Effects and Mechanism of Anlotinib on Radiosensitivity of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines A549
-
摘要:
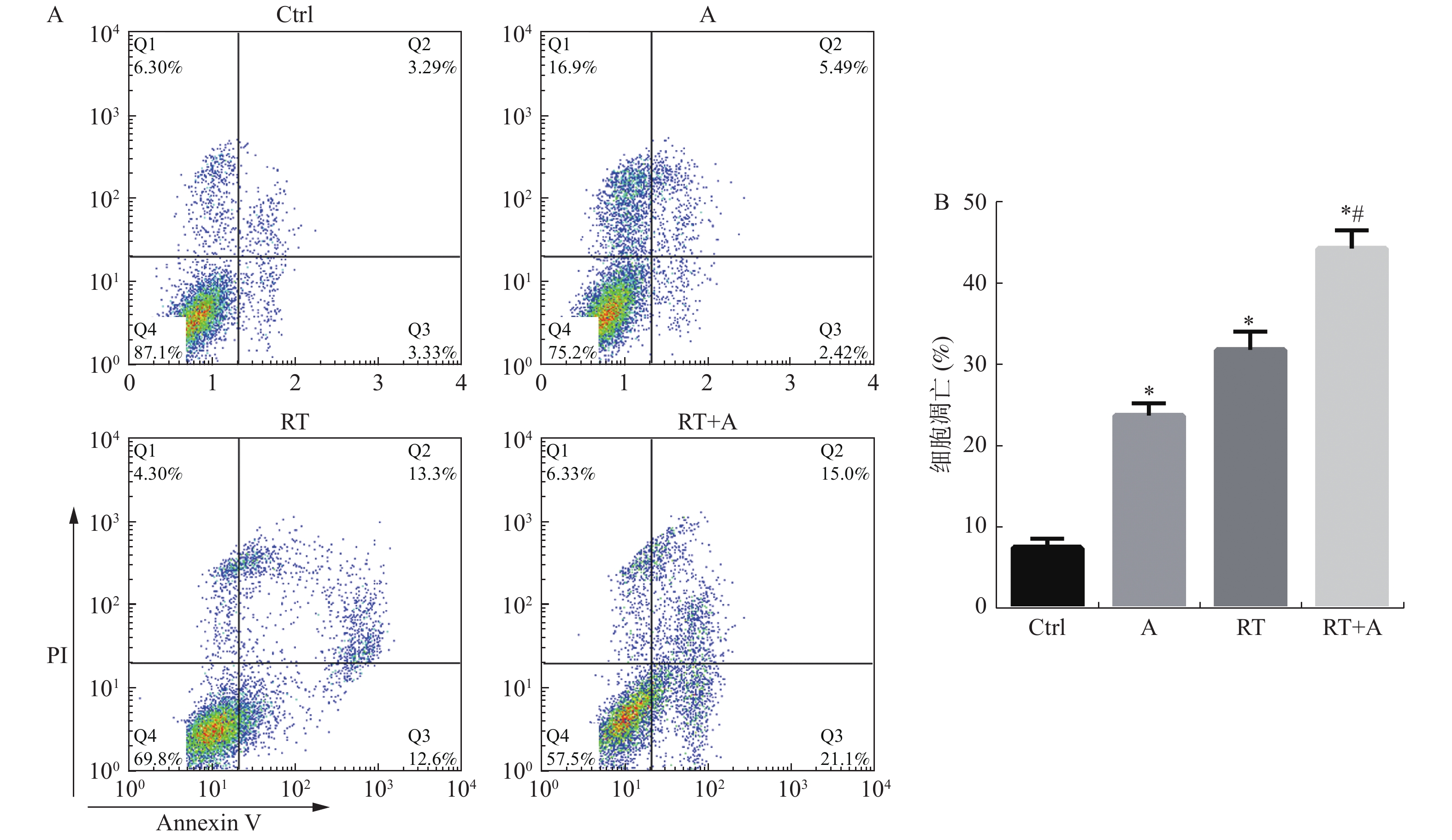
目的 研究安罗替尼对肺腺癌细胞放疗增敏作用及机制。 方法 采用安罗替尼处理人肺腺癌细胞株A549,使用CCK8法测定安罗替尼对细胞增殖的影响;采用克隆形成实验测定安罗替尼联合放疗对细胞的生长抑制作用;使用流式细胞术测定细胞周期和细胞凋亡的变化;采用免疫荧光测定安罗替尼联合放疗对细胞内DNA损伤的影响;采用Western blot检测细胞内DNA损伤标志因子DNA-PKcs的表达变化。 结果 安罗替尼对人肺腺癌细胞A549增殖具有抑制作用,第2、3、4、5天,(P < 0.05)。体外培养克隆形成实验显示,安罗替尼联合放疗组的准予剂量(Dq)、平均致死剂量(D0)及4 Gy照射时的存活分数(SF)均明显低于单纯放疗组( P < 0.05)。安罗替尼能够使细胞阻滞于G1/G0期,与放疗联合作用后,进一步降低了G2和S期细胞比例。安罗替尼能够增加放疗诱导的细胞凋亡比例(31.94±2.25)%和(44.44±2.30)%,( P < 0.001),增加γH2AX阳性细胞数量(25.67±2.52)%和(54.67±3.79)%,( P < 0.001)。安罗替尼能够降低放疗诱导的DNA断裂损伤标志因子DNA-PKcs的表达强度(0.90±0.06)和(0.40±0.06),( P < 0.001)。 结论 安罗替尼具有放疗增敏作用,其机制可能与减少G2/S期细胞、增加细胞凋亡和维持DNA持续损伤有关。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect and mechanism of anlotinib on radiosensitization of human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549. Methods Human lung adenocarcinom cell line A549 was treated with anlotinib and/or radiotherapy, then divided in to four groups, control group (Ctrl), Anlotinib treatment group (A), irradiation group (RT) and anlotinib combined with irradiation group (A + RT). CCK8 method was used to determine cell proliferation; the clone formation experiment was used to determine the inhibitory effect on cell growth; flow cytometry was used to determine cell cycle and apoptosis; immunofluorescence of γ-H2AX was used to determine DNA damage; expression of DNA-PKcs were detected by Western blot. Results Anlotinib inhibited proliferation and clonogenic survival following irradiation. The dose (Dq), the average lethal dose (D0) and the survival score (SF2) in the anlotinib combined radiotherapy group was significantly lower than those in the radiotherapy group. Anlotinib decreased G2/M phase arrest and promoted the cells apoptosis induced by in irradiation. The confocal microscopy results showed the average number of γ-H2AX foci in the A+RT group was more than that in RT group. The protein levels of DNA-PKcs were higher in A + RT group than that in RT group. Conclusion Anlotinib enhances the radiosensitivity of A549 cells, which may be attributed to the delay DNA damage repair. It provides a rationale strategy by Anlotinib combined with irradiation for NSCLC. -
Key words:
- Anlotinib /
- Non-small cell lung cancer /
- Radiosensitization /
- DNA damage repair
-
肿瘤是1个公共卫生问题,2020年全球新诊断癌症1930万例[1],全世界的癌症发病和负担正在迅速增长。由于肿瘤患者的自身体能免疫功能下降、肿瘤治疗对患者认知、平衡和肌肉力量,以及感觉和器官功能的影响导致肿瘤患者更易发生跌倒[2]。据统计,肿瘤患者跌倒发生率高于非肿瘤患者,终末期肿瘤患者的跌倒风险高达50%,其中42%的跌倒会导致严重伤害[2],不仅干扰患者后续治疗进程,还增加了患者和社会的医疗经济成本。
目前,研究显示肿瘤患者发生跌倒的影响因素包括社会人口学因素、治疗因素、心理和运动功能因素等[3]。但在不同研究中肿瘤患者跌倒发生率差异较大,相关因素对跌倒的影响不一致[4-5]。因此,本研究系统评价了国内外肿瘤患者跌倒发生率及其影响因素,旨在为临床医护人员制定肿瘤患者跌倒的风险评估和预防措施提供参考依据。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 纳入与排除标准
研究纳入标准[5]:(1)研究对象:年龄 18岁,经病理学、影像学确诊为恶性肿瘤的患者;(2)暴露因素:不同影响因素的暴露;(3)结局指标:是否发生跌倒,采用世界卫生组织的定义:跌倒指1个人不慎落在地面或地板或其它低于原先位置的表面上的事故;(4)研究类型:队列研究、病例对照研究以及横断面研究。排除标准[5]:(1)无法获取全文或重复发表的文献;(2)文献质量评价偏倚风险高;(3)无法提取发生率和相关因素数据的文献;(4)非中文和英文的文献。
1.2 检索策略
计算机检索PubMed、CINAHL、Embase、The Cochrane Library、中国生物医学文献数据库、中国知网、万方数据库、维普数据库。检索时限为数据库建立至2024年1月。中文检索词为:“癌症/肿瘤/恶性肿瘤、跌倒/摔倒,影响因素/相关因素。英文检索词为:为“cancer*/neoplas*/tumo*/carcinoma*/metasta*/malignan*/ocolog*,accidental fall*/fall*/slip*,relevant factor*/influencing factor*/predictor*/related factor*/associated factor*/determinant*”。同时采通过累计效应的方式追溯纳入文献的参考文献。pubmed检索式:(cancer*[Title/Abstract]) OR (neoplas*[Title/Abstract]) OR (tumo*[Title/Abstract]) OR (ocolog*[Title/Abstract]) AND (accidental fall*[Title/Abstract]) OR (fall*[Title/Abstract]) OR (slip*[Title/Abstract]) AND (relevant factor*[Title/Abstract]) OR (influencing factor*[Title/Abstract]) OR (risk factor*[Title/Abstract]) OR (predictor*[Title/Abstract]) OR (determinant*[Title/Abstract])。
1.3 文献筛选与数据提取
由2名研究者根据文献纳入和排除标准独自筛选文献,获取资料后交叉核对,若存在争议则由其他研究者裁决。将检索到的文献导入Endnote软件,去除重复文献后,2名研究者初步筛选标题和摘要,初筛后阅读全文,确定最终纳入的文献。提取出文献作者、发表时间、国家、研究类型、样本量、发生率和影响因素。
1.4 文献质量评价
由2名通过循证医学学习的研究人员根据偏倚风险评估工具独立对纳入文献进行质量评价,如有分歧请第3名研究者(通信作者)协同裁决。队列研究和病例对照研究使用纽卡斯尔-渥太华量表(the Newcastle Ottawa Scale,NOS)进行文献质量评价,包括研究人群选择、组间可比性、暴露或结果评价3个维度,0~3分、4~6分、7分及以上分别对应低质量、中等质量与高质量文献。 横断面研究采用美国卫生保健质量和研究机构(Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality,AHRQ)推荐的评价标准,总计11个条目,满分为11分,0~3分、4~7分、8分及以上分别对应低质量、中等质量与高质量文献。
1.5 统计学处理
本研究使用RevMan 5.4软件对纳入文献的影响因素进行Meta分析, 连续型变量采用标准化均数差(standardized mean difference,SMD)及95%置信区间(95%CI)表示合并统计量,二分类变量采用比值比(odds radio,OR)及95%CI表示合并统计量,若P ≤ 0.05,则合并统计量具有统计学意义。当异质性检验结果为P > 0.1时或I2 ≤ 50%,表明研究间异质性可接受,采用固定效应模型进行分析;若P ≤ 0.1或I2 > 50%,表示研究间异质性较大,采用随机效应模型进行分析。
2. 结果
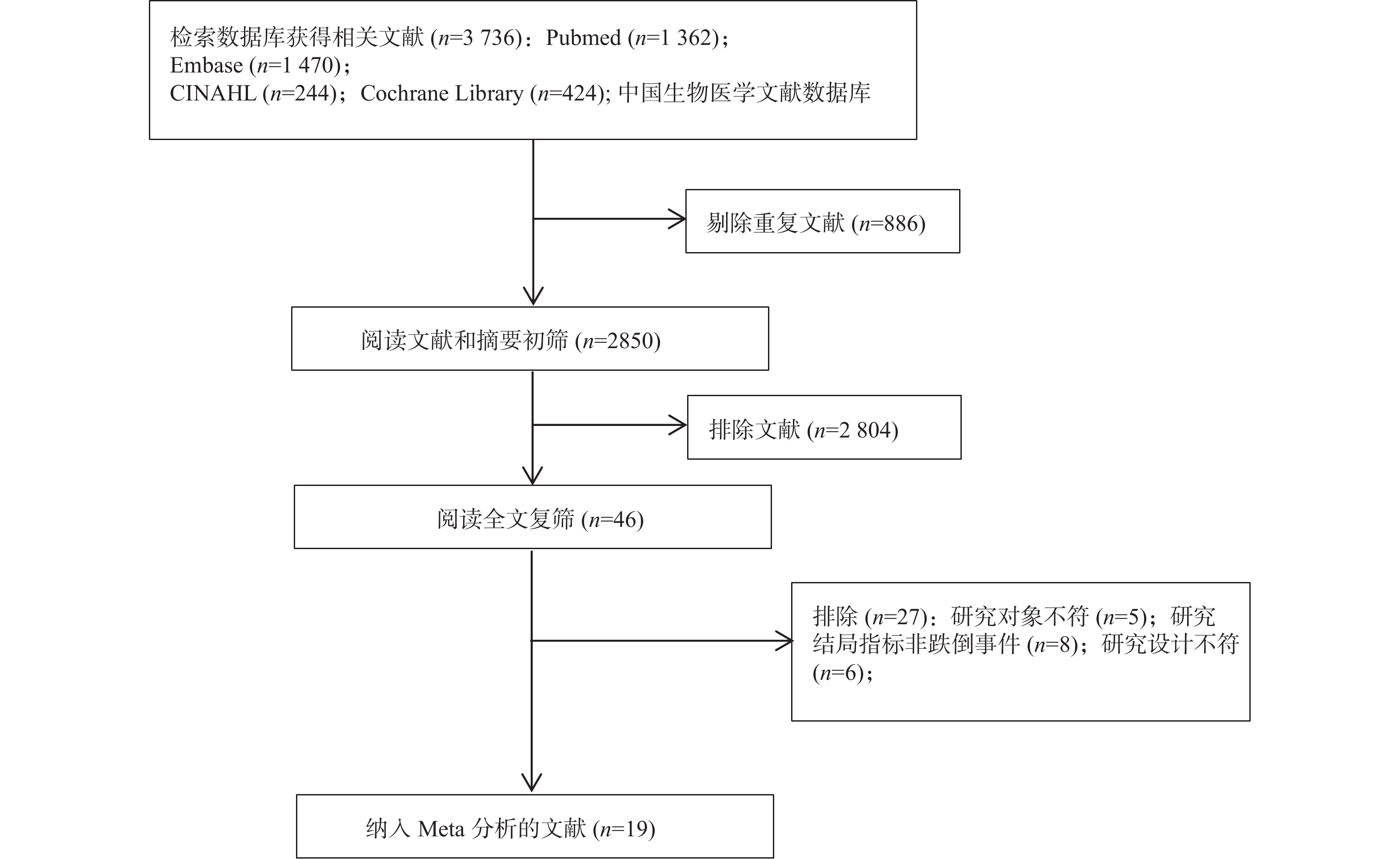
2.1 纳入文献的筛选流程、基本特征及质量评价结果
初步检索获得
3736 篇文献,最终纳入文献19篇,其中英文文献18篇,中文文献1篇。4篇病例对照研究、7篇横断面研究和8篇队列研究,共计样本量70 508例,其中跌倒组17 213例、非跌倒组53 295例,文献筛选流程见图1。纳入文献中,病例对照研究和队列研究的质量评分为6至9分,横断面研究的质量评分为7至11分,文献筛选流程,见图1,纳入文献基本特征和质量评价,结果见表1。表 1 纳入文献的基本信息和质量评价结果(n=19)Table 1. Basic characteristics and evaluation of included literatures (n=19)纳入文献 发表年份 研究类型 国家 样本量 跌倒发生率 影响因素 NOS/AHRQ评分 Komatsu,Hiroko等[6] 2018年 横断面研究 日本 50 0.180 abechr 7 Argyriou,Andreas A等[7] 2020年 队列研究 希腊 122 0.172 bip 6 Bao,Ting等[8] 2016年 横断面研究 美国 296 0.319 p 9 Capone,Luann J等[3] 2012年 病例对照 美国 286 0.030 bfijlnouvwy 6 Chen,Tuo-Yu等[9] 2014年 病例对照 美国 1640 0.303 oy 7 Huang,Min H等[10] 2019年 队列研究 美国 1097 0.233 acdfjmprsy 9 Huang,Min H等[11] 2015年 队列研究 美国 41 0.560 bijmt 8 Kenis,Cindy等[12] 2022年 病例对照 比利时 3681 0.209 bdfgikoqstxz 9 Komatsu,Hiroko等[4] 2019年 横断面研究 日本 88 0.491 aech 9 Kong,Qiu-Huan等[13] 2014年 队列研究 中国 203 0.133 bfhnsxyz 6 Lamba,Nayan等[14] 2021年 病例对照 美国 42759 0.241 bdi 7 Pandya,Chintan等[15] 2016年 横断面研究 美国 17958 0.252 abecdijprsz 11 Saberi,Najmeh等[16] 2022年 横断面研究 伊朗 300 0.353 bedghijm 8 Rattanakrong,Nida等[17] 2022年 队列研究 泰国 123 0.236 lmp 9 Puts,Martine T E等[18] 2013年 队列研究 加拿大 112 0.152 bdhijsz 7 Turner,Justin P等[19] 2017年 横断面研究 澳大利亚 385 0.239 btuvz 7 Vande Walle,Nathalie等[20] 2014年 队列研究 比利时 809 0.176 bdfkoqrstxz 8 Wildes,Tanya M等[21] 2018年 横断面研究 美国 498 0.183 stw 8 刘伟等[22] 2021年 队列研究 中国 60 0.283 m 8 注:影响因素:a:年龄;b:性别;c:文化程度;d:居住情况;e:工作情况;f:跌倒史;g:跌倒恐惧;h:肿瘤分期;i:肿瘤分类;j:肿瘤治疗方式;k:营养状况;l:体重;m:BMI;n:发热;o:疼痛;p:周围神经病变;q:疲乏;r:抑郁;s:共病;t:多重用药;u:抗抑郁药;v:抗精神病药;w:镇静催眠药;x:认知功能;y: 平衡与步态;z:日常生活能力。 2.2 成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生率的Meta分析结果
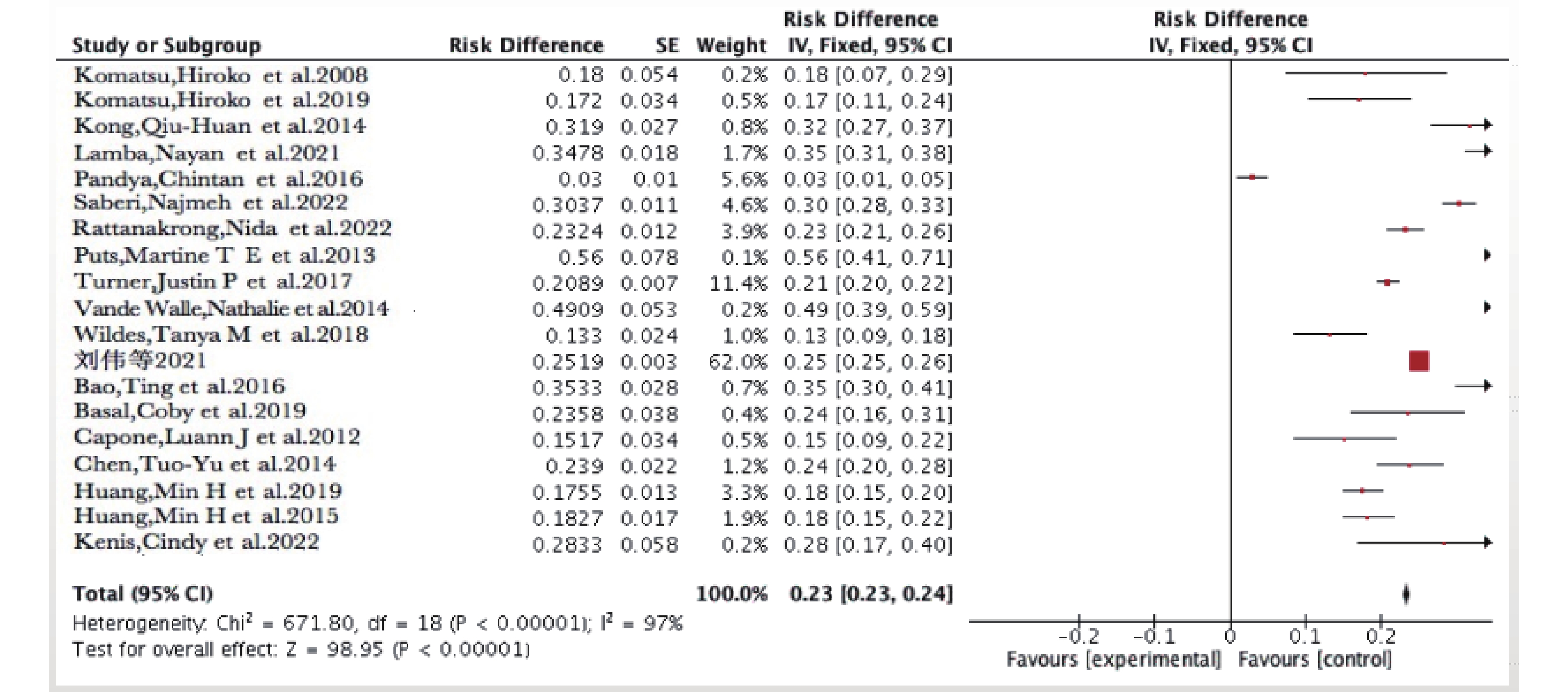
对从19项研究中提取出的成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生率数据进行Meta分析,纳入的研究间异质性大(I2 = 97%,P < 0.001),使用随机效应模型分析,成人肿瘤患者跌倒的合并发生率为0.23(95%CI0.23,0.24)。逐项剔除纳入研究,使用固定效应模型合并效应量,敏感性分析显示,合并的跌倒发生率无显著变化,Meta分析结果较稳定,见图2。
2.3 成人肿瘤患者跌倒相关因素的系统评价
对19篇文献中的26个影响因素数据(研究数量 2篇、变量类型一致、变量分类一致)进行meta分析;包括患者的社会人口学因素、跌倒史及跌倒恐惧、疾病相关因素、治疗相关因素、症状相关因素和机体功能相关因素,见表2。
表 2 成人肿瘤患者跌倒影响因素Meta分析结果(2)Table 2. Meta analysis results on the influencing factors of falls in adult tumor patients(2)2.3.1 社会人口学因素
纳入研究分析了5个社会人口学因素,包括年龄、性别、文化程度、居住和工作情况。Meta分析固定效应模型(I2 ≤ 50%)显示,年龄(SMD = 1.89,95%CI 1.76,2.02),文化程度(OR = 1.11,95%CI 1.03,1.09)和成人肿瘤患者跌倒有关,而工作情况(OR = 1.01,95%CI 0.93,1.10)与其无关。Meta分析随机效应模型(I2 > 50%)的结果显示,性别(OR = 0.88,95%CI 0.77,1.00)和成人肿瘤患者跌倒有关,而居住情况(OR = 1.14,95%CI 0.94,1.39)与其无关。
2.3.2 跌倒史及跌倒恐惧
Meta分析随机效应模型(I2 > 50%)的结果显示,跌倒史(OR = 4.33,95%CI 3.75,5.00)和跌倒恐惧(OR = 2.42,95%CI 1.46,4.03)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒有关。
2.3.3 疾病相关因素
纳入的研究评估了4个疾病相关因素,包括了肿瘤分期、肿瘤类型、是否存在共病及共病数量。固定效应模型(I2 ≤ 50%)的结果显示,肿瘤分期(OR = 0.40,95%CI 0.28,0.57),是否存在共病(OR = 1.11,95%CI 1.02,1.21)以及共病的数量(SMD = 0.68,95%CI 0.44,0.92)、乳腺癌(OR = 1.22,95%CI 1.16,1.29)、生殖系统肿瘤(OR = 2.10,95%CI 1.36,3.24)、前列腺癌(OR = 1.52,95%CI 1.41,1.54)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生有关,而消化道肿瘤(OR = 0.98,95%CI 0.90,1.08)、头颈部肿瘤(OR = 1.19,95%CI 0.26,5.44)与其无关。Meta分析随机效应模型(I2 > 50%)的结果显示,肺癌(OR = 1.14,95%CI 0.59,2.19)和血液肿瘤(OR = 1.88,95%CI 0.61,5.78)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生无关。
2.3.4 治疗相关因素
纳入的研究评估了4个治疗相关因素,包括了肿瘤治疗方式、使用的药物数量、多重用药(n 5)、药物种类。Meta分析固定效应模型(I2 ≤ 50%)的结果显示,化疗(OR = 2.08,95%CI 1.34,3.23)、放疗(OR = 1.43,95%CI 1.32,1.54)、手术治疗(OR=0.91,95%CI 0.85,0.98)、使用药物数量(SMD = 1.62,95%CI 1.42,1.82)、是否多重用药(n 5)(OR = 1.55,95%CI 1.33,1.82)、使用抗抑郁药(OR = 3.23,95%CI 2.02,5.15)、抗精神病药(OR=3.18,95%CI 2.07,4.88)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒有关。Meta分析随机效应模型(I2 > 50%)的结果显示,使用镇静催眠药(OR = 3.28,95%CI 1.62,6.66)与其有关。
2.3.5 症状相关因素
纳入的研究评估了4个治疗相关因素,包括了发热、疼痛、周围神经病变、疲乏和抑郁。Meta分析固定效应模型(I2≤50%)的结果显示,发热(OR = 7.15,95%CI 3.54,13.43)、疲乏(OR = 1.20,95%CI 1.01,1.42)、抑郁(OR = 2.68,95%CI 2.47,2.91)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生有关,Meta分析随机效应模型(I2 > 50%)的结果显示,疼痛(OR = 1.05,95%CI 0.34,3.19)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生无关、周围神经病变(OR = 2.46,95%CI 1.03,5.92)与其有关。
2.3.6 机体功能相关因素
纳入研究包括4个机体功能相关因素,认知功能、营养状况、平衡与步态、日常生活能力。固定效应模型(I2 ≤ 50%)的结果显示,营养状况(OR = 1.35,95%CI 1.13,1.62)、认知功能(OR = 1.77,95%CI 1.47,2.12)、平衡障碍(OR = 2.78,95%CI 2.28,3.40)、步态异常(OR = 11.53,95%CI 6.75,19.68)、ADL(OR = 3.75,95%CI 3.51,4.01)、IADL(OR = 1.81,95%CI 1.55,2.12)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生有关,BMI(SMD = 0.19,95%CI -0.05,0.42)与其无关。Meta分析随机效应模型(I2 > 50%)的结果显示,体重(SMD = −0.32,95%CI -0.52,−0.11)、ECOG(OR = 2.16,95%CI 1.46,3.19)与成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生有关。
2.4 发表偏倚的检测
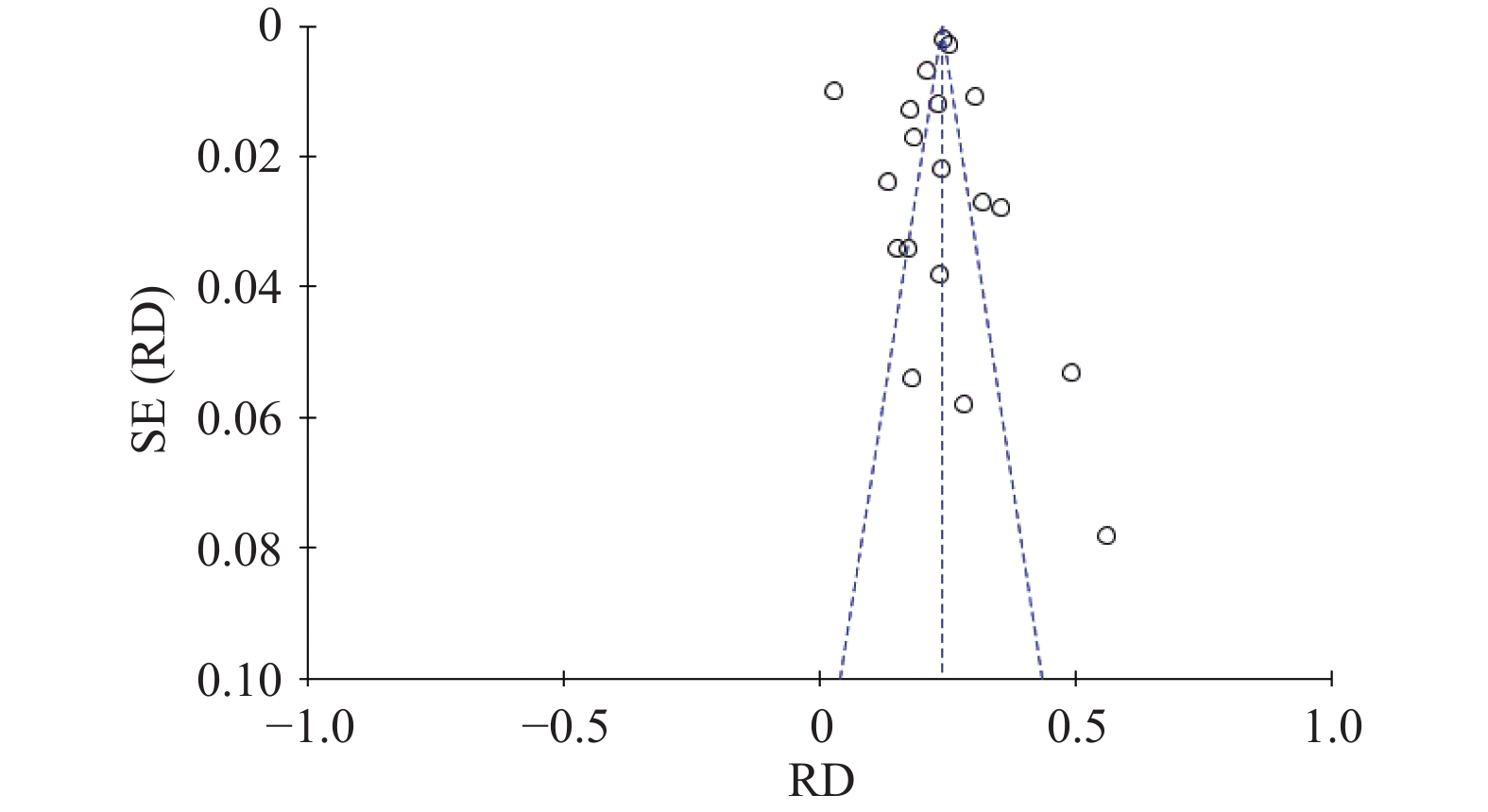
针对发生率对纳入的19篇文献制作漏斗图,图示大部分研究对称分布于竖线2侧,存在部分发表偏倚,见图3。
3. 讨论
3.1 成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生率较高
本研究显示,成人肿瘤患者跌倒的合并发生率为23.0%。纳入研究的异质性较大,一方面,与各研究纳入样本量不同有关;另一方面可能与跌倒结局以患者自我报告为主,受到患者当时状态、回忆偏倚和漏报等影响。美国1项纳入
17958 例老年肿瘤患者的研究显示[15],跌倒发生率25.2%,与本研究结果较为接近。肿瘤患者跌倒发生率高于全球跌倒发生率6.26%[23]以及老年人的跌倒发生率19.3%[24]。肿瘤患者群体面临着较高的跌倒风险,随着肿瘤发病率和负担迅速增加,在肿瘤治疗的同时,医护人员应该及时识别肿瘤患者跌倒的相关因素,重视其跌倒的风险管理,以提高患者的生活质量,减轻医疗负担。3.2 成人肿瘤患者跌倒的相关因素分析
3.2.1 社会人口学因素
年龄、女性、受教育程度低是成人肿瘤患者跌倒的风险因素。在本研究中,跌倒组的肿瘤患者年龄高于非跌倒者(组间平均年龄差异为1.89岁)。这可能与随着年龄的增大患者容易出现自理能力缺陷、营养不良,抗肿瘤治疗耐受性差等情况且研究显示[25],老年人存在跌倒风险感知偏差,跌倒的风险随之增大。因此,在临床护理过程中,要考虑年龄对肿瘤患者跌倒的影响,加强对老年肿瘤患者的防跌倒知识宣教,积极改善医院环境设施,加强保护性预防。女性肿瘤患者相较于男性跌倒风险更高,这可能与骨质疏松症或雌激素减少等原因有关[17],肿瘤治疗期间,应指导女性患者定期监测骨密度,做好体重管理,鼓励患者参与中等强度的身体运动[26]。低文化程度的肿瘤患者更容易跌倒,可能与其接受和理解信息能力较低有关,提示护理人员应针对性地采用通俗易懂的方式告知患者跌倒的风险危害和预防跌倒的措施,如采用动画、卡通图册、地区方言等方式耐心引导,提高其对防跌倒的认知。
3.2.2 跌倒史及跌倒恐惧
跌倒史是发生跌倒重要的预测因素,已被应用于各类跌倒风险评估量表中。既往研究中,关于评估肿瘤患者跌倒史的时间间隔不同,分别有6个月、12个月以及无限制时间间隔。不同时间间隔跌倒史之间发生跌倒是否异同,目前尚未清楚。2020年国际老年肿瘤学会护理组建议[27],肿瘤患者的跌倒风险在治疗期间动态变化,因此每次临床就诊时护理人员都应该询问跌倒情况。关于肿瘤患者跌倒恐惧发生率的报道较少,本研究中纳入的2篇文献[12,16]显示肿瘤患者跌倒恐惧的发生率分别为43.5%和69.3%,高于脑卒中患者跌倒恐惧发生率34%[28],跌倒恐惧导致肿瘤患者跌倒可能由于治疗导致疲乏、食欲下降等不良反应以及身体功能下降、对平衡和活动缺乏信心有关,提示医护人员应该评估肿瘤患者是否存在跌倒恐惧,并给予积极引导,增加其信心,改善患者活动能力,以减少跌倒的发生。
3.2.3 疾病相关因素
本研究显示,肿瘤越发展到晚期,跌倒的风险就越高,Ⅲ/Ⅳ期患者跌倒发生率是Ⅰ/Ⅱ期的2.5倍。这可能与中晚期患者通常存在更广泛的局部浸润、淋巴结受累和远处转移,不仅导致患者容易出现器官衰竭,还导致患者接受的治疗更多,出现的毒副作用更复杂,进一步增加了跌倒的发生率。本研究显示,肿瘤分类中,乳腺癌、生殖系统肿瘤、前列腺癌比其他类型肿瘤患者更容易跌倒。这可能与乳腺癌患者和生殖系统肿瘤患者接受性激素剥夺治疗以及使用芳香化酶抑制剂有关[8]。疼痛,关节僵硬以及骨质疏松是此类药物常见的不良反应。前列腺癌患者接受雄激素剥夺治疗以及并发尿失禁是其发生跌倒的重要相关因素[21],提示临床医护人员应该对上述肿瘤患者制定个性化的防跌倒策略,重视肿瘤患者疼痛症状的预防管理。研究显示[22],肿瘤科护士对癌痛护理知识知晓率不高,仅为 48.67%,提示护理管理者需加强对肿瘤科护士癌痛护理基础知识和临床护理实践的教育培训。在本研究中,存在共病的肿瘤患者发生跌倒是无共病肿瘤患者的1.11倍且跌倒组的肿瘤患者共病数量高于非跌倒组的患者。这可能与共病肿瘤患者病情和功能受损更为严重,化疗药物毒副反应更强有关[30],目前我国关于癌症共病模式的研究较少,需进一步探索,以为存在共病的肿瘤患者提供管理依据,进一步解释共病模式对跌倒的影响。
3.2.4 治疗相关因素
化疗、放疗、多重用药(n 5),应用抗抑郁药、抗精神病药、镇静催眠药是肿瘤患者发生跌倒的影响因素。本研究显示接受化疗、放疗的肿瘤患者跌倒发生率分别是未接受化疗、放疗患者的2.08倍和1.43倍。这与化放疗导致的恶心、呕吐、疲乏、骨髓抑制和神经病变有关[16,18],但关于不同种类化疗药物和方案的跌倒发生情况是否不同的研究少有报道,需进一步探索,以利于更专业精准的评估肿瘤治疗带来的跌倒风险。目前,肿瘤患者中多重用药(每天服用 5 种药物)和潜在不适当用药(potentially inappropriate medication,PIM)的发生率高[21]。多重用药和PIM 可能导致肿瘤患者出现平衡问题、晕厥等健康损害相关,进而导致跌倒风险增加。提示医护人员应该密切关注患者使用的药物,尤其是抗抑郁药物、抗精神病药物和镇静催眠类药物与较高的跌倒风险相关,深化专业知识掌握,增强安全用药能力。
3.2.5 症状相关因素
发热、周围神经病变、疲乏、抑郁是肿瘤患者发生跌倒的影响因素。本研究显示发热肿瘤患者发生跌倒是非发热患者的7.15倍,提示护理人员在评估跌倒风险时,应该关注患者是否存在发热症状。但本次纳入的2篇文献样本量较少,且发表年限较早,待进一步研究探讨发热与跌倒之间的关系。约50%~90%的化疗患者发生周围神经病变[31],本研究显示发生周围神经病变的肿瘤患者跌倒发生率为未发生患者的2.46倍。这可能与患者出现四肢末端感觉异常、麻木、刺痛有关。医护人员应使用专业评估工具并结合患者自我报告评估患者是否发生周围神经病变,并积极干预,减少患者的跌倒风险。患者发生疲乏的肿瘤患者跌倒的发生率是未发生疲乏患者的1.2倍。这可能与疲乏患者活动减少,机体耐受力差有关。有报道显示,肿瘤患者癌因性疲乏的发生率高达50%以上[32]。医护人员在评估跌倒风险时,应该关注患者疲乏症状和严重程度,并给予针对性的护理干预。抑郁肿瘤患者跌倒风险是非抑郁患者的2.68倍,与Strini V[33]的研究结果相似,这可能由于负性情绪会让病人思维迟缓,意志力消退,致使肿瘤患者活动耐力下降,跌倒风险随之升高。在临床护理实践中,要鼓励引导患者表达内心体验和情绪,在缓解其心理负担的同时降低其发生跌倒的风险。
3.2.6 机体功能相关因素
营养不良、低体重、认知功能和平衡障碍、步态异常、低日常生活能力是成人肿瘤患者跌倒的影响因素。存在营养不良的肿瘤患者发生跌倒风险是营养状态正常患者的1.35倍,跌倒组的肿瘤患者平均体重低于非跌倒组(组间平均体重差异为−0.32岁)。这可能与营养不良和低体重导致患者肌肉含量减少[34]和对治疗耐受性差[35]有关,本研究纳入的2篇文献均采用微型营养评估量表(mininutritional assessment,MNA)评估肿瘤患者的营养状况,可进一步探究不同营养评估工具对跌倒风险的敏感性。认知障碍的肿瘤患者跌倒风险高于认知正常患者1.77倍,这可能与此类肿瘤患者记忆、注意力和执行功能障碍有关。研究显示,多达75%的癌症幸存者存在认知障碍[36],国外已开发了众多评估癌症相关认知功能障碍量表,本次研究纳入3篇文献均使用简易精神状态评价量表评估患者的认知功能,但国内相关研究尚处于起步阶段,认知功能障碍的评估在肿瘤患者中应用较少,下一步可探索将其评估用于肿瘤患者跌倒风险的评估。存在平衡障碍和步态异常的肿瘤患者跌倒发生率分别是普通肿瘤患者的2.78倍和11.58倍,提示医护人员应早期识别肿瘤患者的平衡和步态问题,以减少跌倒的发生。发生跌倒的肿瘤患者日常生活能力低于未发生跌倒的患者。本次研究纳入的3篇文献分别使用美国东部肿瘤协作组日常活动能力评分系统(Eastern Cooperative Oncology group performance status,ECOG)、ADL评分和复杂性ADL(instrumental ADL,IADL)评估肿瘤患者的日常生活能力,Meta分析结果显示ADL(OR=3.75,95%CI 3.51,4.01)较IADL(OR=1.81,95%CI 1.55,2.12)和ECOG(OR=2.16,95%CI 1.46,3.19)对成人肿瘤患者跌倒风险敏感性性更强,提示医护人员在评估肿瘤患者跌倒风险时需加强对穿衣、进食、保持个人卫生等基础日常活动能力的评估。
成人肿瘤患者跌倒发生率较高,Meta分析结果显示年龄、女性、低文化程度等26项为成人肿瘤患者发生跌倒的影响因素。临床医护人员可参照本研究结果对成人肿瘤患者跌倒风险进行全面评估和预防,并制定相应干预措施降低肿瘤患者的跌倒发生率,保障患者的医疗安全。研究的局限性:(1)是否发生跌倒的结局指标以患者自我报告为主,有回忆偏差和遗漏报告的可能性;(2)纳入的文献中的样本特征、研究区域和时间等存在异质性,对合并结果的稳定性造成影响;(3)部分影响因素的分析仅纳入2篇文献,影响到合并结果的代表性;部分影响因素由于文献数量少,数据类型不一致等无法进行Meta分析合并结果;(4)纳入的部分质量中等的文献,期待后续相关研究可进一步纳入更大规模样本量、高质量的文献对本次研究结果进行论证。
-
-
[1] 李娜,邢书娟,黄国友,等. 抗肿瘤血管生成治疗的研究进展及应对策略[J]. 生命科学研究,2020,24(1):62-67. [2] Goedegebuure R S,De Klerk L K,Bass A J,et al. Combining radiotherapy with anti-angiogenic therapy and immunotherapy; a therapeutic triad for cancer?[J]. Frontiers in Immunology,2019,9(1):3107. [3] 罗详冲,李高峰. 安罗替尼治疗肺癌的临床研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2019,26(6):710-714. [4] Ruan X,Shi X,Dong Q,et al. Antitumor effects of anlotinib in thyroid cancer[J]. Endocrine-related cancer,2019,26(1):153-164. doi: 10.1530/ERC-17-0558 [5] Yunus M,Jansson P J,Kovacevic Z,et al. Tumor-induced neoangiogenesis and receptor tyrosine kinases–mechanisms and strategies for acquired resistance[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta(BBA)-General Subjects,2019,1863(7):1217-1225. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.04.017 [6] Bhanumathy K,Balagopal A,Vizeacoumar F S,et al. Protein tyrosine kinases:Their roles and their targeting in leukemia[J]. Cancers,2021,13(2):184-204. doi: 10.3390/cancers13020184 [7] Karimian A,Mir S M,Parsian H,et al. Crosstalk between Phosphoinositide 3‐kinase/Akt signaling pathway with DNA damage response and oxidative stress in cancer[J]. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry,2019,120(6):10248-10272. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28309 [8] Cuneo K C,Nyati M K,Ray D,et al. EGFR targeted therapies and radiation:Optimizing efficacy by appropriate drug scheduling and patient selection[J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2015,154(5):67-77. [9] Bossi P,Platini F. Radiotherapy plus EGFR inhibitors:Synergistic modalities[J]. Cancers of the Head & Neck,2017,2(1):2. [10] 倪莲芳,聂立功. 2017ASCO及WCLC晚期非鳞NSCLC抗血管生成治疗进展[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer,2018,21(5):425. [11] 吴霞,冯国生. EGFR-TKI在局部晚期非小细胞肺癌中的应用[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志,2016,43(4):312. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-422X.2016.04.020 [12] 徐萍,李红梅. 贝伐珠单抗在非小细胞肺癌中的应用进展[J]. Chinese Journal of Lung Cancer,2017,20(4):272. [13] Mok T S,Cheng Y,Zhou X,et al. Updated overall survival in a randomized study comparing dacomitinib with gefitinib as first-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR-activating mutations[J]. Drugs,2021,81(2):257-266. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01441-6 [14] Xing L,Wu G,Wang L,et al. Erlotinib versus etoposide/cisplatin with radiation therapy in unresectable stage III epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer:A multicenter,randomized,open-label,phase 2 trial[J]. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics,2021,109(5):1349-1358. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.11.026 [15] Ye H,Li Z,Liu K,et al. Anlotinib,a novel TKI,as a third-line or further-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer in China:A systemic review and meta-analysis of its efficacy and safety[J]. Medicine,2021,100(23):e25709. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025709 [16] Toulany M. Targeting DNA double-strand break repair pathways to improve radiotherapy response[J]. Genes,2019,10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/genes10010025 [17] Jachimowicz R D,Goergens J,Reinhardt H C. DNA double-strand break repair pathway choice-from basic biology to clinical exploitation[J]. Cell Cycle,2019,18(13):1423-1434. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1618542 [18] 曹喆,庄亮,陈元. 吉非替尼对肺癌细胞株A549和H1975放射敏感度的影响及其机制[J]. 肿瘤防治研究,2014,41(4):324-330. [19] Tanaka T,Munshi A,Brooks C,et al. Gefitinib radiosensitizes non–small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing cellular DNA repair capacity[J]. Clinical Cancer Research,2008,14(4):1266-1273. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-1606 期刊类型引用(6)
1. 丁妍华,门帅,张江霞,张旭,张善存,刘璐,吕宏伟,肖正红. 贝伐珠单抗联合安罗替尼治疗非小细胞肺癌的临床疗效及对免疫状态的影响. 哈尔滨医药. 2024(01): 41-44 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 解燕茹. 安罗替尼联合伊立替康和洛铂二线治疗晚期小细胞肺癌的临床研究. 基层医学论坛. 2024(07): 51-53 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 张全,曹志坤,丁成智,刘孟博,李基伟,魏立. 安罗替尼通过核因子信号通路抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并促进细胞凋亡. 中华实验外科杂志. 2024(12): 2778-2782 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 王帅,刘景春. 安罗替尼联合TC化疗方案治疗驱动基因阴性晚期肺腺癌患者的效果. 河南医学研究. 2023(05): 912-916 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 林征,周进,黄开荣. 安罗替尼联合AN方案一线治疗晚期野生型肺腺癌的回顾性研究. 中国医学创新. 2023(31): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 马闻. 替雷利珠单抗联合安罗替尼治疗晚期肺腺癌的效果及对血清肿瘤标志物的影响. 中国医学创新. 2022(17): 124-127 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载: