Observation on the Efficacy of Optimal Pulse Technology in the Treatment of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction Related Dry Eyes Based on in Vivo Confocal Microscopy Classification
-
摘要:
目的 通过活体共聚焦显微镜(IVCM)对睑板腺功能障碍(MGD)分类,比较优化脉冲光技术(OPT)联合睑板腺按摩(MGX)治疗不同类型MGD相关干眼的疗效。 方法 选取2021年11月至2022年10月来昆明医科大学附属甘美医院门诊就诊的MGD相关干眼患者60例(60眼),通过IVCM检查睑板腺并将其分为严重程度增加阶段的3种类型:阻塞型29例,炎症型18例,纤维化型13例;均采用每2周1次,共3次的OPT联合MGX治疗。观察并记录3型患者在治疗前、治疗后1月、治疗后3月眼表疾病指数(OSDI)评分、非侵入泪膜破裂时间(NIBUT)、角膜荧光素钠染色(CFS)评分、脂质层厚度(LLT)、睑板腺分泌评分(MGYSS)的结果。 结果 (1)OSDI评分:3型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较OSDI评分均下降,阻塞型和炎症型治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较OSDI评分持续下降,治疗后1月阻塞型OSDI评分下降优于炎症型,治疗后3月阻塞型OSDI评分下降优于炎症型和纤维化型(P < 0.05);(2)BUT:3型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较BUT均上升,阻塞型治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较BUT持续上升,治疗后1月和治疗后3月阻塞型BUT升高优于炎症型和纤维化型(P < 0.05);(3)CFS评分:阻塞型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较CFS评分均下降,炎症型和纤维化型治疗后3月与治疗前比较CFS评分下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),治疗后3型组间比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);(4)LLT:阻塞型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较LLT上升,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),炎症型和纤维化型在治疗前后比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),治疗后3型组间比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);(5)MGYSS:3型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较MGYSS均下降,3型治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较MGYSS持续下降,阻塞型治疗后1月和治疗后3月MGYSS下降优于炎症型和纤维化型(P < 0.05);(6)IVCM分类的MGD严重程度增加的阶段与睑板腺缺失评分呈正相关(rs = 0.474,P < 0.001)。 结论 (1)通过ICVM对MGD分类,可将其分为严重程度增加阶段的3种类型:阻塞型、炎症型、纤维化型。IVCM对MGD分类是一种新分类方法,且IVCM分类的MGD严重程度增加的阶段与睑板腺缺失评分呈正相关。(2)在IVCM对MGD分类的基础上,通过OPT联合MGX治疗不同类型MGD相关干眼,阻塞型疗效更佳。 -
关键词:
- 睑板腺功能障碍相关干眼 /
- 活体共聚焦显微镜 /
- 分类 /
- 优化脉冲光 /
- 临床治疗效果
Abstract:Objective To classify the meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) with the use of in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM), and to compare optimal pulse technology (OPT) combined with meibomian gland expression (MGX) in the treatment of different types of MGD-related dry eyes. Methods A total of 60 patients (60 eyes) with dry eyes associated with MGD were selected from November 2021 to October 2022 in Outpatient clinic of our hospital.The meibomian glands were examined by IVCM and divided into three types in the stage of increased severity: obstructive type (n = 29), inflammatory type (n = 18) and fibrotic type (n = 13). All patients were treated with OPT combined with MGX once every 2 weeks. The ocular surface disease index (OSDI) score, Noninvasive break-up time (NIBUT), corneal fluorescein staining (CFS), lipid layer thickness (LLT) and meibomian gland yielding secretion score (MGYSS) were observed and recorded before treatment, 1 month and 3 months after treatment. Results (1) OSDI score: The OSDI score of the three groups decreased 1 month and 3 months after treatment, and the OSDI score of obstructive type and inflammatory type decreased continuously 1 month after treatment compared with 3 months after treatment, the decrease of OSDI score of obstructive type was better than that of inflammatory type 1 months after treatment, and the decrease of OSDI score of obstructive type was better than that of inflammatory type and fibrotic type 3 months after treatment (P < 0.05); (2) BUT: BUT of the three groups increased 1 month and 3 months after treatment, and the BUT of obstructive type increased continuously 1 month after treatment compared with 3 months after treatment, and the increase of BUT of obstructive type was better than that of inflammatory type and fibrotic type 1 month and 3 months after treatment (P < 0.05); (3) CFS score:The CFS score of obstructive type decreased 1 month and 3 months after treatment, and the CFS score of inflammatory type and fibrotic type decreased 3 months after treatment, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), There was no significant difference among the three types after treatment (P > 0.05); (4) LLT: The LLT of obstructive type increased 1 month and 3 months after treatment, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05), There was no significant difference between inflammatory type and fibrotic type before and after treatment (P > 0.05), There was no significant difference among the three types after treatment (P > 0.05); (5) MGYSS:MGYSS of the three groups decreased 1 month and 3 months after treatment, and MGYSS decreased continuously in 1 month and 3 months after treatment in the three groups. the decrease of MGYSS in the obstructive type was better than that in the inflammatory type and fibrotic type (P < 0.05); (6) According to IVCM classification, the stage of increased severity of MGD was positively correlated with the score of loss of meibomian gland (rs = 0.474, P < 0.001). Conclusion (1) According to the classification of MGD by ICVM, it can be divided into three types in the stage of increased severity: obstruction type, inflammatory type and fibrotic type. IVCM is a new classification method for MGD, and according to IVCM classification, the stage of increased severity of MGD was positively correlated with the score of loss of meibomian gland; (2) On the basis of IVCM's classification of MGD, Treatment of different types of MGD-related dry eyes with OPT combined with MGX, The effect of obstruction type treatment is better. -
睑板腺功能障碍(meibomian gland dysfunction,MGD)是睑板腺的慢性、非特异性炎症,以睑板腺终末导管阻塞或睑板腺分泌物异常为特征,可造成眼部多种不适症状[1]。MGD是质脂异常型干眼最常见的病因[2],也是干眼症状的主要决定因素[3]。随着电子终端产品的广泛使用及人口逐渐老年化,MGD患病率逐年攀升,有研究表明在西方国家的患病率为5%~20%,在亚洲人群中为45%~70%[4]。MGD及其相关干眼成为眼科门诊常见病,影响患者的眼部舒适度、视觉功能、生活质量以及心理健康,所以逐渐重视对MGD及其相关干眼的治疗。近年来研究较多的是强脉冲光(intense pulsed light,IPL),治疗有效且疗效维持时间相对较长,但通过对MGD分类,探讨IPL治疗不同类型的MGD及其相关干眼的研究少。活体共聚焦显微镜(in vivo confocal microscopy,IVCM)是一种具有实时且高放大倍数的辅助检查设备,广泛应用于角膜及角膜病。随着IVCM逐渐运用到睑板腺的观察,展示了其微观结构,通过观察睑板腺开口、睑板腺腺泡直径和密度、腺泡周围炎症细胞密度等微观改变,以及对螨虫的检测,在辅助MGD早期诊断、探寻病因、了解发病机制、指导治疗等发挥着不可替代的作用,也为MGD的分类带来了新视野,本研究使用IVCM对MGD进行分类,采用第五代IPL的优化脉冲光技术(optimal pulse technology,OPT),观察OPT联合睑板腺按摩(meibomian gland expression,MGX)治疗不同类型MGD相关干眼的疗效。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 研究对象
选取2021年11月至2022年10月来昆明医科大学附属甘美医院就诊的MGD相关干眼患者82例(82眼),如双眼都符合入组标准,选择右眼进行观察,取得患者知情同意后进行检查和治疗,其中60例按要求完成治疗和随访,男性18例,女性42例。阻塞型29例,女性20例(69%),年龄20~62岁,平均(42.55±13.06)岁;炎症型18例,女性13例(72.2%),年龄27~72岁,平均(44.56±13.27)岁;纤维化型13例,女性9例(69.2%),年龄23~67岁,平均(45.62±14.49)岁。3型患者年龄和性别差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),具有可比性。
1.1.1 入选标准
(1)符合干眼诊断[5];(2)符合MGD诊断原则和依据[1];(3)年龄≥18岁;(4)Fitzpatrick(皮肤色素沉着等级)皮肤类型 I~IV;(5)自愿参加本研究。
1.1.2 排除标准
(1)任意一眼有活动性炎性疾病;(2)3个月内眼部手术、创伤者;(3)患有干燥综合征或其它可导致干眼的系统性疾病;(4)任何眼睑结构异常者;(5)不能耐受OPT治疗者;(6)孕妇、哺乳期妇女;(7)未能按时治疗及随访者。
1.2 研究方法
检查顺序:(1)OSDI评分;(2)裂隙灯显微镜检查;(3)NIBUT;(4)CFS评分;(5)LLT 和睑板腺缺失评分;(6)IVCM;(7)MGYSS。
1.2.1 OSDI评分
所有入组患者均在同一医师指导下完成,按照过去1周症状出现的频率进行作答,共12个问题,分值为0~4分或该题不作答。OSDI评分 = (总分值×25)/总答题数,分数越高主观症状越重。
1.2.2 裂隙灯显微镜检查
整体评估外眼、眼前节形态及炎症情况,重点观察睑缘形态变化和睑板腺开口的变化。
1.2.3 NIBUT
使用操作杆调整焦距,对准焦点后嘱患者瞬目2次,且尽量坚持不瞬目直至设备自动识别并计量出平均泪膜破裂时间,重复3次取平均值。
1.2.4 CFS评分
将角膜分为4个象限,每个象限单独计算,无染色为0分;1~30个点状着色为1分;>30个点状着色但各点无融合为2分;点状着色融合、大片染色为3分[6]。
1.2.5 LLT和睑板腺缺失评分
使用眼表面干涉仪自动测量泪膜脂质层厚度,然后翻转上下眼睑后获取睑板腺图像,无睑板腺缺失为0分;睑板腺缺失<1/3为1分:睑板腺缺失1/3~2/3为2分:睑板腺缺失>2/3为3分[1]。
1.2.6 IVCM检查及分型
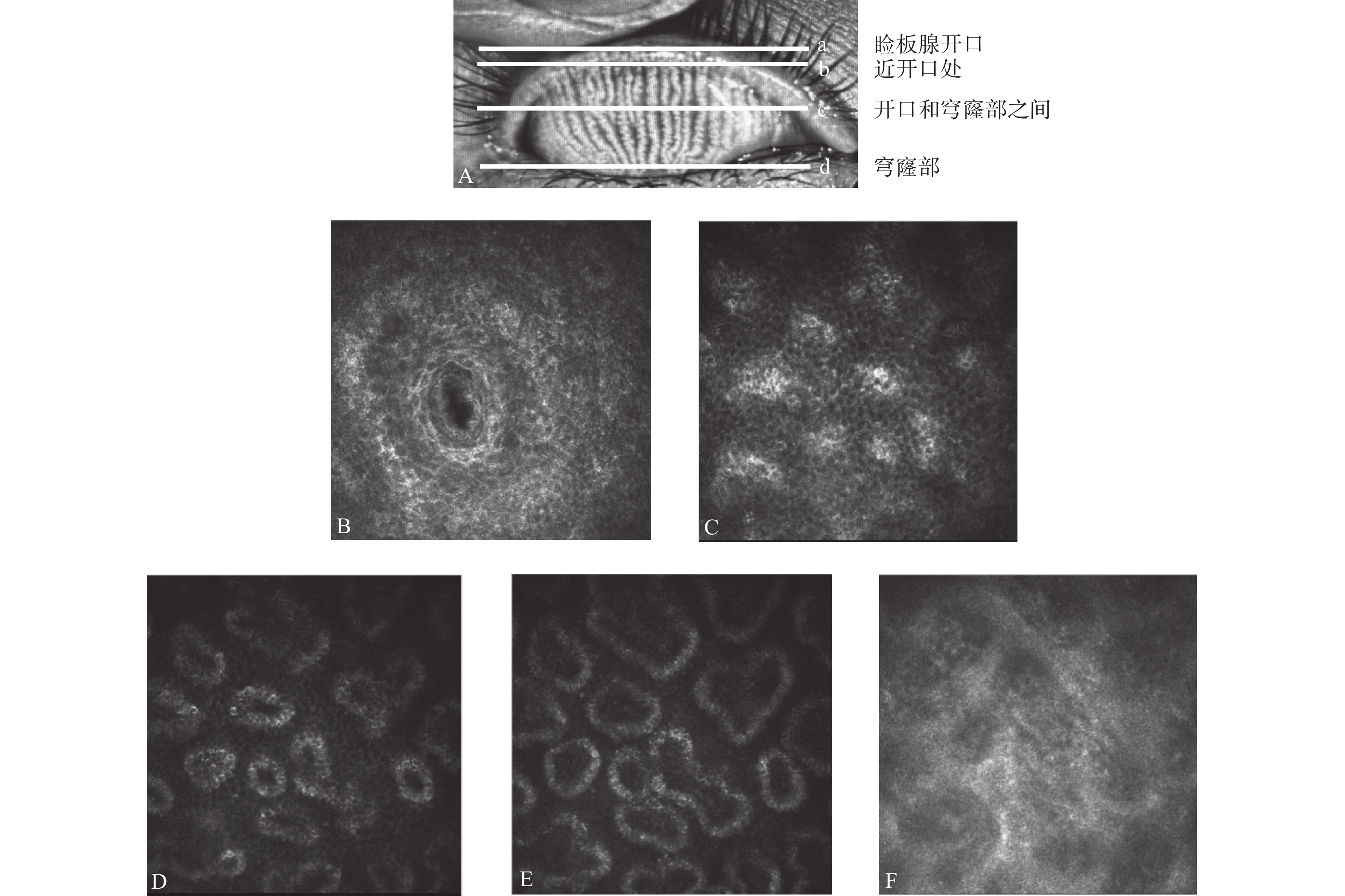
本研究使用的是Heideiberg Engineering GmbH德国海德堡公司生产HRT3共聚焦显微镜。检查方法:检查前需对受检眼进行一次表面麻醉,并在显微镜镜头上涂上眼用透明凝胶,安装一次性角膜接触帽,受检者前额及下颌分别固定于前额托及下颌托上,将受检眼上睑翻起,嘱患者向下注视,当观察到第一个表面结膜细胞时,测厚仪设置为零,从鼻侧的睑缘开始,垂直扫描至穹窿部,然后依次平行扫描,直至整个睑板腺扫描完毕(图1)。每位患者睑板腺鼻侧、中央、颞侧至少各拍摄10张照片。
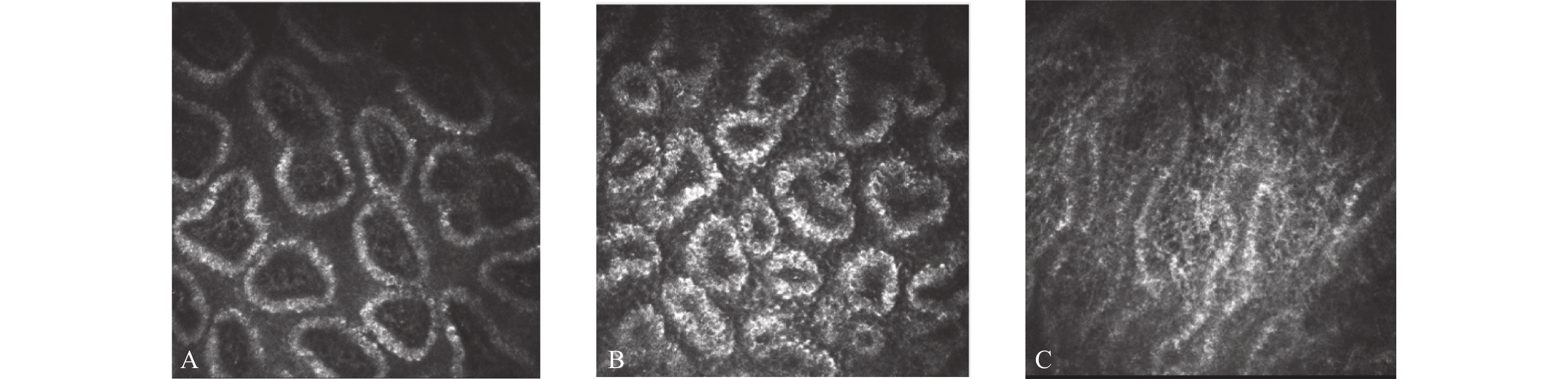
记录分析:从照片中挑选出处于睑缘和穹窿部之间的拍摄清晰睑板腺腺泡照片 9 张(鼻侧、中央、颞侧各 3 张)。通过观察腺泡分泌物反射状态、上皮和腺泡间的不均匀外观程度、上皮纤维化,将MGD分为严重程度增加阶段的3种类型,即阻塞型、炎症型和纤维化型[7-9](图2)。
1.2.7 睑板腺分泌评分(MGYSS)评估
上下睑鼻侧、中央及颞侧各5个腺体,共30条睑板腺。0分:清亮、透明的液体;1分:混浊的液体;2分:混浊颗粒状分泌物;3分:浓稠如牙膏状分泌物;4分:未检测到睑酯排出。
1.3 治疗方法
(1)雾化熏蒸:使用WH-V型超声雾化器,雾化熏蒸治疗20 min,温度维持在42 ℃; (2)OPT:使用M22优化脉冲光技术,设定参数:波长590 nm、脉宽6.0 ms、脉冲延迟50 ms,脉冲方式为3个同步脉冲,针对不同肤色患者设置不同的治疗能量,10 J~16 J连续可调。患者面部清洁,眼盾护眼,涂耦合凝胶,强光治疗范围从耳际到耳际,包括鼻部,每侧约9个治疗光斑,共进行2次;(3)表麻1次,使上下睑睑板腺充分暴露,用睑板腺镊从鼻侧到颞侧轻轻挤压睑板腺;(4)医用冷疗贴冷敷10 min;(5)以上治疗每2周1次,共3次,治疗期间0.3%玻璃酸钠眼液点双眼3次/d和建议患者居家继续热敷治疗,每天1次,10 min。
1.4 观察指标
分别于治疗前、治疗后1月、治疗后3月监测OSDI评分、NIBUT、CFS评分、LLT、MGYSS。
1.5 统计学处理
采用IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0进行统计学分析。计数资料采用n(%)表示,性别差异采用χ2检验,年龄差异采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)。连续变量运用Shapiro-Wik进行正态性检验,符合正态分布的计量资料采用 (
$\bar x \pm s $ )表示,采用重复测量方差分析,组间和组内两两比较行LSD-t检验;不符合正态分布的计量资料采用M(P25,P75)表示,采用广义估计方程模型检验。相关性分析采用Spearman秩相关分析。以P < 0.05 为差异具有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 3型OSDI评分治疗前后及组间比较
进行2因素重复测量方差分析,F组别 = 2.310,P = 0.108;F时间 = 83.518,P < 0.001;F交互作用 = 9.124,P < 0.001;组别和时间存在交互作用,时间和组别对OSDI评分的影响进行单独效应检验。3型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较OSDI评分均下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);阻塞型和炎症型治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较OSDI评分持续下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),纤维化型差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。3型治疗前OSDI评分比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),治疗后1月组间比较差异有统计学意义(F = 3.780,P = 0.029),两两比较,阻塞型OSDI下降优于炎症型,差异有统计学意义(P = 0.011 < 0.05),纤维化型分别与阻塞型、炎症型比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);治疗后3月组间比较差异有统计学意义(F = 6.180,P = 0.004),两两比较,阻塞型OSDI评分下降优于炎症型和纤维化型,差异有统计学意义(P炎症型 = 0.009 < 0.05,P纤维化型 = 0.004 < 0.05),炎症型和纤维化型比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表1。
表 1 3型MGD相关干眼OSDI评分治疗前后及组间比较[($\bar x \pm s $ ),分]Table 1. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye OSDI score before and after treatment and between groups [($\bar x \pm s $ ),points]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 阻塞型 32.65 ± 8.87 19.80 ± 6.23 a 15.46 ± 6.82 a,c 111.505 < 0.001*** 炎症型 33.57 ± 8.59 26.37 ± 10.36 a 23.21 ± 11.53 a,c 25.412 < 0.001*** 纤维化型 30.05 ± 8.48 24.54 ± 9.48 a 25.06 ± 11.50 a 7.567 0.001* F
P0.648
0.5273.780
0.029*6.180
0.004*与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 2.2 3型BUT治疗前后及组间比较
进行2因素重复测量方差分析,F组别 = 8.022,P = 0.001;F时间 = 34.212,P < 0.001;F交互作用 = 4.213,P = 0.003;组别和时间存在交互作用,时间和组别对BUT的影响进行单独效应检验。3型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较BUT均上升,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);阻塞型治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较BUT持续上升,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),炎症型和纤维化型差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。3型治疗前BUT比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),治疗后1月和治疗后3月组间比较差异有统计学意义(F1月 = 3.799,P = 0.028;F3月 = 11.145, P < 0.001),两两比较,阻塞型BUT升高优于炎症型和纤维化型,差异有统计学意义(P1月炎症型 = 0.024 < 0.05,P1月纤维化 = 0.031 < 0.05;P3月炎症型 < 0.001,P3月纤维化型 < 0.001),炎症型和纤维化型比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表2。
表 2 3型MGD相关干眼BUT治疗前后及组间比较[($\bar x \pm s $ ),秒]Table 2. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye BUT before and after treatment and between groups [($\bar x \pm s $ ),s]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 阻塞型 5.81 ± 2.18 10.02 ± 2.74 a 13.75 ± 4.59 a,c 50.197 < 0.001*** 炎症型 6.07 ± 2.40 8.19 ± 2.90 a 9.07 ± 3.16 a 5.705 0.006* 纤维化型 5.94 ± 2.06 8.07 ± 1.96 a 8.59 ± 3.63 a 3.808 0.028* F 0.074 3.799 11.145 P 0.929 0.028* < 0.001*** 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 2.3 3型CFS评分治疗前后及组间比较
采用广义估计方程模型检验,Waldχ2组别 = 1.623,P = 0.444;Waldχ2时间 = 26.181,P < 0.001;Waldχ2交互作用 = 2.346,P = 0.672;组别和时间不存在交互作用,对时间和组别主效应进行分析。时间因素对CFS评分的影响有统计学意义,两两比较,治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较CFS评分下降,差异有统计学意义(P1月 = 0.003 < 0.05,P3月 = 0.002 < 0.05)。对3型分别分析时间因素对CFS评分的影响,阻塞型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较CFS评分下降,差异有统计学意义(P1月 = 0.003 < 0.05,P3月 = 0.002 < 0.05),治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。炎症型和纤维化型治疗后3月与治疗前比较差异有统计学意义(P炎症型 = 0.003 < 0.05、P纤维化型 = 0.002 < 0.05),治疗后1月分别与治疗前、治疗后3月比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。组别因素对CFS评分的影响无统计学意义,3型治疗前后组间比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表3。
表 3 3型MGD相关干眼CFS评分治疗前后及组间比较[M(P25,P75),分]Table 3. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye CFS score before and after treatment and between groups [M(P25,P75),points]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 Waldχ2 P 总体 0.00(0.00,2.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 26.181 < 0.001*** 阻塞型 0.00(0.00,1.50) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 9.369 0.009* 炎症型 0.00(0.00,2.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 9.000 0.011* 纤维化型 0.00(0.00,2.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 9.628 0.008 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 2.4 3型LLT治疗前后及组间比较
进行2因素重复测量方差分析,F组别 = 0.360,P = 0.699;F时间 = 4.234,P = 0.019;F交互作用 = 1.307,P = 0.272;组别和时间不存在交互作用,对时间和组别主效应进行分析。时间因素对LLT的影响有统计学意义,两两比较,治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较LLT上升,差异有统计学意义(P1月 = 0.016 < 0.05,P3月 = 0.005 < 0.05)。对3型分别分析时间因素对LLT的影响,进行单因素重复测量方差分析,阻塞型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较LLT上升,差异有统计学意义(P1月 = 0.001 < 0.05,P3月 = 0.001 < 0.05),治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),炎症型、纤维化型治疗前后差异均无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。组别因素对LLT的影响无统计学意义,3型治疗前后组间比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表4。
表 4 3型MGD相关干眼LLT治疗前后及组间比较[($\bar x \pm s $ ),nm]Table 4. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye LLT score before and after treatment and between groups [($\bar x \pm s $ ),nm]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 总体 66.92 ± 12.67 72.83 ± 13.82 a 74.60 ± 15.23 a 4.234 0.019* 阻塞型 65.41 ± 12.33 74.41 ± 12.16 a 76.90 ± 14.34 a 10.251 < 0.001*** 炎症型 67.72 ± 14.20 73.67 ± 13.32 74.33 ± 14.77 2.642 0.107 纤维化型 69.15 ± 11.73 68.15 ± 17.66 69.85 ± 17.73 0.096 0.814 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 2.5 3型MGYSS治疗前后及组间比较
进行2因素重复测量方差分析进行比较,F组别 = 6.871,P = 0.002;F时间 = 67.354,P < 0.001;F交互作用 = 3.559,P = 0.009;组别和时间存在交互作用,时间和组别对MGYSS的影响进行单独效应检验。3型治疗后1月、治疗后3月与治疗前比较和治疗后1月与治疗后3月比较MGYSS均下降,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。3型治疗前MGYSS比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),治疗后1月和治疗后3月组间比较差异有统计学意义(F1月 = 6.091,P = 0.004;F3月 = 11.598,P < 0.001),两两比较,阻塞型MGYSS下降优于炎症型和纤维化型,差异有统计学意义(P1月炎症型 = 0.004 < 0.05,P1月纤维化 = 0.010 < 0.05;P3月炎症型 < 0.001,P3月纤维化型 < 0.001),炎症型和纤维化型比较差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见表5。
表 5 3型MGD相关干眼MGYSS治疗前后及组间比较[($\bar x \pm s $ ),分]Table 5. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye MGYSS score before and after treatment and between groups [($\bar x \pm s $ ) ,scores]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 阻塞型 57.28 ± 16.56 44.48 ± 17.03 a 34.83 ± 14.79 a,c 74.809 < 0.001*** 炎症型 66.39 ± 10.26 58.33 ± 11.50 a 52.78 ± 11.79 a,c 16.250 < 0.001*** 纤维化型 65.00 ± 17.80 58.08 ± 15.48 a 53.46 ± 17.72 a,c 8.287 0.001* F 2.374 6.091 11.598 P 0.102 0.004* < 0.001*** 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 2.6 IVCM分类与睑板腺缺失相关性分析
IVCM分类下MGD严重程度增加阶段与睑板腺缺失评分呈正相关(rs = 0.474,P < 0.001)。在阻塞型中,28%、45%、21%和6%的患者的睑板腺缺失评分分别为0、1、2和3。在炎症型中,6%、50%、33%和11%的患者的睑板腺缺失评分分别为0、1、2和3。在纤维化型中,15%、46%和39%的患者的睑板腺缺失评分分别为1、2和3。
3. 讨论
随着工作和生活越发离不开各种电子终端产品及人口逐渐老年化,MGD及其相关干眼患者群体不断增加且呈低龄化发展趋势,重视针对发病机制的治疗。MGD的发病机制[10]主要为睑板腺终末导管及开口的过度角化,睑酯淤滞,细菌增殖和炎症反应,脂肪酶和酯酶的释放以及睑脂熔化温度升高,睑板腺阻塞及腺泡萎缩,随着睑酯淤滞和睑板腺开口阻塞的恶性循环,睑酯长期排不出,压力升高导致微观可观察到腺泡纤维化和萎缩,宏观可检测到睑板腺缺失。OPT作为目前最新的第五代IPL技术,针对MGD发病机制的各个方面,其作用机制为[11]:OPT通过选择性光热作用,封闭眼睑周围扩张的毛细血管,消除或减轻引发MGD的炎症因子和蠕形螨,降低细菌载量;同时能恢复睑板腺低氧环境,促进睑板腺上皮细胞分化。热辐射效应可软化并促进睑脂的分泌和排出。而MGX对改善睑酯淤滞以及睑板腺开口阻塞,促进睑酯排出,打破这个恶性循环有着不可替代的作用,所以本研究选择OPT联合MGX治疗,再配合居家热敷治疗。
在眼科使用IVCM这台设备,首先想到的一定是在角膜病上的运用,IVCM对睑板腺的观察是其非常规使用,就和过去IPL默认为用于皮肤美容科的治疗,而现在广泛用于MGD及其相关干眼的治疗,IVCM正逐渐用于睑板腺的观察和研究。图1展示了IVCM下1例阻塞型患者同一部位从开口到穹窿部睑板腺腺泡及其周围组织形态的变化:睑板腺开口边界欠光滑,近开口和穹窿部之间的腺泡出现扩张,近穹窿部出现了纤维化,这些改变和过去IVCM对MGD患者睑板腺形态的研究类似[12-13],MGD发生发展过程伴随着腺泡的扩张和纤维化,这个主要用于MGD的早期诊断。而本研究在充分考虑MGD发病机制全过程的基础上,结合IVCM对睑板腺的微观观察,侧重于观察腺泡分泌物反射状态、上皮和腺泡间的不均匀外观程度、上皮纤维化,将MGD分为严重程度增加阶段的3种类型,阻塞型、炎症型和纤维化型,IVCM对MGD分类是一种新分类方法。其中腺泡分泌物反射状态反应睑酯阻塞,上皮和腺泡单元间隙不均匀外观反应睑板腺炎症状态,上皮纤维化代表睑板腺萎缩状态。MGD病理变化是个动态的过程,此分类是以其中一型为主,该分类和MGD的发病机制相呼应,阻塞型对应睑板腺终末导管及开口的过度角化,睑酯淤滞,睑板腺开口开始阻塞,炎症型对应睑板腺开口阻塞后,睑酯排不出,细菌增殖和炎症反应,脂肪酶和酯酶的释放,纤维化型对应在上述基础上,睑脂熔化温度升高,睑板腺阻塞加剧及腺泡萎缩。
既往通过IVCM对MGD分类的研究指出炎症型患者的OSDI评分较阻塞型和纤维化型高,炎症是患者症状相对明显的重要原因,但本研究中3型MGD相关干眼患者在治疗前OSDI比较组间差异无统计学意义,可能是因为既往研究的分类是基于下睑睑板腺完成的,下睑睑板腺缺失情况相对于上睑更严重,而IVCM分类的MGD严重程度增加阶段与睑板腺缺失评分呈正相关,导致分类上存在差异。在重力以及眼轮匝肌的作用下,上睑的睑酯相对于下睑更容易排出,阻塞的风险也降低,而本研究侧重点在于治疗的疗效,笔者对MGD的治疗是整个眼睑,所以选择了上睑完成IVCM检查并分类,这也是本研究结果阻塞型MGD患者偏多,纤维化型患者偏少的原因。
本研究结果还可以解释过去一些相关研究结果存在的差异,Ren X等[14]根据睑板腺缺失情况划分严重程度,发现在重度睑板腺缺失患者中,IPL联合MGX在治疗后症状改善明显。因为之前有研究[15]表明重度睑板腺缺失患者经过IPL治疗无明显改善。更有研究表明IPL/MGX治疗MGD的疗效与睑板腺缺失程度相关,当睑板腺缺失面积<50%时,治疗后症状和体征显著改善,而当睑板腺缺失面积≥70%时,治疗前后各项指标均未见明显改善[16]。这些差异都指向了睑板腺缺失程度,可能与睑酯自身分泌特点有关,正常生理状态下,只要存在约45%睑板腺间歇性分泌睑酯,这些量的睑酯足够维持泪膜稳定。本研究IVCM分类阶段的演变与睑板腺缺失评分呈正相关,表明随着睑板腺缺失增加,炎症型和纤维化型MGD相关干眼患者增多,且通过OPT/MGX治疗阻塞型疗效优于炎症型和纤维化型,但阻塞型患者中也存在睑板腺缺失严重的情况,而本研究中阻塞型MGYSS下降优于炎症型和纤维化型,表明阻塞型通过治疗睑酯的质改善相对明显,这解释了重度睑板腺缺失患者的疗效存在差异的原因,也可以理解为睑板腺缺失达到某个临界点,剩余的睑板腺分泌的量不足以滋润眼表,虽然量不足,但改善了睑酯的质。LLT这个指标在过去的研究也存在差异,通过IPL联合MGX治疗,有研究指出LLT上升[17],也存在LLT无明显变化[4],这些研究结果的差异也都指向了睑板腺缺失程度,本研究阻塞型MGD相关干眼患者LLT在治疗后1月和治疗后3月LLT升高,而炎症型和纤维化型治疗前后无明显改变。不可否认睑板腺缺失程度是衡量MGD严重程度的重要指标。
本研究阻塞型MGD相关干眼通过OPT联合MGX治疗后症状和体征改善最快最明显,而且OSDI、BUT、MGYSS从治疗后1月到治疗后3月持续改善,在治疗后3月阻塞型OSDI评分下降、BUT升高、MGYSS下降优于炎症型和纤维化型,患者获益最大;而炎症型疗效不如阻塞型,可能是OPT清除眼表炎症因子的能力有限,纤维化型疗效欠佳是整个腺泡分泌功能遭到破坏,虽然通过IPL联合MGX治疗,但恢复睑板腺低氧状态,促进睑板腺上皮细胞分化的功能有限,导致睑板腺分泌的质和量改善并没有阻塞型明显。虽然炎症型和纤维化型也从治疗中获益,但是其疗效远差于阻塞型,其获益主要来源于OPT还是MGX,以及炎症型患者在结合抗炎治疗后是否获益会更大,单纯的MGX治疗纤维化型MGD相关干眼的疗效和OPT联合MGX治疗的疗效是否有差异,都需要进一步研究。
本研究的不足之处在于治疗后没有复查IVCM检查,因为目前IVCM并没有定位功能,不能对比治疗前后的睑板腺微观状态。2型及3型患者样本量偏少,需要进一步扩大样本量。综上所述,本研究通过IVCM对MGD分类,该分类和MGD发病机制相联系,通过OPT联合MGX治疗,观察到阻塞型MGD相关干眼患者疗效优于炎症型和纤维化型,在指导临床治疗上有一定的意义。
-
表 1 3型MGD相关干眼OSDI评分治疗前后及组间比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),分]Table 1. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye OSDI score before and after treatment and between groups [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),points]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 阻塞型 32.65 ± 8.87 19.80 ± 6.23 a 15.46 ± 6.82 a,c 111.505 < 0.001*** 炎症型 33.57 ± 8.59 26.37 ± 10.36 a 23.21 ± 11.53 a,c 25.412 < 0.001*** 纤维化型 30.05 ± 8.48 24.54 ± 9.48 a 25.06 ± 11.50 a 7.567 0.001* F
P0.648
0.5273.780
0.029*6.180
0.004*与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 表 2 3型MGD相关干眼BUT治疗前后及组间比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),秒]Table 2. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye BUT before and after treatment and between groups [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),s]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 阻塞型 5.81 ± 2.18 10.02 ± 2.74 a 13.75 ± 4.59 a,c 50.197 < 0.001*** 炎症型 6.07 ± 2.40 8.19 ± 2.90 a 9.07 ± 3.16 a 5.705 0.006* 纤维化型 5.94 ± 2.06 8.07 ± 1.96 a 8.59 ± 3.63 a 3.808 0.028* F 0.074 3.799 11.145 P 0.929 0.028* < 0.001*** 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 表 3 3型MGD相关干眼CFS评分治疗前后及组间比较[M(P25,P75),分]
Table 3. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye CFS score before and after treatment and between groups [M(P25,P75),points]
组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 Waldχ2 P 总体 0.00(0.00,2.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 26.181 < 0.001*** 阻塞型 0.00(0.00,1.50) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 9.369 0.009* 炎症型 0.00(0.00,2.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 9.000 0.011* 纤维化型 0.00(0.00,2.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) 0.00(0.00,0.00) a 9.628 0.008 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 表 4 3型MGD相关干眼LLT治疗前后及组间比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),nm]Table 4. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye LLT score before and after treatment and between groups [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),nm]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 总体 66.92 ± 12.67 72.83 ± 13.82 a 74.60 ± 15.23 a 4.234 0.019* 阻塞型 65.41 ± 12.33 74.41 ± 12.16 a 76.90 ± 14.34 a 10.251 < 0.001*** 炎症型 67.72 ± 14.20 73.67 ± 13.32 74.33 ± 14.77 2.642 0.107 纤维化型 69.15 ± 11.73 68.15 ± 17.66 69.85 ± 17.73 0.096 0.814 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 表 5 3型MGD相关干眼MGYSS治疗前后及组间比较[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),分]Table 5. Comparison of type 3 MGD related dry eye MGYSS score before and after treatment and between groups [(
$\bar x \pm s $ ) ,scores]组别 治疗前 治疗后1月 治疗后3月 F P 阻塞型 57.28 ± 16.56 44.48 ± 17.03 a 34.83 ± 14.79 a,c 74.809 < 0.001*** 炎症型 66.39 ± 10.26 58.33 ± 11.50 a 52.78 ± 11.79 a,c 16.250 < 0.001*** 纤维化型 65.00 ± 17.80 58.08 ± 15.48 a 53.46 ± 17.72 a,c 8.287 0.001* F 2.374 6.091 11.598 P 0.102 0.004* < 0.001*** 与治疗前比较,aP < 0.05;与治疗后1月比较,cP < 0.05;*P < 0.05,***P < 0.001。 -
[1] 亚洲干眼协会中国分会,海峡两岸医药交流协会眼科专业委员会眼表与泪液病学组. 我国睑板腺功能障碍诊断与治疗专家共识(2017年)[J]. 中华眼科杂志,2017,53(9):657-661. [2] Chan T C Y,Chow S S W,Wan K H N,et al. Update on the association between dry eye disease and meibomian gland dysfunction[J]. Hong Kong Med J,2019,25(1):38-47. [3] Qiao C,Li L,Wang H,et al. Adverse events of intense pulsed light combined with meibomian gland expression versus meibomian gland expression in the treatment of meibomian gland dysfunction[J]. Lasers Surg Med,2021,53(5):664-670. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23339 [4] Dell S J,Gaster R N,Barbarino S C,et al. Prospective evaluation of intense pulsed light and meibomian gland expression efficacy on relieving signs and symptoms of dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction[J]. Clin Ophthalmol,2017,11(1):817-827. [5] 亚洲干眼协会中国分会,海峡两岸医药卫生交流协会眼科学专业委员会眼表与泪液病学组,中国医师协会眼科医师分会眼表与干眼学组. 中国干眼专家共识: 检查和诊断(2020年)[J]. 中华眼科杂志,2020,56(10):741-747. [6] 中华医学会眼科学分会角膜病学组. 干眼临床诊疗专家共识(2013年)[J]. 中华眼科杂志,2013,49(1):73-75. [7] Villani E,Beretta S,De Capitani M,et al. In vivo confocal microscopy of meibomian glands in Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2011,52(2):933-939. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-5995 [8] Randon M,Liang H,Abbas R,et al. A new classification for meibomian gland diseases with in vivo confocal microscopy[J]. J Fr Ophtalmol,2016,39(3):239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2015.07.015 [9] Randon M,Aragno V,Abbas R,et al. In vivo confocal microscopy classification in the diagnosis of meibomian gland dysfunction[J]. Eye (Lond),2019,33(5):754-760. doi: 10.1038/s41433-018-0307-9 [10] Baudouin C,Messmer E M,Aragona P,et al. Revisiting the vicious circle of dry eye disease: A focus on the pathophysiology of meibomian gland dysfunction[J]. Br J Ophthalmol,2016,100(3):300-306. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-307415 [11] 干眼强脉冲光临床应用专家共识专家组,中国康复医学会视觉康复专委会干眼康复专业组. 强脉冲光治疗睑板腺功能障碍及其相关干眼专家共识(2022)[J]. 中华实验眼科杂志,2022,40(2):97-103. [12] 梁庆丰,高超,梁虹,等. 活体共聚焦显微镜对睑板腺功能障碍患者睑板腺形态检测的应用研究[J]. 中华眼科杂志,2016,52(9):649-656. [13] 熊超,赖瑶,艾丽珍,等. 红外线照相技术联合活体共聚焦显微镜对轻度睑板腺功能障碍患者早期诊断价值的研究[J]. 眼科新进展,2021,41(1):69-74. [14] Ren X,Chou Y,Wang Y,et al. Comparison of intense pulsed light and near-infrared light in the treatment of dry eye disease: A prospective randomized study[J]. Acta Ophthalmol,2021,99(8):e1307-e1314. [15] Yurttaser Ocak S,Karakus S,Ocak OB,et al. Intense pulse light therapy treatment for refractory dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction[J]. Int Ophthalmol,2020,40(5):1135-1141. doi: 10.1007/s10792-019-01278-3 [16] 王梦格,谌丹,李丽平,等. 强脉冲光联合睑板腺按摩治疗睑板腺功能障碍的短期疗效[J]. 中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2019,21(10):769-775. [17] 肖宇,殷鸿波,张又尹,等. 强脉冲光联合睑板腺按摩治疗睑板腺功能障碍[J]. 国际眼科杂志,2021,21(1):124-131. -






 下载:
下载:
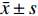
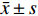
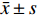
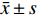
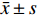
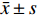

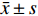
 下载:
下载:

