Clinical Study of Aumolertinib Versus Osimertinib in the Treatment of EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
-
摘要:
目的 比较阿美替尼和奥希替尼治疗表皮生长因子受体(epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR)突变晚期非小细胞肺癌(non-small cell lung carcinoma,NSCLC)的临床疗效及安全性。 方法 回顾性收集2019年1月至2022年12月于云南省第一人民医院接受治疗的EGFR突变晚期NSCLC患者共计139例,经纳排标准筛选后共有104例患者纳入本次研究,按治疗药物分为奥希替尼组和阿美替尼组,每组52例。奥希替尼组使用甲磺酸奥希替尼片80 mg,每天1次,阿美替尼组使用甲磺酸阿美替尼片110 mg,每天1次。观察两组患者的疾病控制率(disease control rate,DCR)、客观缓解率(objective remission rate,ORR)、无进展生存期(progression-free survival,PFS)和总生存期(overall survival,OS),评估患者不良反应发生情况,利用COX回归模型分析影响患者生存期的关键因素。 结果 两组患者的DCR无统计学意义,阿美替尼组的ORR显著高于奥希替尼组,阿美替尼组患者的中位无进展生存期(median progression-free survival,mPFS)显著优于奥希替尼组(P = 0.045)。COX回归模型显示,临床分期为Ⅲ期(HR = 2.25,95%Cl 1.28~3.95,P = 0.005)、无脑转移(HR = 0.59,95%Cl 0.35~0.98,P = 0.040)、三代TKI类型为阿美替尼(HR = 1.82,95%Cl 1.15~2.87,P = 0.011)的患者死亡风险明显降低。 结论 阿美替尼与奥希替尼治疗EGFR突变晚期NSCLC患者的近期疗效相当,长期疗效方面,阿美替尼的mPFS和总OS都显著优于奥希替尼,且安全性更佳。 Abstract:Objective To compare the efficacy and safety of osimertinib and aumolertinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation. Methods A total of 139 patients with EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC treated in the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January, 2019 to December, 2022 were retrospectively collected. After screening by that row of criteria, 104 patients were included in this study. According to the treatment drugs, they were divided into osimertinib group and aumolertinib group, with 52 cases in each group. The osimertinib group received osimertinib mesylate tablets 80 mg once daily, and the aumolertinib group received aumolertinib mesylate tablets 110 mg once daily. The disease control rate (DCR), objective remission rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) of the two groups were observed. PFS and overall survival (OS) were evaluated. The Cox regression model was used to analyze the key factors affecting patient survival. Results The ORR of aumolertinib group was significantly higher than that of osimertinib group. The median progression-free survival (mPFS) of aumolertinib group was significantly longer than that of osimertinib group (P = 0.045). Cox regression model showed that clinical stage Ⅲ(HR = 2.25, 95%Cl 1.28~3.95, P = 0.005), no brain metastasis (HR = 0.59, 95%Cl 0.35~0.98, P = 0.040), third generation TKI type aumolertinib (HR = 1.82, 95%CI 1.15~2.87, P = 0.011). Conclusion Aumolertinib and osimertinib have similar clinical efficacy in the treatment of advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation. However, in terms of long-term efficacy, aumolertinib has significantly better median PFS and overall OS, and higher safety than osimertinib. -
Key words:
- Osimertinib /
- Aumolertinib /
- Clinical efficacy /
- Adverse drug reactions /
- Non-small cell lung cancer
-
表 1 两组患者的基本信息比较[n = 104,n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of basic information between the two groups[n = 104,n(%)]
项目 阿美替尼组(n = 52) 奥希替尼组(n = 52) χ2 P 性别 0.040 0.842 男 21(40.38) 22(42.31) 女 31(59.62) 30(57.69) 年龄(岁) 0.979 0.322 < 60 25(48.08) 20(38.46) ≥ 60 27(51.92) 32(61.54) 吸烟史 0.187 0.665 是 14(26.92) 16(30.77) 否 38(73.08) 36(69.23) 临床分期 0.782 0.377 Ⅲ期 12(23.08) 16(30.77) Ⅳ期 40(76.92) 36(69.23) 脑转移 0.000 1.000 是 12(23.08) 12(23.08) 否 40(76.92) 40(76.92) 突变类型 0.048 0.827 EGFR T790M 37(71.15) 38(73.08) EGFR19/21外显子 15(28.85) 14(26.92) 一代EGFR-TKI类型 3.071 0.080 吉非替尼 14(40.00) 23(60.53) 埃克替尼 21(60.00) 15(39.47) 注:阿美替尼组突变类型中包含2例原发性T790M突变患者。 表 2 两组患者的近期临床疗效比较[n = 104,n(%)]
Table 2. Comparison of short-term clinical efficacy between the two groups[n = 104,n(%)]
组别 n CR PR SD PD ORR DCR 阿美替尼 52 1(1.92) 10(19.23) 37(71.15) 4(7.69) 11(21.15) 48(92.31) 奥希替尼 52 1(1.92) 5(9.62) 41(78.85) 5(9.62) 6(11.54) 47(90.38) χ2 1.125 0.122 P 0.298 0.721 表 3 两组患者的PFS比较
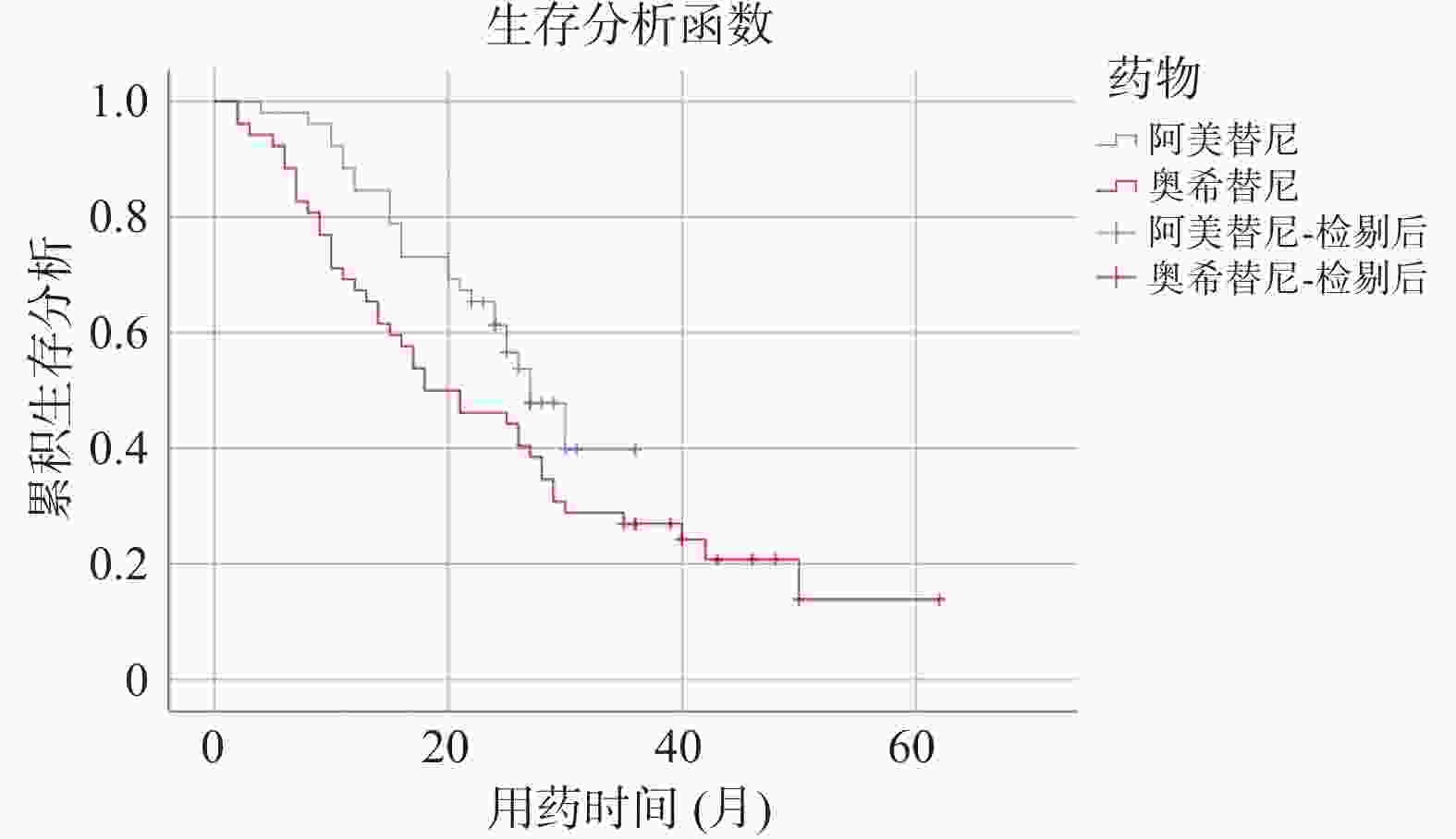
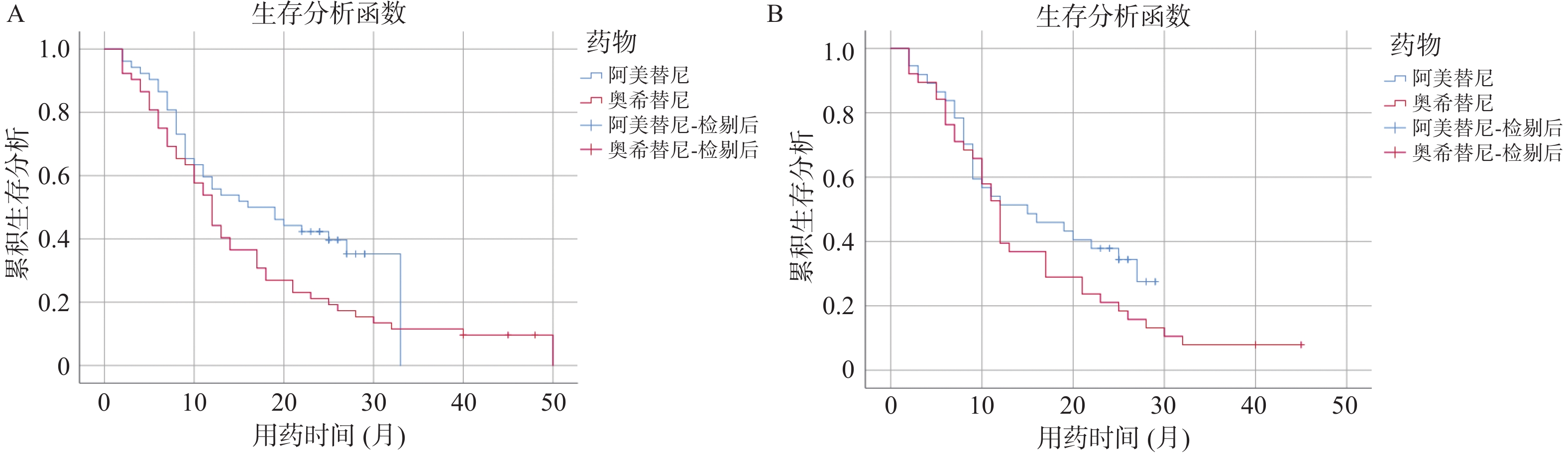
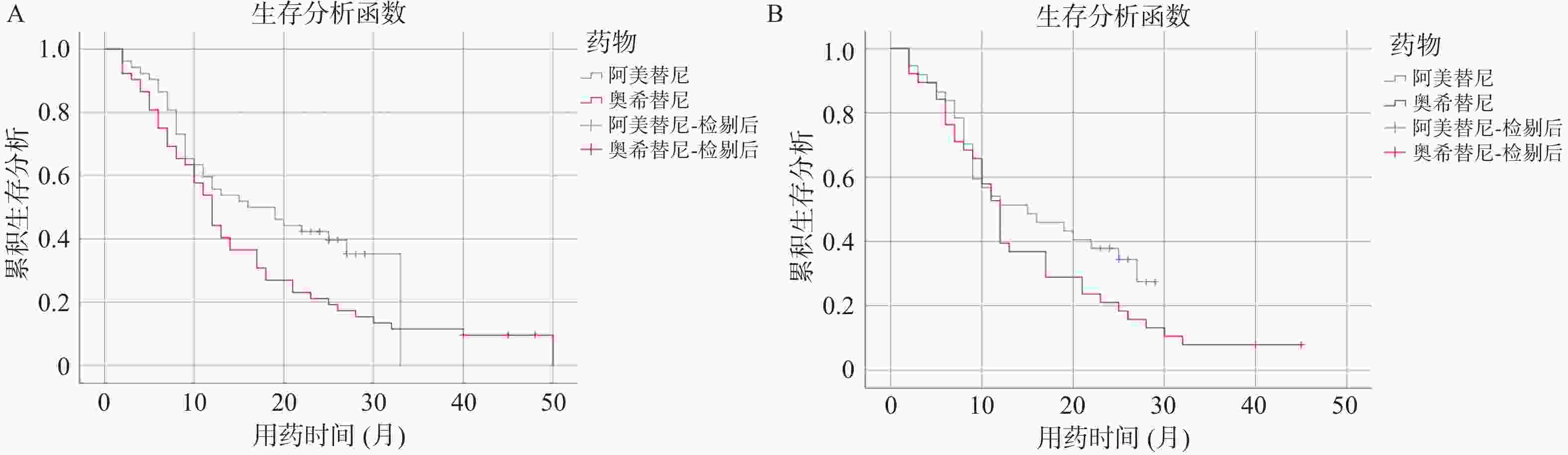
Table 3. PFS comparision of the two groups of patients
药物/PFS 阿美替尼 奥希替尼 P 总体 16.00(6.58-25.42) 12.00(9.99-14.01) 0.045* 一线 N/A 13.00(5.67-20.33) 0.177 二线 15.00(4.27-25.73) 12.00(10.31-13.69) 0.188 N/A:不可用;*P < 0.05 表 4 患者生存期的影响因素分析结果
Table 4. Results of analysis of factors influencing the survival time of patients
变量 单变量分析 多变量分析 HR 95%CI P HR 95%CI P 性别(男性或女性) 1.24 0.79~1.95 0.351 年龄(≥60岁或<60岁) 1.06 0.68~1.66 0.791 吸烟史(有或无) 1.06 0.65~1.74 0.803 临床分期(Ⅲ期或Ⅳ期) 2.30 1.32~4.01 0.003* 2.25 1.28~3.95 0.005* 脑转移(有或无) 0.55 0.34~0.90 0.017* 0.59 0.35~0.98 0.040* 突变类型(19/21外显子或T790M) 0.73 0.44~1.22 0.232 一代TKI类型(吉非替尼和埃克替尼) 1.36 0.78~2.37 0.278 三代TKI类型(阿美替尼和奥希替尼) 1.59 1.01~2.50 0.046* 1.82 1.15~2.87 0.011* *P < 0.05。 表 5 两组患者不良反应发生率[n = 104,n(%)]
Table 5. The incidence of adverse reactions in the two groups[n = 104,n(%)]
不良反应 1~2级不良反应 3~4级不良反应 阿美替尼 奥希替尼 χ2 P 阿美替尼 奥希替尼 腹泻 12(23.08) 22(42.31) 3.539 0.059 1(1.92) 1(1.92) 皮疹/瘙痒 23(44.23) 10(19.23) 6.391 0.011* 1(1.92) 2(3.85) 口腔溃疡 11(21.15) 7(13.46) 0.604 0.437 1(1.92) 1(1.92) 便秘 7(13.46) 2(3.85) 1.946 0.163 0(0) 0(0) 胃肠道反应 7(13.46) 17(32.69) 4.387 0.036* 1(1.92) 2(3.85) 皮肤干燥 2(3.85) 13(25.00) 7.790 0.005* 0(0) 0(0) 贫血 1(1.92) 1(1.92) 0.000 1.000 0(0) 0(0) 眼部疾病 2(3.85) 2(3.85) 0.000 1.000 0(0) 0(0) 头晕 1(1.92) 2(3.85) 0.000 1.000 0(0) 0(0) 其他 20(38.46) 11(21.15) 2.941 0.086 0(0) 2(3.85) *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 赵媛媛,周建英,范云,等. BRAF V600突变型非小细胞肺癌的治疗进展[J]. 中国癌症杂志,2021,31(12):1145-1152. [2] 中华医学会肿瘤学分会,中华医学会杂志社. 中华医学会肿瘤学分会肺癌临床诊疗指南(2021版)[J]. 中华医学杂志,2021,101(23):1725-1757. [3] Giaccone G,He Y. Current knowledge of small cell lung cancer transformation from non-small cell lung cancer [C] //Seminars in Cancer Biology. Academic Press,2023,94: 1-10. [4] Miller K D,Nogueira L,Devasia T,et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics,2022[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2022,72(5):409-436. doi: 10.3322/caac.21731 [5] 吴方雨,陈卫东,夏盼盼,等. 埃克替尼对比吉非替尼治疗EGFR突变型晚期NSCLC的临床观察[J]. 中国药房,2023,34(10):1228-1232. doi: 10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2023.10.14 [6] 左强,江国强,方芳,等. 伏美替尼治疗EGFR突变阳性非小细胞肺癌EGFR-TKI耐药患者的临床观察[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2022,32(14):30-34. [7] 王皓,曾晨欣,李俐,等. 奥希替尼和吉非替尼/厄洛替尼一线治疗EGFR突变阳性非小细胞肺癌的成本-效果分析[J]. 医药导报,2020,39(12):1689-1696. [8] 张聪,史琛,解吉奕,等. 阿美替尼治疗非小细胞肺癌的研究进展[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2022,42(15):1613-1618. [9] Fu K,Xie F,Wang F,et al. Therapeutic strategies for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib resistance[J]. Journal of Hematology & Oncology,2022,15(1):173. [10] Cheng Z,Cui H,Wang Y,et al. The advance of the third‑generation EGFR‑TKI in the treatment of non‑small cell lung cancer[J]. Oncology Reports,2024,51(1):1-13. [11] Du X,Yang B,An Q,et al. Acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs and emerging next-generation EGFR inhibitors[J]. The Innovation,2021,2(2):1-17. [12] Zhang X,Zhang M,Du X,et al. Clinical efficacy and safety analysis of aumolertinib in real-world treatment of EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2024,15(9):1331138. [13] 中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)非小细胞肺癌诊疗指南2023版 [M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,2023: 16-17. [14] 孟新源,张莉,薛淑萍. EGFR突变晚期NSCLC患者第1、2代EGFR-TKI治疗耐药后序贯奥希替尼或阿美替尼治疗的效果观察[J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析,2023,23(9):1079-1081+1085. [15] 杨光霞,程云涛,刘琳琳,等. 阿美替尼片联合贝伐珠单抗注射液治疗表皮生长因子受体突变的晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的临床研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志,2023,39(11):1528-1532. [16] Blonde L,Khunti K,Harris S B,et al. Interpretation and impact of real-world clinical data for the practicing clinician[J]. Advances in therapy,2018,35(11):1763-1774. doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0805-y [17] Wang J,Wu L. An evaluation of aumolertinib for the treatment of EGFR T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy,2022,23(6):647-652. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2022.2050213 [18] Lu S,Wang Q,Zhang G,et al. Efficacy of aumolertinib (HS-10296) in patients with advanced EGFR T790M+ NSCLC: updated post-national medical products administration approval results from the APOLLO registrational trial[J]. Journal of Thoracic Oncology,2022,17(3):411-422. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.10.024 [19] Zhou Q,Zhang H L,Jiang L Y,et al. Real-world evidence of osimertinib in Chinese patients with EGFR T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer: a subgroup analysis from ASTRIS study[J]. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology,2023,149(12):10771-10780. [20] Ramalingam S S,Vansteenkiste J,Planchard D,et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated,EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC[J]. New England Journal of Medicine,2020,382(1):41-50. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1913662 [21] Soria J C,Ohe Y,Vansteenkiste J,et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non–small-cell lung cancer[J]. New England Journal of Medicine,2018,378(2):113-125. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1713137 [22] Shirley M,Keam S J. Aumolertinib: a review in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Drugs,2022,82(5):577-584. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01695-2 [23] Li H,Zhao W,Chang C,et al. Efficacy and patient-reported outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving aumolertinib as first-line therapy: a real-world study[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2024,15(6):1444707. -





 下载:
下载: