Establishment of a Nomogram Model for Predicting Abnormal Bone Mass in Diabetic Patients
-
摘要:
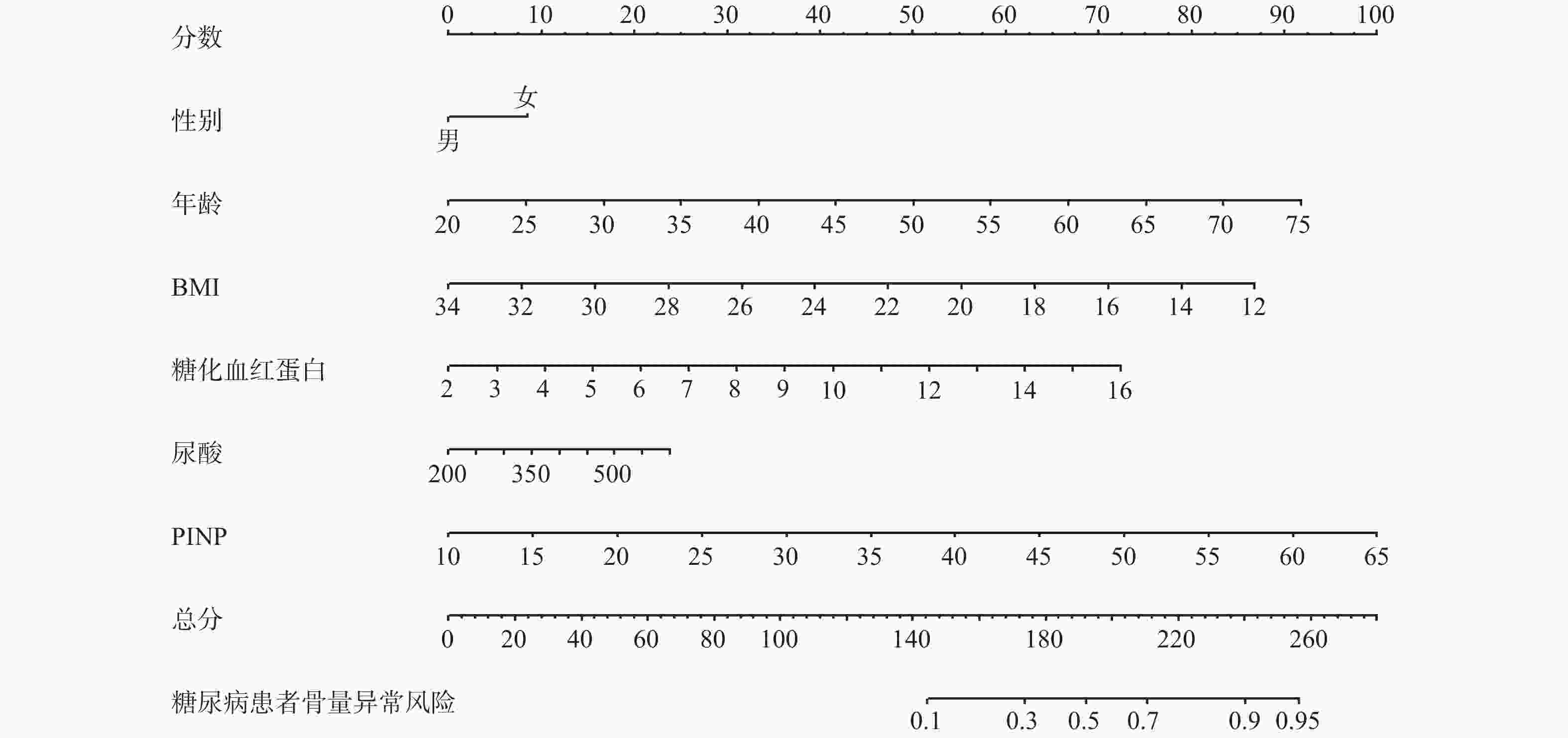
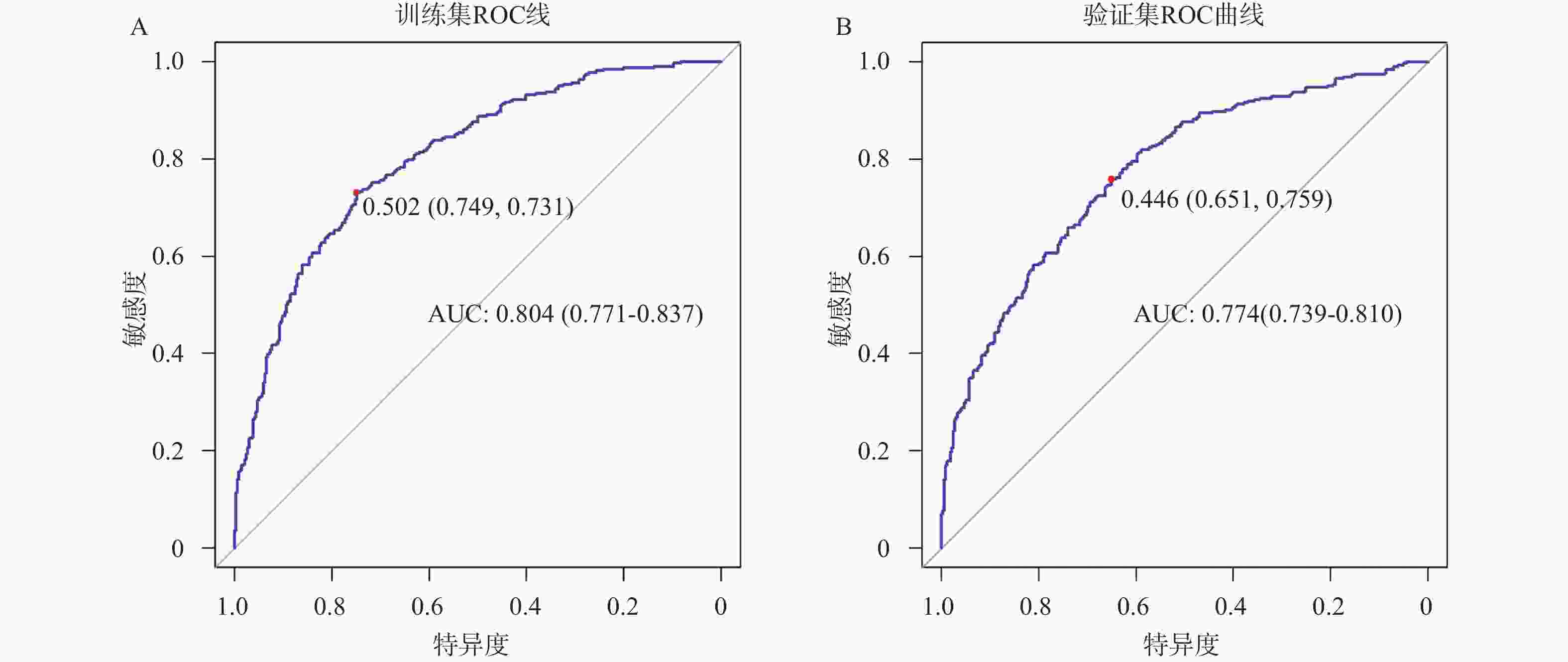
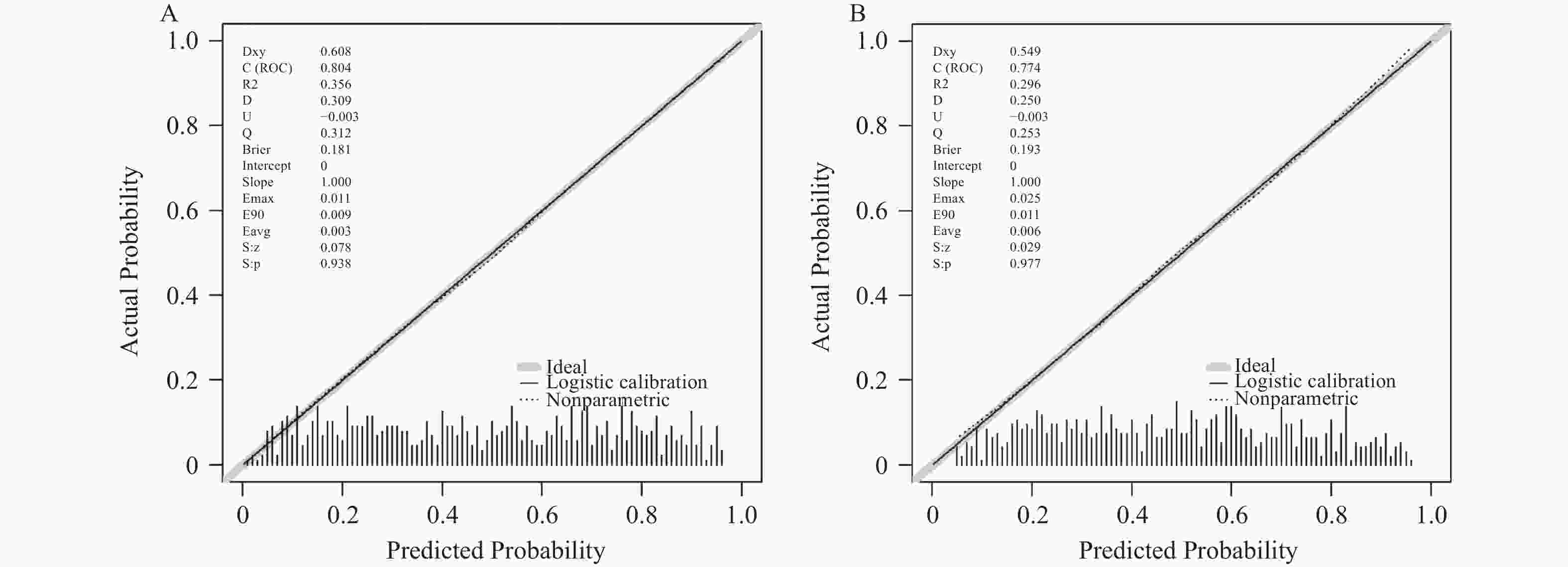
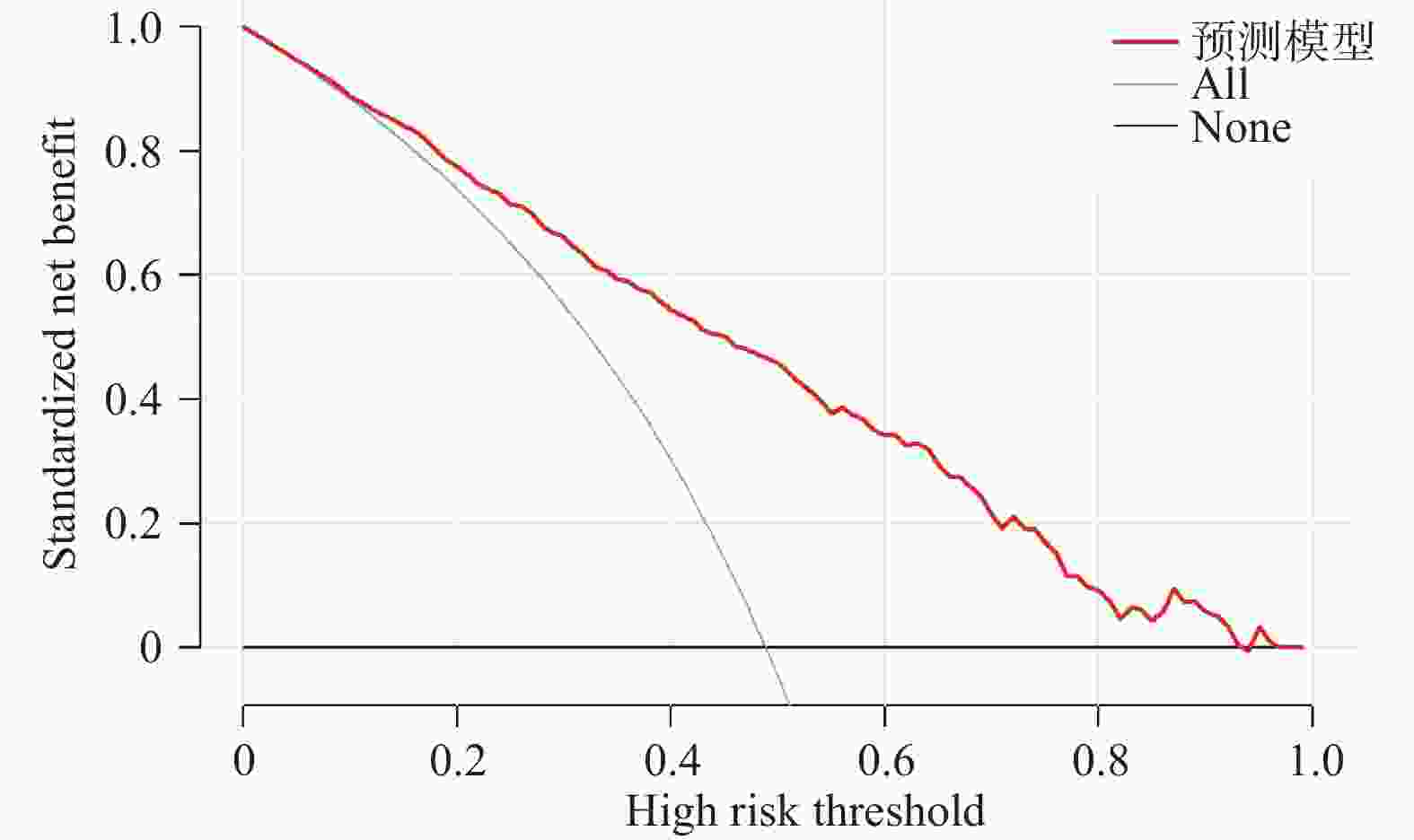
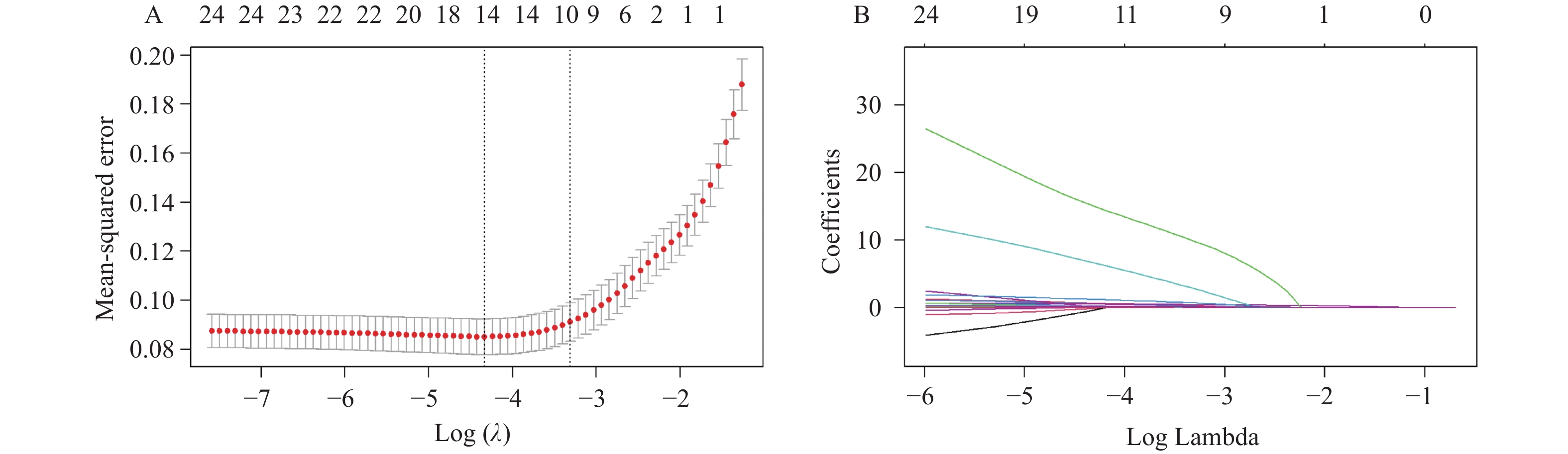
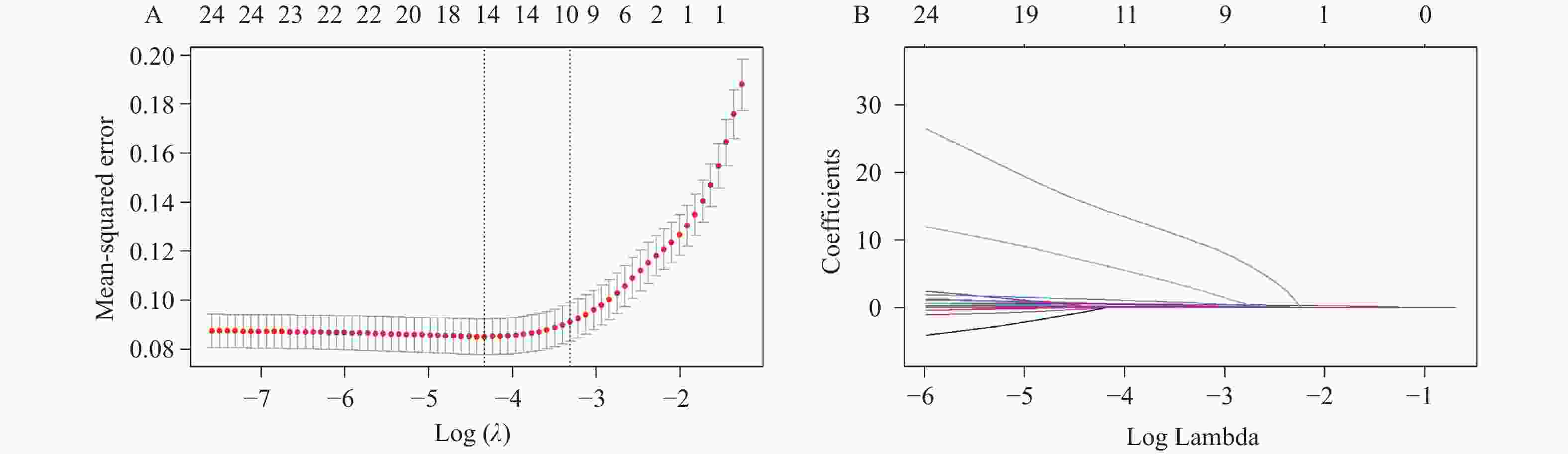
目的 建立糖尿病患者骨量异常预测列线图模型。 方法 选择2024年1月至2025年1月在西南交通大学附属医院(成都市第三人民医院)健康体检的糖尿病患者944例,以7∶3比例分为训练集661例,验证集283例。训练组依T值/Z值分为骨量正常/异常组。比较两组各指标,用LASSO回归筛选潜在因素后行Logistic回归分析,建立列线图并进行验证。 结果 训练集661例患者中共323例(48.87%)出现骨量异常。LASSO回归基础上行Logistic回归分析结果显示:男性、年龄、糖化血红蛋白、尿酸、I型原胶原氨基端延长肽(procollagen I N-terminal propeptide,PINP)为糖尿病患者骨量异常的独立性危险因素,BMI为保护因素(P < 0.05)。训练集预测糖尿病患者骨量异常的AUC为0.804(95%CI:0.771~0.837),敏感度为73.1%,特异度为74.9%;验证集AUC为0.774(95%CI:0.739~0.810),敏感度为75.9%,特异度为65.1%。预测曲线与标准曲线基本拟合,决策曲线中模型预测概率为0.15~0.95时患者获益率最高。 结论 糖尿病患者骨量异常主要受性别、年龄、BMI等因素影响,以此建立的列线图模型可预测糖尿病患者骨量异常风险。 Abstract:Objective To establish a nomogram model for predicting abnormal bone mass in diabetic patients. Methods A total of 944 diabetic patients who underwent health checkups at the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Jiaotong University (Chengdu Third People's Hospital) from January 2024 to January 2025, were selected. The patients were divided into a training set (n = 661) and a validation set (n = 283) in a 7∶3 ratio. The training group was further categorized into normal and abnormal bone mass groups based on T-scores/Z-scores. Various indicators were compared between the two groups, and potential factors were screened using LASSO regression. Logistic regression was then performed to establish a nomogram, which was subsequently validated. Results Among the 661 patients in the training set, 323 (48.87%) exhibited abnormal bone mass. Logistic regression analysis based on LASSO regression results showed that male sex, age, glycated hemoglobin, uric acid, and type I procollagen N-terminal propeptide (PINP) were the independent risk factors for abnormal bone mass in diabetic patients, while BMI served as a protective factor (P < 0.05). The AUC for predicting abnormal bone mass in diabetic patients was 0.804 (95%CI: 0.771~0.837) in the training set, with a sensitivity of 73.1% and a specificity of 74.9%. In the validation set, the AUC was 0.774 (95%CI: 0.739~0.810), with a sensitivity of 75.9% and a specificity of 65.1%. The prediction curve closely matched the standard curve, and the decision curve analysis indicated that the patient benefit rate was highest when the model-predicted probability ranged from 0.15 to 0.95. Conclusion Abnormal bone mass in diabetic patients is primarily influenced by factors such as sex, age, and BMI. The nomogram model established based on these factors can effectively predict the risk of abnormal bone mass in diabetic patients. -
Key words:
- Diabetes /
- Abnormal bone mass /
- Multivariate analysis /
- Nomogram
-
表 1 骨量正常组、骨量异常组患者一般资料比较[($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of data between normal bone mass group and abnormal bone mass group [($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
因素 骨量异常组(n=323) 骨量正常组(n=338) χ2/t P 性别 9.626 0.002* 男 120(37.15) 166(49.11) 女 203(62.85) 172(50.89) 年龄(岁) 47.73 ± 9.68 41.75 ± 7.78 8.722 <0.001* BMI(kg/cm2) 22.19 ± 3.51 24.10 ± 2.75 −7.762 <0.001* 糖尿病病程(年) 8.11 ± 2.04 6.75 ± 1.82 9.053 <0.001* 空腹血糖(mmol/L) 10.22 ± 2.78 9.29 ± 2.45 4.568 <0.001* 糖化血红蛋白(%) 9.61 ± 1.93 8.62 ± 2.08 6.374 <0.001* 三酰甘油(mmol/L) 2.06 ± 0.49 2.11 ± 0.55 −1.232 0.218 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) 2.41 ± 0.52 2.36 ± 0.42 1.363 0.173 高密度指蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) 1.03 ± 0.27 1.08 ± 0.24 −2.519 0.012* 总胆固醇(mmol/L) 3.12 ± 0.58 2.94 ± 0.63 3.817 <0.001* 血肌酐(μmol/L) 79.81 ± 6.92 72.15 ± 8.85 12.359 <0.001* 尿酸(μmol/L) 382.94 ± 73.26 364.37 ± 66.75 3.408 0.001* 白蛋白(g/L) 33.17 ± 6.19 33.12 ± 5.60 0.109 0.913 总胆红(μmol/L) 9.04 ± 2.11 8.81 ± 2.17 1.381 0.168 直接胆红(μmol/L) 7.11 ± 2.28 7.20 ± 2.12 −0.526 0.599 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) 23.81 ± 5.04 23.26 ± 4.89 1.424 0.155 谷草转氨酶(U/L) 26.58 ± 4.99 27.11 ± 5.13 −1.379 0.168 中性粒/淋巴细胞比值 4.23 ± 1.19 4.19 ± 1.22 0.426 0.670 白细胞计数(×109/L) 8.94 ± 2.25 9.03 ± 2.09 −0.533 0.594 血小板计数(×109/L) 193.87 ± 48.15 207.05 ± 51.27 −3.403 <0.001* 骨钙素(μg/L) 4.92 ± 1.13 6.02 ± 1.86 −9.138 <0.001* 降钙素(ng/L) 55.67 ± 13.04 64.19 ± 18.25 −6.878 <0.001* CTX(ng/mL) 0.31 ± 0.08 0.27 ± 0.06 7.293 <0.001* PINP(ng/ mL) 42.17 ± 5.22 38.47 ± 8.02 7.051 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 2 糖尿病患者骨量异常多因素分析
Table 2. Multivariate analysis of abnormal bone mass in diabetic patients
因素 B SE Wald P OR OR的95%置信区间 下限 上限 性别 0.391 0.185 4.443 0.035* 1.478 1.028 2.126 年龄 0.077 0.011 48.288 <0.001* 1.080 1.056 1.103 BMI −0.181 0.030 37.325 <0.001* 0.834 0.787 0.884 糖尿病病程 0.511 0.325 2.472 0.116 1.667 0.882 3.152 糖化血红蛋白 0.237 0.046 26.514 <0.001* 1.268 1.158 1.388 高密度指蛋白胆固醇 0.492 0.282 3.044 0.081 1.636 0.941 2.843 血肌酐 0.577 0.302 3.650 0.056 1.781 0.985 3.219 尿酸 0.003 0.001 4.413 0.036 * 1.003 1.000 1.005 骨钙素 0.383 0.197 3.780 0.052 1.467 0.997 2.158 PINP 0.083 0.014 35.629 <0.001* 1.087 1.058 1.117 常量 −6.050 1.216 24.758 <0.001* 0.002 性别赋值:男=0,女=1; *P < 0.05。 -
[1] 杨雁, 陈颖, 张惠杰, 等. 糖尿病患者体重管理专家共识(2024版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2024, 16(9): 959-971. [2] Hofbauer L C, Busse B, Eastell R, et al. Bone fragility in diabetes: Novel concepts and clinical implications[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol., 2022, 10(3): 207-220. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00347-8 [3] 张萌萌, 徐又佳, 侯建明, 等. 骨质疏松实验室诊断及影响因素专家共识2022[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2022, 28(9): 1249-1259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2022.09.002 [4] 李霞, 赵同峰, 雷涛. 中老年2型糖尿病患者骨代谢特点及骨量丢失危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(1): 105-109. [5] 李隽, 黄娟, 李薇薇. 2型糖尿病患者发生骨质疏松的危险因素及与脂代谢相关性的研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2025, 33(06): 435-438. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2025.06.007 [6] 许慧, 樊勇. 2型糖尿病患者肌少症风险列线图模型开发与验证的研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2025, 33(11): 833-838. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2025.11.007 [7] 中华医学会糖尿病学分会. 中国糖尿病防治指南(2024版)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志, 2025, 17(1): 16-139. doi: 10.13406/j.cnki.cyxb.003749 [8] 张平, 章雨帆, 徐晶晶, 等. 垂体激素和激素替代治疗对骨代谢调控的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2021, 27(10): 1503-1507. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2021.010.019 [9] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2022)[J]. 中国全科医学, 2023, 26(14): 1671-1691. [10] Khosla S, Samakkarnthai P, Monroe D G, et al. Update on the pathogenesis and treatment of skeletal fragility in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2021, 17(11): 685-697. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00555-5 [11] Deng X, Wu X, Sun Z, et al. Associations between new obesity indices and abnormal bone density in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2024, 35(10): 1807-1815. [12] 曾维佳, 张日权. Lasso变量选择的分布式算法[J]. 应用概率统计, 2022, 38(1): 99-110. [13] 王恺怡, 杨盛, 郭彩云, 等. 基于LASSO算法的光谱变量选择方法研究[J]. 分析测试学报, 2022, 41(3): 398-402. doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.21070503 [14] 李梦园, 付泽辉, 卢叶君, 等. 基于临床及超声特征列线图预测C-TIRADS 4A与4B类甲状腺结节的良恶性的诊断价值[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2025, 41(4): 374-377. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0101.2025.04.004 [15] 李弘磊, 杨涛, 范红旗. 不同性别2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松的患病情况分析[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2015, 17(4): 578-579. [16] 张鹏霞. 老年2型糖尿病患者人体成分变化与骨质疏松的相关性研究[D]. 青海: 青海大学, 2023. [17] 岳斌, 张巍, 徐丽, 等. 老年2型糖尿病合并骨质疏松患者骨密度变化与血清激素水平、骨代谢指标及血脂的关系[J]. 海南医学, 2023, 34(2): 185-189. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2023.02.007 [18] Jannin A, Kerlan V, Desailloud R. Endocrinology of bone mineralization: An update[J]. Ann Endocrinol (Paris), 2022, 83(1): 46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2021.12.001 [19] Gu P, Shi B, Zhang Z, et al. Association of visceral fat metabolic score with bone mineral density and osteoporosis: a NHANES cross-sectional study[J]. J Health Popul Nutr, 2025, 44(1): 156-159. doi: 10.1186/s41043-025-00914-2 [20] 黄楠. 血清骨转移标志物、睾酮与老年男性骨质疏松性髋部骨折的相关性研究[D]. 成都医学院, 2023. [21] Liu Y, He H, Qian K, et al. Evaluation of Health Associations With Height-Normalised Abdominal Body Composition Indices: A Single-Centre Cross-Sectional Study[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2024, 15(6): 2651-2659. [22] 丁康致, 王鹏, 张静, 等. 血清肌酐和血红蛋白及BMI与西藏地区藏族中老年居民骨质疏松的相关性及其预测价值分析[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2024, 45(6): 1013-1019. doi: 10.7652/jdyxb202406020 [23] 丁家豪, 林萱, 崔静, 等. 中老年男性2型糖尿病患者葡萄糖目标范围内时间、糖化血红蛋白与骨质疏松的相关性[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2024, 45(10): 1195-1201. doi: 10.14188/j.1671-8852.2023.0319 [24] Zhao H, Qi C, Zhang Y, et al. Correlation between uric acid levels and bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2025, 16: 1415550. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1415550 [25] 虎静, 樊雨曦, 杜婧. 老年超重或肥胖男性体检人群正常血尿酸水平对腰椎骨密度的影响[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志, 2024, 30(10): 1438-1443. [26] 许富贵, 乙红艳, 欧洲, 等. 骨转换标志物PINP和β-CTX在帕金森病患者发生骨质疏松中的预测价值[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 43(8): 1128-1132. doi: 10.7655/NYDXBNS20230813 -





 下载:
下载: