Correlation Between Expression of Serum LncRNA TUG1 and MiR-29a-3p and the Severity and Prognosis in Patients with Severe Pneumonia
-
摘要:
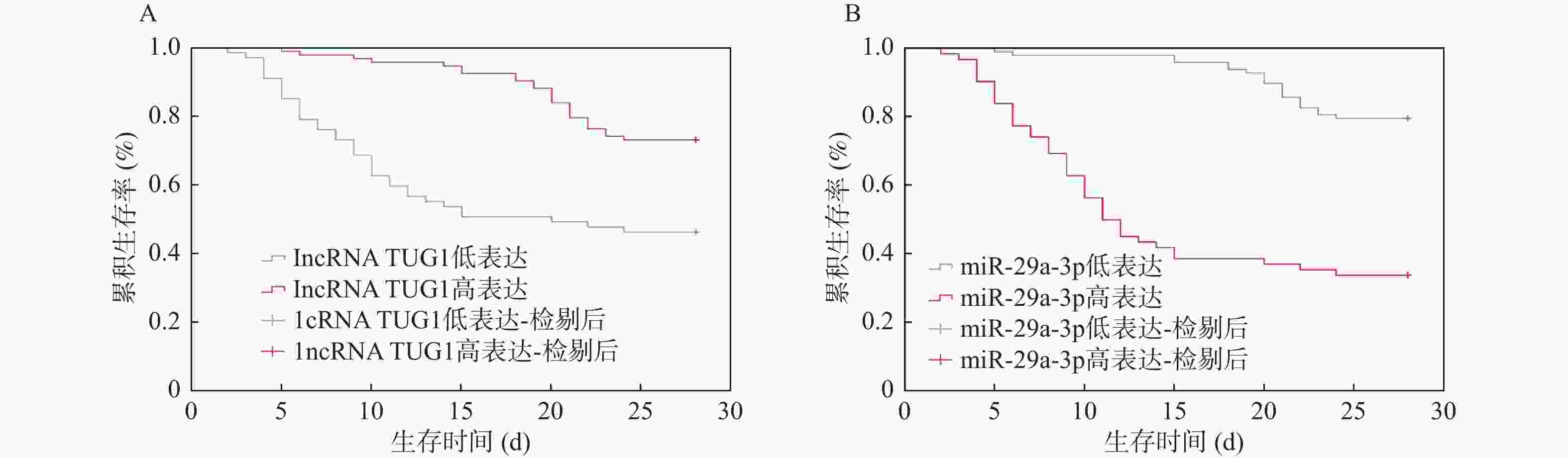
目的 分析血清长非编码 RNA牛磺酸上调基因1(long non-coding RNA taurine upregulated gene 1,lncRNA TUG1)、微小RNA-(microRNA,miRNA)-29a-3p水平变化与重症肺炎(severe pneumonia,SP)患者病情严重程度的关系及对预后的影响。 方法 选取2022年3月至2024年3月期间在南京医科大学第四附属医院接受治疗的160例SP患者作为研究对象。收集患者年龄、性别、基础疾病等基本资料,依据肺炎严重指数(severity index of pneumonia,PSI)评分将患者分为低危组(n = 20)、中危组(n = 58)、高危组(n = 82),实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction,qRT-PCR)法检测lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p表达;患者入重症监护病房(intensive care unit,ICU) 28 d后根据转归效果分为不良组和良好组,多元有序及多因素Logistic模型分析病情及预后影响因素并校正;血清lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p预测病情及预后价值以受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线表示,Pearson法分析相关性;Kaplan-Meier法进行生存分析。 结果 高危组氧合指数、lncRNA TUG1低于中危组、低危组,白介素(interleukin,IL)-6、肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)、C反应蛋白、miR-29a-3p高于中危组、低危组(P < 0.05);中危组lncRNA TUG1低于低危组,miR-29a-3p高于低危组(P < 0.05)。不良组氧合指数、lncRNA TUG1低于良好组,IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白、降钙素原、miR-29a-3p高于良好组(P < 0.05)。相关性分析表明,lncRNA TUG1与氧合指数正相关,与IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白、miR-29a-3p均负相关,miR-29a-3p与氧合指数负相关,与IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白均正相关(P < 0.05)。lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p联合对病情、预后预测的曲线下面积(area under the curve AUC)为0.945、0.935,高于二者单独使用(P < 0.05)。Logistic显示,IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白均是SP患者病情、预后的影响因素,经多重校正后lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p均是SP患者病情、预后的影响因素(P < 0.05)。Kaplan-Meier分析表明,血清lncRNA TUG1高表达患者28 d生存率(68/93,73.12%)高于血清lncRNA TUG1低表达者(31/67,46.27%);血清miR-29a-3p高表达患者28 d生存率(21/62,33.87%)低于血清miR-29a-3p低表达者(78/98,79.59%)。 结论 SP患者血清lncRNA TUG1低表达、miR-29a-3p高表达,二者可能是高危SP及预后不良的可靠预测因子。 -
关键词:
- 重症肺炎 /
- 长非编码 RNA牛磺酸上调基因1 /
- 微小RNA-29a-3p /
- 病情
Abstract:Objective To analyze the correlation between the expression levels of serum long non-coding RNA taurine up-regulated gene 1 (lncRNA TUG1) and microRNA - (miR) -29A-3p and the severity and prognosis of the patients with severe pneumonia (SP) . Methods A total of 160 SP patients who received treatment in the Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from March 2022 to March 2024, were enrolled as the study subjects. Basic information such as age, gender, and underlying diseases were collected. The patients were stratified into low-risk (n = 20), moderate-risk (n = 58), and high-risk groups (n = 82) based on the pneumonia severity index (PSI) score. The expression levels of lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p in serum using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) . The patients were divided into unfavorable and favorable outcome groups based on their 28-day post-ICU admission outcomes. Multivariate ordinal and multivariable Logistic regression models were used to analyze the influencing factors of the disease severity and prognosis, adjusted for confounders. The values of serum lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p in predicting disease condition and prognosis were represented by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and correlation analysis was performed using the Pearson method; survival analysis was performed by Kaplan-Meier method. Results The high-risk group had lower oxygenation index and lncRNA TUG1 than the moderate-risk and low-risk groups, and higher interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, C-reactive protein, and miR-29a-3p than the moderate-risk and low-risk groups (P < 0.05); the moderate-risk group had lower lncRNA TUG1 than the low-risk group, and higher miR-29a-3p than the low-risk group (P < 0.05). Compared to the favorable group, the unfavorable group had lower oxygenation index and lncRNA TUG1, and higher IL-6, TNF-α, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and miR-29a-3p (P < 0.05). Correlation analysis indicated that lncRNA TUG1 was positively correlated with the oxygenation index, while IL-6, TNF-α, C-reactive protein, and miR-29a-3p were all negatively correlated. miR-29a-3p was negatively correlated with the oxygenation index and positively correlated with IL-6, TNF-α, and C-reactive protein (P < 0.05). The area under the curve (AUC) values of the combination of lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p for predicting disease condition and prognosis were 0.945 and 0.935, respectively, which were higher than those of single prediction (P < 0.05). Logistic analysis showed that IL-6, TNF-α, and C-reactive protein were all influencing factors for the condition and prognosis of patients with SP. After multiple adjustments, lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p were both influencing factors for the condition and prognosis of patients with SP (P < 0.05). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the patients with high lncRNA TUG1 expression had significantly higher 28-day survival rate (68/93, 73.12%) compared to those with low expression (31/67, 46.27%), while the patients with high miR-29a-3p expression had lower 28-day survival rate (21/62, 33.87%) compared to those with low miR-29a-3p expression (78/98, 79.59%). Conclusion Low expression of serum lncRNA TUG1 combined with high expression of miR-29a-3p in patients with SP may be reliable predictors for high-risk SP and poor prognosis. -
表 1 不同病情SP患者资料及lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p比较[($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 1. Data of SP patients with different conditions and comparison of lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p [($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
项目 低危组(n = 20) 中危组(n = 58) 高危组(n = 82) χ2/F P 年龄(岁) 59.42 ± 10.64 58.37 ± 10.19 61.25 ± 11.37 1.223 0.297 性别 0.192 0.908 男 12(60.00) 36(62.07) 53(64.63) 女 8(40.00) 22(37.93) 29(35.37) 吸烟 6(30.00) 17(29.31) 26(31.71) 0.096 0.953 饮酒 3(15.00) 10(17.24) 16(19.51) 0.268 0.874 高血压 7(35.00) 22(37.93) 33(40.24) 0.212 0.899 糖尿病 3(15.00) 11(18.97) 16(19.51) 0.218 0.897 感染类型 0.684 0.953 细菌 15(75.00) 46(79.31) 63(76.83) 病毒 2(10.00) 5(8.62) 10(12.20) 真菌 3(15.00) 7(12.07) 9(10.97) 心率(次/min) 86.19 ± 16.13 87.34 ± 15.29 88.47 ± 16.38 0.198 0.821 收缩压(mmHg) 126.59 ± 21.23 127.32 ± 22.33 127.85 ± 23.06 0.028 0.972 舒张压(mmHg) 75.13 ± 8.92 77.25 ± 8.76 78.19 ± 9.12 0.963 0.384 PaO2(mmHg) 81.34 ± 15.34 79.46 ± 13.39 78.32 ± 12.85 0.441 0.644 PaCO2(mmHg) 37.26 ± 8.75 37.85 ± 9.12 36.32 ± 7.65 0.583 0.560 氧合指数 188.24 ± 35.62 185.35 ± 36.17 153.77 ± 31.19△# 18.526 <0.001* 白细胞计数(×109/L) 11.12 ± 2.38 11.38 ± 2.42 12.04 ± 2.58 1.770 0.174 IL-6(pg/mL) 53.14 ± 8.56 56.29 ± 9.17 74.31 ± 11.28△# 68.154 <0.001* TNF-α(pg/mL) 25.86 ± 3.56 27.37 ± 5.29 38.49 ± 8.71△# 52.398 <0.001* C反应蛋白(mg/L) 120.35 ± 34.56 124.47 ± 36.74 148.96 ± 39.17△# 9.235 <0.001* 降钙素原(ng/mL) 4.43 ± 0.26 4.49 ± 0.28 4.52 ± 0.32 0.759 0.470 lncRNA TUG1/GAPDH 0.85 ± 0.21 0.56 ± 0.17a 0.27 ± 0.07△# 178.613 <0.001* miR-29a-3p/U6 1.42 ± 0.34 1.93 ± 0.46a 2.64 ± 0.68△# 48.768 <0.001* *P < 0.05;与低危组比较,△P < 0.05;与中危组比较,#P < 0.05。 表 2 不同感染类型患者血清lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of serum lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p in patients with different infection types ($ \bar x \pm s $)
感染类型 n lncRNA TUG1/GAPDH miR-29a-3p/U6 细菌 124 0.45 ± 0.13 2.23 ± 0.62 病毒 17 0.45 ± 0.12 2.22 ± 0.66 真菌 19 0.43 ± 0.14 2.24 ± 0.69 F 0.198 0.004 P 0.821 0.996 表 3 血清lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p与氧合指数、IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白的相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of serum lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p with oxygenation index,IL-6,TNF-α,and C-reactive protein
项目 lncRNA TUG1 miR-29a-3p r P r P 氧合指数 0.453 <0.001* −0.362 <0.001* IL-6 −0.345 <0.001* 0.394 <0.001* TNF-α −0.412 <0.001* 0.385 <0.001* C反应蛋白 −0.336 <0.001* 0.429 <0.001* miR-29a-3p −0.450 <0.001* − − *P < 0.05。 表 4 多元有序Logistic回归分析SP患者病情影响因素
Table 4. Multivariate ordinal Logistic regression analysis of the influencing factors on disease severity in SP patients
影响因素 B SE Wald P OR 95%CI 反应变量Y 常数项1 0.863 0.329 6.886 0.009* − − 常数项1 1.137 0.238 22.805 <0.001* − − 解释变量X IL-6 0.597 0.213 7.861 0.005* 1.817 1.197~2.758 TNF-α 0.759 0.128 35.155 <0.001* 2.136 1.662~2.745 C反应蛋白 0.661 0.228 8.408 0.004* 1.937 1.239~3.028 lncRNA TUG1 −0.548 0.092 35.504 <0.001* 0.578 0.483~0.692 miR-29a-3p 0.970 0.382 6.448 0.011* 2.638 1.248~5.578 模型1 lncRNA TUG1 −0.524 0.071 54.520 <0.001* 0.592 0.515~0.680 miR-29a-3p 0.883 0.269 10.774 0.001* 2.418 1.427~4.097 模型2 lncRNA TUG1 −0.488 0.085 32.929 <0.001* 0.614 0.520~0.725 miR-29a-3p 0.828 0.115 51.854 <0.001* 2.289 1.827~2.868 模型3 lncRNA TUG1 −0.420 0.098 18.374 <0.001* 0.657 0.542~0.796 miR-29a-3p 0.662 0.225 8.658 0.003* 1.938 1.247~3.012 *P < 0.05;模型1表示校正IL-6后,模型2表示校正IL-6、TNF-α后,模型3表示校正IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白后。 表 5 lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p单独及联合预测患者病情的价值
Table 5. The predictive value of lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p alone and in combination for disease severity in pneumonia patients
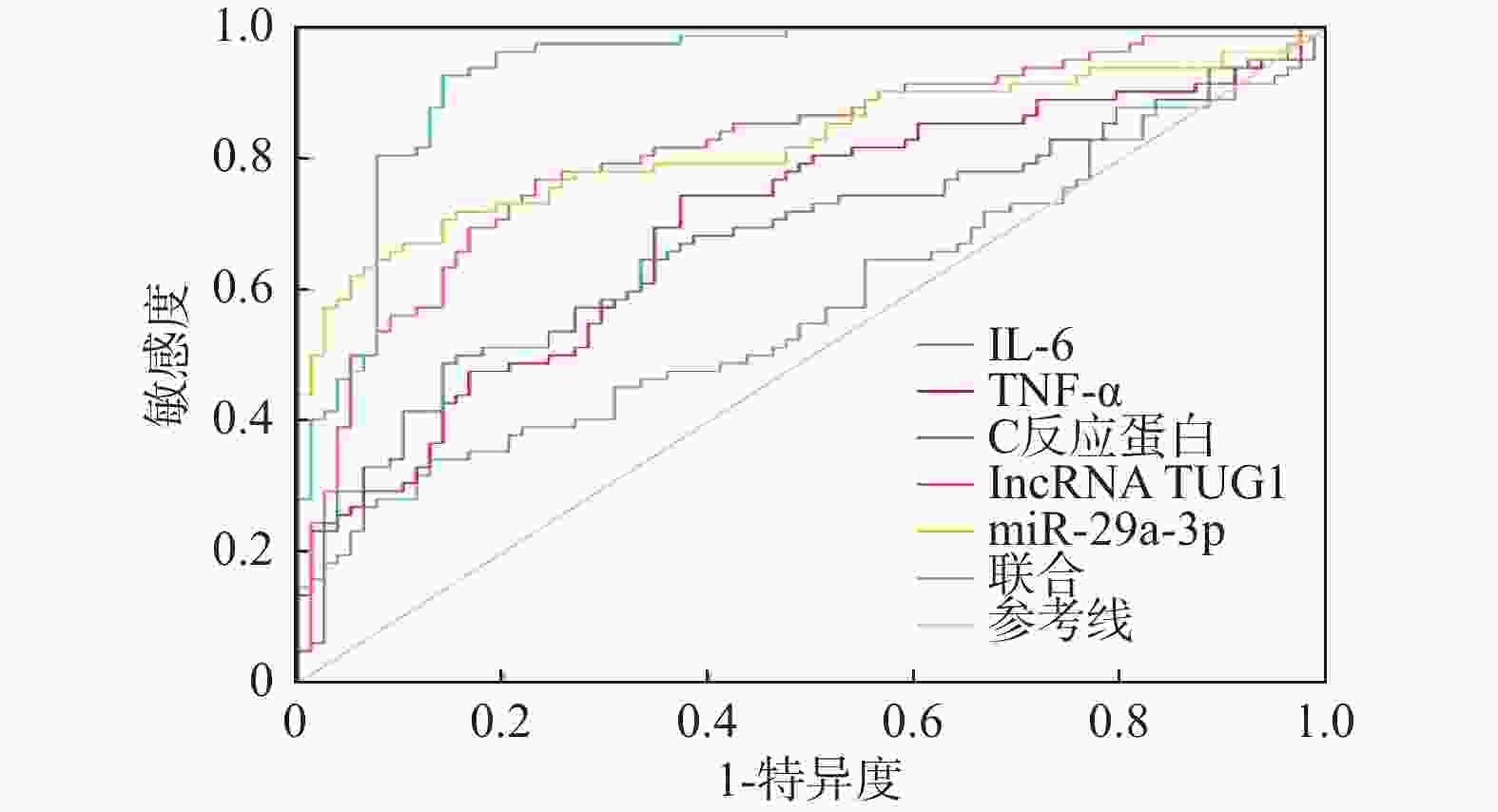
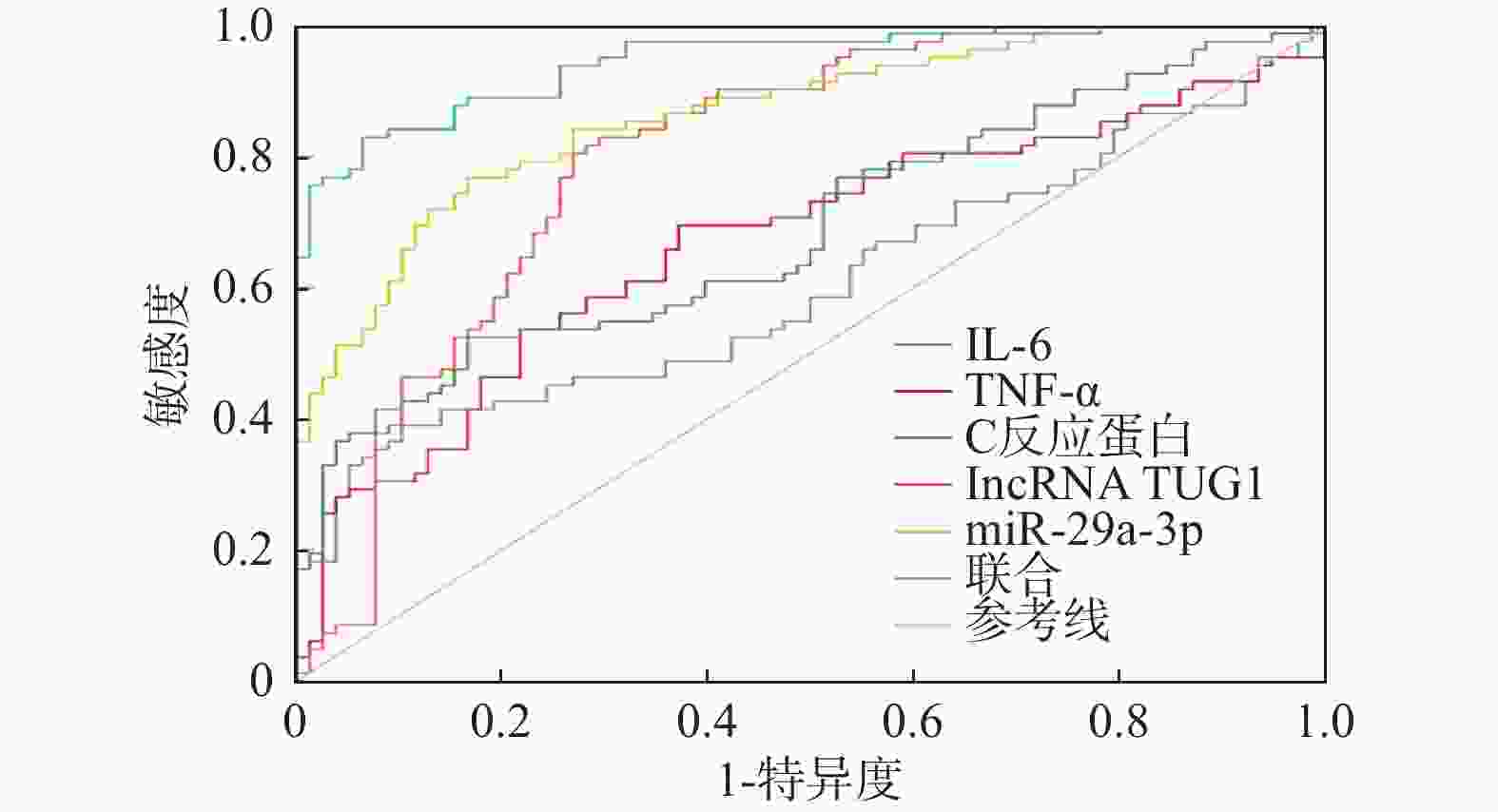
预测项目 AUC 95%CI 敏感度/% 特异度/% 约登指数 界值 IL-6 0.604 0.524~0.681 39.02 89.74 0.288 71.25 TNF-α 0.669 0.591~0.741 69.51 62.82 0.323 35.64 C反应蛋白 0.689 0.611~0.760 52.44 83.33 0.358 134.95 lncRNA TUG1 0.805 0.735~0.863 80.49 73.08 0.536 0.48 miR-29a-3p 0.866 0.803~0.915 76.83 83.33 0.602 2.29 联合 0.945 0.898~0.975 82.93 93.59 0.765 − *P < 0.05。 表 6 不同预后患者一般资料及lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p比较[($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 6. General information of patients with different prognostic conditions and comparison of lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p [($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
项目 良好组(n = 99) 不良组(n = 61) χ2/t P 年龄(岁) 59.13 ± 10.97 61.35 ± 12.36 1.184 0.238 性别 0.029 0.864 男 63(63.64) 38(62.30) 女 36(36.36) 23(37.70) 吸烟 34(34.34) 15(24.59) 1.690 0.194 饮酒 19(19.19) 10(16.39) 0.199 0.655 感染类型 1.930 0.381 细菌 79(79.80) 45(73.77) 病毒 11(11.11) 6(9.84) 真菌 9(9.09) 10(16.39) 高血压 43(43.43) 19(31.15) 2.401 0.121 糖尿病 22(22.22) 8(13.11) 2.055 0.152 心率(次/min) 87.24 ± 15.32 88.64 ± 17.13 0.537 0.592 收缩压(mmHg) 126.38 ± 20.06 129.32 ± 24.46 0.827 0.409 舒张压(mmHg) 76.49 ± 8.14 79.05 ± 10.59 1.719 0.088 PaO2(mmHg) 79.83 ± 15.46 77.94 ± 11.47 0.825 0.411 PaCO2(mmHg) 37.86 ± 8.92 35.58 ± 6.62 1.724 0.087 氧合指数 181.27 ± 32.23 150.47 ± 28.35 6.141 <0.001* 白细胞计数(×109/L) 11.39 ± 2.47 12.17 ± 3.13 1.749 0.082 IL-6(pg/mL) 57.51 ± 9.15 77.50 ± 13.56 11.130 <0.001* TNF-α(pg/mL) 28.44 ± 5.44 40.09 ± 6.73 12.003 <0.001* C反应蛋白(mg/L) 127.68 ± 33.98 150.83 ± 41.25 3.853 <0.001* 降钙素原(ng/mL) 4.41 ± 0.25 4.64 ± 0.41 4.411 <0.001* lncRNA TUG1/GAPDH 0.58 ± 0.16 0.23 ± 0.05 16.576 <0.001* miR-29a-3p/U6 1.91 ± 0.51 2.75 ± 0.74 8.492 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 7 多因素Logistic回归分析SP患者预后影响因素
Table 7. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of prognostic influencing factors in SP patients
影响因素 B SE Wald P OR 95%CI IL-6 0.661 0.109 36.790 <0.001* 1.937 1.564~2.398 TNF-α 0.758 0.158 23.016 <0.001* 2.134 1.566~2.909 C反应蛋白 0.850 0.124 46.958 <0.001* 2.339 1.834~2.983 lncRNA TUG1 −0.566 0.104 29.580 <0.001* 0.568 0.463~0.696 miR-29a-3p 1.010 0.335 9.092 0.003* 2.746 1.424~5.295 模型1 lncRNA TUG1 −0.432 0.088 24.135 <0.001* 0.649 0.546~0.771 miR-29a-3p 0.961 0.355 7.326 0.007* 2.614 1.304~5.242 模型2 lncRNA TUG1 −0.350 0.072 23.571 <0.001* 0.705 0.612~0.812 miR-29a-3p 0.879 0.267 10.843 0.001* 2.409 1.427~4.065 模型3 lncRNA TUG1 −0.309 0.063 24.095 <0.001* 0.734 0.649~0.830 miR-29a-3p 0.777 0.302 6.620 0.010* 2.175 1.203~3.931 *P < 0.05;模型1表示校正IL-6后,模型2表示校正IL-6、TNF-α后,模型3表示校正IL-6、TNF-α、C反应蛋白后。 表 8 lncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p单独及联合预测患者预后的价值
Table 8. The predictive value of lncRNA TUG1 and miR-29a-3p alone and in combination for the prognosis of SP patients
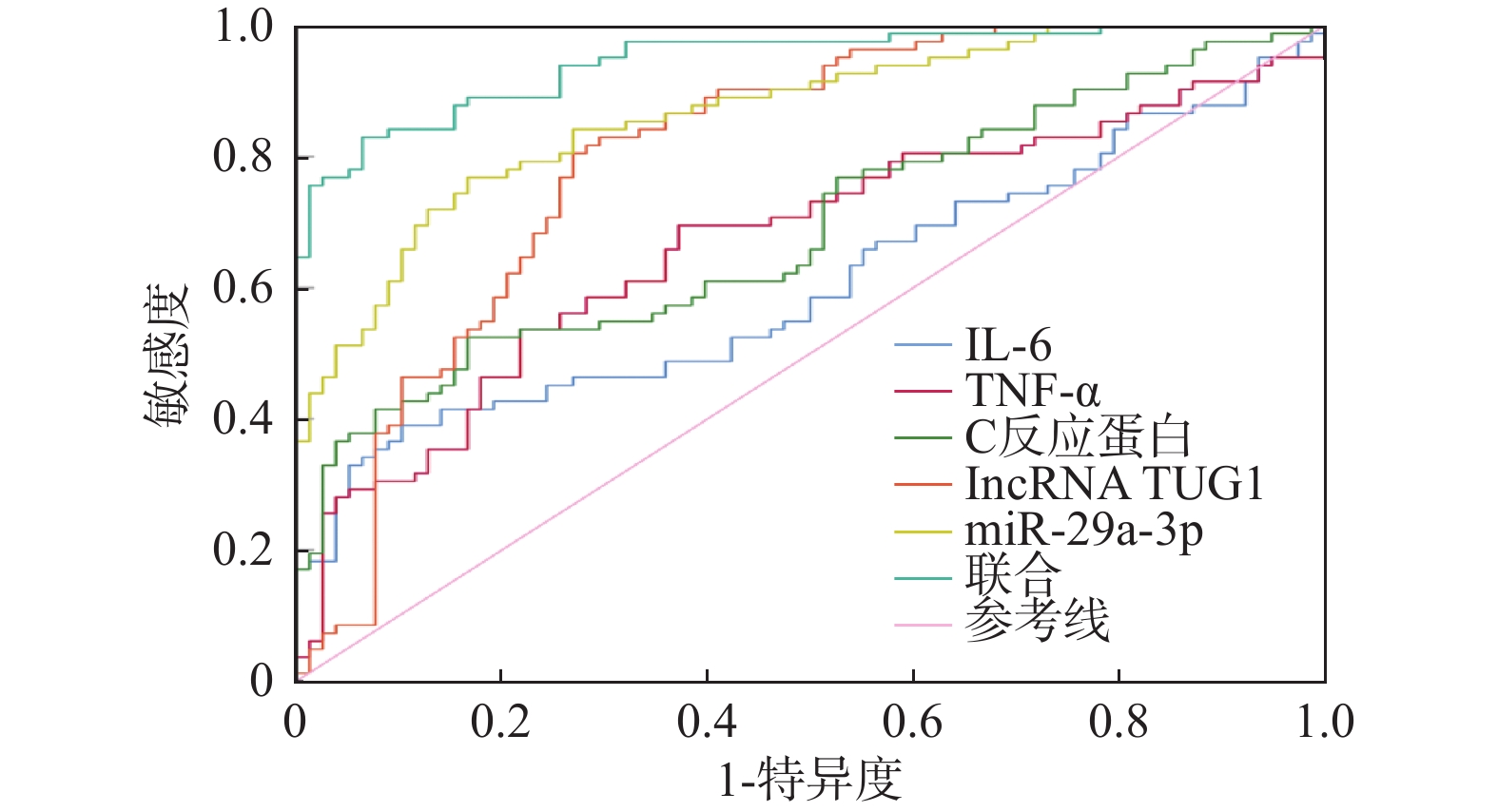
预测项目 AUC 95%CI 敏感度/% 特异度/% 约登指数 界值 IL-6 0.577 0.496~0.654 34.15 87.18 0.213 63.54 TNF-α 0.699 0.622~0.769 74.39 62.82 0.372 32.75 C反应蛋白 0.677 0.599~0.749 48.78 85.90 0.347 140.92 lncRNA TUG1 0.816 0.747~0.873 78.05 74.36 0.524 0.42 miR-29a-3p 0.823 0.755~0.879 64.63 92.31 0.569 2.35 联合 0.935 0.885~0.968 92.68 85.90 0.786 − -
[1] Taşar S, Fidancı İ, Bulut İ, et al. Role of serum endocan levels in children with bacterial and viral pneumonia: a prospective, case-control study[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol Pulmonol, 2022, 35(4): 145-152. doi: 10.1089/ped.2022.0110 [2] 宾松涛, 李明, 谭力, 等. 儿童坏死性肺炎46例临床分析[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2021, 42(1): 124-129. [3] 何晨晗, 师莹莹, 郑天元, 等. 血必净注射液联合利奈唑胺治疗重症肺炎有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54(14): 4615-4622. [4] Ali M S, Singh J, Alam M T, et al. Non-coding RNA in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and Covid-19 pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2022, 49(12): 11535-11546. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07820-4 [5] Chi X, Guo Y, Zhang L, et al. Long non-coding RNA GAS5 regulates th17/treg imbalance in childhood pneumonia by targeting miR-217/STAT5[J]. Cell Immunol, 2021, 364(5): 104357. [6] Gimbel A T, Koziarek S, Theodorou K, et al. Aging-regulated TUG1 is dispensable for endothelial cell function[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(9): e0265160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265160 [7] Qiu N, Xu X, He Y. LncRNA TUG1 alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting miR-34b-5p/GAB1[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2020, 20(1): 49-56. doi: 10.1186/s12890-020-1084-3 [8] Zhang X, Xie J, Sun H, et al. miR‑29a‑3p regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the SPARC/ERK signaling pathway in human bronchial epithelial cells[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2021, 48(3): 171-183. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5004 [9] 周丹, 黄胜, 胡雅萍, 等. 肺结核并发真菌感染CT影像特征及miR-29a-3p、miR-223-3p、IFN-γ、IL-23R水平[J]. 中华医院感染学杂志, 2024, 34(19): 2947-2951. [10] Askari N, Hadizadeh M, Rashidifar M. A new insight into sex-specific non-coding RNAs and networks in response to SARS-CoV-2[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2022, 97(2): 105195. [11] 中华医学会, 中华医学会杂志社, 中华医学会全科医学分会, 等. 成人社区获得性肺炎基层诊疗指南(2018年)[J]. 中华全科医师杂志, 2019, 18(2): 117-126. [12] Wang D, Willis D R, Yih Y. The pneumonia severity index: Assessment and comparison to popular machine learning classifiers[J]. Int J Med Inform, 2022, 163(1): 104778. [13] Torres A, Cilloniz C, Niederman M S, et al. Pneumonia[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2021, 7(1): 25-29. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00259-0 [14] Lv Z, Jiang R, Hu X, et al. Dysregulated lncRNA TUG1 in different pulmonary artery cells under hypoxia[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(10): 879-882. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2040 [15] Tayel S I, El-Masry E A, Abdelaal G A, et al. Interplay of lncRNAs NEAT1 and TUG1 in incidence of cytokine storm in appraisal of COVID-19 infection[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(13): 4901-4913. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.72318 [16] Gong K, Xu J, Tang J. Diagnostic and prognostic value of deregulated circulating long non-coding RNA TUG1 in elderly patients with severe pneumonia[J]. Inflammation, 2023, 46(1): 313-321. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01735-9 [17] Heydari R, Tavassolifar M J, Fayazzadeh S, et al. Long non-coding RNAs in biomarking COVID-19: a machine learning-based approach[J]. Virol J, 2024, 21(1): 134-145. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02408-9 [18] Wang N, Li P, Liu J, et al. MiR-29a-3p promotes nasal epithelial barrier dysfunction via direct targeting of CTNNB1-VCL module in allergic rhinitis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 120(7): 110325. [19] Xu XJ, Liu W, Liland S. MicroRNA-29a-3p accelerates inflammatory damage in neonatal pneumonia via targeting krüppel-like factor 4[J]. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2023, 22(5): 440-451. [20] 张瑜荣, 向永红, 庞宗东, 等. 血清LncRNA TUG1、miR-29a-3p表达与特发性肺纤维化患者病变程度、肺功能及PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路的关系研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2024, 24(24): 4766-4768. [21] Zhong Q, Wang L, Qi Z, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 modulates expression of elastin to relieve bronchopulmonary dysplasia via sponging miR-29a-3p[J]. Front Pediatr, 2020, 8(3): 573099. [22] Song T, Wang P, Xin L. LncRNA TUG1 Contributes to hypoxia-induced myocardial cell Injury through downregulating miR-29a-3p in AC16 cells[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2020, 76(5): 533-539. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000906 -





 下载:
下载: