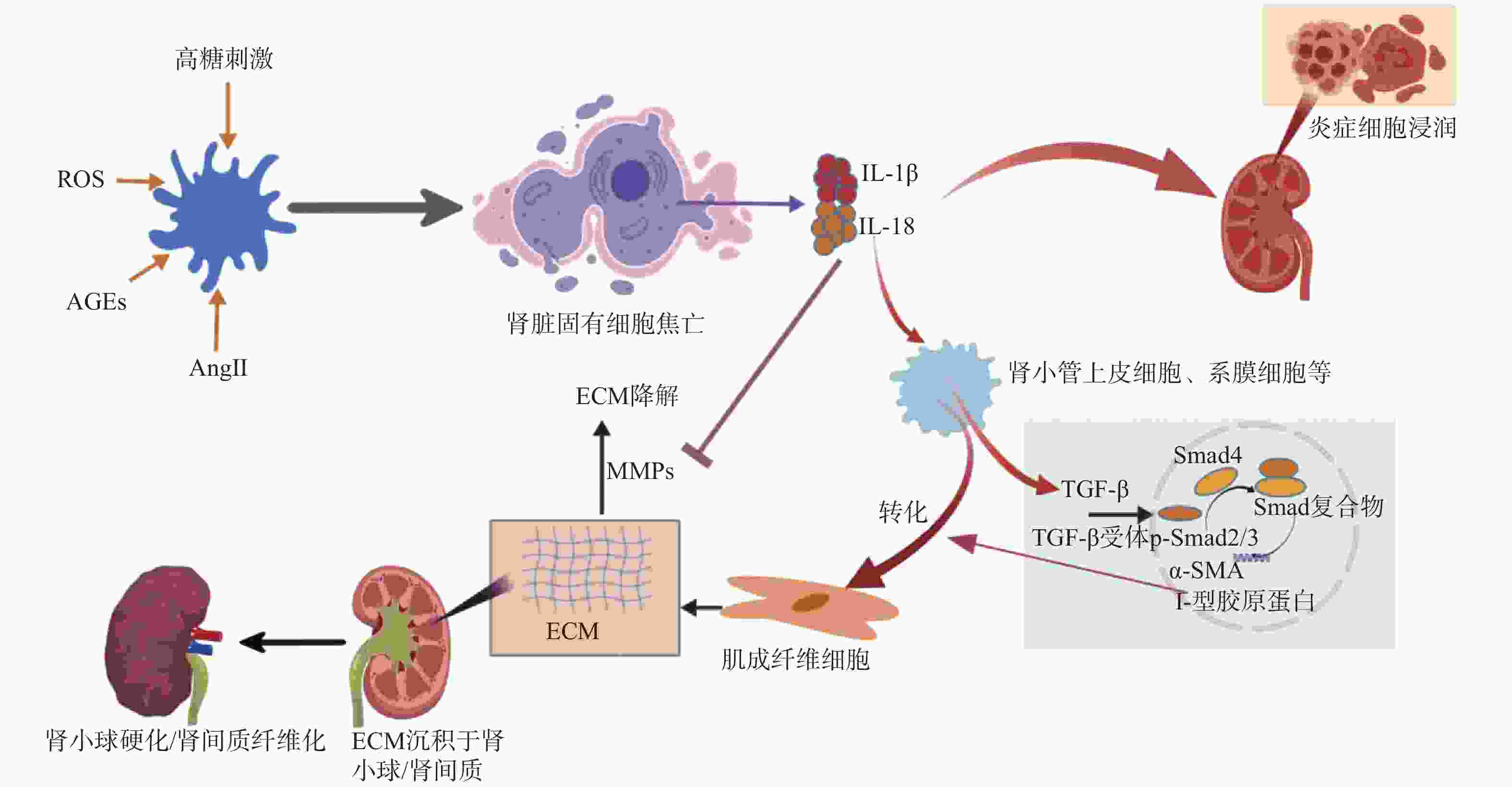
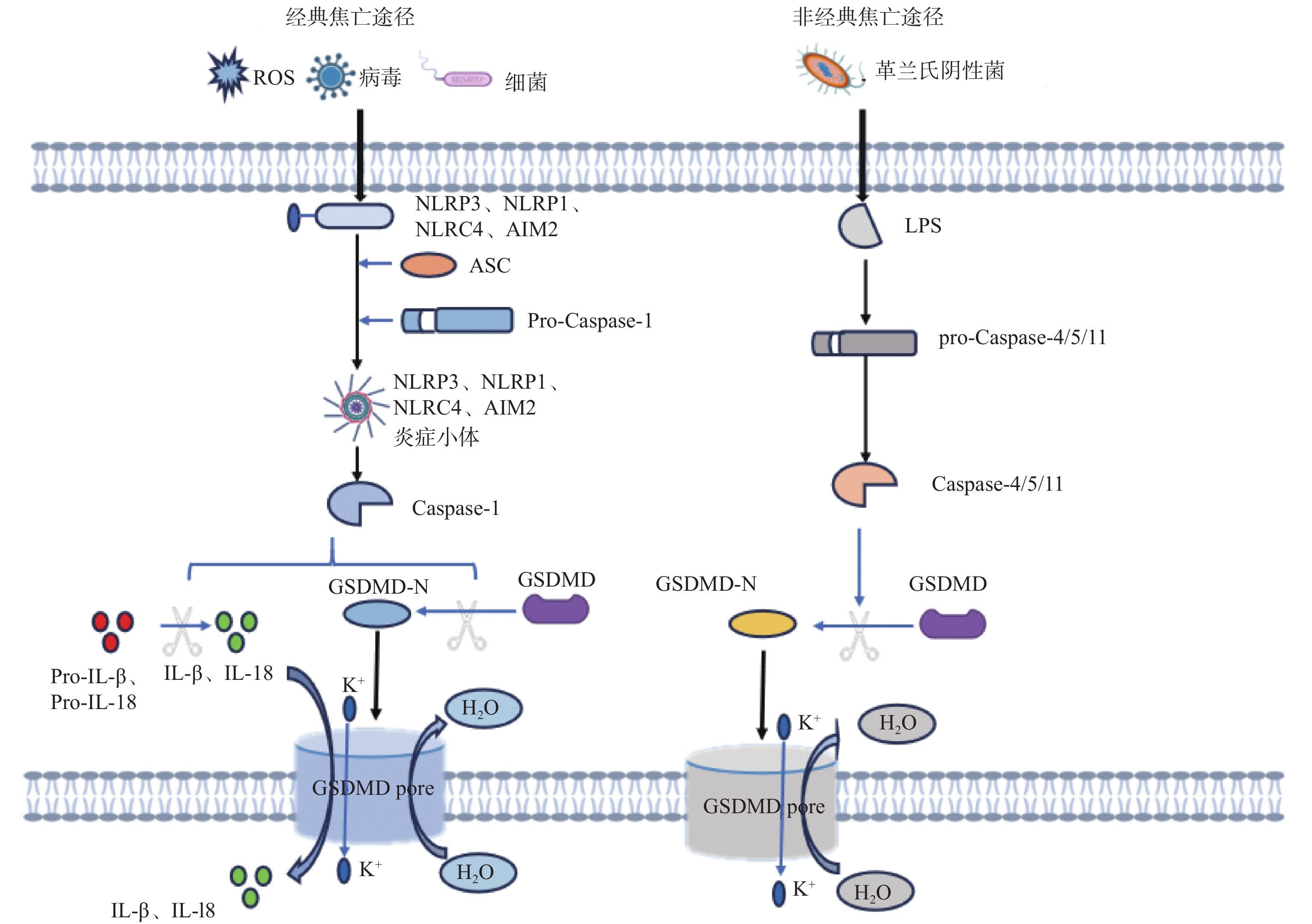
|
[1]
|
Joumaa J P, Raffoul A, Sarkis C, et al. Mechanisms, biomarkers, and treatment approaches for diabetic kidney disease: current insights and future perspectives[J]. J Clin Med, 2025, 14(3): 727.
|
|
[2]
|
He Y, Wang X, Li L, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of chronic type 2 diabetic kidney disease from 1990 to 2021: a trend and health inequality analyses based on the global burden of disease study 2021[J]. J Diabetes, 2025, 17(5): e70098. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.70098
|
|
[3]
|
Zhang H, Wang K, Zhao H, et al. Diabetic kidney disease: from pathogenesis to multimodal therapy-current evidence and future directions[J]. Front Med, 2025, 12: 1631053.
|
|
[4]
|
Efiong E E, Maedler K, Effa E, et al. Decoding diabetic kidney disease: a comprehensive review of interconnected pathways, molecular mediators, and therapeutic insights[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2025, 17(1): 192.
|
|
[5]
|
Fang B, Huang W, Du S, et al. The inflammatory cell death in diabetic kidney disease: integrating multifactorial mechanisms into novel therapeutics[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2025, 26(22): 11033. doi: 10.3390/ijms262211033
|
|
[6]
|
Chen Y, Chen R, Ji X, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis in diabetic nephropathy: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic Targets[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2025, 18: 8399-8418.
|
|
[7]
|
Zheng X, Wan J, Tan G. The mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome/pyroptosis activation and their role in diabetic retinopathy[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1151185. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1151185
|
|
[8]
|
Vasudevan S O, Behl B, Rathinam V A. Pyroptosis-induced inflammation and tissue damage[J]. Semin Immunol, 2023, 69: 101781. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2023.101781
|
|
[9]
|
Wright S S, Vasudevan S O, Rathinam V A. Mechanisms and consequences of noncanonical inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis[J]. J Mol Biol, 2022, 434(4): 167245. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167245
|
|
[10]
|
Du T, Gao J, Li P, et al. Pyroptosis, metabolism, and tumor immune microenvironment[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2021, 11(8): e492.
|
|
[11]
|
Rao Z, Zhu Y, Yang P, et al. Pyroptosis in inflammatory diseases and cancer[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(9): 4310-4329.
|
|
[12]
|
Swanson K V, Deng M, Ting J P. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2019, 19(8): 477-489. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0165-0
|
|
[13]
|
Fu J, Wu H. Structural mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and activation[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2023, 41: 301-316. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-081022-021207
|
|
[14]
|
Zheng X, Chen W, Gong F, et al. The role and mechanism of pyroptosis and potential therapeutic targets in sepsis: A review[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 711939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.711939
|
|
[15]
|
Bauernfried S, Hornung V. Human NLRP1: From the shadows to center stage[J]. J Exp Med, 2022, 219(1): e20211405. doi: 10.1084/jem.20211405
|
|
[16]
|
Romberg N, Vogel T P, Canna S W. NLRC4 inflammasomopathies[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 17(6): 398-404. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000396
|
|
[17]
|
Wang B, Tian Y, Yin Q. AIM2 inflammasome assembly and signaling[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2019, 1172: 143-155. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9367-9_7
|
|
[18]
|
Yu D, Zheng S, Sui L, et al. The role of AIM2 in inflammation and tumors[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1466440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466440
|
|
[19]
|
Oh S, Lee J, Oh J, et al. Integrated NLRP3, AIM2, NLRC4, Pyrin inflammasome activation and assembly drive PANoptosis[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2023, 20(12): 1513-1526.
|
|
[20]
|
Liu Z, Wang C, Lin C. Pyroptosis as a double-edged sword: The pathogenic and therapeutic roles in inflammatory diseases and cancers[J]. Life Sci, 2023, 318: 121498. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121498
|
|
[21]
|
Abu Khweek A, Amer A O. Pyroptotic and non-pyroptotic effector functions of caspase-11[J]. Immunol Rev, 2020, 297(1): e12910.
|
|
[22]
|
Rühl S, Broz P. Caspase-11 activates a canonical NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting K(+) efflux[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2015, 45(10): 2927-2936.
|
|
[23]
|
González P, Lozano P, Ros G, et al. Hyperglycemia and oxidative stress: An integral, updated and critical overview of their metabolic interconnections[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(11): 9352.
|
|
[24]
|
Russell-Guzmán J, Américo-Da Silva L, Cadagan C, et al. Activation of the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 pathway disrupts insulin-dependent glucose uptake in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant obese mice[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2024, 222: 187-198. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.06.011
|
|
[25]
|
Ji K, Chen L, Wang X, et al. Integrating single-cell RNA sequencing with spatial transcriptomics reveals an immune landscape of human myometrium during labour[J]. Clin Transl Med, 2023, 13(4): e1234. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1234
|
|
[26]
|
Liu P, Zhang Z, Li Y. Relevance of the pyroptosis-related inflammasome pathway in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 603416. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.603416
|
|
[27]
|
Liu Y, Lei H, Zhang W, et al. Pyroptosis in renal inflammation and fibrosis: Current knowledge and clinical significance[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14: 472. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06005-6
|
|
[28]
|
Huang R, Fu P, Ma L. Kidney fibrosis: From mechanisms to therapeutic medicines[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 129. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01379-7
|
|
[29]
|
胡雪茹. 吴茱萸次碱对糖尿病肾病足细胞损伤的保护作用及相关机制研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽医科大学, 2022.
|
|
[30]
|
Feng L, Feng Y, Ren Q, et al. Mesangial cells in diabetic kidney disease: from mechanisms to therapeutic implications[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2025, 21(11): 4762-4781. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.114907
|
|
[31]
|
Hu S, Hang X, Wei Y, et al. Crosstalk among podocytes, glomerular endothelial cells and mesangial cells in diabetic kidney disease: an updated review[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2024, 22(1): 136.
|
|
[32]
|
Williams B M, Cliff C L, Lee K, et al. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome in mediating glomerular and tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 13: 907504. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.907504
|
|
[33]
|
Thomas H Y, Ford Versypt A N. Pathophysiology of mesangial expansion in diabetic nephropathy: Mesangial structure, glomerular biomechanics, and biochemical signaling and regulation[J]. J Biol Eng, 2022, 16(1): 19.
|
|
[34]
|
Ostendorf T, Boor P, van Roeyen C R C, et al. Platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) in glomerular and tubulointerstitial fibrosis[J]. Kidney Int Suppl, 2014, 4(1): 65-69.
|
|
[35]
|
Melchinger I, Guo K, Li X, et al. VCAM-1 mediates proximal tubule-immune cell cross talk in failed tubule recovery during AKI-to-CKD transition[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2024, 327(4): F610-F622. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00076.2024
|
|
[36]
|
Thomas J M, Ling Y H, Huuskes B, et al. IL-18 (interleukin-18) produced by renal tubular epithelial cells promotes renal inflammation and injury during deoxycorticosterone/salt-induced hypertension in mice[J]. Hypertension, 2021, 78(5): 1296-1309. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.16437
|
|
[37]
|
Meng X M, Nikolic-Paterson D J, Lan H Y. TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol, 2016, 12(6): 325-338. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.48
|
|
[38]
|
Yu X Y, Sun Q, Zhang Y M, et al. TGF-β/smad signaling pathway in tubulointerstitial fibrosis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 860588. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.860588
|
|
[39]
|
Wang W, Wang X, Chun J, et al. Inflammasome-independent NLRP3 augments TGF-β signaling in kidney epithelium[J]. J Immunol, 2013, 190(3): 1239-1249. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201959
|
|
[40]
|
Liu Y, Lei H, Zhang W, et al. Pyroptosis in renal inflammation and fibrosis: Current knowledge and clinical significance[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(7): 472. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06005-6
|
|
[41]
|
Coll R C, Hill J R, Day C J, et al. MCC950 directly targets the NLRP3 ATP-hydrolysis motif for inflammasome inhibition[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2019, 15(6): 556-559. doi: 10.1038/s41589-019-0277-7
|
|
[42]
|
Jiang H, He H, Chen Y, et al. Identification of a selective and direct NLRP3 inhibitor to treat inflammatory disorders[J]. J Exp Med, 2017, 214(11): 3219-3238. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171419
|
|
[43]
|
Burdette B E, Esparza A N, Zhu H, et al. Gasdermin D in pyroptosis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11(9): 2768-2782. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.006
|
|
[44]
|
Jin Y, Liu Y, Xu L, et al. Novel role for caspase 1 inhibitor VX765 in suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and atherosclerosis via promoting mitophagy and efferocytosis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(5): 512. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04966-8
|
|
[45]
|
Liu Z, Wang C, Rathkey J K, et al. Structures of the gasdermin D C-terminal domains reveal mechanisms of autoinhibition[J]. Structure, 2018, 26(5): 778-784. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2018.03.002
|
|
[46]
|
Dai Z, Liu W C, Chen X Y, et al. Gasdermin D-mediated pyroptosis: Mechanisms, diseases, and inhibitors[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1178662.
|
|
[47]
|
Hu J J, Liu X, Xia S, et al. FDA-approved disulfiram inhibits pyroptosis by blocking gasdermin D pore formation[J]. Nat Immunol, 2020, 21(7): 736-745. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0669-6
|
|
[48]
|
Zahid A, Li B, Kombe A J K, et al. Pharmacological inhibitors of the NLRP3 inflammasome[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02538
|
|
[49]
|
Suganya N, Dornadula S, Chatterjee S, et al. Quercetin improves endothelial function in diabetic rats through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated oxidative stress[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2018, 819: 80-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.11.034
|
|
[50]
|
Choe J Y, Kim S K. Quercetin and ascorbic acid suppress fructose-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation by blocking intracellular shuttling of TXNIP in human macrophage cell lines[J]. Inflammation, 2017, 40(3): 980-994. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0542-4
|





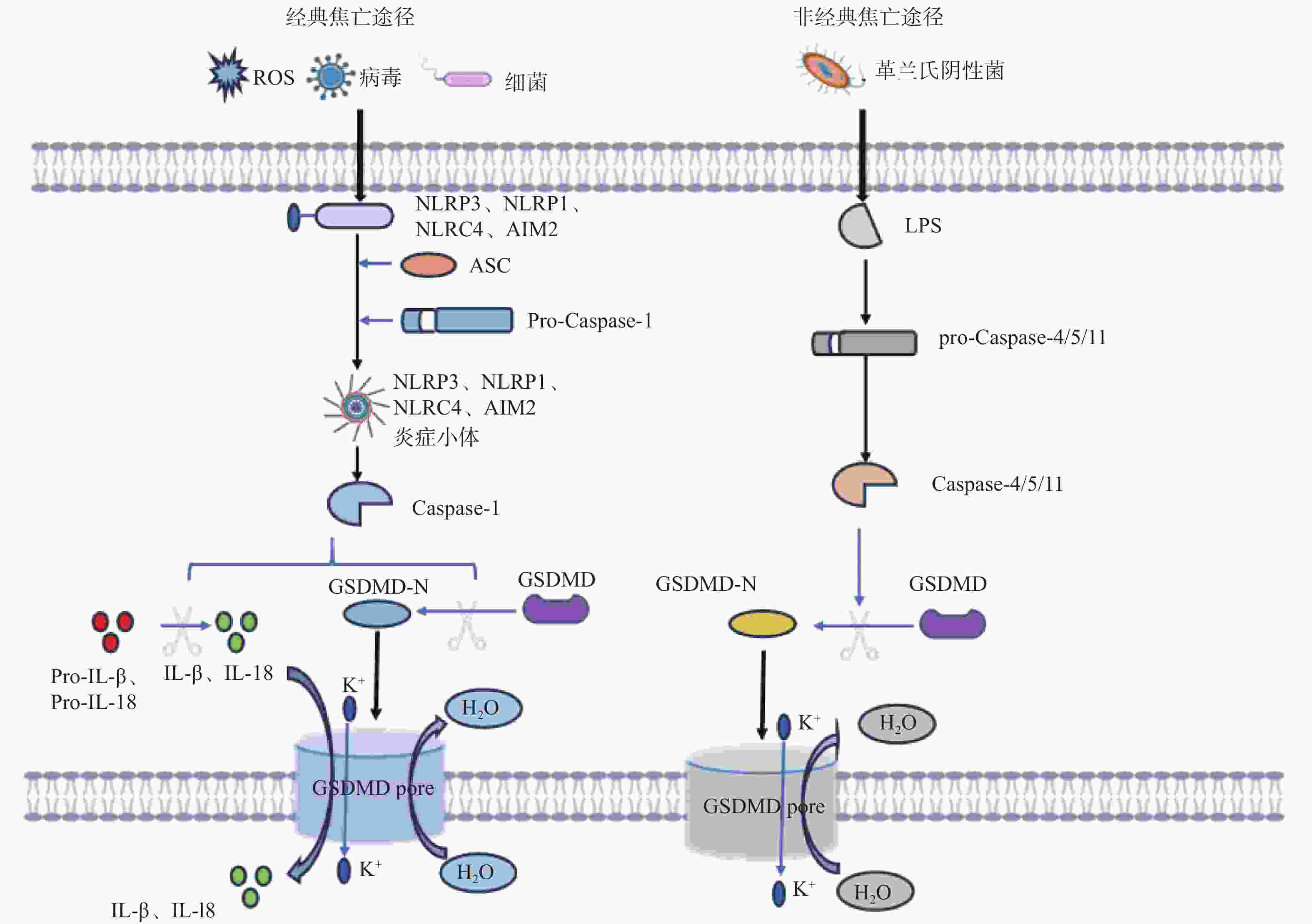
 下载:
下载: