Mechanism of Dendrobium Officinale Against Inflammatory Aging Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
-
摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学、分子对接和动物实验探讨铁皮石斛抗炎性衰老的作用机制。 方法 通过数据库ETCM、Pubchem、Swiss TargetPrediction获得石斛靶点,从Rat Genome Database网站下载衰老大鼠基因,应用 STRING数据库构建PPI蛋白互作网络;利用DAVID数据库对石斛作用于老年大鼠的潜在靶点进行GO、KEGG通路分析;应用分子对接方法对石斛主要活性成分和关键作用靶点进行对接。老年大鼠灌胃石斛溶液10周后ELISA检测IL-6、IL-10蛋白表达。 结果 筛选到主要活性成分齿叶黄皮素、吴茱萸碱、吴茱萸次碱、紫花前胡,关键靶点NOS3、STAT3 、AKT1、GSK3B,主要信号通路PI3K-AKT、Calcium、EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药性、HIF-1、Apelin、VEGF,分子对接显示主要活性成分和关键靶点之间均能自发结合,且形成稳定的氢键。石斛中剂量组IL-6表达量较空白对照组(P < 0.01)、低剂量组(P < 0.01)和百令胶囊组(P < 0.05)降低,低剂量组IL-10表达量较空白组(P < 0.05)升高。 结论 铁皮石斛发挥抗炎性衰老的功能可能与降低老年SD大鼠血清中IL-6的含量,增加血清中IL-10的含量有关,作用机制与石斛中齿叶黄皮素、吴茱萸次碱、紫花前胡、吴茱萸碱等调控关键基因AKT1、STAT3、NOS3、GSK3B表达有关。 Abstract:Objective To explore the mechanism of Dendrobium officinale against inflammatory aging based on network pharmacology and molecular docking and experimental verification. Methods We used related databases to obtain the action targets of the main components of Dendrobium officinale and the genes of aging rats, then intersected them to obtain the final target. STRING database was used to build a protein-protein interaction(PPI) network. DAVID database was used to conduct enrichment analysis of Gene Ontology(GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genomes(KEGG). AutoDock software was to perform molecular docking verification on the main active components and key targets. Then, the aging rats were gavaged with dendrobium polysaccharide solution for ten week, the expression levels of IL-6 and IL-10 proteins were detected to verify the predicted targets. Results Through database retrieval, 28 active components and 492 target genes were screened out. There were 64 intersections. Enrichment analysis yielded 283 GO functional enrichment entries and 71 KEGG pathway enrichment entries. The main pathway is the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Calcium signaling pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, HIF-1 signaling pathway, Apelin signaling pathway, VEGF signaling pathway, etc. The results of molecular docking showed that each target(AKT1, STAT3, NOS3, GSK3B) and active ingredient(Dentatin, Rutaecarpine, Nodakenetin, Evodaiamine) spontaneously combined and formed stable hydrogen bonds. Animal experiments showed that the content of IL-6 in the medium dose group significantly decreased compared to the blank group, low dose group, and Bailing capsule group, and the content of IL-10 in the low dose group increased compared to the blank group. Conclusions Dendrobium officinale has a delaying effect on the decline of the immune system in elderly rats. It is mainly related to the decrease of IL-6 content and the increase of IL-10 content in the serum. Its mechanism may be related to the expression of key genes AKT1, STAT3, NOS3, GSK3B regulated by components in Dendrobium officinale, such as Dentatin, Rutaecarpine, Nodakenetin, and Evodaiamine. -
Key words:
- Dendrobium officinale /
- Inflammatory aging /
- Network pharmacology /
- IL-6 /
- IL-10
-
衰老是生物体不可逆转的自然进程,随年龄增长各系统功能出现退行性改变,其中便有免疫功能的退化[1],使免疫细胞分化、增殖能力下降,出现表型改变和功能缺陷,促炎因子产生增加,血清中炎症介质水平升高[2-4]。2000年,Franceschi[5]第一次提出“炎性衰老”的概念,随着年龄的增长体内各组织发生相关低度炎性反应,被称为炎性衰老[2,4]。在炎性衰老过程中有两个重要的炎性因子IL-6和IL-10 [6-7]。IL-6作为介导急性期炎症反应的重要细胞因子,是炎症介质网络的关键成员[7-8],通过促炎作用对机体造成影响,引起衰老带来的如老年性痴呆、代谢紊乱、动脉粥样硬化等年龄相关的健康问题[9],它的水平对多种疾病的诊断和严重程度判断具有预测价值[8,10],能作为炎症感染的严重程度、预后判断及老年人炎性衰老的预测指标 [6,11-12]。IL-10是公认的免疫抑制因子,具有很强的抗炎作用,可以抑制单核巨噬细胞的增殖和活性,使炎症因子的合成与释放得到有效抑制[13],可以阻断各种炎症通路[14],在慢性炎症的发展过程中能起到一定的延缓作用,对减轻机体的炎症损伤具有重要意义。老年小鼠对肺炎链球菌的先天免疫应答与炎症加剧中有数据表明,炎症加剧与IL-10介导的免疫调节减弱有关,具体表现在IL-10浓度的降低[15]。
铁皮石斛是兰科石斛属草本植物,有抗衰老、抗肿瘤 、降血糖、抗氧化、增强免疫等药理作用,能够有效防止亚健康,有延缓衰老的效果 [16-18]。铁皮石斛是一种有效的免疫调节剂,对免疫功能有增强的作用,能降低TNF-α、IL-6的产生,抑制巨噬细胞炎症[19-21]。衰老时体内细胞因子改变使机体处于慢性低度炎性状态,调节细胞因子、减少炎症反应可达到抗炎性衰老的目的。石斛具有优越的药理作用,具有无毒、无致突变、无遗传毒性的“三无”作用。石斛具有提高免疫、抗衰老的功效,但作用机制尚未被阐明。因此,本研究基于网络药理学方法,利用分子对接技术验证关键成分与靶点结合情况,预测石斛抗衰老的潜在机制,通过实验进一步验证,为石斛抗衰老的后续研究及临床应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 石斛抗炎性衰老网络药理学研究
1.1.1 石斛主要成分检索及靶点预测
利用ETCM检索石斛主要成分,通过Pubchem查询化合物SMILES号,用SMILES号在Swiss TargetPrediction数据库进行成分靶点的预测,获得石斛主要成分作用靶点。将成分靶点导入到Cytoscape 中,构建主要成分靶点网络。
1.1.2 石斛与衰老大鼠作用靶点筛选
从Rat Genome Database(https://rgd.mcw.edu/)网站下载SD衰老大鼠基因。将石斛主要成分作用靶点和衰老大鼠基因进行交集,利用Venny网站输入二者信息,得到石斛主要成分作用于衰老大鼠的靶点。
1.1.3 蛋白-蛋白交联互作网络构建
在STRING数据库,输入交集基因,构建蛋白-蛋白相互作用(protein-protein interaction,PPI)网络,将结果导入Cytoscape软件,根据Degree值作图。
1.1.4 靶点GO和KEGG富集通路分析
利用DAVID数据库进行GO富集分析和KEGG富集通路分析,得到富集信息。选择P ≤ 0.01且位靠前列的20条显著通路,用富集的名字、GeneRatio、FDR、count值通过微生信平台构建富集气泡图。
1.2 石斛活性成分-核心靶点分子对接
利用Cytoscape软件中Centiscape2.2对关键靶点进行筛选,主要参考Betweenness、Closeness和Degree值选取靶点。利用Cytoscape软件中cytoNCA对活性成分进行筛选,degree > 100,并参考相关文献。从ZINC数据库下载主要药物活性成分的2D结构,保存为MOL2格式,从UniProt数据库找到相应蛋白并在AlphaFold Protein Structure Database网站下载靶点蛋白的3D结构,保存为PDB格式,用pymol对大分子进行前处理。利用Autodock软件去水、加氢,对受体和配体进行分子对接,根据对接数值评价其活性,并利用pymol进行可视化展示。
1.3 石斛抗炎性衰老的动物体内实验
1.3.1 实验动物
雄性SD大鼠30只,20月龄,体重(300±20)g,购自昆明医科大学实验动物学部,使用许可证号SYXK(滇)K2015-0002。经昆明医科大学实验动物伦理审查委员会审核批准,伦理审查批准号:KMMU20220834。
1.3.2 实验试剂及配制
铁皮石斛粉末(含30%石斛多糖),陕西西安百川生物科技有限公司购买,将蒸馏水与石斛粉末按1∶1配制为溶液,4 ℃冰箱保存。百令胶囊0.5 g/粒,生产厂家杭州中美华东制药有限公司,1∶20配制为溶液,4 ℃冰箱保存。IL-6、IL-10酶联试剂盒,购自上海酶联生物科技有限公司。
1.3.3 实验动物分组和给药
自然衰老SD雄性大鼠30只,随机分为5组。分别为空白对照组、石斛组(100 mg/kg、200 mg/kg、400 mg/kg)、百令胶囊阳性对照组(40 mg/kg)。空白对照组每天灌胃蒸馏水,每组每天定时灌胃1次,连续灌胃10周。
1.3.4 取材及检测方法
心脏取血,血样离心后取上清液待测。ELISA测定时每孔加入50 μL血清和100 μL HRP酶标记, 37 ℃温育60 min,稀释洗涤液洗涤5次并拍干。加入显色剂A和显色剂B,37 ℃避光显色15 min。最后加入终止液50 μL,以空白组调零,450 nm波长下依次测量各孔的吸光度。
1.4 统计学处理
网络药理数据通过Genecard、KEGG PATHWAY Database等数据库进一步分析。IL-6与IL-10表达量数据用SPSS软件分析,结果用单因素方差检验,最小显著差异法(LSD)进行两两比较,P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 石斛抗炎性衰老网络药理学研究结果
2.1.1 石斛的主要活性成分、作用靶点、蛋白互作网络
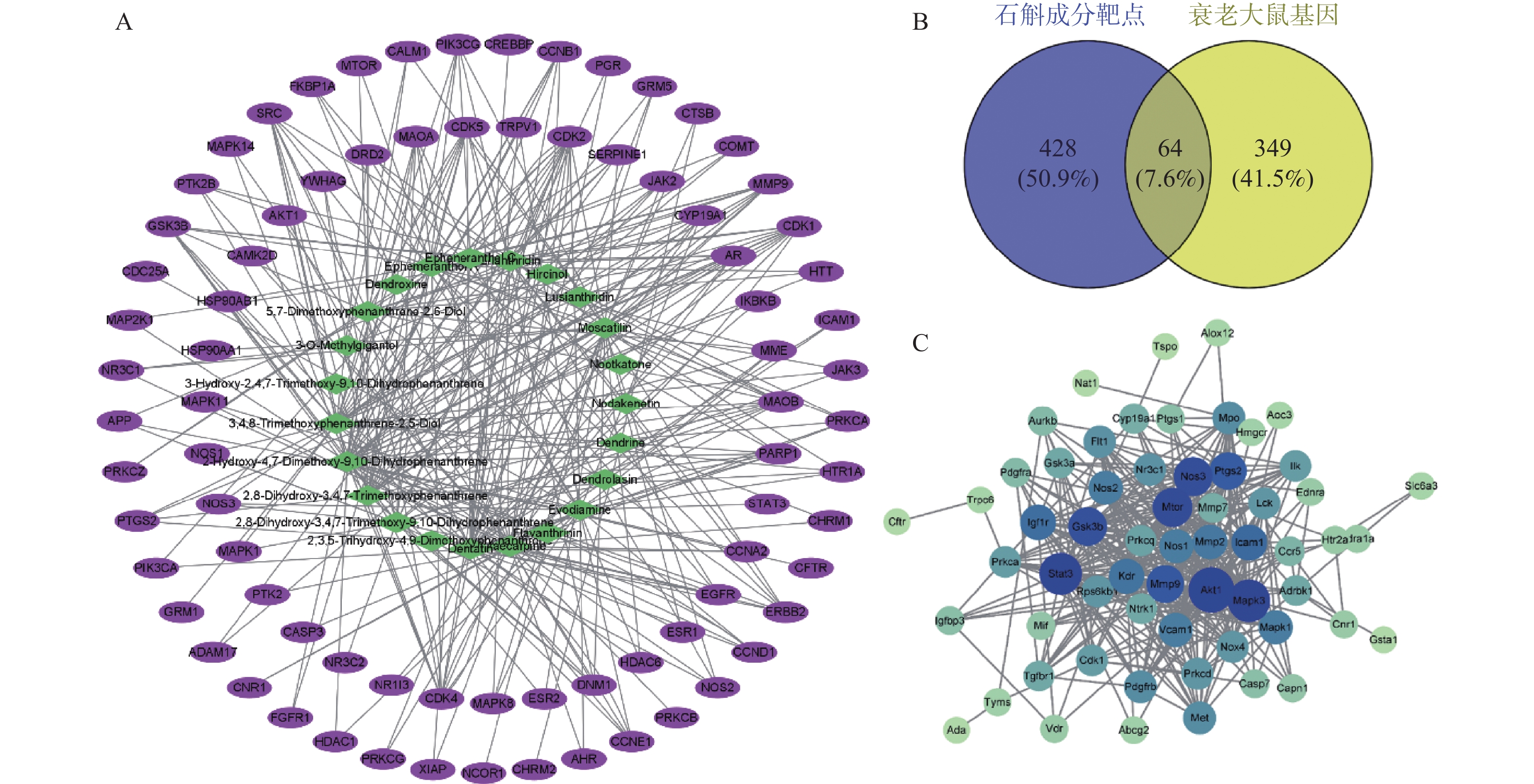
检索到石斛主要成分28项,得到492个作用靶点,见图1A。绿色菱形代表活性成分,紫色椭圆形代表靶点。通过Venny软件,输入成分靶点492个,衰老大鼠基因413个,绘制交集韦恩图,见图1B,获得石斛对衰老大鼠的作用靶点共64个。在STRING数据库输入交集基因靶点绘制PPI网络图,见图1C,节点代表作用靶点,边代表两两之间互相作用关系,节点颜色越蓝大小越大说明越重要。显示石斛抗炎性衰老的关键核心靶点有AKT1、STAT3、NOS3、GSK3B。
2.1.2 石斛主要成分对衰老大鼠GO富集分析和KEGG富集通路分析
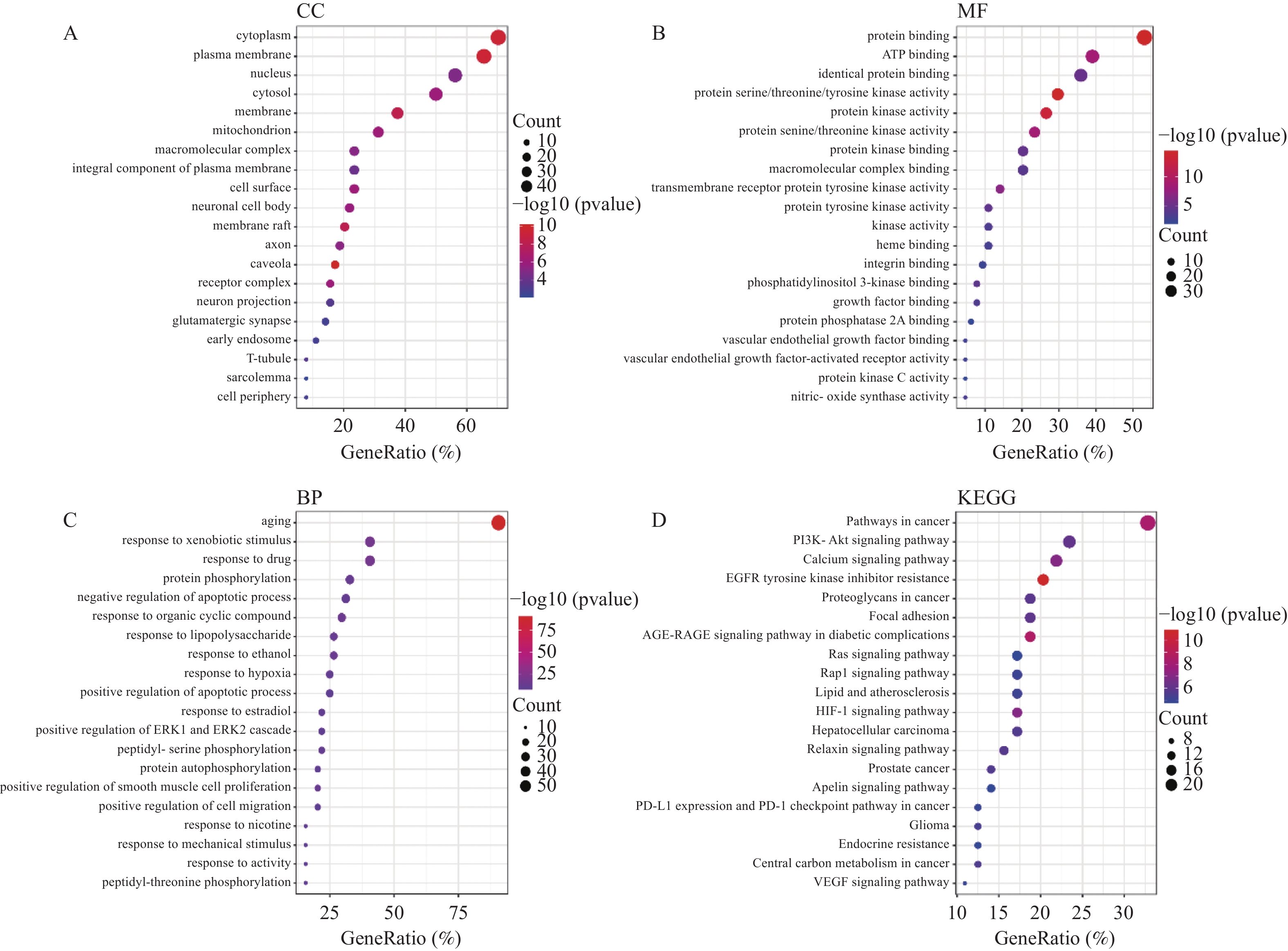
利用DAVID数据库对交集靶点进行生物富集分析得到GO功能富集条目见图2A~2C。结果显示药物作用于细胞质、质膜、核、线粒体等,与ATP结合、蛋白质丝氨酸/苏氨酸/酪氨酸激酶活性、蛋白激酶活性、跨膜受体蛋白酪氨酸激酶活性、血管内皮生长因子结合、蛋白激酶C活性等分子功能有关,参与蛋白质磷酸化、凋亡过程、有机环状化合物反应、对脂多糖反应、EPK1和EPK2级联反应正向调节、肽基丝氨酸磷酸化、蛋白质自磷酸化、细胞迁移正向调节、肽基苏氨酸磷酸化等生物过程,其中石斛参与生物过程中衰老最为显著。
KEGG 富集到较为显著20条信号通路见图2D,主要有:PI3K-AKT、Calcium、EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药性、HIF-1、Apelin、VEGF等信号通路,通路上多个基因与炎症的发生发展关系密切。PI3K-AKT是炎症反应中的关键通路。VEGF、HIF-1、Apelin 3个信号通路中多个基因参与NO的合成,间接影响炎性因子合成。在PI3K-AKT、RAP1信号通路中,通过PI3K→AKT→NF-
${{ \kappa}} {\rm{B}}$ 调节细胞因子合成促进炎症。在AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications中,可能通过PKC和AKT调节NF-$\kappa {\rm{B}} $ (相关通路PI3K-AKT通路、钙通路),间接调节IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1合成。2.2 主要活性成分和核心靶点的分子对接
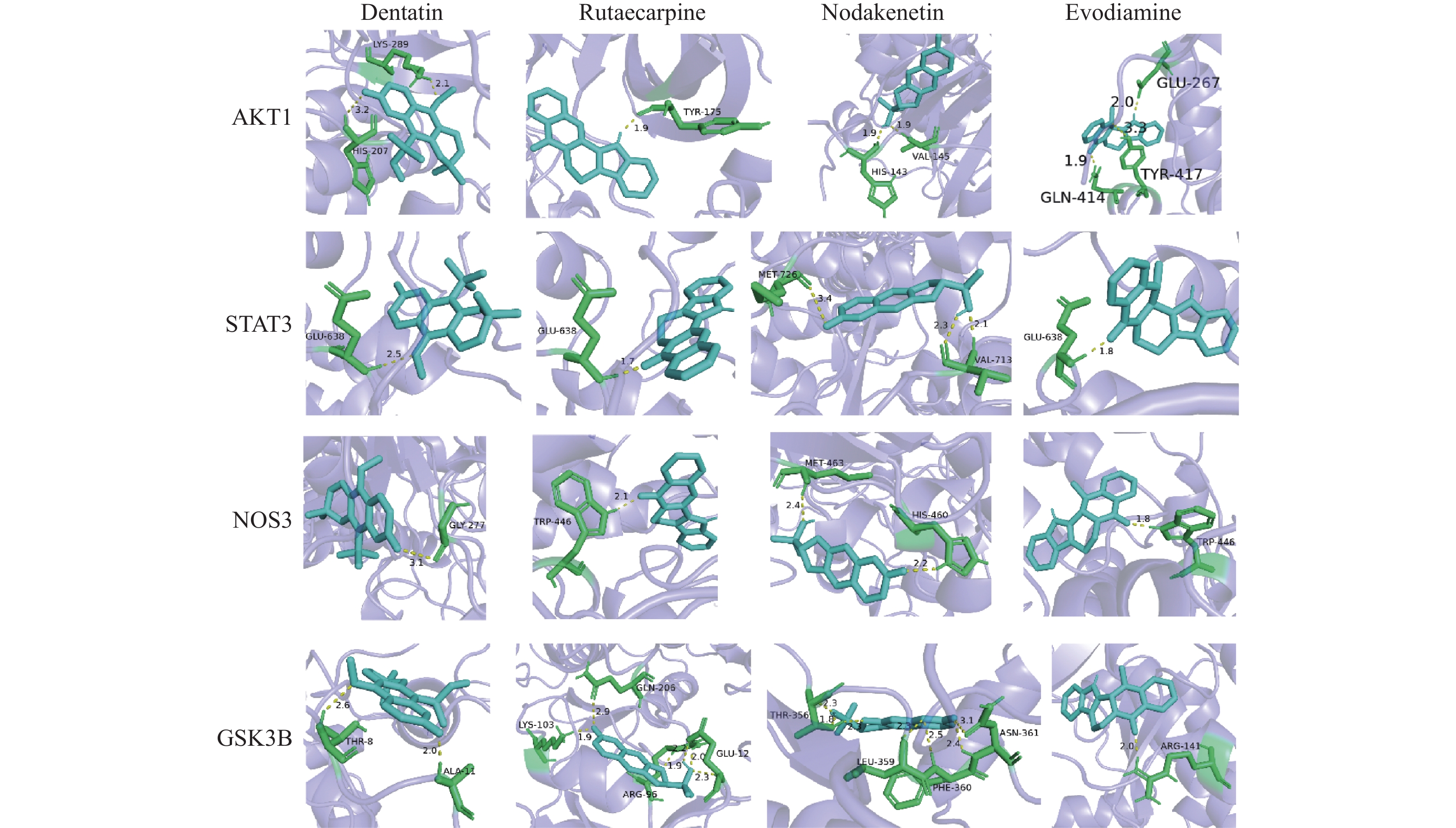
对靶点和成分进行筛选,见表1、表2,Degree(节点的度值)表示与此节点有联系的节点的数量。对靶点AKT1、STAT3、NOS3、GSK3B和成分齿叶黄皮素(Dentatin)、吴茱萸次碱(Rutaecarpine)、紫花前胡(Nodakenetin)、吴茱萸碱(Evodaiamine)分别进行分子对接,见图3、图4、表3,紫色分子为靶点,绿色部分为靶点与活性成分结合部位,蓝色分子为活性成分。以结合能作为判断成分与靶点结合能力大小的标准,结合能小于0表示可以自由结合,越小更易发生结合。结合后出现氢键表示二者结合稳定,提示较好的结合关系。结果显示各成分与各靶点间均能形成数量不等的氢键,AKT1与各活性成分、GSK3B与除紫花前胡外的成分、STAT3和NOS3与齿叶黄皮素、吴茱萸碱结合能均小于−5 KJ/mol,表示结合情况良好。
表 1 靶点网络中Degree排名前10的靶点Table 1. The top 10 target of Degree in the component-target network靶点名称 Degree BC(中介中心性) CC(接近中心性) AKT1 43 0.235981041 0.746835443 MAPK3 37 0.081326682 0.694117647 STAT3 36 0.077079997 0.686046512 NOS3 29 0.053439074 0.621052632 GSK3B 28 0.045054203 0.621052632 PTGS2 25 0.050639569 0.584158416 MTOR 30 0.047754481 0.627659574 MMP9 26 0.020865854 0.584158416 ICAM1 22 0.026581134 0.561904762 VCAM1 18 0.019630032 0.541284404 表 2 靶点网络中Degree排名前9的成分Table 2. The top 9 component of Degree in the component-target network成分 Degree 名称 Dentatin 115 齿叶黄皮素 3-O-Methylgigantol 112 3-O-甲基甘醇 2-Hydroxy-4,7-Dimethoxy-9,10-Dihydrophenanthrene 108 2-羟基-4,7-二甲氧基-9,10-二氢菲 Rutaecarpine 108 吴茱萸次碱 Nodakenetin 108 紫花前胡 3,4,8-Trimethoxyphenanthrene-2,
5-Diol103 3,4,8-三甲氧基菲-2,5-二醇 Moscatilin 102 杓唇石斛素 Evodiamine 100 吴茱萸碱 Nootkatone 71 圆柚酮 表 3 分子对接结合能(单位:Kcal/mol)Table 3. Binding energy of molecular docking靶点名称 齿叶黄皮素 吴茱萸次碱 紫花前胡 吴茱萸碱 AKT1 −5.12 −5.22 −5.56 −5.97 STAT3 −5.01 −4.77 −4.94 −4.94 NOS3 −5.06 −4.42 −4.37 −4.85 GSK3B −5.13 −5.04 −5.46 −5.38 2.3 石斛对IL-6与IL-10蛋白表达的影响
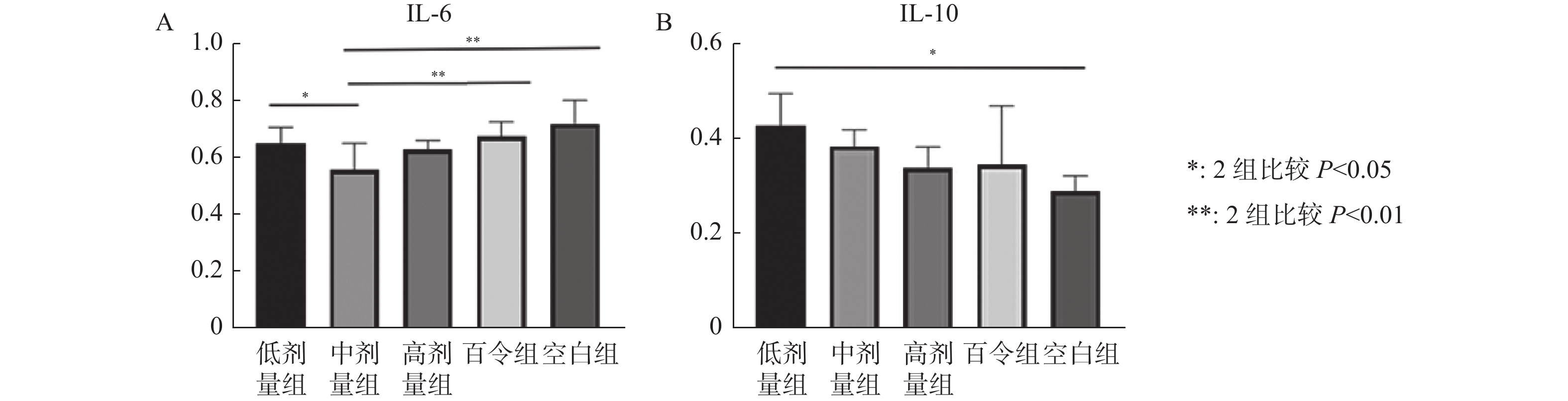
ELISA测得IL-6、IL-10浓度,使用SPSS软件分析,见图5。
中剂量组血清中IL-6含量较空白组(P < 0.01)、百令组(P < 0.01)、低剂量组(P < 0.05)相比均降低,差异具有统计学意义,提示中剂量石斛可以更好的降低IL-6含量。低剂量组、高剂量组、百令组血清与空白组相比、高剂量组与低剂量组相比,IL-6的含量也有所下降,但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。
低剂量组较空白组血清中IL-10含量升高,差异具统计学意义(P < 0.05),较其它组含量升高但不具有统计学意义,提示低剂量石斛能更好的增加IL-10含量。中剂量组、高剂量组、百令组与空白组相比、中剂量组与高剂量组与百令组相比,IL-10含量增加但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。
3. 讨论
本研究通过网络药理学筛选石斛主要活性成分,预测其作用靶点和抗衰老作用机制,对石斛抗衰老的机制进行了初步探讨,并通过分子对接和动物实验进行验证,阐明了石斛抗炎性衰老的物质基础和作用机制,可在实践中为石斛的应用提供新的启示。
本研究检索到石斛活性成分28项,获得潜在靶点492个、交集靶点64个。通过PPI网络得到核心靶点有AKT1、STAT3、NOS3、GSK3B,这4种蛋白都对炎症通路具有调节作用。NF-
$\kappa {\rm{B}} $ 可调节IL-6的生成[22],AKT1(蛋白激酶Bα)是其上游基因[23],是PI3K通路的中心环节,抑制AKT会使IL-6表达下降[24] ,而活化的STAT3(信号转导和转录激活因子3)可激活NF-$\kappa {\rm{B}} $ 信号通路,加剧炎症反应[25];GSK3B是糖原合成酶激酶3β,其活性受AKT的调节 [26],上升可以促进IL-10合成增加;NOS3(一氧化碳合酶3)可诱导NO合成来促进IL-6的生成[27]。对石斛成分进行筛选得到齿叶黄皮素、紫花前胡、吴茱萸次碱、吴茱萸碱四种主要活性成分。紫花前胡可通过抑制NF-$\kappa {\rm{B}} $ 信号通路而对炎症有抑制作用[28]。吴茱萸碱是生物碱类的一种,可抑制巨噬细胞、单核细胞、小胶质细胞抗炎因子的产生,并减少中性粒细胞中活性氧的产生,具有抗炎活性[29]。吴茱萸次碱可改善炎症小鼠模型的炎症反应,调节免疫平衡 [30]。在KEGG富集到的通路中,PI3K-AKT是炎症反应中的关键通路,激活可以促进炎症。 PI3K-AKT、RAP1、AEG-RAGE、EGFR等信号通路中抑制AKT可对NF-
$\kappa {\rm{B}} $ 调控使IL-6表达下降[31]。在FOCAL ADHESION、PI3K-AKT、LIPID AND ATHEROSLEROSIS等信号通路中,提升GSK3B活性可增加IL-10转录。同时,下调AKT和NF-$\kappa {\rm{B}} $ 的活性也可促进IL-10的转录,使体内炎症状态得以抑制[26]。在Apelin、LIPID AND ATHEROSLEROSIS、EGFR等信号通路,抑制STAT3活性可减少IL-6生成[25]。VEGF、Apelin、HIF-1、Calcium等信号通路中NOS1、NOS2、NOS3可促进NO合成,增强促炎介质如IL6和IL8的合成,导致炎症严重程度增加[32] ,对NO进行调节,可在一定程度上减缓炎症反应的进程,改变体内炎性状态。分子对接结果发现,AKT1与各活性成分、GSK3B与除紫花前胡外的其它成分、STAT3和NOS3与齿叶黄皮素、吴茱萸碱对接结果良好,表明石斛主要通过以上四种成分发挥抗炎性作用,主要作用靶点是AKT1。吴茱萸碱和吴茱萸次碱为抑炎物质[29-30,33]与GSK3B结合可促进IL-10产生,吴茱萸碱还可与STAT3作用抑制IL-6生成。紫花前胡作用于AKT1减少IL-6的产生,也可间接调节GSK3B活性进而调节IL-10表达[28]。结合动物实验,石斛组能降低血清中IL-6的含量、增加血清中IL-10的含量,石斛可以调节细胞因子的含量来改善机体炎性状态,进而对炎性衰老起延缓作用,与网络药理学预测结果一致。但IL-6含量与IL-10含量变化没有直接关系,说明不同剂量石斛对IL-6、IL-10的调节作用不同。
综上,石斛可通过多通路、多基因对细胞因子进行调节进而影响炎症反应而具有抗炎性衰老的功能。主要通过齿叶黄皮素、吴茱萸次碱、紫花前胡、吴茱萸碱等活性成分调控AKT1、STAT3、NOS3、GSK3B等关键基因以及PI3K-Akt、Calcium、EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药性、HIF-1、Apelin、VEGF信号通路调节IL-6、IL-10表达量来达到抗炎、抗衰老的作用。但动物实验样本数据较小,结果是否存在普遍性还有待探究,同时机体免疫调节系统是一个极其复杂的网络系统,不能较好地完全反映免疫功能的变化。实验针对铁皮石斛的免疫调节研究仍处于比较浅显的阶段,仅证明了石斛下调促炎因子IL-6的含量,上调抑炎因子IL-10含量。但更深入的机制仍有待于继续深入研究。
-
表 1 靶点网络中Degree排名前10的靶点
Table 1. The top 10 target of Degree in the component-target network
靶点名称 Degree BC(中介中心性) CC(接近中心性) AKT1 43 0.235981041 0.746835443 MAPK3 37 0.081326682 0.694117647 STAT3 36 0.077079997 0.686046512 NOS3 29 0.053439074 0.621052632 GSK3B 28 0.045054203 0.621052632 PTGS2 25 0.050639569 0.584158416 MTOR 30 0.047754481 0.627659574 MMP9 26 0.020865854 0.584158416 ICAM1 22 0.026581134 0.561904762 VCAM1 18 0.019630032 0.541284404 表 2 靶点网络中Degree排名前9的成分
Table 2. The top 9 component of Degree in the component-target network
成分 Degree 名称 Dentatin 115 齿叶黄皮素 3-O-Methylgigantol 112 3-O-甲基甘醇 2-Hydroxy-4,7-Dimethoxy-9,10-Dihydrophenanthrene 108 2-羟基-4,7-二甲氧基-9,10-二氢菲 Rutaecarpine 108 吴茱萸次碱 Nodakenetin 108 紫花前胡 3,4,8-Trimethoxyphenanthrene-2,
5-Diol103 3,4,8-三甲氧基菲-2,5-二醇 Moscatilin 102 杓唇石斛素 Evodiamine 100 吴茱萸碱 Nootkatone 71 圆柚酮 表 3 分子对接结合能(单位:Kcal/mol)
Table 3. Binding energy of molecular docking
靶点名称 齿叶黄皮素 吴茱萸次碱 紫花前胡 吴茱萸碱 AKT1 −5.12 −5.22 −5.56 −5.97 STAT3 −5.01 −4.77 −4.94 −4.94 NOS3 −5.06 −4.42 −4.37 −4.85 GSK3B −5.13 −5.04 −5.46 −5.38 -
[1] 权雅文,李刚. 衰老与免疫的研究进展[J]. 中国临床保健杂志,2022,25(4):455-459. doi: 10.3969/J.issn.1672-6790.2022.04.005 [2] Fulop T,Dupuis G,Baehl S,et al. From inflamm-aging to immune-paralysis: A slippery slope during aging for immune-adaptation[J]. Biogerontology,2016,17(1):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s10522-015-9615-7 [3] Fülöpa T,Larbib A,Witkowskid J. Human inflammaging[J]. Gerontology,2019,65(5):495-504. doi: 10.1159/000497375 [4] 杨巍,路遥平,王放. 免疫衰老—人类疾病的助推器[J]. 国际老年医学杂志,2023,44(2):129-134. [5] Franceschi C,Bonafè M,Valensin S,et al. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences,2000,908(1):244-254. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06651.x [6] 张伟洁,郑宏. IL-6介导免疫炎性反应作用及其与疾病关系的研究进展[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2017,33(5):699-703. doi: 10.13423/j.cnki.cjcmi.008148 [7] 孔婧,周秉舵,汤瑾,等. 清下化瘀方联合西医常规疗法对中重度急性胰腺炎患者内毒素、PCT、IL-6、IL-10的影响[J]. 现代中医药,2023,43(5):63-68. doi: 10.13424/j.cnki.mtcm.2023.05.013 [8] Klimushina M V,Gumanova N G,Kutsenko V A,et al. Association of common polymorphisms in IL-6 and IL6ST genes with levels of inflammatory markers and coronary stenosis[J]. Meta Gene,2019,21(3):100593-100593. [9] Wang Z,Wang J,Geriatrics D O,et al. Advances in the relationship between aging and aging-related diseases[J]. International Journal of Geriatrics,2019,40(3):191-192. [10] 于春月,李依聪,苏泽琦,等. 慢痞消对慢性萎缩性胃炎大鼠血清炎症指标IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α表达水平的影响[J]. 中华中医杂志,2019,34(5):1979-1983. [11] Hunter C A,Jones S A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease[J]. Nature immunology,2015,16(5):448-457. doi: 10.1038/ni.3153 [12] 何建英,陈香美,刘航,等. 血清脱氢表雄酮和白细胞介素-6在健康人衰老过程中的改变[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2004,24(3):195-197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2004.03.002 [13] Fiorentino D F,Zlotnik A,Mosmann T R,et al. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages[J]. The Journal of Immunology,1992,147(11):3815-3822. [14] 童乐,李梅,唐小涵,等. 白细胞介素-10在维持肠道稳态中的作用研究进展[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报,2023,45(9):1409-1418. [15] Williams A E,José,Ricardo J,et al. Enhanced inflammation in aged mice following infection with streptococcus pneumoniae is associated with decreased IL-10 and augmented chemokine production[J]. Ajp Lung Cellular & Molecular Physiology,2015,308(6):L539-L549. [16] 谢苗苗,肖柳,杨磊,等. 金钗石斛多糖的分离纯化及其抗衰老活性研究[J]. 中国现代中药,2018,20(12):1489-1493. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20180622003 [17] Zhang X Q,Zhao T M,Liu J,et al. Advances in chemical compounds and pharmacological effects of dendrobii caulis[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2018,49(13):3174-3182. [18] 马贤炳,何祥林,何家轩,等. 霍山石斛栽培技术及活性成分药理学研究进展[J]. 现代农业科技,2023,847(17):67-71,79. [19] 梁颖敏. 铁皮石斛对雌性衰老小鼠的抗衰老作用及其机理研究[D]. 广州: 广州中医药大学, 2011. [20] 吴蓓丽,吴月国,赵铮蓉,等. 铁皮石斛免疫调节作用及相关活性成分多糖的研究进展[J]. 中草药,2019,50(21):5373-5379. [21] Zeng Q,Ko C H,Siu W S,et al. Inhibitory effect of different cendrobium species on LPS-induced inflammation in macrophages via suppression of MAPK pathways[J]. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines,2018,16(7):481-489. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30083-9 [22] 任晓丽,皇甫和平,王军,等. 黄曲霉毒素B1激活核转录因子-κB信号通路引起牛乳腺上皮细胞发生炎性反应[J]. 动物营养学报,2023,35(7):4587-4595. doi: 10.12418/CJAN2023.426 [23] 杨涵,闫永煌,朱佩轩,等. 柴蜕颗粒通过MAPK/Akt/NF-κB信号通路改善气道炎症治疗咳嗽变异性哮喘的药效及机制研究[J]. 环球中医药,2023,16(9):1735-1742. [24] 赵青婷. ISOC1通过AKT1/PEX11B/过氧化物酶体途径调节巨噬细胞的炎症反应[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2022. [25] 吴茸,王栋,王晶敏,等. 苦参碱调节IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB信号通路对炎症性肠病大鼠Th17/Treg平衡的影响[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2023,44(5):809-816. [26] Wang Y,Wang K,Fu J. HDAC6 mediates poly(I: C)-induced TBK1 and akt phosphorylation in macrophages[J]. Frontiers in lmmunology,2020,11(8):1776. [27] 尚磊晶,孙盈盈,李元海. 吲哚美辛通过NOS3影响线粒体呼吸链对非小细胞肺癌的机制[J]. 中国药理学通报,2022,38(12):1846-1852. [28] Lin Y Q,Chen Y L,Zeng J Y,et al. Nodakenetin alleviates inflammatory pain hypersensitivity by suppressing NF-κB signal pathway[J]. Neuroimmunomodulation,2022,29(4):486-492. doi: 10.1159/000525690 [29] 梁靖蓉,麦凤怡,李陈广,等. 吴茱萸碱的药理学研究进展[J]. 中国药理学通报,2022,38(10):1457-1461. doi: 10.12360/CPB202201066 [30] 顿耿,祁相焕,吴德福,等. 基于IL-4/STAT6通路研究吴茱萸次碱对特应性皮炎模型小鼠的改善作用[J]. 中医学报,2022,37(12):2643-2648. [31] 廖敏,李璇,张樑君,等. 青蒿琥酯对结合型胆汁酸诱导小鼠原代肝细胞IL-6产生的机制研究[J]. 第三军医大学学报,2021,43(12):1133-1139. doi: 10.16016/j.1000-5404.202012225 [32] Stettner N,Rosen C,Bernshtein B,et al. Induction of nitric-oxide metabolism in enterocytes alleviates colitis and inflammation-associated colon cancer[J]. Biotechnology for Biofuels,2018,11(1):1962-1976. [33] 杨哲. 吴茱萸碱调控IL-6/STAT-3信号通路抑制炎症相关性结直肠癌的机制研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2021. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 朱银花,吴青燕,张娜娜,王冬冬. 铁皮石斛多糖调控JAK2/STAT5通路抑制非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠肝脏内质网应激作用分析. 实用中医内科杂志. 2024(03): 80-83+153 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 彭兴富. 不同仿野生栽培方式下铁皮石斛品质指标比较研究. 农业技术与装备. 2024(07): 152-154 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 安彦峰,郭石. 铁皮石斛多糖对动脉粥样硬化大鼠内皮祖细胞的作用研究. 现代医药卫生. 2024(24): 4150-4154+4161 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:

