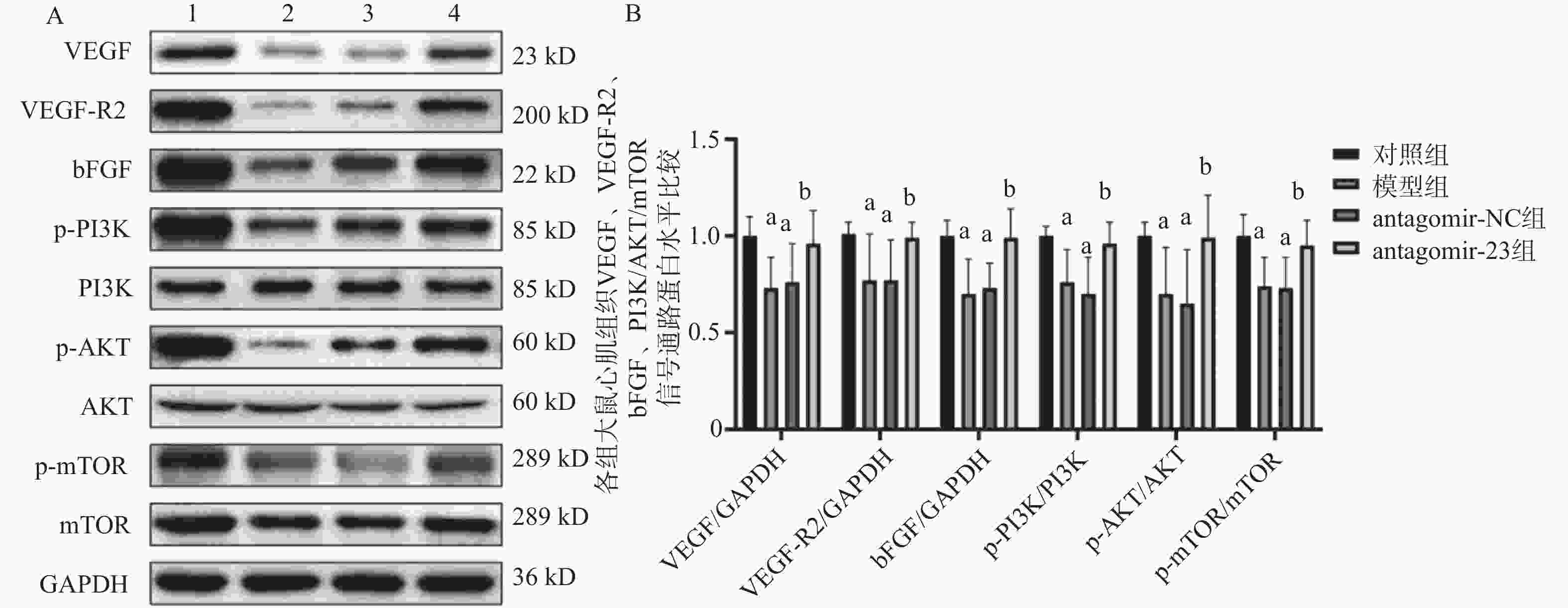
图 5 Western blot检测miR-23抑制对高血压HF大鼠心肌组织中VEGF、VEGF-R2、bFGF及PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路蛋白水平的影响
A:VEGF、VEGF-R2、bFGF及PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路蛋白印迹图;B:VEGF、VEGF-R2、bFGF及PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路蛋白表达统计图;1:对照组;2:模型组;3:antagomir-NC组;4:antagomir-23组。注:与对照组相比,aP < 0.05;与antagomir-NC组相比,bP < 0.05。
Figure 5. Western blot detection of the effects of miR-23 inhibition on protein levels of VEGF,VEGF-R2,bFGF and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in myocardial tissue of hypertensive HF rats
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences
基因 引物序列(5'-3') miR-23 F:AAACCGUT AGGGGTTC R:TTTGGCAATCCCCAAG U6 F:AAGUGGCA ACGAACCG R:TTCACCGUTGCTTGGC PI3K F:GGAATCCAGGGAAGGAAGG R:CAGTTTGGGTGGACGGAAGA 表 2 各组大鼠收缩压比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of systolic blood pressure among groups (n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 收缩压(mmHg) 对照组 134.44 ± 11.23 模型组 180.26 ± 33.09Δ antagomir-NC组 168.04 ± 29.89Δ antagomir-23组 132.33 ± 18.04# F 5.701 P 0.006* *P < 0.05;与对照组相比,ΔP < 0.05;与antagomir-NC组相比,#P < 0.05。 表 3 各组大鼠心功能指标比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of cardiac function indicators among groups(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 LVESP(mmHg) LVEDP(mmHg) +dp/dtmax(×103 mmHg/s) -dp/dtmax(×103 mmHg/s) 对照组 123.48 ± 18.99 13.65 ± 1.40 3.57 ± 0.27 3.08 ± 0.22 模型组 93.06 ± 19.21Δ 18.97 ± 4.92Δ 2.74 ± 0.74Δ 2.42 ± 0.55Δ antagomir-NC组 94.20 ± 30.64Δ 18.51 ± 2.39Δ 2.73 ± 0.75Δ 2.44 ± 0.52Δ antagomir-23组 120.10 ± 15.87# 13.47 ± 2.64# 3.42 ± 0.49# 3.16 ± 0.31# F 3.330 5.545 3.351 5.441 P 0.040* 0.006** 0.040* 0.007** *P < 0.05,**P < 0.01;与对照组相比,ΔP < 0.05;与antagomir-NC组相比,#P < 0.05。 表 4 各组大鼠CVF比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
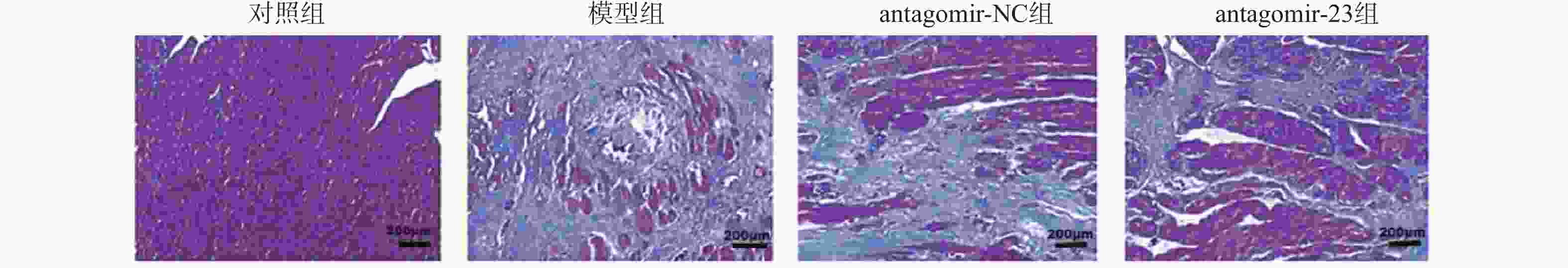
Table 4. Comparison of CVF among groups (n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 CVF(%) 对照组 1.79 ± 0.25 模型组 2.30 ± 0.33Δ antagomir-NC组 2.30 ± 0.65Δ antagomir-23组 1.76 ± 0.24# F 3.413 P 0.037* *P < 0.05;与对照组相比,ΔP < 0.05;与antagomir-NC组相比,#P < 0.05。 表 5 各组大鼠心肌细胞凋亡水平比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
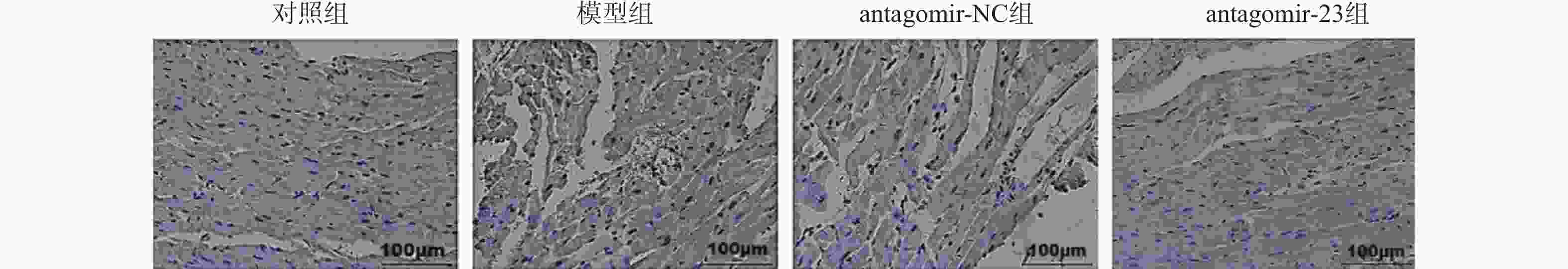
Table 5. Comparison of cardiomyocyte apoptosis levels among groups(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 凋亡指数(%) 对照组 2.28 ± 0.27 模型组 24.20 ± 4.31ΔΔΔ antagomir-NC组 23.78 ± 4.32ΔΔΔ antagomir-23组 16.07 ± 4.35# F 44.839 P <0.001*** ***P < 0.001;与对照组相比,ΔΔΔP < 0.001;与antagomir-NC组相比,#P < 0.05。 表 6 各组大鼠心肌CD31表达水平比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
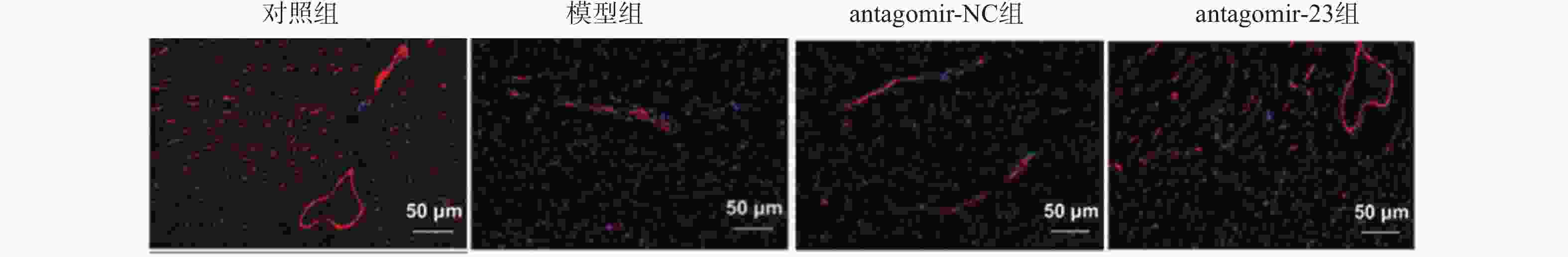
Table 6. Comparison of myocardial CD31 expression levels among groups(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 CD31表达率(%) 对照组 3.66 ± 0.45 模型组 2.86 ± 0.39ΔΔ antagomir-NC组 2.91 ± 0.57ΔΔ antagomir-23组 3.52 ± 0.70# F 3.498 P 0.035* *P < 0.05;与对照组相比,ΔΔP < 0.01;与antagomir-NC组相比,#P < 0.05。 表 7 各组大鼠心肌组织miR-23表达量比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 7. Comparison of myocardial miR-23 expression levels among groups (n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 miR-23 对照组 1.00 ± 0.10 模型组 1.27 ± 0.28Δ antagomir-NC组 1.37 ± 0.35Δ antagomir-23组 1.03 ± 0.14# F 3.267 P 0.043* *P < 0.05;与对照组相比,ΔP < 0.05;与antagomir-NC组相比,#P < 0.05。 表 8 荧光素酶活性比较(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 8. Comparison of luciferase activity(n = 6,$ \bar x \pm s $)
组别 荧光素酶活性 miR-NC+PI3K-WT组 1.02 ± 0.08 miR-23 mimic+PI3K-WT组 0.76 ± 0.18Δ miR-NC+PI3K-MUT组 0.99 ± 0.12 miR-23 mimic+PI3K-MUT组 0.99 ± 0.20 F 3.701 P 0.029* *P < 0.05;与miR-NC+PI3K-WT组相比,ΔP < 0.05。 -
[1] Groenewegen A, Rutten F H, Mosterd A, et al. Epidemiology of heart failure[J]. European J Heart Fail, 2020, 22(8): 1342-1356. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1858 [2] Pezel T, Viallon M, Croisille P, et al. Imaging interstitial fibrosis, left ventricular remodeling, and function in stage a and B heart failure[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2021, 14(5): 1038-1052. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2020.05.036 [3] Yan F, Hu X, He L, et al. ADAM33 silencing inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell migration and regulates cytokine secretion in airway vascular remodeling via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. Can Respir J, 2022, 2022: 8437348. [4] Siasos G, Bletsa E, Stampouloglou P K, et al. microRNAs in cardiovascular disease[J]. Hellenic J Cardiol, 2020, 61(3): 165-173. doi: 10.1016/j.hjc.2020.03.003 [5] Lombari P, Mallardo M, Petrazzuolo O, et al. miRNA-23a modulates sodium-hydrogen exchanger 1 expression: Studies in medullary thick ascending limb of salt-induced hypertensive rats[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2023, 38(3): 586-598. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfac232 [6] Lu M, Xu Y, Wang M, et al. microRNA-23 inhibition protects the ischemia/reperfusion injury via inducing the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2019, 12(3): 1060-1069. [7] Wang S, Olson E N. AngiomiRs—key regulators of angiogenesis[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2009, 19(3): 205-211. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.002 [8] Shu X, Zhan P P, Sun L X, et al. BCAT1 activates PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and contributes to the angiogenesis and tumorigenicity of gastric cancer[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 659260. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.659260 [9] Ahmad A, Nawaz M I. Molecular mechanism of VEGF and its role in pathological angiogenesis[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2022, 123(12): 1938-1965. doi: 10.1002/jcb.30344 [10] Sainsily X, Coquerel D, Giguère H, et al. Elabela protects spontaneously hypertensive rats from hypertension and cardiorenal dysfunctions exacerbated by dietary high-salt intake[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 709467. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.709467 [11] Wang Y, Yang L Z, Yang D G, et al. miR-21 antagomir improves insulin resistance and lipid metabolism disorder in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus rats[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2020, 9(2): 394-404. doi: 10.21037/apm.2020.02.28 [12] Fuchs F D, Whelton P K. High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease[J]. Hypertension, 2020, 75(2): 285-292. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14240 [13] Stacey R B, Hundley W G. Integrating measures of myocardial fibrosis in the transition from hypertensive heart disease to heart failure[J]. Curr Hypertens Rep, 2021, 23(4): 22. doi: 10.1007/s11906-021-01135-8 [14] Wang N, Tan H Y, Feng Y G, et al. microRNA-23a in human cancer: Its roles, mechanisms and therapeutic relevance[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2018, 11(1): E7. doi: 10.3390/cancers11010007 [15] Jiang K, Teng G D, Chen Y Q. microRNA-23 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by targeting the MEF2C-mediated MAPK signaling pathway[J]. J Gene Med, 2020, 22(10): e3216. doi: 10.1002/jgm.3216 [16] Liu L, Cheng Z, Yang J. miR-23 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in coronary heart disease[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2018, 214(11): 1873-1878. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2018.09.004 [17] Friso S, Carvajal C, Pizzolo F, et al. Epigenetics and arterial hypertension: evidences and perspectives [M]. In: Translating Epigenetics to the Clinic. Elsevier, 2017: 159–184. [18] Yang Z, Chen H, Si H, et al. Serum miR-23a, a potential biomarker for diagnosis of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes[J]. Acta Diabetol, 2014, 51(5): 823-831. doi: 10.1007/s00592-014-0617-8 [19] Liang B, Leenen F H. Prevention of salt induced hypertension and fibrosis by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in Dahl S rats[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2007, 152(6): 903-914. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707472 [20] Rincón L M, Rodríguez-Serrano M, Conde E, et al. Serum microRNAs are key predictors of long-term heart failure and cardiovascular death after myocardial infarction[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2022, 9(5): 3367-3379. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13919 [21] Di Y, Zhang D, Hu T, et al. miR-23 regulate the pathogenesis of patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8(7): 11759-11769. [22] Yu R B, Li K, Wang G, et al. miR-23 enhances cardiac fibroblast proliferation and suppresses fibroblast apoptosis via targeting TGF-β1 in atrial fibrillation[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2019, 23(10): 4419-4424. [23] Wang L, Li Q, Diao J, et al. miR-23a is involved in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by directly targeting CX43 and regulating mitophagy[J]. Inflammation, 2021, 44(4): 1581-1591. doi: 10.1007/s10753-021-01443-w [24] Dhumale P, Nielsen J V, Hansen A C S, et al. CD31 defines a subpopulation of human adipose-derived regenerative cells with potent angiogenic effects[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13: 14401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41535-1 [25] Martins B R, Pinto T S, da Costa Fernandes C J, et al. PI3K/AKT signaling drives titanium-induced angiogenic stimulus[J]. J Mater Sci Mater Med, 2021, 32(1): 18. doi: 10.1007/s10856-020-06473-8 -





 下载:
下载: