Risk Factors of Cardiomyopathy in Patients with Diabetes and Their Correlations with the Levels of Serum FOXO1,GDF11 and MMP3
-
摘要:
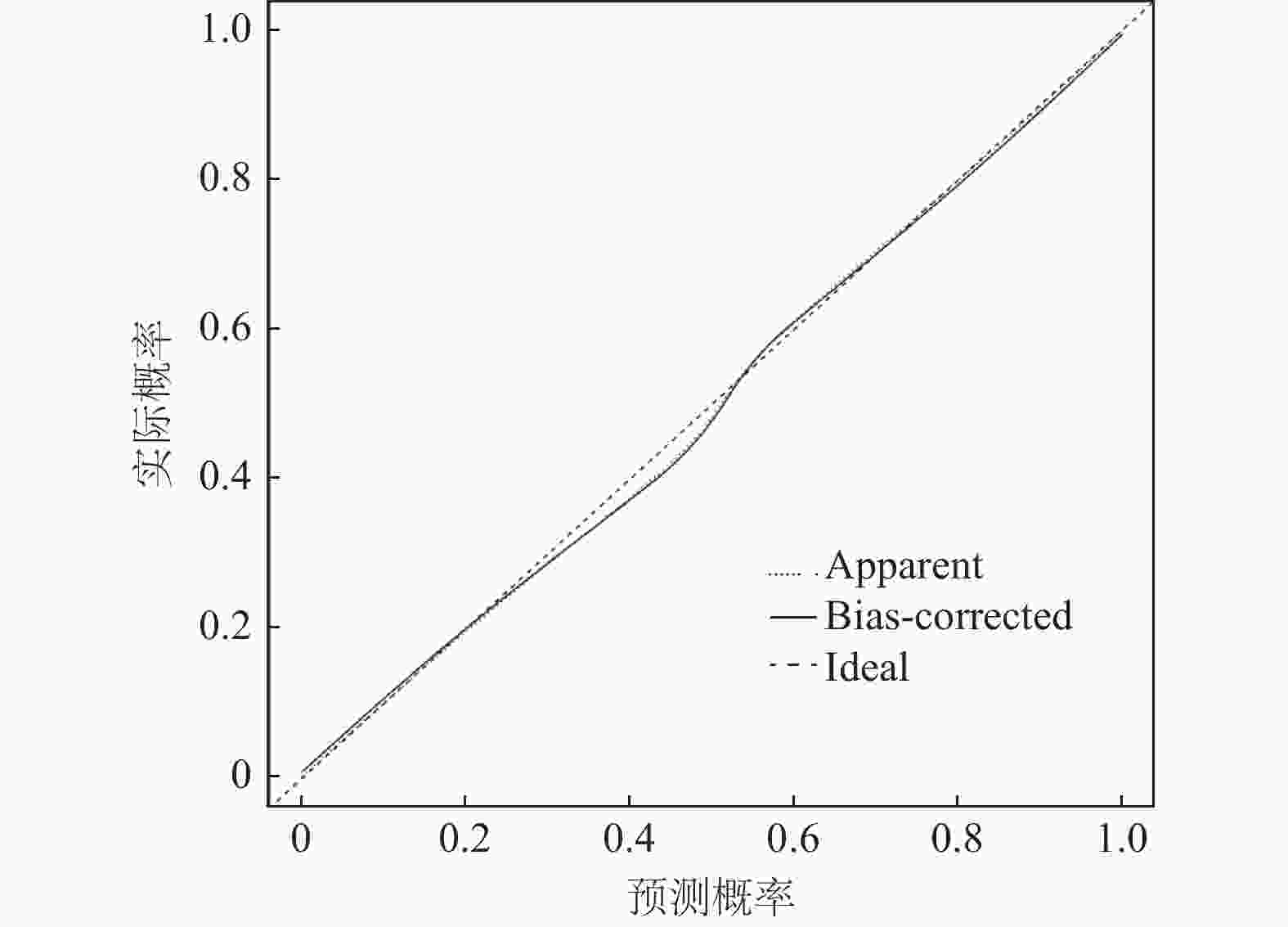
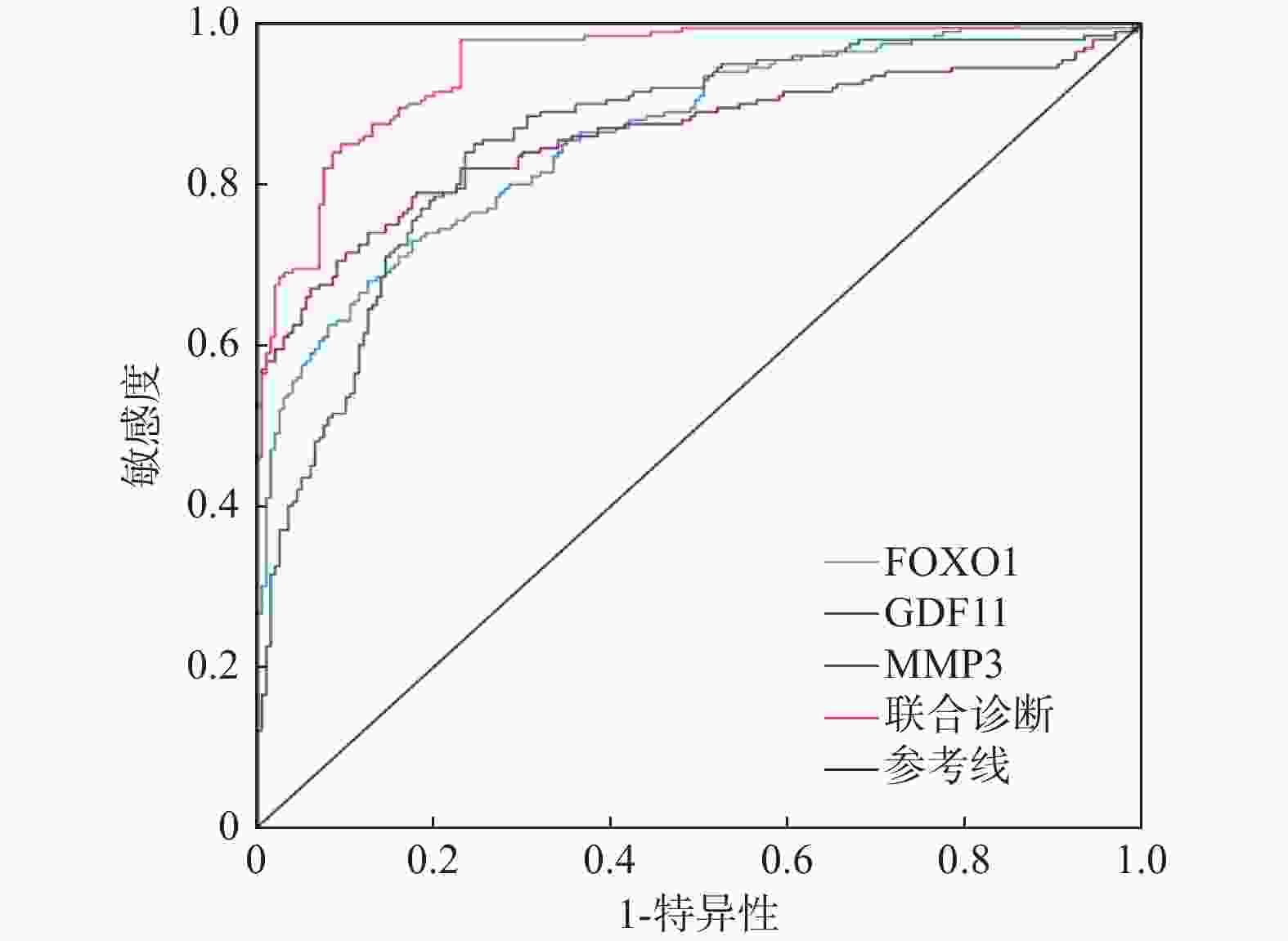
目的 探讨糖尿病患者并发心肌病的危险因素及与血清叉头框蛋白O1(forkhead box protein O1,FOXO1)、生长分化因子11(growth differentiation factor 11,GDF11)、基质金属蛋白酶-3(matrix metalloproteinase-3,MMP3)的相关性。 方法 选取2023年9月至2025年4月新疆维吾尔自治区人民医院收治的200例糖尿病并发心肌病患者及200例单纯糖尿病患者,检测血清FOXO1、GDF11、MMP3水平,分析其与心功能参数的相关性,并通过多因素Logistic回归筛选危险因素,构建列线图模型及受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线并评估诊断价值。 结果 糖尿病心肌病组病程≥10年、活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)表达率≥90%、胰岛素抵抗指数及FOXO1、MMP3水平显著高于单纯糖尿病组患者(P<0.05),GDF11水平低于单纯糖尿病组患者(P < 0.05)。FOXO1、MMP3与E/e'正相关,与LVEF、E/A负相关;GDF11与E/e'负相关,与LVEF、E/A正相关(P < 0.05)。列线图模型显示影响因素权重依次为GDF11、FOXO1、胰岛素抵抗指数、MMP3、ROS表达率、糖尿病病程。模型校准良好(χ2=7.336,P = 0.719)。FOXO1、GDF11、MMP3联合诊断AUC为0.950,优于单一指标(P < 0.05)。 结论 GDF11、FOXO1、胰岛素抵抗指数、MMP3、ROS表达率及糖尿病病程是糖尿病心肌病的危险因素,三者联合诊断价值较高。 Abstract:Objective To explore the risk factors of cardiomyopathy in patients with diabetes and their correlations with the levels of serum fork head box protein O1 (FOXO1), growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11), and matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3). Methods 200 patients with diabetes complicated with cardiomyopathy and 200 patients with simple diabetes admitted to the People's Hospital of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region from September 2023 to April 2025 were selected to detect serum FOXO1, GDF11 and MMP3 levels, analyze their correlation with cardiac function parameters, screen risk factors through multifactor logistic regression, construct a nomogram model and a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and evaluate the diagnostic value. Results The duration of diabetes cardiomyopathy group ≥ 10 years, the expression rate of reactive oxygen species (ROS) ≥ 90%, the insulin resistance index and the levels of FOXO1 and MMP3 were significantly higher than those in the simple diabetes group (P < 0.05), and the level of GDF11 was lower than that in the simple diabetes group (P < 0.05). FOXO1 and MMP3 were positively correlated with E/e 'and negatively correlated with LVEF and E/A; GDF11 was negatively correlated with E/e 'and positively correlated with LVEF and E/A (P < 0.05). The nomogram model showed that the weights of the influencing factors were GDF11, FOXO1, insulin resistance index, MMP3, ROS expression rate, and the course of diabetes. The model calibration was good (χ2=7.336, P = 0.719). The combined diagnostic AUC of FOXO1, GDF11, and MMP3 was 0.950, which was better than that of a single indicator (P < 0.05). Conclusion GDF11, FOXO1, Insulin resistance index, MMP3, ROS expression rate and the course of diabetes are risk factors for diabetes cardiomyopathy, and the combination of the three is of high diagnostic value. -
Key words:
- Diabetes mellitus complicated with cardiomyopathy /
- Risk factors /
- FOXO1 /
- GDF1 /
- MMP3
-
表 1 糖尿病心肌病组和单纯糖尿病组临床资料比较[($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 1. Comparison of clinical data between the diabetic cardiomyopathy group and the simple diabetes group[($ \bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
指标 单纯糖尿病组(n=200) 糖尿病心肌病组(n=200) t/χ2 P 性别 男 109(54.50) 103(51.50) 0.361 0.548 女 91(45.50) 97(48.50) 年龄(岁) 58.42 ± 6.35 57.88 ± 6.64 0.831 0.406 糖尿病病程(年) <10 112(56.00) 74(37.00) 14.511 <0.001* ≥10 88(44.00) 126(63.00) BMI(kg/m2) <24 96(48.00) 85(42.50) 1.221 0.269 ≥24 104(52.00) 115(57.50) FBG(mmol/L) 10.22 ± 1.67 10.43 ± 1.44 1.347 0.179 TC(mmol/L) 4.35 ± 0.74 4.42 ± 0.91 0.844 0.399 TG(mmol/L) 1.55 ± 0.36 1.61 ± 0.44 1.493 0.136 HDL-C(mmol/L) 1.32 ± 0.32 1.26 ± 0.35 1.789 0.074 LDL-C(mmol/L) 3.15 ± 0.68 3.24 ± 0.71 1.295 0.196 ALT(U/L) 29.55 ± 5.47 30.28 ± 5.62 1.316 0.189 AST(U/L) 32.62 ± 6.81 33.46 ± 5.88 1.320 0.187 BUN(mmol/L) 5.41 ± 1.26 5.55 ± 1.34 1.076 0.282 Scr(μmol/L) 64.27 ± 7.48 65.52 ± 7.69 1.648 0.100 胰岛素抵抗指数 4.15 ± 1.14 4.84 ± 1.26 5.743 <0.001* ROS表达率 ≥90% 82(41.00) 121(60.50) 15.213 <0.001* <90% 118(59.00) 79(39.50) 心功能参数 LVEF(%) 59.37 ± 4.15 46.47 ± 3.88 31.614 <0.001* E/A 1.28 ± 0.23 0.94 ± 0.17 16.812 <0.001* E/e' 5.20 ± 0.89 6.42 ± 1.14 11.930 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 2 糖尿病心肌病组和单纯糖尿病组血清FOXO1、GDF11、MMP3水平比较($ \bar x \pm s $)
Table 2. Comparison of serum FOXO1,GDF11 and MMP3 levels between the diabetic cardiomyopathy group and the simple diabetes group ($ \bar x \pm s $)
指标 单纯糖尿病组(n=200) 糖尿病心肌病组(n=200) t P FOXO1(ng/mL) 9.63 ± 2.48 13.45 ± 3.52 9.262 <0.001* GDF11(pg/mL) 521.35 ± 58.67 441.27 ± 46.72 15.100 <0.001* MMP3(ng/mL) 4.64 ± 1.15 7.11 ± 1.88 15.850 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 3 糖尿病心肌病患者血清FOXO1、GDF11、MMP3与心功能参数的相关性
Table 3. Correlation between serum FOXO1,GDF11,MMP3 and cardiac function parameters in patients with diabetic cardiomyopathy
指标 LVEF E/A E/e' r P r P r P FOXO1 −0.509 0.025* −0.495 0.031* 0.526 0.012* GDF11 0.538 0.011* 0.611 <0.001* 0.475 0.033* MMP3 −0.566 0.009* −0.603 0.001* 0.517 0.023* *P < 0.05。 表 4 多因素Logistic分析糖尿病患者并发心肌病的风险因素分析
Table 4. Risk Factors for Myocardial Disease in Diabetic Patients Based on Multivariate Logistic Analysis
影响因素 自变量赋值 β SE Waldχ2 OR 95%CI P 常数项 −3.352 0.352 90.704 0.035 <0.001* 糖尿病病程 <10年=0,≥10年=1 0.970 0.253 14.712 2.639 1.607~4.333 <0.001* 胰岛素抵抗指数 原值输入 1.148 0.274 17.555 3.152 1.842~5.393 <0.001* ROS表达率 ≥90%=1,<90%=0 1.035 0.266 15.149 2.816 1.672~4.743 <0.001* FOXO1 原值输入 1.015 0.281 13.034 2.758 1.590~4.784 <0.001* GDF11 原值输入 −0.889 0.240 13.726 0.411 0.257~0.658 <0.001* MMP3 原值输入 1.201 0.303 15.715 3.324 1.835~6.020 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 5 ROC曲线分析FOXO1、GDF11、MMP3诊断糖尿病患者并发心肌病的价值
Table 5. ROC curve analysis of the value of FOXO1,GDF11,and MMP3 in diagnosing complicated cardiomyopathy in diabetic patients
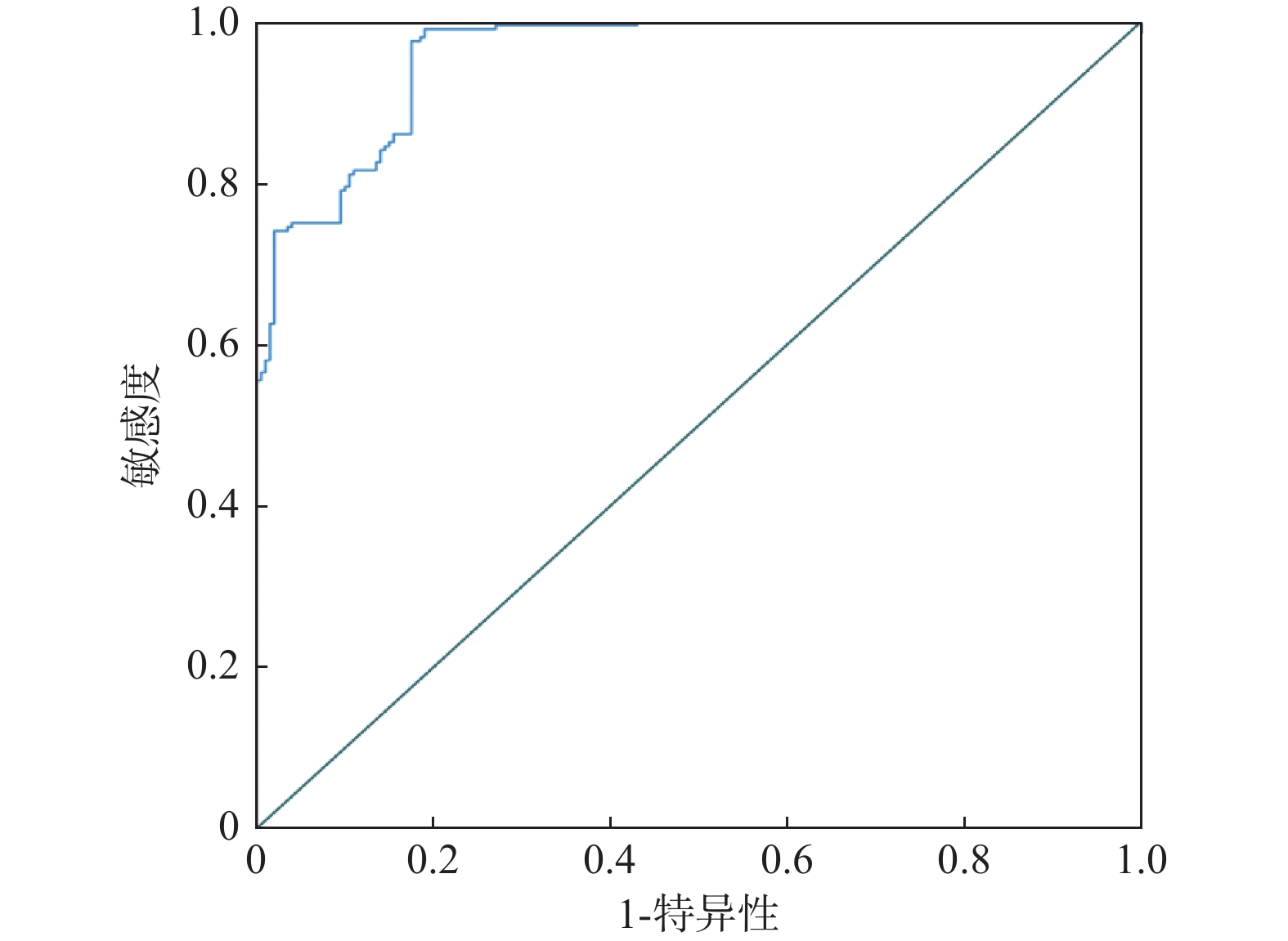
项目 AUC 95%CI 敏感度(%) 特异性(%) 截断值 约登指数 FOXO1 0.860 0.825~0.895 85.50 63.50 10.20 ng/mL 0.490 GDF11 0.858 0.821~0.895 81.50 77.00 474.49 pg/mL 0.585 MMP3 0.861 0.822~0.899 82.00 75.50 5.34 ng/mL 0.575 联合诊断 0.950 0.931~0.969 91.00 80.50 0.715 -
[1] Wang M,Li Y,Li S,et al. Endothelial dysfunction and diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2022,13(1):851941-851952. [2] Zhao X,Liu S,Wang X,et al. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Clinical phenotype and practice[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne),2022,13(3):1032268-1032294. [3] Zhang N,Yu H,Liu T,et al. Bmal1 downregulation leads to diabetic cardiomyopathy by promoting Bcl2/IP3R-mediated mitochondrial Ca overload[J]. Redox Biol,2023,64(1):102788-102803. [4] Zhang M,Sui W,Xing Y,et al. Angiotensin IV attenuates diabetic cardiomyopathy via suppressing FoxO1-induced excessive autophagy,apoptosis and fibrosis[J]. Theranostics,2021,11(18):8624-8639. doi: 10.7150/thno.48561 [5] Zhang Y,Zhang Y Y,Pan Z W,et al. GDF11 promotes wound healing in diabetic mice via stimulating HIF-1ɑ-VEGF/SDF-1ɑ-mediated endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and neovascularization[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin,2023,44(5):999-1013. doi: 10.1038/s41401-022-01013-2 [6] Djuric T,Kuveljic J,Djordjevic A,et al. Association of MMP1 and MMP3 haplotypes with myocardial infarction and echocardiographic parameters of the left ventricle[J]. Mol Genet Genomic Med,2022,10(9):e2022. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.2022 [7] 中华中医药学会糖尿病基层防治专家委员会,杨叔禹. 国家糖尿病基层中医防治管理指南(2022)[J]. 中华糖尿病杂志,2023,15(2):100-117. [8] 中国医师协会中西医结合医师分会内分泌与代谢病学专业委员会. 糖尿病心肌病病证结合诊疗指南(2021-12-31)[J]. 世界中医药,2022,17(12):1641-1653. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7202.2022.12.001 [9] Peng C,Zhang Y,Lang X,et al. Role of mitochondrial metabolic disorder and immune infiltration in diabetic cardiomyopathy: new insights from bioinformatics analysis[J]. J Transl Med,2023,21(1):66-84. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03928-8 [10] Ma X,Mei S,Wuyun Q,et al. Epigenetics in diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Clin Epigenetics,2024,16(1):52-69. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01667-1 [11] Li X,Wan T,Li Y. Role of FoxO1 in regulating autophagy in type 2 diabetes mellitus (Review)[J]. Exp Ther Med,2021,22(1):707-714. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10139 [12] 罗会林,吴志林,杨芸芸. 抑制叉头框蛋白O1通过调控Janus激酶/信号转导与转录激活子3信号通路对糖尿病心肌病大鼠心肌细胞保护作用的研究[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志,2024,32(9):689-694. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6187.2024.09.011 [13] Kyriazis ID,Hoffman M,Gaignebet L,et al. KLF5 is induced by FOXO1 and causes oxidative stress and diabetic cardiomyopathy[J]. Circ Res,2021,128(3):335-357. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316738 [14] 杨敬敬,闫康禄,孟洁,等. 妊娠期糖尿病患者血清Spexin、FoxO1水平与胰岛素抵抗及预后的关系[J]. 天津医药,2025,8(3):1-5. [15] Kraler S,Balbi C,Vdovenko D,et al. Circulating GDF11 exacerbates myocardial injury in mice and associates with increased infarct size in humans[J]. Cardiovasc Res,2023,119(17):2729-2742. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvad153 [16] Shao Y,Li M,Wang Y,et al. GDF11 mitigates high glucose-induced cardiomyocytes apoptosis by inhibiting the ALKBH5-FOXO3-CDR1as/Hippo signaling pathway[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res,2024,1871(3):119656-119667. [17] 王晨鸽,王晓东,骆玉明,等. 血清Metrnl、GDF11表达水平与糖尿病足感染患者下肢血管病变及预后的关系[J]. 疑难病杂志,2025,24(4):412-417. [18] Abdul Y,Jamil S,Li W,et al. Cerebral microvascular matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3) contributes to vascular injury after stroke in female diabetic rats[J]. Neurochem Int,2023,162(4):105462-105487. [19] Shu J,Gu Y,Jin L,et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 3 regulates angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis cell viability,migration and apoptosis[J]. Mol Med Rep,2021,23(2):151-162. [20] Figueiredo R,Adão R,Leite-Moreira AF,et al. Candidate microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers in heart failure: A systematic review[J]. Rev Port Cardiol,2022,41(10):865-885. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2021.03.020 -






 下载:
下载: