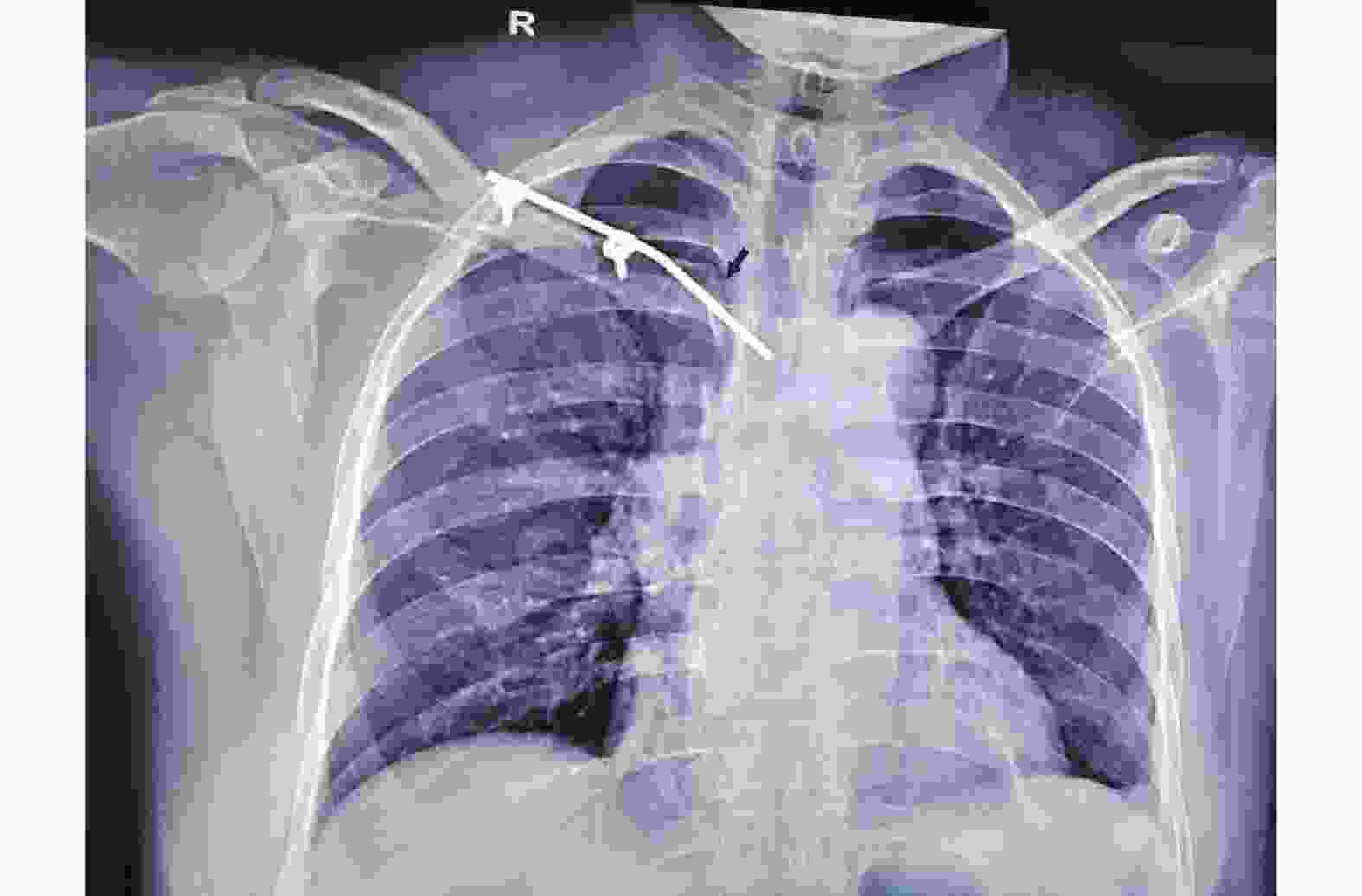
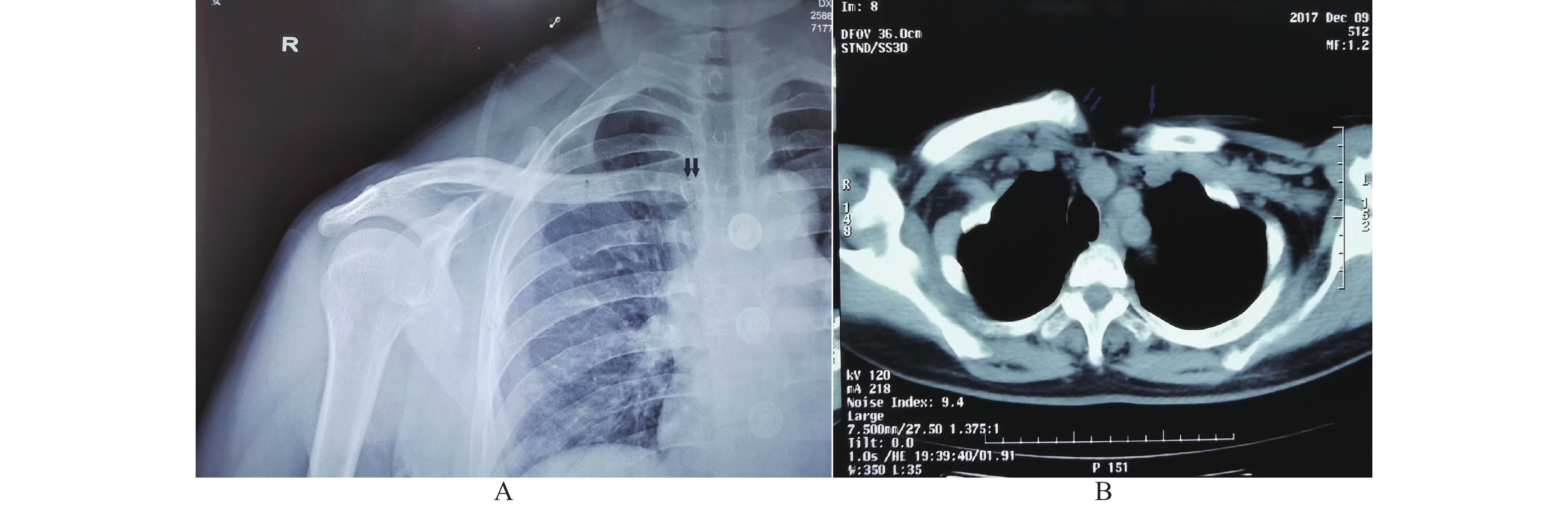
Clinical Effects on Sternoclavicular Joint Dislocation with Bridge-link Combined Fixation System
-
摘要:
目的 观察桥接组合式内固定系统(BCFS)治疗胸锁关节脱位 (SCD) 的临床疗效。 方法 2016年10月至2021年9月,BCFS治疗急性闭合性 SCD 患者29例,27例为前方脱位,2例后脱位,无血管、神经损伤。采用Rockwood评分法评价术后疗效。 结果 手术时间 39~62 min,平均41 min。术中出血量 22~46 mL,平均29 mL。所有患者均获随访,随访时间 6~36个月,取出内固定取出时间6~18个月,单纯脱位6月取出内固定,合并骨折的12~18个月取出。Rockwood 评分法评价疗效,优25例、良4例,与相似临床研究(T形锁定板治疗胸锁关节脱位)结果比较,Rockwood评分差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。合并骨折的全部愈合,无切口感染、内固定断裂及血管、神经、胸膜损伤等并发症发生。 结论 采用BCFS治疗胸锁关节脱位,手术简单,操作时间短,损伤小,可以作为胸锁关节脱位的内固定方式之一。 Abstract:Objective To observe the clinical effect of Bridge-link Combined Fixation System (BCFS) in the treatment of Sternoclavicular dislocations (SCD) . Methods From October 2016 to September 2021, 29 patients with acute closed SCD were treated with BCFS, in which 27 cases were anterior dislocation, and 2 were posterior dislocation with no vascular and nerve injuries. All patients were treated with BCFS for open reduction and internal fixation. Rockwood score was used to evaluate the curative effects. Results The operation time was 39-62 min (mean, 41 min/per operation), intraoperative blood loss was 22-46 ml (mean, 29 ml/per operation). All patients were followed up for 6 to 36 months. The BCFS was removed in 6-18 months postoperation for all of cases, in which simple SCD were removed BCFS 6 months, and SCD combined with fractures removed 12-18 months postoperation. According to Rockwood score, 25 cases were shown to be excellent and 4 cases good, and there was no significant difference in Rockwood scores compared with the results of similar clinical studies (T-shaped locking plate for the treatment of SCD ) (P>0.05). All fractures healed without wound infection, internal fixation breakage and vascular, nerve, or pleural injuries and other complications. Conclusion BCFS is a good treatment option for SCD with short operation times and small damages, which can be used as one of the internal fixation methods for SCD . -
表 1 患者一般资料(n)
Table 1. General information of patients (n)
性别 Allman分型 脱位类型 脱位合并骨折 致伤原因 男 女 Ⅱ型 Ⅲ型 前 后 单纯脱位 合并骨折 高处坠落 车祸 22 7 3 26 27 2 21 8 12 17 表 2 Rockwood评分法
Table 2. Rockwood scoring methods
Category指标 分值 总分 疼痛 优 13-15 无 3 良 10-12 轻度 2 一般 7-9 中度 1 差 < 7分 重度 0 关节活动度 正常 3 轻度受限(<25%) 2 中度受限(25%-50%) 1 重度受限(>50 %) 0 肌力 正常 3 轻度减弱(<25%) 2 中度减弱(25%-50%) 1 重度减弱(>50%) 0 活动受限 无 3 轻度 2 中度 1 重度 0 患者主观判断 优 3 良 2 表 3 接组合式内固定与T形锁定板治疗胸锁关节前脱位Rockwood评分比较(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 3. Comparison of Rockwood score between Bridge-link Combined Fixation System and T-shaped locking plate in the treatments of anterior dislocation of sternoclavicular joint(
$\bar x \pm s $ )治疗方法 n Rockwood评分 P 桥接组合式内固定 27 12.48±1.58 0.417 T 形锁定板内固定 12 13.25±1.36 > 0.05 -
[1] Haley,Isaac,John,et al. Sternoclavicular joint dislocation:A systematic review and meta-analysis.[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma,2019,33(7):e251-e255. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001463 [2] Kendal J K,Thomas K,Lo I K Y,et al. Clinical outcomes and complications following surgical management of traumatic posterior sternoclavicular joint dislocations A systematic review[J]. Jbjs Reviews,2018,6(11):e2. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00157 [3] Swarup I,Hughes M S,Cazzulino A,et al. Open reduction and suture fixation of acute sternoclavicular fracture-dislocations in children[J]. JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques,2020,10(3):e19. [4] Kraus R,Zwingmann J,Jablonski M,et al. Dislocations of the acromioclavicular and sternoclavicular joint in children and adolescents:A retrospective clinical study and big data analysis of routine data[J]. PLoS One,2020,15(12):e0244209. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244209 [5] 高翔,陈玉宏,李建鹏,等. 胸锁关节脱位诊治现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(13):1190-1193. [6] Kusnezov N,Dunn J C,Delong J M,et al. Sternoclavicular reconstruction in the young active patient:Risk factor analysis and clinical outcomes at short-term follow-up[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma,2015,30(4):e111-117. [7] 樊军,罗意,万革,等. 克氏针张力带与锁骨钩钢板固定治疗胸锁关节前脱位63例的临床分析[J]. 重庆医学,2015,(22):3129-3131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2015.22.042 [8] Gowd A K,Liu J N,Garcia G H,et al. Figure-of-eight reconstruction of the sternoclavicular joint:Outcomes of sport and work[J]. Orthopedics,2019,42(4):205-210. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20190523-03 [9] 徐永清,吴一芃,熊鹰,等. 桥接组合式内固定系统治疗四肢骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(6):465-469. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7600.2018.06.002 [10] 任义军,严立,胡锐,等. 桥接组合式内固定系统治疗合并感染的股骨骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(11):956-960. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7600.2016.11.007 [11] Rockwood C A,Groh G I,Wirth M A,et al. Resection arthroplasty of the sternoclavicular joint.[J]. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery-american Volume,1997,79(3):387-393. [12] 孙宝柱,张振华,何钢. 不锈钢材质T形锁定板修复锁骨近端骨折及胸锁关节脱位[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(21):3414-3418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.21.025 [13] Petri M,Greenspoon J A,Horan M P,et al. Clinical outcomes after autograft reconstruction for sternoclavicular joint instability[J]. Journal of Shoulder & Elbow Surgery,2016,25(3):435-441. [14] 杨琨,吴天昊,李根,等. 胸锁关节的解剖学及生物力学特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1695-1700. [15] Lee J T,Campbell K J,Michalski M P,et al. Surgical anatomy of the sternoclavicular joint:a qualitative and quantitative anatomical study[J]. JBJS,2014,96(19):e166. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.M.01451 [16] Allman F L. Fractures and ligamentous injuries of the clavicle and its articulation.[J]. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery-american Volume,1967,49(4):774-784. [17] Quispe J C,Herbert B,Chadayammuri V P,et al. Transarticular plating for acute posterior sternoclavicular joint dislocations:a valid treatment option?[J]. International Orthopaedics,2016,40(7):1503-1508. doi: 10.1007/s00264-015-2952-y [18] Kirby J C,Edwards E,Kamali Moaveni A. Management and functional outcomes following sternoclavicular joint dislocation[J]. Injury-international Journal of the Care of the Injured,2015,46(10):1906-1913. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2015.05.050 [19] Boesmueller S,Wech M,Tiefenboeck T M,et al. Incidence,characteristics,and long-term follow-up of sternoclavicular injuries:An epidemiologic analysis of 92 cases[J]. J Trauma Acute Care Surg,2016,80(2):289-295. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000000888 [20] Tytherleigh-Strong G,Mulligan A,Babu S,et al. Digital tomography is an effective investigation for sternoclavicular joint pathology[J]. European Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery & Traumatology,2019,29(6):1217-1221. [21] Olivos-Meza A,Arturo Almazán-Diaz,José Alberto Calvo,et al. Radiographic displacement of acute acromioclavicular joint dislocations fixed with AC TightRope[J]. JSES International,2020,4(1):49-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2019.11.002 [22] Kennedy B P,Rosenberg Z S,Alaia M J,et al. Radiographic features and complications following coracoclavicular ligament reconstruction[J]. Skeletal Radiology,2020,49(10):1-11. [23] Baessler A M,Wessel R P,Caltoum C B,et al. Ultrasound diagnosis of medial clavicular epiphysis avulsion fracture in a neonate[J]. Pediatric Radiology,2020,50(4):587-590. doi: 10.1007/s00247-019-04583-2 [24] Fournier M N,Sinclair M R,Zheng E T,et al. The frequency of mediastinal injury in acute posterior sternoclavicular dislocations:A multicenter study[J]. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics,2020,40(10):e927-e931. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001649 [25] Swarup I,Cazzulino A,Williams B A,et al. Outcomes after surgical fixation of posterior sternoclavicular physeal fractures and dislocations in children[J]. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics,2021,41(1):11-16. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000001691 [26] Vitali M,Drossinos A,Pironti P,et al. The management of Salter-Harris type II fracture with associated posterior sternoclavicular joint displacement using a locking compression plate:A 14-year-old adolescent's case report[J]. Medicine,2019,98(51):e18433. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018433 [27] Wagner R J ,Symanski J S ,Raasch W G ,et al. Successful nonsurgical management of a posteriorly displaced medial clavicular physeal fracture in an adolescent athlete:A case report[J]. Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine,2021,32(3):e319-e321. [28] Zhang C,Lin L,Liang J,et al. Efficacy analysis of a novel sternoclavicular hook plate for treatment of unstable sternoclavicular joint dislocation or fracture[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery,2017,25(1):2309499016684488. [29] 周继辉、李新志、周游、黄卫、陈文瑶. 创伤性胸锁关节脱位多种内置物治疗优劣的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(3):443-448. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2938 [30] Bonyun M,Nauth A. Techniques for reduction and fixation of the sternoclavicular joint[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma,2020,34:S1-S2. [31] Joseph Portale M F F. Persistent shoulder pain after fall:Posterior dislocation of the sternoclavicular joint[J]. The Journal of Emergency Medicine,2020,58(3):512-513. doi: 10.1016/j.jemermed.2020.02.013 [32] Albors L M ,Lee R J. Chronic posterior sternoclavicular dislocation in a contact athlete:A case report[J]. JBJS Case Connector,2020,10(1):e0032. [33] Chaudhry S. Pediatric posterior sternoclavicular joint injuries[J]. Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,2015,23(8):468. doi: 10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00235 [34] Swarup I,Hughes M S,Cazzulino A,et al. Open reduction and suture fixation of acute sternoclavicular fracture-dislocations in children[J]. JBJS Essential Surgical Techniques,2020,10(3):e19.00074-e19.00074. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.ST.19.00074 [35] Leonard D A,Segovia N A,Kaur J,et al. Posterior sternoclavicular dislocation:Do we need "cardiothoracic backup"? insights from a national sample[J]. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma,2019,34(2):1. -






 下载:
下载: