Exploring the Ameliorative Effect of Rapamycin on Oxidative Stress in Rats with Thyroiditis Rats
-
摘要:
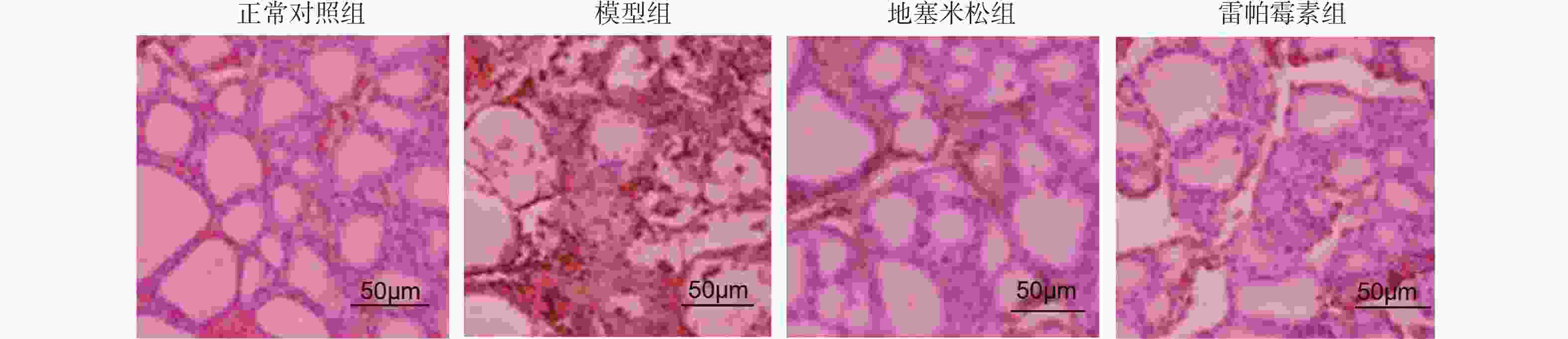
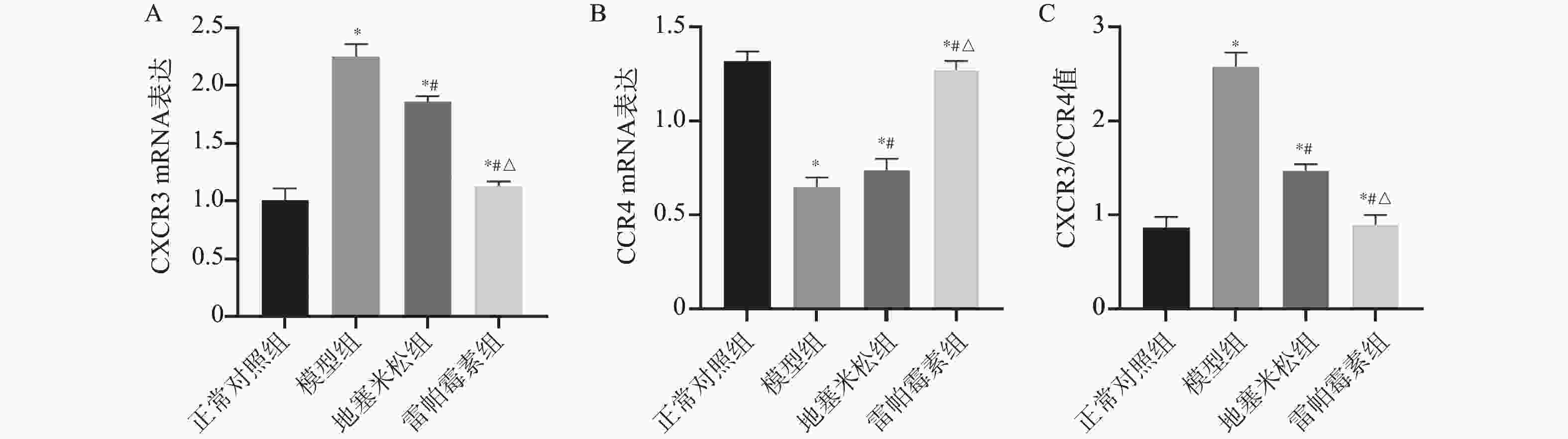
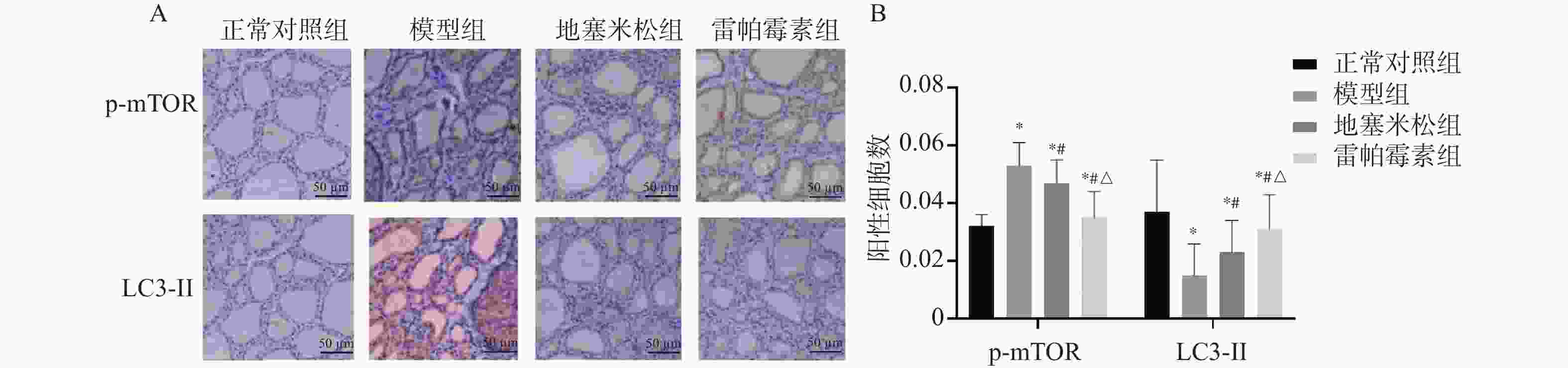
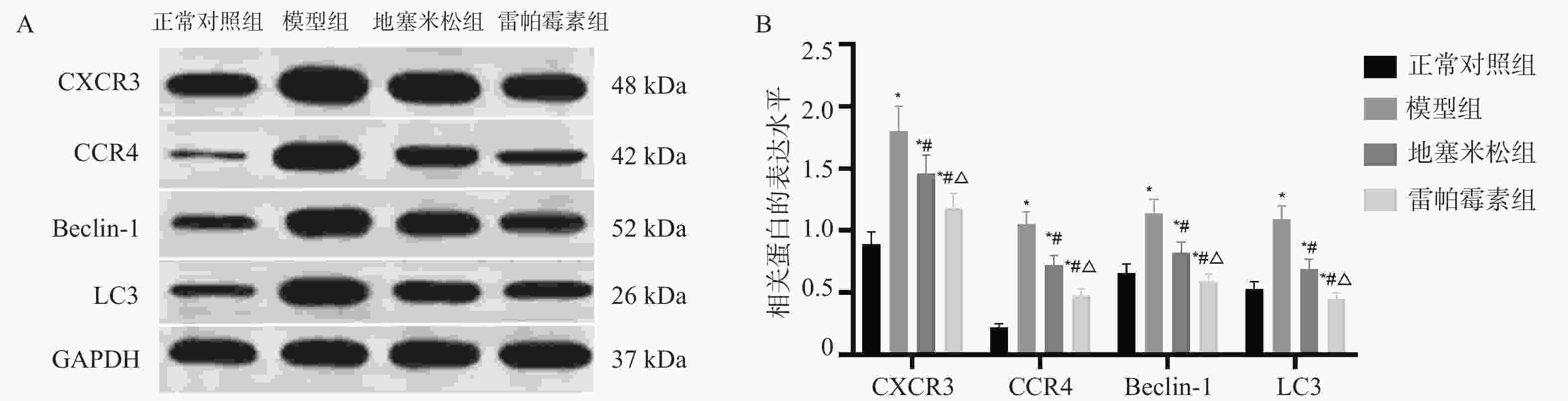
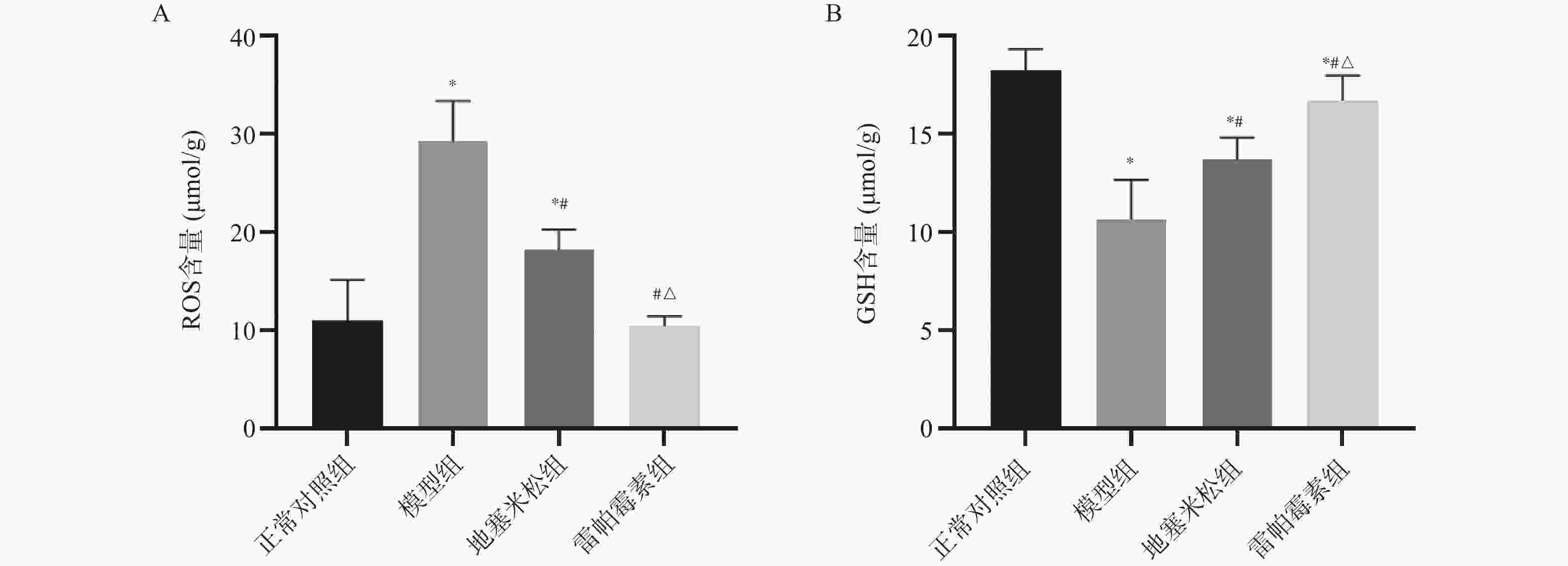
目的 探讨雷帕霉素诱导氧化应激对甲状腺炎大鼠的影响。 方法 构建甲状腺炎大鼠模型,雷帕霉素干预。比色法检测大鼠甲状腺组织中活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)、谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)水平;HE染色观察病理形态;PCR检测大鼠甲状腺组织中CXC趋化因子受体3(C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3,CXCR3)、C-C趋化因子受体4(C-C chemokine receptor 4,CCR4)表达;免疫组化检测大鼠甲状腺组织中,雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)磷酸化水平、自噬蛋白微管相关蛋白1轻链3α-Ⅱ(microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3α-Ⅱ,LC3-Ⅱ)蛋白水平;蛋白免疫印迹检测大鼠甲状腺组织中CXCR3、CCR4、Beclin-1、LC3蛋白表达。 结果 与正常对照组相比,模型组大鼠甲状腺组织中ROS、CXCR3、CXCR3表达及p-mTOR阳性细胞数升高(P < 0.05),GSH、CCR4、Beclin-1、LC3、CCR4表达及LC3-Ⅱ阳性细胞数降低(P < 0.05),与模型组相比,地塞米松组和雷帕霉素组ROS、CXCR3、CXCR3表达及p-mTOR阳性细胞数降低(P < 0.05),且雷帕霉素组低于地塞米松组(P < 0.05),GSH、CCR4、Beclin-1、LC3水平、CCR4 mRNA表达及LC3-Ⅱ阳性细胞数升高(P < 0.05),雷帕霉素组高于地塞米松组(P < 0.05)。 结论 雷帕霉素可改善氧化应激水平,抑制p-mTOR表达,提高LC3-Ⅱ水平及甲状腺炎大鼠的细胞自噬,调节CXCR3/CCR4蛋白表达。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of rapamycin-induced oxidative stress on thyroiditis rats. Methods A rat model of thyroiditis was constructed and rapamycin was intervened. The levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and glutathione (GSH) in thyroid tissue of rats were detected by colorimetry. HE staining was used to observe the pathological morphology; the expression of chemokine receptor 3 (CXCR3) and C-C chemokine receptor (CCR4) in thyroid tissue of rats was detected by PCR. The phosphorylation level of rapamycin target protein (mTOR) and the level of autophagy protein LC3-II protein in thyroid tissue of rats were detected by immunohistochemistry. Western blot was used to detect the expression of CXCR3, CCR4, Beclin-1 and LC3 protein in thyroid tissue of rats. Results Compared with the normal control group, the levels of ROS, CXCR3, CXCR3 mRNA expression and the number of p-mTOR positive cells in the thyroid tissue of the model group were increased (P < 0.05), while the levels of GSH, CCR4, Beclin-1, LC3, CCR4 mRNA expression and the number of LC3-II positive cells were decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the model group, the levels of ROS, CXCR3, CXCR3 mRNA expression and the number of p-mTOR positive cells in the dexamethasone group and the rapamycin group were decreased (P < 0.05), and the rapamycin group was lower(P < 0.05). The levels of GSH, CCR4, Beclin-1 and LC3, the expression of CCR4 mRNA and the number of LC3-II positive cells increased (P < 0.05), and the rapamycin group was higher (P < 0.05). Conclusion Rapamycin can improve the level of oxidative stress, inhibit the expression of p-mTOR, increase the level of LC3-II and autophagy in rats with thyroiditis, and regulate the expression of CXCR3/CCR4 protein. -
Key words:
- Rapamycin /
- Oxidative Stress /
- Thyroiditis /
- Autophagy /
- C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 4
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. primer sequence
基因 引物序列 长度(bp) CXCR3 5'-AGGTCAGTGAACGTCAAGTGCTAG-3' 22 5'-CAAAAAGAGGAGGCTGTAGAGGA-3' CCR4 5'-GCCTCCAACACAGACTTCCTTG-3' 23 5'-AGCGTTCGGTTCTAGTTTCCAC-3' β-actin 5'-GGAGATTACTGCCCTGGCTCCTA-3' 20 5'-GACTCATCGTACTCCTGCTTGCTG-3' -
[1] Albano D, Dondi F, Zilioli V, et al. The role of Hashimoto thyroiditis in predicting radioiodine ablation efficacy and prognosis of low to intermediate risk differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Ann Nucl Med, 2021, 35(10): 1089-1099. doi: 10.1007/s12149-021-01644-1 [2] 李方远, 陆华, 王通, 等. 接绪资冲颗粒对实验性自身免疫性甲状腺炎致卵巢储备功能下降小鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(8): 3799-3804. [3] Poillet-Perez L, Sarry J E, Joffre C. Autophagy is a major metabolic regulator involved in cancer therapy resistance[J]. Cell Reports, 2021, 36(7): 109528. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109528 [4] 张雪琪, 张帆, 滕卫平, 辅助性T细胞17介导桥本甲状腺炎发病机制的研究现状. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2022, 38(11): 1001-1005. [5] Yu X, J Wu, Wu Q, et al. Quantitative analysis of autophagy-related protein LC3B by quantum-dot- based molecular imaging Chapter outline[J]. Methods in Cell Biology, 2021, 165(4): 177-185. [6] 林泽杭, 段志敏, 徐松, 等. 白念珠菌菌丝调控小鼠巨噬细胞自噬关键分子微管相关蛋白1轻链3的实验研究[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志, 2021, 54(3): 189-195. [7] 赵连春, 牛丽霞, 赵振军, 等. CXC趋化因子受体3对甲状腺细胞自噬与炎症的影响及机制[J]. 安徽医学, 2024, 45(5): 542-548. [8] Lu Q, Dou Y, Yu T, et al. Association of thyroglobulin antibody and thyroid peroxidase antibody status with aggressive features in papillary thyroid carcinoma with Hashimoto's thyroiditis[J]. Gland Surg, 2025, 14(6): 1091-1100. doi: 10.21037/gs-2025-47 [9] Zhang L, Sun X, Liu L, et al. Excessive iodine induces thyroid follicular epithelial cells apoptosis by activating HIF-1α-mediated hypoxia pathway in Hashimoto thyroiditis[J]. Mol Biol Rep., 2023, 50(4): 3633-3640. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08273-z [10] 李会云, 孟冉, 迟茹雪, 等. 雷帕霉素上调线粒体自噬保护脓毒症大鼠下丘脑功能[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2025, 25(5): 812-821+854. [11] 贾思锋, 张卓, 段昱宇, 等. 基于中西医临床病证特点的自身免疫性甲状腺炎动物模型分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31(18): 235-243. [12] 吴菁华. 不同治疗方案对自身免疫性甲状腺炎的疗效比较[D]. 广州: 广州医科大学, 2023. [13] 万斌, 陈正涛, 冷玉琳, 等. 肠道菌群和桥本甲状腺炎的关系及中医药调控研究进展[J]. 世界科学技术-中医药现代化, 2025, 27(3): 626-632. [14] 巩博深, 单忠艳. 肠道菌群与炎症小体在自身免疫性甲状腺炎中的相互调控[J]. 国际内分泌代谢杂志, 2021, 41(4): 309-312. [15] da Silva G B, Yamauchi M A, Bagatini M D. Oxidative stress in Hashimoto's thyroiditis: possible adjuvant therapies to attenuate deleterious effects[J]. Mol Cell Biochem., 2023, 478(4): 949-966. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04564-4 [16] 蒋学林, 刘长江. 基于Akt/mTOR信号通路探讨洋地黄毒苷调控甲状腺滤泡上皮细胞自噬与凋亡的机制[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2024, 33(4): 457-464. [17] 何呈燕, 李依雯, 甘玲, 等. PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路通过调控Th17细胞分化参与EAT小鼠甲状腺自身免疫损伤[J]. 中国医科大学学报, 2024, 53(11): 972-978. [18] 姚婷, 万明. 基于Akt/mTOR通路观察补中益气颗粒对实验性自身免疫性甲状腺炎大鼠的保护作用[J]. 陕西中医, 2023, 44(2): 159-164. [19] 杨加宁, 张立然. 雷帕霉素抑制mTOR激活自噬并调控铁死亡降低宫颈癌细胞增殖, 侵袭及迁移能力的实验研究[J]. 现代检验医学杂志, 2025, 40(3): 42-46. [20] Zhu S, Li X, Dang B, et al. Lycium Barbarum polysaccharide protects HaCaT cells from PM2.5-induced apoptosis via inhibiting oxidative stress, ER stress and autophagy[J]. Redox Rep, 2022, 27(1): 32-44. [21] Tang H, Wang J, Ji G, et al. MARCH5 Promotes the Progression of Thyroid cancer by Regulating Mitochondrial Autophagy Protein FUNDC1-mediated Pyroptosis[J]. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2025, 197(4): 2120-2132. [22] Dağdeviren M, Or Koca A, Akkan T, et al. Is oxidative stress a factor in the pathogenesis of subacute thyroiditis?[J]. Endokrynol Pol., 2022, 73(1): 64-70. [23] 刘梅, 黄晶, 王军, 等. 碘化钾通过诱导PARP1表达活化NF-κB/NLRP3炎症小体促进甲状腺滤泡细胞焦亡[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2021, 37(9): 820-829. -





 下载:
下载: