Clinical Study on the Expression Levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in Peripheral Lymphocytes of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
-
摘要:
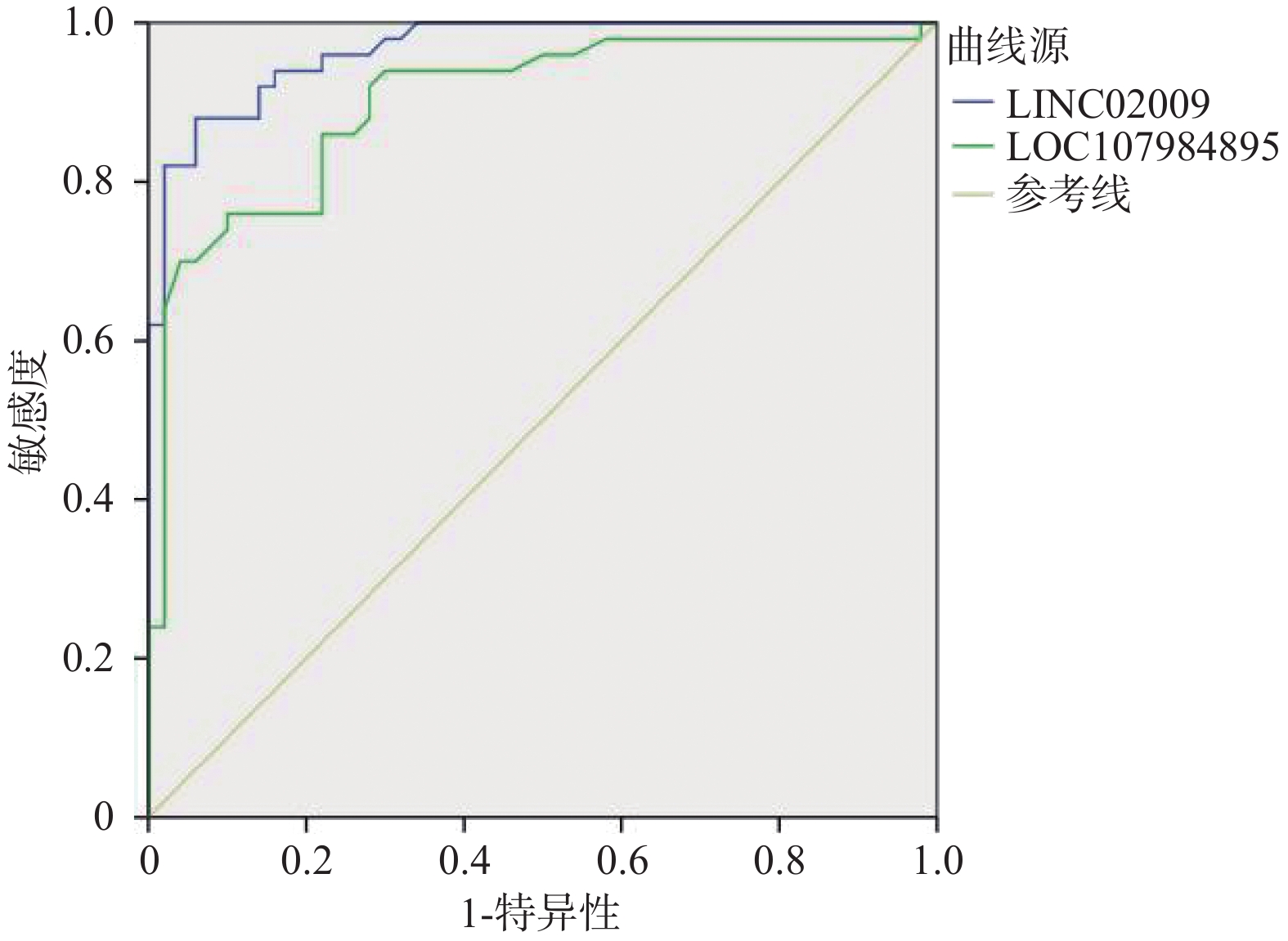
目的 探讨心房颤动患者外周淋巴细胞中LINC02009、LOC107984895表达水平及临床意义。 方法 选择 2023 年1月至2023年12月昆明市第一人民医院住院的75例房颤患者(其中持续性房颤50例,阵发性房颤25例)为研究对象,同期正常对照患者50例。采用实时定量 PCR 检测房颤患者外周血白细胞中LINC02009、LOC107984895的表达水平。运用 Logistic 回归分析评估其表达水平与房颤发生的危险因素及相关性,运用ROC曲线预测LINC02009、LOC107984895诊断房颤的诊断界值。 结果 AF(阵发性房颤、持续性房颤)组、Normal组患者在高血压、冠心病等基础疾病中,在Cr、BNP等生化指标中,在LAd、LVEF等心肌重构指标中差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。房颤(阵发性房颤、持续性房颤)组血浆中LINC02009、LOC107984895表达水平明显高于对照组(P < 0.05);与LVEF呈负相关(P < 0.05)。LINC02009、LOC107984895预测心房颤动的曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)分别为0.967(95%CI 0.938~0.995)、0.900 (95%CI 0.838~0.963);最佳截断值为1.985、0.915;敏感度为88%,76%;特异度为94%、90%。 结论 LINC02009、LOC107984895为心房颤动的独立危险因素,对房颤发生有一定预测价值。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the expression levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in peripheral lymphocytes of patients with atrial fibrillation and their clinical significance. Methods A total of 75 hospitalized patients with atrial fibrillation (50 with persistent atrial fibrillation and 25 with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation) from Kunming First People’ s Hospital between January 2023 and December 2023 were selected as study subjects, along with 50 normal control patients. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in peripheral blood leukocytes of patients with atrial fibrillation. Logistic regression analysis was employed to assess the relationship between expression levels and risk factors for atrial fibrillation, and ROC curves were used to predict the diagnostic cut-off values for LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in diagnosing atrial fibrillation. Results There were statistically significant differences in baseline diseases such as hypertension and coronary heart disease, biochemical indicators such as Cr and BNP, and myocardial remodeling indicators such as LAd and LVEF between the AF (paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and persistent atrial fibrillation) group and the Normal group (P < 0.05). The expression levels of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in the plasma of the atrial fibrillation group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05) and were negatively correlated with LVEF (P < 0.05). The areas under the curve (AUC) of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 in predicting atrial fibrillation were 0.967 (95%CI: 0.938 ~ 0.995) and 0.900 (95%CI: 0.838 ~ 0.963), respectively. The optimal cut-off values were 1.985 and 0.915, with sensitivities of 88% and 76%, respectively, and specificities of 94% and 90%, respectively. Conclusion LINC02009 and LOC107984895 are independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation and have certain predictive value for the occurrence of atrial fibrillation. -
Key words:
- Atrial fibrillation /
- RNA /
- Long non-coding RNA
-
表 1 引物设计序列
Table 1. Primer sequences
Gene Sequence(5'→3') Length Tm GC% LINC02009 Forward Primer ATGTCGAAACCGCCTACTCG 20 55.9 55 Reverse Primer AGTCAGGGTGTGGTCTCCTT 20 55.58 55 LOC107984895 Forward Primer TCTCAGTGGGCTCTTCTCCAG 21 56.7 57 Reverse Primer GTACACTGCCCTTCTTGGTGG 21 56.76 57 GAPDH Forward Primer CTGGGCTACACTGAGCACC 19 55.46 63 Reverse Primer AAGTGGTCGTTGAGGGCAATG 21 57.03 52 表 2 一般临床基线资料比较[($\bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
Table 2. Baseline characteristics of the patients [($\bar x \pm s $)/n(%)]
组别 研究组 对照组 Z/F P 持续性房颤 阵发性房颤 n 50 25 50 性别(男) 27(54) 15(60) 26(52) 0.374 0.596 年龄(岁) 68.12±8.57 65.78±7.32 67.04±6.30 0.362 0.574 BMI(kg/m2) 25.86±1.52 26.24±0.86 25.02±0.25 0.942 0.362 饮酒 16(32) 12(48) 13(26) 0.951 0.351 吸烟 35(70) 18(72) 10(20) 6.896 0.032* 高血压 32(64) 16(64) 11(22) 7.854 0.026* 糖尿病 13(26) 6(24) 3(6) 6.911 0.031* 冠心病 26(52) 10(40) 10(20) 5.434 0.042* 心力衰竭 35(70) 12(48) 6(12) 15.684 0.002* 卒中 36(72) 12(48) 8(16) 6.724 0.036* 持续性房颤组、阵发性房颤组与对照组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 3 3组患者的生化指标比较($\bar x \pm s $)
Table 3. Comparison of biochemical indicators among three groups of patients($\bar x \pm s $)
组别 研究组 对照组(n = 50) F/Z P 持续性房颤(n = 50) 阵发性房颤(n = 25) TC(mmol/L) 4.25±1.02 4.37±0.97 4.16±1.14 0.972 0.375 LDL-C(mmol/L) 3.21±0.63 3.19±0.73 3.01±1.03 0.019 0.891 HDL(mmol/L) 1.01±0.14 1.20±0.33 1.09±0.27 0.022 0.712 TG(mmol/L) 1.75±0.65 1.63±0.45 1.69±0.71 2.698 0.104 HbA1C%(%) 6.7±0.32 6.1±0.58 5.4±0.22 5.662 0.041* Cr(μmol/L) 95.3±10.5 84.2±7.80 68.8±8.93 7.233 0.028* eGFR[mL/(min·1.73 m2)] 67.3±16.2 79.5±18.4 85.6±12.3 6.786 0.036* BNP(pg/mL) 160.6±32.2 95.9±25.3 30.1±12.5 7.331 0.023* RBC(×109L) 135.8±15.2 140.6±18.9 125.4±10.9 0.022 0.713 WBC(×109L) 5.64±0.35 6.12±0.45 4.33±0.21 0.963 0.385 PLt(×109L) 205.5±21.6 223.8±20.9 192.6±12.6 0.363 0.549 CRP(×109L) 35.9±5.9 23.5±6.3 6.7±2.7 9.304 0.017* 持续性房颤组、阵发性房颤组与对照组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 4 3组患者心肌重构指标比较($\bar x \pm s $)
Table 4. Comparison of myocardial remodeling indicators among three groups of patients ($\bar x \pm s $)
组别 n LVEF(%) LAd(mm) RAd(mm) LVEDd(mm) 持续性房颤 50 40.25±5.33 54.02±4.69 52.34±5.61 51.35±5.34 阵发性房颤 25 51.74±6.28 48.06±5.86 45.23±4.54 45.16±4.35 对照组 50 56.74±5.81 35.12±3.07 34.20±2.26 43.25±3.55 χ2/F 18.624 32.652 46.665 9.635 P <0.001* <0.001* <0.001* <0.016* *P < 0.05。 表 5 3组患者LINC02009、LOC107984895表达水平比较($\bar x \pm s $)
Table 5. Comparison of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 expression levels among three patient Groups ($\bar x \pm s $)
组别 n LINC02009 LOC107984895 持续性房颤 50 4.09±2.79 1.85±0.34 阵发性房颤 25 3.11±1.25 1.36±0.39 对照组 50 2.88±1.08 0.96±0.57 χ2/F 21.568 7.536 P <0.001* <0.022* 持续性房颤组、阵发性房颤组与对照组比较,*P < 0.05。 表 6 LINC02009、LOC107984895表达水平心脏重构指标的相关性分析
Table 6. Correlation analysis of LINC02009 and LOC107984895 expression levels with cardiac remodeling indicators
项目 LINC02009 LOC107984895 r P r P LAd(mm) 0.786 <0.001* 0.624 <0.001* RAd(mm) 0.432 <0.001* 0.332 <0.001* LVEDd(mm) 0.375 <0.001* 0.416 <0.001* LVEF(%) −0.676 <0.001* −0.648 <0.001* *P < 0.05。 表 7 Logistic回归分析心房颤动患者的危险因素
Table 7. Logistic regression Analysis of the risk factors of atrial fibrillation patients
自变量 回归系数 标准误 Waldχ2 OR P Age 0.065 0.032 14.326 1.208 <0.001* Smoke 0.816 0.421 4.424 2.341 0.036* Hypertension 0.699 0.206 5.213 2.165 0.025* LAd 0.275 0.035 15.341 1.216 <0.001* LVEDd 0.421 0.052 23.512 1.501 <0.001* LVEF −0.216 0.062 6.512 0.965 0.035* LINC02009 1.352 0.712 5.876 4.625 0.034* LOC107984895 0.954 0.416 6.124 3.662 0.027* *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Hu D,Sun Y. Epidemiology,risk factors for stroke and management or atrial fibrillation in China[J]. J Am Coll Cardial,2008,52(10):865-868. [2] Benjamin E J,Muntner P,Alonso A,et a1. Heart disease and stroke statistics 2019 update: A report from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation,2020,141(2):e33. [3] Staerk L,Sherer J A,Ko D,et a1. Atrial fibrillation: Epidemiology,psychophysiology,and clinical outcomes[J]. CirculationResearch,2017,120(9):1501-1517. [4] Kirchhof P,Benussi S,Kotecha D,et a1. 2016 ESC guidelines forthe management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS[J]. Europace,2016,18(11):1609-1678. doi: 10.1093/europace/euw295 [5] 中国脑卒中防治报告2019编写组. 《中国脑卒中防治报告2019概要》. 中国脑血管病杂志,2020,17(5): 272-281. [6] Ruan Z B,Sun X H,Sheng H H,et a1. Long non-coding RNA expression profile in atrial fibrillation. International[J]. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology,2015,8(7):8402-8410. [7] Cao F,Li Z,Ding W M,et a1. LncRNA PVTl regulates atrial fibrosis via miR-128-3p-SP1-TGF-β1-Smad axis in atrial fibrillation[J]. Molecular Medicine,2019,25(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s10020-019-0074-5 [8] Yang J L,Gu L,Guo X J,et a1. LncRNA ANRIL expression and ANRIL gene polymorphisms contribute to the risk of ischemic stroke in the Chinese Han Population[J]. Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology,2018,38(6):1253-1269. doi: 10.1007/s10571-018-0593-6 [9] Fu R,Wang H L,Liu H,et a1. The study of proliferation relative long non-coding RNA in CD59-cell from paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria patients[J]. Blood,2019,134(S1):5023. [10] 苏忆玲,陆齐. lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA轴与心血管疾病发病相关性的研究进展[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2021,41(10):1552-1557. [11] 罗赤峰,姚 焰,何 丹,等. 心房颤动病人血浆长链非编码RNAH19表达与心肌重构的相关性分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2022,20(7):1275-1279. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2022.07.026 [12] Nattel S. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol,2017,3(5):425-435. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2017.03.002 [13] Wu L,Emmens R W,van Wezenbeek J,et al. Atrial inflammation in different atrial fibrillation subtypes and its relation with clinical risk factors[J]. Clin Res Cardiol,2020,109(10):1271-1281. doi: 10.1007/s00392-020-01619-8 [14] Korodi S,Toganel R,Benedek T,et al. Impact of inflammation mediated myocardial fibrosis on the risk of recurrence after successful ablation of atrial fibrillation - the FIBRO-RISK study: Protocol for a non-randomized clinical trial[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2019,98(9):14504-14510. [15] Xiong X,Liu J,He Q,et al. Long non-coding RNA NORAD aggravates acute myocardial infarction by promoting fibrosis and apoptosis via miR-577/COBLL1 axis[J]. Environ Toxicol,2021,36(11):2256-2265. doi: 10.1002/tox.23339 [16] Wang L,Yuan X,Lian L,et al. Knockdown of lncRNA NORAD inhibits the proliferation,inflammation and fibrosis of human mesangial cells under high-glucose conditions by regulating the miR-485/NRF1 axis[J]. Exp Ther Med,2021,22(2):874-883. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10306 [17] Han Y,Tian H,Gao X. NORAD regulates proliferation and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes under high-glucose treatment through miRNA150-5p/ZEB1 axis[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2020,24(21):11259-11265. [18] Lv X,Li J,Hu Y,et al. Overexpression of miR-27b-3p targeting Wnt3a regulates the signaling pathway of Wnt/β-Catenin and attenuates atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2019(1):5703764-5703776. [19] Yu S,Sun L,Wang H,et al. Autonomic regulation of imbalance induced myocardial fibrosis and its mechanism in rats with cirrhosis[J]. Exp Ther Med,2021,22(3):1040-1048. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10472 [20] Yokota T,Li J,Huang J,et al. p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates chamber-specific perinatal growth in heart[J]. J Clin Invest,2020,130(10):5287-5301. doi: 10.1172/JCI135859 -





 下载:
下载: