miR-147a Regulates Ferroptosis and Affects Invasion and Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Cells
-
摘要:
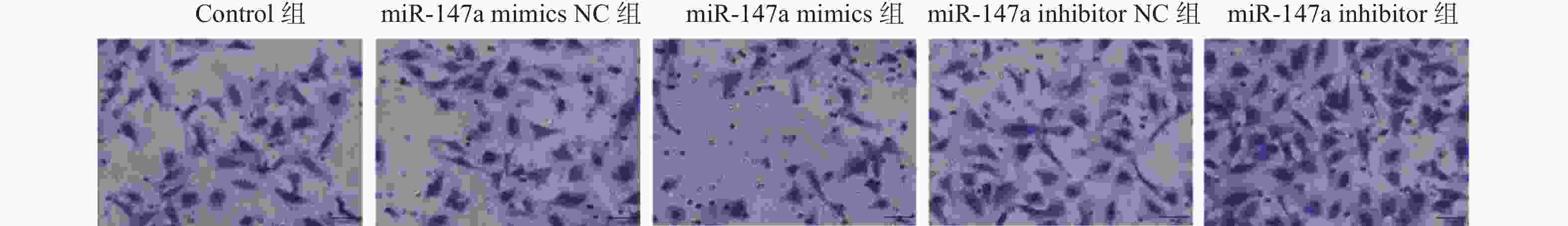
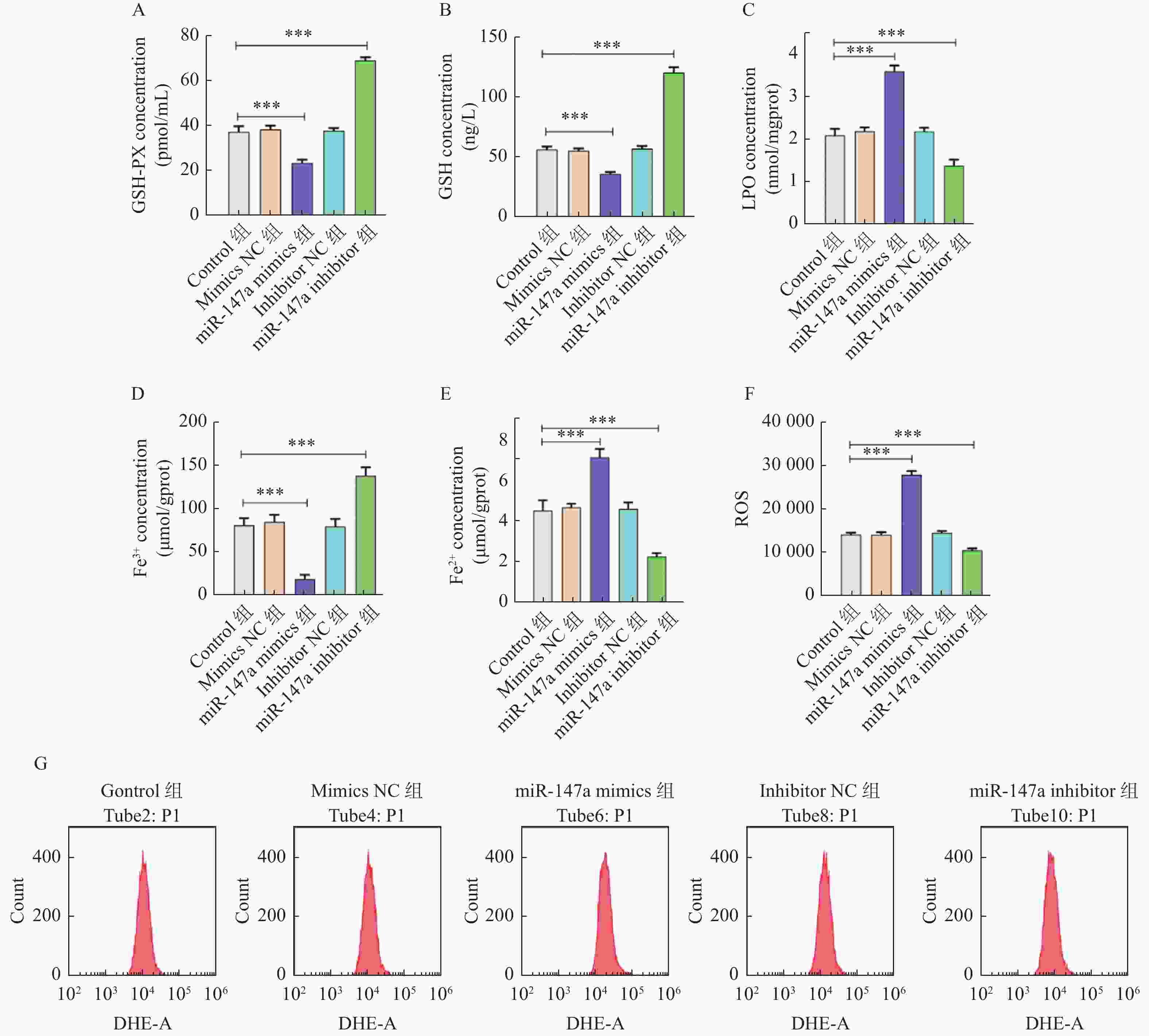
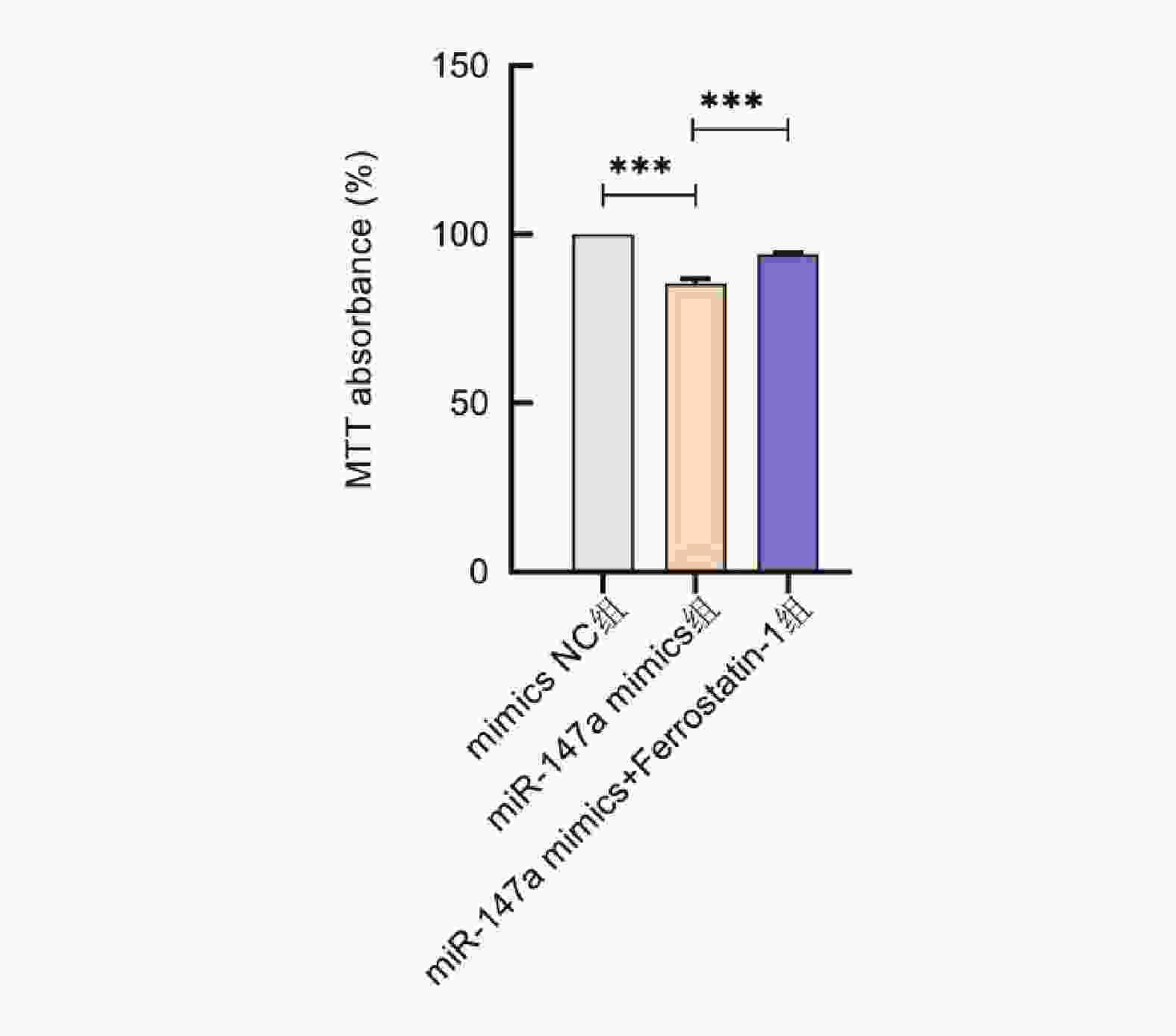
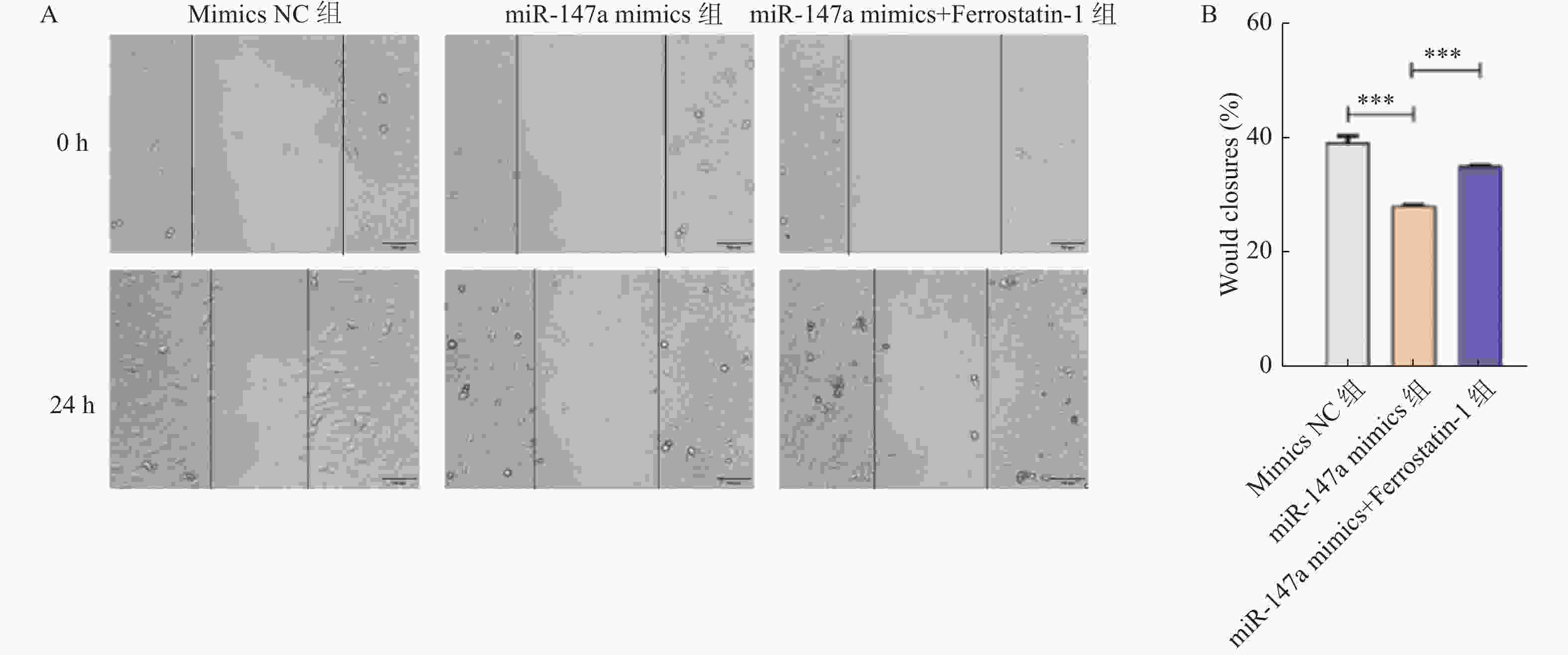
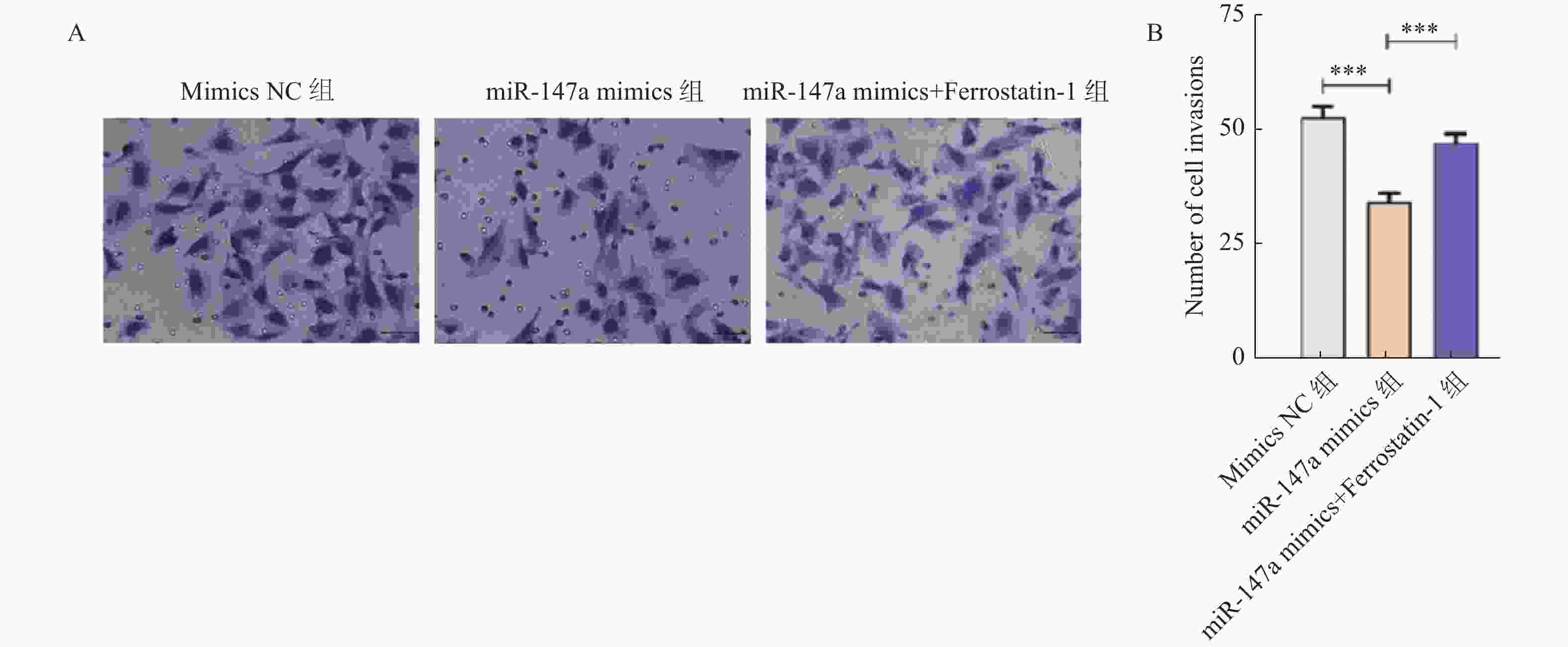
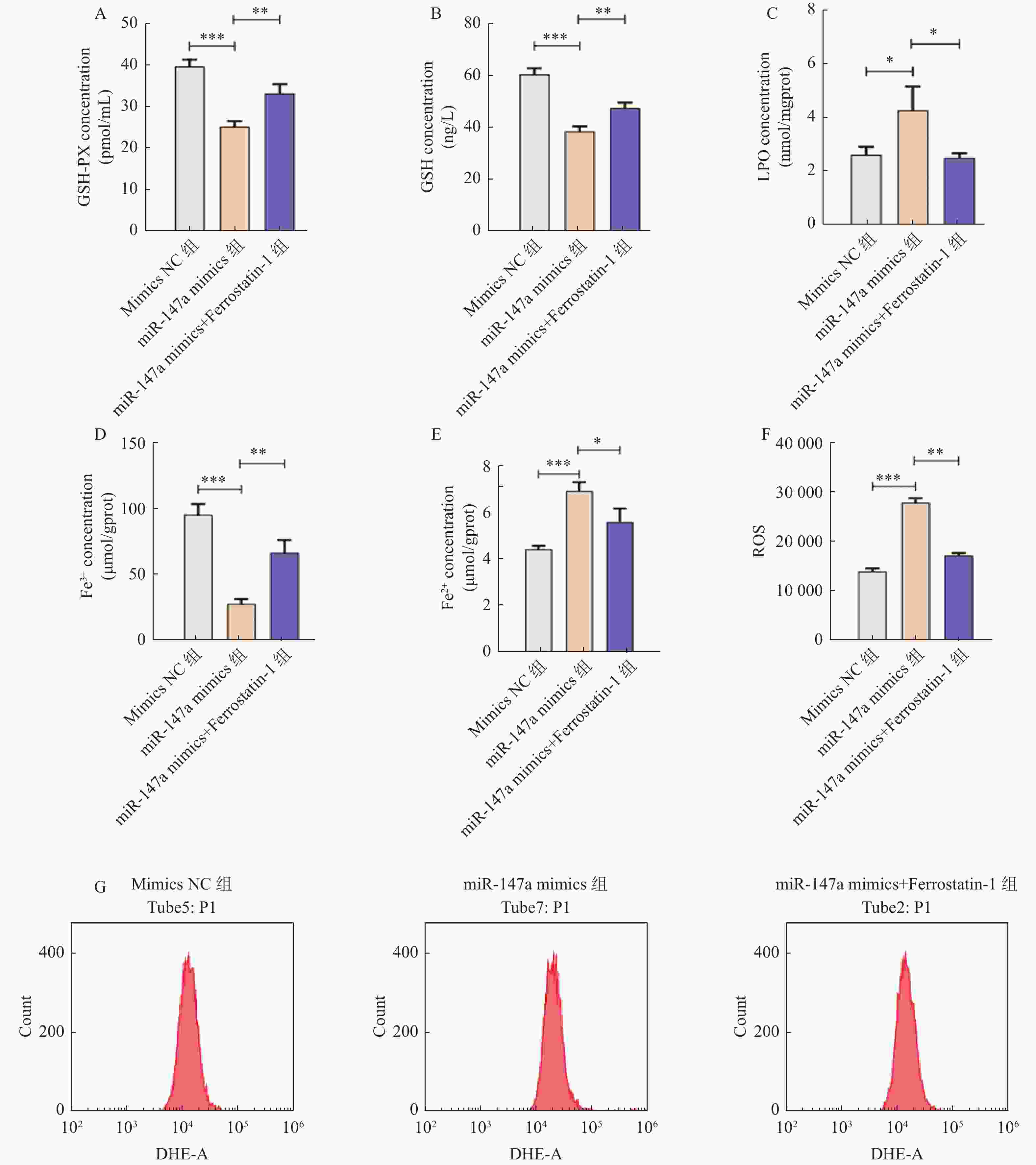
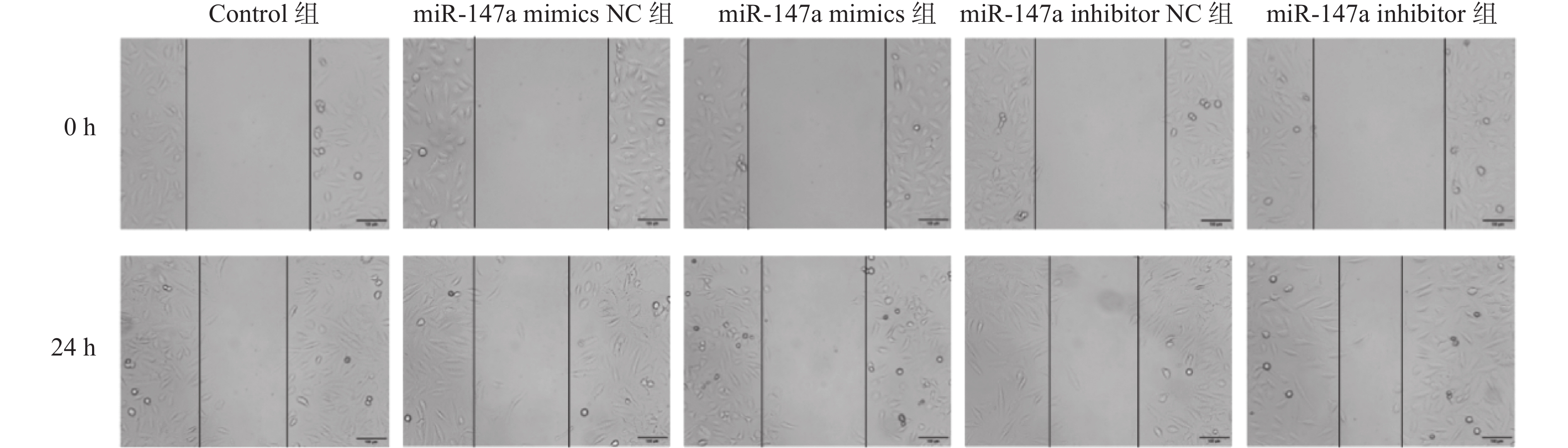
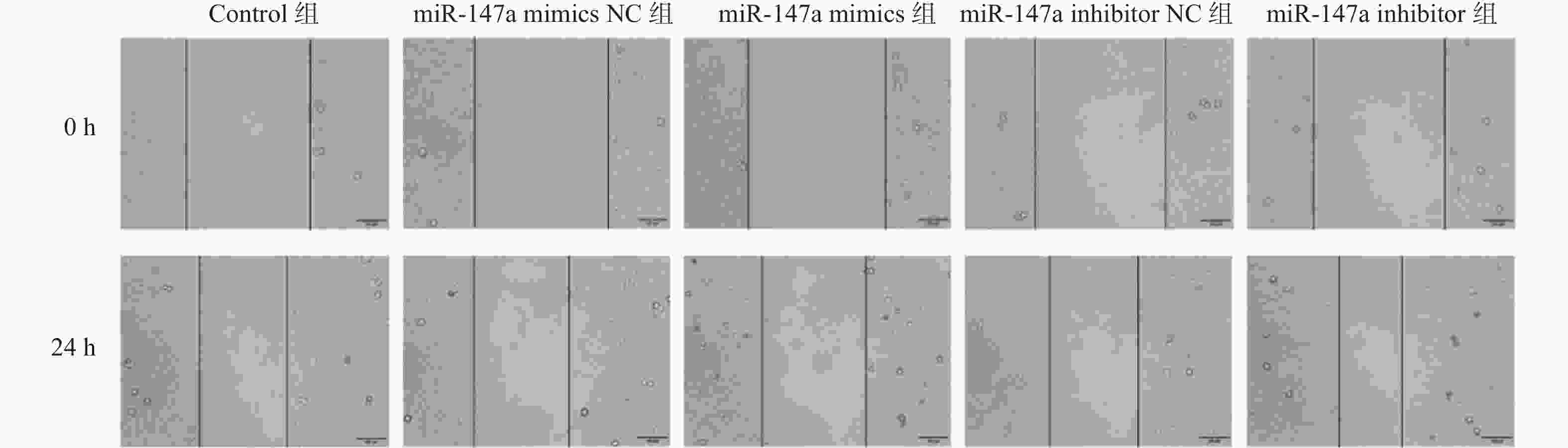
目的 探讨miR-147a通过影响铁死亡过程对宫颈癌Hela细胞增殖和转移的调控作用。 方法 将Hela细胞孵育及传代,制备Hela单细胞悬液进行转染,转染后分为Control组、miR-147a mimics NC组、miR-147a mimics组、miR-147a inhibitor NC组、miR-147a inhibitor组、miR-147a mimics+ Ferrostatin-1 (1 μM)组。采用MTT检测细胞增殖率、Transwell检测细胞侵袭能力,划痕实验检测细胞的愈合能力,流式细胞术检测活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)的表达情况,试剂盒检测亚铁离子(Fe2+)、铁离子(Fe3+)、乳过氧化物酶(Lactoperoxidase,LPO)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-PX)、谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)的表达变化。 结果 miR-147a mimics组的细胞增殖率、细胞侵袭数量和细胞迁移距离较Control组降低(P < 0.05);miR-147a inhibitor组的细胞增殖率、细胞侵袭数量和细胞迁移距离较Control组升高(P < 0.05)。较Control组,miR-147a mimics组的Fe2+、LPO、ROS的表达升高,Fe3+、GSH-PX和GSH的表达降低(P < 0.05)。miR-147a inhibitor组的Fe2+、LPO、ROS的表达降低,Fe3+、GSH-PX和GSH的表达升高(P < 0.05)。miR-147a mimics+Ferrostatin-1组的细胞增殖率、细胞侵袭数量和细胞迁移距离较miR-147a mimics组升高(P < 0.05)。与miR-147a mimics组比较,miR-147a mimics+Ferrostatin-1组的Fe2+、LPO、ROS的表达水平降低,(P < 0.05);Fe3+、GSH-PX和GSH的表达水平升高(P < 0.05)。 结论 miR-147a可以促进铁死亡,抑制宫颈癌细胞的增殖和转移。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the regulatory role of miR-147a in affecting cell proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer Hela cells through ferroptosis. Methods Hela cells were cultured and passaged, and then a Hela single-cell suspension was prepared and transfected. After transfection, the cells were divided into control group, miR-147a mimics NC group, miR-147a mimics group, miR-147a inhibitor NC group, miR-147a inhibitor group, and miR-147a mimics+Ferrostatin-1 (1 μM) group. MTT assay was used to detect cell proliferation, Transwell assay to assess cell invasion capacity, scratch test to evaluate cell healing ability, flow cytometry to detect reactive oxygen species (ROS) expression, and assay kits to measure expression changes of ferrous ions (Fe2+), ferric ions (Fe3+), lactoperoxidase (LPO), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX), and glutathione (GSH). Results Compared to the control group, the miR-147a mimics group showed reduced cell proliferation rate, cell invasion quantity, and cell migration distance (P < 0.05); the miR-147a inhibitor group exhibited increased cell proliferation rate, cell invasion quantity, and cell migration distance (P < 0.05). Compared to the control group, the miR-147a mimics group showed increased Fe2+, LPO, and ROS expression, with decreased Fe3+, GSH-PX, and GSH expression (P < 0.05). The miR-147a inhibitor group showed decreased Fe2+ , LPO, and ROS expression, with increased Fe3+, GSH-PX, and GSH expression(P < 0.05). The miR-147a mimics + Ferrostatin-1 group exhibited increased cell proliferation rate, cell invasion quantity, and cell migration distance compared to the miR-147a mimics group (P < 0.05). Compared to the miR-147a mimics group, the miR-147a mimics + Ferrostatin-1 group showed decreased Fe2+, LPO, and ROS expression levels (P < 0.05), with increased Fe3+, GSH-PX, and GSH expression levels (P < 0.05). Conclusion miR-147a can promote ferroptosis and inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of cervical cancer cells. -
Key words:
- Cervical cancer /
- miR-147a /
- Ferroptosis /
- Metastasis
-
表 1 MTT检测Hela细胞增殖情况[($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 3]
Table 1. Detection of the proliferation of Hela cells by MTT[($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 3]
组别 Hela细胞增殖活性(%) Control组 100.00±0.02 miR-147a mimics NC组 99.95±4.55 miR-147a mimics组 85.36±3.76### miR-147a inhibitor NC组 100.12±1.37 miR-147a inhibitor组 114.39±2.25### F 37.782 P <0.001*** ***P < 0.05;与Control组比较,###P < 0.001。 表 2 不同分组细胞的迁移和侵袭情况[($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 3]
Table 2. Migration and invasion of cells in different groups[($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 3]
组别 细胞迁移距离(%) 细胞侵袭数 Control组 42.12±3.19 52.33±4.04 miR-147a mimics NC组 41.94±4.42 51.33±3.21 miR-147a mimics组 29.13±1.41### 32.67±3.05### miR-147a inhibitor NC组 43.46±7.35 52.00±5.57 miR-147a inhibitor组 55.32±1.27### 72.67±4.73### F 14.769 33.634 P <0.001*** <0.001*** ***P < 0.05;与Control组比较,###P < 0.001。 -
[1] Tewari K S, Colombo N, Monk B J, et al. Pembrolizumab or placebo plus chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for persistent, recurrent, or metastatic cervical cancer: Subgroup analyses from the KEYNOTE-826 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2024, 10(2): 185-192. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.5410 [2] Dai D, Pei Y, Zhu B, et al. Chemoradiotherapy-induced ACKR2(+) tumor cells drive CD8(+) T cell senescence and cervical cancer recurrence[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2024, 5(5): 101550. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101550 [3] Zhou J, Guo Z, Peng X, et al. Chrysotoxine regulates ferroptosis and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to prevent cervical cancer[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 338(Pt 3): 119126. [4] Li L, Zeng J, He S, et al. METTL14 decreases FTH1 mRNA stability via m6A methylation to promote sorafenib-induced ferroptosis of cervical cancer[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2024, 25(1): 2349429. [5] Guo Y, Han Y, Zhang J, et al. Identification and experimental validation of prognostic miRNA signature and ferroptosis-related key genes in cervical squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cancer Med, 2024, 13(21): e70415. [6] Gong Y, Luo G, Zhang S, et al. Transcriptome sequencing analysis reveals miR-30c-5p promotes ferroptosis in cervical cancer and inhibits growth and metastasis of cervical cancer xenografts by targeting the METTL3/KRAS axis[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 117: 111068. [7] 郭清烽, 赖海清, 于鹏. miR-147a、SMARCE1、KGFR 在宫颈癌中的表达及相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2024, 44(19): 4636-4641. [8] Xu P, Ge F H, Li W X, et al. MicroRNA-147a targets SLC40A1 to induce ferroptosis in human glioblastoma[J]. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst), 2022, 2843990. [9] 李雅倩, 罗新鹏, 李宇轩, 等. 肿瘤转移中EMT的作用及其调控网络[J]. 生命的化学, 2024, 44(1): 64-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1336.2024.01.008 [10] 王 慧, 祁玉娟. miRNA与肿瘤转移[J]. 生命的化学, 2024, 44(10): 1813-1822 [11] 刘然, 应曼曼, 张晓楠, 等. miR-147a靶向MCM3抑制脉络膜黑色素瘤细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭[J]. 现代肿瘤医学, 2021, 29(12): 2024-2029. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2021.12.002 [12] Tan Y, Wang K, Kong Y. Circular RNA ZFR promotes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells via the miR-147a/CACUL1 axis[J]. J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 13(4): 1793-1804. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-672 [13] 王艾青, 郑秀花, 刘瑾春, 等. miR-147a靶向ATF2抑制非小细胞肺癌细胞侵袭和迁移[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2022, 38(12): 1469-1474. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2022.12.011 [14] 郭健, 曾友玲, 董晓寒. miR-147a在宫颈癌Hela细胞中的表达及对Hela细胞增殖、黏附及迁移的调控作用[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2024, 21(14): 2047-2052. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9455.2024.14.013 [15] Zhou Q, Meng Y, Li D, et al. Ferroptosis in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 55. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01769-5 [16] Mao C, Wang M, Zhuang L, et al. Metabolic cell death in cancer: ferroptosis, cuproptosis, disulfidptosis, and beyond[J]. Protein Cell, 2024, 15(9): 642-660. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae003 [17] Dai S M, Li F J, Long H Z, et al. Relationship between miRNA and ferroptosis in tumors[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 977062. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.977062 [18] Liu M, Kong X Y, Yao Y, et al. The critical role and molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis in antioxidant systems: A narrative review[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10(6): 368. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6942 [19] Jiang Z, Zhou J, Deng J, et al. Emerging roles of ferroptosis-related miRNAs in tumor metastasis[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2023, 9(1): 193. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01486-y [20] 李培莉, 文丽芳. miR-579-3p靶向角鲨烯单加氧酶调节铁死亡对宫颈癌HeLa细胞的恶性行为研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2023, 39(13): 1894-1898. [21] Wu P, Li C, Ye D M, et al. Circular RNA circEPSTI1 accelerates cervical cancer progression via miR-375/409-3P/515-5p-SLC7A11 axis[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2021, 13(3): 4663-4673. doi: 10.18632/aging.202518 [22] 陆美荣, 孙亮亮, 王彤. FOXM1上调ELK1介导铁死亡促进宫颈癌细胞顺铂耐药性[J]. 局解手术学杂志, 2024, 33(10): 898-905. doi: 10.11659/jjssx.03E024143 [23] 姚雪芹, 肖雪莲, 罗其英, 等. SDC2表达调控铁死亡参与宫颈癌发生的作用及机制[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2025, 60(2): 234-239. -





 下载:
下载: