EGCG Improves Myocardial Fibrosis Induced by High Fat and High Sugar Diet in Obese Rats by Inhibiting TGF-β1/Smads Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
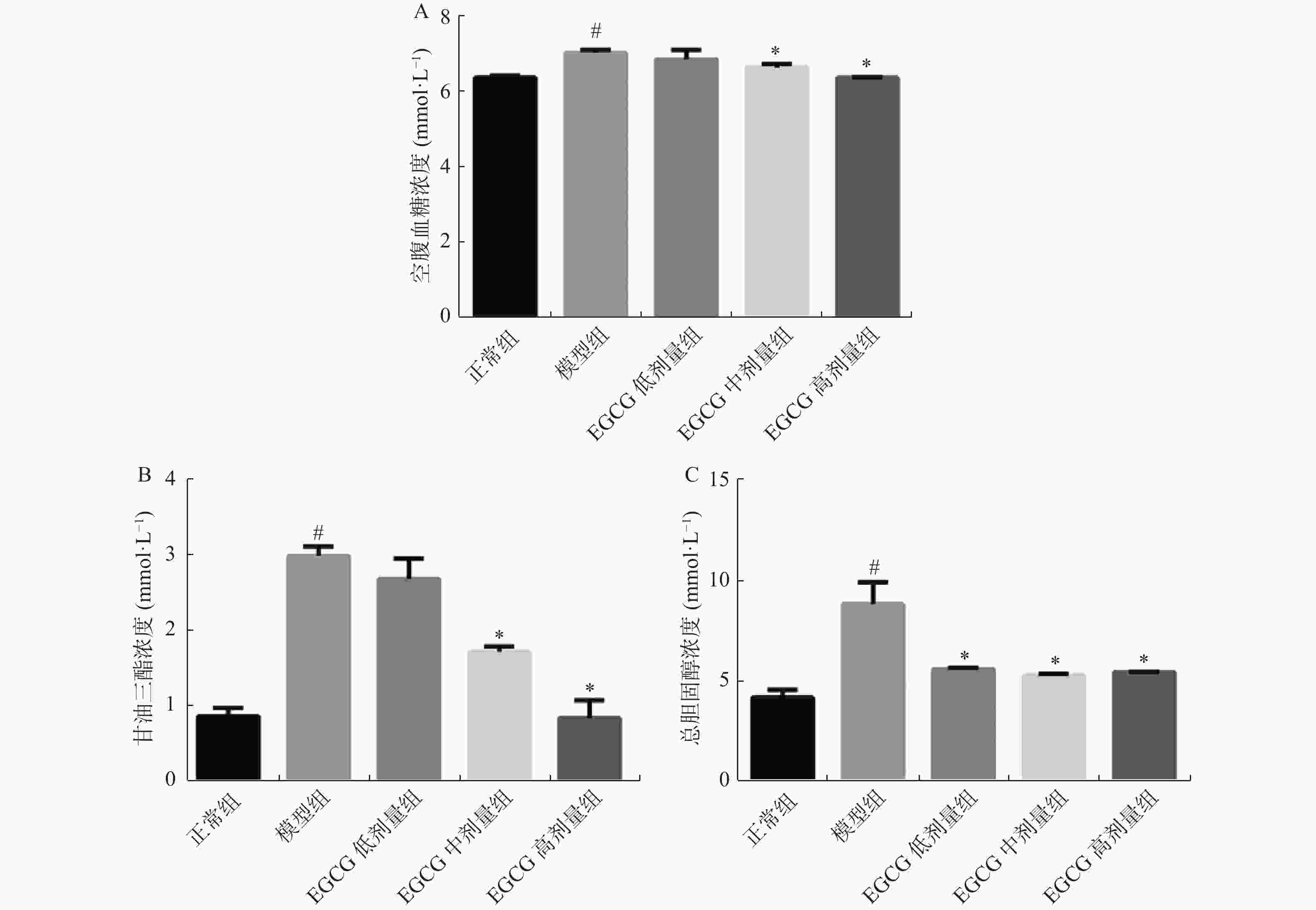
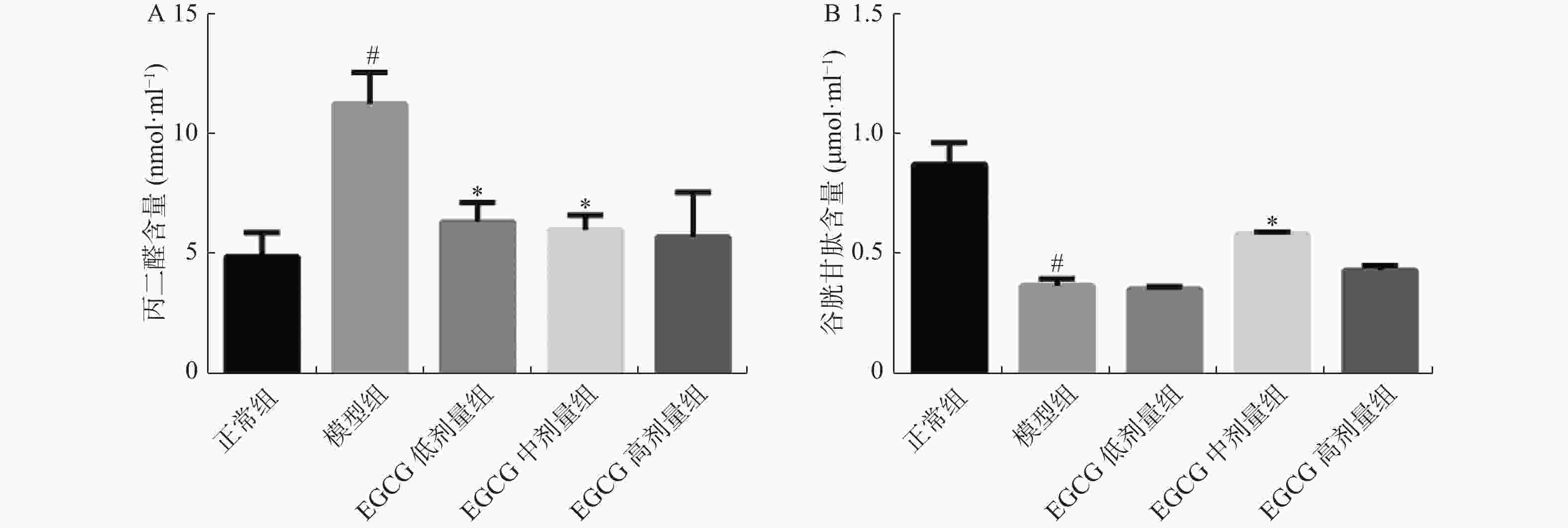
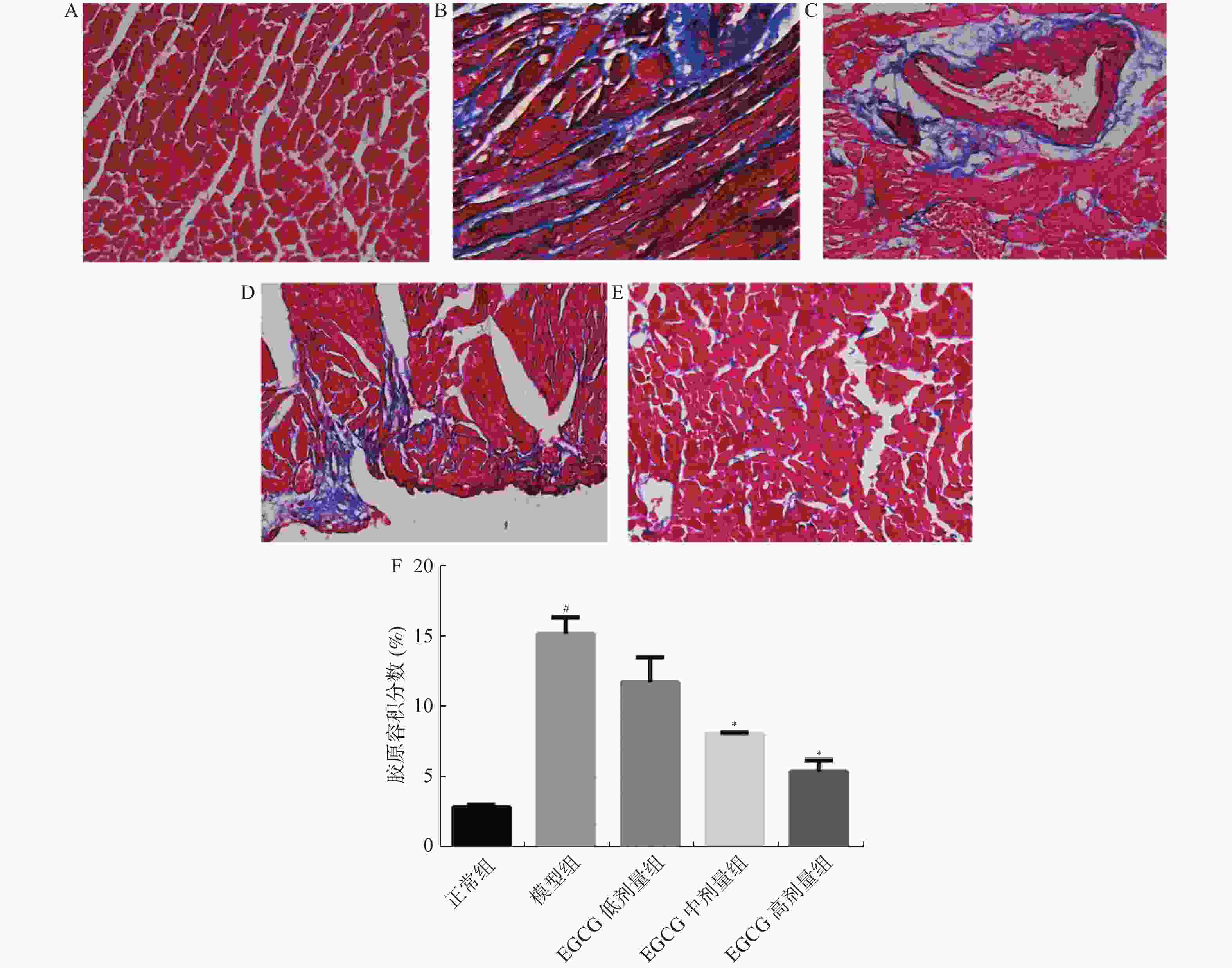
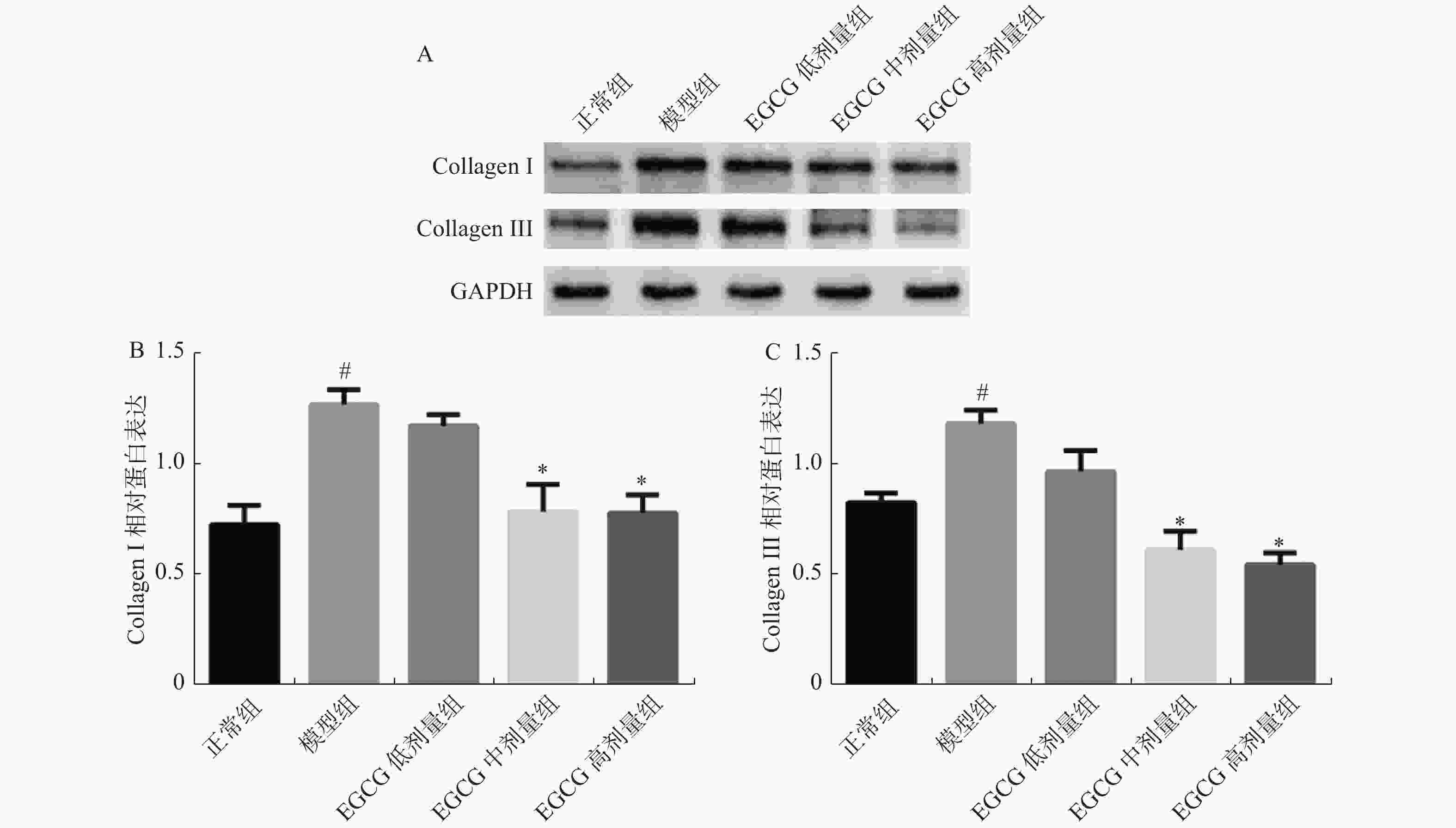
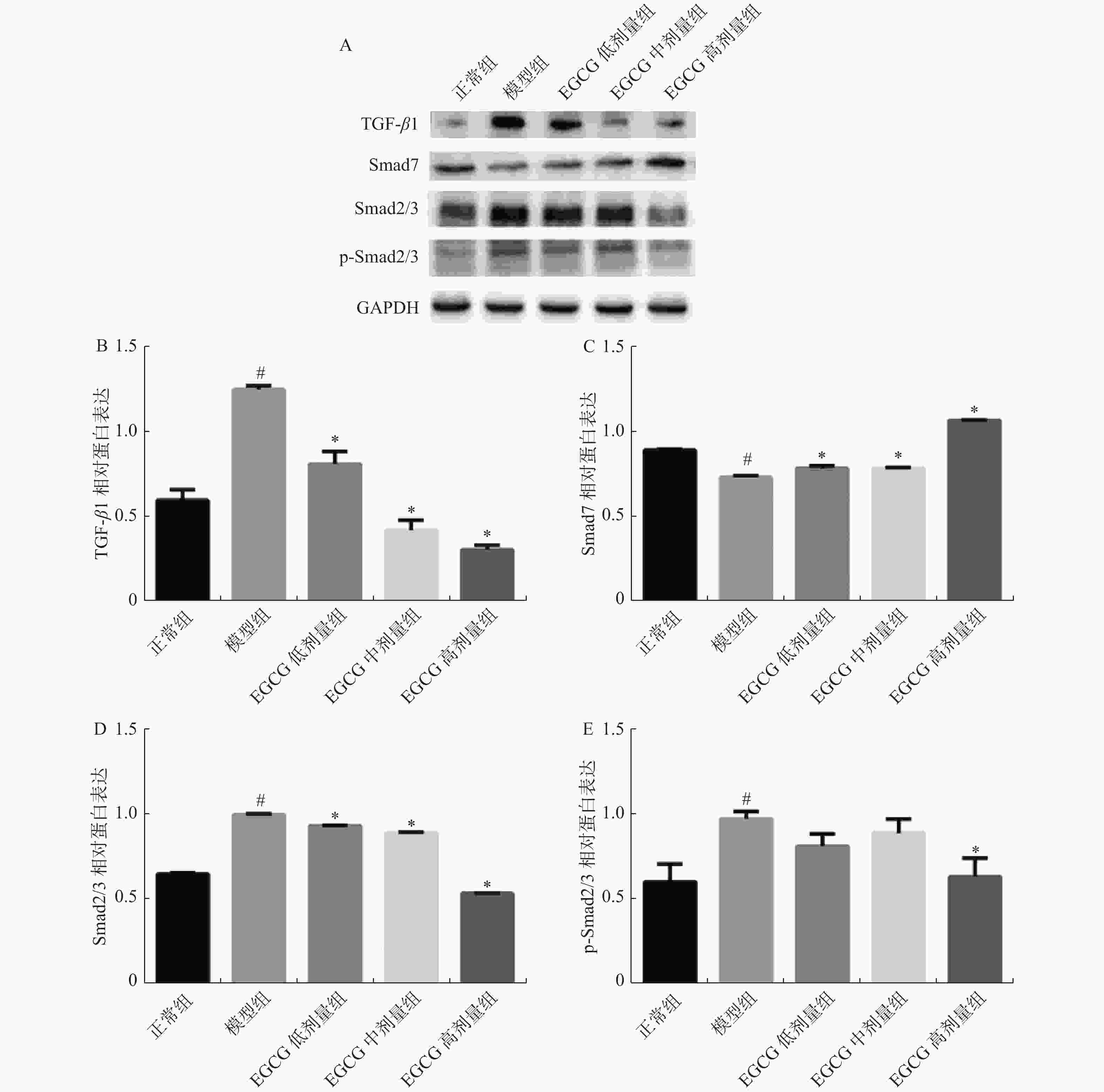
目的 研究表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin gallate,EGCG)对高脂高糖饮食诱导的肥胖大鼠心肌纤维化影响,探讨EGCG能否通过TGF-β1/Smads信号通路减轻心肌纤维化的程度。 方法 采用长期高脂高糖饮食形成肥胖大鼠模型,给予EGCG每天灌胃,治疗4周后,称取各组大鼠体重,Masson染色检测心肌纤维化的程度。生化检测血清中空腹血糖(FBG)、甘油三酯(TG)、总胆固醇(TC)、丙二醛(MDA)和谷胱甘肽(GSH)的含量。Western blotting检测各组大鼠心脏组织中相关蛋白(Collagen Ⅰ、Collagen Ⅲ、TGF-β1、Smad2/3、p-Smad2/3、Smad7)的表达水平。 结果 与正常组比较,模型组大鼠体重增加,给予EGCG治疗后减轻。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠心肌纤维化程度严重,给予EGCG治疗后减轻。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠FBG、TC、TG、MDA高于正常组,给予EGCG治疗后下降。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠GSH活性低于正常组,给予EGCG治疗后升高。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠Collagen Ⅰ、Collagen Ⅲ、TGF-β1、Smad2/3、p-Smad2/3蛋白表达升高,给予EGCG治疗后下降。与正常组比较,模型组大鼠Smad7蛋白表达低于正常组,给予EGCG治疗后升高。 结论 EGCG能够改善肥胖大鼠血糖和脂质代谢紊乱,减轻心肌纤维化程度,其机制可能与氧化应激介导的TGF-β1/Smads信号通路有关。 -
关键词:
- 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 /
- 肥胖 /
- 心肌纤维化 /
- TGF-β1/Smads信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on myocardial fibrosis induced by high fat and high sugar diet in obese rats and to explore whether EGCG can reduce the extent of myocardial fibrosis through TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway. Methods A obese rat model was formed by long-term high fat and high sugar diet. After 4 weeks of EGCG intragastric administration daily in obese rats, the body weight of every group rats was examined. The extent of myocardial fibrosis was detected by Masson staining. The contents of fasting blood glucose (FBG), triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH) in serum were determined by biochemical methods. Western blotting was used to detect the expression levels of Collagen Ⅰ, Collagen Ⅲ, TGF-β1, Smad2/3, p-Smad2/3 and Smad7 in heart tissues of the rats in each group. Results The body weight of the model group rats was incremental than those in the control group and the body weight of EGCG treatment was lower. The extent of myocardial fibrosis was more severe in the model group to the control group, and decreased after EGCG treatment. The contents of FBG, TC, TG and MDA in model group were higher than those in the control group, but decreased after EGCG treatment. The activity of GSH in the model group was lower than that in the control group, but increased after EGCG treatment. Collagen Ⅰ, Collagen Ⅲ, TGF-β1, Smad2/3 and p-Smad2/3 were increased in the model group, but decreased after EGCG treatment. Smad7 protein expression in the model group was lower than that in the control group, but increased after EGCG treatment. Conclusion EGCG can improve the lipid metabolism disorder and reduce MF degree in obese rats, which can be related to TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway mediated by oxidative stress. -
Key words:
- Epigallocatechin gallate /
- Obesity /
- Myocardial fibrosis /
- TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway
-
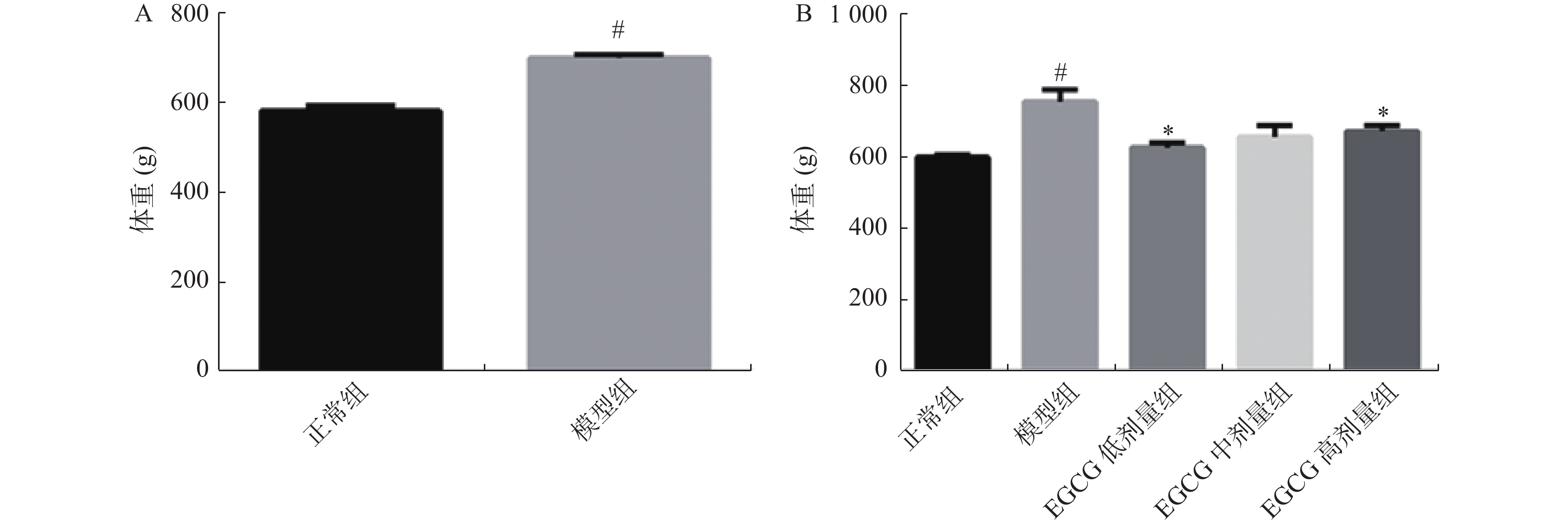
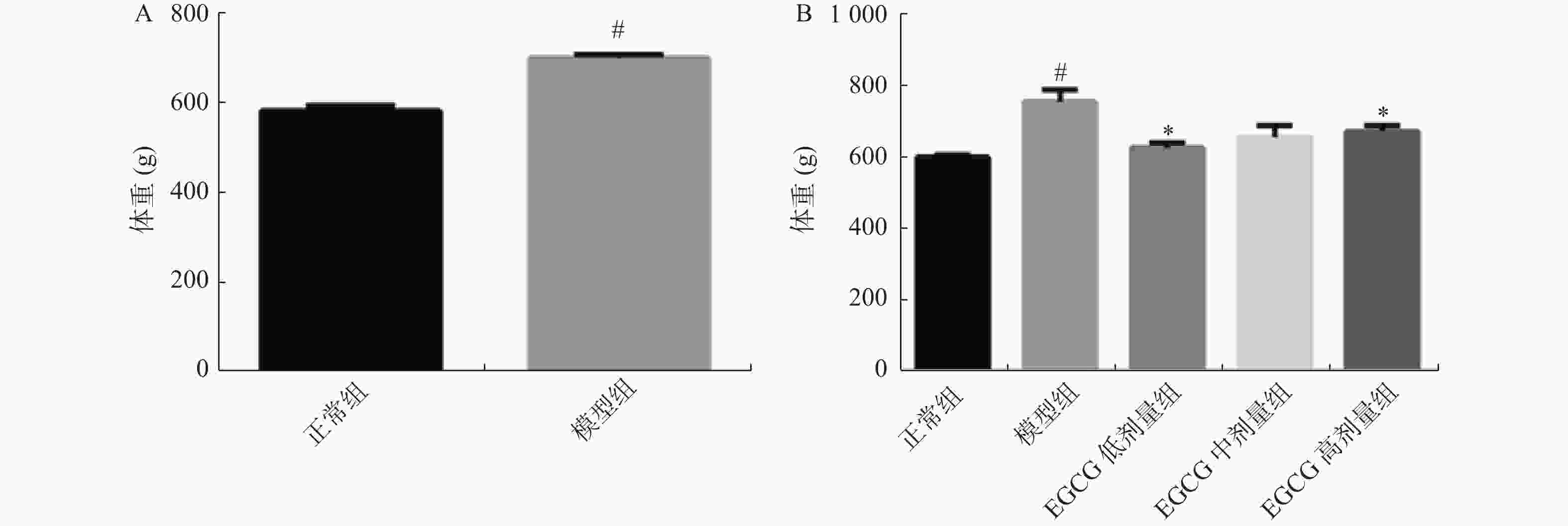
表 1 EGCG给药前大鼠体重(
$\bar x \pm s $ )Table 1. Body wight in the rats before EGCG treatment
项目 正常组(n = 11) 模型组(n = 41) 比率(%) P 体重(g) 582.54 ± 11.94 700.50 ± 7.42# 20.28 < 0.001# 与正常组比较,#P < 0.05。 -
[1] Hepler C,Gupta R K. The expanding problem of adipose depot remodeling and postnatal adipocyte progenitor recruitment[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol,2017,445(C):95-108. [2] Longo M,Zatterale F,Naderi J,et al. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2019,20(9):2358. doi: 10.3390/ijms20092358 [3] Tremmel M,Gerdtham U G,Nilsson P M,et al. Economic burden of obesity:A systematic literature review[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2017,14(4):435. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14040435 [4] Travers J G,Kamal F A,Robbins J,et al. Cardiac fibrosis:The fibroblast awakens[J]. Circ Res,2016,118(6):1021-1040. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306565 [5] Sharifi-Rad M,Pezzani R,Redaelli M,et al. Preclinical pharmacological activities of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in signaling pathways:An update on cancer[J]. Molecules,2020,25(3):467. doi: 10.3390/molecules25030467 [6] Kanwar J,Taskeen M,Mohammad I,et al. Recent advances on tea polyphenols[J]. Front Biosci (Elite Ed),2012,4(1):111-131. [7] Abunofal O,Mohan C. Salubrious effects of green tea catechins on fatty liver disease:A systematic review[J]. Medicines (Basel),2022,9(3):20. doi: 10.3390/medicines9030020 [8] Payne A,Nahashon S,Taka E,et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG):New therapeutic perspectives for neuroprotection,aging,and neuroinflammation for the modern age[J]. Biomolecules,2022,12(3):371. doi: 10.3390/biom12030371 [9] Chandler P C,Viana J B,Oswald K D,et al. Feeding response to melanocortin agonist predicts preference for and obesity from a high-fat diet[J]. Physiol Behav,2005,85(2):221-230. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2005.04.011 [10] Marinou K,Tousoulis D,Antonopoulos A S,et al. Obesity and cardiovascular disease:From pathophysiology to risk stratification[J]. Int J Cardiol,2010,138(1):3-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2009.03.135 [11] Whitlock G,Lewington S,Sherliker P,et al. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900 000 adults:Collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies[J]. Lancet,2009,373(9669):1083-1096. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60318-4 [12] Meng X M,Nikolic-Paterson D J,Lan H Y. TGF-β:The master regulator of fibrosis[J]. Nat Rev Nephrol,2016,12(6):325-338. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2016.48 [13] Ma Y,Zou H,Zhu X X,et al. Transforming growth factor β:A potential biomarker and therapeutic target of ventricular remodeling[J]. Oncotarget,2017,8(32):53780-53790. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17255 [14] Ye Z,Hu Y. TGF-β1:Gentlemanly orchestrator in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (review)[J]. Int J Mol Med,2021,48(1):132. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4965 [15] Lessard S J,MacDonald T L,Pathak P,et al. JNK regulates muscle remodeling via myo-statin/Smad inhibition[J]. Nat Commun,2018,9(1):3030. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05439-3 [16] Hayashi H,Abdollah S,Qiu Y,et al. The MAD-related protein Smad7 associates with the TGF-β receptor and functions as an antagonist of TGF-β signaling[J]. Cell,1997,89(7):1165-1173. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80303-7 [17] Zhang C,Zhou G,Chen Y,et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate interstitial fibrosis and cardiac dysfunction in a dilated cardiomyopathy rat model by inhibiting TNF-α and TGF-β1/ERK1/2 signaling pathways[J]. Mol Med Rep,2018,17(1):71-78. [18] Wang Q,Fu W,Yu X,et al. Ginsenoside Rg2 alleviates myocardial fibrosis by regulating TGF-β1/Smad signalling pathway[J]. Pharm Biol,2021,59(1):106-113. [19] Zheng Q,et al. Qiliqiangxin attenuates cardiac remodeling via inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model of myocardial infarction[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem,2018,45(5):1797-1806. doi: 10.1159/000487871 [20] Yuan Q,Cao S,Dong Q,et al. ALDH2 activation inhibited cardiac fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transformation via the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol,2019,73(4):248-256. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000655 [21] Ma Y,Shi Y,Wu Q,et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates vanadium-induced reduction of antioxidant capacity via Keap1-Nrf2-sMaf pathway in the liver,kidney,and ovary of laying hens[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res,2021,199(7):2707-2716. doi: 10.1007/s12011-020-02398-z [22] Mi Y,Zhang W,Tian H,et al. EGCG evokes Nrf2 nuclear translocation and dampens PTP1B expression to ameliorate metabolic misalignment under insulin resistance condition[J]. Food Funct,2018,9(3):1510-1523. doi: 10.1039/C7FO01554B [23] Kian K,Khalatbary A R,Ahmadvand H,et al. Neuroprotective effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3- gallate (EGCG) against peripheral nerve transection-induced apoptosis[J]. Nutr Neurosci,2019,22(8):578-586. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1419542 [24] Macauley M,Smith F E,Thelwall P E,et al. Diurnal variation in skeletal muscle and liver glycogen in humans with normal health and Type 2 diabetes[J]. Clin Sci (Lond),2015,128(10):707-713. doi: 10.1042/CS20140681 [25] Venables M C,Hulston C J,Cox H R,et al. Green tea extract ingestion,fat oxidation,and glucose tolerance in healthy humans[J]. Am J Clin Nutr,2008,87(3):778-784. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.3.778 [26] Li W,Zhu C,Liu T,et al. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate ameliorates glucolipid metabolism and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic rats[J]. Diab Vasc Dis Res,2020,17(6):1479164120966998. -





 下载:
下载: