RBBP7 Promotes the Malignant Progression and Radioresistance of Esophageal Cancer through Hippo Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
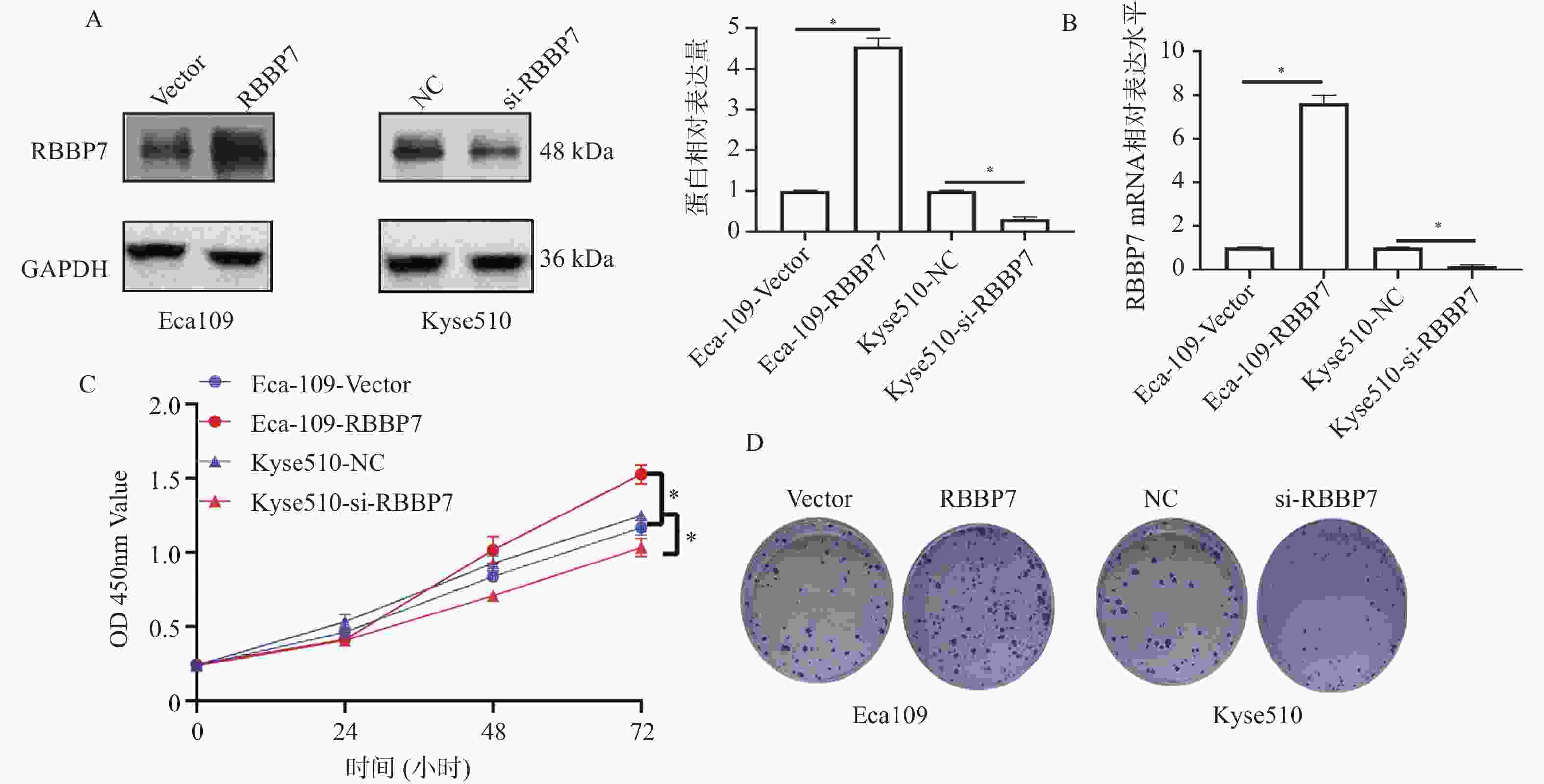
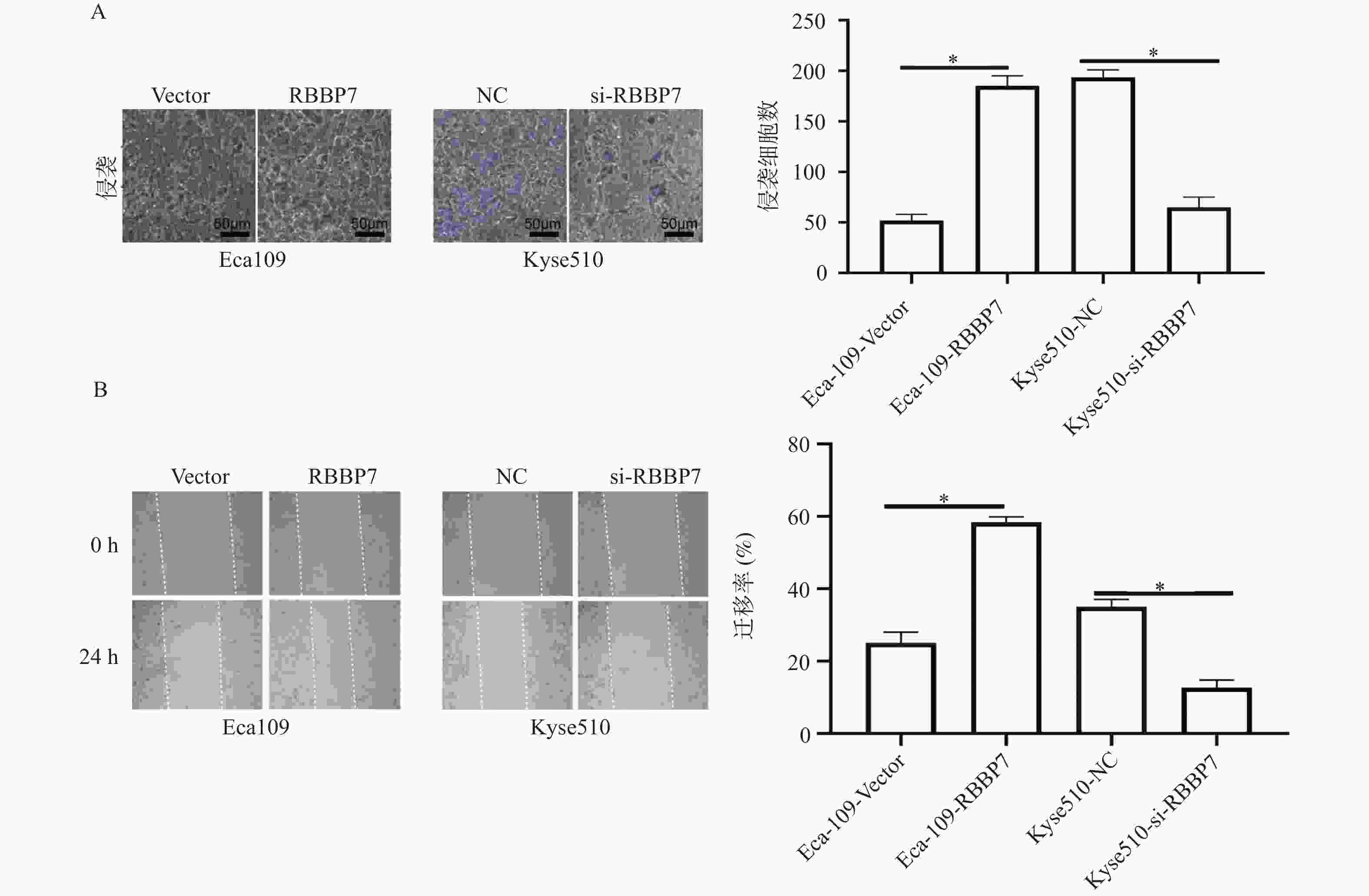
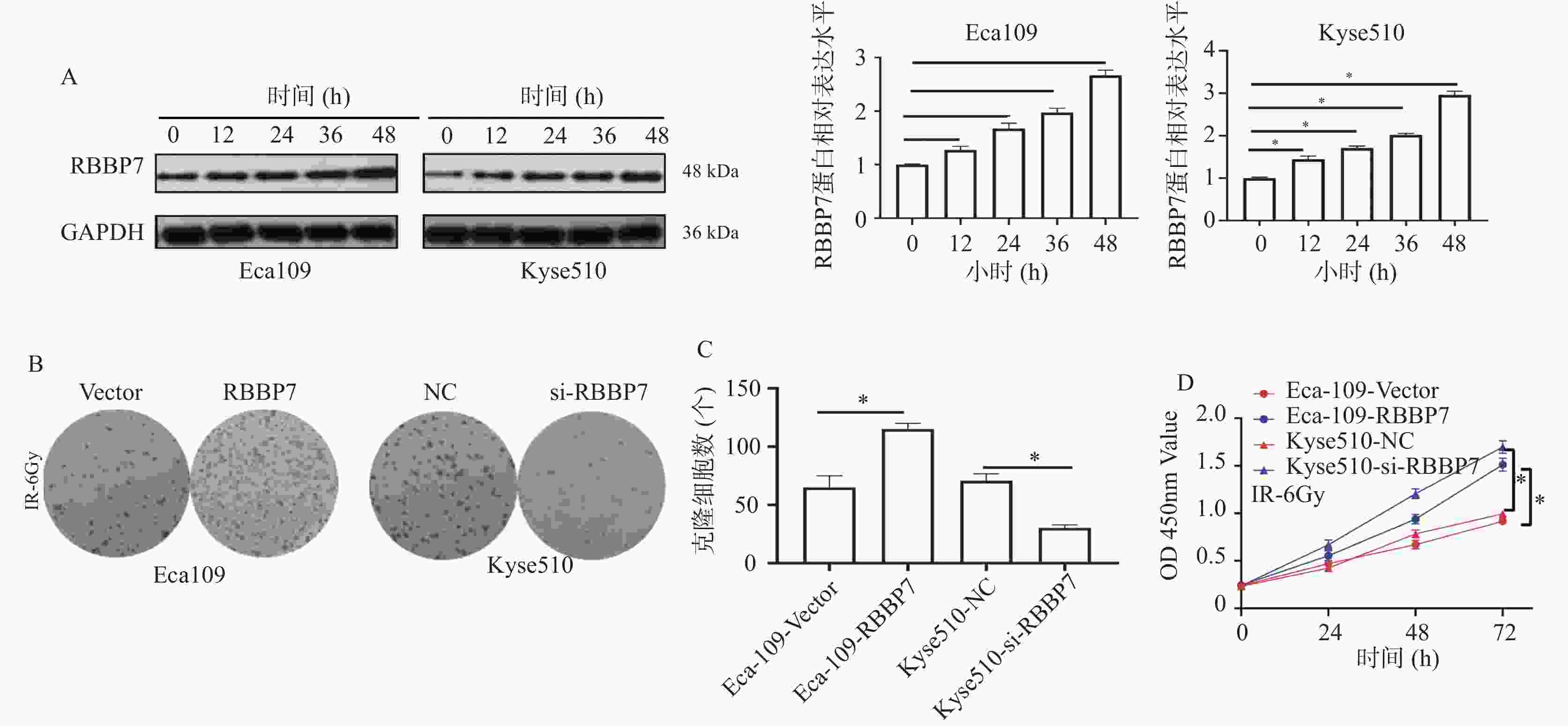
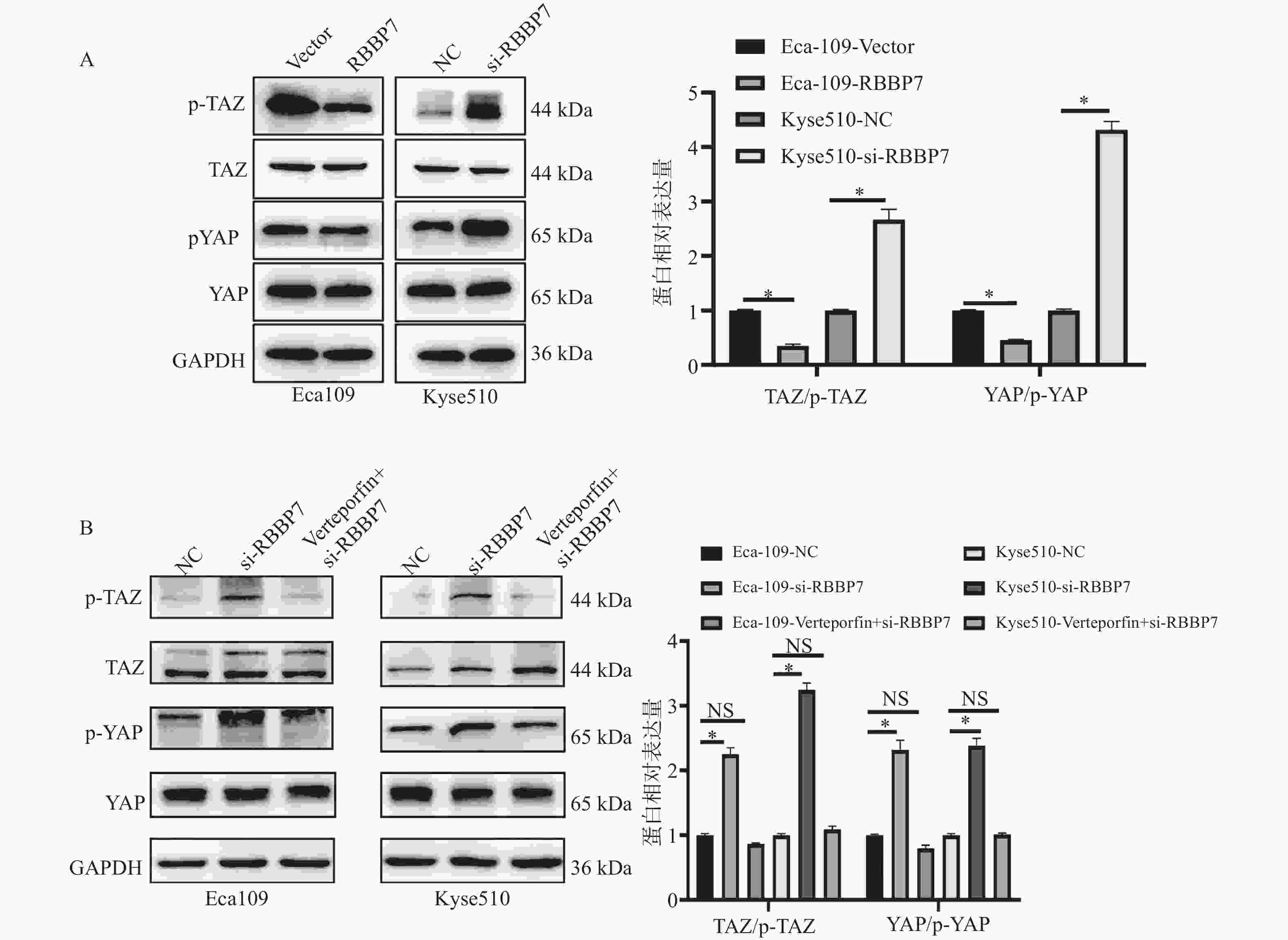
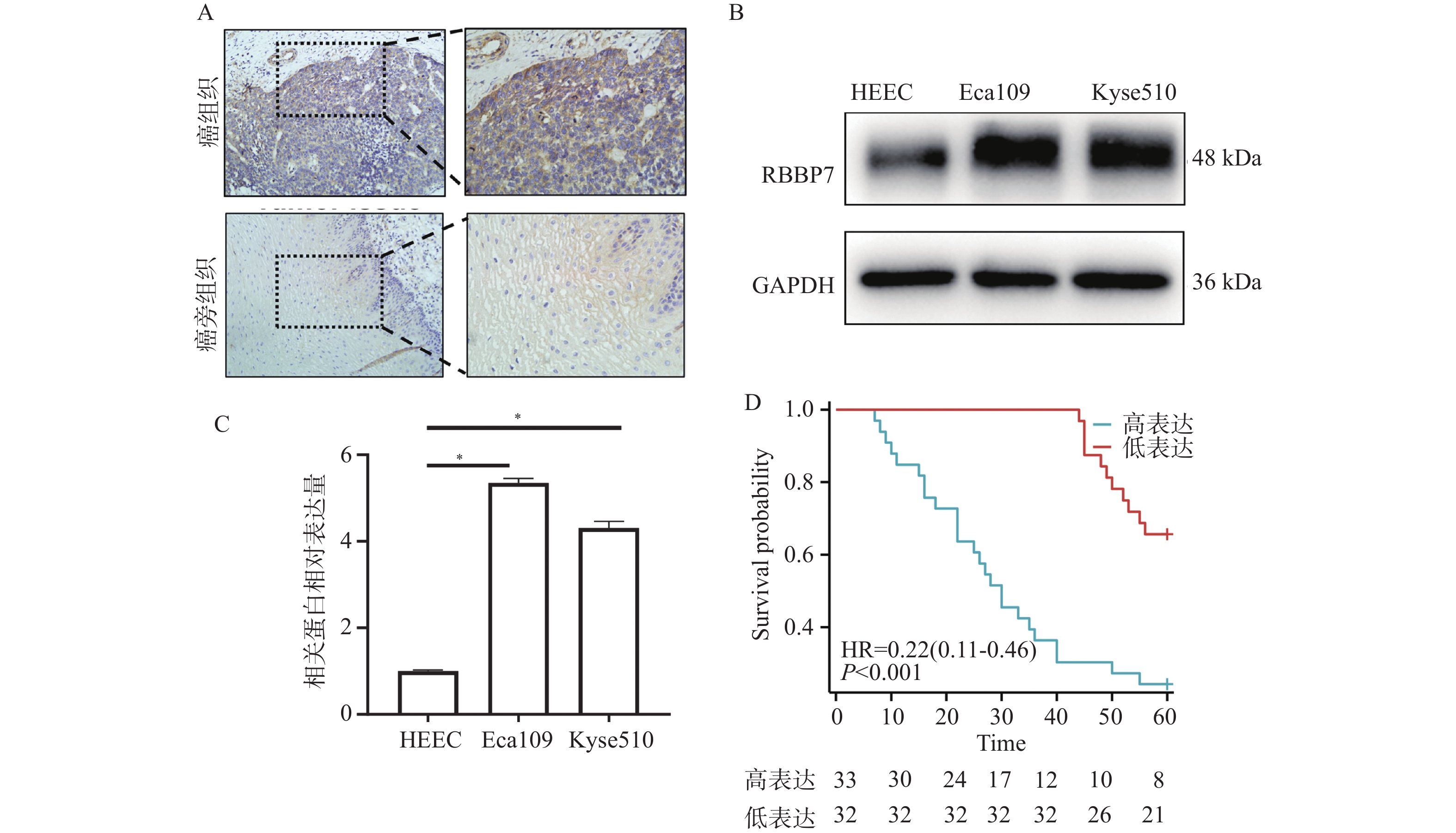
目的 探讨视网膜母细胞瘤结合蛋白7(retinoblastoma-binding protein 7, RBBP7)在食管癌中的表达及影响其进展的分子机制。 方法 收集2018年1月至2019年12月期间蚌埠医科大学附属皖北煤电集团总医院65例结食管癌根治术患者的肿瘤标本及相应的癌旁正常组织标本,通过免疫组化检测RBBP7在食管癌组织中的表达,并进行临床相关性分析。选取Eca109和Kyse510食管癌细胞株利用蛋白印迹实验检测RBBP7在食管癌细胞中的表达水平。通过转染技术将实验分为 Vector组、RBBP7组、NC组、si-RBBP7组。分别通过CCK-8实验,克隆形成实验,Transwell小室实验,划痕实验,蛋白印迹实验,检测RBBP7对食管癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移和放射抵抗的影响及机制。 结果 临床样本免疫组化及食管癌细胞株蛋白印迹实验结果显示,相较于正常癌旁组织,RBBP7在食管癌中高表达(P < 0.05),并且RBBP7高表达食管癌患者预后较差(P < 0.05)。通过体外实验CCK-8及克隆形成实验发现过表达RBBP7促进食管癌细胞增殖(P < 0.05)。Transwell实验及划痕实验发现过表达RBBP7促进食管癌细胞侵袭、迁移及放射抵抗的发生(P < 0.05),反之则抑制食管癌细胞增殖、侵袭、迁移及放射抵抗(P < 0.05)。蛋白印迹实验结果显示,相较于Vector对照组,过表达RBBP7可能通过激活Hippo信号通路调节食管癌的恶性进展及放射抵抗发生(P < 0.05)。 结论 RBBP7通过Hippo信号通路促进食管癌的发展和放射抵抗性。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression of retinoblastoma-binding protein 7 (RBBP7) in esophageal cancer and its molecular mechanism affecting its progression. Methods The tumor specimens and corresponding adjacent normal tissue specimens of 65 patients with esophageal cancer undergoing radical resection in the General Hospital of Wanbei Coal and Electricity Group Affiliated to Bengbu Medical University from January 2018 to December 2019 were collected. The expression of RBBP7 in esophageal cancer tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry, and the clinical correlation was analyzed. Eca109 and Kyse510 esophageal cancer cell lines were selected to detect the expression of RBBP7 in esophageal cancer cells by Western blot. The experiments were divided into Vector group, RBBP7 group, NC group and si-RBBP7 group by transfection technology. CCK-8 assay, colony formation assay, Transwell assay, wound healing assay and Western blot were used to detect the effect of RBBP7 on the proliferation, invasion, migration and radioresistance of esophageal cancer cells and its mechanism. Results The results of immunohistochemistry in clinical samples and Western blot in esophageal cancer cell lines showed that RBBP7 was highly expressed in esophageal cancer tissues compared with normal adjacent tissues (P < 0.05), and esophageal cancer patients with high expression of RBBP7 had a poor prognosis (P < 0.05). In the mechanism study, we found that overexpression of RBBP7 promoted the proliferation of esophageal cancer cells by CCK-8 and colony formation assay in vitro (P < 0.05). Overexpression of RBBP7 promoted the invasion, migration, and radioresistance of esophageal cancer cells (P < 0.05), and vice versa inhibited the proliferation, invasion, migration, and radioresistance of esophageal cancer cells (P < 0.05). The results of Western blot showed that compared with the Vector control group, overexpression of RBBP7 may regulate the malignant progression and radioresistance of esophageal cancer by activating Hippo signaling pathway (P < 0.05). Conclusion RBBP7 promotes the development and radioresistance of esophageal cancer through Hippo signaling pathway -
Key words:
- RBBP7 /
- Radiation resistance /
- Esophageal cancer /
- The Hippo signaling pathway
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequence
基因名称 序列(5'→3') RBBP7 F:ATGGCGAGTAAAGAGATGTT R:TTAAGATCCTTGTCCCTCCA GAPDH F:GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC R:TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA 表 2 RBBP7在食管癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达水平[n(%)]
Table 2. The expression level of RBBP7 in esophageal cancer tissues and adjacent tissues[n(%)]
RBBP7表达 癌组织(n=65) 癌旁组织(n=65) χ2 P 阳性表达 55(84.6) 10(15.4) 54.393 <0.001* 阴性表达 13(20.0) 52(80.0) *P < 0.05。 表 3 食管癌患者RBBP7表达与临床资料的关系[n]
Table 3. Relationship between RBBP7expression and clinical data in patients with esophageal cancer [n]
特征 n RBBP7 表达 χ2 P 高 低 性别 0.758 0.384 男 32 18 14 女 33 15 18 年龄(岁) 0.015 0.903 <60 32 16 16 ≥60 33 17 16 吸烟 7.099 0.008* 有 27 19 8 无 38 14 24 分化程度 0.025 0.875 低分化 25 13 12 中高分化 40 20 20 肿瘤大小(cm) 9.608 0.002* ≤4 32 10 22 >4 33 23 10 TNM 分期 11.555 0.001* Ⅰ-Ⅱ 37 12 25 Ⅲ-Ⅳ 28 21 7 淋巴结转移 9.674 0.002* 有 31 22 9 无 34 11 23 远处转移 10.347 0.001* 有 25 19 6 无 30 14 26 位置 0.393 0.531 上中部 31 17 14 下部 34 16 18 *P < 0.05。 表 4 不同辐射量对食管癌细胞生存率影响($\bar x \pm s $)
Table 4. Effect of different radiation doses on survival rate of esophageal cancer cells ($\bar x \pm s $)
辐射量 Eca-109-Vector Eca-109-RBBP7 t P Kyse510-NC Kyse510-si-RBBP7 t P 0 1.006 ± 0.005 0.995 ± 0.047 0.403 0.725 1.000 ± 0.007 0.988 ± 0.044 0.467 0.685 2 0.870 ± 0.009 0.856 ± 0.033 0.709 0.543 0.782 ± 0.009 0.789 ± 0.034 0.345 0.760 4 0.508 ± 0.015 0.517 ± 0.033 0.430 0.689 0.450 ± 0.037 0.321 ± 0.009 5.868 0.021* 6 0.204 ± 0.015 0.390 ± 0.007 19.462 <0.001* 0.204 ± 0.017 0.109 ± 0.011 8.126 0.001* 8 0.019 ± 0.007 0.248 ± 0.007 40.067 <0.001* 0.082 ± 0.008 0.001 ± 0.001 17.402 0.003* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Xia C, Dong X, Li H, et al. Cancer statistics in China and United States, 2022: Profiles, trends, and determinants[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135(5): 584-590. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002108 [2] Kato H, Nakajima M. Treatments for esophageal cancer: A review[J]. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2013, 61(6): 330-335. doi: 10.1007/s11748-013-0246-0 [3] Barker H E, Paget J T, Khan A A, et al. The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy: Mechanisms of resistance and recurrence[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2015, 15(7): 409-425. doi: 10.1038/nrc3958 [4] Harrington K J, Billingham L J, Brunner T B, et al. Guidelines for preclinical and early phase clinical assessment of novel radiosensitisers[J]. Br J Cancer, 2011, 105(5): 628-639. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.240 [5] Luo Y, Mao Q, Wang X, et al. Radiotherapy for esophageal carcinoma: Dose, response and survival[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2018, 10: 13-21. [6] Cohen D J, Leichman L. Controversies in the treatment of local and locally advanced gastric and esophageal cancers[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2015, 33(16): 1754-1759. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.7765 [7] He H, Kong S, Liu F, et al. Rbbp7 is required for uterine stromal decidualization in mice[J]. Biol Reprod, 2015, 93(1): 13. [8] Wang R, Huang Z, Lin Z, et al. Hypoxia-induced RBBP7 promotes esophagus cancer progression by inducing CDK4 expression[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2022, 54(2): 179-186. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2021027 [9] Guo L, Xia Y, Li H, et al. FIT links c-Myc and P53 acetylation by recruiting RBBP7 during colorectal carcinogenesis[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2023, 30(8): 1124-1133. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00624-z [10] Barreiro-Alonso A, Lamas-Maceiras M, Lorenzo-Catoira L, et al. HMGB1 protein interactions in prostate and ovary cancer models reveal links to RNA processing and ribosome biogenesis through NuRD, THOC and septin complexes[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2021, 13(18): 4686. doi: 10.3390/cancers13184686 [11] 方正华, 朱琛, 杜鸣宇, 等. 长链非编码RNA LINC01006在食管癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2025, 33(5): 764-771. [12] Song Z, Wei Z, Wang Q, et al. The role of DOT1L in the proliferation and prognosis of gastric cancer[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(1): BSR20193515. doi: 10.1042/BSR20193515 [13] 郭东栋, 李晓艳, 苗雄伟. 预后营养指数、D-D及miRNA-21水平对食管癌患者预后的评估及对其生存情况的预测价值分析[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2025, 24(09): 921-925. [14] 宋早智, 王庆康, 孙家和, 等. DOT1L在胃癌组织中的表达及其与预后的相关性[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2019, 35(22): 3498-3502. [15] Siegel R L, Miller K D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020[J]. CA A Cancer J Clinicians, 2020, 70(1): 7-30. [16] Li J, Li H, Zeng H, et al. Trends in high-risk rates and screening rates for the population-based cancer screening program on esophageal, stomach and liver cancer in China, 2010-2016[J]. J Natl Cancer Cent, 2021, 1(3): 101-107. [17] Zhang S, Guo J, Zhang H, et al. Gliotoxin induced ferroptosis by downregulating SUV39H1 expression in esophageal cancer cells[J]. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov, 2023, 18(3): 397-407. doi: 10.2174/1574892817666220905114120 [18] Chen L, Luo C, Xu Y, et al. Circ_0058063 regulates the development of esophageal cancer through miR-377-3p/HOXA1 axis[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2023, 34(4): 495-506. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001454 [19] Yi Q, Zhao Y, Xia R, et al. TRIM29 hypermethylation drives esophageal cancer progression via suppression of ZNF750[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 191. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01491-1 -





 下载:
下载: